Platelet Storage Pool Deficiency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Platelet storage pool deficiency is a type of
 The ''presentation'' (signs/symptoms) of an individual with platelet storage pool deficiency is as follows:
:::::::*Unusual bleeding(after surgical procedure)
:::::::*
The ''presentation'' (signs/symptoms) of an individual with platelet storage pool deficiency is as follows:
:::::::*Unusual bleeding(after surgical procedure)
:::::::*
 The condition of platelet storage pool deficiency can be acquired or inherited (genetically passed on from the individuals parents). Some of the causes of platelet storage pool deficiency when acquired are:
::::::::* Hairy-cell leukemia
::::::::*
The condition of platelet storage pool deficiency can be acquired or inherited (genetically passed on from the individuals parents). Some of the causes of platelet storage pool deficiency when acquired are:
::::::::* Hairy-cell leukemia
::::::::*
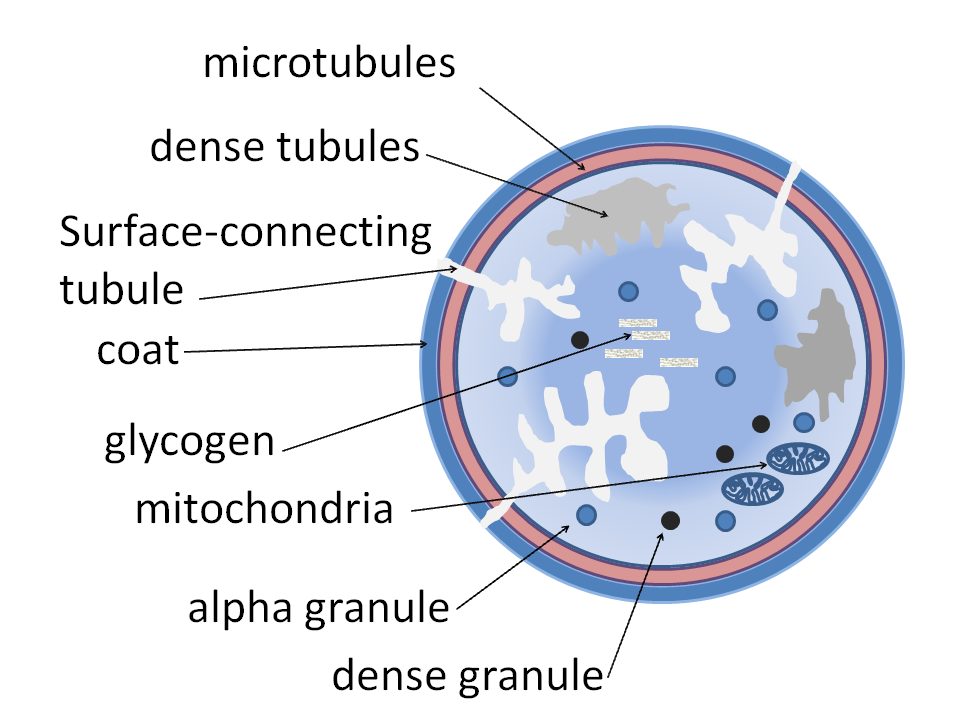 In terms of the pathophysiology of platelet storage pool deficiency one must consider several factors including the human body's normal function prior to such a deficiency, such as platelet alpha-granules one of three types of platelet secretory granule
Platelet α–granules are important in platelet activity, α–granules connect with
In terms of the pathophysiology of platelet storage pool deficiency one must consider several factors including the human body's normal function prior to such a deficiency, such as platelet alpha-granules one of three types of platelet secretory granule
Platelet α–granules are important in platelet activity, α–granules connect with
 The diagnosis of this condition can be done via the following:
*
The diagnosis of this condition can be done via the following:
*
 *
*
PubMed
{{Medicine Coagulopathies
coagulopathy
Coagulopathy (also called a bleeding disorder) is a condition in which the blood's ability to coagulate (form clots) is impaired. This condition can cause a tendency toward prolonged or excessive bleeding (bleeding diathesis), which may occur sp ...
characterized by defects in the granules in platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby i ...
s, particularly a lack of granular non-metabolic adenosine diphosphate. Individuals with adenosine diphosphate deficient ''storage pool disease'' present a prolonged bleeding time
Bleeding time is a medical test done on someone to assess their platelets function. It involves making a patient bleed, then timing how long it takes for them to stop bleeding using a stopwatch or other suitable devices.
The term template bleed ...
due to impaired aggregation response to fibrillar collagen.
Symptoms and signs
 The ''presentation'' (signs/symptoms) of an individual with platelet storage pool deficiency is as follows:
:::::::*Unusual bleeding(after surgical procedure)
:::::::*
The ''presentation'' (signs/symptoms) of an individual with platelet storage pool deficiency is as follows:
:::::::*Unusual bleeding(after surgical procedure)
:::::::*Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, ...
:::::::*Decrease mean platelet volume
Mean platelet volume (MPV) is a machine-calculated measurement of the average size of platelets found in blood and is typically included in blood tests as part of the CBC. Since the average platelet size is larger when the body is producing in ...
:::::::*Myelodysplasia
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may ...
Cause
 The condition of platelet storage pool deficiency can be acquired or inherited (genetically passed on from the individuals parents). Some of the causes of platelet storage pool deficiency when acquired are:
::::::::* Hairy-cell leukemia
::::::::*
The condition of platelet storage pool deficiency can be acquired or inherited (genetically passed on from the individuals parents). Some of the causes of platelet storage pool deficiency when acquired are:
::::::::* Hairy-cell leukemia
::::::::*Cardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
bypass
Mechanism
 In terms of the pathophysiology of platelet storage pool deficiency one must consider several factors including the human body's normal function prior to such a deficiency, such as platelet alpha-granules one of three types of platelet secretory granule
Platelet α–granules are important in platelet activity, α–granules connect with
In terms of the pathophysiology of platelet storage pool deficiency one must consider several factors including the human body's normal function prior to such a deficiency, such as platelet alpha-granules one of three types of platelet secretory granule
Platelet α–granules are important in platelet activity, α–granules connect with plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
. This in turn increases the size of the platelet. Platelet α–granules have an important role in hemostasis
In biology, hemostasis or haemostasis is a process to prevent and stop bleeding, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel (the opposite of hemostasis is hemorrhage). It is the first stage of wound healing. This involves coagulation, wh ...
as well as thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thr ...
. ''SNARE'' accessory proteins control the secretion of α–granule.
Diagnosis
 The diagnosis of this condition can be done via the following:
*
The diagnosis of this condition can be done via the following:
* Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles.
In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the fl ...
* Bleeding time
Bleeding time is a medical test done on someone to assess their platelets function. It involves making a patient bleed, then timing how long it takes for them to stop bleeding using a stopwatch or other suitable devices.
The term template bleed ...
analysis
* Platelet aggregation function
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby ini ...
study:
Types
This condition may involve the alpha granules or the dense granules. Therefore, the following examples include:Platelet alpha-granule
Alpha granules, (α-granules) also known as platelet alpha-granules are a cellular component of platelets. Platelets contain different types of Granule (cell biology), granules that perform different functions, and include alpha granules, dense gra ...
s
** Gray platelet syndrome
Gray platelet syndrome (GPS), or platelet alpha-granule deficiency, is a rare congenital autosomal recessive bleeding disorder caused by a reduction or absence of alpha-granules in blood platelets, and the release of proteins normally contained in ...
** Quebec platelet disorder
* Dense granule
Dense granules (also known as dense bodies or delta granules) are specialized secretory organelles. Dense granules are found only in platelets and are smaller than alpha granules.Michelson, A. D. (2013). ''Platelets'' (Vol. 3rd ed). Amsterdam: Aca ...
s
** δ-Storage pool deficiencyKaushansky K, Lichtman M, Beutler E, Kipps T, Prchal J, Seligsohn U. (2010; edition 8: pages 1946–1948) ''Williams Hematology''. McGraw-Hill.
** Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome
Heřmanský–Pudlák syndrome (often written Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome or abbreviated HPS) is an extremely rare autosomal recessive disorder which results in oculocutaneous albinism (decreased pigmentation), bleeding problems due to a platelet ...
** Chédiak–Higashi syndrome
Chédiak–Higashi syndrome (CHS) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder that arises from a mutation of a lysosomal trafficking regulator protein, which leads to a decrease in phagocytosis. The decrease in phagocytosis results in recurrent pyogen ...
Treatment
Platelet storage pool deficiency has no treatment however management consists ofantifibrinolytic Antifibrinolytics are a class of medication that are inhibitors of fibrinolysis. Examples include aminocaproic acid (ε-aminocaproic acid) and tranexamic acid. These lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor t ...
medications if the individual has unusual bleeding event, additionally caution should be taken with usage of NSAIDS
See also
*Hypocoagulability
In medicine (hematology), bleeding diathesis is an unusual susceptibility to bleed (hemorrhage) mostly due to hypocoagulability (a condition of irregular and slow blood clotting), in turn caused by a coagulopathy (a defect in the system of coagula ...
* Hypercoagulability
Thrombophilia (sometimes called hypercoagulability or a prothrombotic state) is an abnormality of blood coagulation that increases the risk of thrombosis (blood clots in blood vessels). Such abnormalities can be identified in 50% of people who ...
References
Further reading
* *External links
PubMed
{{Medicine Coagulopathies