Phosphorylation Cascade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A phosphorylation cascade is a sequence of signaling pathway events where one enzyme phosphorylates another, causing a chain reaction leading to the 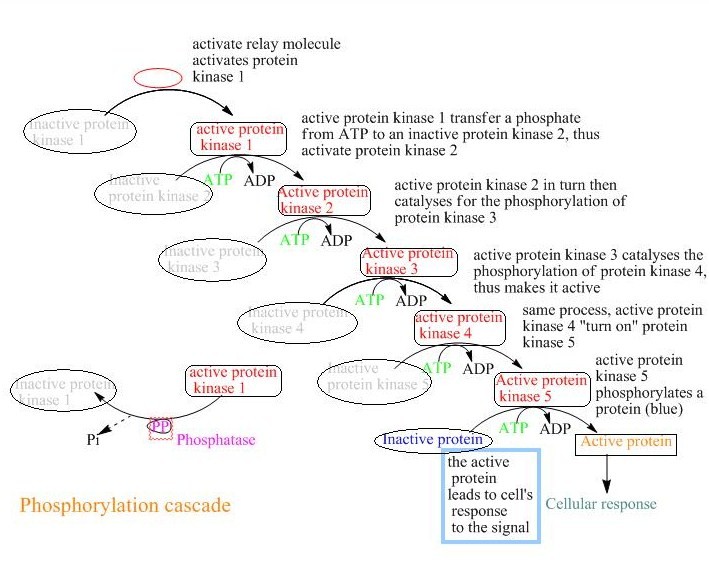 A signaling pathway begins at the cell surface where a hormone or protein binds to a receptor at the
A signaling pathway begins at the cell surface where a hormone or protein binds to a receptor at the
phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, ...
of thousands of proteins. This can be seen in signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular ...
of hormone messages.
 A signaling pathway begins at the cell surface where a hormone or protein binds to a receptor at the
A signaling pathway begins at the cell surface where a hormone or protein binds to a receptor at the Extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide struc ...
. The interactions between the molecule and receptor cause a Conformational change
In biochemistry, a conformational change is a change in the shape of a macromolecule, often induced by environmental factors.
A macromolecule is usually flexible and dynamic. Its shape can change in response to changes in its environment or oth ...
at the receptor, which activates multiple enzymes or proteins. These enzymes activate secondary messengers, which leads to the phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, ...
of thousands of proteins. The end product of a Phosphorylation cascade is the changes occurring inside the cell.
One best example that explains this phenomenon is mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase or ERK kinase. MAP kinase not only plays an important function during growth of cell in the M phase phosphorylation cascade but also plays an important role during the sequence of signaling pathway. In order to regulate its functions so it does not cause chaos, it can only be active when both tyrosine and threonine/serine residues are phosphorylated.
References
* Cell biology {{biochem-stub