Portsmouth Naval Shipyard on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Portsmouth Naval Shipyard (PNS), often called the Portsmouth Navy Yard, is a
/ref> On November 2, 1842, Commodore John Drake Sloat responded to a request by Navy Secretary Abel P. Upshur for information about wages and working hours at the shipyard. Sloat said the "time of work is from sunrise until sunset, except when the sun rises before 7 o'clock or sets after 6 when they commence work at 7 and quit at 6 o clock, not exceeding 10 hours labor at any season of the year." He added that wages "are always fluctuating according to the demand for mechanics".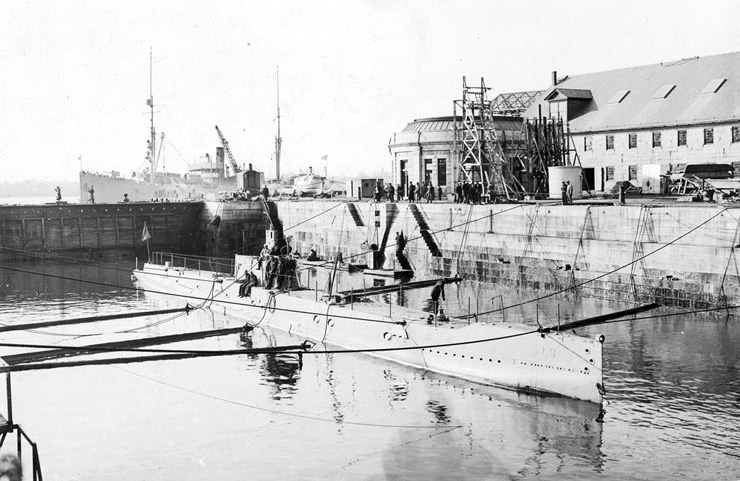 During
During
 * 1814 — - (74-gun
* 1814 — - (74-gun 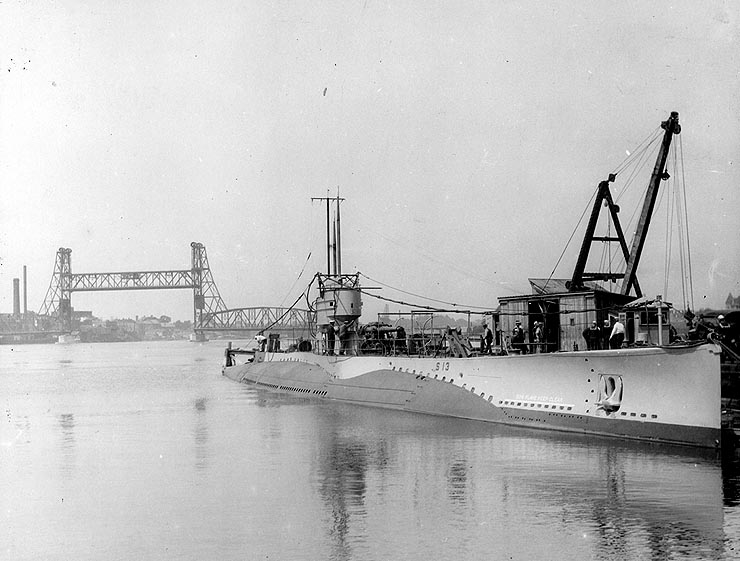 * 1905 — - ( training brigantine)
* 1908 — - (
* 1905 — - ( training brigantine)
* 1908 — - ( * 1934 — - ( USCG ''Calumet''-class harbor tug)Fahey 1941 p. 43
* 4 of 10 s
** 1935 — - sank 2 ships in 6
* 1934 — - ( USCG ''Calumet''-class harbor tug)Fahey 1941 p. 43
* 4 of 10 s
** 1935 — - sank 2 ships in 6 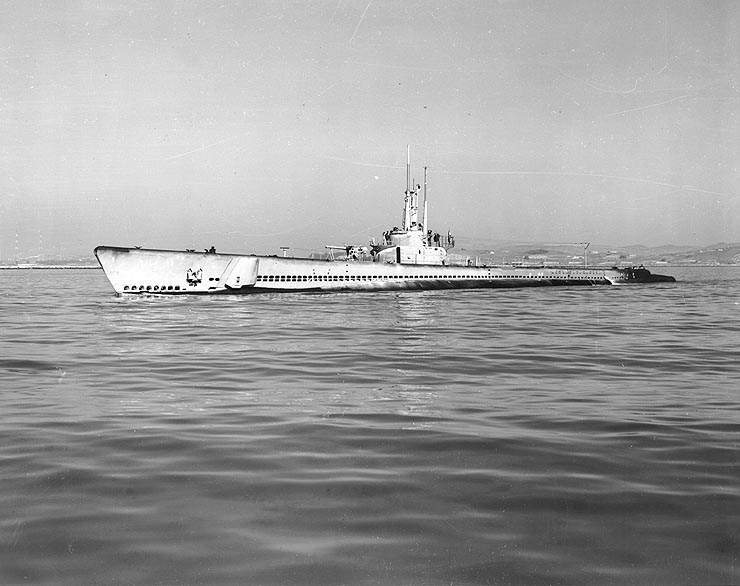 * 42 of 120 s Alden 1964 p. 93
** 1942 — - sank 6 ships in 10
* 42 of 120 s Alden 1964 p. 93
** 1942 — - sank 6 ships in 10
Naval Shipyard official website
''USS Albacore'' Museum
{{Authority control United States Navy shipyards Shipyards of Maine Military installations in Maine Military Superfund sites Economic history of Maine Military history of Maine History of New Hampshire Buildings and structures in Kittery, Maine Superfund sites in Maine Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Maine 1800 establishments in the United States National Register of Historic Places in York County, Maine Shipyards on the National Register of Historic Places Shipyards building World War II warships Former submarine builders
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are shipbuilding, built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Compared to shipyards, which are sometimes m ...
on Seavey's Island in Kittery, Maine
Kittery is a town in York County, Maine, United States, and the oldest incorporated town in Maine. Home to the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard on Seavey's Island, Kittery includes Badger's Island, the seaside district of Kittery Point, and part of ...
, bordering Portsmouth, New Hampshire
Portsmouth is a city in Rockingham County, New Hampshire, Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census it had a population of 21,956. A historic seaport and popular summer tourist destination on ...
. The naval yard lies along the southern boundary of Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
on the Piscataqua River
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki language, Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River to the Atlant ...
.
Founded on June 12, 1800, PNS is the U.S. Navy's oldest continuously operating shipyard. Today, most of its work concerns the overhaul, repair, and modernization of submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
s.
As of November 2021, the shipyard employed more than 6,500 federal employees. As well, some of the work is performed by private corporations (e.g., Delphinius Engineering of Eddystone, Pennsylvania; Oceaneering International of Chesapeake, Virginia; Orbis Sibro of Mount Pleasant, South Carolina; and Q.E.D. Systems Inc. of Virginia Beach, Virginia).
History
The Portsmouth Naval Shipyard was established on June 12, 1800, during the administration of PresidentJohn Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before Presidency of John Adams, his presidency, he was a leader of ...
. It sits on a cluster of conjoined islands called Seavey's Island in the Piscataqua River
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki language, Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River to the Atlant ...
, whose swift tidal current prevents ice from blocking navigation to the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
.
The area has a long tradition of shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other Watercraft, floating vessels. In modern times, it normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation th ...
. Since colonial settlement, New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
and Maine forests provided lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into uniform and useful sizes (dimensional lumber), including beams and planks or boards. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). ...
for wooden boat construction. , considered the first British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
warship
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is used for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the navy branch of the armed forces of a nation, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations. As well as b ...
built in the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
, was commissioned here in 1696. During the Revolution
In political science, a revolution (, 'a turn around') is a rapid, fundamental transformation of a society's class, state, ethnic or religious structures. According to sociologist Jack Goldstone, all revolutions contain "a common set of elements ...
, the was built in 1776 on Badger's Island in Kittery, and became the first vessel to fly an American flag
The national flag of the United States, often referred to as the American flag or the U.S. flag, consists of thirteen horizontal Bar (heraldry), stripes, Variation of the field, alternating red and white, with a blue rectangle in the Canton ( ...
into battle. ''Raleigh'' has been depicted on the Seal of New Hampshire
The U.S. state of New Hampshire has held two Seal (emblem), seals since it declared its independence from Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain on January 5, 1776. While both seals have been retained, most people are only familiar with the G ...
since 1784, even though she was captured and served in the British Navy. Other warships followed, including launched in 1777; Commanded by Captain John Paul Jones
John Paul Jones (born John Paul; July 6, 1747 – July 18, 1792) was a Scottish-born naval officer who served in the Continental Navy during the American Revolutionary War. Often referred to as the "Father of the American Navy", Jones is regard ...
, it became the first U. S. Navy vessel to receive an official salute at sea from a foreign power. The 36-gun frigate , one of the first six frigates of the United States Navy, was built at the shipyard from 1795 to 1799.
In the 1790s, Navy Secretary Benjamin Stoddert decided to build the first federal shipyard. He put it where a proven workforce
In macroeconomics, the workforce or labour force is the sum of people either working (i.e., the employed) or looking for work (i.e., the unemployed):
\text = \text + \text
Those neither working in the marketplace nor looking for work are out ...
had access to abundant raw materials: Fernald's Island, for which the government paid $5,500. To protect the new installation, old Fort William and Mary at the mouth of Portsmouth Harbor was rebuilt and renamed Fort Constitution.
Commodore Isaac Hull
Commodore (rank), Commodore Isaac Hull (March 9, 1773 – February 13, 1843) was a United States Navy officer who served in the Quasi-War, Barbary Wars and War of 1812. During his military career, he commanded the warships , , , and . During the ...
was the first naval officer to command the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard; he led it from 1800 until 1802, and again in 1812 during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
. The yard's first product was the 74-gun ship of the line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactics in the Age of Sail, naval tactic known as the line of battl ...
, supervised by local master shipbuilder William Badger and launched in 1814. Barracks
Barracks are buildings used to accommodate military personnel and quasi-military personnel such as police. The English word originates from the 17th century via French and Italian from an old Spanish word 'soldier's tent', but today barracks ar ...
were built in 1820, with Marine barracks added in 1827. A hospital was established in 1834. Architect Alexander Parris was appointed chief engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, build, maintain and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials. They aim to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while ...
for the base. In 1838, the Franklin Shiphouse was completed: long, wide, and measuring from floor to center of its ridgepole. It carried 130 tons of slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous, metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade, regional metamorphism. It is the finest-grained foliated metamorphic ro ...
on a gambrel
A gambrel or gambrel roof is a usually symmetrical two-sided roof with two slopes on each side. The upper slope is positioned at a shallow angle, while the lower slope is steep. This design provides the advantages of a sloped roof while maxim ...
roof. It was lengthened in 1854 to accommodate (from which it took its name); the largest wooden warship built at the yard, it required a decade to finish. The structure was considered one of the largest shiphouses in the country until it burned at 5 a.m. on March 10, 1936. Perhaps the most famous vessel ever overhauled at the yard was , also called "Old Ironsides," in 1855.Brief History of the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard/ref> On November 2, 1842, Commodore John Drake Sloat responded to a request by Navy Secretary Abel P. Upshur for information about wages and working hours at the shipyard. Sloat said the "time of work is from sunrise until sunset, except when the sun rises before 7 o'clock or sets after 6 when they commence work at 7 and quit at 6 o clock, not exceeding 10 hours labor at any season of the year." He added that wages "are always fluctuating according to the demand for mechanics".
Prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a ...
from the Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the ...
were encamped in 1898 on the grounds of the base. In 1905, construction began on the Portsmouth Naval Prison, a military prison dubbed "The Castle" because of its resemblance to a crenellated
A battlement, in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at intervals ...
castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private ...
. It was the principal prison for the Navy and Marine Corps, as well as housing for many German U-boat
U-boats are Submarine#Military, naval submarines operated by Germany, including during the World War I, First and Second World Wars. The term is an Anglicization#Loanwords, anglicized form of the German word , a shortening of (), though the G ...
crews after capture, until it closed in 1974. Also in 1905, the Portsmouth Navy Yard hosted the Treaty of Portsmouth which ended the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 – 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the ...
. For arranging the peace conference
A peace conference is a diplomatic meeting where representatives of states, armies, or other warring parties converge to end hostilities by negotiation and signing and ratifying a peace treaty.
Significant international peace conferences in ...
, President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
won the 1906 Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize (Swedish language, Swedish and ) is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the Will and testament, will of Sweden, Swedish industrialist, inventor, and armaments manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Nobe ...
. Delegates met in the General Stores Building, now the Administration Building (called Building 86). In 2005, a summer-long series of events marked the 100th anniversary of the signing of the treaty, including a visit by a Navy destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, maneuverable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy, or carrier battle group and defend them against a wide range of general threats. They were conceived i ...
, a parade, and a re-enactment of the arrival of diplomat
A diplomat (from ; romanization, romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state (polity), state, International organization, intergovernmental, or Non-governmental organization, nongovernmental institution to conduct diplomacy with one ...
s from the two nations.
 During
During World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the shipyard began constructing submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
s, with being the first ever built by a U. S. navy yard. Meanwhile, the base continued to overhaul and repair surface vessels. Consequently, the workforce grew to nearly 5,000 civilians. It grew to almost 25,000 civilians in World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
when over 70 submarines were constructed at the yard, with a record of 4 launched in a single day. When the war ended, the shipyard became the Navy's center for submarine design and development. In 1953, revolutionized submarine design around the world with its teardrop hull
A teardrop hull is a submarine hull design which emphasizes submerged performance over surfaced performance. It was somewhat commonly used in the early stages of submarine development, but was gradually abandoned in the early 20th century in favo ...
and round cross-section. It is now a museum and tourist attraction in Portsmouth. , the first nuclear-powered
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
submarine built at the base, was launched in 1957. The last submarine built here was , launched in 1969. Today the shipyard provides overhaul, refueling, and modernization work.
In 1965, Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara
Robert Strange McNamara (; June 9, 1916 – July 6, 2009) was an American businessman and government official who served as the eighth United States secretary of defense from 1961 to 1968 under presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson ...
ordered the closure of 95 military bases which included the Portsmouth Naval Yard, but Portsmouth received a ten-year extension before the order to close was ultimately rescinded by President Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 until Resignation of Richard Nixon, his resignation in 1974. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
in 1971.
In the early years of submarine construction, the wood from lignum vitae tree logs was used for propeller shaft bearings. A small pond at Portsmouth, near the Naval Prison, was used to keep the lignum vitae logs submerged in water in order to prevent the wood from cracking. Although the use of wood was discontinued as construction techniques improved, many of the logs were still present during the construction of between 1963 and 1967.
The 2005 Base Realignment and Closure Commission placed the yard on a list for base closures, effective by 2008. Employees organized the Save Our Shipyard campaign to influence the committee to reverse its decision. On 24 August 2005, the base was taken off the list and continues operating under its motto, "From Sails to Atoms."
The shipyard earned the Meritorious Unit Commendation in 2005. The MUC recognized the shipyard for meritorious service from September 11, 2001, to August 30, 2004. Portsmouth Naval Shipyard accomplishments achieved during that period included completion of six major submarine availabilities early, exceeding Net Operation Results financial goals, reducing injuries by more than 50 percent, and exceeding the Secretary of Defense's Fiscal Year 2006 Stretch Goal for lost workday compensation rates two years early.
In addition to the Navy presence, the United States Army New England Recruiting Battalion moved to PNSY in June 2010 from the closed Naval Air Station Brunswick. The United States Coast Guard uses the Portsmouth Navy Yard as the home port for the medium-endurance cutters , , and .
PNS is undergoing substantial construction and infrastructure upgrades. In fiscal 2020, Navy contracts were issued to renovate the communications building, build a super flood basin and extend crane rails in Dry Dock 1, upgrade crane rails in Dry Dock 2, renovate Building 2, and implement sundry waterfront projects.
The summer of 2021 saw an uptick in construction contracts issued for Portsmouth Naval Shipyard, including purchase and installation of three 12,000-gallon-per-minute dewatering pumps for the Dry Dock 1 extension, ongoing construction of the Dry Dock 2 complex, commencement of construction on the Virginia-class submarine waterfront support facility (Building 178), and a $1.73 billion contract for building a dry dock for maintenance and upgrade of Virginia-class submarines.
Superfund site
In 1994, the shipyard was placed on the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency National Priorities List (NPL) for environmental investigations/restorations under CERCLA (Superfund
Superfund is a United States federal environmental remediation program established by the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 (CERCLA). The program is administered by the United States Environmental Pro ...
) after an investigation found groundwater, soil and sediment contamination with polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs), metals and benzene. In 2024, the EPA removed the shipyard from the National Priorities List of contaminated Superfund. The removal followed 30 years of extensive remediation at the 278-acre shipyard, including the removal of contaminated soil, sediment and other hazardous materials.
Boundary dispute
New Hampshire laid claim to the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard until theU.S. Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that turn on question ...
dismissed the case in 2001, asserting judicial estoppel In the common law, judicial estoppel (also known as estoppel by inconsistent positions) is an estoppel that precludes a Party (law), party from taking a position in a case that is contrary to a position it has taken in earlier legal proceedings. Alt ...
. Had it been found to belong to New Hampshire, base employees (and their spouses regardless of whether they themselves worked in Maine) from that state would no longer be required to pay Maine income tax. Despite the court's ruling, New Hampshire's 2006 Session House Joint Resolution 1 reaffirmed its sovereignty assertion over Seavey's Island and the base.
Safety concerns
ACDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, ...
/ NIOSH
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury, illness, disability, and death. It ...
study released in 2005 examined the cases of 115 employees at the shipyard who had died of leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
between 1952 and 1992. The results suggested that leukemia mortality risk increased with increasing cumulative occupational ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
dose among PNS workers.
Dry docks and slipways
Notable ships built at shipyard predecessors
Piscataqua River region * 1690 — HMS ''Falkland'' - (50-gunfourth-rate
In 1603 all English warships with a complement of fewer than 160 men were known as 'small ships'. In 1625/26 to establish pay rates for officers, a six-tier naval ship rating system was introduced.Winfield 2009 These small ships were divided ...
)Alden 1964 p. 92
* 1696 — HMS ''Bedford Galley'' - (32-gun fifth-rate)
* 1749 — HMS ''America'' - (60-gun fourth-rate
In 1603 all English warships with a complement of fewer than 160 men were known as 'small ships'. In 1625/26 to establish pay rates for officers, a six-tier naval ship rating system was introduced.Winfield 2009 These small ships were divided ...
)
Badger's Island
* 1776 — - (32-gun frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuvera ...
)
* 1777 — - (18-gun sloop-of-war
During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all u ...
)
* 1782 — - (74-gun ship of the line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactics in the Age of Sail, naval tactic known as the line of battl ...
)
* 1791 — - (revenue cutter
A cutter is any of various types of watercraft. The term can refer to the rig (sail plan) of a sailing vessel (but with regional differences in definition), to a governmental enforcement agency vessel (such as a coast guard or border force cut ...
)
* 1797 — - (36-gun frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuvera ...
)
* 1798 — - (24-gun sloop-of-war
During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all u ...
)
* 1799 — - (38-gun frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuvera ...
)
Notable ships built at the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard
 * 1814 — - (74-gun
* 1814 — - (74-gun ship of the line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactics in the Age of Sail, naval tactic known as the line of battl ...
)
* 1820 — - (11-gun schooner
A schooner ( ) is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel defined by its Rig (sailing), rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more Mast (sailing), masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than t ...
)
* 1828 — - (24-gun sloop-of-war
During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all u ...
)
* 1839 — - (20-gun sloop-of-war
During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all u ...
)
* 1841 — - (50-gun frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuvera ...
)
* 1842 — - (24-gun sloop-of-war
During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all u ...
)
* 1843 — - (24-gun sloop-of-war
During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all u ...
)
* 1848 — - (steam sloop)
* 1855 — - (44-gun frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuvera ...
)
* 1855 — LV-1 - Lightship ''Nantucket''
* 1859 — - (steam sloop)
* 1861 — - (steam sloop)
* 1861 — - (steam sloop)
* 1861 — - (side-wheel steam gunboat)
* 1861 — - (side-wheel steam gunboat)
* 1862 — - (side-wheel steam gunboat)
* 1862 — - (side-wheel steam gunboat)
* 1862 — - (side-wheel steam gunboat)
* 1862 — - (steam sloop)
* 1863 — - (steam gunboat)
* 1863 — - (steam gunboat)
* 1863 — - ( Miantonomoh-class monitor)
* 1864 — - (74-gun ship of the line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactics in the Age of Sail, naval tactic known as the line of battl ...
)
* 1864 — - (steam sloop)
* 1864 — - (steam frigate)
* 1864 — - (side-wheel steam gunboat)
* 1864 — - (tugboat
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, suc ...
)
* 1864 — - (tugboat
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, suc ...
)
* 1865 — - (steam gunboat)
* 1866 — - (steam frigate)
* 1867 — - (steam frigate)
* 1868 — - (steam sloop)
* 1874 — - (steam sloop)
 * 1905 — - ( training brigantine)
* 1908 — - (
* 1905 — - ( training brigantine)
* 1908 — - (tugboat
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, suc ...
)
* 1917 — - (United States L-class submarine
The United States L-class submarines were a class of 11 coastal defense submarines built 1914–1917, and were the most modern and capable submarines available to United States Navy when the country entered World War I. Despite being considered a ...
)
* 1918 — - ( United States O-class submarine)
* 1918 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1919 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1919 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1919 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1920 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1920 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1920 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1920 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1921 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1921 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1921 — - (United States S-class submarine
The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats (sometimes "Sugar" boats, after the then-contemporary Navy phonetic alphabet for "S"), were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy d ...
)
* 1924 — - (diesel submarine)
* 1924 — - (diesel submarine)
* 1924 — - (diesel submarine)
* 1928 — - (diesel submarine minelayer) 3 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrolsBlair(1975)pp.875-957
* 1929 — - (diesel submarine cruiser) sank 6 ships in 15 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
* 1932 — - (diesel submarine) 3 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
* 1933 — - (diesel submarine) 3 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols  * 1934 — - ( USCG ''Calumet''-class harbor tug)Fahey 1941 p. 43
* 4 of 10 s
** 1935 — - sank 2 ships in 6
* 1934 — - ( USCG ''Calumet''-class harbor tug)Fahey 1941 p. 43
* 4 of 10 s
** 1935 — - sank 2 ships in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1935 — - sank 1 ship in 8 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1936 — - sank 13 ships in 12 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1936 — - sank 11 ships in 11 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
* 2 of 6 s
** 1937 — - sank 4 ships in 11 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1937 — - sank 2 ships in 16 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
* 4 of 10 s
** 1938 — - sank 3 ships in 9 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1939 — - sank 7 ships in 12 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1939 — - sank 3 ships in 13 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1939 — - sank 18 ships in 15 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
* 4 of 12 s
** 1940 — - sank 11 ships in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1940 — - sank 12 ships in 11 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1940 — - sank 2 ships in 8 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1940 — - sank 1 ship in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
* 1 of 2 s
** 1941 —
* 14 of 77 s
** 1941 — - sank 12 ships in 13 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1941 — - sank 15 ships in 12 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1941 — - sank 11 ships in 12 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1941 — - sank 8 ships in 13 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1941 — - sank 12 ships in 10 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 6 ships in 5 Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
and 3 Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 14 ships in 12 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 3 ships in 11 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - 3 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 6 ships in 10 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 5 ships in 8 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 4 ships in 4 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 17 ships in 9 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 4 ships in 7 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
 * 42 of 120 s Alden 1964 p. 93
** 1942 — - sank 6 ships in 10
* 42 of 120 s Alden 1964 p. 93
** 1942 — - sank 6 ships in 10 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 3 ships in 8 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 16 ships in 9 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 7 ships in 8 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1942 — - sank 1 ship in 1 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrol
** 1942 — - 1 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrol
** 1943 — - sank 8 ships in 7 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 3 ships in 8 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 6 ships in 7 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 6 ships in 7 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 2 ships in 7 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 1 ship in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 10 ships in 5 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 13 ships in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 5 ships in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 8 ships in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 8 ships in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 8 ships in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 2 ships in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 2 ships in 5 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 4 ships in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 4 ships in 6 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 4 ships in 5 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1943 — - sank 8 ships in 5 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - 5 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 5 ships in 2 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 2 ships in 5 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - 5 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 2 ships in 5 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - 2 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 5 ships in 5 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 9 ships in 4 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - Alden 1964 p. 93 4 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 6 ships in 4 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 1 ship in 4 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 2 ships in 3 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - 4 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 6 ships in 3 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 7 ships in 4 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - 3 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 3 ships in 3 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
* 24 of 29 s
** 1944 — - sank 4 ships in 3 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - 1 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrol
** 1944 — - 2 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 8 ships in 2 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - 2 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - 2 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - sank 3 ships in 2 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 — - 1 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrol
** 1944 — - sank 1 ship in 1 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrol
** 1944 — - sank 1 ship in 2 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrols
** 1944 —
** 1944 — - 1 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrol
** 1944 — - 1 World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
patrol
** 1944 —
** 1945 —
** 1945 —
** 1945 —
** 1945 —
** 1945 —
** 1945 —
** 1945 —
** 1945 —
** 1945 —
** 1945 —
* 1951 — - ( diesel submarine)
* 1951 — - ( diesel submarine)
* 1951 — - ( diesel submarine)
* 1953 — - (experimental diesel submarine)
* 1955 — - (RADAR picket submarine)
* 1956 — - (RADAR picket submarine)
* 1958 — - (guided missile diesel submarine)
* 1958 — - (nuclear submarine
A nuclear submarine is a submarine powered by a nuclear reactor, but not necessarily nuclear-armed.
Nuclear submarines have considerable performance advantages over "conventional" (typically diesel-electric) submarines. Nuclear propulsion ...
)
* 1958 — - ( fast diesel submarine)
* 1958 — - (nuclear submarine
A nuclear submarine is a submarine powered by a nuclear reactor, but not necessarily nuclear-armed.
Nuclear submarines have considerable performance advantages over "conventional" (typically diesel-electric) submarines. Nuclear propulsion ...
)
* 1960 — - ( nuclear fast attack submarine)
* 1960 — - ( nuclear ballistic missile submarine)
* 1963 — - ( nuclear fast attack submarine)
* 1961 — - ( nuclear fast attack submarine)
* 1963 — - ( nuclear ballistic missile submarine)
* 1964 — - ( nuclear ballistic missile submarine)
* 1967 — - ( nuclear fast attack submarine)Blackman 1970-71 p. 466
* 1968 — - (experimental diesel submarine)Blackman 1970-71 p. 476
* 1969 — - ( nuclear fast attack submarine)
See also
* National Register of Historic Places listings in York County, MaineReferences
Sources
* Portsmouth Naval Shipyard Museum & Research Library (Building 31) * * * * * *External links
Naval Shipyard official website
''USS Albacore'' Museum
{{Authority control United States Navy shipyards Shipyards of Maine Military installations in Maine Military Superfund sites Economic history of Maine Military history of Maine History of New Hampshire Buildings and structures in Kittery, Maine Superfund sites in Maine Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Maine 1800 establishments in the United States National Register of Historic Places in York County, Maine Shipyards on the National Register of Historic Places Shipyards building World War II warships Former submarine builders