Plant Load Factor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full
 Nuclear power plants are at the high end of the range of capacity factors, ideally reduced only by the
Nuclear power plants are at the high end of the range of capacity factors, ideally reduced only by the
 For
For
Spain Pioneers Grid-Connected Solar-Tower Thermal Power
SolarPACES, OECD/ IEA, p. 3.
and !!Other Biomass
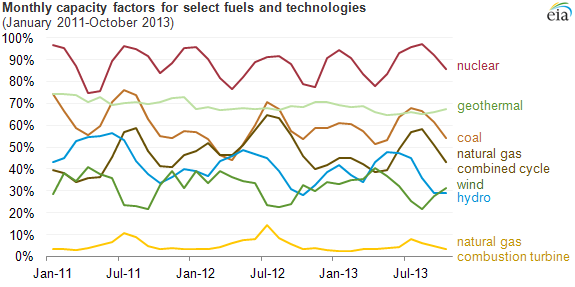
including Wood !! Geothermal !! !! !! !! !! !! !! !! , - , 89.9% , , 38.9% , , 32.4% , , NA , , NA , , 68.9% , , 56.7% , , 73.6% , , 59.8% , , 48.2% , , 4.9% , , 10.6% , , 6.1% , , 12.1% , , 0.8% , , 2.2% , - , 91.7% , , 37.3% , , 34.0% , , 25.9% , , 19.8% , , 68.9% , , 58.9% , , 74.0% , , 61.1% , , 48.3% , , 5.2% , , 10.4% , , 8.5% , , 12.5% , , 1.1% , , 1.4% , - , 92.3% , , 35.8% , , 32.2% , , 25.8% , , 22.1% , , 68.7% , , 55.3% , , 74.3% , , 54.7% , , 55.9% , , 6.9% , , 11.5% , , 8.9% , , 13.3% , , 1.1% , , 2.2% , - , 92.3% , , 38.2% , , 34.5% , , 25.1% , , 22.2% , , 69.7% , , 55.6% , , 73.9% , , 53.3% , , 55.5% , , 8.3% , , 12.4% , , 9.6% , , 11.5% , , 1.1% , , 2.6% , - , 92.2% , , 43.1% , , 34.6% , , 25.7% , , 21.8% , , 68.0% , , 57.8% , , 74.0% , , 53.7% , , 51.3% , , 6.7% , , 10.5% , , 9.9% , , 13.5% , , 0.9% , , 2.3% , - , 92.6% , , 42.8% , , 37.4% , , 26.1% , , 23.6% , , 73.3% , , 49.3% , , 77.3% , , 54.0% , , 57.6% , , 11.8% , , 13.7% , , NA , , 13.9% , , 2.5% , , NA However, these values often vary significantly by month.
 The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity
Nameplate capacity, also known as the rated capacity, nominal capacity, installed capacity, maximum effect or gross capacity,fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work (physics), work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chem ...
consuming power plant
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the electricity generation, generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electr ...
or one using renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
, such as wind, the sun or hydro-electric installations. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production.
The actual energy output during that period and the capacity factor vary greatly depending on a range of factors. The capacity factor can never exceed the availability factor
The availability factor of a power plant is the duration it achieves production of electricity divided by the duration that it was planned to produce electricity. In the field of reliability engineering, ''availability factor'' is known as operat ...
, or uptime
Uptime is a Measurement, measure of system reliability, expressed as the period of system time, time a machine, typically a computer, has been continuously working and available. Uptime is the opposite of downtime.
It is often used as a measure ...
during the period. Uptime can be reduced due to, for example, reliability issues and maintenance, scheduled or unscheduled. Other factors include the design of the installation, its location, the type of electricity production and with it either the fuel being used or, for renewable energy, the local weather conditions. Additionally, the capacity factor can be subject to regulatory constraints and market forces
In economics, a market is a composition of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations or infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering ...
, potentially affecting both its fuel purchase and its electricity sale.
The capacity factor is often computed over a timescale of a year, averaging out most temporal fluctuations. However, it can also be computed for a month to gain insight into seasonal fluctuations. Alternatively, it can be computed over the lifetime of the power source, both while operational and after decommissioning. A capacity factor can also be expressed and converted to full load hours.
Definition
:Sample calculations
Nuclear power plant
 Nuclear power plants are at the high end of the range of capacity factors, ideally reduced only by the
Nuclear power plants are at the high end of the range of capacity factors, ideally reduced only by the availability factor
The availability factor of a power plant is the duration it achieves production of electricity divided by the duration that it was planned to produce electricity. In the field of reliability engineering, ''availability factor'' is known as operat ...
, i.e. maintenance and refueling. The largest nuclear plant in the US, Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station
The Palo Verde Generating Station is a nuclear power plant located near Tonopah, Arizona about west of downtown Phoenix. Palo Verde generates the most electricity of any power plant in the United States per year, and is the largest power pl ...
has between its three reactors a nameplate capacity of 3,942 MW. In 2010 its annual generation was 31,200,000 MWh, leading to a capacity factor of:
:
Each of Palo Verde’s three reactors is refueled every 18 months, with one refueling every spring and fall. In 2014, a refueling was completed in a record 28 days, compared to the 35 days of downtime that the 2010 capacity factor corresponds to.
In 2019, Prairie Island 1 was the US unit with the highest factor and actually reached 104.4%.
Wind farm
The Danish offshore wind farmHorns Rev 2
Horns Rev is an offshore wind farm in Danish waters in the North Sea.
The wind farm was built in three phases, the first coming online in 2002, the second in 2009 and the third in 2019.
Horns Rev 1, the first phase, was the first large-scale o ...
has a nameplate capacity of 209.3 MW.
it has produced 6416 GWh since its commissioning 7 years ago, i.e. an average annual production of 875 GWh/year and a capacity factor of:
:
Sites with lower capacity factors may be deemed feasible for wind farms, for example the onshore 1 GW Fosen Vind which is under construction in Norway has a projected capacity factor of 39%. Feasibility calculations may be affected by seasonality. For example in Finland, capacity factor during the cold winter months is more than double compared to July. While the annual average in Finland is 29.5%, the high demand for heating energy correlates with the higher capacity factor during the winter.
Certain onshore wind farms can reach capacity factors of over 60%, for example the 44 MW Eolo plant in Nicaragua had a net generation of 232.132 GWh in 2015, equivalent to a capacity factor of 60.2%, while United States annual capacity factors from 2013 through 2016 range from 32.2% to 34.7%.
Since the capacity factor of a wind turbine measures actual production relative to possible production, it is unrelated to Betz's coefficient of 16/27 59.3%, which limits production vs. energy available in the wind.
Hydroelectric dam
Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam (), officially known as Yangtze River Three Gorges Water Conservancy Project () is a hydroelectric gravity dam that spans the Yangtze River near Sandouping in Yiling District, Yichang, Hubei province, central China, downs ...
in China is, with its nameplate capacity of 22,500 MW, the largest power generating station in the world by installed capacity.
In 2015 it generated 87 TWh, for a capacity factor of:
:
Hoover Dam
The Hoover Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado, Black Canyon of the Colorado River (U.S.), Colorado River, on the border between the U.S. states of Nevada and Arizona. Constructed between 1931 and 1936, d ...
has a nameplate capacity of 2080 MW and an annual generation averaging 4.2 TW·h. (The annual generation has varied between a high of 10.348 TW·h in 1984, and a low of 2.648 TW·h in 1956.).
Taking the average figure for annual generation gives a capacity factor of:
:
Photovoltaic power station
At the low range of capacity factors is thephotovoltaic power station
A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park, solar farm, or solar power plant, is a large-scale grid-connected photovoltaic power system (PV system) designed for the supply of merchant power. They are different from most building ...
, which supplies power to the electricity grid from a large-scale photovoltaic system
A photovoltaic system, also called a PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to abso ...
(PV system).
An inherent limit to its capacity factor comes from its requirement of daylight
Daylight is the combination of all direct and indirect sunlight during the daytime. This includes direct sunlight, diffuse sky radiation, and (often) both of these reflected by Earth and terrestrial objects, like landforms and buildings. Sunlig ...
, preferably with a sun unobstructed by clouds, smoke or smog
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words ''smoke'' and ''fog'' to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odour. The word was then inte ...
, shade from trees and building structures.
Since the amount of sunlight varies both with the time of the day and the seasons of the year, the capacity factor is typically computed on an annual basis.
The amount of available sunlight is mostly determined by the latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
of the installation and the local cloud cover.
The actual production is also influenced by local factors such as dust and ambient temperature, which ideally should be low. As for any power station, the maximum possible power production is the nameplate capacity times the number of hours in a year, while the actual production is the amount of electricity delivered annually to the grid.
For example, Agua Caliente Solar Project, located in Arizona
Arizona is a U.S. state, state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States, sharing the Four Corners region of the western United States with Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. It also borders Nevada to the nort ...
near the 33rd parallel and awarded for its excellence in renewable energy has a nameplate capacity of 290 MW and an actual average annual production of 740 GWh/year.
Its capacity factor is thus:
:.
A significantly lower capacity factor is achieved by Lauingen Energy Park located in Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
, near the 49th parallel. With a nameplate capacity of 25.7 MW and an actual average annual production of 26.98 GWh/year it has a capacity factor of 12.0%.
Determinants of a plant capacity factor
There are several reasons why a plant would have a capacity factor lower than 100%. These include technical constraints, such as operational availability of the plant (known asavailability factor
The availability factor of a power plant is the duration it achieves production of electricity divided by the duration that it was planned to produce electricity. In the field of reliability engineering, ''availability factor'' is known as operat ...
for electricity generators), economic reasons, and availability of an energy resource.
A plant can be out of service or operating at reduced output for part of the time due to equipment failures or routine maintenance.
This accounts for most of the unused capacity of base load power plants. Base load plants usually have low costs per unit of electricity because they are designed for maximum efficiency and are operated continuously at high output.
Geothermal power plants, nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP), also known as a nuclear power station (NPS), nuclear generating station (NGS) or atomic power station (APS) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power st ...
s, coal-fired plants and bioenergy plants that burn solid material are almost always operated as base load plants, as they can be difficult to adjust to suit demand.
A plant can also have its output curtailed or intentionally left idle because the electricity is not needed or because the price of electricity is too low to make production economical.
This accounts for most of the unused capacity of peaking power plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the powe ...
s and load following power plant
A load-following power plant, regarded as producing mid-merit or mid-priced electricity, is a power plant that adjusts its power output as demand for electricity fluctuates throughout the day. Load-following plants are typically in between base l ...
s.
Peaking plants may operate for only a few hours per year or up to several hours per day.
Many other power plants operate only at certain times of the day or year because of variation in loads and electricity prices.
If a plant is only needed during the day, for example, even if it operates at full power output from 8 am to 8 pm every day (12 hours) all year long, it would only have a 50% capacity factor.
Due to low capacity factors, electricity from peaking power plants is relatively expensive because the limited generation has to cover the plant fixed costs.
A third reason is that a plant may not have the fuel available to operate all of the time.
This can apply to fossil generating stations with restricted fuels supplies, but most notably applies to intermittent renewable resources.
Solar PV and wind turbines have a capacity factor limited by the availability of their "fuel", sunshine and wind respectively.
A hydroelectricity plant may have a capacity factor lower than 100% due to restriction or scarcity of water, or its output may be regulated to match the current power need, conserving its stored water for later usage.
Governments differ in their wiliness to accept risks of power outages
A power outage, also called a blackout, a power failure, a power blackout, a power loss, a power cut, or a power out is the complete loss of the electrical power network supply to an end user.
There are many causes of power failures in an el ...
and lack of resilience against natural disasters and military attack on electricity grids. Examples of historical events impacting grid resilience are the 1991 Gulf War air campaign against civilian infrastructure, 2015 Ukraine power grid hack, 2021 Texas power crisis
In February 2021, the state of Texas suffered a major Energy crisis, power crisis, which came about during three severe winter storms sweeping across the United States on February 2021 North American ice storm, February 10–11, February 13� ...
and Russian strikes against Ukrainian infrastructure (2022–present). Low risk tolerance may require electricity grids to be more significantly overbuilt to mitigate the potential costs of electricity grid interruptions and outages, impacting on a technology-by-technology basis the amount of generation curtailment necessary under normal grid conditions.
Other reasons that a power plant may not have a capacity factor of 100% include restrictions or limitations on air permits and limitations on transmission that force the plant to curtail output.
Capacity factor of renewable energy
 For
For renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
sources such as solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
, wind power
Wind power is the use of wind energy to generate useful work. Historically, wind power was used by sails, windmills and windpumps, but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. This article deals only with wind power for electricity ge ...
and hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
, the main reason for reduced capacity factor is generally the availability of the energy source.
The plant may be capable of producing electricity, but its "fuel" (wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heatin ...
, sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
or water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
) may not be available.
A hydroelectric plant's production may also be affected by requirements to keep the water level from getting too high or low and to provide water for fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
downstream.
However, solar, wind and hydroelectric plants do have high availability factor
The availability factor of a power plant is the duration it achieves production of electricity divided by the duration that it was planned to produce electricity. In the field of reliability engineering, ''availability factor'' is known as operat ...
s, so when they have fuel available, they are almost always able to produce electricity.
When hydroelectric plants have water available, they are also useful for load following, because of their high ''dispatchability''. A typical hydroelectric plant's operators can bring it from a stopped condition to full power in just a few minutes.
Wind farm
A wind farm, also called a wind park or wind power plant, is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electricity. Wind farms vary in size from a small number of turbines to several hundred wind turbines covering an exten ...
s are variable, due to the natural variability of the wind.
For a wind farm, the capacity factor is determined by the availability of wind, the swept area of the turbine and the size of the generator.
Transmission line capacity and electricity demand also affect the capacity factor.
Typical capacity factors of current wind farms are between 25 and 45%. In the United Kingdom during the five year period from 2011 to 2019 the annual capacity factor for wind was over 30%.
Solar energy
Solar energy is the radiant energy from the Sun's sunlight, light and heat, which can be harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating) and solar architecture. It is a ...
is variable because of the daily rotation of the earth, seasonal changes, and because of cloud cover.
For example, the Sacramento Municipal Utility District observed a 15% capacity factor in 2005.
However, according to the SolarPACES programme of the International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the global energy sector. The 31 member countries and 13 associatio ...
(IEA), solar power plants designed for solar-only generation are well matched to summer noon peak loads in areas with significant cooling demands, such as Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
or the south-western United States, although in some locations solar PV does not reduce the need for generation of network upgrades given that air conditioner peak demand often occurs in the late afternoon or early evening when solar output is reduced.
SolarPACES states that by using thermal energy storage systems the operating periods of solar thermal power (CSP) stations can be extended to become dispatchable (load following).Thomas R. Mancini and Michael Geyer (2006)Spain Pioneers Grid-Connected Solar-Tower Thermal Power
SolarPACES, OECD/ IEA, p. 3.
Geothermal Geothermal is related to energy and may refer to:
* Geothermal energy, useful energy generated and stored in the Earth
* Geothermal activity, the range of natural phenomena at or near the surface, associated with release of the Earth's internal he ...
has a higher capacity factor than many other power sources, and geothermal resources are generally available all the time.
Capacity factors by energy source
Worldwide
*Nuclear power 88.7% (2006 - 2012 average of US's plants). * Hydroelectricity, worldwide average 44%, range of 10% - 99% depending on water availability (with or without regulation via storage dam). * Wind farms 21-52% (as of 2022). * CSP solar with storage and Natural Gas backup in Spain 63%, California 33%. * Photovoltaic solar in Germany 10%, Arizona 19%, Massachusetts 13.35% (8 year average as of July 2018).United States
According to the US Energy Information Administration (EIA), from 2013 to 2017 the capacity factors of utility-scale generators were as follows: , - ! colspan="8", Non-fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
!! Coal !! colspan="4" , Natural Gas !! colspan="3" , Petroleum Liquids
, -
!Nuclear !! Hydro !!Wind !!Solar PV !!Solar CSP !!Landfill Gas and !!Other Biomass
including Wood !! Geothermal !! !! !! !! !! !! !! !! , - , 89.9% , , 38.9% , , 32.4% , , NA , , NA , , 68.9% , , 56.7% , , 73.6% , , 59.8% , , 48.2% , , 4.9% , , 10.6% , , 6.1% , , 12.1% , , 0.8% , , 2.2% , - , 91.7% , , 37.3% , , 34.0% , , 25.9% , , 19.8% , , 68.9% , , 58.9% , , 74.0% , , 61.1% , , 48.3% , , 5.2% , , 10.4% , , 8.5% , , 12.5% , , 1.1% , , 1.4% , - , 92.3% , , 35.8% , , 32.2% , , 25.8% , , 22.1% , , 68.7% , , 55.3% , , 74.3% , , 54.7% , , 55.9% , , 6.9% , , 11.5% , , 8.9% , , 13.3% , , 1.1% , , 2.2% , - , 92.3% , , 38.2% , , 34.5% , , 25.1% , , 22.2% , , 69.7% , , 55.6% , , 73.9% , , 53.3% , , 55.5% , , 8.3% , , 12.4% , , 9.6% , , 11.5% , , 1.1% , , 2.6% , - , 92.2% , , 43.1% , , 34.6% , , 25.7% , , 21.8% , , 68.0% , , 57.8% , , 74.0% , , 53.7% , , 51.3% , , 6.7% , , 10.5% , , 9.9% , , 13.5% , , 0.9% , , 2.3% , - , 92.6% , , 42.8% , , 37.4% , , 26.1% , , 23.6% , , 73.3% , , 49.3% , , 77.3% , , 54.0% , , 57.6% , , 11.8% , , 13.7% , , NA , , 13.9% , , 2.5% , , NA However, these values often vary significantly by month.
United Kingdom
The following figures were collected by theDepartment of Energy and Climate Change
The Department of Energy and Climate Change (DECC) was a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, department of the government of the United Kingdom created on 3 October 2008, by Prime Minister Gordon Brown to take over some of the ...
on the capacity factors for various types of plants in UK grid:
See also
*Demand factor
In telecommunications, electronics and the electrical power industry, the term demand factor is used to refer to the fractional amount of some quantity being used relative to the maximum amount that could be used by the same system. The demand fac ...
* Intermittent power source
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable ener ...
References
{{Authority control Power station technology