Organoid Intelligence on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
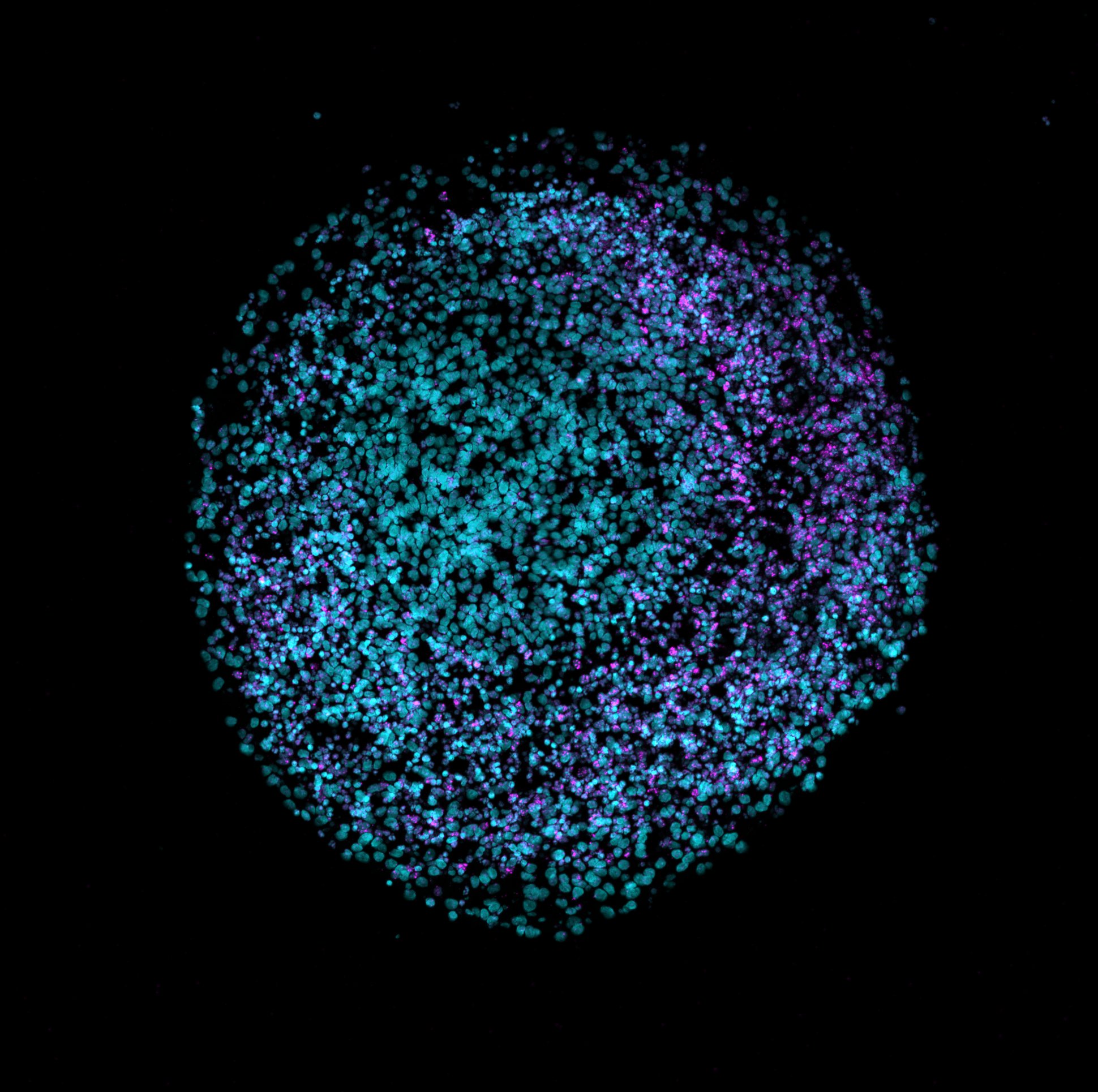 Organoid intelligence (OI) is an emerging
Organoid intelligence (OI) is an emerging
 Organoid intelligence (OI) is an emerging
Organoid intelligence (OI) is an emerging field of study
An academic discipline or academic field is a subdivision of knowledge that is taught and researched at the college or university level. Disciplines are defined (in part) and recognized by the academic journals in which research is published, a ...
in computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
and biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
that develops and studies biological wetware computing using 3D cultures of human brain cells (or brain organoids) and brain-machine interface technologies. Such technologies may be referred to as OIs.
Organoid intelligent computer systems can be an example of biohybrid systems.
Differences with non-organic computing
As opposed to traditional non-organic silicon-based approaches, OI seeks to use lab-grown cerebral organoids to serve as "biological hardware." Scientists hope that such organoids can provide faster, more efficient, and more powerful computing power than regular silicon-based computing and AI while requiring only a fraction of the energy. However, while these structures are still far from being able to think like a regular humanbrain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
and do not yet possess strong computing capabilities, OI research currently offers the potential to improve the understanding of brain development, learning and memory, potentially finding treatments for neurological disorders
Neurological disorders represent a complex array of medical conditions that fundamentally disrupt the functioning of the nervous system. These Disorder of consciousness, disorders affect the brain, spinal cord, and nerve networks, presenting unique ...
such as dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
.
Thomas Hartung, a professor from Johns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University (often abbreviated as Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1876 based on the European research institution model, J ...
, argues that "while silicon-based computers are certainly better with numbers, brains are better at learning." Furthermore, he claimed that with "superior learning and storing" capabilities than AIs, being more energy efficient, and that in the future, it might not be possible to add more transistors
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
to a single computer chip
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
, while brains are wired differently and have more potential for storage and computing power, OIs can potentially harness more power than current computers.
Some researchers claim that even though human brains are slower than machines at processing simple information, they are far better at processing complex information as brains can deal with fewer and more uncertain data, perform both sequential
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is call ...
and parallel
Parallel may refer to:
Mathematics
* Parallel (geometry), two lines in the Euclidean plane which never intersect
* Parallel (operator), mathematical operation named after the composition of electrical resistance in parallel circuits
Science a ...
processing, being highly heterogenous, use incomplete datasets, and is said to outperform non-organic machines in decision-making.
Training OIs involve the process of biological learning (BL) as opposed to machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
(ML) for AIs. BL is said to be much more energy efficient than ML.
Bioinformatics in OI
OI generates complex biological data, necessitating sophisticated methods for processing and analysis.Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, ...
provides the tools and techniques to decipher raw data, uncovering the patterns and insights. A Python interface is currently available for processing and interaction with brain organoids.
Intended functions
Brain-inspired computing hardware aims to emulate the structure and working principles of the brain and could be used to address current limitations in artificial intelligence technologies. However, brain-inspired silicon chips are still limited in their ability to fully mimic brain function, as most examples are built on digital electronic principles. One study performed OI computation (which they termed ''Brainoware'') by sending and receiving information from the brain organoid using a high-density multielectrode array. By applying spatiotemporal electrical stimulation, nonlinear dynamics, and fading memory properties, as well as unsupervised learning from training data by reshaping the organoid functional connectivity, the study showed the potential of this technology by using it forspeech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
and nonlinear equation prediction in a reservoir computing framework.
Ethical concerns
While researchers are hoping to use OI and biological computing to complement traditional silicon-based computing, there are also questions about the ethics of such an approach. Examples of such ethical issues include OIs gaining consciousness and sentience asorganoids
An organoid is a miniaturised and simplified version of an Organ (anatomy), organ produced ''in vitro'' in three dimensions that mimics the key functional, structural, and biological complexity of that organ. It is derived from one or a few Cel ...
and the question of the relationship between a stem cell donor (for growing the organoid) and the respective OI system.
Enforced amnesia and limits on duration of operation without memory reset have been proposed as a way to mitigate the potential risk of silent suffering in brain organoids.
See also
*Biohybrid system
Biohybrid systems refer to the integration of biological materials, such as cells or tissues, with artificial components, including electronics or mechanical structure. This combination uses the capabilities of living organisms alongside the precis ...
* Cerebral organoid
A neural, or brain organoid, describes an artificially grown, ''in vitro,'' tissue resembling parts of the human brain. Neural organoids are created by culturing pluripotent stem cells into a three-dimensional culture that can be maintained fo ...
* Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
References
{{Evolutionary computation Artificial intelligence Computational fields of study Computational neuroscience Developmental neuroscience Formal sciences Intelligence by type Stem cells Synthetic biology