Polymer Capacitor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
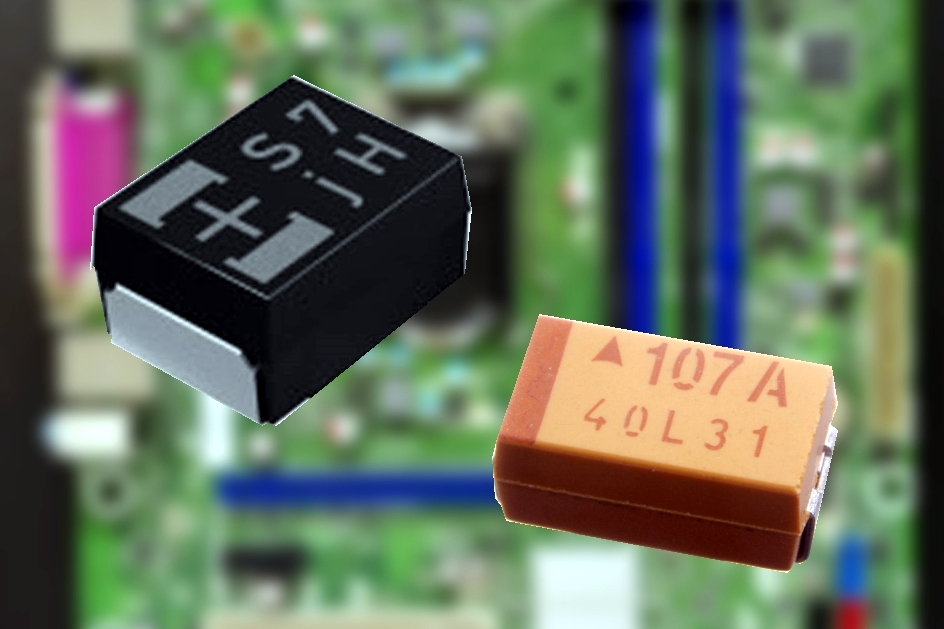
 A polymer capacitor, or more accurately a polymer electrolytic capacitor, is an
A polymer capacitor, or more accurately a polymer electrolytic capacitor, is an
 During the 1970s, the increasing digitization of electronic circuits came with decreasing operating voltages, and increasing switching frequencies and ripple current loads. This had consequences for power supplies and their electrolytic capacitors. Capacitors with lower ESR and lower
During the 1970s, the increasing digitization of electronic circuits came with decreasing operating voltages, and increasing switching frequencies and ripple current loads. This had consequences for power supplies and their electrolytic capacitors. Capacitors with lower ESR and lower  The first Al-e-caps to use the charge transfer salt TTF-TCNQ as a solid organic electrolyte was the OS-CON series offered in 1983 from
The first Al-e-caps to use the charge transfer salt TTF-TCNQ as a solid organic electrolyte was the OS-CON series offered in 1983 from
/ref> By 1995, the Sanyo OS-CON became the preferred decoupling capacitor for Pentium processor-based IBM personal computers. The Sanyo OS-CON e-cap product line was sold in 2010 to Panasonic. Panasonic then replaced the TCNQ salt with a conducting polymer under the same brand. The next step in ESR reduction was the development of
 The change to digital electronic equipment led to the development of switching power supplies with higher frequencies and "on-board" DC/DC converter, lower supply voltages and higher supply currents. Capacitors for this applications needed lower ESR values, which at that time with Al-e-caps could only be realized with larger case sizes or by replacement with much more expensive solid Ta-caps.
The reason how the ESR influences the functionality of an integrated circuit is simple. If the circuit, f. e. a
The change to digital electronic equipment led to the development of switching power supplies with higher frequencies and "on-board" DC/DC converter, lower supply voltages and higher supply currents. Capacitors for this applications needed lower ESR values, which at that time with Al-e-caps could only be realized with larger case sizes or by replacement with much more expensive solid Ta-caps.
The reason how the ESR influences the functionality of an integrated circuit is simple. If the circuit, f. e. a
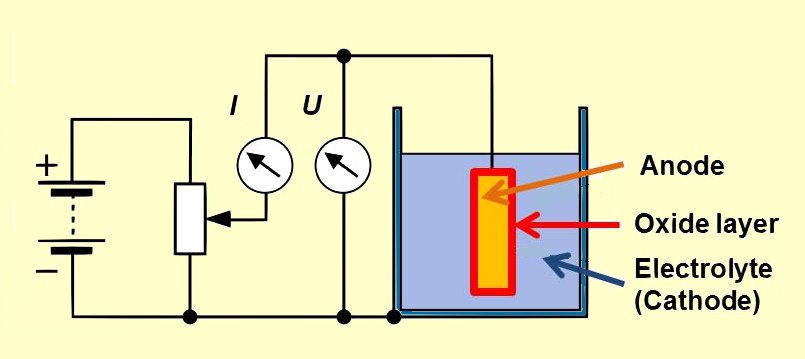 Electrolytic capacitors use a chemical feature of some special metals, earlier called "valve metals", that by
Electrolytic capacitors use a chemical feature of some special metals, earlier called "valve metals", that by  Every e-cap in principle forms a "plate capacitor" whose capacitance is an increasing function of the electrode area A, the permittivity ε of the dielectric material and the thickness of the dielectric (d).
:
Capacitance is proportional to the product of the area of one plate multiplied by the permittivity and divided by the dielectric thickness.
The dielectric thickness is in the range of
Every e-cap in principle forms a "plate capacitor" whose capacitance is an increasing function of the electrode area A, the permittivity ε of the dielectric material and the thickness of the dielectric (d).
:
Capacitance is proportional to the product of the area of one plate multiplied by the permittivity and divided by the dielectric thickness.
The dielectric thickness is in the range of
 Electrolytic capacitors with the charge transfer salt tetracyanoquinodimethane TCNQ as electrolyte, formerly produced by
Electrolytic capacitors with the charge transfer salt tetracyanoquinodimethane TCNQ as electrolyte, formerly produced by
''Organic chemistry''
Oxford University Press pp. 1450–1466 Usually polymers are electrically insulators, at best, semiconductors. For use as an electrolyte in e-caps, electrical



 A polymer capacitor, or more accurately a polymer electrolytic capacitor, is an
A polymer capacitor, or more accurately a polymer electrolytic capacitor, is an electrolytic capacitor
An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A solid, liquid, or gel ...
(e-cap) with a solid conductive polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymer ...
electrolyte. There are four different types:
* Polymer tantalum electrolytic capacitor (Polymer Ta-e-cap)
* Polymer aluminium electrolytic capacitor (Polymer Al-e-cap)
* Hybrid polymer capacitor (Hybrid polymer Al-e-cap)
* Polymer niobium electrolytic capacitors
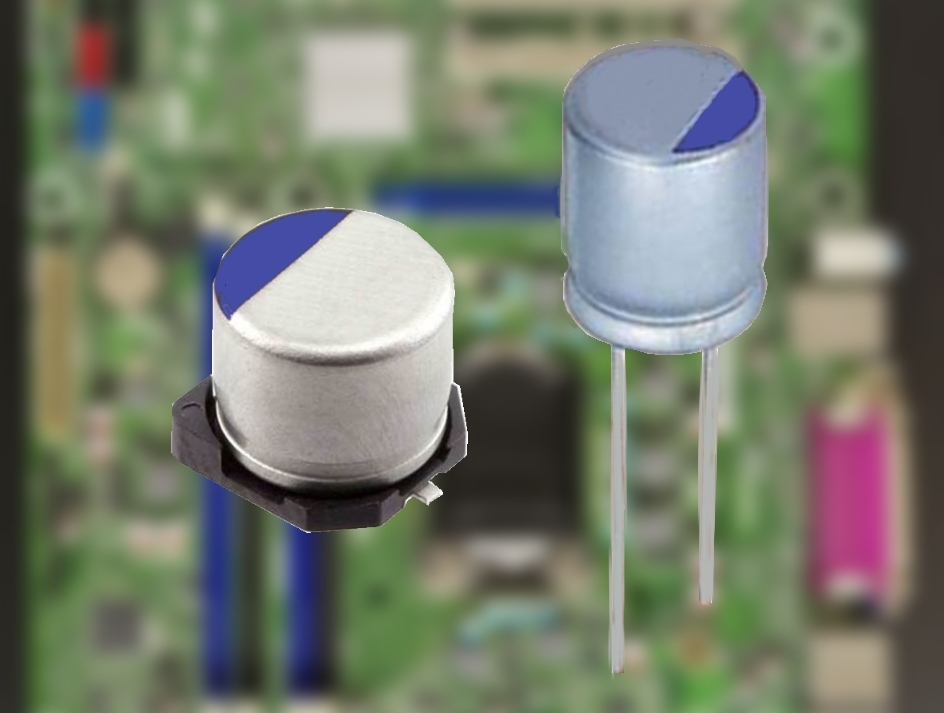
Polymer Ta-e-caps are available in rectangular surface-mounted device ( SMD) chip style. Polymer Al-e-caps and hybrid polymer Al-e-caps are available in rectangular surface-mounted device (SMD) chip style, in cylindrical SMDs (V-chips) style or as radial leaded versions (single-ended).
Polymer electrolytic capacitors are characterized by particularly low internal equivalent series resistance
Practical capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series ...
s (ESR) and high ripple current ratings. Their electrical parameters have similar temperature dependence, reliability and service life compared to solid tantalum capacitors, but have a much better temperature dependence and a considerably longer service life than aluminium electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolytes. In general polymer e-caps have a higher leakage current rating than the other solid or non-solid electrolytic capacitors.
Polymer electrolytic capacitors are also available in a hybrid construction. The hybrid polymer aluminium electrolytic capacitors combine a solid polymer electrolyte with a liquid electrolyte. These types are characterized by low ESR values but have low leakage currents and are insensitive to transients, however they have a temperature-dependent service life similar to non-solid e-caps.
Polymer electrolytic capacitors are mainly used in power supplies
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a r ...
of integrated electronic circuits as buffer, bypass and decoupling capacitors, especially in devices with flat or compact design. Thus they compete with MLCC capacitor
A ceramic capacitor is a fixed-value capacitor where the ceramic material acts as the dielectric. It is constructed of two or more alternating layers of ceramic and a metal layer acting as the electrodes. The composition of the ceramic material de ...
s, but offer higher capacitance values than MLCC, and they display no microphonic
Microphonics, microphony, or microphonism describes the phenomenon wherein certain components in electronic devices transform mechanical vibrations into an undesired electrical signal (noise). The term comes from analogy with a microphone, which ...
effect (such as class 2 and 3 ceramic capacitor
A ceramic capacitor is a fixed-value capacitor where the ceramic material acts as the dielectric. It is constructed of two or more alternating layers of ceramic and a metal layer acting as the electrodes. The composition of the ceramic material de ...
s).
History
Aluminiumelectrolytic capacitors
An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A solid, liquid, or gel ...
(Al-e-caps) with liquid electrolytes were invented in 1896 by Charles Pollak.
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with solid manganese dioxide
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-cel ...
(MnO2) electrolytes were invented by Bell Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mul ...
in the early 1950s, as a miniaturized and more reliable low-voltage support capacitor to complement the newly invented transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
, see Tantalum capacitor
A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor, a passive component of electronic circuits. It consists of a pellet of porous tantalum metal as an anode, covered by an insulating oxide layer that forms the dielectric, surrounde ...
. The first Ta-e-caps with MnO2 electrolytes had 10 times better conductivity
Conductivity may refer to:
*Electrical conductivity, a measure of a material's ability to conduct an electric current
**Conductivity (electrolytic), the electrical conductivity of an electrolyte in solution
** Ionic conductivity (solid state), ele ...
and a higher ripple current load than earlier types Al-e-caps with liquid electrolyte. Additionally, unlike standard Al-e-caps, the equivalent series resistance
Practical capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series ...
(ESR) of Ta-caps is stable in varying temperatures.
 During the 1970s, the increasing digitization of electronic circuits came with decreasing operating voltages, and increasing switching frequencies and ripple current loads. This had consequences for power supplies and their electrolytic capacitors. Capacitors with lower ESR and lower
During the 1970s, the increasing digitization of electronic circuits came with decreasing operating voltages, and increasing switching frequencies and ripple current loads. This had consequences for power supplies and their electrolytic capacitors. Capacitors with lower ESR and lower equivalent series inductance
Equivalent series inductance (ESL) is an effective inductance that is used to describe the inductive part of the impedance of certain electrical components.
Overview
The theoretical treatment of devices such as capacitors and resistors tends to ...
(ESL) for bypass and decoupling capacitors used in power supply lines were needed. see Role of ESR, ESL and capacitance.
A breakthrough came in 1973, with the discovery by A. Heeger and F. Wudl of an organic conductor, the charge-transfer salt TCNQ. TCNQ (7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane
Tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) is the organic compound with the formula . This cyanocarbon, a relative of para-quinone, is an electron acceptor that is used to prepare charge transfer salts, which are of interest in molecular electronics.
Pr ...
or N-n-butyl isoquinolinium in combination with TTF (Tetrathiafulvalene
Tetrathiafulvalene is an organosulfur compound with the formula (. Studies on this heterocyclic compound contributed to the development of molecular electronics. TTF is related to the hydrocarbon fulvalene, , by replacement of four CH groups ...
)) is a chain molecule of almost perfect one-dimensional structure that has a 10-fold better conductivity along the chains than does MnO2, and has a 100-fold better conductivity than non-solid electrolytes.
 The first Al-e-caps to use the charge transfer salt TTF-TCNQ as a solid organic electrolyte was the OS-CON series offered in 1983 from
The first Al-e-caps to use the charge transfer salt TTF-TCNQ as a solid organic electrolyte was the OS-CON series offered in 1983 from Sanyo
, stylized as SANYO, is a Japanese electronics company and formerly a member of the ''Fortune'' Global 500 whose headquarters was located in Moriguchi, Osaka prefecture, Japan. Sanyo had over 230 subsidiaries and affiliates, and was founded b ...
. These were wound, cylindrical capacitors with 10x increased electrolyte conductivity compared with MnO2
These capacitors were used in devices for applications that required the lowest possible ESR or highest possible ripple current. One OS-CON e-cap could replace three more bulky "wet" e-caps or two Ta-caps.J. Both, "Electrolytic Capacitors from the Postwar Period to the Present", IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine, Vol.32, Issue:2, pp.8-26, March–April 2016, ,/ref> By 1995, the Sanyo OS-CON became the preferred decoupling capacitor for Pentium processor-based IBM personal computers. The Sanyo OS-CON e-cap product line was sold in 2010 to Panasonic. Panasonic then replaced the TCNQ salt with a conducting polymer under the same brand. The next step in ESR reduction was the development of
conducting polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymer ...
s by Alan J. Heeger
Alan Jay Heeger (born January 22, 1936) is an American physicist, academic and Nobel Prize laureate in chemistry.
Heegar was elected as a member into the National Academy of Engineering in 2002 for co-founding the field of conducting polymers a ...
, Alan MacDiarmid
Alan Graham MacDiarmid, ONZ FRS (14 April 1927 – 7 February 2007) was a New Zealand-born American chemist, and one of three recipients of the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 2000.
Early life and education
MacDiarmid was born in Masterton, Ne ...
and Hideki Shirakawa
is a Japanese chemist, engineer, and Professor Emeritus at the University of Tsukuba and Zhejiang University. He is best known for his discovery of conductive polymers. He was co-recipient of the 2000 Nobel Prize in Chemistry jointly with ...
in 1975. The conductivity of conductive polymers such as polypyrrole
Polypyrrole (PPy) is an organic polymer obtained by oxidative polymerization of pyrrole. It is a solid with the formula H(C4H2NH)nH. It is an intrinsically conducting polymer, used in electronics, optical, biological and medical fields.
History
...
(PPy) or PEDOT
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT or PEDT; ''IUPAC'' name poly(2,3-dihydrothieno ,4-''b''1,4]dioxane-5,7-diyl)) is a conducting polymer based on 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene or EDOT. It was first reported by Bayer AG in 1989.
Polymer
PEDOT p ...
is better than that of TCNQ by a factor of 100 to 500, and close to the conductivity of metals.
In 1988 the first polymer electrolyte e-cap, "APYCAP" with PPy polymer electrolyte, was launched by the Japanese manufacturer Nitsuko. The product was not successful, in part because it was not available in SMD versions.
In 1991 Panasonic launched its polymer Al-e-cap series "SP-Cap", These e-caps used PPy polymer electrolyte and reached ESR values that were directly comparable to Ceramic capacitor, ceramic multilayer capacitors (MLCCs). They were still less expensive than tantalum capacitors and with their flat design useful in compact devices such as laptops and cell phones they competed with tantalum chip capacitors as well.
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors with PPy polymer electrolyte cathode followed three years later. In 1993 NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It provides IT and network soluti ...
introduced its SMD polymer Ta-e-caps called "NeoCap". In 1997 Sanyo followed with the "POSCAP" polymer tantalum chips.
A new conductive polymer for tantalum polymer capacitors was presented by Kemet
Kemet, kmt or km.t may refer to:
* Kemet or km.t, an ancient name of Egypt
* KEMET Corporation, American capacitor manufacturer
* Kemetism, revivals of the ancient Egyptian religion
* ''Kmt'' (magazine), an academic journal of ancient Egypt
* A f ...
at the "1999 Carts" conference. This capacitor used the newly developed organic conductive polymer PEDT (Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT or PEDT; ''IUPAC'' name poly(2,3-dihydrothieno ,4-''b''1,4]dioxane-5,7-diyl)) is a conducting polymer based on 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene or EDOT. It was first reported by Bayer AG in 1989.
Polymer
PEDOT ...
), also known as PEDOT
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT or PEDT; ''IUPAC'' name poly(2,3-dihydrothieno ,4-''b''1,4]dioxane-5,7-diyl)) is a conducting polymer based on 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene or EDOT. It was first reported by Bayer AG in 1989.
Polymer
PEDOT p ...
(trade name Baytron®).
Two years later at the 2001 APEC Conference, Kemet introduced PEDOT polymer aluminium e-caps to the market. PEDOT polymer has a higher temperature stability, and as PEDOT:PSS solution this electrolyte could be inserted only by dipping instead of in-situ polymerization like for PPy which makes the production faster and cheaper. Its AO-Cap series included SMD capacitors with stacked anode in "D" size with heights from 1.0 to 4.0 mm, in competition to the Panasonic SP-Caps using PPy at that time.
Around the turn of the millennium hybrid polymer capacitors were developed, which have in addition to the solid polymer electrolyte a liquid electrolyte connecting the polymer layers covering the dielectric layer on the anode and the cathode foil. The non-solid electrolyte provide oxygen for self-healing purposes to reduce the leakage current. In 2001, NIC Components, NIC launched a hybrid polymer e-cap to replace a polymer type at lower price and with lower leakage current. As of 2016 hybrid polymer capacitors are available from multiple manufacturers.
Application basics
Role of ESR, ESL and capacitance
The predominant application of all electrolytic capacitors is inpower supplies
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a r ...
. They are used in input and output smoothing capacitors, as decoupling capacitor
A decoupling capacitor is a capacitor used to decouple one part of an electrical network (circuit) from another. Noise caused by other circuit elements is shunted through the capacitor, reducing its effect on the rest of the circuit. For high ...
s to circulate the harmonic current in a short loop, as bypass capacitor
A decoupling capacitor is a capacitor used to decouple one part of an electrical network (circuit) from another. Noise caused by other circuit elements is shunted through the capacitor, reducing its effect on the rest of the circuit. For hig ...
s to shunt AC noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference aris ...
to the ground by bypassing the power supply lines, as backup capacitors to mitigate the drop in line voltage during sudden power demand or as filter capacitor
Capacitors have many uses in electronic and electrical systems. They are so ubiquitous that it is rare that an electrical product does not include at least one for some purpose.
Energy storage
A capacitor can store electric energy when it is c ...
in low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
to reduce switching noises. In these applications, in addition to the size, are the capacitance, the impedance ''Z'', the ESR, and the inductance ESL important electrical characteristics for the functionality of these capacitors in the circuits.
 The change to digital electronic equipment led to the development of switching power supplies with higher frequencies and "on-board" DC/DC converter, lower supply voltages and higher supply currents. Capacitors for this applications needed lower ESR values, which at that time with Al-e-caps could only be realized with larger case sizes or by replacement with much more expensive solid Ta-caps.
The reason how the ESR influences the functionality of an integrated circuit is simple. If the circuit, f. e. a
The change to digital electronic equipment led to the development of switching power supplies with higher frequencies and "on-board" DC/DC converter, lower supply voltages and higher supply currents. Capacitors for this applications needed lower ESR values, which at that time with Al-e-caps could only be realized with larger case sizes or by replacement with much more expensive solid Ta-caps.
The reason how the ESR influences the functionality of an integrated circuit is simple. If the circuit, f. e. a microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
, has a sudden power demand, the supply voltage drops by ESL, ESR and capacitance charge loss. Because in case of a sudden current demand the voltage of the power line drops:
:Δ''U'' = ESR × ''I''.
For example:
Given a supply voltage of 3 V, with a tolerance of 10% (300 mV) and supply current of a maximum of 10 A, a sudden power demand drops the voltage by
: ESR = ''U''/''I'' = (0.3 V)/(10 A) = 30 mΩ.
This means that the ESR in a CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, an ...
power supply must be less than 30 mΩ, otherwise the circuit malfunctions.
Similar rules are valid for capacitance and ESL. The specific capacitance could be increased over the years by higher etched anode foils respectively by smaller and finer tantalum powder grains by a factor of 10 to 15 and could follow the trend of miniaturizing. The ESL challenge has led to the stacked foil versions of polymer Al e-caps. However, for lowering the ESR only the development of new, solid conductive materials, first TCNQ, after that the conductive polymers, which led to the development of the polymer electrolyte capacitors with their very low ESR values, the ESR challenge of digitization of electronic circuits could be accepted.
Electrolytic capacitors – basics
Anodic oxidation
 Electrolytic capacitors use a chemical feature of some special metals, earlier called "valve metals", that by
Electrolytic capacitors use a chemical feature of some special metals, earlier called "valve metals", that by anodic
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
form an insulating oxide layer. By applying a positive voltage to the anode (+) material in an electrolytic bath an oxide barrier layer with a thickness corresponding to the applied voltage can be formed. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric in an e-cap. To increase the capacitors capacitance the anode surface is roughened and so the oxide layer surface also is roughened. To complete a capacitor a counter electrode has to match the rough insulating oxide surface. This is accomplished by the electrolyte, which acts as the cathode (-) electrode of an electrolytic capacitor.
The main difference between the polymer capacitors is the anode material and its oxide used as the dielectric:
* Polymer tantalum electrolytic capacitors use high purity sintered tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as ''tantalium'', it is named after Tantalus, a villain in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is ...
powder as an anode with tantalum pentoxide
Tantalum pentoxide, also known as tantalum(V) oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid that is insoluble in all solvents but is attacked by strong bases and hydrofluoric acid. is an inert material with a high refrac ...
(Ta2O5) as a dielectric and
* Polymer aluminium electrolytic capacitors use a high purity and electrochemically etched (roughened) aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in AmE, American and CanE, Canadian English) is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately o ...
foil as an anode with aluminium oxide (Al2O3) as the dielectric
The properties of the aluminium oxide layer compared with tantalum pentoxide dielectric layer are given in the following table:
nanometers
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, ...
per volt. On the other hand, the breakdown voltage of these oxide layers is quite high. Using etched or sintered anodes, with their much higher surface area compared to a smooth surface of the same size or volume, e-caps can achieve a high volumetric capacitance. The latest developments in high etched or sintered anodes increases the capacitance value, depending on the rated voltage, by a factor of up to 200 for Al-e-caps or Ta-e-caps compared with smooth anodes.
Because the forming voltage defines the oxide thickness, the desired voltage tolerance can be easily produced. Therefore, the volume of a capacitor is defined by the product of capacitance and voltage, the so-called "CV product".
Comparing the dielectric constants of tantalum and aluminium oxides, Ta2O5 has permittivity approximately 3-fold higher than Al2O3. Ta-caps therefore theoretically can be smaller than Al-caps with the same capacitance and rated voltage.
For real tantalum electrolytic capacitors, the oxide layer thicknesses are much thicker than the rated voltage of the capacitor actually requires. This is done for safety reasons to avoid shorts coming from field crystallization. For this reason the real differences of sizes that derive from the different permittivities, are partially ineffective.
Electrolytes
The most important electrical property of an electrolyte in an electrolytic capacitor is its electricalconductivity
Conductivity may refer to:
*Electrical conductivity, a measure of a material's ability to conduct an electric current
**Conductivity (electrolytic), the electrical conductivity of an electrolyte in solution
** Ionic conductivity (solid state), ele ...
. The electrolyte forms the counter electrode, of the e-cap, the cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction i ...
. The roughened structures of the anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemoni ...
surface continue in the structure of the oxide layer, the dielectric, the cathode must adapt precisely to the roughened structure. With a liquid, as in the conventional "wet" e-caps that is easy to achieve. In polymer e-caps in which a solid conductive polymer forms the electrolyte, this is much more difficult to achieve, because its conductivity comes by a chemical process of polymerization. However, the benefits of a solid polymer electrolyte, the significantly lower ESR of the capacitor and the low temperature dependence of the electrical parameters, in many cases justify the additional production steps as well as higher costs.
Conducting salt TCNQ electrolyte
Sanyo
, stylized as SANYO, is a Japanese electronics company and formerly a member of the ''Fortune'' Global 500 whose headquarters was located in Moriguchi, Osaka prefecture, Japan. Sanyo had over 230 subsidiaries and affiliates, and was founded b ...
with the trade name "OS-CON", in the true sense of the term "polymer" were not "polymer capacitors". TCNQ electrolytic capacitors are mentioned here to point out the danger of confusion with 'real' polymer capacitors, which are sold nowadays under the same trade name OS-CON. The original OS-CON capacitors with TCNQ electrolyte sold by the former manufacturer Sanyo has been discontinued with the integration of Sanyo capacitor businesses by Panasonic 2010. Panasonic keep the trade name OS-CON but change the TCNQ electrolyte into a conductive polymer electrolyte (PPy).
Electrolytic capacitors with TCNQ electrolyte are not available anymore.
Polymer electrolyte
Polymers are formed by achemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and break ...
, polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many fo ...
. In this reaction monomers are continuously attached to a growing polymer strand.Clayden, J., Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2000)''Organic chemistry''
Oxford University Press pp. 1450–1466 Usually polymers are electrically insulators, at best, semiconductors. For use as an electrolyte in e-caps, electrical
conductive
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. Electric current is gen ...
polymers are employed. The conductivity of a polymer is obtained by conjugated double bonds
In theoretical chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule, which in general lowers the overall energy of the molecule and increases stability. It is conventionally represent ...
which permit free movement of charge carrier
In physics, a charge carrier is a particle or quasiparticle that is free to move, carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric charges in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons, ions and holes. The term is u ...
s in the doped state. As charge carriers serve electron hole
In physics, chemistry, and electronic engineering, an electron hole (often simply called a hole) is a quasiparticle which is the lack of an electron at a position where one could exist in an atom or atomic lattice. Since in a normal atom or ...
s. That means, the conductivity of conducting polymers, which is nearly comparable with metallic conductors, only starts when the polymers are doped oxidatively or reductively.
A polymer electrolyte must be able to penetrate the anode's finest pores to form a complete, homogeneous layer, because only anode oxide sections covered by the electrolyte contribute to the capacitance. For this the precursors of the polymer has to consist of very small base materials that can penetrate even the smallest pores. The size of this precursors are the limiting factor in the size of the pores in the etched aluminium anode foils or of the size of tantalum powder. The rate of polymerization must be controlled for capacitor manufacturing. Too rapid polymerization does not lead to a complete anode coverage, while too slow polymerization increases production costs. Neither the precursors nor the polymer or its residues may attack the anodes oxide chemically or mechanically. The polymer electrolyte must have high stability over a wide temperature range over long times. The polymer film is not only the counter electrode of the e-cap it also protects the dielectric even against external influences such as the direct contact of graphite in this capacitors, which are provided with a cathode contact via graphite and silver.
Polymer e-caps employ either polypyrrole
Polypyrrole (PPy) is an organic polymer obtained by oxidative polymerization of pyrrole. It is a solid with the formula H(C4H2NH)nH. It is an intrinsically conducting polymer, used in electronics, optical, biological and medical fields.
History
...
(PPy) or polythiophene
Polythiophenes (PTs) are polymerized thiophenes, a sulfur heterocycle. The parent PT is an insoluble colored solid with the formula (C4H2S)n. The rings are linked through the 2- and 5-positions. Poly(alkylthiophene)s have alkyl substituents ...
(PEDOT or PEDT)
Polypyrrole PPy
