Plutonium-244 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Plutonium-244 (Pu) is an isotope of plutonium that has a
 Plutonium-244 is one of several extinct radionuclides that preceded the formation of the Solar System. Its half-life of 80 million years ensured its circulation across the
Plutonium-244 is one of several extinct radionuclides that preceded the formation of the Solar System. Its half-life of 80 million years ensured its circulation across the
half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
of 81.3 million years. This is longer than any other isotope of plutonium and longer than any other known isotope of an element beyond bismuth, except for the three naturally abundant ones: uranium-235
Uranium-235 ( or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exists in nat ...
(704 million years), uranium-238
Uranium-238 ( or U-238) is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature, with a relative abundance of 99%. Unlike uranium-235, it is non-fissile, which means it cannot sustain a chain reaction in a thermal-neutron reactor. However, it i ...
(4.468 billion years), and thorium-232
Thorium-232 () is the main naturally occurring isotope of thorium, with a relative abundance of 99.98%. It has a half life of 14.05 billion years, which makes it the longest-lived isotope of thorium. It decays by alpha decay to radium-228; its de ...
(14.05 billion years). Given the half-life of Pu, an exceedingly small amount should still be present on Earth, making plutonium a likely but unproven candidate as the shortest-lived primordial element.
Natural occurrence
Accurate measurements, beginning in the early 1970s, appeared to detect primordial plutonium-244, making it the shortest-livedprimordial nuclide
In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Primordial nuclides were present in the ...
. The amount of Pu in the pre-Solar nebula
There is evidence that the formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 bya, billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, whil ...
(4.57×10 years ago) was estimated as 0.8% the amount of U. As the age of the Earth
The age of Earth is estimated to be 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years. This age may represent the age of Earth's accretion (astrophysics), accretion, or Internal structure of Earth, core formation, or of the material from which Earth formed. This dating ...
is about 56 half-lives of Pu, the amount of Pu left should be very small; Hoffman et al. estimated its content in the rare-earth mineral bastnasite as = 1.0×10 g/g, which corresponded to the content in the Earth crust as low as 3×10 g/g (i.e. the total mass of plutonium-244 in Earth's crust is about 9 g). Since Pu cannot be easily produced by natural neutron capture
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, wh ...
in the low neutron activity environment of uranium ore
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the most common Chemical element, elements in Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than ...
s (see below), its presence cannot plausibly be explained by any other means than creation by r-process
In nuclear astrophysics, the rapid neutron-capture process, also known as the ''r''-process, is a set of nuclear reactions that is responsible for nucleosynthesis, the creation of approximately half of the Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei Heavy meta ...
nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons (protons and neutrons) and nuclei. According to current theories, the first nuclei were formed a few minutes after the Big Bang, through nuclear reactions in ...
in supernovae
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original ob ...
or neutron star merger
A neutron star merger is the stellar collision of neutron stars. When two neutron stars fall into mutual orbit, they gradually inspiral, spiral inward due to the loss of energy emitted as gravitational radiation. When they finally meet, their me ...
s.
However, the detection of primordial Pu in 1971 is not confirmed by recent, more sensitive measurements using accelerator mass spectrometry. In a 2012 study, no traces of Pu in the samples of bastnasite (taken from the same mine as in the early study) were observed, so only an upper limit on the Pu content was obtained: < 1.5×10 g/g: 370 (or fewer) atoms per gram of the sample, at least seven times lower than the abundance measured by Hoffman et al. A 2022 study, once again using accelerator mass spectrometry, could not detect Pu in Bayan Obo bastnasite, finding an upper limit of < 2.1×10 g/g (about seven times lower than the 2012 study). Thus, the 1971 detection cannot have been a signal of primordial Pu. Considering the likely abundance ratio of Pu to U in the early solar system (~0.008), this upper limit is still 18x greater than the expected present Pu content in the bastnasite sample (1.2×10 g/g).
Trace amounts of Pu (that arrived on Earth within the last 10 million years) were found in rock from the Pacific ocean by a Japanese oil exploration company.
Live interstellar plutonium-244 has been detected in meteorite dust in marine sediments, though the levels detected are much lower than would be expected from current modelling of the in-fall from the interstellar medium
The interstellar medium (ISM) is the matter and radiation that exists in the outer space, space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as cosmic dust, dust and cosmic rays. It f ...
. It is important to recall, however, that in order to be a primordial nuclide
In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Primordial nuclides were present in the ...
– one constituting the amalgam orbiting the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
that ultimately coalesced into the Earth – plutonium-244 must have comprised some of the solar nebula, rather than having been replenished by extrasolar meteoritic dust. The presence of Pu in a meteor without evidence that the meteor originated in the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
's formational disc, supports the hypothesis that Pu was abundant enough to have been a part of that disc, if an extrasolar meteor contained it in some other gravitationally supported system, but such a meteor cannot prove the hypothesis. Only the unlikely discovery of live Pu within the Earth's composition could do that.
As an extinct radionuclide
 Plutonium-244 is one of several extinct radionuclides that preceded the formation of the Solar System. Its half-life of 80 million years ensured its circulation across the
Plutonium-244 is one of several extinct radionuclides that preceded the formation of the Solar System. Its half-life of 80 million years ensured its circulation across the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
before its extinction, and indeed, Pu has not yet been found in matter other than meteorites. Radionuclides such as Pu, decay to produce fissiogenic (i.e., arising from fission) xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
isotopes that can then be used to time the events of the early Solar System. In fact, by analyzing data from Earth's mantle which indicates that about 30% of existing fissiogenic xenon is from Pu decay, it can be inferred that the Earth formed nearly 50–70 million years after the Solar System formed.
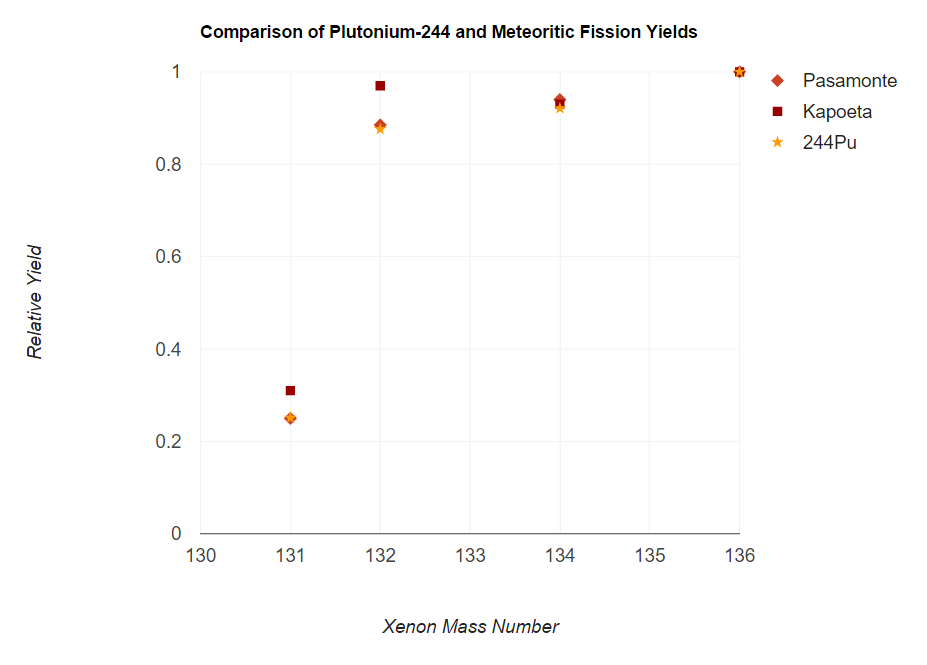
Before the analysis of mass spectroscopy data from analyzing samples found in meteorites, it was inferential at best to credit Pu as being the nuclide responsible for the fissiogenic xenon found. However, an analysis of a laboratory sample of Pu compared with that of fissiogenic xenon gathered from the meteorites Pasamonte and Kapoeta produced matching spectra that immediately left little doubt as to the source of the isotopic xenon anomalies. Spectra data was further acquired for another actinide isotope, Cm, but such data proved contradictory and helped erase further doubts that the fission was appropriately attributed to Pu.
Both the examination of spectra data and study of fission tracks led to several findings of plutonium-244. In Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
, the analysis of the mass spectrum of xenon in 4.1–4.2-billion-year-old zircons was met with findings of diverse levels of Pu fission. Presence of Pu fission tracks can be established by using the initial ratio of Pu to U (Pu/U) at a time T = years, when Xe formation first began in meteorites, and by considering how the ratio of Pu/U fission tracks varies over time. Examination of a whitlockite crystal within a lunar rock specimen brought by Apollo 14
Apollo 14 (January 31February 9, 1971) was the eighth crewed mission in the United States Apollo program, the third to Moon landing, land on the Moon, and the first to land in the Geology of the Moon#Highlands, lunar highlands. It was the las ...
, established proportions of Pu/U fission tracks consistent with the (Pu/U) time dependence.
Production
Unlike plutonium-238,plutonium-239
Plutonium-239 ( or Pu-239) is an isotope of plutonium. Plutonium-239 is the primary fissile isotope used for the production of nuclear weapons, although uranium-235 is also used for that purpose. Plutonium-239 is also one of the three main iso ...
, plutonium-240
Plutonium-240 ( or Pu-240) is an isotope of plutonium formed when plutonium-239 captures a neutron. The detection of its spontaneous fission led to its discovery in 1944 at Los Alamos and had important consequences for the Manhattan Project.
...
, plutonium-241, and plutonium-242, plutonium-244 is not produced in quantity by the nuclear fuel cycle, because further neutron capture
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, wh ...
on plutonium-242 produces plutonium-243 which has a short half-life (5 hours) and quickly beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron ...
s to americium-243 before having much opportunity to further capture neutrons in any but very high neutron flux environments. The global inventory of Pu is about 20 grams. Plutonium-244 is also a minor constituent of thermonuclear fallout, with a global Pu/Pu fallout ratio of (5.7 ± 1.0) × 10.
Applications
Plutonium-244 is used as an internal standard for isotope dilution mass spectrometry analysis of plutonium.References
{{Isotopes of plutonium Nuclear materials Isotopes of plutonium