Overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
 As early as 1873, a United States military commission recommended attempting to obtain
As early as 1873, a United States military commission recommended attempting to obtain
 On January 20, 1887, the United States began leasing Pearl Harbor. Shortly afterwards, a group of mostly non-Hawaiians calling themselves the Hawaiian Patriotic League began the Rebellion of 1887. They drafted their own constitution on July 6, 1887. The new constitution was written by Lorrin Thurston, the Hawaiian Minister of the Interior who used the Hawaiian militia as threat against Kalākaua. Kalākaua was forced under threat of assassination to dismiss his cabinet ministers and sign a new constitution which greatly lessened his power. It would become known as the " Bayonet Constitution" because of the threat of force used.
The Bayonet Constitution allowed the monarch to appoint cabinet ministers, but had stripped him of the power to dismiss them without approval from the Legislature. Eligibility to vote for the House of Nobles was also altered, stipulating that both candidates and voters were now required to own property valuing at least three thousand dollars, or have an annual income of no less than six hundred dollars. This resulted in disenfranchising two-thirds of the native Hawaiians as well as other
On January 20, 1887, the United States began leasing Pearl Harbor. Shortly afterwards, a group of mostly non-Hawaiians calling themselves the Hawaiian Patriotic League began the Rebellion of 1887. They drafted their own constitution on July 6, 1887. The new constitution was written by Lorrin Thurston, the Hawaiian Minister of the Interior who used the Hawaiian militia as threat against Kalākaua. Kalākaua was forced under threat of assassination to dismiss his cabinet ministers and sign a new constitution which greatly lessened his power. It would become known as the " Bayonet Constitution" because of the threat of force used.
The Bayonet Constitution allowed the monarch to appoint cabinet ministers, but had stripped him of the power to dismiss them without approval from the Legislature. Eligibility to vote for the House of Nobles was also altered, stipulating that both candidates and voters were now required to own property valuing at least three thousand dollars, or have an annual income of no less than six hundred dollars. This resulted in disenfranchising two-thirds of the native Hawaiians as well as other
 The Wilcox rebellion of 1888 was a plot to overthrow King
The Wilcox rebellion of 1888 was a plot to overthrow King
 A provisional government was set up with the strong support of the Honolulu Rifles, a militia group which had defended the system of government promulgated by the Bayonet Constitution against the Wilcox rebellion of 1889.
The Queen's statement yielding authority, on January 17, 1893, protested against the overthrow:
On December 19, 1898, the queen would amend the declaration with the ''"Memorial of Queen Liliuokalani in relation to the Crown lands of Hawaii"'', further protesting the overthrow and loss of property.
A provisional government was set up with the strong support of the Honolulu Rifles, a militia group which had defended the system of government promulgated by the Bayonet Constitution against the Wilcox rebellion of 1889.
The Queen's statement yielding authority, on January 17, 1893, protested against the overthrow:
On December 19, 1898, the queen would amend the declaration with the ''"Memorial of Queen Liliuokalani in relation to the Crown lands of Hawaii"'', further protesting the overthrow and loss of property.
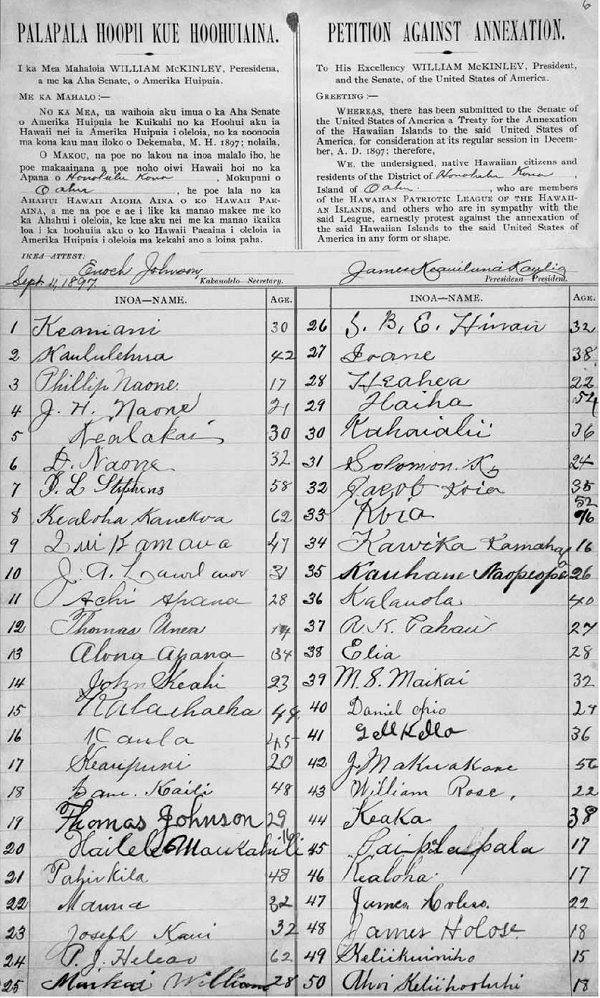 The Committee of Safety declared Sanford Dole president of the new Provisional Government of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi on January 17, 1893, only removing the queen, her cabinet, and her marshal from office. On July 4, 1894, the Republic of Hawaiʻi was proclaimed. Dole was president of both governments. As a republic, it was the government's intention to campaign for Hawaii's annexation to the United States. The rationale behind the annexation of Hawaii included a strong economic component—Hawaiian goods and services which were exported to the mainland would not be subjected to United States tariffs, and the United States and Hawaii would both benefit from each other's domestic bounties, if Hawaii was part of the United States.
In 1897,
The Committee of Safety declared Sanford Dole president of the new Provisional Government of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi on January 17, 1893, only removing the queen, her cabinet, and her marshal from office. On July 4, 1894, the Republic of Hawaiʻi was proclaimed. Dole was president of both governments. As a republic, it was the government's intention to campaign for Hawaii's annexation to the United States. The rationale behind the annexation of Hawaii included a strong economic component—Hawaiian goods and services which were exported to the mainland would not be subjected to United States tariffs, and the United States and Hawaii would both benefit from each other's domestic bounties, if Hawaii was part of the United States.
In 1897,
morganreport.org
Online images and transcriptions of the entire 1894 Morgan Report * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Hawaiian Kingdom, overthrow of the 1890s coups d'état and coup attempts 1893 in Hawaii Battles and conflicts without fatalities Conflicts in 1893 History of United States expansionism January 1893 United States Marine Corps in the 18th and 19th centuries United States involvement in regime change American imperialism
Hawaiian Kingdom
The Hawaiian Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi ( Hawaiian: ɛ ɐwˈpuni həˈvɐjʔi, was an archipelagic country from 1795 to 1893, which eventually encompassed all of the inhabited Hawaiian Islands. It was established in 1795 w ...
was overthrown in a ''coup d'état
A coup d'état (; ; ), or simply a coup
, is typically an illegal and overt attempt by a military organization or other government elites to unseat an incumbent leadership. A self-coup is said to take place when a leader, having come to powe ...
'' against Queen Liliʻuokalani
Queen Liliʻuokalani (; Lydia Liliʻu Loloku Walania Kamakaʻeha; September 2, 1838 – November 11, 1917) was the only queen regnant and the last sovereign monarch of the Hawaiian Kingdom, ruling from January 29, 1891, until the overthrow of th ...
that took place on January 17, 1893, on the island of Oahu
Oahu (, , sometimes written Oahu) is the third-largest and most populated island of the Hawaiian Islands and of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oahu's southeast coast. The island of Oahu and the uninhabited Northwe ...
. The coup was led by the Committee of Safety, composed of seven foreign residents (five Americans, one Scotsman, and one German) and six Hawaiian Kingdom subjects of American descent in Honolulu
Honolulu ( ; ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, located in the Pacific Ocean. It is the county seat of the Consolidated city-county, consolidated City and County of Honol ...
. The Committee prevailed upon American minister John L. Stevens to call in the US Marines
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines or simply the Marines, is the Marines, maritime land force service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for conducting expedi ...
to protect the national interest
The national interest is a sovereign state's goals and ambitions – be they economic, military, cultural, or otherwise – taken to be the aim of its government.
Etymology
The Italian phrase ''ragione degli stati'' was first used by Giovanni de ...
of the United States of America. The insurgents established the Republic of Hawaii
The Republic of Hawaii (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Lepupalika o Hawaii'' epupəˈlikə o həˈvɐjʔi was a short-lived one-party state in Hawaii, Hawaii between July 4, 1894, when the Provisional Government of Hawaii had Black Week (H ...
, but their ultimate goal was the annexation
Annexation, in international law, is the forcible acquisition and assertion of legal title over one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. In current international law, it is generally held t ...
of the islands to the United States, which occurred in 1898.
The 1993 Apology Resolution
Public Law 103-150, informally known as the Apology Resolution, is a Joint Resolution of the U.S. Congress adopted in 1993 that "acknowledges that the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii occurred with the active participation of agents and citiz ...
by the US Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
concedes that "the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii occurred with the active participation of agents and citizens of the United States and ..the Native Hawaiian people never directly relinquished to the United States their claims to their inherent sovereignty as a people over their national lands, either through the Hawaiian Kingdom or through a plebiscite or referendum". Debates regarding the event play an important role in the Hawaiian sovereignty movement
The Hawaiian sovereignty movement () is a grassroots political and cultural campaign to reestablish an autonomous or independent nation or kingdom of Hawaii out of a desire for sovereignty, self-determination, and self-governance.
Some group ...
.
Background
The Kamehameha dynasty was the reigning monarchy of the Hawaiian Kingdom, beginning with its founding byKamehameha I
Kamehameha I (; Kalani Paiʻea Wohi o Kaleikini Kealiʻikui Kamehameha o ʻIolani i Kaiwikapu kauʻi Ka Liholiho Kūnuiākea; to May 8 or 14, 1819), also known as Kamehameha the Great, was the conqueror and first ruler of the Kingdom of Hawaii ...
in 1795, until the death of Kamehameha V
Kamehameha V (Lota Kapuāiwa Kalanimakua Aliʻiōlani Kalanikupuapaʻīkalaninui; December 11, 1830 – December 11, 1872), reigned as the fifth monarch of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi from 1863 to 1872. His motto was "Onipaʻa": immovable, firm, s ...
in 1872 and Lunalilo
Lunalilo (William Charles Lunalilo; January 31, 1835 – February 3, 1874) was the sixth monarch of the Kingdom of Hawaii from his election on January 8, 1873, until his death a year later.
Born to Kekāuluohi and High Chief Charles Kanaʻin ...
in 1874. On July 6, 1846, US Secretary of State John C. Calhoun, on behalf of President Tyler, formally recognized Hawaii's independence under the reign of Kamehameha III
Kamehameha III (born Kauikeaouli) (March 17, 1814 – December 15, 1854) was the third king of the Kingdom of Hawaii from 1825 to 1854. His full Hawaiian name was Keaweaweula Kīwalaō Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa and then lengthened to Keaweaweula K ...
. As a result of the recognition of Hawaiian independence, the Hawaiian Kingdom entered into treaties with the major nations of the world and established over ninety legations and consulates in multiple seaports and cities. The kingdom would continue for another 21 years until its overthrow in 1893 with the fall of the House of Kalākaua
The House of Kalākaua, or Kalākaua Dynasty, also known as the Keawe-a-Heulu line, was the reigning family of the Hawaiian Kingdom, Kingdom of Hawaiʻi under Kalākaua, King Kalākaua and Liliʻuokalani, Queen Liliʻuokalani. They assumed power ...
.
Sugar reciprocity
Sugar had been a major export from Hawaii since CaptainJames Cook
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 176 ...
arrived in 1778. The first permanent plantation in the islands was on Kauai
Kauai (), anglicized as Kauai ( or ), is one of the main Hawaiian Islands.
It has an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), making it the fourth-largest of the islands and the 21st-largest island in the United States. Kauai lies 73 m ...
in 1835. William Hooper leased 980 acres (4 km2) of land from Kamehameha III
Kamehameha III (born Kauikeaouli) (March 17, 1814 – December 15, 1854) was the third king of the Kingdom of Hawaii from 1825 to 1854. His full Hawaiian name was Keaweaweula Kīwalaō Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa and then lengthened to Keaweaweula K ...
and began growing sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
. Within thirty years there would be plantations on four of the main islands. Sugar had completely altered Hawaii's economy.
The influence of the United States in Hawaiian government began with American-born plantation owners advocating for fair representation in the Kingdom's politics, owing to the significant tax contributions made from the plantations to both the Royal family and national economy. This was driven by missionary religion and the economics of the sugar industry
The sugar industry subsumes the production, Sugar refinery, processing and marketing of sugars (mostly sucrose and fructose). Globally, about 80% of sugar is extracted from sugar cane, grown predominantly in the tropics, and 20% from sugar beet, ...
. Pressure from these foreign-born politicians was being felt by the King and chiefs with demands of land tenure. The 1839 Hawaiian Bill of Rights, also known as the 1839 Constitution of Hawaii, was an attempt by Kamehameha III and his chiefs to guarantee that the Hawaiian people would not lose their tenured land, and provided the groundwork for a free enterprise
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
system. After a five-month occupation by George Paulet in 1843, Kamehameha III relented to the foreign advisors to private land demands with the Great Māhele, distributing the lands as pushed on heavily by the missionaries, including Gerrit P. Judd. During the 1850s, the US import tariff on sugar from Hawaii was much higher than the import tariffs Hawaiians were charging the US, and Kamehameha III sought reciprocity. The monarch wished to lower the tariffs being paid out to the U.S. while still maintaining the Kingdom's sovereignty and making Hawaiian sugar competitive with other foreign markets. In 1854 Kamehameha III proposed a policy of reciprocity between the countries but the proposal died in the U.S. Senate.
 As early as 1873, a United States military commission recommended attempting to obtain
As early as 1873, a United States military commission recommended attempting to obtain Ford Island
Ford Island () is an islet in the center of Pearl Harbor, Oahu, in the U.S. state of Hawaii. It has been known as Rabbit Island, Marín's Island, and Little Goats Island; its native Hawaiian name is ''Mokuumeume''. The island had an area of ...
in exchange for the tax-free importation of sugar to the US. Major General John Schofield, U.S. commander of the military division of the Pacific, and Brevet Brigadier General Burton S. Alexander arrived in Hawaii to ascertain its defensive capabilities. United States control of Hawaii was considered vital for the defense of the west coast of the United States, and they were especially interested in Pu'uloa, Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reci ...
. The sale of one of Hawaii's harbors was proposed by Charles Reed Bishop, a foreigner who had married into the Kamehameha family, had risen in the government to be Hawaiian Minister of Foreign Affairs, and owned a country home near Pu'uloa. He showed the two U.S. officers around the lochs, although his wife, Bernice Pauahi Bishop
Bernice Pauahi Pākī Bishop KGCOK RoK (December 19, 1831 – October 16, 1884) was an '' alii'' (noble) of the royal family of the Kingdom of Hawaii and a well known philanthropist.
Ancestry, birth and early life
Pauahi was born in Hon ...
, privately disapproved of selling Hawaiian lands. As monarch, William Charles Lunalilo, was content to let Bishop run almost all business affairs but the ceding of lands would become unpopular with the native Hawaiians. Many islanders thought that all the islands, rather than just Pearl Harbor, might be lost and opposed any cession of land. By November 1873, Lunalilo canceled negotiations and returned to drinking, against his doctor's advice; his health declined swiftly, and he died on February 3, 1874.
Lunalilo left no heirs. The legislature was empowered by the constitution to elect the monarch in these instances and chose David Kalākaua as the next monarch. The new ruler was pressured by the U.S. government to surrender Pearl Harbor to the Navy. Kalākaua was concerned that this would lead to annexation by the U.S. and to the contravention of the traditions of the Hawaiian people, who believed that the land ('Āina) was fertile, sacred, and not for sale to anyone. In 1874 through 1875, Kalākaua traveled to the United States for a state visit to Washington, DC to help gain support for a new treaty. Congress agreed to the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875 for seven years in exchange for Ford Island. After the treaty, sugar production expanded from of farm land to in 1891. At the end of the seven-year reciprocity agreement, the United States showed little interest in renewal.
Rebellion of 1887 and the Bayonet Constitution
 On January 20, 1887, the United States began leasing Pearl Harbor. Shortly afterwards, a group of mostly non-Hawaiians calling themselves the Hawaiian Patriotic League began the Rebellion of 1887. They drafted their own constitution on July 6, 1887. The new constitution was written by Lorrin Thurston, the Hawaiian Minister of the Interior who used the Hawaiian militia as threat against Kalākaua. Kalākaua was forced under threat of assassination to dismiss his cabinet ministers and sign a new constitution which greatly lessened his power. It would become known as the " Bayonet Constitution" because of the threat of force used.
The Bayonet Constitution allowed the monarch to appoint cabinet ministers, but had stripped him of the power to dismiss them without approval from the Legislature. Eligibility to vote for the House of Nobles was also altered, stipulating that both candidates and voters were now required to own property valuing at least three thousand dollars, or have an annual income of no less than six hundred dollars. This resulted in disenfranchising two-thirds of the native Hawaiians as well as other
On January 20, 1887, the United States began leasing Pearl Harbor. Shortly afterwards, a group of mostly non-Hawaiians calling themselves the Hawaiian Patriotic League began the Rebellion of 1887. They drafted their own constitution on July 6, 1887. The new constitution was written by Lorrin Thurston, the Hawaiian Minister of the Interior who used the Hawaiian militia as threat against Kalākaua. Kalākaua was forced under threat of assassination to dismiss his cabinet ministers and sign a new constitution which greatly lessened his power. It would become known as the " Bayonet Constitution" because of the threat of force used.
The Bayonet Constitution allowed the monarch to appoint cabinet ministers, but had stripped him of the power to dismiss them without approval from the Legislature. Eligibility to vote for the House of Nobles was also altered, stipulating that both candidates and voters were now required to own property valuing at least three thousand dollars, or have an annual income of no less than six hundred dollars. This resulted in disenfranchising two-thirds of the native Hawaiians as well as other ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
s who had previously held the right to vote but were no longer able to meet the new voting requirements. This new constitution benefited the white, foreign plantation owners. With the legislature now responsible for naturalizing citizens, Americans and Europeans could retain their home country citizenship and vote as citizens of the kingdom. Along with voting privileges, Americans could now run for office and still retain their United States citizenship, something not afforded in any other nation of the world and even allowed Americans to vote without becoming naturalized. Asian immigrants were completely shut out and were no longer able to acquire citizenship or vote at all.
At the time of the Bayonet Constitution Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States, serving from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. He was the first U.S. president to serve nonconsecutive terms and the first Hist ...
was president, and his secretary of state Thomas F. Bayard sent written instructions to the American minister George W. Merrill that in the event of another revolution in Hawaii, it was a priority to protect American commerce, lives and property. Bayard specified, "the assistance of the officers of our Government vessels, if found necessary, will therefore be promptly afforded to promote the reign of law and respect for orderly government in Hawaii." In July 1889, there was a small scale rebellion, and Minister Merrill landed Marines to protect Americans; the State Department explicitly approved his action. Merrill's replacement, minister John L. Stevens, read those official instructions, and followed them in his controversial actions of 1893.
Wilcox rebellion of 1888
 The Wilcox rebellion of 1888 was a plot to overthrow King
The Wilcox rebellion of 1888 was a plot to overthrow King Kalākaua
Kalākaua (David Laʻamea Kamanakapuʻu Māhinulani Nālaʻiaʻehuokalani Lumialani Kalākaua; November 16, 1836 – January 20, 1891), was the last king and penultimate monarch of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi, reigning from February 12, 1874, u ...
of Hawaii and replace him with his sister in a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; ; ), or simply a coup
, is typically an illegal and overt attempt by a military organization or other government elites to unseat an incumbent leadership. A self-coup is said to take place when a leader, having come to powe ...
in response to increased political tension between the legislature and the king after the 1887 constitution. Kalākaua's sister, Princess Liliʻuokalani and his wife, Queen Kapiolani, returned from Queen Victoria's Golden Jubilee immediately after news reached them in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
.
In October 1887, Robert William Wilcox, a native Hawaiian officer and veteran of the Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
, returned to Hawaii. The funding had stopped for his study program when the new constitution was signed. They had 300 Hawaiian conspirators hidden in ʻIolani Barracks and an alliance with the Royal Guard, but the plot was accidentally discovered in January 1888, less than 48 hours before the revolt would have been initiated. No one was prosecuted but Wilcox was exile
Exile or banishment is primarily penal expulsion from one's native country, and secondarily expatriation or prolonged absence from one's homeland under either the compulsion of circumstance or the rigors of some high purpose. Usually persons ...
d. So on February 11, 1888, Wilcox left Hawaii for San Francisco, intending to return to Italy with his wife.
Princess Liliʻuokalani was offered the throne several times by the Missionary Party who had forced the Bayonet Constitution on her brother, but she believed she would become a powerless figurehead like her brother and rejected the offers outright.
Liliʻuokalani attempts to re-write Constitution
In November 1889, Kalākaua traveled to San Francisco for his health, staying at the Palace Hotel. He died there on January 20, 1891. His sister Liliʻuokalani assumed the throne in the middle of an economic crisis. The McKinley Act had crippled the Hawaiian sugar industry by removing the duties on sugar imports from other countries into the US, eliminating the previous Hawaiian advantage gained via the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875. Many Hawaii businesses and citizens felt pressure from the loss of revenue; in response Liliʻuokalani proposed alottery
A lottery (or lotto) is a form of gambling that involves the drawing of numbers at random for a prize. Some governments outlaw lotteries, while others endorse it to the extent of organizing a national or state lottery. It is common to find som ...
system to raise money for her government. Also proposed was a controversial opium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid mor ...
licensing bill. Her ministers, and closest friends, were all opposed to this plan; they unsuccessfully tried to dissuade her from pursuing these initiatives, both of which came to be used against her in the brewing constitutional crisis.
Liliʻuokalani's chief desire was to restore power to the monarch by abrogating the 1887 Bayonet Constitution and promulgating a new one, an idea that seems to have been broadly supported by the Hawaiian population. The 1893 Constitution would have increased suffrage by reducing some property requirements, and eliminated the voting privileges extended to European and American residents. It would have disenfranchised many resident European and American businessmen who were not citizens of Hawaii. The Queen toured several of the islands on horseback, talking to the people about her ideas and receiving overwhelming support, including a lengthy petition in support of a new constitution. However, when the Queen informed her cabinet of her plans, they withheld their support due to an understanding of what her opponents' likely response to these plans would be.
Though there were threats to Hawaii's sovereignty throughout the kingdom's history, it was not until the signing of the Bayonet Constitution in 1887 that this threat began to be realized. The precipitating event leading to the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom on January 17, 1893, was the attempt by Queen Liliʻuokalani to promulgate a new constitution that would have strengthened the power of the monarch relative to the legislature, where Euro-American business elites held disproportionate power. The stated goals of the conspirators, who were non-native Hawaiian Kingdom subjects (five United States nationals, one English national, and one German national) were to depose the queen, overthrow the monarchy, and seek Hawaii's annexation to the United States.
1893 Hawaiian coup d'état and overthrow of the kingdom
The overthrow of the monarchy was started by newspaper publisher Lorrin Thurston, a Hawaiian subject and former Minister of the Interior who was the grandson of American missionaries, and formally led by the Chairman of the Committee of Safety, Henry E. Cooper, an American lawyer. They derived their support primarily from the American and European business class residing in Hawaii and other supporters of the Reform Party of the Hawaiian Kingdom. Most of the leaders of the Committee of Safety that deposed the queen were United States and European citizens who were also Kingdom subjects. They included legislators, government officers, and a Supreme Court Justice of the Hawaiian Kingdom. On January 16, the Marshal of the Kingdom, Charles B. Wilson, was tipped off by detectives to the imminent planned overthrow. Wilson requested warrants to arrest the 13-member council of the Committee of Safety, and put the Kingdom undermartial law
Martial law is the replacement of civilian government by military rule and the suspension of civilian legal processes for military powers. Martial law can continue for a specified amount of time, or indefinitely, and standard civil liberties ...
. Because the members had strong political ties with United States Government Minister John L. Stevens, the requests were repeatedly denied by Attorney General Arthur P. Peterson and the Queen's cabinet, fearing if approved, the arrests would escalate the situation. After a failed negotiation with Thurston, Wilson began to collect his men for the confrontation. Wilson and Captain of the Royal Household Guard, Samuel Nowlein, had rallied a force of 496 men who were kept at hand to protect the Queen.
The events began on January 17, 1893, when John Good, a revolutionist, shot Leialoha, a native policeman who was trying to stop a wagon carrying weapons to the Committee of Safety led by Lorrin Thurston. The Committee of Safety feared the shooting would bring government forces to rout out the conspirators and stop the overthrow before it could begin. The Committee of Safety initiated the overthrow by organizing armed non-native men, under their leadership, intending to depose Queen Liliʻuokalani. The Committee of Safety issued an ultimatum to the Queen, who was forced to remain in ‘Iolani Palace under armed guard: relinquish her power and role as Queen of the Kingdom of Hawai’i, or have her subjects face violence at the hands of the Committee and the militia. The forces garrisoned Ali'iolani Hale across the street from ʻIolani Palace and waited for the Queen's response.
As these events were unfolding, the Committee of Safety expressed concern for the safety and property of American residents in Honolulu.
On January 17, 1893, the Chairman of the Committee of Safety, Henry E. Cooper, addressed a crowd assembled in front of ʻIolani Palace (the official royal residence) and read aloud a proclamation that formally deposed Queen Liliʻuokalani, abolished the Hawaiian monarchy, and established a Provisional Government of Hawaii
The Provisional Government of Hawaii (abbr.: P.G.; Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Aupuni Kūikawā o Hawaiʻi'') was proclaimed after the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom on January 17, 1893, by the 13-member Committee of Safety (Hawaii), Co ...
under President Sanford B. Dole.
United States involvement
President Harrison's Secretary of StateJohn W. Foster
John Watson Foster (March 2, 1836 – November 15, 1917) was an American diplomat, military officer, lawyer and journalist who was U.S. secretary of state from 1892 to 1893, under President Benjamin Harrison. He was influential as a lawyer in t ...
from June 1892 to February 1893 actively worked for the annexation of Hawaii. Pro-American business interests had overthrown the Queen when she rejected constitutional limits on her powers. The new government realized that Hawaii was too small and militarily weak to survive in a world of aggressive imperialism, especially on the part of Japan. It was eager for American annexation. Foster believed Hawaii was vital to American interests in the Pacific.
The annexation program was coordinated by the chief American diplomat on the scene, John L. Stevens. He decided to send in a U.S. military detachment after the Queen was deposed to support the new government and prevent a vacuum that might open the way for Japan. Advised about supposed threats to non-combatant American lives and property by the Committee of Safety, Stevens obliged their request and summoned 162 U.S. sailors
A sailor, seaman, mariner, or seafarer is a person who works aboard a watercraft as part of its crew, and may work in any one of a number of different fields that are related to the operation and maintenance of a ship. While the term ''sailor'' ...
and Marines
Marines (or naval infantry) are military personnel generally trained to operate on both land and sea, with a particular focus on amphibious warfare. Historically, the main tasks undertaken by marines have included Raid (military), raiding ashor ...
from the USS ''Boston'' to land on Oahu under orders of neutrality and take up positions at the U.S. Legation, Consulate, and Arion Hall on the afternoon of January 16, 1893.
The deposed Queen was kept in ʻIolani Palace under house arrest. The American sailors and Marines did not enter the Palace grounds or take over any buildings, and never fired a shot, but their presence served effectively. The Queen never had an army, the local police did not support her, and no one mobilized any pro-royalist forces. Historian William Russ states, "the injunction to prevent fighting of any kind made it impossible for the monarchy to protect itself." Due to the Queen's desire "to avoid any collision of armed forces, and perhaps the loss of life" for her subjects and after some deliberation, at the urging of advisers and friends, the Queen ordered her forces to surrender. The Honolulu Rifles took over government buildings, disarmed the Royal Guard, and declared a provisional government.
According to the ''Queen's Book'', her friend and minister J.S. Walker "came and told me that he had come on a painful duty, that the opposition party had requested that I should abdicate." After consulting with her ministers, including Walker, the Queen concluded that "since the troops of the United States had been landed to support the revolutionists, by the order of the American minister, it would be impossible for us to make any resistance." Despite repeated claims that the overthrow was "bloodless", the ''Queen's Book'' notes that Liliʻuokalani received "friends hoexpressed their sympathy in person; amongst these Mrs. J. S. Walker, who had lost her husband by the treatment he received from the hands of the insurgents. He was one of many who from persecution had succumbed to death."
Immediate annexation was prevented by President Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States, serving from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. He was the first U.S. president to serve nonconsecutive terms and the first Hist ...
who told Congress:
... the military demonstration upon the soil of Honolulu was of itself an act of war; unless made either with the consent of the government of Hawaii or for the bona fide purpose of protecting the imperiled lives and property of citizens of the United States. But there is no pretense of any such consent on the part of the government of the queen ... the existing government, instead of requesting the presence of an armed force, protested against it. There is as little basis for the pretense that forces were landed for the security of American life and property. If so, they would have been stationed in the vicinity of such property and so as to protect it, instead of at a distance and so as to command the Hawaiian Government Building and palace ... When these armed men were landed, the city of Honolulu was in its customary orderly and peaceful condition ...The Republic of Hawaii was nonetheless declared in 1894 by the same parties which had established the
provisional government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, a transitional government or provisional leadership, is a temporary government formed to manage a period of transition, often following state collapse, revoluti ...
. Among them was Lorrin A. Thurston, a drafter of the Bayonet Constitution. The Committee of Safety asked Sanford Dole to become President of the forcibly instated Republic. He agreed, and became president on July 4, 1894.
Aftermath
 A provisional government was set up with the strong support of the Honolulu Rifles, a militia group which had defended the system of government promulgated by the Bayonet Constitution against the Wilcox rebellion of 1889.
The Queen's statement yielding authority, on January 17, 1893, protested against the overthrow:
On December 19, 1898, the queen would amend the declaration with the ''"Memorial of Queen Liliuokalani in relation to the Crown lands of Hawaii"'', further protesting the overthrow and loss of property.
A provisional government was set up with the strong support of the Honolulu Rifles, a militia group which had defended the system of government promulgated by the Bayonet Constitution against the Wilcox rebellion of 1889.
The Queen's statement yielding authority, on January 17, 1893, protested against the overthrow:
On December 19, 1898, the queen would amend the declaration with the ''"Memorial of Queen Liliuokalani in relation to the Crown lands of Hawaii"'', further protesting the overthrow and loss of property.
Response
United States
Newly inaugurated PresidentGrover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States, serving from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. He was the first U.S. president to serve nonconsecutive terms and the first Hist ...
called for an investigation into the overthrow. This investigation was conducted by former Congressman James Henderson Blount. Blount concluded in his report
A report is a document or a statement that presents information in an organized format for a specific audience and purpose. Although summaries of reports may be delivered orally, complete reports are usually given in the form of written documen ...
on July 17, 1893, "United States diplomatic and military representatives had abused their authority and were responsible for the change in government." Minister Stevens was recalled, and the military commander of forces in Hawaii was forced to resign his commission. President Cleveland stated, "Substantial wrong has thus been done which a due regard for our national character as well as the rights of the injured people requires we should endeavor to repair the monarchy." Cleveland further stated in his 1893 State of the Union Address that, "Upon the facts developed it seemed to me the only honorable course for our Government to pursue was to undo the wrong that had been done by those representing us and to restore as far as practicable the status existing at the time of our forcible intervention." The matter was referred by Cleveland to Congress on December 18, 1893, after the Queen refused to accept amnesty for the traitors as a condition of reinstatement.
The Senate Foreign Relations Committee, chaired by Senator John Tyler Morgan (D-Alabama) and composed mostly of senators in favor of annexation, initiated their own investigation to discredit Blount's earlier report, using pro-annexationist affidavits from Hawaii, and testimony provided to the US Senate
The United States Senate is a chamber of the bicameral United States Congress; it is the upper house, with the U.S. House of Representatives being the lower house. Together, the Senate and House have the authority under Article One of the ...
in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
The Morgan Report
The Morgan Report was an 1894 report concluding an official U.S. Congressional investigation into the events surrounding the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom, including the alleged role of U.S. military troops (both bluejackets and marines) in ...
contradicted the Blount Report, and exonerated Minister Stevens and the US military troops finding them "not guilty" of involvement in the overthrow. Cleveland became stalled with his earlier efforts to restore the queen and adopted a position of recognition of the so-called Provisional Government and the Republic of Hawaii
The Republic of Hawaii (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Lepupalika o Hawaii'' epupəˈlikə o həˈvɐjʔi was a short-lived one-party state in Hawaii, Hawaii between July 4, 1894, when the Provisional Government of Hawaii had Black Week (H ...
which followed.
The Native Hawaiian Study Commission of the United States Congress in its 1983 final report found no historical, legal, or moral obligation for the US government to provide reparations, assistance, or group rights to Native Hawaiians.
In 1993, the 100th anniversary of the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom, Congress passed a resolution, which President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
signed into law, offering an apology to Native Hawaiians on behalf of the United States for its involvement in the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom. The law is known as the Apology Resolution
Public Law 103-150, informally known as the Apology Resolution, is a Joint Resolution of the U.S. Congress adopted in 1993 that "acknowledges that the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii occurred with the active participation of agents and citiz ...
, and represents one of the few times that the United States government has formally apologized for its actions.
International
Every government with a diplomatic presence in Hawaii, except for the United Kingdom, recognized the Provisional Government within 48 hours of the overthrow via their consulates. Countries recognizing the new Provisional Government included Chile, Austria-Hungary, Mexico, Russia, the Netherlands, Germany, Sweden, Spain, Japan, Italy, Portugal, Denmark, Belgium, China, Peru, and France. When the Republic of Hawaii was declared on July 4, 1894, immediate de facto recognition was given by every nation with diplomatic relations with Hawaii, except for Britain, whose response came in November 1894.Hawaiian counter-revolution
A four-day uprising between January 6–9, 1895, began with an attempted coup d'état to restore the monarchy, and included battles between royalists and the republican rebels. Later, after a weapons cache was found on the palace grounds after the attempted rebellion in 1895, Queen Lili'uokalani was placed under arrest, tried by a military tribunal of the Republic of Hawaiʻi, convicted of misprision of treason and imprisoned in her own home. On January 24, Lili'uokalani abdicated, formally ending the Hawaiian monarchy.Republic, United States annexation, United States territory
 The Committee of Safety declared Sanford Dole president of the new Provisional Government of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi on January 17, 1893, only removing the queen, her cabinet, and her marshal from office. On July 4, 1894, the Republic of Hawaiʻi was proclaimed. Dole was president of both governments. As a republic, it was the government's intention to campaign for Hawaii's annexation to the United States. The rationale behind the annexation of Hawaii included a strong economic component—Hawaiian goods and services which were exported to the mainland would not be subjected to United States tariffs, and the United States and Hawaii would both benefit from each other's domestic bounties, if Hawaii was part of the United States.
In 1897,
The Committee of Safety declared Sanford Dole president of the new Provisional Government of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi on January 17, 1893, only removing the queen, her cabinet, and her marshal from office. On July 4, 1894, the Republic of Hawaiʻi was proclaimed. Dole was president of both governments. As a republic, it was the government's intention to campaign for Hawaii's annexation to the United States. The rationale behind the annexation of Hawaii included a strong economic component—Hawaiian goods and services which were exported to the mainland would not be subjected to United States tariffs, and the United States and Hawaii would both benefit from each other's domestic bounties, if Hawaii was part of the United States.
In 1897, William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until Assassination of William McKinley, his assassination in 1901. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Repub ...
succeeded Cleveland as United States president. In his first year in office, the U.S. Senate failed twice to ratify a Treaty to Annex the Hawaiian Islands. A year later, he signed the Newlands Resolution
The Newlands Resolution, , was a joint resolution passed on July 7, 1898, by the United States Congress to annexation, annex the independent Republic of Hawaii. In 1900, Congress created the Territory of Hawaii.
The resolution was drafted by R ...
, which stated that the annexation of Hawaii would occur on July 7, 1898. The formal ceremony which marked the annexation of Hawaii to the United States was held at the Iolani Palace on August 12, 1898. Almost no Native Hawaiians attended the annexation ceremony, and those few Hawaiians who were on the streets wore royalist ilima blossoms in their hats or hair, and on their breasts, they wore Hawaiian flags which were emblazoned with the motto: ''Kuu Hae Aloha'' ('my beloved flag'). Most of the 40,000 Native Hawaiians, including Lili'uokalani and the Hawaiian royal family, protested against the action by shuttering themselves in their homes. "When the news of the Annexation came, it was bitterer than death to me", Lili'uokalani's niece, Princess Kaʻiulani
Princess Kaʻiulani (; Victoria Kawēkiu Kaʻiulani Lunalilo Kalaninuiahilapalapa Cleghorn; October 16, 1875 – March 6, 1899) was a Hawaiian royal, the only child of Princess Miriam Likelike, and the last heir apparent to the thron ...
, told the ''San Francisco Chronicle
The ''San Francisco Chronicle'' is a newspaper serving primarily the San Francisco Bay Area of Northern California. It was founded in 1865 as ''The Daily Dramatic Chronicle'' by teenage brothers Charles de Young and M. H. de Young, Michael H. ...
''. "It was bad enough to lose the throne, but it was infinitely worse to have the flag go down." The Hawaiian flag was lowered for the last time while the Royal Hawaiian Band played the Hawaiian national anthem, '' Hawaiʻi Ponoʻī''.
The Hawaiian Islands, together with the distant Palmyra Island and the Stewart Islands, became the Territory of Hawaii
The Territory of Hawaii or Hawaii Territory (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Panalāʻau o Hawaiʻi'') was an organized incorporated territories of the United States, organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from Apri ...
, a United States organized incorporated territory, with a new government which was established on February 22, 1900. Sanford Dole was appointed the territory's first governor. The Iolani Palace served as the capitol building of the Hawaiian government until 1969.
See also
*Aliʻi
The aliʻi were the traditional nobility of the Hawaiian islands. They were part of a hereditary line of rulers, the ''noho aliʻi''.
Cognates of the word ''aliʻi'' have a similar meaning in other Polynesian languages; in Māori it is pronoun ...
* Democratic Revolution of 1954
* ''Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
'' – historical novel by James Michener has fictionalized account of the Overthrow in Chapter IV "From the Starving Village"
* Hawaiian home land
* Hawaiian sovereignty movement
The Hawaiian sovereignty movement () is a grassroots political and cultural campaign to reestablish an autonomous or independent nation or kingdom of Hawaii out of a desire for sovereignty, self-determination, and self-governance.
Some group ...
* Hawaiian Kingdom–United States relations
* Kalākaua dynasty
* Legal status of Hawaii
* List of bilateral treaties signed by the Hawaiian Kingdom
* Paulet affair
* '' Unfamiliar Fishes'' by Sarah Vowell
* United States involvement in regime change
Since the 19th century, the United States government has participated and interfered, both overtly and covertly, in the replacement of many foreign governments. In the latter half of the 19th century, the U.S. government initiated actions for ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * *External links
morganreport.org
Online images and transcriptions of the entire 1894 Morgan Report * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Hawaiian Kingdom, overthrow of the 1890s coups d'état and coup attempts 1893 in Hawaii Battles and conflicts without fatalities Conflicts in 1893 History of United States expansionism January 1893 United States Marine Corps in the 18th and 19th centuries United States involvement in regime change American imperialism