Polar Projection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The azimuthal equidistant projection is an azimuthal map projection. It has the useful properties that all points on the map are at proportionally correct distances from the center point, and that all points on the map are at the correct azimuth (direction) from the center point. A useful application for this type of projection is a polar projection which shows all meridians (lines of longitude) as straight, with distances from the pole represented correctly. The
The azimuthal equidistant projection is an azimuthal map projection. It has the useful properties that all points on the map are at proportionally correct distances from the center point, and that all points on the map are at the correct azimuth (direction) from the center point. A useful application for this type of projection is a polar projection which shows all meridians (lines of longitude) as straight, with distances from the pole represented correctly. The
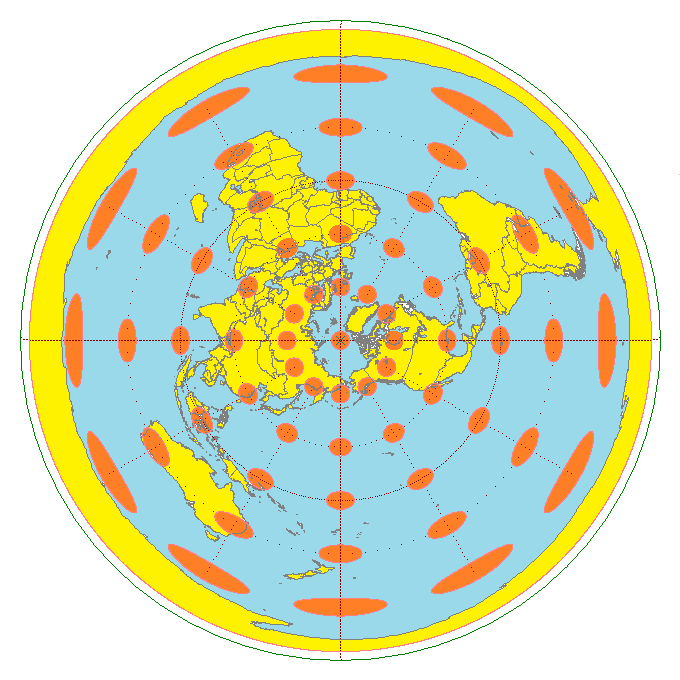 A point on the globe is chosen as "the center" in the sense that mapped distances and azimuth directions from that point to any other point will be correct. That point, (''φ'', ''λ''), will project to the center of a circular projection, with ''φ'' referring to latitude and ''λ'' referring to longitude. All points along a given azimuth will project along a straight line from the center, and the angle ''θ'' that the line subtends from the vertical is the azimuth angle. The distance from the center point to another projected point ''ρ'' is the arc length along a
A point on the globe is chosen as "the center" in the sense that mapped distances and azimuth directions from that point to any other point will be correct. That point, (''φ'', ''λ''), will project to the center of a circular projection, with ''φ'' referring to latitude and ''λ'' referring to longitude. All points along a given azimuth will project along a straight line from the center, and the angle ''θ'' that the line subtends from the vertical is the azimuth angle. The distance from the center point to another projected point ''ρ'' is the arc length along a
File:Los Angeles centered azimuthal equidistant projection.gif, Map centered about Los Angeles, whose antipodal point is in the south Indian Ocean.
File:Taipei centered azimuthal equidistant projection.gif, Map centered about Taipei, whose antipodal point is near the Argentina–Paraguay border.
· · · · ·
 Azimuthal equidistant projection maps can be useful in terrestrial
Azimuthal equidistant projection maps can be useful in terrestrial  Azimuthal equidistant projection maps can also be useful to show ranges of missiles, as demonstrated by the map on the right.
Azimuthal equidistant projection maps can also be useful to show ranges of missiles, as demonstrated by the map on the right.
Table of examples and properties of all common projections
from radicalcartography.net
Online Azimuthal Equidistant Map Generator
* ttps://geographiclib.sourceforge.io GeographicLibprovides a class for performing azimuthal equidistant projections centered at any point on the ellipsoid.
Animated US National Weather Service Wind Data for Azimuthal equidistant projection
from ns6t.net. {{Authority control Map projections Equidistant projections


flag of the United Nations
The flag of the United Nations consists of the emblem depicting the white azimuthal equidistant projection of the world map, centred on the North Pole, with two white olive branches placed on to its right and left, located on the sky blue backg ...
contains an example of a polar azimuthal equidistant projection.
History
While it may have been used by ancient Egyptians for star maps in some holy books,, p.29 the earliest text describing the azimuthal equidistant projection is an 11th-century work by al-Biruni. An example of this system is the world map by ‛Ali b. Ahmad al-Sharafi of Sfax in 1571. The projection appears in many Renaissance maps, andGerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented ...
used it for an inset of the north polar regions in sheet 13 and legend 6 of his well-known 1569 map. In France and Russia this projection is named "Postel projection" after Guillaume Postel, who used it for a map in 1581.Snyder 1997, p. 29 Many modern star chart planispheres use the polar azimuthal equidistant projection.
Mathematical definition
 A point on the globe is chosen as "the center" in the sense that mapped distances and azimuth directions from that point to any other point will be correct. That point, (''φ'', ''λ''), will project to the center of a circular projection, with ''φ'' referring to latitude and ''λ'' referring to longitude. All points along a given azimuth will project along a straight line from the center, and the angle ''θ'' that the line subtends from the vertical is the azimuth angle. The distance from the center point to another projected point ''ρ'' is the arc length along a
A point on the globe is chosen as "the center" in the sense that mapped distances and azimuth directions from that point to any other point will be correct. That point, (''φ'', ''λ''), will project to the center of a circular projection, with ''φ'' referring to latitude and ''λ'' referring to longitude. All points along a given azimuth will project along a straight line from the center, and the angle ''θ'' that the line subtends from the vertical is the azimuth angle. The distance from the center point to another projected point ''ρ'' is the arc length along a great circle
In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point.
Any arc of a great circle is a geodesic of the sphere, so that great circles in spherical geomet ...
between them on the globe. By this description, then, the point on the plane specified by (''θ'',''ρ'') will be projected to Cartesian coordinates:
:
The relationship between the coordinates (''θ'',''ρ'') of the point on the globe, and its latitude and longitude coordinates (''φ'', ''λ'') is given by the equations:
:
When the center point is the north pole, ''φ''1 equals and ''λ'' is arbitrary, so it is most convenient to assign it the value of 0. This assignment significantly simplifies the equations for ''ρ''u and ''θ'' to:
:
Limitation
With thecircumference of the Earth
Earth's circumference is the distance around Earth. Measured around the Equator, it is . Measured around the poles, the circumference is .
Measurement of Earth's circumference has been important to navigation since ancient times. The first kno ...
being approximately , the maximum distance that can be displayed on an azimuthal equidistant projection map is half the circumference, or about . For distances less than distortions are minimal. For distances the distortions are moderate. Distances greater than are severely distorted.
If the azimuthal equidistant projection map is centered about a point whose antipodal point lies on land and the map is extended to the maximum distance of the antipode point smears into a large circle. This is shown in the example of two maps centered about Los Angeles, and Taipei. The antipode for Los Angeles is in the south Indian Ocean hence there is not much significant distortion of land masses for the Los Angeles centered map except for East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
and Madagascar. On the other hand, Taipei's antipode is near the Argentina–Paraguay border, causing the Taipei centered map to severely distort South America.
;Sample azimuthal equidistant projection maps
;Red circles = 10,000 km radius circles
;Purple circles = 15,000 km radius circles
· · · · ·
Applications
 Azimuthal equidistant projection maps can be useful in terrestrial
Azimuthal equidistant projection maps can be useful in terrestrial point to point communication
In telecommunications, a point-to-point connection refers to a communications connection between two communication endpoints or nodes. An example is a telephone call, in which one telephone is connected with one other, and what is said by one ...
. This type of projection allows the operator to easily determine in which direction to point their directional antenna
A directional antenna or beam antenna is an antenna which radiates or receives greater power in specific directions allowing increased performance and reduced interference from unwanted sources. Directional antennas provide increased performance ...
. The operator simply finds on the map the location of the target transmitter or receiver (i.e. the other antenna being communicated with) and uses the map to determine the azimuth angle needed to point the operator's antenna. The operator would use an electric rotator to point the antenna. The map can also be used in one way communication. For example if the operator is looking to receive signals from a distant radio station, this type of projection could help identify the direction of the distant radio station. In order for the map to be useful, the map should be centered as close as possible about the location of the operator's antenna.
See also
* Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection *List of map projections
This is a summary of map projections that have articles of their own on Wikipedia or that are otherwise notable
Notability is the property
of being worthy of notice, having fame, or being considered to be of a high degree of interest, signif ...
* Modern flat Earth beliefs
Modern flat Earth beliefs are promoted by organizations and individuals which make claims that the Earth is flat while denying the Earth's sphericity, contrary to over two millennia of scientific consensus. Flat Earth beliefs are pseudoscie ...
References
External links
Table of examples and properties of all common projections
from radicalcartography.net
Online Azimuthal Equidistant Map Generator
* ttps://geographiclib.sourceforge.io GeographicLibprovides a class for performing azimuthal equidistant projections centered at any point on the ellipsoid.
Animated US National Weather Service Wind Data for Azimuthal equidistant projection
from ns6t.net. {{Authority control Map projections Equidistant projections