Polk Administration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The abolitionist Liberty party nominated Michigan's James G. Birney, while the
The abolitionist Liberty party nominated Michigan's James G. Birney, while the
 Polk was inaugurated as the nation's 11th president on March 4, 1845, in a ceremony held on the East Portico of the
Polk was inaugurated as the nation's 11th president on March 4, 1845, in a ceremony held on the East Portico of the
 Polk governed with the help of his cabinet, in which he placed great importance. The cabinet regularly met twice a week, and Polk and his six cabinet members discussed all major issues during these meetings.Merry, pg. 134–135 Despite his reliance on his cabinet, Polk involved himself in the minutiae of the various departments, especially regarding the military.Merry, pg. 269–270
In selecting a new cabinet, Polk generally heeded Jackson's advice to avoid individuals who were themselves interested in the presidency, though he chose to nominate Buchanan for the crucial and prestigious position of Secretary of State.Merry, pg. 114–117Seigenthaler, pp. 104–106 Polk respected Buchanan's opinion and Buchanan played an important role in Polk's presidency, but the two often clashed over foreign policy and appointments. Polk frequently considered dismissing Buchanan from office, as he suspected Buchanan of placing his own presidential aspirations above service to Polk, but Buchanan always managed to convince Polk of his loyalty.Merry, pg. 439–440
Polk put together an initial slate of cabinet choices that met with the approval of Andrew Jackson, who Polk met with in January 1845 for the last time, as Jackson died in June 1845.
Polk governed with the help of his cabinet, in which he placed great importance. The cabinet regularly met twice a week, and Polk and his six cabinet members discussed all major issues during these meetings.Merry, pg. 134–135 Despite his reliance on his cabinet, Polk involved himself in the minutiae of the various departments, especially regarding the military.Merry, pg. 269–270
In selecting a new cabinet, Polk generally heeded Jackson's advice to avoid individuals who were themselves interested in the presidency, though he chose to nominate Buchanan for the crucial and prestigious position of Secretary of State.Merry, pg. 114–117Seigenthaler, pp. 104–106 Polk respected Buchanan's opinion and Buchanan played an important role in Polk's presidency, but the two often clashed over foreign policy and appointments. Polk frequently considered dismissing Buchanan from office, as he suspected Buchanan of placing his own presidential aspirations above service to Polk, but Buchanan always managed to convince Polk of his loyalty.Merry, pg. 439–440
Polk put together an initial slate of cabinet choices that met with the approval of Andrew Jackson, who Polk met with in January 1845 for the last time, as Jackson died in June 1845.
 The
The
 Since the signing of the
Since the signing of the
 In September 1847,
In September 1847,

 Polk had been anxious to establish a territorial government for Oregon once the treaty was effective in 1846, but the matter became embroiled in the arguments over slavery, though few thought Oregon suitable for that institution. A bill to establish an Oregon territorial government passed the House after being amended to bar slavery; the bill died in the Senate when opponents ran out the clock on the congressional session. A resurrected bill, still barring slavery, again passed the House in January 1847, but it was not considered by the Senate before Congress adjourned in March. By the time Congress met again in December, California and New Mexico were in U.S. hands, and Polk in his annual message urged the establishment of territorial governments in California, New Mexico, and Oregon. The
Polk had been anxious to establish a territorial government for Oregon once the treaty was effective in 1846, but the matter became embroiled in the arguments over slavery, though few thought Oregon suitable for that institution. A bill to establish an Oregon territorial government passed the House after being amended to bar slavery; the bill died in the Senate when opponents ran out the clock on the congressional session. A resurrected bill, still barring slavery, again passed the House in January 1847, but it was not considered by the Senate before Congress adjourned in March. By the time Congress met again in December, California and New Mexico were in U.S. hands, and Polk in his annual message urged the establishment of territorial governments in California, New Mexico, and Oregon. The

 Authoritative word of the discovery of gold in California did not arrive in Washington until after the 1848 election, by which time Polk was a lame duck. Polk was delighted by the discovery of gold, seeing it as validation of his stance on expansion, and he referred to the discovery several times in his final annual message to Congress that December. Shortly thereafter, actual samples of the California gold arrived, and Polk sent a special message to Congress on the subject. The message, confirming less authoritative reports, caused large numbers of people to move to California, both from the U.S. and abroad, thus helping to spark the
Authoritative word of the discovery of gold in California did not arrive in Washington until after the 1848 election, by which time Polk was a lame duck. Polk was delighted by the discovery of gold, seeing it as validation of his stance on expansion, and he referred to the discovery several times in his final annual message to Congress that December. Shortly thereafter, actual samples of the California gold arrived, and Polk sent a special message to Congress on the subject. The message, confirming less authoritative reports, caused large numbers of people to move to California, both from the U.S. and abroad, thus helping to spark the
 Honoring his pledge to serve only one term, Polk declined to seek re-election in 1848. With Polk out of the race, the Democratic Party remained fractured along geographic lines.Merry, pg. 376–377 Polk privately favored Lewis Cass as his successor, but resisted becoming closely involved in the election. At the
Honoring his pledge to serve only one term, Polk declined to seek re-election in 1848. With Polk out of the race, the Democratic Party remained fractured along geographic lines.Merry, pg. 376–377 Polk privately favored Lewis Cass as his successor, but resisted becoming closely involved in the election. At the
 Polk's historic reputation was largely formed by the attacks made on him in his own time. Whig politicians claimed that he was drawn from a well-deserved obscurity.
Polk's historic reputation was largely formed by the attacks made on him in his own time. Whig politicians claimed that he was drawn from a well-deserved obscurity.
online
* Devoti, John. "The patriotic business of seeking office: James K. Polk and the patronage" (PhD dissertation, Temple University; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 2005. 3203004). * De Voto, Bernard. ''The Year of Decision: 1846''. Houghton Mifflin, 1943. * Eisenhower, John S. D. "The Election of James K. Polk, 1844". ''Tennessee Historical Quarterly''. 53.2 (1994): 74–87. ; popular. * Graff, Henry F., ed. ''The Presidents: A Reference History'' (3rd ed. 2002)
online
* Greenstein, Fred I. "The policy-driven leadership of James K. Polk: making the most of a weak presidency." ''Presidential Studies Quarterly'' 40#4 (2010), p. 725+
online
* Heidt, Stephen J. “Presidential Power and National Violence: James K. Polk’s Rhetorical Transfer of Savagery.” ''Rhetoric and Public Affairs'' 19#3 (2016), pp. 365–96
online
* Kornblith, Gary J. "Rethinking the Coming of the Civil War: a Counterfactual Exercise". ''Journal of American History'' 90.1 (2003): 76–105. . Asks what if Polk had not gone to war? * Leonard, Thomas. ''James K. Polk: A Clear and Unquestionable Destiny'' (Scholarly Resources Inc, 2001). * McCormac, Eugene Irving. ''James K. Polk: A Political Biography to the End of a Career, 1845–1849''. Univ. of California Press, 1922. (1995 reprint has .) hostile to Jacksonians * Merk, Frederick. ''Manifest Destiny and Mission in American History: A Reinterpretation'' (Vintage Books, 1966). * Morrison, Michael A. "Martin Van Buren, the Democracy, and the Partisan Politics of Texas Annexation". ''Journal of Southern History'' 61.4 (1995): 695–724. . Discusses the election of 1844. * Nau, Henry R. “James K. Polk: Manifest Destiny.” in ''Conservative Internationalism: Armed Diplomacy under Jefferson, Polk, Truman, and Reagan'' (Princeton University Press, 2013), pp. 110–46
online
* Nelson, Anna Louise Kasten. "The Secret Diplomacy of James K. Polk during the Mexican War, 1846–1847" PhD dissertation, The George Washington University; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 1972. 7304017). * Palmer‐Mehta, Valerie. "Sarah Polk: Ideas of Her Own." in ''A Companion to First Ladies'' (2016): 159–175. * Paul; James C. N. ''Rift in the Democracy.'' (1951). on 1844 election * * Rowe, Christopher. "American society through the prism of the Walker Tariff of 1846." ''Economic Affairs'' 40.2 (2020): 180–197. * Ruiz, Ramon, ed. ''The Mexican War: Was it Manifest Destiny?'' (1963) excerpts from primary and secondary sources. * Schoenbeck, Henry Fred. "The economic views of James K. Polk as expressed in the course of his political career" (PhD dissertation, The University of Nebraska – Lincoln; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 1951. DP13923). * Sellers, Charles. ''James K. Polk, Jacksonian, 1795–1843'' (1957
vol 1 online
and ''James K. Polk, Continentalist, 1843–1846''. (1966
vol 2 online
long scholarly biography * pp 195–290 * Smith, Justin Harvey. ''The War with Mexico, Vol 1.'' (2 vol 1919)
full text online
** Smith, Justin Harvey. ''The War with Mexico, Vol. 2''. (2 vol 1919)
full text online
Pulitzer prize; still a major standard source, * Weinberg, Albert. ''Manifest Destiny: A Study of Nationalist Expansionism in American History'' (1935
online
* Williams, Frank J. “James K. Polk.” in ''The Presidents and the Constitution: A Living History'', edited by Ken Gormley, NYU Press, 2016, pp. 149–58
online
* Winders, Richard Bruce. ''Mr. Polk's army: the American military experience in the Mexican war'' (Texas A&M University Press, 2001).
online
online vol 13, August 1847 to March 1848
* Polk, James K. ''The Diary of James K. Polk During His Presidency, 1845–1849'' edited by Milo Milton Quaife, 4 vols. 1910. Abridged version by Allan Nevins. 1929/
James K. Polk: A Resource Guide
from the
James K. Polk's Personal Correspondence
Shapell Manuscript Foundation
Extensive essay on James K. Polk and shorter essays on each member of his cabinet and First Lady
from the
Inaugural Address of James K. Polk
from The Avalon Project at the
Biography of James K. Polk
from the official
President James K. Polk State Historic Site, Pineville, North Carolina
from a
"Life Portrait of James K. Polk"
from
James K. Polk
James Knox Polk (; November 2, 1795 – June 15, 1849) was the 11th president of the United States, serving from 1845 to 1849. A protégé of Andrew Jackson and a member of the Democratic Party, he was an advocate of Jacksonian democracy and ...
served as the 11th president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
from March 4, 1845, to March 4, 1849. A Democrat
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:
Politics
*A proponent of democracy, or democratic government; a form of government involving rule by the people.
*A member of a Democratic Party:
**Democratic Party (Cyprus) (DCY)
**Democratic Part ...
, Polk assumed office after defeating Whig Henry Clay
Henry Clay (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the United States Senate, U.S. Senate and United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives. He was the seventh Spea ...
in the 1844 presidential election. Polk left office after one term, fulfilling a campaign pledge he made in 1844, and he was succeeded by Whig Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor (November 24, 1784 – July 9, 1850) was an American military officer and politician who was the 12th president of the United States, serving from 1849 until his death in 1850. Taylor was a career officer in the United States ...
. A close ally of Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses ...
, Polk's presidency reflected his adherence to the ideals of Jacksonian democracy
Jacksonian democracy, also known as Jacksonianism, was a 19th-century political ideology in the United States that restructured a number of federal institutions. Originating with the seventh U.S. president, Andrew Jackson and his supporters, i ...
and manifest destiny
Manifest destiny was the belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American pioneer, American settlers were destined to expand westward across North America, and that this belief was both obvious ("''m ...
.
Polk is regarded as the last effective pre-Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
president, having met during his four years in office every major domestic and foreign policy goal set during his campaign and the transition to his administration. Polk's presidency was particularly influential in U.S. foreign policy, and his presidency saw the last major expansions of the Contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
. When Mexico rejected the U.S. annexation of Texas
The Republic of Texas was annexed into the United States and admitted to the Union as the 28th state on December 29, 1845.
The Republic of Texas declared independence from the Republic of Mexico on March 2, 1836. It applied for annexatio ...
, Polk achieved a sweeping victory in the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
, which resulted in the cession by Mexico of nearly the whole of what is now the American Southwest
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural list of regions of the United States, region of the United States that includes Arizona and New Mexico, along with adjacen ...
. He threatened war with Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
over control of the Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long Oregon boundary dispute, dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been demarcat ...
, eventually reaching an agreement in which both nations agreed to partition the region at the 49th parallel.
Polk also accomplished his goals in domestic policy. He ensured a substantial reduction of tariff rates by replacing the "Black Tariff
The Tariff of 1842, or Black Tariff as it became known, was a protectionist tariff schedule adopted in the United States. It reversed the effects of the Compromise Tariff of 1833, which contained a provision that successively lowered the tarif ...
" with the Walker tariff of 1846, which pleased the less-industrialized states of his native Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is List of regions of the United States, census regions defined by the United States Cens ...
by rendering less expensive both imported and, through competition, domestic goods. Additionally, he built an independent treasury system that lasted until 1913, oversaw the opening of the U.S. Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (USNA, Navy, or Annapolis) is a federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as Secretary of the Navy. The Naval Academy is the sec ...
and of the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase a ...
, the groundbreaking for the Washington Monument
The Washington Monument is an obelisk on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., built to commemorate George Washington, a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father of the United States, victorious commander-in-chief of the Continen ...
, and the issuance of the first United States postage stamp.
Polk did not closely involve himself in the 1848 presidential election, but his actions strongly affected the race. General Zachary Taylor, who had served in the Mexican–American War, won the Whig presidential nomination and defeated Polk's preferred candidate, Democratic Senator Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass (October 9, 1782June 17, 1866) was a United States Army officer and politician. He represented Michigan in the United States Senate and served in the Cabinets of two U.S. Presidents, Andrew Jackson and James Buchanan. He was also the 1 ...
. Scholars have ranked
A ranking is a relationship between a set of items, often recorded in a list, such that, for any two items, the first is either "ranked higher than", "ranked lower than", or "ranked equal to" the second. In mathematics, this is known as a weak ...
Polk favorably for his ability to promote, obtain support for, and achieve all of the major items on his presidential agenda. However, he has also been criticized for leading the country into war against Mexico and for exacerbating sectional divides. Polk has been called the "least known consequential president" of the United States.
1844 election
In the months leading up to the1844 Democratic National Convention
The 1844 Democratic National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held in Baltimore, Maryland from May 27 through 30. The convention nominated former Governor James K. Polk of Tennessee for president and former Senator George M. ...
, former President Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was the eighth president of the United States, serving from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served as Attorney General o ...
was widely seen as the front-runner for the Democratic presidential nomination. Polk, who desired to be the party's vice-presidential nominee in the 1844 election,Merry p. 43-44 engaged in a delicate and subtle campaign to become Van Buren's running mate.Merry p. 50-53 The proposed annexation
Annexation, in international law, is the forcible acquisition and assertion of legal title over one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. In current international law, it is generally held t ...
of the Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas (), or simply Texas, was a country in North America that existed for close to 10 years, from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846. Texas shared borders with Centralist Republic of Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande, an ...
by President John Tyler
John Tyler (March 29, 1790 – January 18, 1862) was the tenth president of the United States, serving from 1841 to 1845, after briefly holding office as the tenth vice president of the United States, vice president in 1841. He was elected ...
upended the presidential race. Van Buren and the Whig frontrunner, Henry Clay
Henry Clay (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the United States Senate, U.S. Senate and United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives. He was the seventh Spea ...
, opposed the annexation and a potential war with Mexico over the disputed territory, Polk and former President Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses ...
strongly supported the acquisition of the independent country. Disappointed by Van Buren's position, Jackson threw his support behind Polk for the nomination.
When the Democratic National Convention began on May 27, 1844, the key question was whether the convention would adopt a rule requiring the presidential nominee to receive the vote of two-thirds of the delegates. With the strong support of the Southern states, the two thirds-rule was passed by the convention, effectively ending the possibility of Van Buren's nomination due to the strong opposition he faced from an unyielding and significant minority of delegates.Merry, pg. 87–88 Van Buren won a majority on the first presidential ballot, but failed to win the necessary super-majority, and support for Van Buren faded on subsequent ballots. On the eighth presidential ballot, Polk won 44 of the 266 delegates, as support for all candidates other than Polk, Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass (October 9, 1782June 17, 1866) was a United States Army officer and politician. He represented Michigan in the United States Senate and served in the Cabinets of two U.S. Presidents, Andrew Jackson and James Buchanan. He was also the 1 ...
, and Van Buren dissipated.Merry, pg. 92–94 Following the eighth ballot, several delegates rose to speak in support of Polk's candidacy. Van Buren, then realizing that he had no chance of ever winning the 1844 presidential nomination, threw his support behind Polk, who won on the next ballot. In doing so, Polk became the first "dark horse
A dark horse is a previously lesser-known person, team or thing that emerges to prominence in a situation, especially in a competition involving multiple rivals, that is unlikely to succeed but has a fighting chance, unlike the underdog who is exp ...
" candidate ever to win a major U.S. political party's presidential nomination. After Senator Silas Wright
Silas Wright Jr. (May 24, 1795 – August 27, 1847) was an American attorney and Democratic politician. A member of the Albany Regency, he served as a member of the United States House of Representatives, New York State Comptroller, United Stat ...
, a close Van Buren ally, declined the vice presidential nomination, the convention nominated former Senator George M. Dallas of Pennsylvania as Polk's running mate.
After learning of his nomination, Polk promised to serve only one term, believing that this would help him win the support of Democratic leaders such as Cass, Wright, John C. Calhoun
John Caldwell Calhoun (; March 18, 1782March 31, 1850) was an American statesman and political theorist who served as the seventh vice president of the United States from 1825 to 1832. Born in South Carolina, he adamantly defended American s ...
, Thomas Hart Benton, and James Buchanan
James Buchanan Jr. ( ; April 23, 1791June 1, 1868) was the 15th president of the United States, serving from 1857 to 1861. He also served as the United States Secretary of State, secretary of state from 1845 to 1849 and represented Pennsylvan ...
, all of whom had presidential aspirations.Merry, pp. 103–104 Further, he avoided taking a position on the protectionist
Protectionism, sometimes referred to as trade protectionism, is the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, import quotas, and a variety of other government regulations. ...
Tariff of 1842
The Tariff of 1842, or Black Tariff as it became known, was a protectionist tariff schedule adopted in the United States. It reversed the effects of the Compromise Tariff of 1833, which contained a provision that successively lowered the tariff ...
, but appealed to the key state of Pennsylvania by using rhetoric favorable towards high tariffs.Merry, pg. 99–100 In New York, another key swing state, Polk's campaign was greatly aided by the gubernatorial candidacy of Wright, who managed to unite the factions of the New York Democratic Party.
 The abolitionist Liberty party nominated Michigan's James G. Birney, while the
The abolitionist Liberty party nominated Michigan's James G. Birney, while the 1844 Whig National Convention
The 1844 Whig National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held on May 1, 1844, at Universalist Church in Baltimore, Maryland. It nominated the Whig Party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1844 election. The ...
nominated Henry Clay on the first ballot. Notwithstanding that Polk had been Speaker of the House of Representatives and governor of Tennessee, Whig speeches and editorials scorned Polk, mocking him with the chant "Who is James K. Polk?" in reference to Polk's relative obscurity compared to both Van Buren or Clay.Merry, pg. 96–97 The Whigs blanketed the nation with hundreds of thousands of anti-Polk tracts, accusing him of being a puppet of the " slaveocracy" and a radical who would destroy the United States over the annexation of Texas. Democrats like Robert Walker recast the issue of Texas annexation, arguing that Texas and as Oregon were rightfully American but had been lost during the Monroe administration. Walker further argued that Texas would provide a market for Northern goods and would allow for the "diffusion" of slavery, which in turn would lead to gradual emancipation. In response, Clay argued that the annexation of Texas would bring war with Mexico and increase sectional tensions.
Ultimately, Polk triumphed in an extremely close election, defeating Clay 170–105 in the Electoral College
An electoral college is a body whose task is to elect a candidate to a particular office. It is mostly used in the political context for a constitutional body that appoints the head of state or government, and sometimes the upper parliament ...
; the flip of just a few thousand voters in New York would have given the election to Clay. Birney won several thousand anti-annexation votes in New York, and his presence in the race may have cost Clay the election.
Inauguration
 Polk was inaugurated as the nation's 11th president on March 4, 1845, in a ceremony held on the East Portico of the
Polk was inaugurated as the nation's 11th president on March 4, 1845, in a ceremony held on the East Portico of the United States Capitol
The United States Capitol, often called the Capitol or the Capitol Building, is the Seat of government, seat of the United States Congress, the United States Congress, legislative branch of the Federal government of the United States, federal g ...
. Chief Justice Roger Taney
Roger Brooke Taney ( ; March 17, 1777 – October 12, 1864) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the fifth chief justice of the United States, holding that office from 1836 until his death in 1864. Taney delivered the majority opin ...
administered the oath of office
An oath of office is an oath or affirmation a person takes before assuming the duties of an office, usually a position in government or within a religious body, although such oaths are sometimes required of officers of other organizations. Suc ...
. Polk's inauguration was the first presidential inauguration to be reported by telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas ...
and shown in a newspaper illustration (in ''The Illustrated London News
''The Illustrated London News'', founded by Herbert Ingram and first published on Saturday 14 May 1842, was the world's first illustrated weekly news magazine. The magazine was published weekly for most of its existence, switched to a less freq ...
'').
Polk's inaugural address, written with the help of Amos Kendall
Amos Kendall (August 16, 1789 – November 12, 1869) was an American lawyer, journalist and politician. He rose to prominence as editor-in-chief of the ''Argus of Western America'', an influential newspaper in Frankfort, Kentucky, Frankfort, the ...
, was a message of hope and confidence. At 4,476 words, it is the second longest inaugural address, behind only that of William Henry Harrison
William Henry Harrison (February 9, 1773April 4, 1841) was the ninth president of the United States, serving from March 4 to April 4, 1841, the shortest presidency in U.S. history. He was also the first U.S. president to die in office, causin ...
. In his inaugural address, Polk touched on the Jacksonian principles that had guided his political career and Democratic Party positions that would guide his administration. A major theme of the speech was the nation's westward expansion
The United States of America was formed after thirteen British colonies in North America declared independence from the British Empire on July 4, 1776. In the Lee Resolution, passed by the Second Continental Congress two days prior, the colon ...
. He detailed how important the addition of Texas to the Union was, and noted that Americans were moving into lands even further west (California and Oregon). He declared:
At the time that Polk became president, the nation's population had doubled every twenty years since the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
and had reached demographic parity with Britain.Merry, pg. 132–133 Polk's tenure saw continued technological improvements, including the expansion of railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
s and increased use of the telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas ...
. These improved communications and growing demographics increasingly made the United States into a strong military power, and also stoked expansionism
Expansionism refers to states obtaining greater territory through military Imperialism, empire-building or colonialism.
In the classical age of conquest moral justification for territorial expansion at the direct expense of another established p ...
.
Administration
Cabinet
 Polk governed with the help of his cabinet, in which he placed great importance. The cabinet regularly met twice a week, and Polk and his six cabinet members discussed all major issues during these meetings.Merry, pg. 134–135 Despite his reliance on his cabinet, Polk involved himself in the minutiae of the various departments, especially regarding the military.Merry, pg. 269–270
In selecting a new cabinet, Polk generally heeded Jackson's advice to avoid individuals who were themselves interested in the presidency, though he chose to nominate Buchanan for the crucial and prestigious position of Secretary of State.Merry, pg. 114–117Seigenthaler, pp. 104–106 Polk respected Buchanan's opinion and Buchanan played an important role in Polk's presidency, but the two often clashed over foreign policy and appointments. Polk frequently considered dismissing Buchanan from office, as he suspected Buchanan of placing his own presidential aspirations above service to Polk, but Buchanan always managed to convince Polk of his loyalty.Merry, pg. 439–440
Polk put together an initial slate of cabinet choices that met with the approval of Andrew Jackson, who Polk met with in January 1845 for the last time, as Jackson died in June 1845.
Polk governed with the help of his cabinet, in which he placed great importance. The cabinet regularly met twice a week, and Polk and his six cabinet members discussed all major issues during these meetings.Merry, pg. 134–135 Despite his reliance on his cabinet, Polk involved himself in the minutiae of the various departments, especially regarding the military.Merry, pg. 269–270
In selecting a new cabinet, Polk generally heeded Jackson's advice to avoid individuals who were themselves interested in the presidency, though he chose to nominate Buchanan for the crucial and prestigious position of Secretary of State.Merry, pg. 114–117Seigenthaler, pp. 104–106 Polk respected Buchanan's opinion and Buchanan played an important role in Polk's presidency, but the two often clashed over foreign policy and appointments. Polk frequently considered dismissing Buchanan from office, as he suspected Buchanan of placing his own presidential aspirations above service to Polk, but Buchanan always managed to convince Polk of his loyalty.Merry, pg. 439–440
Polk put together an initial slate of cabinet choices that met with the approval of Andrew Jackson, who Polk met with in January 1845 for the last time, as Jackson died in June 1845. Cave Johnson
Cave Johnson (January 11, 1793 – November 23, 1866) was an American politician who served the state of Tennessee as a Democratic congressman in the United States House of Representatives. Johnson was the 12th United States Postmaster Gener ...
, a close friend and ally of Polk, would be nominated for the position of Postmaster General. Though Polk was personally close with the incumbent Navy Secretary, John Y. Mason
John Young Mason (April 18, 1799October 3, 1859) was an attorney, planter, judge and politician from Virginia. Mason served in the U.S. House of Representatives after serving in both houses of the Virginia General Assembly, then became the Unit ...
, he replaced him after Jackson insisted that none of Tyler's cabinet be retained. In his place, Polk selected George Bancroft
George Bancroft (October 3, 1800 – January 17, 1891) was an American historian, statesman and Democratic Party (United States), Democratic politician who was prominent in promoting secondary education both in his home state of Massachusetts ...
, a historian who had played a crucial role in Polk's nomination. Polk also selected Senator Robert J. Walker
Robert James Walker (July 19, 1801November 11, 1869) was an American lawyer, economist and politician. An active member of the Democratic Party, he served as a member of the U.S. Senate from Mississippi from 1835 until 1845, as Secretary of t ...
of Mississippi as Attorney General.Merry, pg. 117–119
However, after news of Buchanan's selection for State was leaked, Vice President Dallas (an in-state rival of Buchanan) and a slew of Southerners insisted that Walker receive the higher position at Treasury.Merry, pg. 124–126 Polk instead chose to nominate Bancroft as a compromise at Treasury while nominating Mason as Attorney General and a New Yorker, William L. Marcy
William Learned Marcy (December 12, 1786July 4, 1857) was an American lawyer, politician, and judge who served as U.S. Senator, the eleventh Governor of New York, U.S. Secretary of War and the twenty-first U.S. Secretary of State. In the la ...
, as Secretary of War. Polk had intended the Marcy appointment to mollify Van Buren, but Van Buren was outraged at the move, in part due to Marcy's affiliation with the rival " Hunker" faction. Polk then further enraged Van Buren by finally choosing Walker for Treasury; Bancroft was shifted back to Navy Secretary.Merry, pg. 127
After the outbreak of the Mexican-American War, Polk shook up his cabinet, sending Bancroft to Great Britain as an ambassador, shifting Mason to his old position of Navy Secretary, and successfully nominating Nathan Clifford
Nathan Clifford (August 18, 1803 – July 25, 1881) was an American statesman, diplomat and jurist.
Clifford is one of the few people who have held a constitutional office in each of the three branches of the U.S. federal government. He ...
as Attorney General.Merry, pg. 282
Goals
According to a story told decades later by George Bancroft, Polk set four clearly defined goals for his administration:Merry, pg. 131–132 * Reestablish theIndependent Treasury System
The Independent Treasury was the system for managing the money supply of the United States federal government through the U.S. Treasury and its sub-treasuries, independently of the national banking and financial systems. It was created on August 6, ...
.
* Reduce tariffs
A tariff or import tax is a duty imposed by a national government, customs territory, or supranational union on imports of goods and is paid by the importer. Exceptionally, an export tax may be levied on exports of goods or raw materials and is ...
.
* Acquire some or all of Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long Oregon boundary dispute, dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been demarcat ...
.
* Acquire California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
and New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
from Mexico.
While his domestic aims represented continuity with past Democratic policies, successful completion of Polk's foreign policy goals would represent the first major American territorial gains since the Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Spanish Cession, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p. 168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to ...
of 1819.
Judicial appointments
The 1844 death of Justice Henry Baldwin had created a vacancy on the Supreme Court, and Tyler's failure to fill the seat left a Supreme Court seat open when Polk took office. Polk's attempt to fill Baldwin's seat became embroiled in Pennsylvania politics and the efforts of factional leaders to secure the lucrative post of Collector of Customs for the Port of Philadelphia. As Polk sought to find his way through the minefield of Pennsylvania politics, a second position on the high court became vacant with the death, in September 1845, of JusticeJoseph Story
Joseph Story (September18, 1779September10, 1845) was an American lawyer, jurist, and politician who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1812 to 1845. He is most remembered for his opinions in ''Martin ...
; his replacement was expected to come from his native New England. Because Story's death had occurred while the Senate was not in session, Polk was able to make a recess appointment
In the United States, a recess appointment is an appointment by the President of the United States, president of a Officer of the United States, federal official when the United States Senate, U.S. Senate is in Recess (motion), recess. Under the ...
, choosing Senator Levi Woodbury
Levi Woodbury (December 22, 1789September 4, 1851) was an American attorney, jurist, and Democratic politician from New Hampshire. During a four-decade career in public office, Woodbury served as Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the U ...
of New Hampshire, and when the Senate reconvened in December 1845, the Senate confirmed the appointment of Woodbury. Polk's initial nominee for Baldwin's seat, George W. Woodward, was rejected by the Senate in January 1846, in large part due to the opposition of Buchanan and Pennsylvania Senator Simon Cameron
Simon Cameron (March 8, 1799June 26, 1889) was an American businessman and politician who represented Pennsylvania in the United States Senate and served as United States Secretary of War under President Abraham Lincoln at the start of the Ameri ...
.
Polk eventually offered Buchanan the open seat, but Buchanan, after some indecision, turned it down. Polk subsequently nominated Robert Cooper Grier
Robert Cooper Grier (March 5, 1794 – September 25, 1870) was an American jurist who served on the Supreme Court of the United States.
A Jacksonian Democrat from Pennsylvania who served from 1846 to 1870, Grier weighed in on some of the most i ...
, who won confirmation. Justice Woodbury served until his death in 1851, but Grier served until 1870. In the slavery case of ''Dred Scott v. Sandford
''Dred Scott v. Sandford'', 60 U.S. (19 How.) 393 (1857), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that held the U.S. Constitution did not extend American citizenship to people of black African descent, and therefore they ...
'' (1857), Grier wrote a concurring opinion stating that slaves were property and could not sue.
Polk appointed eight other federal judges, one to the United States Circuit Court of the District of Columbia
The United States Circuit Court of the District of Columbia (in case citations, C.C.D.C.) was a United States federal court which existed from 1801 to 1863. The court was created by the District of Columbia Organic Act of 1801.
History
The D.C. ...
, and seven to various United States district court
The United States district courts are the trial courts of the United States federal judiciary, U.S. federal judiciary. There is one district court for each United States federal judicial district, federal judicial district. Each district cov ...
s.
Foreign affairs
Polk's main achievements in foreign policy were: * Oregon Boundary: Polk successfully resolved the long-standing dispute between the United States and Britain over the Oregon Country (modern-day Oregon, Washington, and parts of Idaho, Wyoming, and Montana). Through diplomatic negotiations, Washington and London agreed to the 49th parallel as the boundary line, securing American control over present-day Oregon and Washington. * Annexation of Texas: President Polk was a strong advocate for the annexation of Texas, which had been independent from Mexico in 1836. He successfully pushed for the admission of Texas as a state in 1845, expanding the territory of the United States and fulfilling a main goal ofmanifest destiny
Manifest destiny was the belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American pioneer, American settlers were destined to expand westward across North America, and that this belief was both obvious ("''m ...
.
* Victory against Mexico. The U.S. military, under Polk's direction, achieved a series of military victories without major defeats. This led to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848. The Treaty secured vast territories for the United States, including California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, and parts of Colorado and Wyoming. Acquisition of Texas and California were Polk's original goals.
*Reduction of Tariffs: Polk successfully advocated for the low tariffs. The Walker Tariff of 1846, named after Polk's Treasury Secretary Robert J. Walker, significantly reduced import duties. This policy change aimed to lower prices paid by American consumers.
The United States added more territory during the one term administration of President Polk than during any other president's administration.
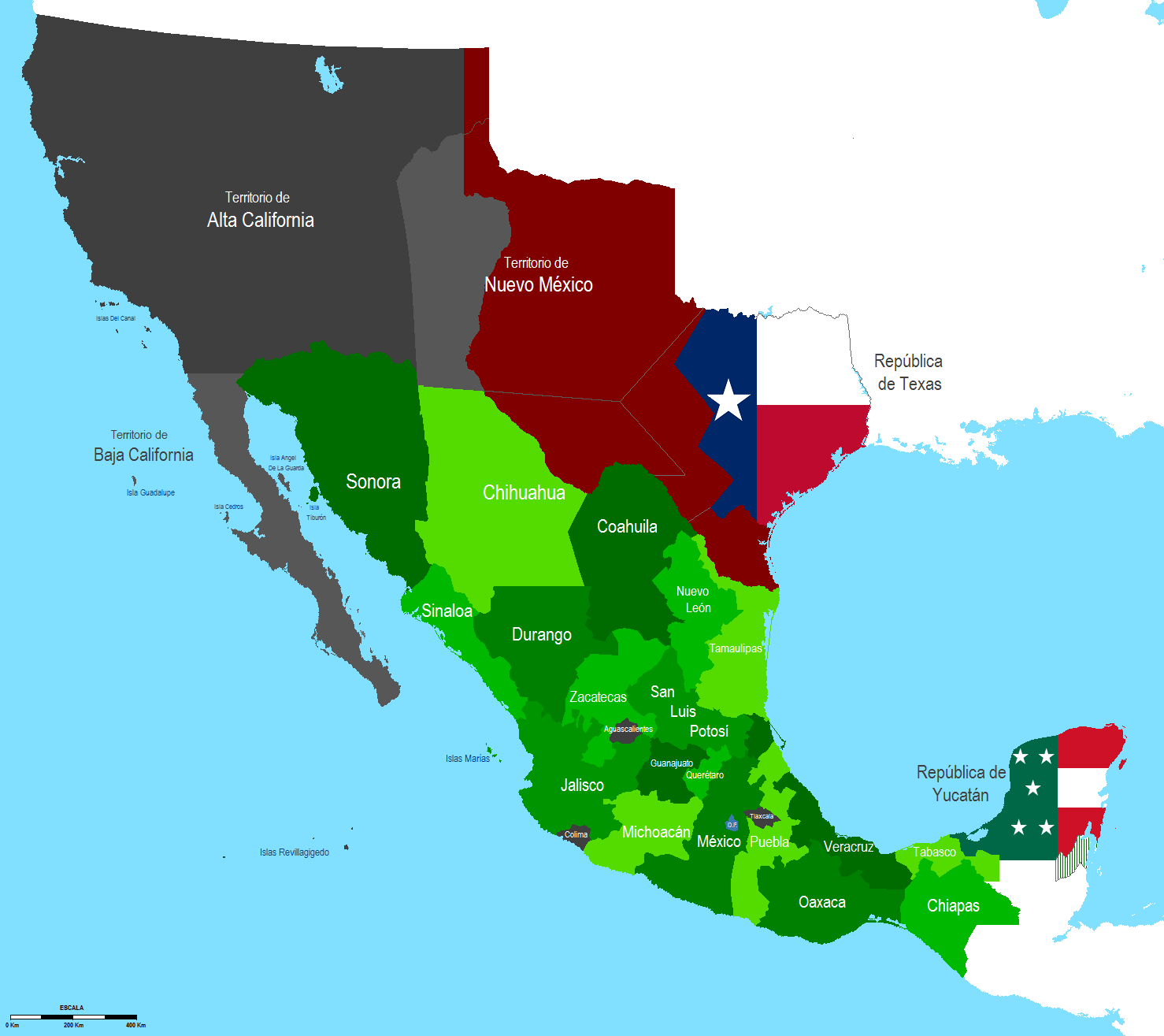
Annexation of Texas
Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas (), or simply Texas, was a country in North America that existed for close to 10 years, from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846. Texas shared borders with Centralist Republic of Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande, an ...
had gained independence from Mexico following the Texas Revolution
The Texas Revolution (October 2, 1835 – April 21, 1836) was a rebellion of colonists from the United States and Tejanos (Hispanic Texans) against the Centralist Republic of Mexico, centralist government of Mexico in the Mexican state of ...
of 1836, and, partly because Texas had been settled by a large number of Americans, there was a strong sentiment in both Texas and the United States for the annexation of Texas by the United States. During the transition period after the 1844 election, President Tyler sought to complete the annexation of Texas. Lacking a two-thirds majority, an earlier treaty that would annex the republic was defeated in the Senate. Tyler proposed that Congress accomplish annexation through a joint resolution.Merry, pg. 120–124 Due to disagreements regarding the extension of slavery, Senator Benton of Missouri and Secretary of State Calhoun disagreed on the best way to annex Texas, and Polk became involved in negotiations to break the impasse. With Polk's help, the annexation resolution narrowly cleared the Senate.
In a surprise move two days before Polk's inauguration, Tyler extended to Texas a formal offer of annexation.Merry, pg. 127–128 Polk's first major decision in office was whether to recall Tyler's emissary to Texas, who bore an offer of annexation based on that act of Congress.Merry, pg. 136–137 Though it was within Polk's power to recall the messenger, he chose to allow the emissary to continue, with the hope that Texas would accept the offer. Polk also retained the United States Ambassador to Texas
The United States recognized the Republic of Texas, created by a new constitution on March 2, 1836, as a new independent nation and commissioned its first representative, Alcee La Branche as the chargé d'affaires in 1837. The U.S. never sent a ...
, Andrew Jackson Donelson
Andrew Jackson Donelson (August 25, 1799 – June 26, 1871) was an American diplomat and politician. He served in various positions as a Democrat and was the Know Nothing nominee for US vice president in 1856.
After the death of his father, Done ...
, who sought to convince the Texan leaders to accept annexation under the terms proposed by the Tyler administration.Merry, pg. 148–151 Though public sentiment in Texas favored annexation, some Texas leaders disliked the strict terms for annexation, which offered little leeway for negotiation and gave public lands to the federal government. Nonetheless, in July 1845, a convention in Austin, Texas
Austin ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Texas. It is the county seat and most populous city of Travis County, Texas, Travis County, with portions extending into Hays County, Texas, Hays and W ...
ratified the annexation of Texas. In December 1845, Polk signed a resolution annexing Texas, and Texas became the 28th state in the union. The annexation of Texas would lead to increased tensions with Mexico, which had never recognized Texan independence.
Partition of Oregon Country
Background
 Since the signing of the
Since the signing of the Treaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, is an international treaty signed in 1818 betw ...
, the largely unsettled Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long Oregon boundary dispute, dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been demarcat ...
had been under the joint occupation and control of Great Britain and the United States. Previous U.S. administrations had offered to divide the region along the 49th parallel, which was not acceptable to Britain, as it had commercial interests along the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook language, Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin language, Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river headwater ...
.Merry, pp. 168–169 Britain's preferred partition, which would have awarded Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ; ) is a complex estuary, estuarine system of interconnected Marine habitat, marine waterways and basins located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington. As a part of the Salish Sea, the sound ...
and all lands north of the Columbia River to Britain, was unacceptable to Polk. Edward Everett
Edward Everett (April 11, 1794 – January 15, 1865) was an American politician, Unitarian pastor, educator, diplomat, and orator from Massachusetts. Everett, as a Whig, served as U.S. representative, U.S. senator, the 15th governor of Mas ...
, President Tyler's minister to Britain, had informally proposed dividing the territory at the 49th parallel with the strategic Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest ...
granted to the British. However, when the new British minister Richard Pakenham
Sir Richard Pakenham PC (19 May 1797 – 28 October 1868) was a British diplomat of Anglo-Irish background. He served as British Ambassador to the United States from 1843 until 1847, during which time he unsuccessfully worked to prevent t ...
arrived in Washington in 1844, he found that many Americans desired the entire territory. Oregon had not been a major issue in the 1844 election, but the recent heavy influx of settlers to the Oregon Country and the rising spirit of expansionism in the United States made a treaty with Britain more urgent.
Partition
Though both the British and the Americans sought an acceptable compromise regarding Oregon Country, each also saw the territory as an important geopolitical asset that would play a large part in determining the dominant power in North America. In his inaugural address, Polk announced that he viewed the American claim to the land as "clear and unquestionable", provoking threats of war from British leaders should Polk attempt to take control of the entire territory.Merry, pp. 170–171 Polk had refrained in his address from asserting a claim to the entire territory, which extended north to 54 degrees, 40 minutes north latitude, although the Democratic Party platform called for such a claim. Despite Polk's hawkish rhetoric, he viewed war with the British as unwise, and Polk and Buchanan opened up negotiations with the British.Merry, pp. 173–175 Like his predecessors, Polk again proposed a division along the 49th parallel, which was immediately rejected by Pakenham. Secretary of State Buchanan was wary of a two-front war with Mexico and Britain, but Polk was willing to risk war with both countries in pursuit of a favorable settlement.Merry, pp. 190–191 In his December 1845 annual message to Congress, Polk requested approval of giving Britain a one-year notice (as required in the Treaty of 1818) of his intention to terminate the joint occupancy of Oregon. In that message, he quoted from the Monroe Doctrine to denote America's intention of keeping European powers out, the first significant use of it since its origin in 1823. After much debate, Congress eventually passed the resolution in April 1846, attaching its hope that the dispute would be settled amicably. When the British Foreign Secretary,Lord Aberdeen
George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen (28 January 178414 December 1860), styled Lord Haddo from 1791 to 1801, was a British statesman, diplomat and landowner, successively a Tory, Conservative and Peelite politician and specialist in fo ...
, learned of the proposal rejected by Pakenham, Aberdeen asked the United States to re-open negotiations, but Polk was unwilling to do so unless a proposal was made by the British.Merry, pp. 196–197
With Britain moving towards free trade with the repeal of the Corn Laws, good trade relations with the United States were more important to Aberdeen than a distant territory. In February 1846, Polk allowed Buchanan to inform Louis McLane
Louis McLane (May 28, 1786 – October 7, 1857) was an American lawyer and politician from Wilmington, Delaware, Wilmington, in New Castle County, Delaware, and Baltimore, Baltimore, Maryland. He was a veteran of the War of 1812, a member of t ...
, the American ambassador to Britain, that Polk's administration would look favorably on a British proposal based around a division at the 49th parallel. In June 1846, Pakenham presented an offer to the Polk administration, calling for a boundary line at the 49th parallel, with the exception that Britain would retain all of Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest ...
, and British subjects would be granted limited navigation rights on the Columbia River until 1859. Polk and most of his cabinet were prepared to accept the proposal, but Buchanan, in a reversal, urged that the United States seek control of all of the Oregon Territory.
After winning the reluctant approval of Buchanan, Polk submitted the full treaty to the Senate for ratification. The Senate ratified the Oregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty was a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to ...
in a 41–14 vote, with opposition coming from those who sought the full territory. Polk's willingness to risk war with Britain had frightened many, but his tough negotiation tactics may have gained the United States concessions from the British (particularly regarding the Columbia River) that a more conciliatory president might not have won.Merry, pp. 266–267
Mexican–American War
Background
The United States had been the first country to recognize Mexico's independence following theMexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence (, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from the Spanish Empire. It was not a single, coherent event, but local and regional ...
, but relations between the two countries began to sour in the 1830s.Merry, pg. 184–186 In the 1830s and 1840s, the United States, like France and Britain, sought a reparations treaty with Mexico for various acts committed by Mexican citizens and authorities, including the seizure of American ships. Though the United States and Mexico had agreed to a joint board to settle the various claims prior to Polk's presidency, many Americans accused the Mexican government of acting in bad faith in settling the claims. For its part, Mexico believed that the United States sought to acquire Mexican territory, and believed that many Americans filed specious or exaggerated claims. The already-troubled Mexico–United States relations
Mexico and the United States have a complex history, with war in the 1840s and the subsequent American acquisition of more than 50% of former Mexican territory, including Texas, Arizona, California, and New Mexico. Pressure from Washington was on ...
were further inflamed by the possibility of the annexation of Texas, as Mexico still viewed Texas as an integral part of their republic.Merry, pg. 176–177 Additionally, Texas laid claim to all land north of the Rio Grande River
The Rio Grande ( or ) in the United States or the Río Bravo (del Norte) in Mexico (), also known as Tó Ba'áadi in Navajo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the Southwestern United States and in northern Me ...
, while Mexico argued that the more northern Nueces River
The Nueces River ( ; , ) is a river in the U.S. state of Texas, about long. It drains a region in central and southern Texas southeastward into the Gulf of Mexico. It is the southernmost major river in Texas northeast of the Rio Grande. ''Nu ...
was the proper Texan border.Merry, pg. 187 Though the United States had a population more than twice as numerous and an economy thirteen times greater than that of Mexico, Mexico was not prepared to give up its claim to Texas, even if it meant war.Merry, pg. 180
The Mexican province of Alta California
Alta California (, ), also known as Nueva California () among other names, was a province of New Spain formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but was made a separat ...
enjoyed a large degree of autonomy, and the central government neglected its defenses; a report from a French diplomat stated that "whatever nation chooses to send there a man-of-war
In Royal Navy jargon, a man-of-war (also man-o'-war, or simply man) was a powerful warship or frigate of the 16th to the 19th century, that was frequently used in Europe. Although the term never acquired a specific meaning, it was usually rese ...
and 200 men" could conquer California. Polk placed great value in the acquisition of California, which represented new lands to settle as well as a potential gateway to trade in Asia. He feared that the British or another European power would eventually establish control over California if it remained in Mexican hands. In late 1845, Polk sent diplomat John Slidell
John Slidell (1793July 9, 1871) was an American politician, lawyer, slaveholder, and businessman. Database at A native of New York, Slidell moved to Louisiana as a young man. He was a member of the Louisiana House of Representatives, U.S. House ...
to Mexico to win Mexico's acceptance of the Rio Grande border. Slidell was further authorized to purchase California for $20 million and New Mexico
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States. It is one of the Mountain States of the southern Rocky Mountains, sharing the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona. It also ...
for $5 million. Polk also sent Lieutenant Archibald H. Gillespie
Major Archibald H. Gillespie (October 10, 1812 – August 16, 1873) was an officer in the United States Marine Corps during the Mexican–American War.
Biography
Born in New York City, Gillespie was commissioned in the Marine Corps in 1832. He ...
to California with orders to foment a pro-American rebellion that could be used to justify annexation of the territory.Merry, pg. 295–296
Outbreak of war
Following the Texan ratification of annexation in 1845, both Mexicans and Americans saw war as a likely possibility. Polk began preparations for a potential war, sending an army led by GeneralZachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor (November 24, 1784 – July 9, 1850) was an American military officer and politician who was the 12th president of the United States, serving from 1849 until his death in 1850. Taylor was a career officer in the United States ...
into Texas.Merry, pg. 188–189 Taylor and Commodore David Conner of the U.S. Navy were both ordered to avoid provoking a war, but were authorized to respond to any Mexican breach of peace. Though Mexican President José Joaquín de Herrera
José Joaquín Antonio Florencio de Herrera y Ricardos (February 23, 1792 – February 10, 1854) was a Mexican statesman who served as president of Mexico three times (1844, 1844–1845 and 1848–1851), and as a general in the Mexican Army d ...
was open to negotiations, Slidell's ambassadorial credentials were refused by a Mexican council of government.Merry, pg. 209–210 In December 1845, Herrera's government collapsed largely due to his willingness to negotiate with the United States; the possibility of the sale of large portions of Mexico aroused anger among both Mexican elites and the broader populace.Merry, pg. 218–219
As successful negotiations with the unstable Mexican government appeared unlikely, Secretary of War Marcy ordered General Taylor to advance to the Rio Grande River. Polk began preparations to support a potential new government led by the exiled Mexican General Antonio López de Santa Anna
Antonio de Padua María Severino López de Santa Anna y Pérez de Lebrón (21 February 1794 – 21 June 1876),Callcott, Wilfred H., "Santa Anna, Antonio Lopez De,''Handbook of Texas Online'' Retrieved 18 April 2017. often known as Santa Anna, wa ...
with the hope that Santa Anna would sell parts of California. Polk had been advised by Alejandro Atocha, an associate of Santa Anna, that only the threat of war would allow the Mexican government the leeway to sell parts of Mexico.Merry, pg. 238–240 In March 1846, Slidell finally left Mexico after the government refused his demand to be formally received.Merry, pg. 232–233 Slidell returned to Washington in May 1846, and gave his opinion that negotiations with the Mexican government were unlikely to be successful. Polk regarded the treatment of his diplomat as an insult and an "ample cause of war", and he prepared to ask Congress for a declaration of war.
Meanwhile, in late March 1846, General Taylor reached the Rio Grande, and his army camped across the river from Matamoros, Tamaulipas
Matamoros, officially known as Heroica Matamoros, is a city in the northeastern Mexican state of Tamaulipas, and the municipal seat of the homonymous municipality. It is on the southern bank of the Rio Grande, directly across the border from Bro ...
. In April, after Mexican general Pedro de Ampudia
Pedro Nolasco Martín José María de la Candelaria Francisco Javier Ampudia y Grimarest (January 30, 1805 – August 7, 1868) was born in Havana, Cuba, and served Mexico as a Northern army officer for most of his life. At various points he wa ...
demanded that Taylor return to the Nueces River, Taylor began a blockade of Matamoros.Merry, pg. 240–242 A skirmish on the northern side of the Rio Grande ended in the death or capture of dozens of American soldiers, and became known as the Thornton Affair
The Thornton Affair, also known as the Thornton Skirmish, Thornton's Defeat, or Rancho Carricitos, was a battle in 1846 between the military forces of the United States and Mexico west upriver from Zachary Taylor's camp along the Rio Grande ...
. While the administration was in the process of asking for a declaration of war, Polk received word of the outbreak of hostilities on the Rio Grande. In a message to Congress, Polk explained his decision to send Taylor to the Rio Grande, and stated that Mexico had invaded American territory by crossing the river.Merry, pg. 244–245 Polk contended that a state of war already existed, and he asked Congress to grant him the power to bring the war to a close. Polk's message was crafted to present the war as a just and necessary defense of the country against a neighbor that had long troubled the United States.Lee, pgs. 517–518 In his message, Polk noted that Slidell had gone to Mexico to negotiate a recognition of the Texas annexation, but did not mention that he also sought the purchase of California.
Some Whigs, such as Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
, challenged Polk's version of events. One Whig congressman declared "the river Nueces is the true western boundary of Texas. It is our own president who began this war. He has been carrying it on for months." Nonetheless, the House overwhelmingly approved of a resolution authorizing the president to call up fifty thousand volunteers.Merry, pg. 245–246 In the Senate, war opponents led by Calhoun also questioned Polk's version of events, but the House resolution passed the Senate in a 40–2 vote, marking the beginning of the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
.Merry, pg. 246–247 Many congressmen who were skeptical about the wisdom of going to war with Mexico feared that publicly opposing the war would cost them politically.
Early war
In May 1846, Taylor led U.S. forces in the inconclusiveBattle of Palo Alto
The Battle of Palo Alto () was the first major battle of the Mexican–American War and was fought on May 8, 1846, on disputed ground five miles (8 km) from the modern-day city of Brownsville, Texas. A force of some 3,700 Mexico, Mexican t ...
, the first major battle of the war. The next day, Taylor led the army to victory in the Battle of Resaca de la Palma
The Battle of Resaca de la Palma was one of the early engagements of the Mexican–American War, where the United States Army under General Zachary Taylor engaged the retreating forces of the Mexican ''Ejército del Norte'' ("Army of the Nor ...
, eliminating the possibility of a Mexican incursion into the United States. Taylor's force moved south towards Monterrey
Monterrey (, , abbreviated as MtY) is the capital and largest city of the northeastern Mexican state of Nuevo León. It is the ninth-largest city and the second largest metropolitan area, after Greater Mexico City. Located at the foothills of th ...
, which served as the capital of the province of Nuevo León
Nuevo León, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nuevo León, is a Administrative divisions of Mexico, state in northeastern Mexico. The state borders the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Coahuila, Zacatecas, and San Luis Potosí, San Luis ...
. In the September 1846 Battle of Monterrey
In the Battle of Monterrey (September 21–24, 1846) during the Mexican–American War, General Pedro de Ampudia and the Mexican Army of the North was defeated by the Army of Occupation, a force of United States Regulars, Volunteers, an ...
, Taylor defeated a Mexican force led by Ampudia, but allowed Ampudia's forces to withdraw, much to Polk's consternation.Merry, pg. 311–313
Meanwhile, Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as Commanding General of the United States Army from 1841 to 1861, and was a veteran of the War of 1812, American Indian Wars, Mexica ...
, the army's lone major general at the outbreak of the war, was offered the position of top commander in the war. Polk, War Secretary Marcy, and Scott agreed on a strategy in which the US would capture northern Mexico and then pursue a favorable peace settlement.Merry, pg. 256–257 However, Polk and Scott experienced mutual distrust from the beginning of their relationship, in part due to Scott's Whig affiliation and former rivalry with Andrew Jackson.Merry, pg. 253–254 Additionally, Polk sought to ensure that both Whigs and Democrats would serve in important positions in the war, and was offended when Scott suggested otherwise; Scott also angered Polk by opposing Polk's effort to increase the number of generals.Merry, pg. 258–259 Having been alienated from Scott, Polk ordered Scott to remain in Washington, leaving Taylor in command of Mexican operations.Merry, pg. 259–260 Polk also ordered Commodore Conner to allow Santa Anna to return to Mexico from his exile, and sent an army expedition led by Stephen W. Kearny towards Santa Fe.
While Taylor fought the Mexican army in east, U.S. forces took control of California and New Mexico. Army Captain John C. Frémont
Major general (United States), Major-General John Charles Frémont (January 21, 1813July 13, 1890) was a United States Army officer, explorer, and politician. He was a United States senator from California and was the first History of the Repub ...
led settlers in Northern California in an attack on the Mexican garrison in Sonoma, beginning the Bear Flag Revolt
The California Republic, or Bear Flag Republic, was an List of historical unrecognized states#Americas, unrecognized breakaway state from Second Federal Republic of Mexico, Mexico, that existed from June 14, 1846 to July 9, 1846. It milita ...
.Merry, pg. 302–304 In August 1846, American forces under Kearny captured Santa Fe, capital of the province of New Mexico.Merry, pg. 293–294 He captured Santa Fe without firing a shot, as the Mexican Governor, Manuel Armijo
Manuel Armijo ( – 1853) was a New Mexican soldier and statesman who served three times as governor of New Mexico between 1827 and 1846. He was instrumental in putting down the Revolt of 1837; he led the military forces that captured the invad ...
, fled from the province.Merry, pg. 298–299 After establishing a provisional government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, a transitional government or provisional leadership, is a temporary government formed to manage a period of transition, often following state collapse, revoluti ...
in New Mexico, Kearny took a force west to aid in the conquest of California. After Kearny's departure, Mexicans and Puebloans
The Pueblo peoples are Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Among the currently inhabited Pueblos, Taos Pueblo, Taos, San Il ...
rebelled against the provisional government in the Taos Revolt
The Taos Revolt was a popular insurrection in January 1847 by Hispano and Pueblo allies against the United States' occupation of present-day northern New Mexico during the Mexican–American War. Provisional governor Charles Bent and severa ...
, but U.S. forces crushed the uprising. At roughly the same time that Kearny captured Santa Fe, Commodore Robert F. Stockton
Robert Field Stockton (August 20, 1795 – October 7, 1866) was a United States Navy commodore, notable in the capture of California during the Mexican–American War. He was a naval innovator and an early advocate for a propeller-driven, steam- ...
landed in Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
and proclaimed the capture of California. Californio
Californios (singular Californio) are Californians of Spaniards, Spanish descent, especially those descended from settlers of the 17th through 19th centuries before California was annexed by the United States. California's Spanish language in C ...
s rose up in rebellion against U.S. occupation, but Stockton and Kearny suppressed the revolt with a victory in the Battle of La Mesa
The Battle of La Mesa (also known as the Battle of Los Angeles) was the final battle of the California Campaign during the Mexican–American War, occurring on January 9, 1847, in present-day Vernon, California, the day after the Battle of Ri ...
. After the battle, Kearny and Frémont became embroiled in a dispute over the establishment of a government in California. The controversy between Frémont and Kearny led to a break between Polk and the powerful Missouri Senator Thomas Hart Benton, who was the father-in-law of Frémont.Merry, pg. 423–424
Growing domestic resistance
Whig opposition to the war grew after 1845, while some Democrats lost their initial enthusiasm. In August 1846, Polk asked Congress to appropriate $2 million in hopes of using that money as a down payment for the purchase of California in a treaty with Mexico.Merry, pg. 283–285 Polk's request ignited opposition to the war, as Polk had never before made public his desire to annex parts of Mexico (aside from lands claimed by Texas). A freshman Democratic Congressman,David Wilmot David Wilmot may refer to:
* David Wilmot (politician)
* David Wilmot (actor)
David Wilmot is an Ireland, Irish actor best known for his roles in ''Michael Collins (film), Michael Collins'' (1996), ''I Went Down'' (1997), ''Intermission (fil ...
of Pennsylvania, offered an amendment known as the Wilmot Proviso
The Wilmot Proviso was an unsuccessful 1846 proposal in the United States Congress to ban slavery in territory acquired from Mexico in the Mexican–American War. The conflict over the Wilmot Proviso was one of the major events leading to the ...
that would ban slavery in any newly acquired lands.Merry, pg. 286–289 The appropriations bill, including the Wilmot Proviso, passed the House with the support Northern Whigs and Northern Democrats, breaking the normal pattern of partisan division in congressional votes. Wilmot himself held anti-slavery views, but many pro-slavery Northern Democrats voted for the bill out of anger at Polk's perceived bias towards the South. The partition of Oregon, the debate over the tariff, and Van Buren's antagonism towards Polk all contributed to Northern anger. The appropriations bill, including the ban on slavery, was defeated in the Senate, but the Wilmot Proviso injected the slavery debate into national politics.
Polk's Democrats would pay a price for the resistance to the war and the growing issue of slavery, as Democrats lost control of the House in the 1846 elections. However, in early 1847, Polk was successful in passing a bill raising further regiments, and he also finally won approval for the money he wanted to use for the purchase of California.Merry, pg. 343–349
Late war
Santa Anna returned to Mexico City in September 1846, declaring that he would fight against the Americans.Merry, pg. 309–310 With the duplicity of Santa Anna now clear, and with the Mexicans declining his peace offers, Polk ordered an American landing inVeracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
, the most important Mexican port on the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
. As a march from Monterrey to Mexico City was implausible due to rough terrain, Polk had decided that a force would land in Veracruz and then march on Mexico City. Taylor was ordered to remain near Monterrey, while Polk reluctantly chose Winfield Scott to lead the attack on Veracruz.Merry, pg. 318-20 Though Polk continued to distrust Scott, Marcy and the other cabinet members prevailed on Polk to select the army's most senior general for the command.Seigenthaler, pg. 139–140
In March 1847, Polk learned that Taylor had ignored orders and had continued to march south, capturing the northern Mexican town of Saltillo
Saltillo () is the capital and largest city of the northeastern Mexican state of Coahuila and is also the municipal seat of the municipality of the same name. Mexico City, Monterrey, and Saltillo are all connected by a major railroad and high ...
.Merry, pg. 352–355 Taylor's army had repulsed a larger Mexican force, led by Santa Anna, in the February 1847 Battle of Buena Vista
The Battle of Buena Vista (February 22–23, 1847), known as the Battle of La Angostura in Mexico, and sometimes as Battle of Buena Vista/La Angostura, was a battle of the Mexican–American War. It was fought between U.S. forces, largely vol ...
. Taylor won acclaim for the result of the battle, but the theater remained inconclusive. Rather than pursuing Santa Anna's forces, Taylor withdrew back to Monterrey. Meanwhile, Scott landed in Veracruz and quickly won control of the city.Merry, pg. 358–359 Following the capture of Veracruz, Polk dispatched Nicholas Trist
Nicholas Philip Trist (June 2, 1800 – February 11, 1874) was an American lawyer, diplomat, planter, and businessman. Even though he had been dismissed by President James K. Polk as the negotiator with the Mexican government, he negotiated the T ...
, Buchanan's chief clerk, to negotiate a peace treaty with Mexican leaders. Trist was ordered to seek the cession of Alta California, New Mexico, and Baja California
Baja California, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northwesternmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of B ...
, recognition of the Rio Grande as the southern border of Texas, and American access across the Isthmus of Tehuantepec
The Isthmus of Tehuantepec () is an isthmus in Mexico. It represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Before the opening of the Panama Canal, it was a major overland transport route known simply as the T ...
.Merry, pg. 360–361
In April 1847, Scott defeated a Mexican force led by Santa Anna at the Battle of Cerro Gordo
The Battle of Cerro Gordo, or Battle of Sierra Gordo, was an engagement in the Mexican–American War on April 18, 1847. The battle saw Winfield Scott's United States troops outflank Antonio López de Santa Anna's larger Mexican army, driving ...
, clearing the way for a march on Mexico City.Merry, pg. 363–364 In August, Scott defeated Santa Anna again at the Battle of Contreras
The Battle of Contreras, also known as the Battle of Padierna, took place on 19–20 August 1847, in one of the final encounters of the Mexican–American War, as invading U.S. forces under Winfield Scott approached the Mexican capital. Ameri ...
and the Battle of Churubusco
The Battle of Churubusco took place on August 20, 1847, while Santa Anna's army was in retreat from the Battle of Contreras or Battle of Padierna during the Mexican–American War. It was the battle where the San Patricio Battalion, made u ...
.Merry, pg. 381–382 With these victories over a larger force, Scott's army was positioned to besiege Mexico's capital. Santa Anna negotiated a truce with Scott, and the Mexican foreign minister notified Trist that they were ready to begin negotiations to end the war.Merry, pg. 383–384 However, the Mexican and American delegations remained far apart on terms; Mexico was only willing to yield portions of Alta California, and still refused to agree to the Rio Grande border.Merry, pg. 384–385 While negotiations continued, Scott captured the Mexican capital in the Battle for Mexico City
The Battle for Mexico City refers to the series of engagements from September 8 to September 15, 1847, in the general vicinity of Mexico City during the Mexican–American War. Included are major actions at the battles of Molino del Rey and ...
.Merry, pg. 387–388
In the United States, a heated political debate emerged regarding how much of Mexico the United States should seek to annex, with Whigs such as Henry Clay arguing that the United States should only seek to settle the Texas border question, and some expansionists arguing for the annexation of all of Mexico.Merry, pg. 394–397 Frustrated by the lack of progress in negotiations, and troubled by rumors that Trist was willing to negotiate on the Rio Grande border, Polk ordered Trist to return to Washington.Merry, pg. 386 Polk decided to occupy large portions of Mexico and wait for a Mexican peace offer.Merry, pg. 403–404 In late 1847, Polk learned that Scott had court-martialed a close ally of Polk's, Gideon Johnson Pillow
Gideon Johnson Pillow (June 8, 1806October 8, 1878) was a senior officer of the Confederate States Army in the Western Theater of the American Civil War, having previously served as a general of United States Volunteers during the Mexican–Ame ...
.Merry, pg. 407–409 Outraged by that event, Polk demanded Scott's return to Washington, with William Orlando Butler
William Orlando Butler (April 19, 1791 – August 6, 1880) was an American politician and U.S. Army major general from Kentucky. He served as a Democratic representative from Kentucky from 1839 to 1843, and was the Democratic vice-presidentia ...
tapped as his replacement.
Peace: the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
 In September 1847,
In September 1847, Manuel de la Peña y Peña
José Manuel de la Peña y Peña (10 March 1789 – 2 January 1850) was a Mexican lawyer and judge who served two non-consecutive, but closely following, terms as the president of Mexico during the Mexican American War. In contrast to many ot ...
replaced Santa Anna as President of Mexico, and Pena and his Moderado allies showed a willingness to negotiate based on the terms Polk had relayed to Trist.Merry, pg. 397–400 In November 1847, Trist received Polk's order to return to Washington. After a period of indecision, and with the backing of Scott and the Mexican government (which was aware that Polk had ordered Trist's recall), Trist decided to enter into negotiations with the Mexican government. As Polk had made no plans to send an envoy to replace him, Trist thought that he could not pass up the opportunity to end the war on favorable terms. Though Polk was outraged by Trist's decision, he decided to allow Trist some time to negotiate a treaty.Merry, pg. 420–421
Throughout January 1848, Trist regularly met with Mexican officials in Guadalupe Hidalgo, a small town north of Mexico City.Merry, pg. 424–425 Trist was willing to allow Mexico to keep Lower California, but successfully haggled for the inclusion of the important harbor of San Diego
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
in a cession of Upper California. The Mexican delegation agreed to recognize the Rio Grande border, while Trist agreed to have the United States cover prior American claims against the Mexican government. The two sides also agreed to the right of Mexicans in annexed territory to leave or become U.S. citizens, American responsibility to prevent cross-border Indian raids, protection of church property, and a $15 million payment to Mexico. On February 2, 1848, Trist and the Mexican delegation signed the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo officially ended the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). It was signed on 2 February 1848 in the town of Villa de Guadalupe, Mexico City, Guadalupe Hidalgo.
After the defeat of its army and the fall of the cap ...
.
Polk received the document on February 19, and, after the Cabinet met on the 20th, decided he had no choice but to accept it. If he turned it down, with the House by then controlled by the Whigs, there was no assurance Congress would vote funding to continue the war. Both Buchanan and Walker dissented, wanting more land from Mexico. Some senators opposed the treaty because they wanted to take no Mexican territory; others hesitated because of the irregular nature of Trist's negotiations. Polk waited in suspense for two weeks as the Senate considered it, sometimes hearing that it would likely be defeated, and that Buchanan and Walker were working against it. On March 10, the Senate ratified the treaty in a 38–14 vote that cut across partisan and geographic lines. The Senate made some modifications to treaty, and Polk worried that the Mexican government would reject the new terms. Despite those fears, on June 7, Polk learned that Mexico had ratified the treaty.Merry, pp. 448–450 Polk declared the treaty in effect as of July 4, 1848, thus ending the war.Leonard, p. 180
The Mexican Cession
The Mexican Cession () is the region in the modern-day Western United States that Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United S ...
added 600,000 square miles of territory to the United States, including a long Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
coastline. The treaty also recognized the annexation of Texas and acknowledged American control over the disputed territory between the Nueces River and the Rio Grande. Mexico, in turn, received $15 million. The war had cost the lives of nearly 14,000 Americans and 25,000 Mexicans, and had cost the United States roughly one hundred million dollars. With the exception of the territory acquired by the 1853 Gadsden Purchase
The Gadsden Purchase ( "La Mesilla sale") is a region of present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico that the United States acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Mesilla, which took effect on June 8, 1854. The purchase included lan ...
, the territorial acquisitions under Polk established the modern borders of the Contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
.
Governing the new territories

 Polk had been anxious to establish a territorial government for Oregon once the treaty was effective in 1846, but the matter became embroiled in the arguments over slavery, though few thought Oregon suitable for that institution. A bill to establish an Oregon territorial government passed the House after being amended to bar slavery; the bill died in the Senate when opponents ran out the clock on the congressional session. A resurrected bill, still barring slavery, again passed the House in January 1847, but it was not considered by the Senate before Congress adjourned in March. By the time Congress met again in December, California and New Mexico were in U.S. hands, and Polk in his annual message urged the establishment of territorial governments in California, New Mexico, and Oregon. The
Polk had been anxious to establish a territorial government for Oregon once the treaty was effective in 1846, but the matter became embroiled in the arguments over slavery, though few thought Oregon suitable for that institution. A bill to establish an Oregon territorial government passed the House after being amended to bar slavery; the bill died in the Senate when opponents ran out the clock on the congressional session. A resurrected bill, still barring slavery, again passed the House in January 1847, but it was not considered by the Senate before Congress adjourned in March. By the time Congress met again in December, California and New Mexico were in U.S. hands, and Polk in his annual message urged the establishment of territorial governments in California, New Mexico, and Oregon. The Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise (also known as the Compromise of 1820) was federal legislation of the United States that balanced the desires of northern states to prevent the expansion of slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand ...
had settled the issue of the geographic reach of slavery within the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
territories by prohibiting slavery in states north of 36°30′ latitude. Polk sought to extend this line into the newly acquired territory.Merry, pp. 452–453 If extended to the Pacific, this would have made slavery illegal in Northern California, but would have allowed it in Southern California. A plan to accomplish the extension was defeated in the House by a bipartisan alliance of Northerners. As the last congressional session before the 1848 election came to a close, Polk signed the lone territorial bill passed by Congress, which established the Territory of Oregon
The Territory of Oregon was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 14, 1848, until February 14, 1859, when the southwestern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Oregon. O ...
and prohibited slavery in it.
When Congress reconvened in December 1848, Polk again called for the establishment territorial governments in California and New Mexico, a task made especially urgent by the onset of the California Gold Rush
The California gold rush (1848–1855) began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California from the rest of the U ...
. However, the divisive issue of slavery blocked any such legislation. Polk made it clear that he would veto a territorial bill that would have had the laws Mexico apply to the southwest territories until Congress, considering it to be the Wilmot Proviso in another guise. It was not until the Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that temporarily defused tensions between slave and free states during the years leading up to the American Civil War. Designe ...
that the matter of the territories was resolved.
Other initiatives
Panama
Polk's ambassador to theRepublic of New Granada
The Republic of New Granada was a Centralism, centralist unitary republic consisting primarily of present-day Colombia and Panama with smaller portions of today's Costa Rica, Ecuador, Venezuela, Peru and Brazil that existed from 1831 to 1858. ...
, Benjamin Alden Bidlack
Benjamin Alden Bidlack (September 8, 1804 – February 6, 1849) was an American politician, diplomat, and attorney who served as a member of the US House of Representatives and was later appointed chargé d'affaires to New Granada. While se ...
, negotiated the Mallarino–Bidlack Treaty
The Mallarino–Bidlack Treaty (also known as the Bidlack Treaty and Treaty of New Granada) was a treaty signed between New Granada (today Colombia and Panama) and the United States, on December 12, 1846.Kellogg Institute at the University of Notr ...
with the government of New Granada in 1846. Though Bidlack had initially only sought to remove tariffs on American goods, Bidlack and New Granadan Foreign Minister Manuel María Mallarino
Manuel María Mallarino Ibargüen (18 June 1808 – 6 January 1872) was the List of Vice Presidents of Colombia, 8th Vice President of Colombia, Vice President of Republic of New Granada, New Granada, and as such served as Acting President from ...
negotiated a broader agreement that deepened military and trade ties between the two countries. The treaty also allowed for the construction of the Panama Railway
The Panama Canal Railway (PCR, ) is a railway line linking the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean in Central America. The route stretches across the Isthmus of Panama from Colón (Atlantic) to Balboa (Pacific, near Panama City). Because of ...
. In an era of slow overland travel, the treaty gave the United States a route to more rapidly travel between its eastern and western coasts. In exchange, Bidlack agreed to have the United States guarantee New Granada's sovereignty over the Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama, historically known as the Isthmus of Darien, is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North America, North and South America. The country of Panama is located on the i ...
. The treaty won ratification in both countries in 1848. The agreement helped to establish a stronger American influence in the region, as the Polk administration sought to ensure that Great Britain would not dominate Central America. The United States would use the Mallarino-Bidlack Treaty as justification for numerous military interventions in Panama.
Cuba
In mid-1848, President Polk authorized his ambassador to Spain,Romulus Mitchell Saunders
Romulus Mitchell Saunders (March 3, 1791 – April 21, 1867) was an American politician from North Carolina.
Early life and education
Saunders was born near Milton, Caswell County, North Carolina, the son of William and Hannah Mitchell Saunders ...
, to negotiate the purchase of Cuba and offer Spain up to $100 million, an astounding sum at the time for one territory, equal to $ in present-day terms. Cuba was close to the United States and had slavery, so the idea appealed to Southerners but was unwelcome in the North. However, Spain was still making huge profits in Cuba (notably in sugar, molasses, rum, and tobacco), and thus the Spanish government rejected Saunders' overtures. Though Polk was eager to acquire Cuba, he refused to support the proposed filibuster
A filibuster is a political procedure in which one or more members of a legislative body prolong debate on proposed legislation so as to delay or entirely prevent a decision. It is sometimes referred to as "talking a bill to death" or "talking ...
expedition of Narciso López
Narciso López de Urriola (November 2, 1797 – September 1, 1851) was a Venezuelan-born adventurer and Spanish Army general who is best known for his expeditions aimed at liberating Cuba from Spanish rule in the 1850s. His troops carried a flag ...
, who sought to invade and annex Cuba.
Domestic affairs

Tariff reduction
TheTariff of 1842
The Tariff of 1842, or Black Tariff as it became known, was a protectionist tariff schedule adopted in the United States. It reversed the effects of the Compromise Tariff of 1833, which contained a provision that successively lowered the tariff ...
had set relatively high tariff rates, and Polk made a reduction of tariff rates the top priority of his domestic agenda.Bergeron, pp. 185–186 Though he had taken an ambivalent position on the tariff during the 1844 campaign in order to win Northern votes, Polk had long opposed a high tariff.Seigenthaler, pp. 113–114 Many Americans, especially in the North, favored high tariffs as a means of protecting domestic manufacturing from foreign competition. Polk believed that protective tariffs were unfair to other economic activities, and he favored reducing tariff rates to the minimum level necessary for funding the federal government. Upon
taking office, Polk directed Secretary of the Treasury Walker to draft a law that would lower tariff rates. Though foreign policy and other issues prevented Congress and the administration from focusing on tariff reduction in 1845 and early 1846, Walker worked with Congressman James Iver McKay
James Iver McKay (July 17, 1792September 14, 1853) was an American lawyer and politician who served nine terms as a member of the United States House of Representatives from North Carolina from 1831 to 1849.
Early life and education
He was bor ...
to develop a tariff reduction bill. In April 1846, McKay reported the bill out of the House Ways and Means Committee
A ways and means committee is a government body that is charged with reviewing and making recommendations for government budgets. Because the raising of revenue is vital to carrying out governmental operations, such a committee is tasked with fi ...
for consideration by the full House of Representatives.Bergeron, pp. 186–188
After intense lobbying by both sides, the bill passed the House on July 3, with the vast majority of favorable votes coming from Democrats. Consideration then moved to the Senate, and Polk intensely lobbied a group of wavering senators to assure passage of the bill. In a close vote that required Vice President Dallas to break a tie, the Senate approved the tariff bill in July 1846.Seigenthaler, pp. 115–116 Dallas, from protectionist Pennsylvania, voted for the bill because he decided that his best political prospects lay in supporting the administration. Following the congressional passage of the bill, Polk signed the Walker Tariff into law, substantially reducing the rates that had been set by the Tariff of 1842. The Walker Tariff would remain in place until the passage of the Tariff of 1857
The Tariff of 1857 was a major tax reduction in the United States that amended the Walker Tariff of 1846 by lowering rates to between 15% and 24%.
The Tariff of 1857 was developed in response to a federal budget surplus in the mid-1850s. The fir ...
, staying in effect longer than any other tariff measure of the nineteenth century. The reduction of tariffs in the United States and the repeal of the Corn Laws in Great Britain led to a boom in Anglo-American trade and, in large part due to growing international trade, the economy entered a strong period of growth in the late 1840s.
Banking policy
In his inaugural address, Polk called upon Congress to re-establish theIndependent Treasury
The Independent Treasury was the system for managing the money supply of the United States federal government through the U.S. Treasury and its sub-treasuries, independently of the national banking and financial systems. It was created on August 6, ...
System under which government funds were held in the Treasury and not in banks or other financial institutions.Merry, pg. 206–207 Under that system, the government would store federal funds in vaults in the Treasury Building and other government buildings, where those funds would remain until they were used to fund the government.Bergeron, p. 192 President Van Buren had previously established the Independent Treasury system, but it had been abolished during the Tyler administration.Seigenthaler, pp. 121–122 Under the status quo that prevailed when Polk took office, the government deposited its funds in state banks, which could then use those funds in ordinary banking operations. Polk believed that this policy resulted in inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
, and was also philosophically opposed to involving the government in banking.Bergeron, pp. 191–192 The Whigs had wanted to create a new national bank since the expiration of the charter of the Second Bank of the United States
The Second Bank of the United States was the second federally authorized Second Report on Public Credit, Hamiltonian national bank in the United States. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the bank was chartered from February 1816 to January ...
in 1836, but their efforts had been vetoed by President Tyler, and Polk strongly opposed the re-establishment of a national bank. In a party-line vote, the House of Representatives approved Polk's Independent Treasury bill in April 1846. After personally winning the support of Senator Dixon Lewis, the chairman of the Senate Finance Committee, Polk was able to push the Independent Treasury Act through the Senate, and he signed the act into law on August 6, 1846. The system would remain in place until the passage of the Federal Reserve Act
The Federal Reserve Act was passed by the 63rd United States Congress and signed into law by President Woodrow Wilson on December 23, 1913. The law created the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States.
After Dem ...
in 1913.Merry, pg. 276–277
Opposition to internal improvements bills
During Polk's presidency, Congress passed bills to provide federal funding forinternal improvements
Internal improvements is the term used historically in the United States for public works from the end of the American Revolution through much of the 19th century, mainly for the creation of a transportation infrastructure: roads, turnpikes, can ...
such as roads, canals, and harbors. Those who favored such funding, many of whom were Whigs, believed that internal improvements aided economic development and Western settlement. Unlike tariffs and monetary policy, support for federally-funded internal improvements split the Democratic Party, and a coalition of Democrats and Whigs arranged for the passage of internal improvement bills despite Polk's opposition. Polk considered internal improvements to be matters for the states, and feared that the passage of federal internal improvements bill would encourage legislators to compete for favors for their home district; Polk felt that such competition for federal resources damaged the virtue of the republic. When Congress passed the Rivers and Harbors Bill in 1846 to provide $500,000 to improve port facilities, Polk vetoed it. Polk believed that the bill was unconstitutional because it unfairly favored particular areas, including ports that had no foreign trade. In this regard he followed his hero Jackson, who had vetoed the Maysville Road Bill in 1830 on similar grounds. In 1847, Polk pocket veto
A pocket veto is a legislative maneuver that allows a president or other official with veto power to exercise that power over a bill by taking no action ("keeping it in their pocket"), thus effectively killing the bill without affirmatively vetoin ...
ed another internal improvements bill, and Congress would not pass a similar bill during his presidency.
Other domestic issues
Slavery
Like Jackson, Polk saw slavery as a side issue compared to other matters such as territorial expansion and economic policy.Merry, pg. 129–130 However, the issue of slavery became increasingly polarizing during the 1840s, and Polk's expansionary policies increased its divisiveness. During his presidency, many abolitionists harshly criticized him as an instrument of the "Slave Power
The Slave Power, or Slavocracy, referred to the perceived political power held by American slaveholders in the federal government of the United States during the Antebellum period. Antislavery campaigners charged that this small group of wealth ...
", and claimed that he supported western expansion because he wanted to extend slavery into new territories. For his part, Polk accused both northern and southern leaders of attempting to use the slavery issue for political gain.Merry, pg. 356–358 The divisive debate over slavery in the territories led to the creation of the Free Soil Party
The Free Soil Party, also called the Free Democratic Party or the Free Democracy, was a political party in the United States from 1848 to 1854, when it merged into the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party. The party was focused o ...
, an anti-slavery (though not abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the political movement to end slavery and liberate enslaved individuals around the world.
The first country to fully outlaw slavery was Kingdom of France, France in 1315, but it was later used ...
) party that attracted Democrats, Whigs, and members of the Liberty Party.
California Gold Rush and the Coinage Act of 1849
 Authoritative word of the discovery of gold in California did not arrive in Washington until after the 1848 election, by which time Polk was a lame duck. Polk was delighted by the discovery of gold, seeing it as validation of his stance on expansion, and he referred to the discovery several times in his final annual message to Congress that December. Shortly thereafter, actual samples of the California gold arrived, and Polk sent a special message to Congress on the subject. The message, confirming less authoritative reports, caused large numbers of people to move to California, both from the U.S. and abroad, thus helping to spark the
Authoritative word of the discovery of gold in California did not arrive in Washington until after the 1848 election, by which time Polk was a lame duck. Polk was delighted by the discovery of gold, seeing it as validation of his stance on expansion, and he referred to the discovery several times in his final annual message to Congress that December. Shortly thereafter, actual samples of the California gold arrived, and Polk sent a special message to Congress on the subject. The message, confirming less authoritative reports, caused large numbers of people to move to California, both from the U.S. and abroad, thus helping to spark the California Gold Rush
The California gold rush (1848–1855) began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California from the rest of the U ...
. The California gold rush injected large quantities of gold into the U.S. economy, helping to ease a long-term shortage of gold coins
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by ...
. In large because of this gold, the Whigs were unable to whip up popular enthusiasm for a revival of the national bank after Polk left office.
In response to the Gold Rush, the House introduced the Coinage Act of 1849
The Coinage Act of 1849 was an Act of the United States Congress passed during the California Gold Rush authorizing the Mint to produce two new gold coins in response to the increased gold supply: the small gold dollar and the large double e ...
which allowed for the minting of two new denominations of gold coins, the gold dollar and the gold $20 or double eagle. It further defined the variances which were permissible in United States gold coinage. The act was approved on March 3, 1849, and Polk signed it on that same day, marking one of his final acts as president. The act contains four sections.
Department of the Interior
One of Polk's last acts as president was to sign the bill creating theDepartment of the Interior
The United States Department of the Interior (DOI) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the management and conservation of most federal lands and natural resources. It also administers programs relatin ...
(March 3, 1849). This was the first new cabinet position created since the early days of the Republic. Polk had misgivings about the federal government usurping power over public lands from the states. Nevertheless, the delivery of the legislation on his last full day in office gave him no time to find constitutional grounds for a veto, or to draft a sufficient veto message, so he signed the bill.
States admitted to the Union
Three states wereadmitted to the Union
Admission to the Union is provided by the Admissions Clause of the United States Constitution in Article IV, Section 3, Clause 1, which authorizes the United States Congress to admit new states into the Union beyond the thirteen states that a ...
during Polk's presidency:
* Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
December 29, 1845
* Iowa
Iowa ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the upper Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west; Wisconsin to the northeast, Ill ...
December 28, 1846
* Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
May 29, 1848
1848 election
 Honoring his pledge to serve only one term, Polk declined to seek re-election in 1848. With Polk out of the race, the Democratic Party remained fractured along geographic lines.Merry, pg. 376–377 Polk privately favored Lewis Cass as his successor, but resisted becoming closely involved in the election. At the
Honoring his pledge to serve only one term, Polk declined to seek re-election in 1848. With Polk out of the race, the Democratic Party remained fractured along geographic lines.Merry, pg. 376–377 Polk privately favored Lewis Cass as his successor, but resisted becoming closely involved in the election. At the 1848 Democratic National Convention
The 1848 Democratic National Convention was a presidential nominating convention that met from Monday May 22 to Friday May 26 in Baltimore, Maryland. It was held to nominate the Democratic Party's candidates for President and Vice president i ...
, Buchanan, Cass, and Supreme Court Justice Levi Woodbury emerged as the main contenders.Merry, pg. 446–447 Cass drew support from both the North and South with his doctrine of popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the leaders of a state and its government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associativ ...
, under which each territory would decide the legal status of slavery. Cass led after the first ballot, and slowly gained support until he clinched the nomination on the fourth ballot. William Butler, who had replaced Winfield Scott as the commanding general in Mexico City, won the vice presidential nomination. Cass's nomination alienated many northerners and southerners, each of whom saw Cass as insufficiently committed to their position on the slavery issue.
During the course of the Mexican War, Generals Taylor and Scott emerged as strong Whig candidates.Merry, pg. 374–375 As the war continued, Taylor's stature with the public grew, and he announced in 1847 that he would not refuse the presidency. The 1848 Whig National Convention
The 1848 Whig National Convention was a presidential nominating convention held from June 7 to 9 in Philadelphia. It nominated the Whig Party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1848 election. The convention selected General ...
took place on June 8, with Taylor, Scott, Henry Clay, and Massachusetts Senator Daniel Webster
Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the 14th and 19th United States Secretary of State, U.S. secretary o ...
emerging as the major candidates.Merry, pg. 447–448 Taylor narrowly led Clay after the first ballot, and his support steadily grew until he captured the nomination on the fourth ballot. The Whigs chose former Congressman Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore (January 7, 1800 – March 8, 1874) was the 13th president of the United States, serving from 1850 to 1853. He was the last president to be a member of the Whig Party while in the White House, and the last to be neither a De ...
of New York as Taylor's running mate.
In New York, an anti-slavery Democratic faction known as the Barnburners
The Barnburners and Hunkers were the names of two opposing factions of the New York Democratic Party in the mid-19th century. The main issue dividing the two factions was that of slavery, with the Barnburners being the anti-slavery faction. Whil ...
strongly supported the Wilmot Proviso and rejected Cass.Merry, pg. 455–456 Joined by other anti-slavery Democrats from other states, the Barnburners held a convention nominating former President Martin Van Buren as their own presidential nominee, and Van Buren eventually became the Free Soil Party's nominee. Though Van Buren had not been known for his anti-slavery views while president, he embraced them in 1848. Van Buren's decision to run was also affected by Polk's decision to give patronage to rival factions in New York. Polk was surprised and disappointed by his former ally's political conversion, and he worried about the divisiveness of a sectional party organized around anti-slavery principles. Van Buren was joined on the Free Soil Party's ticket by Charles Francis Adams Sr., son of former president and prominent Whig John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was the sixth president of the United States, serving from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States secretary of state from 1817 to 1825. During his long diploma ...
.
In the election, Taylor won 47.3% of the popular vote and a majority of the electoral vote, giving the Whigs control of the presidency. Cass won 42.5% of the vote, while Van Buren finished with 10.1% of the popular vote, more than any other third-party presidential candidate at that time. Despite the increasingly polarizing slavery debate, Taylor and Cass both won a mix of northern and southern states, while most of Van Buren's support came from northern Democrats.Merry, pg. 462–463 Polk was very disappointed by the outcome as he had a low opinion of Taylor, seeing the general as someone with poor judgment and few opinions. Polk left office in March 1849, and he died the following June.
Historical reputation
Sam Houston
Samuel Houston (, ; March 2, 1793 – July 26, 1863) was an American general and statesman who played a prominent role in the Texas Revolution. He served as the first and third president of the Republic of Texas and was one of the first two indi ...
is said to have observed that Polk was "a victim of the use of water as a beverage". Senator Tom Corwin of Ohio remarked "James K. Polk, of Tennessee? ''After that'', who is safe?" The Republican historians of the nineteenth century inherited this view. Polk was a compromise between the Democrats of the North, like David Wilmot David Wilmot may refer to:
* David Wilmot (politician)
* David Wilmot (actor)
David Wilmot is an Ireland, Irish actor best known for his roles in ''Michael Collins (film), Michael Collins'' (1996), ''I Went Down'' (1997), ''Intermission (fil ...
and Silas Wright
Silas Wright Jr. (May 24, 1795 – August 27, 1847) was an American attorney and Democratic politician. A member of the Albany Regency, he served as a member of the United States House of Representatives, New York State Comptroller, United Stat ...
, and Southern plantation owners led by John C. Calhoun
John Caldwell Calhoun (; March 18, 1782March 31, 1850) was an American statesman and political theorist who served as the seventh vice president of the United States from 1825 to 1832. Born in South Carolina, he adamantly defended American s ...
. The Northern Democrats thought that when they did not get their way, it was because he was the tool of the slaveholders, and the conservatives of the South insisted that he was the tool of the Northern Democrats. These views were long reflected in the historical literature, until Arthur M. Schlesinger Jr.
Arthur Meier Schlesinger Jr. ( ; born Arthur Bancroft Schlesinger; October 15, 1917 – February 28, 2007) was an American historian, social critic, and public intellectual. The son of the influential historian Arthur M. Schlesinger Sr. and a ...
and Bernard De Voto argued that Polk was nobody's tool, but set his own goals and achieved them.
Polls of historians and political scientists have generally ranked
A ranking is a relationship between a set of items, often recorded in a list, such that, for any two items, the first is either "ranked higher than", "ranked lower than", or "ranked equal to" the second. In mathematics, this is known as a weak ...
Polk as an above-average president, and Polk tends to rank higher than every other president who served between the presidencies of Andrew Jackson and Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
. A 2018 poll of the American Political Science Association
The American Political Science Association (APSA) is a professional association of political scientists in the United States. Founded in 1903 in the Tilton Memorial Library (now Tilton Hall) of Tulane University in New Orleans, it publishes four ...
’s Presidents and Executive Politics section ranked Polk as the 21st best president. A 2017 C-SPAN
Cable-Satellite Public Affairs Network (C-SPAN ) is an American Cable television in the United States, cable and Satellite television in the United States, satellite television network, created in 1979 by the cable television industry as a Non ...
poll of historians ranked Polk as the 14th best president.
Polk biographers over the years have sized up the magnitude of Polk's achievements and his legacy, particularly his two most recent. "There are three key reasons why James K. Polk deserves recognition as a significant and influential American president," Walter Borneman wrote. First, Polk accomplished the objectives of his presidential term as he defined them; second, he was the most decisive chief executive before the Civil War; and third, he greatly expanded the executive power of the presidency, particularly its war powers, its role as commander-in-chief, and its oversight of the executive branch.Political scientist Leonard White summed up Polk's command system: :He determined the general strategy of military and naval operations; he chose commanding officers; he gave personal attention to supply problems; he energized so far as he could the General Staff; he controlled the military and naval estimates; and he used the cabinet as a major coordinating agency for the conduct of the campaign. Polk's most outstanding legacy is the map of the
continental United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
, whose landmass he increased by a third. "To look at that map," Robert Merry concluded, "and to take in the western and southwestern expanse included in it, is to see the magnitude of Polk's presidential accomplishments." Though there were powerful forces compelling Americans to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
, some historians, such as Gary Kornblith, have posited that a Clay presidency would have seen the permanent independence of Texas and California.
Nevertheless, Polk's aggressive expansionism has been criticized on ethical grounds. He believed in "Manifest Destiny
Manifest destiny was the belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American pioneer, American settlers were destined to expand westward across North America, and that this belief was both obvious ("''m ...
" even more than most. Referencing the Mexican–American War, ex-president Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
stated: I was bitterly opposed to the exas annexation and to this day regard the war, which resulted, as one of the most unjust ever waged by a stronger against a weaker nation. It was an instance of a republic following the bad example of European monarchies, in not considering justice in their desire to acquire additional territory.Whig politicians, including
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
and John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was the sixth president of the United States, serving from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States secretary of state from 1817 to 1825. During his long diploma ...
, contended that the Texas Annexation
The Republic of Texas was annexation, annexed into the United States and Admission to the Union, admitted to the Union as the List of U.S. states by date of admission to the Union, 28th state on December 29, 1845.
The Republic of Texas Texas ...
and the Mexican Cession
The Mexican Cession () is the region in the modern-day Western United States that Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United S ...
enhanced the pro-slavery factions of the United States. Unsatisfactory conditions pertaining to the status of slavery in the territories acquired during the Polk administration led to the Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that temporarily defused tensions between slave and free states during the years leading up to the American Civil War. Designe ...
, one of the primary factors in the establishment of the Republican Party and later the beginning of the American Civil War.Holt, Michael F. ''The Political Crisis of the 1850s'' (1978).
References
Works cited
* * * * * * * * . * * * * * White, Leonard D. 1954. ''The Jacksonians: A Study in Administrative History, 1829-1861''. *Further reading
* Campbell, Karlyn K. “James Knox Polk: The first imperial president?" in '' Before the Rhetorical Presidency,'' edited by Martin Medhurst, (Texas A&M University Press, 2008), pp. 83–102. * Campbell, Karlyn K., & Kathleen Jamieson. ''Deeds Done in Words'' (University of Chicago Press, 1990). * Chaffin, Tom. ''Met His Every Goal? James K. Polk and the Legends of Manifest Destiny'' (University of Tennessee Press; 2014) 124 pages. * Dallas, George M. "James Knox Polk." in ''African Americans and the Presidents: Politics and Policies from Washington to Trump'' (2019): 38online
* Devoti, John. "The patriotic business of seeking office: James K. Polk and the patronage" (PhD dissertation, Temple University; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 2005. 3203004). * De Voto, Bernard. ''The Year of Decision: 1846''. Houghton Mifflin, 1943. * Eisenhower, John S. D. "The Election of James K. Polk, 1844". ''Tennessee Historical Quarterly''. 53.2 (1994): 74–87. ; popular. * Graff, Henry F., ed. ''The Presidents: A Reference History'' (3rd ed. 2002)
online
* Greenstein, Fred I. "The policy-driven leadership of James K. Polk: making the most of a weak presidency." ''Presidential Studies Quarterly'' 40#4 (2010), p. 725+
online
* Heidt, Stephen J. “Presidential Power and National Violence: James K. Polk’s Rhetorical Transfer of Savagery.” ''Rhetoric and Public Affairs'' 19#3 (2016), pp. 365–96
online
* Kornblith, Gary J. "Rethinking the Coming of the Civil War: a Counterfactual Exercise". ''Journal of American History'' 90.1 (2003): 76–105. . Asks what if Polk had not gone to war? * Leonard, Thomas. ''James K. Polk: A Clear and Unquestionable Destiny'' (Scholarly Resources Inc, 2001). * McCormac, Eugene Irving. ''James K. Polk: A Political Biography to the End of a Career, 1845–1849''. Univ. of California Press, 1922. (1995 reprint has .) hostile to Jacksonians * Merk, Frederick. ''Manifest Destiny and Mission in American History: A Reinterpretation'' (Vintage Books, 1966). * Morrison, Michael A. "Martin Van Buren, the Democracy, and the Partisan Politics of Texas Annexation". ''Journal of Southern History'' 61.4 (1995): 695–724. . Discusses the election of 1844. * Nau, Henry R. “James K. Polk: Manifest Destiny.” in ''Conservative Internationalism: Armed Diplomacy under Jefferson, Polk, Truman, and Reagan'' (Princeton University Press, 2013), pp. 110–46
online
* Nelson, Anna Louise Kasten. "The Secret Diplomacy of James K. Polk during the Mexican War, 1846–1847" PhD dissertation, The George Washington University; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 1972. 7304017). * Palmer‐Mehta, Valerie. "Sarah Polk: Ideas of Her Own." in ''A Companion to First Ladies'' (2016): 159–175. * Paul; James C. N. ''Rift in the Democracy.'' (1951). on 1844 election * * Rowe, Christopher. "American society through the prism of the Walker Tariff of 1846." ''Economic Affairs'' 40.2 (2020): 180–197. * Ruiz, Ramon, ed. ''The Mexican War: Was it Manifest Destiny?'' (1963) excerpts from primary and secondary sources. * Schoenbeck, Henry Fred. "The economic views of James K. Polk as expressed in the course of his political career" (PhD dissertation, The University of Nebraska – Lincoln; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 1951. DP13923). * Sellers, Charles. ''James K. Polk, Jacksonian, 1795–1843'' (1957
vol 1 online
and ''James K. Polk, Continentalist, 1843–1846''. (1966
vol 2 online
long scholarly biography * pp 195–290 * Smith, Justin Harvey. ''The War with Mexico, Vol 1.'' (2 vol 1919)
full text online
** Smith, Justin Harvey. ''The War with Mexico, Vol. 2''. (2 vol 1919)
full text online
Pulitzer prize; still a major standard source, * Weinberg, Albert. ''Manifest Destiny: A Study of Nationalist Expansionism in American History'' (1935
online
* Williams, Frank J. “James K. Polk.” in ''The Presidents and the Constitution: A Living History'', edited by Ken Gormley, NYU Press, 2016, pp. 149–58
online
* Winders, Richard Bruce. ''Mr. Polk's army: the American military experience in the Mexican war'' (Texas A&M University Press, 2001).
Historiography
* Notaro, Carmen. “Biography and James K. Polk: Observations on an Historiography Spanning Two Centuries.” ''Tennessee Historical Quarterly'' 75#4 (2016), pp. 260–75online
Primary sources
* Cutler, Wayne, et al. ''Correspondence of James K. Polk''. 1972–2004. . Multivolume scholarly edition of the complete correspondence to and from Polk. *online vol 13, August 1847 to March 1848
* Polk, James K. ''The Diary of James K. Polk During His Presidency, 1845–1849'' edited by Milo Milton Quaife, 4 vols. 1910. Abridged version by Allan Nevins. 1929/
External links
*James K. Polk: A Resource Guide
from the
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is a research library in Washington, D.C., serving as the library and research service for the United States Congress and the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It also administers Copyright law o ...
James K. Polk's Personal Correspondence
Shapell Manuscript Foundation
Extensive essay on James K. Polk and shorter essays on each member of his cabinet and First Lady
from the
Miller Center of Public Affairs
The Miller Center is a nonpartisan affiliate of the University of Virginia that specializes in United States presidential scholarship, public policy, and political history. It is headquartered at Faulkner House.
History
The Miller Center wa ...
Inaugural Address of James K. Polk
from The Avalon Project at the
Yale Law School
Yale Law School (YLS) is the law school of Yale University, a Private university, private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. It was established in 1824. The 2020–21 acceptance rate was 4%, the lowest of any law school in the United ...
Biography of James K. Polk
from the official
White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Northwest (Washington, D.C.), NW in Washington, D.C., it has served as the residence of every U.S. president ...
website
President James K. Polk State Historic Site, Pineville, North Carolina
from a
State of North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
website"Life Portrait of James K. Polk"
from
C-SPAN
Cable-Satellite Public Affairs Network (C-SPAN ) is an American Cable television in the United States, cable and Satellite television in the United States, satellite television network, created in 1979 by the cable television industry as a Non ...
's '' American Presidents: Life Portraits'', May 28, 1999
{{Democratic Party (United States)
1840s in the United States
Polk, James K.
1845 establishments in the United States
1849 disestablishments in the United States
James K. Polk
George M. Dallas
James Buchanan
William R. King