Pacific–North American Teleconnection Pattern on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Pacific–North American teleconnection pattern (PNA) is a large-scale weather pattern with two modes, denoted positive and negative, and which relates the
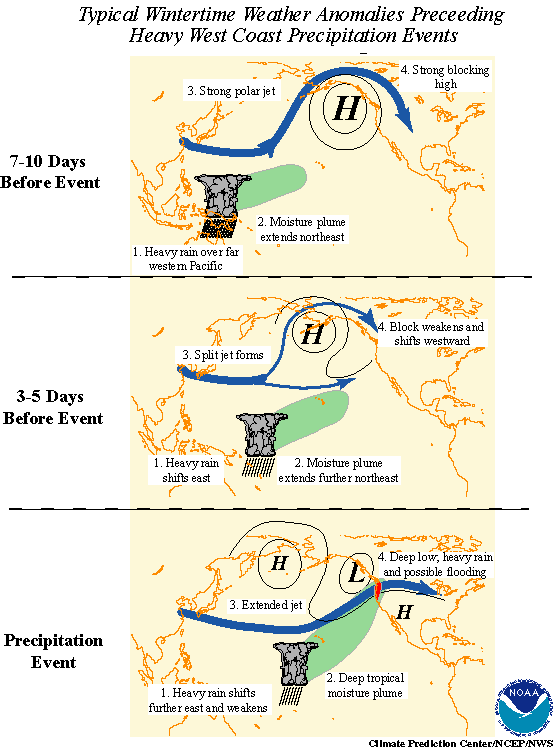 Although the PNA is usually defined based on anomalies relative to monthly or seasonal averages, the PNA often varies at weekly timescales. However, as a pattern of internal climate variability, the state of the PNA occasionally changes without a clear and identifiable cause. This reduces the predictability of the PNA and can complicate long-range seasonal weather forecasts. Predictability of the PNA is limited to roughly within 10 days. The PNA is associated with changes in the intensity and positioning of the East Asian
Although the PNA is usually defined based on anomalies relative to monthly or seasonal averages, the PNA often varies at weekly timescales. However, as a pattern of internal climate variability, the state of the PNA occasionally changes without a clear and identifiable cause. This reduces the predictability of the PNA and can complicate long-range seasonal weather forecasts. Predictability of the PNA is limited to roughly within 10 days. The PNA is associated with changes in the intensity and positioning of the East Asian
atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of Atmosphere of Earth, air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies fro ...
pattern over the North Pacific Ocean
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' ...
with the one over the North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
n continent. It is the second leading mode of natural climate variability in the higher latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere (behind the Arctic Oscillation
The Arctic oscillation (AO) or Northern Annular Mode/Northern Hemisphere Annular Mode (NAM) is a weather phenomenon at the Arctic pole north of 55 degrees latitude. It is an important mode of climate variability for the Northern Hemisphere. The s ...
or North Atlantic Oscillation) and can be diagnosed using the arrangement of anomalous geopotential height
Geopotential height, also known as geopotential altitude or geopotential elevation, is a vertical coordinate (with dimension of length) representing the work involved in lifting one unit of mass over one unit of length through a hypothetical spac ...
s or air pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The Standard atmosphere (unit), standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , whi ...
s over the North Pacific and North America.
On average, the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
over North America features a ridge
A ridge is a long, narrow, elevated geomorphologic landform, structural feature, or a combination of both separated from the surrounding terrain by steep sides. The sides of a ridge slope away from a narrow top, the crest or ridgecrest, wi ...
on the western part of the continent and a trough
Trough may refer to:
In science
* Trough (geology), a long depression less steep than a trench
* Trough (meteorology), an elongated region of low atmospheric pressure
* Trough (physics), the lowest point on a wave
* Trough level (medicine), the l ...
over the eastern part of the continent. The ''positive phase'' of the PNA teleconnection is identified by anomalously low geopotential heights south of the Aleutian Islands and over Southeastern U.S. straddling high geopotential heights over the North Pacific from Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
to the U.S. Intermountain West
The Intermountain West, or Intermountain Region, is a geographic and geological region of the Western United States. It is located between the Rocky Mountain Front on the east and the Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada on the west.
Topography
...
. This represents an amplification of the long-term average conditions. The ''negative phase'' features the opposite pattern over the same regions, with above-average geopotential heights straddling below-average heights. This represents a damping of the long-term average conditions.
Indices
The PNA is typically quantified using an index usinggeopotential height
Geopotential height, also known as geopotential altitude or geopotential elevation, is a vertical coordinate (with dimension of length) representing the work involved in lifting one unit of mass over one unit of length through a hypothetical spac ...
anomalies at the 500-hPa
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI). It is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is an S ...
pressure level, with positive and negative PNA phases based on the sign
A sign is an object, quality, event, or entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to its object—for instance, thunder is a sign of storm, or me ...
of the index. Wallace and Gutzler (1981) expressed the PNA index as the average of normalized height anomalies at the four centers of action most relevant to the PNA,
:
where describes the normalized 500-hPa height anomaly as a function of location. The subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Ge ...
center at (20°N, 160°W) can be excluded, though the difference between the resulting index and the index is small.
Applying rotated principal component analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a linear dimensionality reduction technique with applications in exploratory data analysis, visualization and data preprocessing.
The data is linearly transformed onto a new coordinate system such that th ...
to the 500-hPa geopotential height anomaly field in the Northern Hemisphere can also provide a quantification of the PNA (), with the canonical PNA pattern emerging as the second-leading principal component. This methodology is used by the U.S. Climate Prediction Center
The Climate Prediction Center (CPC) is a United States federal agency that is one of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction, which are a part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service. CPC is hea ...
to compute its PNA index.
Dynamics
 Although the PNA is usually defined based on anomalies relative to monthly or seasonal averages, the PNA often varies at weekly timescales. However, as a pattern of internal climate variability, the state of the PNA occasionally changes without a clear and identifiable cause. This reduces the predictability of the PNA and can complicate long-range seasonal weather forecasts. Predictability of the PNA is limited to roughly within 10 days. The PNA is associated with changes in the intensity and positioning of the East Asian
Although the PNA is usually defined based on anomalies relative to monthly or seasonal averages, the PNA often varies at weekly timescales. However, as a pattern of internal climate variability, the state of the PNA occasionally changes without a clear and identifiable cause. This reduces the predictability of the PNA and can complicate long-range seasonal weather forecasts. Predictability of the PNA is limited to roughly within 10 days. The PNA is associated with changes in the intensity and positioning of the East Asian jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow thermal wind, air currents in the Earth's Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere.
The main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds, flowing west to east around the gl ...
. During the positive phase of the PNA, the East Asian jet intensifies and extends eastward across the North Pacific towards the western U.S. During the negative phase, the jet stream is retracted over East Asia, producing a blocking weather pattern over the North Pacific. Some of the energy that drives the PNA originates from the barotropic instability produced by the jet, potentially exciting Rossby wave
Rossby waves, also known as planetary waves, are a type of inertial wave naturally occurring in rotating fluids. They were first identified by Sweden-born American meteorologist Carl-Gustaf Arvid Rossby in the Earth's atmosphere in 1939. They ...
s. Shifts in the jet stream can induce changes in air pressure distributions both near and downstream of the jet.
Storms over the tropical Pacific and Indian oceans may play a role in exciting the positive and negative phases of the PNA by influencing the East Asian jet. Tropical convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
can induce a low-amplitude PNA pattern that amplifies to its peak strength after 8–12 days. Atmospheric eddies and Rossby waves can further intensify the PNA pattern. Positive PNA is correlated with increased convective activity over western tropical Pacific and reduced convective activity over the tropical Indian Ocean, while negative PNA is correlated with the opposite convective anomalies. The Rossby waves associated with positive PNA tend to track eastward and undergo cyclonic wavebreaking, while those associated with negative PNA tend to track equatorward towards the subtropics
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones immediately to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately ...
and break anticyclonically; the wavebreaking behavior of the Rossby waves is determined by the meridional gradient of potential vorticity
In fluid mechanics, potential vorticity (PV) is a quantity which is proportional to the dot product of vorticity and stratification. This quantity, following a parcel of air or water, can only be changed by diabatic or frictional processes. I ...
and the magnitude and orientation of wind shear
Wind shear (; also written windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical ...
, which in turn are modulated by variations in the East Asian jet stream. In either case, positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects ...
s associated with the wavebreaking sustain amplified PNA patterns.
Other teleconnections can modulate the PNA by modifying the jet stream. The El Niño–Southern Oscillation
El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a global climate phenomenon that emerges from variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical Pacific Ocean. Those variations have an irregular pattern but do have some semblance of cyc ...
(ENSO) impacts the behavior of PNA, with the positive phase of the PNA more commonly associated with El Niño
EL, El or el may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional entities
* El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit
* Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things''
* El, fami ...
and the negative phase more commonly associated with La Niña
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second most populous city in the United States of America.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
*La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
*"L.A.", a song by Elliott Smit ...
. This relationship is most evident at seasonal timescales, making the seasonal PNA more predictable than the monthly PNA. The negative phase is also favored when the Madden–Julian oscillation (MJO) enhances convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
over the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
and Maritime Continent; the positive phase is favored when the MJO enhances convection closer to the central Pacific. The MJO's influence on the PNA arises from the interaction between the enhanced convection and the Pacific jet stream.
Effects on weather
The regional variations in weather associated with the PNA are generally the result of the PNA's influence on the East Asian jet. The temperature pattern associated with the PNA follows the pattern of anomalous ridging and troughing. The positive phase of the PNA is correlated with above-average temperatures over the U.S. Pacific Coast andWestern Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West, or Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a list of regions of Canada, Canadian region that includes the four western provinces and t ...
. During the positive phase, an anomalously strong ridge of high pressure over Canada reduces the frequency of cold air outbreaks over western Northern America
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America, as well as the northernmost region in the Americas. The boundaries may be drawn significantly differently depending on the source of the definition. In one definition, it lies dir ...
. Below-average temperatures over the South-Central U.S., Southeastern U.S., and U.S. East Coast are associated with the positive phase due to the presence of anomalously low pressure. The influence of the PNA on surface temperatures over North America is reduced during the summer.
Correlations between precipitation patterns and the PNA are weaker than temperature patterns, but are nonetheless evident. Anomalously high precipitation over the Gulf of Alaska
The Gulf of Alaska ( Tlingit: ''Yéil T'ooch’'') is an arm of the Pacific Ocean defined by the curve of the southern coast of Alaska, stretching from the Alaska Peninsula and Kodiak Island in the west to the Alexander Archipelago in the ...
and Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (PNW; ) is a geographic region in Western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common ...
accompany the positive phase, along with below-average precipitation totals over the Pacific Northwest, Northern Rocky Mountains, and Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
and Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
river valleys. The negative PNA phase exhibits the opposite departures from average.
See also
* Teleconnection * Arctic dipole anomaly *Kuroshio Current
The , also known as the Black Current or is a north-flowing, warm ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean basin. It was named for the deep blue appearance of its waters. Similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, the Ku ...
* North Pacific Gyre
* Pacific Decadal Oscillation
The Pacific decadal oscillation (PDO) is a robust, recurring pattern of ocean-atmosphere climate variability centered over the mid-latitude Pacific basin. The PDO is detected as warm or cool surface waters in the Pacific Ocean, north of 20°N. O ...
* Pineapple Express
* Walker circulation
The Walker circulation, also known as the Walker cell, is a conceptual model of the air flow in the tropics in the lower atmosphere (troposphere). According to this model, parcels of air follow a closed circulation in the zonal and vertical dir ...
References
Sources
* * Regional climate effects Physical oceanography {{climatology-stub