Pillar Of Ashoka on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The pillars of Ashoka are a series of
 Ashoka ascended to the throne in 269 BC inheriting the
Ashoka ascended to the throne in 269 BC inheriting the

 *
*
p.36-40
/ref> * Delhi-Meerut, Delhi ridge,
 There are altogether seven remaining complete capitals, five with lions, one with an elephant and one with a
There are altogether seven remaining complete capitals, five with lions, one with an elephant and one with a  Various foreign influences have been described in the design of these capitals. The animal on top of a lotiform capital reminds of
Various foreign influences have been described in the design of these capitals. The animal on top of a lotiform capital reminds of
p.240
/ref> ;Chronological order Based on stylistic and technical analysis, it is possible to establish a tentative chronological orders for the pillars. The earliest one seems to be the Vaishali pillar, with its stout and short column, the rigid lion and the undecorated square abacus. Next would follow the
/ref> According to Irwin, the A few more possibly Ashokan capitals were also found without their pillars:
*
A few more possibly Ashokan capitals were also found without their pillars:
*
p.19
/ref> to the
p.361
/ref>). It is also known from various ancient sculptures (reliefs from
 The inscriptions on the columns include a fairly standard text. The inscriptions on the columns join other, more numerous, Ashokan inscriptions on natural rock faces to form the body of texts known as the Edicts of Ashoka. These inscriptions were dispersed throughout the areas of modern-day
The inscriptions on the columns include a fairly standard text. The inscriptions on the columns join other, more numerous, Ashokan inscriptions on natural rock faces to form the body of texts known as the Edicts of Ashoka. These inscriptions were dispersed throughout the areas of modern-day
File:Allahabad Kausambi Edict.jpg, Kosambi-Allahabad Schism Edict.
File:Sanchi pillar Ashokan inscription.jpg, Sanchi Schism Edict.
File:Sarnath pillar inscription.jpg, Sarnath Schism Edit.
File:Lumbini - Pillar Edict in Brahmi Script, Lumbini (9241396121).jpg, Rummindei, in
 Asoka's 6 Major Pillar Edicts have been found at Kausambhi (Allahabad), Topra (now Delhi), Meerut (now Delhi), Lauriya-Araraj, Lauriya-Nandangarh, Rampurva (Champaran), and a 7th one on the Delhi-Topra pillar.
These pillar edicts include:
*I Asoka's principle of protection to people
*II Defines dhamma as minimum of sins, many virtues, compassion, liberality, truthfulness and purity
*III Abolishes sins of harshness, cruelty, anger, pride etc.
*IV Deals with duties of government officials
*V List of animals and birds which should not be killed on some days and another list of animals which cannot be killed on any occasion. Describes release of 25 prisoners by Asoka.
*VI Works done by Asoka for Dhamma Policy. He says that all sects desire both self-control and purity of mind.
*VII Testimental edict.
Asoka's 6 Major Pillar Edicts have been found at Kausambhi (Allahabad), Topra (now Delhi), Meerut (now Delhi), Lauriya-Araraj, Lauriya-Nandangarh, Rampurva (Champaran), and a 7th one on the Delhi-Topra pillar.
These pillar edicts include:
*I Asoka's principle of protection to people
*II Defines dhamma as minimum of sins, many virtues, compassion, liberality, truthfulness and purity
*III Abolishes sins of harshness, cruelty, anger, pride etc.
*IV Deals with duties of government officials
*V List of animals and birds which should not be killed on some days and another list of animals which cannot be killed on any occasion. Describes release of 25 prisoners by Asoka.
*VI Works done by Asoka for Dhamma Policy. He says that all sects desire both self-control and purity of mind.
*VII Testimental edict.
File:Delhi-Topra I II III.jpg, Major Pillar Edicts I, II, III (Delhi-Topra)
File:Delhi-Topra IV.jpg, Major Pillar Edicts IV (Delhi-Topra)
File:Delhi-Topra VI-VII.jpg, Major Pillar Edicts V-VII (Delhi-Topra)
File:Delhi-Topra VII (second part).jpg, Major Pillar Edicts VII, second part (Delhi-Topra)
 The pillar at Sanchi also has a similar but damaged four-lion capital. There are two pillars at Rampurva, one crowned with a bull and the other with a lion.
The pillar at Sanchi also has a similar but damaged four-lion capital. There are two pillars at Rampurva, one crowned with a bull and the other with a lion.
 A number of the pillars were thrown down by either natural causes or iconoclasts, and gradually rediscovered. One was noticed in the 16th century by the English traveller
A number of the pillars were thrown down by either natural causes or iconoclasts, and gradually rediscovered. One was noticed in the 16th century by the English traveller
p.570ff
/ref>Buddhist Architecture, Huu Phuoc L
p.240
/ref> This purely Buddhist monument to the Buddha is a thick slab of polished grey
p.19
Public Domain text The sculpted decorations on the Diamond Throne clearly echo the decorations found on the Pillars of Ashoka. The Diamond Throne has a decorative band made of
p.4ff
Public Domain text
google books
* Boardman, John (1998), "Reflections on the Origins of Indian Stone Architecture", ''Bulletin of the Asia Institute'', pp. 15–19, 1998, New Series, Vol. 12, (''Alexander's Legacy in the East: Studies in Honor of Paul Bernard''), p. 13-22
JSTOR
*"Companion": Brown, Rebecca M., Hutton, Deborah S., eds., ''A Companion to Asian Art and Architecture'', Volume 3 of Blackwell companions to art history, 2011, John Wiley & Sons, 2011, , 9781444396324
google books
*Harle, J.C., ''The Art and Architecture of the Indian Subcontinent'', 2nd edn. 1994, Yale University Press Pelican History of Art, *Krishnaswamy, C.S., Sahib, Rao, and Ghosh, Amalananda, "A Note on the Allahabad Pillar of Aśoka", ''The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland'', No. 4 (Oct., 1935), pp. 697–706,
JSTOR
*Falk, H. ''Asokan Sites and Artefacts: a A Source-book with Bibliography'', 2006, ''Volume 18 of Monographien zur indischen Archäologie, Kunst und Philologie'', Von Zabern, ISSN 0170-8864
Archaeological Survey of India
British Museum, collections online
- See "lioncapital" for pictures of the original "Lion Capital of Ashoka" preserved at the
monolithic
A monolith is a monument or natural feature consisting of a single massive stone or rock.
Monolith or monolithic may also refer to:
Architecture
* Monolithic architecture, a style of construction in which a building is carved, cast or excavated f ...
columns dispersed throughout the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, erected—or at least inscribed with edicts
An edict is a decree or announcement of a law, often associated with monarchies, but it can be under any official authority. Synonyms include "dictum" and "pronouncement". ''Edict'' derives from the Latin edictum.
Notable edicts
* Telepinu ...
—by the 3rd Mauryan
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
Emperor Ashoka the Great
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
, who reigned from to 232 BC. Ashoka used the expression ''Dhaṃma thaṃbhā'' (Dharma
Dharma (; , ) is a key concept in various Indian religions. The term ''dharma'' does not have a single, clear Untranslatability, translation and conveys a multifaceted idea. Etymologically, it comes from the Sanskrit ''dhr-'', meaning ''to hold ...
stambha
A stambha () is a pillar or a column employed in Indian architecture. A stambha sometimes bears inscriptions and religious emblems.
Religion
In Hindu mythology, a stambha is believed to be a cosmic column that functions as a bond, joining h ...
), i.e. "pillars of the Dharma
Dharma (; , ) is a key concept in various Indian religions. The term ''dharma'' does not have a single, clear Untranslatability, translation and conveys a multifaceted idea. Etymologically, it comes from the Sanskrit ''dhr-'', meaning ''to hold ...
" to describe his own pillars. These pillars constitute important monuments of the architecture of India
Indian architecture is rooted in the History of India, history, Culture of India, culture, and Indian religions, religion of India. Among several architectural styles and traditions, the best-known include the many varieties of Hindu temple a ...
, most of them exhibiting the characteristic Mauryan polish
Mauryan polish describes one of the frequent characteristics of architecture and sculptures of the Maurya Empire in India (325 to 185 BCE), which gives a very smooth and shiny surface to the stone material, generally of sandstone or granite.The roo ...
. Twenty of the pillars erected by Ashoka still survive, including those with inscriptions of his edicts. Only a few with animal capitals survive of which seven complete specimens are known. Two pillars were relocated by Firuz Shah Tughlaq
Firuz Shah Tughlaq (1309 – 20 September 1388), also known as Firuz III, was Sultan of Delhi from 1351 until his death in 1388. He succeeded his cousin Muhammad bin Tughlaq following the latter's death at Thatta, Sindh. His father was ...
to Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
. Several pillars were relocated later by Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
rulers, the animal capitals being removed.Krishnaswamy, 697-698 Averaging between in height, and weighing up to 50 tons each, the pillars were dragged, sometimes hundreds of miles, to where they were erected.
The pillars of Ashoka are among the earliest known stone sculptural remains from India. Only another pillar fragment, the Pataliputra capital
The Pataliputra capital is a monumental rectangular capital with volutes and Classical Greek designs, that was discovered in the palace ruins of the ancient Mauryan Empire capital city of Pataliputra (modern Patna, Eastern India). It is dated t ...
, is possibly from a slightly earlier date. It is thought that before the 3rd century BC, wood rather than stone was used as the main material for Indian architectural constructions, and that stone may have been adopted following interaction with the Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
and the Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
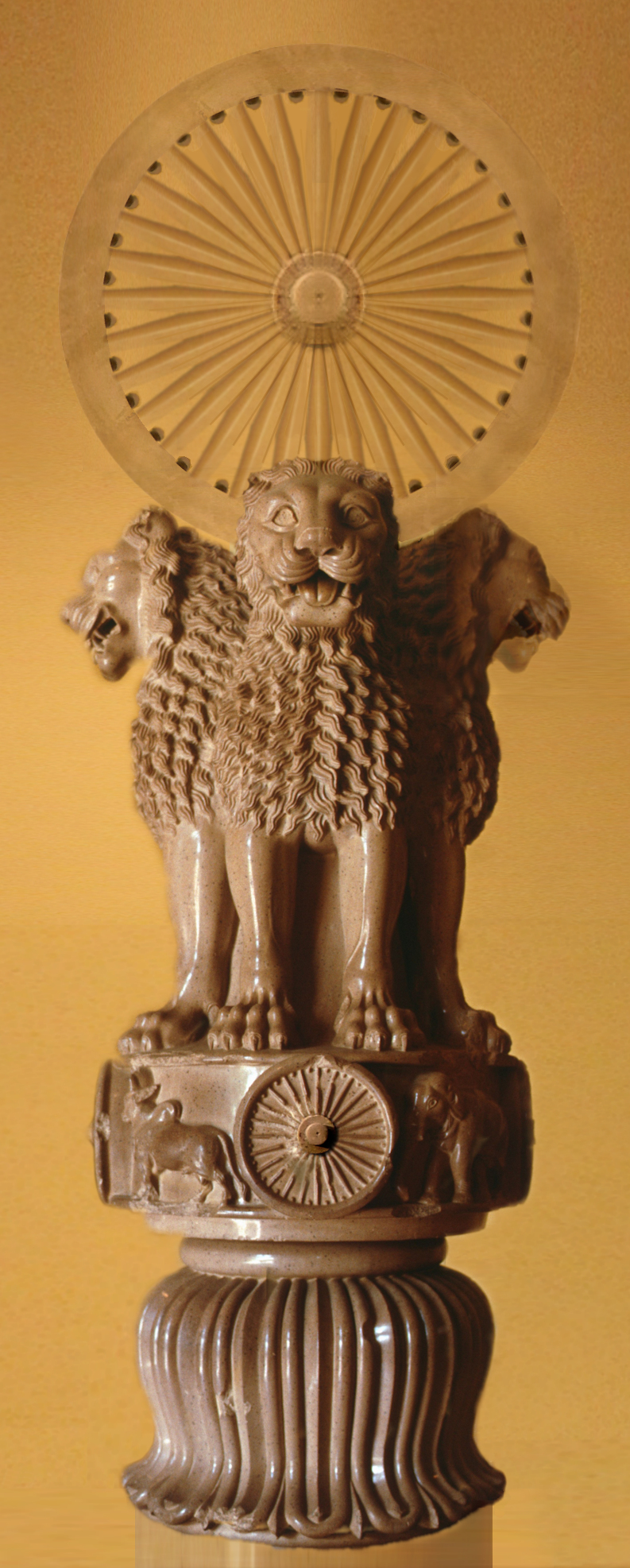
. A graphic representation of the Lion Capital of Ashoka
The Lion Capital of Ashoka is the capital, or head, of a column erected by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka in Sarnath, India, . Its crowning features are four life-sized lions set back to back on a drum-shaped abacus. The side of the abacus is ad ...
from the column there was adopted as the official State Emblem of India
The State Emblem of India is the national emblem of the Republic of India and is used by the union government, many state governments, and other government agencies. The emblem is an adaptation of the Lion Capital of Ashoka, an ancient scul ...
in 1950.
All the pillars of Ashoka were built at Buddhist monasteries, many important sites from the life of the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist legends, he was ...
and places of pilgrimage. Some of the columns carry inscriptions addressed to the monks and nuns. Some were erected to commemorate visits by Ashoka. Major pillars are present in the Indian State
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
s of Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
, Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (; ; ) is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and the largest city is Indore, Indore. Other major cities includes Gwalior, Jabalpur, and Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar. Madhya Pradesh is the List of states and union te ...
and some parts of Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
.
Ashoka and Buddhism
 Ashoka ascended to the throne in 269 BC inheriting the
Ashoka ascended to the throne in 269 BC inheriting the Mauryan empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sourc ...
founded by his grandfather Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (Sanskrit: elp:IPA/Sanskrit, t̪͡ɕɐn̪d̪ɾɐgupt̪ɐ mɐʊɾjɐ (reigned 320 BCE – c. 298 BCE) was the founder and the first emperor of the Maurya Empire, based in Magadha (present-day Bihar) in the Indian ...
. Ashoka was reputedly a tyrant at the outset of his reign. Eight years after his accession he campaigned in Kalinga where in his own words, "a hundred and fifty thousand people were deported, a hundred thousand were killed and as many as that perished..." As he explains in his edicts, after this event Ashoka converted to Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
in remorse for the loss of life. Buddhism became a state religion and with Ashoka's support it spread rapidly. The inscriptions on the pillars set out edicts about morality based on Buddhist tenets.Time Life Lost Civilizations series: Ancient India: Land Of Mystery (1994) p. 84-85,94-97Oliphant, Margaret "The Atlas Of The Ancient World" 1992 p. 156-7
They were added in the 3rd century BC.
Construction
The traditional idea that all were originally quarried atChunar
Chunar is a city located in Mirzapur district of Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is nearby Mirzapur city. The railway tracks passing through Chunar Junction railway station leads to major destinations of India, including Howrah, Delhi, Ta ...
, just south of Varanasi
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tradition of I ...
and taken to their sites, before or after carving, "can no longer be confidently asserted", and instead it seems that the columns were carved in two types of stone. Some were of the spotted red and white sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
from the region of Mathura, the others of buff-colored fine grained hard sandstone usually with small black spots quarried in the Chunar near Varanasi. The uniformity of style in the pillar capitals suggests that they were all sculpted by craftsmen from the same region. It would therefore seem that stone was transported from Mathura and Chunar to the various sites where the pillars have been found, and there was cut and carved by craftsmen.Thapar, Romila (2001). '' and the Decline of the Mauryan'', New Delhi: Oxford University Press, , pp.267-70
The pillars have four component parts in two pieces: the three sections of the capitals are made in a single piece, often of a different stone to that of the monolith
A monolith is a geological feature consisting of a single massive stone or rock, such as some mountains. Erosion usually exposes the geological formations, which are often made of very hard and solid igneous or metamorphic rock. Some monolit ...
ic shaft to which they are attached by a large metal dowel
The dowel is a cylindrical shape made of wood, plastic, or metal. In its original manufactured form, a dowel is long and called a ''dowel rod'', which are often cut into shorter ''dowel pins''. Dowels are commonly used as structural reinforceme ...
. The shafts are always plain and smooth, circular in cross-section, slightly tapering upwards and always chiselled out of a single piece of stone. There is no distinct base at the bottom of the shaft. The lower parts of the capitals have the shape and appearance of a gently arched bell formed of lotus petals. The abaci are of two types: square and plain and circular and decorated and these are of different proportions. The crowning animals are masterpieces of Mauryan art
Mauryan art is art produced during the period of the Mauryan Empire, the first empire to rule over most of the Indian subcontinent, between 322 and 185 BCE. It represented an important transition in Indian art from the use of wood to stone. It ...
, shown either seated or standing, always in the round and chiselled as a single piece with the abaci. Presumably all or most of the other columns that now lack them once had capitals and animals. They are also used to commemorate the events of the Buddha's life.
Currently seven animal sculptures from Ashoka pillars survive. These form "the first important group of Indian stone sculpture", though it is thought they derive from an existing tradition of wooden columns topped by animal sculptures in copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, none of which have survived. It is also possible that some of the stone pillars predate Ashoka's reign.Boardman (1998), 15
Origin
Western origin
There has been much discussion of the extent of influence fromAchaemenid Persia
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larges ...
, where the column capitals supporting the roofs at Persepolis
Persepolis (; ; ) was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire (). It is situated in the plains of Marvdasht, encircled by the southern Zagros mountains, Fars province of Iran. It is one of the key Iranian cultural heritage sites and ...
have similarities, and the "rather cold, hieratic style" of the Sarnath Lion Capital of Ashoka
The Lion Capital of Ashoka is the capital, or head, of a column erected by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka in Sarnath, India, . Its crowning features are four life-sized lions set back to back on a drum-shaped abacus. The side of the abacus is ad ...
especially shows "obvious Achaemenid and Sargonid influence". India and the Achaemenid Empire had been in close contact since the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley
Around 535 BCE, the Persian king Cyrus the Great initiated a protracted campaign to absorb parts of India into his nascent Achaemenid Empire. In this initial incursion, the Persian army annexed a large region to the west of the Indus River, con ...
, from c. 500 to 330 BC.
Hellenistic influence has also been suggested. In particular the abaci of some of the pillars (especially the Rampurva bull, the Sankissa elephant and the Allahabad pillar capital) use bands of motifs, like the bead and reel
Bead and reel is an architectural motif, usually found in sculptures, moldings and numismatics. It consists in a thin line where beadlike elements alternate with cylindrical ones. It is found throughout the modern Western world in architectural det ...
pattern, the ovolo
Ovolo is an Italian language, Italian word that means "little egg". The ovolo or echinus is a convex molding (decorative), decorative molding profile used in Ornament (architecture), architectural ornamentation. Its profile is a quarter to a half ...
, the flame palmettes, lotuses, which likely originated from Greek and Near-Eastern arts. Such examples can also be seen in the remains of the Mauryan capital city of Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
.
It has also been suggested that 6th century Greek columns such as the Sphinx of Naxos
A sphinx ( ; , ; or sphinges ) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of an eagle.
In Greek tradition, the sphinx is a treacherous and merciless being with the head of a woman, the haunches of a l ...
, a 12.5m Ionic column crowned by an animal in the religious centre of Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
, may have been an inspiration for the pillars of Ashoka. Many similar columns crowned by sphinxes were discovered in ancient Greece, as in Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas rive ...
, Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
or Spata
Spata () is a town east of downtown Athens, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Spata-Artemida, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit (officially named Spata-Loutsa) has an a ...
, and some were used as funerary steles. The Greek sphinx
A sphinx ( ; , ; or sphinges ) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of an eagle.
In Culture of Greece, Greek tradition, the sphinx is a treacherous and merciless being with the head of a woman, th ...
, a lion with the face of a human female, was considered as having ferocious strength, and was thought of as a guardian, often flanking the entrances to temples or royal tombs.
Indian origin
Some scholars such as John Irwin emphasized a reassessment from popular belief of Persian or Greek origin of Ashokan pillars. He makes the argument that Ashokan pillars representDhvaja
Dhvaja (; ) is the Sanskrit term for a banner or a flag. Flags are featured in the iconography, mythology, and architecture of Indian religions such as Buddhism, Hinduism, and Jainism. They are one of the ashtamangala, the eight auspicious embl ...
or standard which Indian soldiers carried with them during battle and it was believed that the destruction of the enemy's dhvaja brought misfortune to their opponents. A relief of Bharhut stupa railing portrays a queenly personage on horseback carrying a ''Garudadhvaja.'' Heliodorus pillar
The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BCE in central India in Besnagar (Vidisha), Madhya Pradesh. The pillar is commonly named after Heliodorus (identified by him as a Garuda-standard), who was an ambassador of the In ...
has been called Garudadhvaja, literally Garuda-standard, the pillar dated to 2nd century BC is perhaps the earliest recorded stone pillar which has been declared a dhvaja.
Ashokan edicts themselves state that his words should be carved on any stone slab or pillars available indicating that the tradition of carving stone pillars was present before the period of Ashoka.
John Irwin also highlights the fact that carvings on pillars such as Allahabad pillar
The Allahabad Pillar is a ''stambha'', containing one of the pillar edicts of Ashoka, erected by Ashoka, emperor of the Maurya dynasty, who reigned in the 3rd century BCE. While it is one of the few extant pillars that carry Ashokan edicts, it ...
was done when it had already been erected indicating its pre Ashokan origins.
Stylistic argument
Though influence from the west is generally accepted, especially thePersian column
Persian columns or Persepolitan columns are the distinctive form of column developed in the Achaemenid architecture of ancient Persia, probably beginning shortly before 500 BCE. They are mainly known from Persepolis, where the massive main columns ...
s of Achaemenid Persia, there are a number of differences between these and the pillars. Persian columns are built in segments whereas Ashokan pillars are monolith
A monolith is a geological feature consisting of a single massive stone or rock, such as some mountains. Erosion usually exposes the geological formations, which are often made of very hard and solid igneous or metamorphic rock. Some monolit ...
s, like some much later Roman columns. Most of the Persian pillars have a fluted shaft while the Mauryan pillars are smooth, and Persian pillars serve as supporting structures whereas Ashokan pillars are individual free-standing monuments. There are also other differences in the decoration. Indian historian Upinder Singh
Upinder Singh (born 22 June 1959) is an Indian historian who is a professor of History and Dean of Faculty at Ashoka University. She is the former head of the History Department at the University of Delhi. She is also the recipient of the ina ...
comments on some of the differences and similarities, writing that "If the Ashokan pillars cannot in their entirety be attributed to Persian influence, they must have had an undocumented prehistory within the subcontinent, perhaps a tradition of wooden carving. But the transition from stone to wood was made in one magnificent leap, no doubt spurred by the imperial tastes and ambitions of the Maurya emperors."
Whatever the cultural and artistic borrowings from the west, the pillars of Ashoka, together with much of Mauryan art
Mauryan art is art produced during the period of the Mauryan Empire, the first empire to rule over most of the Indian subcontinent, between 322 and 185 BCE. It represented an important transition in Indian art from the use of wood to stone. It ...
and architectural prowesses such as the city of Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
or the Barabar Caves
The Barabar Hill Caves are the oldest surviving rock-cut caves in India, dating from the Maurya Empire (322–185 BCE), some with Ashokan inscriptions, located in the Makhdumpur region of Jehanabad district, Bihar, India, north of Gaya.
The ...
, remain outstanding in their achievements, and often compare favourably with the rest of the world at that time. Commenting on Mauryan sculpture, John Marshall
John Marshall (September 24, 1755July 6, 1835) was an American statesman, jurist, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fourth chief justice of the United States from 1801 until his death in 1835. He remai ...
once wrote about the "extraordinary precision and accuracy which characterizes all Mauryan works, and which has never, we venture to say, been surpassed even by the finest workmanship on Athenian buildings".
Complete list of the pillars
Five of the pillars of Ashoka, two atRampurva
The Rampurva capitals are the capitals of a pair of Ashoka Pillars discovered in by A. C. L. Carlleyle. The archaeological site is called Rampurva, and is located in the West Champaran district of the Indian state of Bihar, situated very cl ...
, one each at Vaishali, Lauriya Araraj
Lauriya Areraj, also Lauriya Areraj, is a location name in the East Champaran District of the State of Bihar in India.
It is known for the presence of one of the Pillars of Ashoka. The pillar capital is missing, but the pillar bear six Edicts ...
and Lauria Nandangarh
Lauria Nandangarh, also Lauriya Navandgarh, is a city or town about 14 km from Narkatiaganj (or Shikarpur) and 28 km from Bettiah in West Champaran district of Bihar state in northern India. It is situated near the banks of the B ...
possibly marked the course of the ancient Royal highway from Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
to Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
. Several pillars were relocated by later Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
rulers, the animal capitals being removed.
The two Chinese medieval pilgrim accounts record sightings of several columns that have now vanished: Faxian
Faxian (337–), formerly romanization of Chinese, romanized as Fa-hien and Fa-hsien, was a Han Chinese, Chinese Chinese Buddhism, Buddhist bhikkhu, monk and translator who traveled on foot from Eastern Jin dynasty, Jin China to medieval India t ...
records six and Xuanzang
Xuanzang (; ; 6 April 6025 February 664), born Chen Hui or Chen Yi (), also known by his Sanskrit Dharma name Mokṣadeva, was a 7th-century Chinese Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, traveller, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making ...
fifteen, of which only five at most can be identified with surviving pillars. All surviving pillars, listed with any crowning animal sculptures and the edicts inscribed, are as follows:Mahajan V.D. (1960, reprint 2007). ''Ancient India'', S.Chand & Company, New Delhi, , pp.350-3
Complete standing pillars, or pillars with Ashokan inscriptions
 *
*Delhi-Topra pillar
The Delhi-Topra pillar is one of the pillars of Ashoka, inscribed with the moral edicts promulgated by Ashoka, the Mauryan Emperor who ruled in the Indian subcontinent during the 3rd century BCE. The Edicts of Ashoka were either carved on in-sit ...
, in the fortress of Feroz Shah Kotla
The Feroz Shah Kotla or Kotla ("fortress", "citadel") was a fortress built circa 1354 by Feroz Shah Tughlaq to house his version of Delhi called Firozabad.
A pristine polished sandstone Topra Ashokan pillar from the 3rd century BC rises from ...
, Delhi (Pillar Edicts I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII); moved in AD 1356 from Topra Kalan
Topra, combined name for the larger Topra Kalan and adjacent smaller Topra Khurd, is a Mauryan Empire-era village in Yamunanagar district of Haryana state in India.
It lies 14 km west of Yamunanagar, 14 km from Radaur and 90 ...
in Yamunanagar district
Yamunanagar district is one of the 22 districts of the Indian state of Haryana. The district came into existence on 1November 1989 and occupies an area of . Yamunanagar town is the district headquarters.
Yamunanagar's average rainfall in Mons ...
of Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
to Delhi by Firuz Shah Tughluq.''Buddhist Architecture'', Huu Phuoc Le, Grafikol, 201p.36-40
/ref> * Delhi-Meerut, Delhi ridge,
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
(Pillar Edicts I, II, III, IV, V, VI); moved from Meerut
Meerut (, ISO 15919, ISO: ''Mēraṭh'') is a city in the western region of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. Located in the Meerut district, it is northeast of the national capital, New Delhi, and is ...
to Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
by Firuz Shah Tughluq in 1356.
*Nigali Sagar
Nigali Sagar (also called Nigliva, Nigali Sagar pillar, Nighihawa pillar, Nigliva pillar, or Araurakot pillar) is an archaeological site in Nepal containing the remains of a pillar of Ashoka. The site is located in Nigalihawa, about 20 kilometer ...
(or Nigliva, Nigalihawa), near Lumbini
Lumbinī (, "the lovely") is a Buddhist pilgrimage site in the Rupandehi District of Lumbini Province in Nepal. The Buddhist commentaries state that Maya Devi gave birth to Siddhartha Gautama in Lumbini around 624 BCE. Gautama is bel ...
, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
. Pillar missing capital, one Ashoka edict. Erected in the 20th regnal year of Ashoka ().
*Rupandehi
Rupandehi District (; ), a part of Lumbini Province, is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal and covers an area of . The district headquarter is Bhairahawa. As per the national census 2011, the population of Rupandehi was 880,196.
Etymol ...
, near Lumbini
Lumbinī (, "the lovely") is a Buddhist pilgrimage site in the Rupandehi District of Lumbini Province in Nepal. The Buddhist commentaries state that Maya Devi gave birth to Siddhartha Gautama in Lumbini around 624 BCE. Gautama is bel ...
, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
. Also erected in the 20th regnal year of Ashoka (), to commemorate Ashoka's pilgrimage to Lumbini
Lumbinī (, "the lovely") is a Buddhist pilgrimage site in the Rupandehi District of Lumbini Province in Nepal. The Buddhist commentaries state that Maya Devi gave birth to Siddhartha Gautama in Lumbini around 624 BCE. Gautama is bel ...
. Capital missing, but was apparently a horse.
*Allahabad pillar
The Allahabad Pillar is a ''stambha'', containing one of the pillar edicts of Ashoka, erected by Ashoka, emperor of the Maurya dynasty, who reigned in the 3rd century BCE. While it is one of the few extant pillars that carry Ashokan edicts, it ...
, Uttar Pradesh (originally located at Kausambi
Kosambi (Pali) or Kaushambi (Sanskrit) was an ancient city in India, characterized by its importance as a trading center along the Ganges Plain and its status as the capital of the Vatsa Kingdom, one of the sixteen mahajanapadas. It was locat ...
and probably moved to Allahabad by Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
; Pillar Edicts I-VI, Queen's Edict, Schism Edict).
*Rampurva
The Rampurva capitals are the capitals of a pair of Ashoka Pillars discovered in by A. C. L. Carlleyle. The archaeological site is called Rampurva, and is located in the West Champaran district of the Indian state of Bihar, situated very cl ...
, Champaran
Champaran is a region in Bihar, India. It is now divided into two districts: East Champaran and West Champaran.
History
Champaran is identified with the ''Champāraṇya'' mentioned in the Bheraghat inscription as a place "devastated" b ...
, Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
. Two columns: a lion with Pillar Edicts I, II, III, IV, V, VI; a bull without inscriptions. The abacus
An abacus ( abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a hand-operated calculating tool which was used from ancient times in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, until the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. A ...
of the bull capital features honeysuckle
Honeysuckles are arching shrubs or Vine#Twining vines, twining vines in the genus ''Lonicera'' () of the family Caprifoliaceae. The genus includes 158 species native to northern latitudes in North America, Eurasia, and North Africa. Widely kno ...
and palmette
The palmette is a motif in decorative art which, in its most characteristic expression, resembles the fan-shaped leaves of a palm tree. It has a far-reaching history, originating in ancient Egypt with a subsequent development through the art o ...
designs derived from Greek designs.
*Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
, near Bhopal
Bhopal (; ISO 15919, ISO: Bhōpāl, ) is the capital (political), capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes,'' due to ...
, Madhya Pradesh, four lions, Schism Edict.
*Sarnath
Sarnath (also known as Deer Park, ''Sarangnath'', ''Isipatana Deer Park'', ''Rishipattana'', ''Migadaya'', or ''Mrigadava'')Gabe Hiemstra, "Buddha Chronicle 24: Kassapa Buddhavaṃsa". ''Wisdom Library'', 14 September 2019. is a town nort ...
, near Varanasi
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tradition of I ...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
, four lions, Pillar Inscription, Schism Edict. This is the famous "Lion Capital of Ashoka
The Lion Capital of Ashoka is the capital, or head, of a column erected by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka in Sarnath, India, . Its crowning features are four life-sized lions set back to back on a drum-shaped abacus. The side of the abacus is ad ...
" used in the national emblem of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
.
* Lauriya-Nandangarth, Champaran, Bihar, single lion, Pillar Edicts I, II, III, IV, V, VI.
*Lauriya Araraj
Lauriya Areraj, also Lauriya Areraj, is a location name in the East Champaran District of the State of Bihar in India.
It is known for the presence of one of the Pillars of Ashoka. The pillar capital is missing, but the pillar bear six Edicts ...
, Champaran, Bihar (Pillar Edicts I, II, III, IV, V, VI).
* Vaishali, Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
, single lion, with no inscription.
The Amaravati
Amaravati ( , Telugu language, Telugu: ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located in Guntur district on the right bank of the Krishna River, southwest of Vijayawada. The city derives its name from the nearby his ...
pillar fragment is rather problematic. It consists of only six lines in Brahmi
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or ...
which are hardly decipherable. Only the word ''vijaya'' (victory) can be made out, arguably a word also used by Ashoka. Sircar Sircar is the surname of:
* Birendranath Sircar (1901–1980), Indian film producer and the founder of New Theatres, Calcutta
* Dineshchandra Sircar (1907–1985), Indian epigraphist, historian, numismatist and folklorist
* Joydeep Sircar (born 194 ...
, who provides a detailed study, considers it as probably belonging to an Ashokan pillar.
Pillars without Ashokan inscriptions
There are also several known fragments of Ashokan pillars, without recovered Ashokan inscriptions, such as the pillars inBodh Gaya
Bodh Gayā is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple complex, situated in the Gaya district in the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Bihar. It is famous for being the place where Gautam ...
, Kausambi
Kosambi (Pali) or Kaushambi (Sanskrit) was an ancient city in India, characterized by its importance as a trading center along the Ganges Plain and its status as the capital of the Vatsa Kingdom, one of the sixteen mahajanapadas. It was locat ...
, Gotihawa
Gotihawa (formerly called Gutivā in Western sources) is a village development committee located about southeast of Kapilavastu, in Kapilvastu District, in the Lumbini Zone of southern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a popula ...
, Prahladpur (now in the Government Sanskrit College, Varanasi), Fatehabad, Bhopal
Bhopal (; ISO 15919, ISO: Bhōpāl, ) is the capital (political), capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes,'' due to ...
, Sadagarli, Udaigiri-Vidisha, Kushinagar
Kushinagar (Pali: ; Sanskrit: ) is a town in the Kushinagar district in Uttar Pradesh, India, east of Gorakhpur on National Highway 27, Kushinagar is a Buddhist pilgrimage site, where Buddhists believe Gautama Buddha died.
Etymology
Acc ...
, Arrah
Arrah (also transliterated as Ara) is a city and a municipal corporation in Bhojpur district, India, Bhojpur district (formerly known as Shahabad district) in the Indian state of Bihar. It is the headquarters of Bhojpur district, India, Bhojpur ...
( Masarh) Basti, Bhikana Pahari, Bulandi Bagh (Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
), Sandalpu and a few others, as well as a broken pillar in Bhairon ("Lat Bhairo" in Benares
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges, Ganges river in North India, northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hinduism, Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city ...
) which was destroyed to a stump during riots in 1809.Buddhist Architecture, Le Huu Phuoc, Grafikol 2009, p.40 The Chinese monks Fa-Hsien and Hsuantsang also reported pillars in Kushinagar
Kushinagar (Pali: ; Sanskrit: ) is a town in the Kushinagar district in Uttar Pradesh, India, east of Gorakhpur on National Highway 27, Kushinagar is a Buddhist pilgrimage site, where Buddhists believe Gautama Buddha died.
Etymology
Acc ...
, the Jetavana
Jetavana () was one of the most famous of the Buddhist monasteries or viharas in India (present-day Uttar Pradesh). It was the second vihara donated to Gautama Buddha after the Venuvana in Rajgir. The monastery was given to him by his chi ...
monastery in Sravasti
Shravasti (, ; ) is a town in Shravasti district in Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It was the capital of the ancient Indian kingdom of Kosala which was ruled by Lava and the place where the Buddha lived most after his enlightenment. It is ne ...
, Rajagriha
Rajgir, old name Rajagriha, meaning "The City of Kings," is an ancient city and university town in the Nalanda district of Bihar, India. It was the capital of the Haryanka dynasty, the Pradyota dynasty, the Brihadratha dynasty, the Mauryan Em ...
and Mahasala, which have not been recovered to this day.
The capitals (Top Pieces)
 There are altogether seven remaining complete capitals, five with lions, one with an elephant and one with a
There are altogether seven remaining complete capitals, five with lions, one with an elephant and one with a zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus''), also known as indicine cattle and humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of Bos taurus, domestic cattle originating in South Asia. Zebu, like many Sanga cattle breeds, differs from taurine cattle by a fatty hump ...
bull. One of them, the four lions of Sarnath
Sarnath (also known as Deer Park, ''Sarangnath'', ''Isipatana Deer Park'', ''Rishipattana'', ''Migadaya'', or ''Mrigadava'')Gabe Hiemstra, "Buddha Chronicle 24: Kassapa Buddhavaṃsa". ''Wisdom Library'', 14 September 2019. is a town nort ...
, has become the State Emblem of India
The State Emblem of India is the national emblem of the Republic of India and is used by the union government, many state governments, and other government agencies. The emblem is an adaptation of the Lion Capital of Ashoka, an ancient scul ...
. The animal capitals are composed of a lotiform base, with an abacus
An abacus ( abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a hand-operated calculating tool which was used from ancient times in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, until the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. A ...
decorated with floral, symbolic or animal designs, topped by the realistic depiction of an animal, thought to each represent a traditional directions in India.
 Various foreign influences have been described in the design of these capitals. The animal on top of a lotiform capital reminds of
Various foreign influences have been described in the design of these capitals. The animal on top of a lotiform capital reminds of Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the large ...
column shapes. The abacus also often seems to display some influence of Greek art: in the case of the Rampurva
The Rampurva capitals are the capitals of a pair of Ashoka Pillars discovered in by A. C. L. Carlleyle. The archaeological site is called Rampurva, and is located in the West Champaran district of the Indian state of Bihar, situated very cl ...
bull or the Sankassa
Sankissa (also ''Sankasia'', ''Sankassa'' and ''Sankasya'') is an ancient city in India renown for the descent of Gautama Buddha from the Tushita heavens where he taught his mother before landing at Sankissa. Considered among the eight great ...
elephant, it is composed of honeysuckles alternated with stylized palmette
The palmette is a motif in decorative art which, in its most characteristic expression, resembles the fan-shaped leaves of a palm tree. It has a far-reaching history, originating in ancient Egypt with a subsequent development through the art o ...
s and small rosettes. A similar kind of design can be seen in the frieze of the lost capital of the Allahabad pillar
The Allahabad Pillar is a ''stambha'', containing one of the pillar edicts of Ashoka, erected by Ashoka, emperor of the Maurya dynasty, who reigned in the 3rd century BCE. While it is one of the few extant pillars that carry Ashokan edicts, it ...
. These designs likely originated in Greek and Near-Eastern arts. They would probably have come from the neighboring Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
, and specifically from a Hellenistic city such as Ai-Khanoum
Ai-Khanoum (, meaning 'Lady Moon'; ) is the archaeological site of a Hellenistic city in Takhar Province, Afghanistan. The city, whose original name is unknown, was likely founded by an early ruler of the Seleucid Empire and served as a mili ...
, located at the doorstep of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. Most of these designs and motifs can also be seen in the Pataliputra capital
The Pataliputra capital is a monumental rectangular capital with volutes and Classical Greek designs, that was discovered in the palace ruins of the ancient Mauryan Empire capital city of Pataliputra (modern Patna, Eastern India). It is dated t ...
.
The Diamond throne
The Vajrasana (; ''diamond throne''), or Enlightenment Throne of the Buddha, is an ancient stone slab located under the Bodhi tree, directly beside the Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya. It is considered as bodhimanda ('; ''seat'' or ''platform ...
of Bodh Gaya
Bodh Gayā is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple complex, situated in the Gaya district in the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Bihar. It is famous for being the place where Gautam ...
is another example of Ashokan architecture circa 260 BC, and displays a band of carvings with palmette
The palmette is a motif in decorative art which, in its most characteristic expression, resembles the fan-shaped leaves of a palm tree. It has a far-reaching history, originating in ancient Egypt with a subsequent development through the art o ...
s and geese
A goose (: geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera '' Anser'' (grey geese and white geese) and ''Branta'' (black geese). Some members of the Tadorninae subfamily (e.g., Egyp ...
, similar to those found on several of the Pillars of Ashoka.Buddhist Architecture, Huu Phuoc Le, Grafikol, 201p.240
/ref> ;Chronological order Based on stylistic and technical analysis, it is possible to establish a tentative chronological orders for the pillars. The earliest one seems to be the Vaishali pillar, with its stout and short column, the rigid lion and the undecorated square abacus. Next would follow the
Sankissa
Sankissa (also ''Sankasia'', ''Sankassa'' and ''Sankasya'') is an ancient city in India renown for the descent of Gautama Buddha from the Tushita heavens where he taught his mother before landing at Sankissa. Considered among the eight great p ...
elephant and the Rampurva
The Rampurva capitals are the capitals of a pair of Ashoka Pillars discovered in by A. C. L. Carlleyle. The archaeological site is called Rampurva, and is located in the West Champaran district of the Indian state of Bihar, situated very cl ...
bull, also not yet benefiting from Mauryan polish
Mauryan polish describes one of the frequent characteristics of architecture and sculptures of the Maurya Empire in India (325 to 185 BCE), which gives a very smooth and shiny surface to the stone material, generally of sandstone or granite.The roo ...
, and using a Hellenistic abacus of lotus and palmette
The palmette is a motif in decorative art which, in its most characteristic expression, resembles the fan-shaped leaves of a palm tree. It has a far-reaching history, originating in ancient Egypt with a subsequent development through the art o ...
s for decoration. The abacus would then adopt the Hamsa
The ''hamsa'' (, referring to images of 'the five fingers of the hand'),Zenner, 1988p. 284World Institute for Advanced Phenomenological Research and Learning (Belmont, Estados Unidos), 1991p. 219Drazin, 2009p. 268 also known as the hand of Fa ...
goose as an animal decorative symbol, in Lauria Nandangarh
Lauria Nandangarh, also Lauriya Navandgarh, is a city or town about 14 km from Narkatiaganj (or Shikarpur) and 28 km from Bettiah in West Champaran district of Bihar state in northern India. It is situated near the banks of the B ...
and the Rampurva
The Rampurva capitals are the capitals of a pair of Ashoka Pillars discovered in by A. C. L. Carlleyle. The archaeological site is called Rampurva, and is located in the West Champaran district of the Indian state of Bihar, situated very cl ...
lion. Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
and Sarnath
Sarnath (also known as Deer Park, ''Sarangnath'', ''Isipatana Deer Park'', ''Rishipattana'', ''Migadaya'', or ''Mrigadava'')Gabe Hiemstra, "Buddha Chronicle 24: Kassapa Buddhavaṃsa". ''Wisdom Library'', 14 September 2019. is a town nort ...
would mark the culmination with four animals back-to-back instead of just one, and a new and sophisticated animal and symbolic abacus (the elephant, the bull, the lion, the horse alternating with the Dharma wheel
The dharmachakra (Sanskrit: धर्मचक्र, ) or wheel of dharma is a symbol used in the Dharmic religions. It has a widespread use in Buddhism.John C. Huntington, Dina Bangdel, ''The Circle of Bliss: Buddhist Meditational Art,'' p ...
) for the Sarnath lion.Le Huu Phuoc, Buddhist Architecture, p.42
Other chronological orders have also been proposed, for example based on the style of the Ashokan inscriptions on the pillars, since the stylistically most sophisticated pillars actually have the engravings of the Edicts of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who ruled most of the Indian subcontinent from 268 BCE to 2 ...
of the worst quality, namely, very poorly engraved Schism Edicts on the Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
and Sarnath
Sarnath (also known as Deer Park, ''Sarangnath'', ''Isipatana Deer Park'', ''Rishipattana'', ''Migadaya'', or ''Mrigadava'')Gabe Hiemstra, "Buddha Chronicle 24: Kassapa Buddhavaṃsa". ''Wisdom Library'', 14 September 2019. is a town nort ...
pillars, their only inscriptions. This approach offers an almost reverse chronological order to the preceding one.The True Chronology of Aśokan Pillars, John Irwin, Artibus Asiae, Vol. 44, No. 4 (1983), pp. 247-26/ref> According to Irwin, the
Sankissa
Sankissa (also ''Sankasia'', ''Sankassa'' and ''Sankasya'') is an ancient city in India renown for the descent of Gautama Buddha from the Tushita heavens where he taught his mother before landing at Sankissa. Considered among the eight great p ...
elephant and Rampurva
The Rampurva capitals are the capitals of a pair of Ashoka Pillars discovered in by A. C. L. Carlleyle. The archaeological site is called Rampurva, and is located in the West Champaran district of the Indian state of Bihar, situated very cl ...
bull pillars with their Hellenistic abacus are pre-Ashokan. Ashoka would then have commissioned the Sarnath pillar with its famous Lion Capital of Ashoka
The Lion Capital of Ashoka is the capital, or head, of a column erected by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka in Sarnath, India, . Its crowning features are four life-sized lions set back to back on a drum-shaped abacus. The side of the abacus is ad ...
to be built under the tutelage of craftsmen from the former Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
, trained in Perso-Hellenistic statuary, whereas the Brahmi engraving on the very same pillar (and on pillars of the same period such as Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
and Kosambi-Allahabad) was made by inexperienced Indian engravers at a time when stone engraving was still new in India. After Ashoka sent back the foreign artists, style degraded over a short period of time, down to the time when the Major Pillar Edicts
The Major Pillar Edicts of Indian Emperor Ashoka refer to 7 separate major Edicts of Ashoka inscribed on columns (the Pillars of Ashoka), which are significantly detailed and are among the earliest dated inscriptions of any Indian monarch. An E ...
were engraved at the end of Ashoka's reign, which now displayed very good inscriptional craftsmanship but a much more solemn and less elegant style for the associated lion capitals, as for the Lauria Nandangarh
Lauria Nandangarh, also Lauriya Navandgarh, is a city or town about 14 km from Narkatiaganj (or Shikarpur) and 28 km from Bettiah in West Champaran district of Bihar state in northern India. It is situated near the banks of the B ...
lion and the Rampurva
The Rampurva capitals are the capitals of a pair of Ashoka Pillars discovered in by A. C. L. Carlleyle. The archaeological site is called Rampurva, and is located in the West Champaran district of the Indian state of Bihar, situated very cl ...
lion.
Of the Allahabad pillar
The Allahabad Pillar is a ''stambha'', containing one of the pillar edicts of Ashoka, erected by Ashoka, emperor of the Maurya dynasty, who reigned in the 3rd century BCE. While it is one of the few extant pillars that carry Ashokan edicts, it ...
, only the abacus remains, the bottom bulb and the crowning animal having been lost. The remains are now located in the Allahabad Museum
The Allahabad Museum is a national-level museum in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh.
Established in 1931, it is known for its rich collection and unique objects of art, and is funded by Ministry of Culture. Moreover, it is a premier research centre for ...
.
 A few more possibly Ashokan capitals were also found without their pillars:
*
A few more possibly Ashokan capitals were also found without their pillars:
*Kesariya
Kesaria, also known as Kesariya is a town in the district of East Champaran, in the Indian state of Bihar. It is the site of a stupa built by the Mauryan king Ashoka.
Geography
Kesaria is near the River Gandak and Rampur Khajuria. The neare ...
(capital). Only the capital was found in the Kesaria stupa
Kesariya stupa is a Buddhist stupa in Kesariya, located at a distance of from Patna, in the East Champaran district of Bihar, India. Construction of the stupa at this site began in the 3rd century BCE.Le Huu Phuoc, Buddhist Architecture, Gra ...
. It was discovered by Markham Kittoe in 1862, and said to be similar to the lion of the Lauriya Nandangarh pillar, except for the hind legs of the lion, which did not protrude beyond the abacus. This capital is now lost.
* Udaigiri-Vidisha (capital only at the Udayagiri Caves
The Udayagiri Caves are twenty rock-cut caves near Vidisha, Madhya Pradesh primarily denoted to the Hindu gods Vishnu and Shiva from the early years of the 3rd century CE to 5th century CE. They contain some of the oldest surviving Hindu templ ...
, visible here
Here may refer to:
Music
* ''Here'' (Adrian Belew album), 1994
* ''Here'' (Alicia Keys album), 2016
* ''Here'' (Cal Tjader album), 1979
* ''Here'' (Edward Sharpe album), 2012
* ''Here'' (Idina Menzel album), 2004
* ''Here'' (Merzbow album), ...
). Attribution to Ashoka however is disputed (ranging from the 2nd century BC Sunga period,Story of the Delhi Iron Pillar, R. Balasubramaniap.19
/ref> to the
Gupta
Gupta () is a common surname of Indian origin, meaning "guardian" or "protector".
Origins and distribution
The name is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means "guardian" or "protector".
According to historian ...
period.The Past Before Us, Romila Thapap.361
/ref>). It is also known from various ancient sculptures (reliefs from
Bharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut st ...
, 100 BC), and later narrative account by Chinese pilgrims (5-6th century AD), that there was a pillar of Ashoka at the Mahabodhi Temple
The Mahabodhi Temple (literally: "Great Awakening Temple") or the Mahābodhi Mahāvihāra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is an ancient, but restored Buddhist temple in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, India, marking the location where the Buddha is said to hav ...
founded by Ashoka, that it was crowned by an elephant.Buddhist Architecture, Le Huu Phuoc, Grafikol 2009, pp 238-248
The same Chinese pilgrims have reported that the capital of the Lumbini
Lumbinī (, "the lovely") is a Buddhist pilgrimage site in the Rupandehi District of Lumbini Province in Nepal. The Buddhist commentaries state that Maya Devi gave birth to Siddhartha Gautama in Lumbini around 624 BCE. Gautama is bel ...
pillar was a horse (now lost), which, by their time had already fallen to the ground.
Inscriptions
 The inscriptions on the columns include a fairly standard text. The inscriptions on the columns join other, more numerous, Ashokan inscriptions on natural rock faces to form the body of texts known as the Edicts of Ashoka. These inscriptions were dispersed throughout the areas of modern-day
The inscriptions on the columns include a fairly standard text. The inscriptions on the columns join other, more numerous, Ashokan inscriptions on natural rock faces to form the body of texts known as the Edicts of Ashoka. These inscriptions were dispersed throughout the areas of modern-day Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, Afghanistan and Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
and represent the first tangible evidence of Buddhism. The edicts describe in detail Ashoka's policy of Dhamma, an earnest attempt to solve some of problems that a complex society faced. In these inscriptions, Ashoka refers to himself as "Beloved servant of the Gods" (''Devanampiyadasi''). The inscriptions revolve around a few recurring themes: Ashoka's conversion to Buddhism, the description of his efforts to spread Buddhism, his moral and religious precepts, and his social and animal welfare
Animal welfare is the quality of life and overall well-being of animals. Formal standards of animal welfare vary between contexts, but are debated mostly by animal welfare groups, legislators, and academics. Animal welfare science uses measures ...
program. The edicts were based on Ashoka's ideas on administration and behaviour of people towards one another and religion.
Alexander Cunningham
Major General Sir Alexander Cunningham (23 January 1814 – 28 November 1893) was a British Army engineer with the Bengal Sappers who later took an interest in the history and archaeology of India. In 1861, he was appointed to the newly crea ...
, one of the first to study the inscriptions on the pillars, remarks that they are written in eastern, middle and western Prakrit
Prakrit ( ) is a group of vernacular classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 5th century BCE to the 12th century CE. The term Prakrit is usually applied to the middle period of Middle Ind ...
s which he calls "the Punjabi or north-western dialect, the Ujjeni or middle dialect, and the Magadhi or eastern dialect." They are written in the Brahmi script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as ...
.
Minor Pillar Edicts
These contain inscriptions recording their dedication, as well as the Schism Edicts and the Queen's Edict. They were inscribed around the 13th year of Ashoka's reign. *Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
pillar (Schism Edict)
* Sarnath
Sarnath (also known as Deer Park, ''Sarangnath'', ''Isipatana Deer Park'', ''Rishipattana'', ''Migadaya'', or ''Mrigadava'')Gabe Hiemstra, "Buddha Chronicle 24: Kassapa Buddhavaṃsa". ''Wisdom Library'', 14 September 2019. is a town nort ...
pillar (Schism Edict)
* Allahabad
Prayagraj (, ; ISO 15919, ISO: ), formerly and colloquially known as Allahabad, is a metropolis in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.The other five cities were: Agra, Kanpur, Kanpur (Cawnpore), Lucknow, Meerut, and Varanasi, Varanasi (Benar ...
pillar (Schism Edict, Queen Edict, and also Major Pillar Edicts)
* Lumbini
Lumbinī (, "the lovely") is a Buddhist pilgrimage site in the Rupandehi District of Lumbini Province in Nepal. The Buddhist commentaries state that Maya Devi gave birth to Siddhartha Gautama in Lumbini around 624 BCE. Gautama is bel ...
(Rummindei), Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
(the upper part broke off when struck by lightning; the original horse capital mentioned by Xuanzang
Xuanzang (; ; 6 April 6025 February 664), born Chen Hui or Chen Yi (), also known by his Sanskrit Dharma name Mokṣadeva, was a 7th-century Chinese Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, traveller, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making ...
is missing) was erected by Ashoka where Buddha was born.
* Nigali Sagar
Nigali Sagar (also called Nigliva, Nigali Sagar pillar, Nighihawa pillar, Nigliva pillar, or Araurakot pillar) is an archaeological site in Nepal containing the remains of a pillar of Ashoka. The site is located in Nigalihawa, about 20 kilometer ...
(or Nigliva), near Lumbini, Rupandehi district, Nepal (originally near the Buddha Konakarnana stupa)
Lumbini
Lumbinī (, "the lovely") is a Buddhist pilgrimage site in the Rupandehi District of Lumbini Province in Nepal. The Buddhist commentaries state that Maya Devi gave birth to Siddhartha Gautama in Lumbini around 624 BCE. Gautama is bel ...
.
File:Nigali Sagar Ashokan inscription.jpg, Nigali Sagar
Nigali Sagar (also called Nigliva, Nigali Sagar pillar, Nighihawa pillar, Nigliva pillar, or Araurakot pillar) is an archaeological site in Nepal containing the remains of a pillar of Ashoka. The site is located in Nigalihawa, about 20 kilometer ...
.
Major Pillar Edicts
Description of the pillars
Pillars retaining their animals
The most celebrated capital is the four-lion one atSarnath
Sarnath (also known as Deer Park, ''Sarangnath'', ''Isipatana Deer Park'', ''Rishipattana'', ''Migadaya'', or ''Mrigadava'')Gabe Hiemstra, "Buddha Chronicle 24: Kassapa Buddhavaṃsa". ''Wisdom Library'', 14 September 2019. is a town nort ...
(Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
), erected by Emperor Ashoka circa 250 BC. Four lions are seated back to back. At present the column remains in the same place whereas the Lion Capital is at the Sarnath Museum. This Lion Capital of Ashoka from Sarnath has been adopted as the National Emblem of India
The State Emblem of India is the national emblem of the Republic of India and is used by the union government, many state governments, and other government agencies. The emblem is an adaptation of the Lion Capital of Ashoka, an ancient sculpt ...
and the wheel "Ashoka Chakra" from its base was placed onto the centre of the flag of India
The national flag of India, Colloquialism, colloquially called Tiraṅgā (the tricolour), is a horizontal rectangular tricolour flag, the colours being of India Saffron (color)#Political & religious uses, saffron, white and Variations of gree ...
.
The lions probably originally supported a Dharma Chakra
The dharmachakra (Sanskrit: धर्मचक्र, ) or wheel of dharma is a symbol used in the Dharmic religions. It has a widespread use in Buddhism.John C. Huntington, Dina Bangdel, ''The Circle of Bliss: Buddhist Meditational Art,'' p. ...
wheel with 24 spokes, such as is preserved in the 13th century replica erected at Wat Umong
Wat Umong (complete name: Wat Umong Suan Puthatham) is a 700-year-old Buddhist Chedi (temple), temple in Chiang Mai, Thailand.
Location
Wat Umong is located against the mountains of Doi Suthep and is about 1 km south of the main campus of ...
near Chiang Mai
Chiang Mai, sometimes written as Chiengmai or Chiangmai, is the largest city in northern Thailand, the capital of Chiang Mai province and the List of municipalities in Thailand#Largest cities by urban population, second largest city in Thailan ...
, Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
by Thai king Mangrai
Mangrai (; ; c. 1238–1311) was the 25th king of Ngoenyang (r. 1261–1292) and the first king of Lanna (r. 1292–1311). He established a new city, Chiang Mai, as the capital of the Lanna Kingdom (1296–1558).Wyatt, D. K. Thailand, A Short Hi ...
.
 The pillar at Sanchi also has a similar but damaged four-lion capital. There are two pillars at Rampurva, one crowned with a bull and the other with a lion.
The pillar at Sanchi also has a similar but damaged four-lion capital. There are two pillars at Rampurva, one crowned with a bull and the other with a lion. Sankissa
Sankissa (also ''Sankasia'', ''Sankassa'' and ''Sankasya'') is an ancient city in India renown for the descent of Gautama Buddha from the Tushita heavens where he taught his mother before landing at Sankissa. Considered among the eight great p ...
has only a damaged elephant capital, which is mainly unpolished, though the abacus is at least partly so. No pillar shaft has been found, and perhaps this was never erected at the site.
The Vaishali pillar has a single lion capital. The location of this pillar is contiguous to the site where a Buddhist monastery and a sacred coronation tank stood. Several stupas suggesting a far-flung campus for the monastery have been discovered. The lion faces north, the direction Buddha took on his last voyage. Identification of the site for excavation in 1969 was aided by the fact that this pillar still jutted out of the soil. More such pillars exist in this greater area but they are all devoid of the capital.
Pillar at Prayagraj
InPrayagraj
Prayagraj (, ; ISO 15919, ISO: ), formerly and colloquially known as Allahabad, is a metropolis in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.The other five cities were: Agra, Kanpur, Kanpur (Cawnpore), Lucknow, Meerut, and Varanasi, Varanasi (Benar ...
there is a pillar with inscriptions from Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
and later inscriptions attributed to Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', ( 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India. A military genius and a patron of arts, he is regarded among the greatest rulers in Indian history. As a son of th ...
and Jehangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
. It is clear from the inscription that the pillar was first erected at Kaushambi, an ancient town some 30 kilometres west of Allahabad that was the capital of the Koshala
Kosala, sometimes referred to as Uttara Kosala () was one of the Mahajanapadas of ancient India. It emerged as a small state during the Late Vedic period and became (along with Magadha) one of the earliest states to transition from a lineage- ...
kingdom, and moved to Allahabad, presumably under Muslim rule.
The pillar is now located inside the Allahabad Fort, also the royal palace, built during the 16th century by Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, – ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
at the confluence of the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
and Yamuna
The Yamuna (; ) is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Low ...
rivers. As the fort is occupied by the Indian Army
The Indian Army (IA) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the Land warfare, land-based branch and largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head ...
it is essentially closed to the public and special permission is required to see the pillar. The Ashokan inscription is in Brahmi
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or ...
and is dated around 232 BC. A later inscription attributed to the second king of the Gupta empire
The Gupta Empire was an Indian empire during the classical period of the Indian subcontinent which existed from the mid 3rd century to mid 6th century CE. At its zenith, the dynasty ruled over an empire that spanned much of the northern Indian ...
, Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', ( 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India. A military genius and a patron of arts, he is regarded among the greatest rulers in Indian history. As a son of th ...
, is in the more refined Gupta script
The Gupta script (sometimes referred to as Gupta Brahmi script or Late Brahmi script)Sharma, Ram. '' 'Brahmi Script' ''. Delhi: BR Publishing Corp, 2002 was used for writing Sanskrit and is associated with the Gupta Empire of the Indian subcon ...
, a later version of Brahmi, and is dated to around 375 AD. This inscription lists the extent of the empire that Samudragupta built during his long reign. He had already been king for forty years at that time and would rule for another five. A still later inscription in Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
is from the Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
emperor Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
. The Akbar Fort also houses the Akshay Vat
Akshayavata (), also rendered Akshayavat, is a sacred banyan tree mentioned in the Hindu mythology and in Jainism. It is also the name of a sacred lake mentioned in the Puranas.
In Hinduism
The Padma Purana states that those who venerate th ...
, an Indian fig tree of great antiquity. The Ramayana
The ''Ramayana'' (; ), also known as ''Valmiki Ramayana'', as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics ...
refers to this tree under which Lord Rama
Rama (; , , ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the seventh and one of the most popular avatars of Vishnu. In Rama-centric Hindu traditions, he is considered the Supreme Being. Also considered as the ideal man (''maryāda' ...
is supposed to have prayed while on exile.
Pillars at Lauriya-Areraj and Lauriya-Nandangarh
The column atLauriya-Nandangarh
Lauria Nandangarh, also Lauriya Navandgarh, is a city or town about 14 km from Narkatiaganj (or Shikarpur) and 28 km from Bettiah in West Champaran district of Bihar state in northern India. It is situated near the banks of the B ...
, 23 km from Bettiah
Bettiah is a city and the administrative headquarters of West Champaran district ( Tirhut Division) - ( Tirhut). It is near the Indo-Nepal border, northwest of Patna, in the state of Bihar, India.
History
In 1244 A.D., Gangeshwar Dev, a B ...
in West Champaran district
West Champaran is an administrative district in the state of Bihar in India, located just west of Birgunj. It is the largest district in Bihar with an area of 5,228 km2(2,019sq mi). It is a part of Tirhut Division. The district headquart ...
, Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
has single lion capital. The hump and the hind legs of the lion project beyond the abacus. The pillar at Lauriya-Areraj in East Champaran district
East Champaran or Purvi Champaran is an administrative district in the Tirhut division of the state of Bihar in India. The district headquarter is located at Motihari. Prior to 1971, there was a single Champaran District. On 1 December 1971, it ...
, Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
is presently devoid of any capital.
Erecting the Pillars
The Pillars of Ashoka may have been erected using the same methods that were used to erect the ancientobelisk
An obelisk (; , diminutive of (') ' spit, nail, pointed pillar') is a tall, slender, tapered monument with four sides and a pyramidal or pyramidion top. Originally constructed by Ancient Egyptians and called ''tekhenu'', the Greeks used th ...
s. Roger Hopkins and Mark Lehrner conducted several obelisk erecting experiments including a successful attempt to erect a 25ton obelisk in 1999. This followed two experiments to erect smaller obelisks and two failed attempts to erect a 25-ton obelisk.
Rediscoveries
 A number of the pillars were thrown down by either natural causes or iconoclasts, and gradually rediscovered. One was noticed in the 16th century by the English traveller
A number of the pillars were thrown down by either natural causes or iconoclasts, and gradually rediscovered. One was noticed in the 16th century by the English traveller Thomas Coryat
Thomas Coryat (also Coryate) (c. 15771617) was an English traveller and writer of the late Elizabethan and early Jacobean age. He is principally remembered for two volumes of writings he left regarding his travels, often on foot, through E ...
in the ruins of Old Delhi
Shahjahanabad colloquially known as Old Delhi( Hindustani: ''Purāni Dillī'') is an area in the Central Delhi district of Delhi, India. It was founded as a walled city and officially named Shahjahanabad in 1648, when Shah Jahan decided to shi ...
. Initially he assumed that from the way it glowed that it was made of brass, but on closer examination he realized it was made of highly polished sandstone with upright script that resembled a form of Greek. In the 1830s James Prinsep
James Prinsep (20 August 1799 – 22 April 1840) was an English scholar, Orientalism, orientalist and antiquary. He was the founding editor of the ''Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal'' and is best remembered for deciphering the Kharost ...
began to decipher them with the help of Captain Edward Smith and George Turnour
George Turnour Jnr, CCS (1799–1843) was a British colonial administrator, scholar and a historian. A member of the Ceylon Civil Service, he served as a Government Agent, Assistant Colonial Secretary and Treasurer of the Colony. He is known for ...
. They determined that the script referred to King Piyadasi which was also the epithet of an Indian ruler known as Ashoka who came to the throne 218 years after Buddha's enlightenment. Scholars have since found 150 of Ashoka's inscriptions, carved into the face of rocks or on stone pillars marking out a domain that stretched across northern India and south below the central plateau of the Deccan. These pillars were placed in strategic sites near border cities and trade routes.
The Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
pillar was found by F.O. Oertelin in 1851 in excavations led by Sir Alexander Cunningham
Major General Sir Alexander Cunningham (23 January 1814 – 28 November 1893) was a British Army engineer with the Bengal Sappers who later took an interest in the history and archaeology of India. In 1861, he was appointed to the newly crea ...
, first head of the Archaeological Survey of India
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural historical monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexander ...
. There were no surviving traces above ground of the Sarnath pillar, mentioned in the accounts of medieval Chinese pilgrims, when the Indian Civil Service engineer F.O. Oertel, with no real experience in archaeology, was allowed to excavate there in the winter of 1904–05. He first uncovered the remains of a Gupta
Gupta () is a common surname of Indian origin, meaning "guardian" or "protector".
Origins and distribution
The name is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means "guardian" or "protector".
According to historian ...
shrine west of the main stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
, overlying an Ashokan structure. To the west of that he found the lowest section of the pillar, upright but broken off near ground level. Most of the rest of the pillar was found in three sections nearby, and then, since the Sanchi capital had been excavated in 1851, the search for an equivalent was continued, and the Lion Capital of Ashoka
The Lion Capital of Ashoka is the capital, or head, of a column erected by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka in Sarnath, India, . Its crowning features are four life-sized lions set back to back on a drum-shaped abacus. The side of the abacus is ad ...
, the most famous of the group, was found close by. It was both finer in execution and in much better condition than that at Sanchi. The pillar appeared to have been deliberately destroyed at some point. The finds were recognised as so important that the first onsite museum in India (and one of the few then in the world) was set up to house them.
Other Ashokan structures
;Stupas According to legend, Ashoka built 84,000stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
s commemorating the events and relics of Buddha's life. Some of these stupas contained networks of walls containing the hub, spokes and rim of a wheel, while others contained interior walls in a swastika
The swastika (卐 or 卍, ) is a symbol used in various Eurasian religions and cultures, as well as a few Indigenous peoples of Africa, African and Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American cultures. In the Western world, it is widely rec ...
(卐) shape. The wheel represents the sun, time, and Buddhist law (the wheel of law, or dharmachakra), while the swastika stands for the cosmic dance around a fixed centre and guards against evil.
;"Diamond throne" in Bodh Gaya
Ashoka also built the Diamond Throne
The Vajrasana (; ''diamond throne''), or Enlightenment Throne of the Buddha, is an ancient stone slab located under the Bodhi tree, directly beside the Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya. It is considered as bodhimanda ('; ''seat'' or ''platform ...
in Bodh Gaya
Bodh Gayā is a religious site and place of pilgrimage associated with the Mahabodhi Temple complex, situated in the Gaya district in the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Bihar. It is famous for being the place where Gautam ...
, at the location where the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist legends, he was ...
had reached enlightenment some 200 years earlier.A Global History of Architecture, Francis D. K. Ching, Mark M. Jarzombek, Vikramaditya Prakash, John Wiley & Sons, 201p.570ff
/ref>Buddhist Architecture, Huu Phuoc L
p.240
/ref> This purely Buddhist monument to the Buddha is a thick slab of polished grey
sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
with Mauryan polish
Mauryan polish describes one of the frequent characteristics of architecture and sculptures of the Maurya Empire in India (325 to 185 BCE), which gives a very smooth and shiny surface to the stone material, generally of sandstone or granite.The roo ...
Alexander Cunningham, Mahâbodhi, or the great Buddhist temple under the Bodhi tree at Buddha-Gayp.19
Public Domain text The sculpted decorations on the Diamond Throne clearly echo the decorations found on the Pillars of Ashoka. The Diamond Throne has a decorative band made of
honeysuckle
Honeysuckles are arching shrubs or Vine#Twining vines, twining vines in the genus ''Lonicera'' () of the family Caprifoliaceae. The genus includes 158 species native to northern latitudes in North America, Eurasia, and North Africa. Widely kno ...
s and geese
A goose (: geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera '' Anser'' (grey geese and white geese) and ''Branta'' (black geese). Some members of the Tadorninae subfamily (e.g., Egyp ...
, which can also be found on several of the Pillars of Ashoka, such as the Rampurva capitals or the Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen ...
capital. The geese (hamsa
The ''hamsa'' (, referring to images of 'the five fingers of the hand'),Zenner, 1988p. 284World Institute for Advanced Phenomenological Research and Learning (Belmont, Estados Unidos), 1991p. 219Drazin, 2009p. 268 also known as the hand of Fa ...
) in particular are a very recurrent symbol on the pillars of Ashoka, and may refer to the devotees flocking to the faith. The same throne is also illustrated in later reliefs from Bharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut st ...
, dated to circa 100 BC.Mahâbodhi, Cunninghap.4ff
Public Domain text
See also
Related topics *Major Rock Edicts
The Major Rock Edicts of Indian emperor Ashoka refer to 14 separate major Edicts of Ashoka which are significantly detailed and represent some of the earliest dated rock inscriptions of any Indian monarch. These edicts are preceded chronologica ...
* Minor Rock Edicts
The Minor Rock Edicts of Ashoka (r. 269–233 BCE) are rock inscriptions which form the earliest part of the Edicts of Ashoka, and predate Ashoka's Major Rock Edicts. These are the first edicts in the Indian language of Emperor Ashoka, written ...
* Dhar iron pillar
The Dhar iron pillar is a now-fragmented iron column located in the Dhar town of Madhya Pradesh, India. The exact origins of the pillar are unknown, but according to the local tradition, it was a victory column erected by the 11th century Para ...
* Iron pillar of Delhi
The iron pillar of Delhi is a metal structure high with a diameter that was constructed by Chandragupta II (reigned c. 375–415 Common Era, CE), and now stands in the Qutb complex at Mehrauli in Delhi, India.Finbarr Barry Flood, 2003"Pillar, ...
* List of Edicts of Ashoka
* Hall of 80 pillars
* Ashoka's Hell
* Barabar Caves
The Barabar Hill Caves are the oldest surviving rock-cut caves in India, dating from the Maurya Empire (322–185 BCE), some with Ashokan inscriptions, located in the Makhdumpur region of Jehanabad district, Bihar, India, north of Gaya.
The ...
Other similar topics
* Early Indian epigraphy
The earliest deciphered epigraphy found in the Indian subcontinent are the Edicts of Ashoka of the 3rd century BCE, in the Brahmi script.
If epigraphy of proto-writing is included, undeciphered markings with symbol systems that may or ma ...
* Hindu temple architecture
Hindu temple architecture as the main form of Hindu architecture has many different styles, though the basic nature of the Hindu temple remains the same, with the essential feature an inner sanctum, the ''Garbhagriha, garbha griha'' or womb-ch ...
* History of India
Anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. The earliest known human remains in South Asia date to 30,000 years ago. Sedentism, Sedentariness began in South Asia around 7000 BCE; ...
* Indian copper plate inscriptions
Indian copper plate inscriptions are legal records engraved on copper plates. The practice was widespread and long-running in the Indian subcontinent; it may date back to as early as the 3rd millennium BCE, however the vast majority of recovered ...
* Indian rock-cut architecture
Indian rock-cut architecture is more various and found in greater abundance in that country than any other form of rock-cut architecture around the world. Rock-cut architecture is the practice of creating a structure by carving it out of solid na ...
* Lak Mueang
Lak mueang (, ) are city pillars found in most cities of Thailand. Usually housed in a shrine (, ) which is also believed to house Chao Pho Lak Mueang (, ), the city spirit deity. It was constructed because the continuation of ancient traditio ...
* List of rock-cut temples in India
This is a partial List of caves, list of Indian rock-cut architecture, rock-cut temples by state or union territory.
Andhra Pradesh
* Akkana and Madanna cave temple, Akkanna Madanna Caves, Vijayawada
* Belum Caves, Kurnool district
* Prakasa ...
* Outline of ancient India
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient India:
Ancient India is the Indian subcontinent from prehistoric times to the start of Medieval India, which is typically dated (when the term is still used) to ...
* South Indian Inscriptions
* Tagundaing
* Stambha
A stambha () is a pillar or a column employed in Indian architecture. A stambha sometimes bears inscriptions and religious emblems.
Religion
In Hindu mythology, a stambha is believed to be a cosmic column that functions as a bond, joining h ...
* Huabiao
Huabiao () is a type of ceremonial column used in traditional Chinese architecture. ''Huabiao'' are traditionally erected in pairs in front of palaces and tombs. The prominence of their placement have made them one of the emblems of tradition ...
Notes
References
*Ashoka, Emperor, ''Edicts of Ashoka'', eds. N. A. Nikam, Richard P. McKeon, 1978, University of Chicago Press, , 9780226586113google books
* Boardman, John (1998), "Reflections on the Origins of Indian Stone Architecture", ''Bulletin of the Asia Institute'', pp. 15–19, 1998, New Series, Vol. 12, (''Alexander's Legacy in the East: Studies in Honor of Paul Bernard''), p. 13-22
JSTOR
*"Companion": Brown, Rebecca M., Hutton, Deborah S., eds., ''A Companion to Asian Art and Architecture'', Volume 3 of Blackwell companions to art history, 2011, John Wiley & Sons, 2011, , 9781444396324
google books
*Harle, J.C., ''The Art and Architecture of the Indian Subcontinent'', 2nd edn. 1994, Yale University Press Pelican History of Art, *Krishnaswamy, C.S., Sahib, Rao, and Ghosh, Amalananda, "A Note on the Allahabad Pillar of Aśoka", ''The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland'', No. 4 (Oct., 1935), pp. 697–706,
Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland
The Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, commonly known as the Royal Asiatic Society, was established, according to its royal charter of 11 August 1824, to further "the investigation of subjects connected with and for the encourag ...
JSTOR
*Falk, H. ''Asokan Sites and Artefacts: a A Source-book with Bibliography'', 2006, ''Volume 18 of Monographien zur indischen Archäologie, Kunst und Philologie'', Von Zabern, ISSN 0170-8864
Further reading
*External links
Archaeological Survey of India
British Museum, collections online
- See "lioncapital" for pictures of the original "Lion Capital of Ashoka" preserved at the
Sarnath Museum
Sarnath Museum is the oldest site museum of the Archaeological Survey of India. It houses the findings and excavations at the archaeological site of Sarnath, by the Archaeological Survey of India. Sarnath is located near Varanasi, in the state ...
which has been adopted as the "National Emblem of India" and the Ashoka Chakra (Wheel) from which has been placed in the centre of the "National Flag of India".
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pillars Of Ashoka
Monumental columns in India
Buddhist architecture
Monuments and memorials in Bihar
Edicts of Ashoka
Memorials to Ashoka
Ancient Indian sculpture
Mauryan art
Indian Buddhist sculpture