Pneumatode on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In botany, pneumatodes are air-containing structures in plant roots. Their function is to allow gaseous exchange in root tissues. This can be beneficial to semi-aquatic plants, such as neo-tropical palms. Plants with photosynthetic roots, such as epiphytic orchids like '' Dendrophylax lindenii'' also possess these structures. They play a role in fungal interactions.
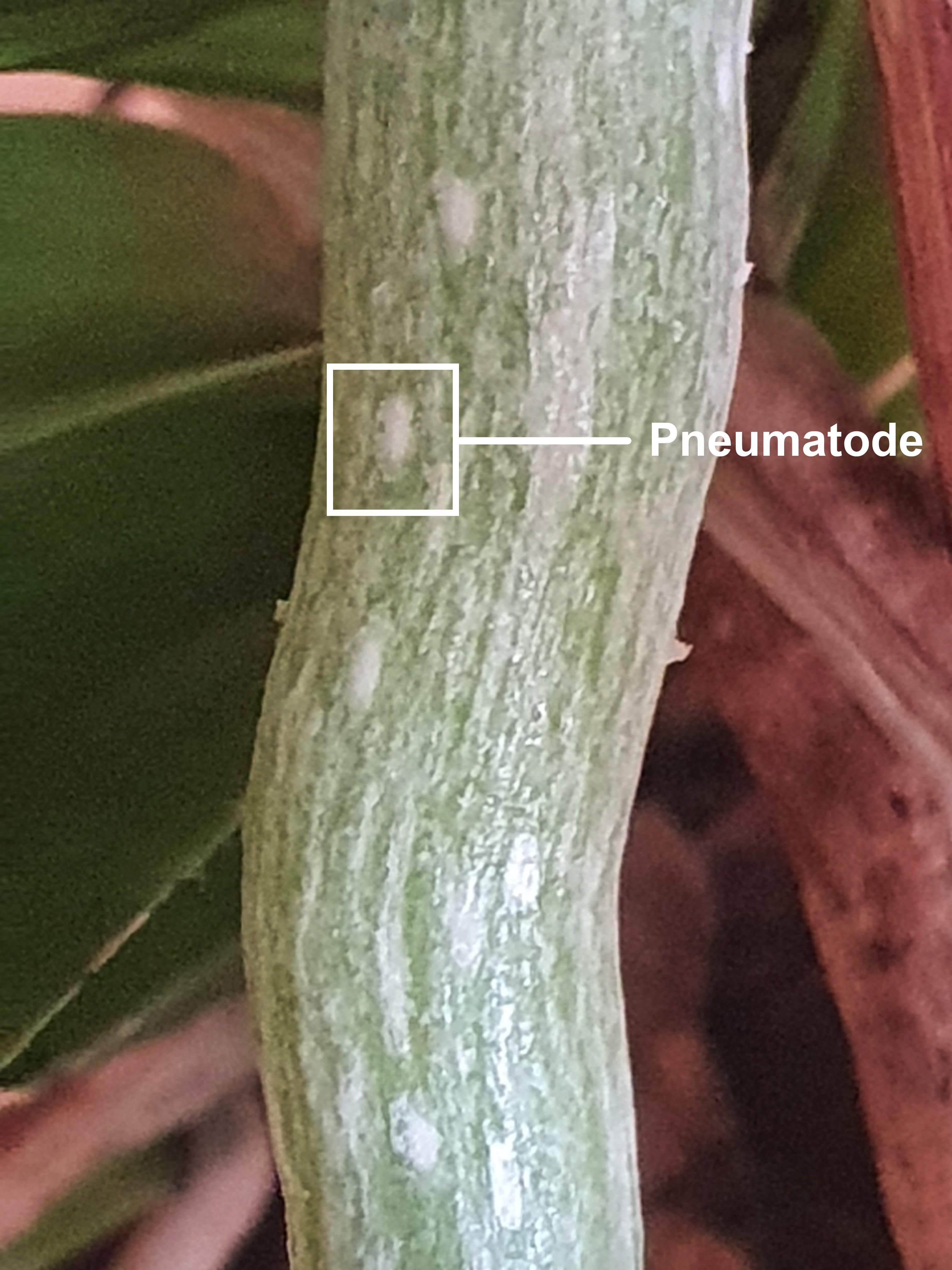



Etymology
The name of the structure is derived from the Greek word πνεῦμα (pneûma), meaning breath and ὁδός (hodós), meaning pathway.Fungal interactions
Fungal infections of plants may begin through penetration of the roots through pneumatodes.Functional analogy to stomata
Pneumatodes are considered as a special type of cyclocytic stomata. The entire structure may rise above the adjacent epidermis. The pneumatodes may function as double structures for gas exchange and liquid water elimination (guttation
Guttation is the exudation of drops of internal liquid out of the tips or edges of leaves of some vascular plants, and also a number of fungi. Ancient Latin gutta means "a drop of fluid", whence modern botany formed the word guttation to designa ...
). Leafless orchids with photosynthetic roots rely on the gas exchange through pneumatodes for photosynthesis.
Taxonomic importance
These structures are characteristic for different species and can be used to differentiate between them. These features can be used to distinguish between palm species. They can also be used in the field ofpaleobotany
Paleobotany or palaeobotany, also known as paleophytology, is the branch of botany dealing with the recovery and identification of plant fossils from geological contexts, and their use for the biological reconstruction of past environments ( pal ...
, as the structures may be preserved in fossilized roots.Plaziat, J. C. (1995). Modern and fossil mangroves and mangals: their climatic and biogeographic variability. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 83(1), 73-96.
References
{{Reflist Plant anatomy Plant physiology Plant roots