Light therapy, also called phototherapy or bright light therapy is the exposure to direct sunlight or artificial light at controlled wavelengths in order to treat a variety of medical disorders, including
seasonal affective disorder
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a mood disorder subset in which people who typically have normal mental health throughout most of the year exhibit depressive symptoms at the same time each year. It is commonly, but not always, associated w ...
(SAD),
circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
sleep-wake disorders, cancers, neonatal jaundice, and skin wound infections. Treating skin conditions such as neurodermatitis,
psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete b ...
,
acne vulgaris
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, ...
, and
eczema
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
with ultraviolet light is called
ultraviolet light therapy
Ultraviolet light therapy or ultraviolet phototherapy is a treatment for psoriasis, atopic skin disorder, vitiligo and other skin diseases.
Mechanism of action
Ultraviolet light exerts its therapeutic effects largely by modulating cutaneous ...
.
Medical uses

Nutrient deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency
Exposure to
UV-B light at wavelengths of 290-300 nanometers enables the body to produce
vitamin D3
Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3, colecalciferol or calciol, is a type of vitamin D that is produced by the skin when exposed to UVB light; it is found in certain foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.
Cholecalciferol is ...
to treat
vitamin D3 deficiency.
Skin conditions
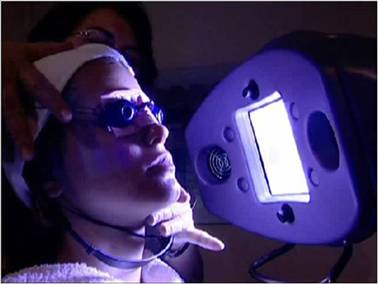
Light therapy treatments for the skin usually involve exposure to
ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of th ...
. The exposures can be to a small area of the skin or over the whole body surface, as in a
tanning bed
Indoor tanning involves using a device that emits ultraviolet radiation to produce a cosmetic tan. Typically found in tanning salons, gyms, spas, hotels, and sporting facilities, and less often in private residences, the most common device is a h ...
. The most common treatment is with
narrowband
Narrowband signals are signals that occupy a narrow range of frequencies or that have a small fractional bandwidth. In the audio spectrum, ''narrowband sounds'' are sounds that occupy a narrow range of frequencies. In telephony, narrowband is ...
UVB, which has a wavelength of approximately 311–313 nanometers. Full body phototherapy can be delivered at a doctor's office or at home using a large high-power UVB booth. Tanning beds, however, generate mostly UVA light, and only 4% to 10% of tanning-bed light is in the UVB spectrum.
Acne vulgaris
evidence for light therapy and lasers in the treatment of acne vulgaris was not sufficient to recommend them. There is moderate evidence for the efficacy of blue and blue-red light therapies in treating mild acne, but most studies are of low quality. While light therapy appears to provide short-term benefit, there is a lack of long-term outcome data or data in those with severe acne.
Atopic dermatitis
Light therapy is considered one of the best monotherapy treatments for
atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditi ...
(AD) when applied to patients who have not responded to traditional topical treatments. The therapy offers a wide range of options: UVA1 for acute AD, NB-UVB for chronic AD, and
balneophototherapy have proven their efficacy. Patients tolerate the therapy safely but, as in any therapy, there are potential adverse effects and care must be taken in its application, particularly to children. According to a study involving 21 adults with severe atopic dermatitis, narrowband UVB phototherapy administered three times per week for 12 weeks reduced atopic dermatitis severity scores by 68%. In this open study, 15 patients still experienced long-term benefits six months later.
Cancer
According to the
American Cancer Society
The American Cancer Society (ACS) is a nationwide non-profit organization dedicated to eliminating cancer. The ACS publishes the journals ''Cancer'', '' CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians'' and '' Cancer Cytopathology''.
History
The society w ...
, there is some evidence that ultraviolet light therapy may be effective in helping treat certain kinds of
skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the Human skin, skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells (biology), cells that have the ability to invade or metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. It occurs when skin cells grow ...
, and ultraviolet
blood irradiation therapy
Blood irradiation therapy is an alternative medical procedure in which the blood is exposed to low-level light (often laser light) for therapeutic reasons. The practice was originally developed in the United States, but most recent research on i ...
is established for this application. However, alternative uses of light for cancer treatment – light box therapy and
colored light therapy – are not supported by evidence.
Photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy involving light and a photosensitizing chemical substance used in conjunction with molecular oxygen to elicit cell death ( phototoxicity).
PDT is used in treating acne, wet age-related macula ...
(often with red light) is used to treat certain superficial non-melanoma skin cancers.
Psoriasis
For
psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete b ...
, UVB phototherapy has been shown to be effective. A feature of psoriasis is localized
inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
mediated by the
immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
.
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
radiation is known to suppress the
immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
and reduce inflammatory responses. Light therapy for skin conditions like psoriasis usually use 313 nanometer UVB though it may use UVA (315–400 nm wavelength) or a broader spectrum UVB (280–315 nm wavelength). UVA combined with
psoralen
Psoralen (also called psoralene) is the parent compound in a family of naturally occurring organic compounds known as the linear furanocoumarins. It is structurally related to coumarin by the addition of a fused furan ring, and may be considered a ...
, a drug taken orally, is known as
PUVA
PUVA (psoralen and UVA) is an ultraviolet light therapy treatment for skin diseases: vitiligo, eczema, psoriasis, graft-versus-host disease, mycosis fungoides, large plaque parapsoriasis, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, using the sensitizing e ...
treatment. In UVB phototherapy the exposure time is very short, seconds to minutes depending on intensity of lamps and the person's skin pigment and sensitivity.
Vitiligo
About 1% of the human population has
vitiligo
Vitiligo (, ) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes patches of skin to lose pigment or color. The cause of vitiligo is unknown, but it may be related to immune system changes, genetic factors, stress, or sun exposure, and susceptibili ...
which causes painless distinct light-colored patches of the skin on the face, hands, and legs. Phototherapy is an effective treatment because it forces skin cells to manufacture
melanin
Melanin (; ) is a family of biomolecules organized as oligomers or polymers, which among other functions provide the pigments of many organisms. Melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes.
There are ...
to protect the body from UV damage. Prescribed treatment is generally 3 times a week in a clinic or daily at home. About 1 month usually results in re-pigmentation in the face and neck, and 2–4 months in the hands and legs. Narrowband UVB is more suitable to the face and neck and PUVA is more effective at the hands and legs.
Other skin conditions
Some types of phototherapy may be effective in the treatment of
polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) presents with itchy red small bumps on sun-exposed skin, particularly face, neck, forearms and legs. It generally appears 30 minutes to a few hours after sun exposure and may last between one and 14 days. The b ...
,
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B cell, B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The ma ...
and
lichen planus
Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and autoimmune disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, but is named for its appearance. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous p ...
. Narrowband UVB between 311 and 313 nanometers is the most common treatment.
Retinal conditions
There is preliminary evidence that light therapy is an effective treatment for
diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy (also known as diabetic eye disease) is a medical condition in which damage occurs to the retina due to diabetes. It is a leading cause of blindness in developed countries and one of the lead causes of sight loss in the wor ...
and
diabetic macular oedema.
Mood and sleep related
Seasonal affective disorder
The effectiveness of light therapy for treating
seasonal affective disorder
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a mood disorder subset in which people who typically have normal mental health throughout most of the year exhibit depressive symptoms at the same time each year. It is commonly, but not always, associated w ...
(SAD) may be linked to reduced
sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
exposure in the winter months. Light resets the body's internal clock. Studies show that light therapy helps reduce the debilitating depressive symptoms of SAD, such as excessive sleepiness and fatigue, with results lasting for at least 1 month. Light therapy is preferred over
antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
s in the treatment of SAD because it is a relatively safe and easy therapy with minimal side effects.
Two methods of light therapy, bright light and dawn simulation, have similar success rates in the treatment of SAD.
It is possible that response to light therapy for SAD could be
season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's axial tilt, tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperat ...
dependent. Morning therapy has provided the best results because light in the early morning aids in regulating the
circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
.
People affected by SAD often have low energy, tend to eat more carbohydrates and sleep longer, but symptoms can vary between people.
A
Cochrane review conducted in 2019 states the evidence that light therapy's effectiveness as a treatment for the ''prevention'' of seasonal affective disorder is limited, although the risk of adverse effects are minimal. Therefore, the decision to use light therapy should be based on a person's preference of treatment.
Non-seasonal depression
Light therapy has also been suggested in the treatment of non-seasonal depression and other psychiatric mood disturbances, including
major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally ...
,
bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
and
postpartum depression
Postpartum depression (PPD), also called perinatal depression, is a mood disorder which may be experienced by pregnant or postpartum women. Symptoms include extreme sadness, low energy, anxiety, crying episodes, irritability, and extreme cha ...
. A meta-analysis by the
Cochrane Collaboration
Cochrane is a British international charitable organisation formed to synthesize medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes ...
concluded that "for patients suffering from non-seasonal depression, light therapy offers modest though promising antidepressive efficacy." A 2008
systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
concluded that "overall, bright light therapy is an excellent candidate for inclusion into the therapeutic inventory available for the treatment of nonseasonal depression today, as adjuvant therapy to antidepressant medication, or eventually as stand-alone treatment for specific subgroups of depressed patients." A 2015 review found that supporting evidence for light therapy was limited due to serious
methodological
In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bri ...
flaws.
A 2016 meta-analysis showed that bright light therapy appeared to be efficacious, particularly when administered for 2–5 weeks' duration and as monotherapy.
Chronic circadian rhythm sleep disorders (CRSD)
In the management of
circadian rhythm disorders such as
delayed sleep phase disorder
Delayed sleep phase disorder (DSPD), more often known as delayed sleep phase syndrome and also as delayed sleep–wake phase disorder, is the delaying of a person's circadian rhythm (biological clock) compared to those of societal norms. The dis ...
(DSPD), the timing of light exposure is critical. Light exposure administered to the eyes before or after the
nadir
The nadir is the direction pointing directly ''below'' a particular location; that is, it is one of two vertical directions at a specified location, orthogonal to a horizontal flat surface.
The direction opposite of the nadir is the zenith.
Et ...
of the core body temperature rhythm can affect the
phase response curve
A phase response curve (PRC) illustrates the transient change (phase response) in the cycle period of an oscillation induced by a perturbation as a function of the phase at which it is received. PRCs are used in various fields; examples of biolog ...
. Use upon awakening may also be effective for
non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder
Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder (non-24, N24SWD, or N24) is one of several chronic circadian rhythm sleep disorders (CRSDs). It is defined as a "chronic steady pattern comprising ..daily delays in sleep onset and wake times in an individual ...
. Some users have reported success with lights that turn on shortly ''before'' awakening (
dawn simulation). Evening use is recommended for people with
advanced sleep phase disorder
Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder (ASPD), also known as the advanced sleep-phase type (ASPT) of circadian rhythm sleep disorder, is a condition that is characterized by a recurrent pattern of early evening (e.g. 7-9 PM) sleepiness and very early morn ...
. Some, but not all, totally
blind people whose
retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
e are intact, may benefit from light therapy.
Circadian rhythm sleep disorders and jet lag
Source:
= Situational CRSD
=
Light therapy has been tested for individuals with
shift work sleep disorder
Shift work sleep disorder (SWSD) is a circadian rhythm sleep disorder characterized by insomnia, excessive Somnolence, sleepiness, or both affecting people whose work hours overlap with the typical sleep period. Insomnia can be the difficulty to ...
and for
jet lag
Jet lag is a temporary physiological condition that occurs when a person's circadian rhythm is out of sync with the time zone they are in, and is a typical result from travelling rapidly across multiple time zones (east–west or west–east). ...
.
= Sleep disorder in Parkinson's disease
=
Light therapy has been trialed in treating sleep disorders experienced by patients with
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
.
= Sleep disorder in Alzheimer's disease
=
Studies have shown that daytime and evening light therapy for nursing home patients with
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
, who often struggle with agitation and fragmented wake/rest cycles effectively led to more consolidated sleep and an increase in circadian rhythm stability.
Neonatal jaundice (Postnatal Jaundice)

Light therapy is used to treat cases of
neonatal jaundice
Neonatal jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the white part of the eyes and skin in a newborn baby due to high bilirubin levels. Other symptoms may include excess sleepiness or poor feeding. Complications may include seizures, cerebral ...
.
Bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (adopted from German, originally bili—bile—plus ruber—red—from Latin) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normcomponent of the straw-yellow color in urine. Another breakdown product, stercobilin, causes the brown ...
, a yellow pigment normally formed in the
liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
during the breakdown of old red blood cells, cannot always be effectively cleared by a neonate's liver causing neonatal jaundice. Accumulation of excess bilirubin can cause
central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
damage, and so this buildup of bilirubin must be treated. Phototherapy uses the energy from light to isomerize the bilirubin and consequently transform it into compounds that the newborn can excrete via urine and stools. Bilirubin is most successful absorbing light in the blue region of the visible light spectrum, which falls between 460 and 490 nm.
Therefore, light therapy technologies that utilize these blue wavelengths are the most successful at isomerizing bilirubin.
Techniques
Photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy using nontoxic light-sensitive compounds (
photosensitizers) that are exposed selectively to light at a controlled wavelength, laser intensity, and irradiation time, whereupon they generate toxic
reactive oxygen species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl ...
(ROS) that target malignant and other diseased cells. Oxygen is thus required for activity, lowering efficacy in highly developed tumors and other
hypoxic
Hypoxia means a lower than normal level of oxygen, and may refer to:
Reduced or insufficient oxygen
* Hypoxia (environmental), abnormally low oxygen content of a specific environment
** Hypoxia in fish, responses of fish to hypoxia
* Hypoxia (medi ...
environments. Selective apoptosis of diseased cells is difficult due to the radical nature of ROS, but may be controlled for through membrane potential and other cell-type specific properties'
effects on permeability or through
photoimmunotherapy. In developing any phototherapeutic agent, the phototoxicity of the treatment wavelength should be considered.
Photodynamic cancer therapy
Various cancer treatments utilizing PDT have been approved by the FDA. Treatments are available for
actinic keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK), sometimes called solar keratosis or senile keratosis, is a Premalignant condition, pre-cancerous area of thick, scaly, or crusty skin.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed. ...
(blue light with
aminolevulinic acid),
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B cell, B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The ma ...
,
Barrett esophagus,
basal cell skin cancer,
esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer (American English) or oesophageal cancer (British English) is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include dysphagia, difficulty in swallowing and weigh ...
,
non-small cell lung cancer
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), or non-small-cell lung carcinoma, is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitiv ...
, and
squamous cell skin cancer (Stage 0). Photosensitizing agents clinically-approved or undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of cancers include
Photofrin,
Temoporfin
Temoporfin (INN) is a photosensitizer (based on chlorin) used in photodynamic therapy for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
It is marketed in the European Union under the brand name Foscan. The U.S. Food and Drug Ad ...
,
Motexafin lutetium,
Palladium bacteriopheophorbide
Palladium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1802 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas (formally 2 Pallas), wh ...
,
Purlytin, and
Talaporfin
Talaporfin ( INN, also known as aspartyl chlorin, mono-L-aspartyl chlorin e6, NPe6, or LS11) is a chlorin based photosensitizer used in photodynamic therapy (PDT).
It absorbs red light at 664-667 nm normally provided by a laser tuned t ...
.
Verteporfin
Verteporfin (trade name Visudyne), a benzoporphyrin derivative, is a medication used as a photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy to eliminate the abnormal blood vessels in the eye associated with conditions such as the wet form of macular dege ...
is approved to treat eye conditions such as
macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred vision, blurred or vision loss, no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no sym ...
,
myopia
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry, while close objects appear normal. ...
, and
ocular histoplasmosis. Third-generation photosensitizers are currently in development, but none are yet approved for clinical trials.
Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy
PDT may also be utilized to treat
multidrug-resistant skin, wound, or other superficial infections. This is known as
antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) or photodynamic inactivation (PDI). aPDT has been observed to be effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria such as ''
Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'', ''
Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can c ...
,'' and ''
Mycobacterium
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis (''Mycobacterium tuberculo ...
''. aPDT has shown lowered efficacy on some other bacterial species, such as ''
Klebsiella pneumoniae
''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose- fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It appears as a mucoid lactose fermenter on MacConkey agar.
Although found in the normal flora of the mo ...
'' and ''
Acinetobacter baumannii
''Acinetobacter baumannii'' is a typically short, almost round, rod-shaped (coccobacillus) Gram-negative bacterium. It is named after the bacteriologist Paul Baumann. It can be an opportunistic pathogen in humans, affecting people with compromis ...
''. This is likely due to factors such as cell wall thickness and membrane potential.
Many studies utilizing aPDT focus on the application of the photosensitizer through leakage from a
hydrogel
A hydrogel is a Phase (matter), biphasic material, a mixture of Porosity, porous and Permeation, permeable solids and at least 10% of water or other interstitial fluid. The solid phase is a water Solubility, insoluble three dimensional network ...
, which has been found to increase wound healing speed of skin infections through the upregulation of
vascular endothelial growth factor
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, ), originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors ...
(VEGF) and
hypoxia inducible factor
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are transcription factors that respond to decreases in available oxygen in the cellular environment, or hypoxia. They also respond to instances of pseudohypoxia, such as thiamine deficiency. Both hypoxia an ...
(HIF). This controlled leakage allows for prolonged but limited generation of ROS, lowering the impact on human cell viability due to ROS cytotoxicity. It is unlikely for
drug resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is ...
to
photosensitizers to form due to the nontoxic nature of the photosensitizer itself as well as the ROS generation mechanism of action, which cannot be prevented outside of hypoxic environments. Certain dental infections (
peri-implantitis
Peri-implantitis is a destructive Inflammation, inflammatory process affecting the soft and hard tissues surrounding dental implants. The soft tissues become inflamed whereas the Alveolar process, alveolar bone (hard tissue), which surrounds the ...
,
periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main c ...
) are more difficult to treat with PDT as opposed to photothermal therapy due to the requirement of oxygen, though a significant response is still observed.
Increased antimicrobial activity and wound healing speeds are typically observed when PDT is combined with
photothermal therapy Photothermal therapy (PTT) refers to efforts to use electromagnetic radiation (most often in infrared wavelengths) for the treatment of various medical conditions, including cancer. This neurotherapy is an extension of photodynamic therapy, in which ...
in
photodynamic/photothermal combination therapy.
Photothermal Therapy
Photothermal therapy (PTT) is a form of phototherapy that uses non-toxic compounds called photothermal agents (PTA) that, when irradiated at a certain wavelength of light, converts the light energy directly to heat energy. The photothermal conversion efficiency determines the amount of light converted to heat, which can dictate the necessary irradiation time and/or laser intensity for treatments. Typically PTT treatments use wavelengths in the
near-infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of ...
(NIR) spectra, which can be further divided into NIR-I (760-900 nm), NIR-II (900-1880 nm), and NIR-III (2080-2340 nm) windows. Wavelengths in these regions are typically less phototoxic than UV or high-energy visible light. In addition, NIR-II wavelengths have been observed to show deeper penetration than NIR-I wavelengths, allowing for treatment of deeper wounds, infections, and cancers. Important considerations for the development of a PTA include photothermal conversion efficiency, phototoxicity, laser intensity, irradiation time, and the temperature at which human cell viability is impaired (around 46-60 °C). Currently, the only FDA-approved photothermal agent is
indocyanine green
Indocyanine green (ICG) is a cyanine dye used in medical diagnostics. It is used for determining cardiac output, hepatic function, liver and gastric blood flow, and for ophthalmic and cerebral angiography. which is active against both tumor and bacterial cells.
PTT is less selective than photodynamic therapy (PDT, see above) due to its heat-based
mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical Drug interaction, interaction through which a Medication, drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention o ...
, but also less likely to promote
drug resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is ...
than most, if not all, currently developed treatments. In addition, PTT can be used in hypoxic environments and on deeper wounds, infections, and tumors than PDT due to the higher wavelength of light. Due to PTT activity in hypoxic environments, it may be also used on more developed tumors than PDT. Low-temperature PTT (≤ 45 °C) for treatment of infections is also a possibility when combined with an antibiotic compound due to heat's proportionality with
membrane permeability
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extrac ...
- a hotter environment causes heightened membrane permeability, which thus allows the drug into the cell. This would reduce/eliminate the impact on human cell viability, and aiding in antibiotic accumulation within the target cell may assist in restoring activity in antibiotics that pathogens had developed resistance to.
PTT is typically seen to have improved antimicrobial and wound healing activity when combined with an additional mechanism of action through PDT or added antibiotic compounds in the application.
Light boxes
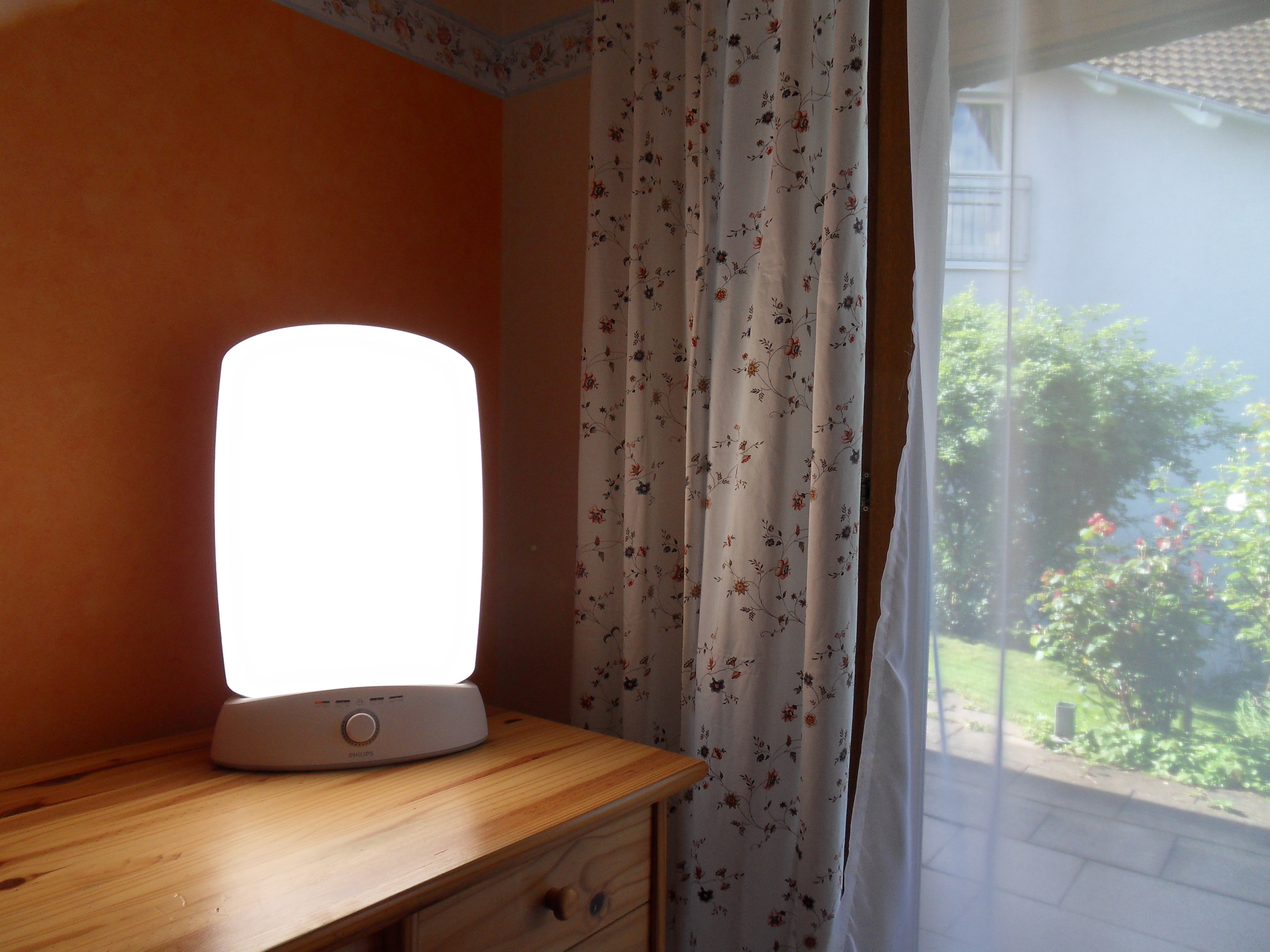

The production of the hormone
melatonin
Melatonin, an indoleamine, is a natural compound produced by various organisms, including bacteria and eukaryotes. Its discovery in 1958 by Aaron B. Lerner and colleagues stemmed from the isolation of a substance from the pineal gland of cow ...
, a sleep regulator, is inhibited by light and permitted by darkness as registered by
photosensitive ganglion cell
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), also called photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGC), or melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells (mRGCs), are a type of neuron in the retina of the mammalian eye. The presence ...
s in the
retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
. To some degree, the reverse is true for
serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
, which has been linked to mood disorders. Hence, for the purpose of manipulating melatonin levels or timing, light boxes providing very specific types of artificial lighting, illumination to the retina of the eye are effective.
Light therapy uses either a light box which emits up to 10,000 lux of light at a specified distance, much brighter than a customary lamp, or a lower intensity of specific wavelengths of light from the blue (460 nanometer, nm) to the green (525 nm) areas of the visible spectrum. A 1995 study showed that green light therapy at doses of 350 lux produces melatonin suppression and phase shifts equivalent to 10,000 lux white light therapy, but another study published in May 2010 suggests that the blue light often used for SAD treatment should perhaps be replaced by green or white illumination, because of a possible involvement of the cone cell, cones in melatonin suppression.
Risks and complications
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
light causes progressive damage to human skin and erythema even from small doses.
This is mediated by genetic damage, collagen damage, as well as destruction of vitamin A and vitamin C in the skin and free radical generation. Ultraviolet light is also known to be a factor in formation of cataracts. Ultraviolet radiation exposure is strongly linked to incidence of
skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the Human skin, skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells (biology), cells that have the ability to invade or metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. It occurs when skin cells grow ...
.
Visible light
Optical radiation of any kind with enough intensity can cause damage to the eyes and skin including photoconjunctivitis and photokeratitis. Researchers have questioned whether limiting blue light exposure could reduce the risk of Macular degeneration#Age-related macular degeneration, age-related macular degeneration. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, there is no scientific evidence showing that exposure to blue light emitting devices result in eye damage. According to Harriet Hall, blue light exposure is reported to suppress the production of
melatonin
Melatonin, an indoleamine, is a natural compound produced by various organisms, including bacteria and eukaryotes. Its discovery in 1958 by Aaron B. Lerner and colleagues stemmed from the isolation of a substance from the pineal gland of cow ...
, which affects our body's
circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
and can decrease sleep quality. It is reported that, in reproductive-age females, bright light therapy may activate the production of reproductive hormones, such as luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and estradiol
Modern phototherapy lamps used in the treatment of seasonal affective disorder and sleep disorders either filter out or do not emit ultraviolet light and are considered safe and effective for the intended purpose, as long as photosensitizing drugs are not being taken at the same time and in the absence of any existing eye conditions. Light therapy is a mood altering treatment, and just as with drug treatments, there is a possibility of triggering a manic state from a depressive state, causing anxiety disorder, anxiety and other side effects. While these side effects are usually controllable, it is recommended that patients undertake light therapy under the supervision of an experienced clinician, rather than attempting to self-medicate.
Contraindications to light therapy for seasonal affective disorder include conditions that might render the eyes more vulnerable to phototoxicity, tendency toward mania, photosensitive skin conditions, or use of a photosensitizing herb (such as St. John's wort) or medication. Patients with porphyria should avoid most forms of light therapy. Patients on certain drugs such as methotrexate or chloroquine should use caution with light therapy as there is a chance that these drugs could cause porphyria.
Side effects of light therapy for sleep phase disorders include jumpiness or jitteriness, headache, eye irritation and nausea. Some non-depressive physical complaints, such as poor vision and skin rash or irritation, may improve with light therapy.
History

Many ancient cultures practiced various forms of heliotherapy, including people of Ancient Greece, Ancient Egypt, and Ancient Rome. The Inca, Assyrian and early Germanic peoples also worshipped the sun as a health bringing deity. Indian medical literature dating to 1500 BCE describes a treatment combining herbs with natural sunlight to treat non-pigmented skin areas. Buddhist literature from about 200 CE and 10th-century Chinese documents make similar references.
The Faroe Islanders, Faroese physician Niels Ryberg Finsen, Niels Finsen is believed to be the father of modern phototherapy. He developed the first artificial light source for this purpose. Finsen used short wavelength light to treat lupus vulgaris, a skin infection caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. He thought that the beneficial effect was due to ultraviolet light killing the bacteria, but recent studies showed that his lens and filter system did not allow such short wavelengths to pass through, leading instead to the conclusion that light of approximately 400 nanometers generated reactive oxygen that would kill the bacteria. Finsen also used red light to treat smallpox lesions. He received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1903. Scientific evidence for some of his treatments is lacking, and later eradication of smallpox and development of antibiotics for tuberculosis rendered light therapy obsolete for these diseases. In the early 20th-century light therapy was promoted by Auguste Rollier and John Harvey Kellogg. In 1924, Caleb Saleeby founded The Sunlight League.
From the late nineteenth century until the early 1930s, light therapy was considered an effective and mainstream medical therapy in the UK for conditions such as varicose ulcer, 'sickly children' and a wide range of other conditions. Controlled trials by the medical scientist Dora Colebrook, supported by the Medical Research Council, indicated that light therapy was not effective for such a wide range of conditions.
Controversy
Red light therapy involves exposure to low levels of red light or near-infrared light, typically through lamps or masks.
It is promoted for various skin-related benefits, including improved appearance and reduced signed of aging.
However, there is currently insufficient scientific evidence to support many of these claims.
There has been some indication that it may reduce inflammation associated with conditions such as acne or rosacea, but evidence supporting its anti-aging effects remain limited.
Most existing research has focused on in-office treatments, while at-home devices are generally less powerful and precise, which may lead to inconsistent results.
It is generally considered safe, however if misused red light therapy could cause eye or skin damage.
See also
* Blood irradiation therapy
* Chromotherapy
* Crib A'Glow
* Free-running sleep
* Low level laser therapy
* Neuromodulation (medicine), Neuromodulation
* Neurostimulation
* Neurotechnology
*
Photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy involving light and a photosensitizing chemical substance used in conjunction with molecular oxygen to elicit cell death ( phototoxicity).
PDT is used in treating acne, wet age-related macula ...
* Sun tanning
* UV-B lamps
References
External links
Our Friend, the Sun: Images of Light Therapeutics from the Osler Library Collection, c. 1901–1944 Digital exhibition by the Osler Library of the History of Medicine, McGill University
{{Authority control
Light therapy,
Psoriasis
Circadian rhythm
Acne treatments
Treatment of bipolar disorder
Neonatology
Psychotherapy by type

 Light therapy treatments for the skin usually involve exposure to
Light therapy treatments for the skin usually involve exposure to  Light therapy is used to treat cases of
Light therapy is used to treat cases of  The production of the hormone
The production of the hormone  Many ancient cultures practiced various forms of heliotherapy, including people of Ancient Greece, Ancient Egypt, and Ancient Rome. The Inca, Assyrian and early Germanic peoples also worshipped the sun as a health bringing deity. Indian medical literature dating to 1500 BCE describes a treatment combining herbs with natural sunlight to treat non-pigmented skin areas. Buddhist literature from about 200 CE and 10th-century Chinese documents make similar references.
The Faroe Islanders, Faroese physician Niels Ryberg Finsen, Niels Finsen is believed to be the father of modern phototherapy. He developed the first artificial light source for this purpose. Finsen used short wavelength light to treat lupus vulgaris, a skin infection caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. He thought that the beneficial effect was due to ultraviolet light killing the bacteria, but recent studies showed that his lens and filter system did not allow such short wavelengths to pass through, leading instead to the conclusion that light of approximately 400 nanometers generated reactive oxygen that would kill the bacteria. Finsen also used red light to treat smallpox lesions. He received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1903. Scientific evidence for some of his treatments is lacking, and later eradication of smallpox and development of antibiotics for tuberculosis rendered light therapy obsolete for these diseases. In the early 20th-century light therapy was promoted by Auguste Rollier and John Harvey Kellogg. In 1924, Caleb Saleeby founded The Sunlight League.
From the late nineteenth century until the early 1930s, light therapy was considered an effective and mainstream medical therapy in the UK for conditions such as varicose ulcer, 'sickly children' and a wide range of other conditions. Controlled trials by the medical scientist Dora Colebrook, supported by the Medical Research Council, indicated that light therapy was not effective for such a wide range of conditions.
Many ancient cultures practiced various forms of heliotherapy, including people of Ancient Greece, Ancient Egypt, and Ancient Rome. The Inca, Assyrian and early Germanic peoples also worshipped the sun as a health bringing deity. Indian medical literature dating to 1500 BCE describes a treatment combining herbs with natural sunlight to treat non-pigmented skin areas. Buddhist literature from about 200 CE and 10th-century Chinese documents make similar references.
The Faroe Islanders, Faroese physician Niels Ryberg Finsen, Niels Finsen is believed to be the father of modern phototherapy. He developed the first artificial light source for this purpose. Finsen used short wavelength light to treat lupus vulgaris, a skin infection caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. He thought that the beneficial effect was due to ultraviolet light killing the bacteria, but recent studies showed that his lens and filter system did not allow such short wavelengths to pass through, leading instead to the conclusion that light of approximately 400 nanometers generated reactive oxygen that would kill the bacteria. Finsen also used red light to treat smallpox lesions. He received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1903. Scientific evidence for some of his treatments is lacking, and later eradication of smallpox and development of antibiotics for tuberculosis rendered light therapy obsolete for these diseases. In the early 20th-century light therapy was promoted by Auguste Rollier and John Harvey Kellogg. In 1924, Caleb Saleeby founded The Sunlight League.
From the late nineteenth century until the early 1930s, light therapy was considered an effective and mainstream medical therapy in the UK for conditions such as varicose ulcer, 'sickly children' and a wide range of other conditions. Controlled trials by the medical scientist Dora Colebrook, supported by the Medical Research Council, indicated that light therapy was not effective for such a wide range of conditions.