Paul Jaeschke on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
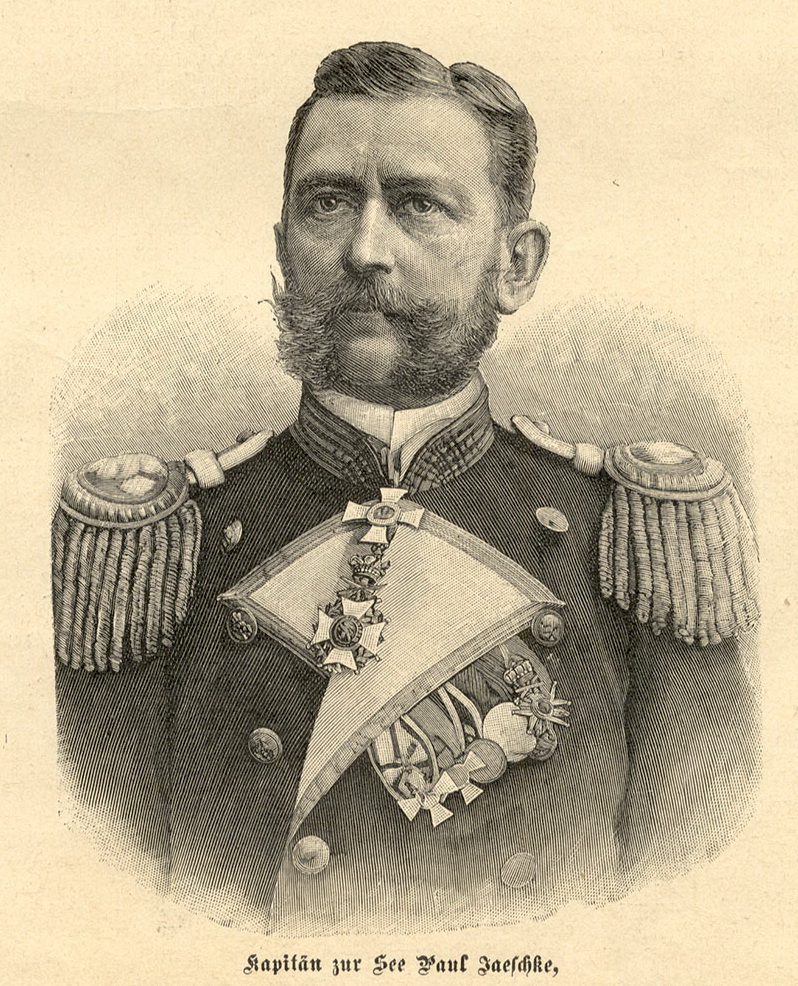 Carl Otto Ferdinand Paul Jaeschke (4 August 1851 – 27 January 1901) was a German naval officer and governor of the German-leased
Carl Otto Ferdinand Paul Jaeschke (4 August 1851 – 27 January 1901) was a German naval officer and governor of the German-leased
Big Swords, Jesuits, and Bondelswarts: Wilhelmine Imperialism, Overseas Resistance, and German Political Catholicism, 1897–1906
{{DEFAULTSORT:Jaeschke, Paul Imperial German Navy personnel 1851 births 1901 deaths Deaths from typhoid fever
 Carl Otto Ferdinand Paul Jaeschke (4 August 1851 – 27 January 1901) was a German naval officer and governor of the German-leased
Carl Otto Ferdinand Paul Jaeschke (4 August 1851 – 27 January 1901) was a German naval officer and governor of the German-leased Kiautschou Bay concession
The Kiautschou Bay Leased Territory was a German colonial empire, German leased territory in Qing dynasty, Imperial and Republic of China (1912–1949), Early Republican China from 1898 to 1914. Covering an area of , it centered on Kiautschou ...
from 19 February 1899 to 27 January 1901.
Biography
Jaeschke was born the son of a banker in Breslau. When he passed a one-year exam, he entered on 26 April 1868, as a midshipman in theNorth German Federal Navy
The North German Federal Navy (''Norddeutsche Bundesmarine'' or ''Marine des Norddeutschen Bundes''), was the Navy of the North German Confederation, formed out of the Prussian Navy in 1867. It was eventually succeeded by the Imperial German Navy ...
. On 18 November 1875, Jaeschke was promoted to lieutenant and subsequently he went through various land and sea uses, which also included foreign uses e.g. in 1875 with the ''Augusta'' on the foreign station for the east coast of North America and the West Indies area.
On 16 April 1881, Jaeschke was promoted to and speaker in the inspection of the torpedo. From 1886 to 1888, he was commander of the gunboat on the East Asian foreign station. On 15 November 1888, he was promoted to corvette captain and in the same year commander of the torpedo department in Kiel
Kiel ( ; ) is the capital and most populous city in the northern Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein. With a population of around 250,000, it is Germany's largest city on the Baltic Sea. It is located on the Kieler Förde inlet of the Ba ...
. In 1895, he became captain at sea
Captain is the name most often given in English-speaking navies to the rank corresponding to command of the largest ships. The rank is equal to the army rank of colonel and air force rank of group captain.
Equivalent ranks worldwide include ...
and assigned to command .
In May 1896, Jaeschke was ordered back to Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
to take over the Foreign Department in the German Imperial Naval High Command
The German Imperial Naval High Command () was an office of the German Empire which existed from 1 April 1889 until 14 March 1899 to command the German Imperial Navy. A similarly named office existed in the Prussian Navy and the ''Kriegsmarine'' o ...
. On 10 October 1898, Jaeschke was appointed by Alfred von Tirpitz
Alfred Peter Friedrich von Tirpitz (; born Alfred Peter Friedrich Tirpitz; 19 March 1849 – 6 March 1930) was a German grand admiral and State Secretary of the German Imperial Naval Office, the powerful administrative branch of the German Imperi ...
as governor of the German-leased Kiautschou Bay concession
The Kiautschou Bay Leased Territory was a German colonial empire, German leased territory in Qing dynasty, Imperial and Republic of China (1912–1949), Early Republican China from 1898 to 1914. Covering an area of , it centered on Kiautschou ...
, but only arrived at Tsingtau
Qingdao, Mandarin: , (Qingdao Mandarin: t͡ɕʰiŋ˧˩ tɒ˥) is a prefecture-level city in the eastern Shandong Province of China. Located on China's Yellow Sea coast, Qingdao was long an important fortress. In 1897, the city was ceded to Ger ...
on 18 February 1899.
Jaeschke died on 27 January 1901, of typhoid fever
Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella enterica'' serotype Typhi bacteria, also called ''Salmonella'' Typhi. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often th ...
.
References
External links
Big Swords, Jesuits, and Bondelswarts: Wilhelmine Imperialism, Overseas Resistance, and German Political Catholicism, 1897–1906
{{DEFAULTSORT:Jaeschke, Paul Imperial German Navy personnel 1851 births 1901 deaths Deaths from typhoid fever