Organic Act Of 1801 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The District of Columbia Organic Act of 1801, officially An Act Concerning the District of Columbia (6th Congress, 2nd Sess., ch. 15, , February 27, 1801), is an
 On May 3, 1802, the City of Washington was granted a municipal government consisting of a mayor appointed by the
On May 3, 1802, the City of Washington was granted a municipal government consisting of a mayor appointed by the
An Act concerning the District of Columbia
as enacted
2 Stat. 103
in the US Statutes at Large {{John Adams United States federal territory and statehood legislation Legal history of the District of Columbia 1801 in American law 6th United States Congress
organic act
In United States law, an organic act is an act of the United States Congress that establishes an administrative agency or local government, for example, the laws that established territory of the United States and specified how they are to ...
enacted by the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
in accordance with Article 1, Section 8 of the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally includi ...
. It formally placed the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
under the control of the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
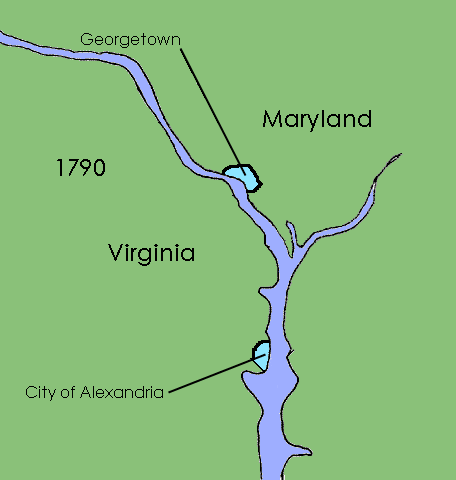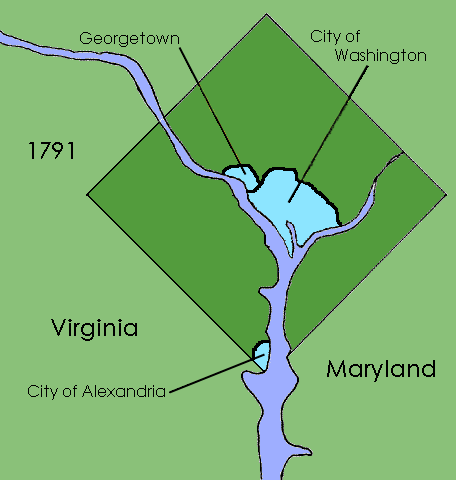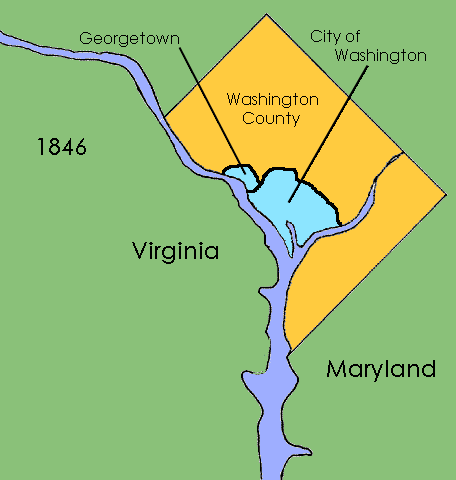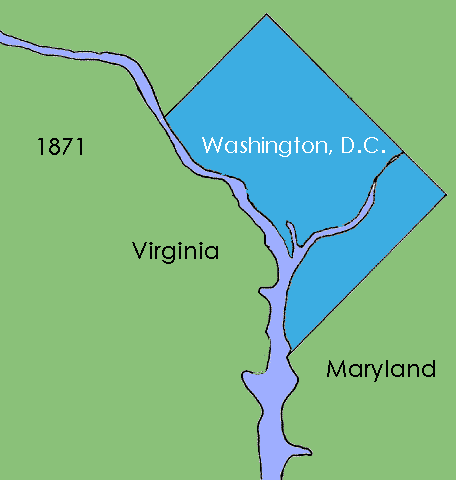
and organized the territory within the district into two counties: Washington County to the north and east of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () is in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography D ...
and Alexandria County
Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the national capital.
Arlington ...
to the west and south. The charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the ...
s of the existing cities of Georgetown and Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
were left in place and no change was made to their status. The common law
Common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law primarily developed through judicial decisions rather than statutes. Although common law may incorporate certain statutes, it is largely based on prece ...
of both Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
remained in force within the district. A court was established in each of the new counties.
Subsequent history
 On May 3, 1802, the City of Washington was granted a municipal government consisting of a mayor appointed by the
On May 3, 1802, the City of Washington was granted a municipal government consisting of a mayor appointed by the president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
. The portion of the District of Columbia ceded by Virginia was returned to that state in 1846-47. The District of Columbia Organic Act of 1871
The District of Columbia Organic Act of 1871 is an Act of Congress that repealed the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown, D.C., Georgetown and established a new territorial government for the whole District of Columbi ...
replaced the municipal governments of the City of Washington, Georgetown, and Washington County with a single, unified district government for the whole district.
District voting rights
Following the passage of this Act, residents of the District of Columbia were no longer considered to be residents of either Maryland or Virginia. This left district residents unable to vote for members of Congress. They have voted in presidential elections since the adoption of the Twenty-third Amendment in 1961 (which first applied in the election of 1964). District residents are represented in the House of Representatives by a non-voting delegate who can vote in committee and participate in debate, but cannot vote for final passage of a bill in theHouse
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air c ...
. There have been several efforts to give the inhabitants of the district representation, but the United States remains perhaps the only modern republic where residents of its own capital are disenfranchised.
See also
*Residence Act
The Residence Act of 1790, officially titled An Act for establishing the temporary and permanent seat of the Government of the United States (), is a United States federal statute adopted during the second session of the 1st United States Cong ...
, 1790 Act of Congress that set where along the Potomac River the permanent capital of the United States would be established
*'' United States v. More'' (1805)
Notes
External links
An Act concerning the District of Columbia
as enacted
2 Stat. 103
in the US Statutes at Large {{John Adams United States federal territory and statehood legislation Legal history of the District of Columbia 1801 in American law 6th United States Congress