Posterior Cruciate Ligament on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is a
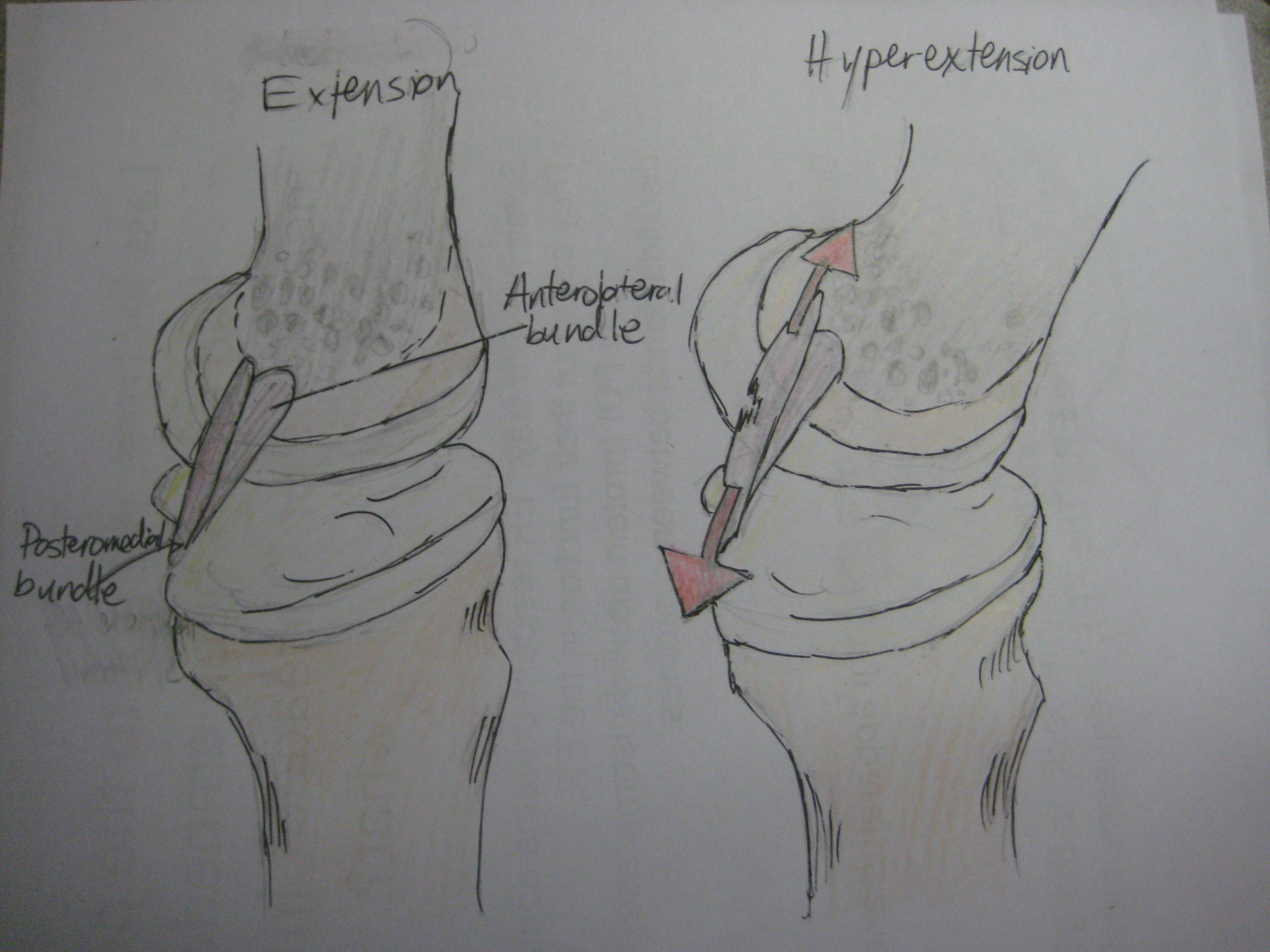

 In this position, the PCL functions to prevent movement of the tibia in the posterior direction and to prevent the tilting or shifting of the patella. However, the respective laxity of the two sections makes the PCL susceptible to injury during hyperflexion, hyperextension, and in a mechanism known as a dashboard injury. Because
In this position, the PCL functions to prevent movement of the tibia in the posterior direction and to prevent the tilting or shifting of the patella. However, the respective laxity of the two sections makes the PCL susceptible to injury during hyperflexion, hyperextension, and in a mechanism known as a dashboard injury. Because
Image:Gray349.png, Head of right tibia seen from above, showing menisci and attachments of ligaments.
Image:Gray352.png, Capsule of right knee-joint (distended). Posterior aspect.
File:MRT ACL PCL 01.jpg, Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation demonstrating normal signal of both anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments (arrows).
File:Slide2CAC.JPG, Anterior view of knee.
File:Slide3ecce.JPG, Knee joint. Deep dissection. Anterior view
Dealing with Torn Ligament in the Knee
* http://www.orthspec.com/pdfs/PCL-injuries.pdf {{Authority control Knee ligaments
ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
in each knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
of humans and various other animals. It works as a counterpart to the anterior cruciate ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments (the other being the posterior cruciate ligament) in the human knee. The two ligaments are called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In ...
(ACL). It connects the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
to the medial condyle of the femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
. This configuration allows the PCL to resist forces pushing the tibia posteriorly relative to the femur.
The PCL and ACL are intracapsular ligaments because they lie deep within the knee joint. They are both isolated from the fluid-filled synovial cavity, with the synovial membrane wrapped around them. The PCL gets its name by attaching to the posterior portion of the tibia.
The PCL, ACL, MCL, and LCL are the four main ligaments of the knee in primates.
Structure
The PCL is located within theknee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
joint where it stabilizes the articulating bones, particularly the femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
and the tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
, during movement. It originates from the lateral edge of the medial femoral condyle and the roof of the intercondyle notch then stretches, at a posterior and lateral angle, toward the posterior of the tibia just below its articular surface.

Function
Although each PCL is a unified unit, they are described as separate anterolateral and posteromedial sections based on where each section's attachment site and function. During knee joint movement, the PCL rotates such that the anterolateral section stretches in knee flexion but not in knee extension and the posteromedial bundle stretches in extension rather than flexion. The function of the PCL is to prevent the femur from sliding off the anterior edge of the tibia and to prevent the tibia from displacing posterior to the femur. The posterior cruciate ligament is located within the knee.Ligaments
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have ligam ...
are sturdy bands of tissues that connect bones. Similar to the anterior cruciate ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments (the other being the posterior cruciate ligament) in the human knee. The two ligaments are called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In ...
, the PCL connects the femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
to the tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
.
Clinical significance
Common causes of injuries are direct blows to the flexed knee, such as the knee hitting the dashboard in a car accident or falling hard on the knee, both instances displacing the tibia posterior to the femur. An additional test of posterior cruciate ligament injury is the ''posterior sag test'', where, in contrast to the drawer test, no active force is applied. Rather, the person lies supine with the leg held by another person so that the hip is flexed to 90 degrees and the knee 90 degrees. The main parameter in this test is ''step-off'', which is the shortest distance from the femur to a hypothetical line thattangent
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is, intuitively, the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points o ...
s the surface of the tibia from the tibial tuberosity and upwards. Normally, the ''step-off'' is approximately 1 cm, but is decreased (Grade I) or even absent (Grade II) or inverse (Grade III) in injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament. The posterior drawer test is one of the tests used by doctors and physiotherapists to detect injury to the PCL. Patients who are suspected to have a posterior cruciate ligament injury should always be evaluated for other knee injuries that often occur in combination with an PCL injuries. These include cartilage/ meniscus injuries, bone bruises, ACL tears, fractures, posterolateral injuries
Posterolateral corner injuries (PLC injuries) of the knee are injuries to a complex area formed by the interaction of multiple structures. Injuries to the posterolateral corner can be debilitating to the person and require recognition and treatment ...
and collateral ligament injuries.
There are four different grades of classification in which medical doctors classify a PCL injury:
:Grade I, the PCL has a slight tear.
:Grade II, the PCL ligament is minimally torn and becomes loose.
:Grade III, the PCL is torn completely and the knee can now be categorized as unstable.
:Grade IV, the ligament is damaged along with another ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
housed in the knee (i.e. ACL).
With these grades of PCL injuries, there are different treatments available for such injuries.

Mechanism
 In this position, the PCL functions to prevent movement of the tibia in the posterior direction and to prevent the tilting or shifting of the patella. However, the respective laxity of the two sections makes the PCL susceptible to injury during hyperflexion, hyperextension, and in a mechanism known as a dashboard injury. Because
In this position, the PCL functions to prevent movement of the tibia in the posterior direction and to prevent the tilting or shifting of the patella. However, the respective laxity of the two sections makes the PCL susceptible to injury during hyperflexion, hyperextension, and in a mechanism known as a dashboard injury. Because ligaments
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have ligam ...
are viscoelastic
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both Viscosity, viscous and Elasticity (physics), elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation (engineering), deformation. Viscous mate ...
) they can handle higher amounts of stress only when the load is increased slowly. When hyperflexion and hyperextension occur suddenly in combination with this viscoelastic behavior, the PCL deforms or tears. In the third and most common mechanism, the dashboard injury mechanism, the knee experiences impact in a posterior direction during knee flexion toward the space above the tibia. These mechanisms occur in excessive external tibial rotation and during falls that induce a combination of extension and adduction
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
of the tibia, which is referred to as varus-extension stress, or that occur while the knee is flexed.
Treatment
It is possible for the PCL to heal on its own. Even if the PCL does not heal normally, it is unusual for surgery to be required. Treatment is usually physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee; usually they provide adequate stability even without a functional PCL. Only if there are ongoing symptoms down the track, or if there are other injuries in the knee (e.g. posterolateral corner injury) will ligament reconstruction be required. Ligament reconstruction is used to replace the torn PCL with a new ligament, which is usually a graft taken from the hamstring or Achilles tendon from a host cadaver. An arthroscope allows a complete evaluation of the entire knee joint, including the knee cap (patella), the cartilage surfaces, the meniscus, the ligaments (ACL & PCL), and the joint lining. Then, the new ligament is attached to the bone of the thigh and lower leg with screws to hold it in place. Surgery to repair the posterior cruciate ligament is controversial due to its placement and technical difficulty. It is possible for the PCL to heal on its own without surgery when it is a Grade I or Grade II injury. PCL injuries that are diagnosed in these categories can have their recovery times reduced by performing certain rehabilitative exercises. Fernandez and Pugh(2012) found that following a PCL grade II diagnosis, a multimodal treatment that spanned the course of 8 weeks consisting ofchiropractic
Chiropractic () is a form of alternative medicine concerned with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of mechanical disorders of the musculoskeletal system, especially of the spine. It is based on several pseudoscientific ideas.
Many c ...
lumbopelvic manipulation, physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
, and implementing an exercise program that emphasized eccentric muscle contraction ( lunges, 1-leg squats, and trunk stabilization proved to be an effective way to recover from the PCL injury. For Grades III and IV, operative surgery is recommended or is usually needed. Grafts
Grafting refers to a surgical procedure to move tissue from one site to another on the body, or from another creature, without bringing its own blood supply with it. Instead, a new blood supply grows in after it is placed. A similar techniqu ...
is the method when addressing PCL injuries that are in need of operative surgery. With grafts, there are different methods such as the tibial inlay or tunnel method.
Other animals
In thequadruped
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion in which animals have four legs that are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four legs is said to be a quadruped (fr ...
stifle (analogous to the human knee), based on its anatomical position
Anatomical terminology is a specialized system of terms used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals, such as doctors, surgeons, and pharmacists, to describe the structures and functions of the body.
This terminology incorpor ...
, it is referred to as the caudal cruciate ligament.
Additional images
References
External links
* ()Dealing with Torn Ligament in the Knee
* http://www.orthspec.com/pdfs/PCL-injuries.pdf {{Authority control Knee ligaments