Prephenate Dehydrogenase (NADP ) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Prephenate dehydrogenase is an enzyme found in the shikimate pathway, and helps catalyze the reaction from prephenate to tyrosine.
This enzyme so far has been found in sixteen different organisms; twelve different kinds of bacteria (mostly
 In
In
Nomenclature
Gene: (Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have be ...
) TYR1
Shikimate pathway
The shikimate pathway (shikimic acid pathway) is a seven-step metabolic pathway used by bacteria, archaea, fungi, algae, some protozoans, and plants for the biosynthesis of folates and aromatic amino acids (tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine) ...
: Arogenate
Arogenic acid is an Metabolic intermediate, intermediate in the biosynthesis of phenylalanine and tyrosine. At physiological pH it exists as its conjugate base arogenate as the acid form is unstable.
Metabolism
Arogenate is synthesized from prep ...
/Prephenate
Prephenic acid, commonly also known by its anionic form prephenate, is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the aromatic amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine, as well as of a large number of secondary metabolites of the shikimate pathway.
Oc ...
(ADH/PDH). Although in the shikimate pathway arogenate
Arogenic acid is an Metabolic intermediate, intermediate in the biosynthesis of phenylalanine and tyrosine. At physiological pH it exists as its conjugate base arogenate as the acid form is unstable.
Metabolism
Arogenate is synthesized from prep ...
and prephenate dehydrogenase catalyze different reactions, they can at times be used interchangeably.
* TyrA (tyrosine A: within the tyrosine pathway)
* Prephenate dehydrogenase
* Prephenate (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) dehydrogenase
* Prephenate dehydrogenase (NADP)
* NADP+ oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually ut ...
cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
) and four different kinds of plants (mostly different kinds of beans).
Bacteria organisms (examples): Acenitobacter calcoaceticus, Fischerella sp., Flavobacterium so., Comamonas testosteroni
Comamonas testosteroni is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, aerobic bacterium belonging to the family Comamonadaceae. It is commonly found in environmental sources such as soil, water, sewage, wastewater, and industrial effluents—particularly where ...
, and nostoc sp.
Plant organisms: phaseolus coccineus
''Phaseolus coccineus'', known as runner bean, scarlet runner bean, or multiflora bean, is a plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. Another common name is butter bean, which, however, can also refer to the lima bean, a different species.
It is ...
, phaseolus vulgaris
''Phaseolus vulgaris'', the common bean,, is a herbaceous annual plant grown worldwide for its edible dry seeds or green, unripe pods. Its leaf is also occasionally used as a vegetable and the straw as fodder. Its botanical classification, alo ...
, vicia faba
''Vicia faba'', commonly known as the broad bean, fava bean, or faba bean, is a species of vetch, a flowering plant in the pea and bean family Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated as a crop for human consumption, and also as a cover crop. Vari ...
, vigna radiata
The mung bean or green gram (''Vigna radiata'') is a plant species in the Fabaceae, legume family.Brief Introduction of Mung Bean. Vigna Radiata Extract Green Mung Bean Extract Powder Phaseolus aureus Roxb Vigna radiata L R Wilczek. MDidea-E ...
Function
Present in the shikimate pathway, in the pathway to synthesizetyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
(a non-essential amino acid in both bacteria and plants). It catalyzes the oxidative
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is ...
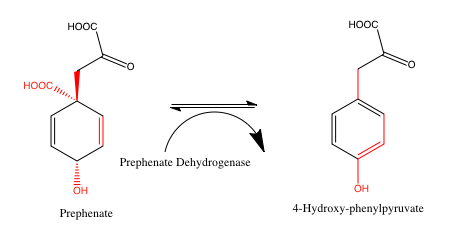
reaction of prephenate to 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate.
Reaction
 In
In enzymology
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
, a prephenate dehydrogenase () is an enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
that catalyzes
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quick ...
the chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
: prephenate + NAD+ 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate + CO2 + NADH
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are prephenate
Prephenic acid, commonly also known by its anionic form prephenate, is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the aromatic amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine, as well as of a large number of secondary metabolites of the shikimate pathway.
Oc ...
and NAD+, whereas its 3 products
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that can be offered to a market to satisfy the desire or need of a customer.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
...
are 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid (4-HPPA) is an intermediate in the metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. The aromatic side chain of phenylalanine is hydroxylated by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase to form tyrosine. The conversion from tyr ...
, CO2, and NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an ade ...
.
Structure
This enzyme belongs to the family ofoxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually ut ...
s, specifically those acting on the CH-CH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name
A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature.
A semisystematic name or semitrivi ...
of this enzyme class is prephenate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (decarboxylating). Other names in common use include hydroxyphenylpyruvate synthase, and chorismate mutase---prephenate dehydrogenase. This enzyme participates in phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis and novobiocin biosynthesis.
Also found in haemophilus influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, Motility, non-motile, Coccobacillus, coccobacillary, facultative anaerobic organism, facultatively anaerobic, Capnophile, capnophili ...
, synechocystis
''Synechocystis'' is a genus of unicellular, freshwater cyanobacteria in the family Merismopediaceae. It includes a strain, ''Synechocystis'' sp. PCC 6803, which is a well studied model organism
A model organism is a non-human species ...
(bacteria), and aquifex aeolicus
''Aquifex'' is a bacterial genus, belonging to phylum Aquificota. There is one species of ''Aquifex'' with a validly published name – '' A. pyrophilus'' – but "'' A. aeolicus''" is sometimes considered as species though it has no standing as ...
(plant).
However, in haemophilus influenzae, prephenate dehydrogenase is fused with the enzyme chorismate mutase
In enzymology, chorismate mutase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction for the conversion of chorismate to prephenate in the pathway to the production of phenylalanine and tyrosine, also known as the shikimate pathway.
Hence, thi ...
. This fusion is not found in plants or animals.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, twostructures
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes and .
References
{{Portal bar, Biology, border=no Enzymes of known structure EC 1.3.1 NADH-dependent enzymes