Paleoseismological on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
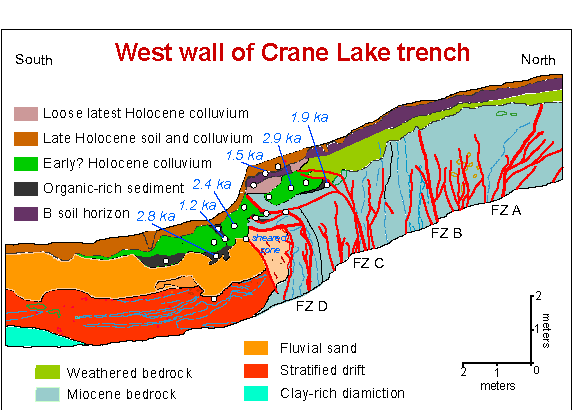

 Paleoseismology is the study of ancient
Paleoseismology is the study of ancient


Paleoseismicity.org – Online platform for paleoseismologists
TERPRO Commission, International Union for Quaternary Research {{Authority control Historical geology Fields of seismology


 Paleoseismology is the study of ancient
Paleoseismology is the study of ancient earthquakes
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they c ...
using geologic evidence, such as geologic
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth s ...
sediments
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
and rocks
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's ...
. It is used to supplement seismic monitoring
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic w ...
to calculate seismic hazard
A seismic hazard is the probability that an earthquake will occur in a given geographic area, within a given window of time, and with ground motion intensity exceeding a given threshold. With a hazard thus estimated, risk can be assessed and inc ...
. Paleoseismology is usually restricted to geologic regimes that have undergone continuous sediment creation for the last few thousand years, such as swamps
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
, lakes
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from t ...
, river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
beds and shorelines.
Methodology
Procedure
Paleoseismology studies start with finding an active fault. The definition of an active fault can vary, but it is usually based on having tectonically deformed quaternary-age materials that can potentially cause earthquakes. Satellite imaging with high resolution is often used to find such faults, but because of its resolution limitations, there are also other methods such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR), aeromagnetic surveys, and seismic reflection surveys. Faults can be dated in absolute terms usingradiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
.
Paleoseismic evidence
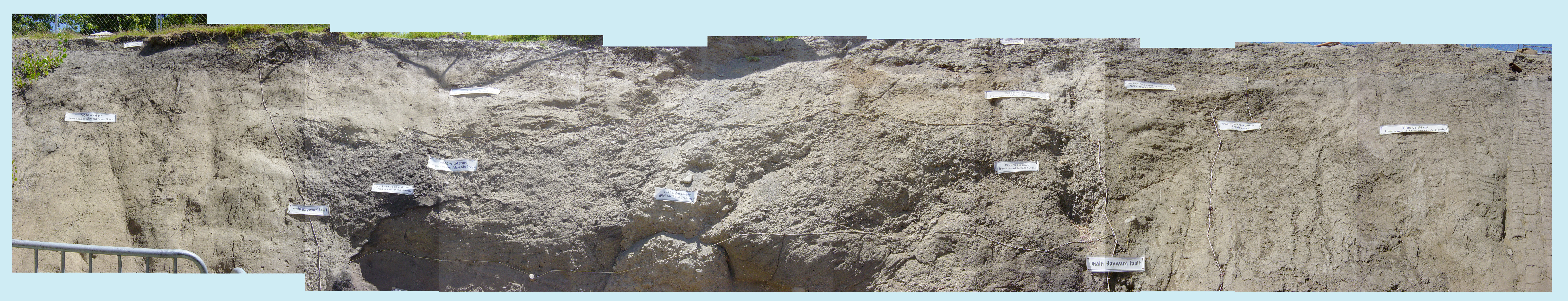
Evidence of paleoearthquakes is classified into three levels: primary or secondary, location, and timing. For level 1, primary evidence is tectonic deformation, while secondary evidence is effects of this such as sediment deposition and elevation changes. However, distinguishing these is not always clear. Level 2 is the location, which is on or off fault. Level 3 is timing, which is either instantaneous (coseismic, or the same time as the earthquake) or delayed (postseismic, or after the earthquake). Types of evidence to identify paleoearthquakes were usually first identified as evidence after historical earthquakes. Paleoseismic investigations are commonly performed through trenching studies. A trench is dug, and geologists record the attributes of the rock layers. On-fault evidence includes warping and disconformity,angular unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval ...
, fracturing, fissures
A fissure is a long, narrow crack opening along the surface of Earth. The term is derived from the Latin word , which means 'cleft' or 'crack'. Fissures emerge in Earth's crust, on ice sheets and glaciers, and on volcanoes.
Ground fissure
A ...
, and colluvial wedges. Off-fault evidence includes liquefaction
In materials science, liquefaction is a process that generates a liquid from a solid or a gas or that generates a non-liquid phase which behaves in accordance with fluid dynamics.
It occurs both naturally and artificially. As an example of t ...
of sand, tsunami deposits, turbidite
A turbidite is the geologic Deposition (geology), deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean.
Sequencing
...
, and marine terrace uplift.
Studies and findings
Using paleoseismology, it is now known that nearly all movement of the fault takes place with large earthquakes. All seismic events with amoment magnitude
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mwg, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. was defined in a 1979 paper ...
of over 8 leave some trace in the sedimentation record.
Another example involves the megathrust earthquakes
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthq ...
of the Pacific Northwest. It was thought that seismic hazard in the region was low because relatively few modern earthquakes have been recorded. However, paleoseismology studies showed evidence of extremely large earthquakes (the most recent being in 1700
As of March 1 ( O.S. February 19), where the Julian calendar acknowledged a leap day and the Gregorian calendar did not, the Julian calendar fell one day further behind, bringing the difference to 11 days until February 28 ( O.S. February 17) ...
), along with historical tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
records. In effect, paleoseismology found that the subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second p ...
zone under British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and far northern California, is hazardous in the long term and can generating coastal tsunamis of several hundred feet in height at the coast. Periodically, a slip will occur, which causes the coastal portion to reduce in elevation and thrust toward the west, leading to tsunamis in the central and eastern north Pacific Ocean (with several hours of warning) and a reflux of water toward the coastal shore.

See also
*Archaeoseismology
Archaeoseismology is the study of ancient earthquakes by analysis of archaeological sites before Robert Mallet's protomodern seismology in the mid-19th century. Such analyses reveal information about seismic events that was not historically recorde ...
* Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
* Earthquake magnitude
Seismic magnitude scales are used to describe the overall strength or "size" of an earthquake. These are distinguished from seismic intensity scales that categorize the intensity or severity of ground shaking (quaking) caused by an earthquake at ...
* Fault
* Historical earthquakes
Historical earthquakes is a list of significant earthquakes known to have occurred prior to the early 20th century. As the events listed here occurred before routine instrumental recordings, they rely mainly on the analysis of written sources, ...
* Paleotempestology
Paleotempestology is the study of past tropical cyclone activity by means of geological proxies as well as historical documentary records. The term was coined by American meteorologist Kerry Emanuel.
The usual approach in paleotempestology is ...
* Paleotsunami
A paleotsunami is a tsunami that occurs prior to written history where there are no documented observations. Paleotsunamis are evidenced by modern technology and scientific research. One of the largest was a megatsunami resulting from the Chicxul ...
* Seismite
{{Earthquakes
Seismites are sedimentary beds and structures deformed by seismic shaking. The German paleontologist Adolf Seilacher first used the term in 1969 to describe earthquake-deformed layers. Today, the term is applied to both sedimentar ...
* Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic ...
* Tectonics
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons.
These processes ...
* Tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
* Unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval ...
References
Sources
*James P. McCalpin (2009) Paleoseismology (2nd Edition), Academic Press, , *James P. McCalpin (1996) Paleoseismology, Elsevier,External links
Paleoseismicity.org – Online platform for paleoseismologists
TERPRO Commission, International Union for Quaternary Research {{Authority control Historical geology Fields of seismology