Orbital Emphysema on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Orbital emphysema (/ˈɔː(r)bɪt(ə)l ˌemfɪˈsiːmə/, also known as pneumo-orbit) is a medical condition that refers to the trapping of air within the loose subcutaneous around the

orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
that is generally characterized by sudden onset swelling and bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur clo ...
at the impacted eye, with or without deterioration of vision, which the severity depends on the density of air trapped under the orbital soft tissue spaces.
It is most commonly result from forceful sneezing
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth a ...
, nose blowing, or cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
ing among patients with a history of periorbital trauma or orbital fractures that happened several hours-days in advance. Rare occasions have also been reported in relation to individuals with no traumatic past events that include: infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
, esophageal rupture
Esophageal rupture, also known as Boerhaave syndrome, is a rupture of the esophageal wall. Iatrogenic causes account for approximately 56% of esophageal perforations, usually due to medical instrumentation such as an endoscopy or paraesophageal s ...
, postoperative complications, pulmonary barotrauma
Barotrauma is physical damage to body tissues caused by a difference in pressure between a gas space inside, or in contact with, the body and the surrounding gas or liquid. The initial damage is usually due to over-stretching the tissues in ...
, with the same predisposing factors (sneezing
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth a ...
, nose blowing, or cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
ing). A four-stage system of orbital emphysema was developed for severity classification. Clinical diagnosis can be made based on a combination of medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
, physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
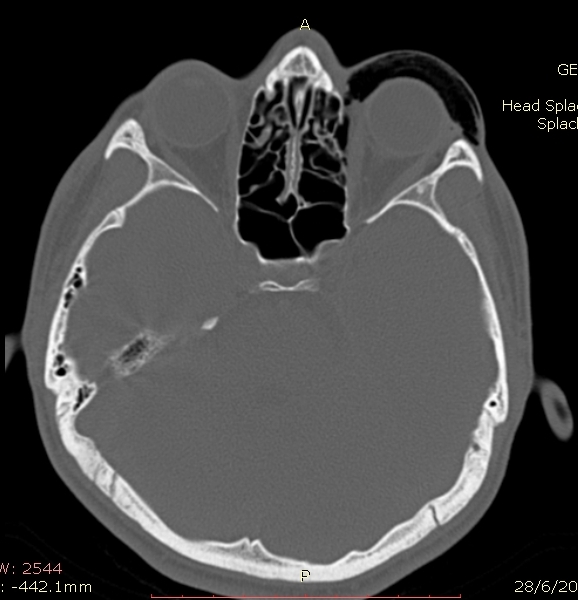
, and computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
. There are three kinds of orbital emphysema including palpebral emphysema, true orbital emphysema, and orbitopalpebral emphysema.
Orbital emphysema on its own is a mild and self-limiting disease, and usually requires no treatment. If related visual symptoms or other acute orbital compression symptoms are present, lateral canthotomy or cantholysis, orbital decompression by needle aspiration, and bone decompression may be required to relieve orbital pressure and preserve vision.
Cause
Trauma
Blunt trauma caused by a direct blow at the orbital is the major leading cause of orbital emphysema. Any object with force and/or speed, typically a ball, fist or vehicle accidents, can result in orbital floor and/or medial wall fractures. These disruptions permit air entry into the orbital subcutaneous from thesinus
Sinus may refer to:
History
* a sac in front of body worn into a toga, in the typical style of wearing it
Anatomy
* Sinus (anatomy), a sac or cavity in any organ or tissue
** Paranasal sinuses, air cavities in the cranial bones, especially those ...
, with a one-way check valve mechanism that forbids the air from exiting. Victims are often found in sport-related concussion, automobile vehicle accidents, or snowboarding accidents.
Traumatic injuries do not cause onset swelling unless there is a forceful injection of air from vigorous sneezing
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth a ...
, nose-blowing
Nose-blowing is the act of expelling nasal mucus by exhaling forcefully through the nose. This is usually done into a facial tissue or handkerchief, facial tissues being more hygienic as they are disposed of after each use while handkerchiefs are ...
, or cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
ing. These generate an acute increase in intraorbital pressure, compromising the intraorbital neurovascular structures, which subsequently trigger the development of orbital emphysema.
Postoperative complications
Orbital emphysema is a common result of certain types of surgery, in particular the ones that involve orbital medial wall. It may also occur in otheroral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or ora ...
, nasal, and maxillofacial
Oral and maxillofacial surgery (OMFS) is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the mouth, head and neck, and jaws, as well as facial plastic surgery including cleft lip and cleft palate s ...
surgical interventions, in which the occurrence is unexpected. They can weaken sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoi ...
, bony structure, induce deep orbital tissue damages, or globe perforation that cause air leakage into the periorbital soft tissues and superiorly into the supraorbital fat. These surgical procedures may possibly introduce staphylococci
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillale ...
, streptococci
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a sing ...
, and anaerobic bacteria
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenat ...
via a compromised bony wall that can cause periorbital infection. The corresponding weakened or degenerated tissues cannot withstand the sudden increase in intraocular pressure and impaired ocular perfusion, driven by severe cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
ing or sneezing
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth a ...
. It subsequently results in air trapped in the periorbital subcutaneous tissue and the development of orbital emphysema, which is often mistaken as allergic reactions
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, alle ...
. Without proper management can lead to cardiac life-threatening conditions such as cardiopulmonary embolism, cardiac tamponade
Cardiac tamponade, also known as pericardial tamponade (), is a compression of the heart due to pericardial effusion (the build-up of pericardial fluid in the pericardium, sac around the heart). Onset may be rapid or gradual. Symptoms typically i ...
, and respiratory distress
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that c ...
, depending on the volume of air trapped under the facial soft tissues.
Infection
Infections can spread beyond their initial location, includinglamina papyracea
The orbital lamina of ethmoid bone (or lamina papyracea or orbital lamina) is a smooth, oblong, paper-thin bone plate which forms the lateral wall of the labyrinth of the ethmoid bone. It covers the middle and posterior ethmoidal cells, and forms ...
.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of orbital emphysema vary depending on the original cause, but it is preliminary associated with swelling,bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur clo ...
, and tenderness around the impacted eye. It may also involve proptosis
Exophthalmos (also called exophthalmus, exophthalmia, proptosis, or exorbitism) is a bulging of the eye anteriorly out of the orbit. Exophthalmos can be either bilateral (as is often seen in Graves' disease) or unilateral (as is often seen in ...
or the deterioration of vision, typically diplopia
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occ ...
. The entrapped air may cause an acute increase in the intraocular pressure or vascular compromise that restrict ocular motility, prohibit the closure of eyelids, and the loss of sensation over the upper cheek areas.
Server entrapment in the soft tissues tends to stimulate oculocardiac reflex
The oculocardiac reflex, also known as Aschner phenomenon, Aschner reflex, or Aschner–Dagnini reflex, is a decrease in pulse rate associated with traction applied to extraocular muscles and/or compression of the eyeball. The reflex is mediated b ...
, which is likely to generate significant vagal responses including nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to Balance disorder, disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.
Dizziness is a ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
, bradycardia
Bradycardia, also called bradyarrhythmia, is a resting heart rate under 60 beats per minute (BPM). While bradycardia can result from various pathological processes, it is commonly a physiological response to cardiovascular conditioning or due ...
, syncope and heart block
Heart block (HB) is a disorder in the heart's rhythm due to a fault in the natural pacemaker. This is caused by an obstruction – a block – in the electrical conduction system of the heart. Sometimes a disorder can be inherited. Despite the ...
. Without treating it promptly may subsequently result in compromisation of ocular function and visual impairment
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
.
Pathophysiology
Orbital emphysema occurs following forceful injection of air into the soft tissues of the orbit through a breach in one of the orbital walls which is typically associated with orbital fracture after blunt trauma, or less frequently with compressed air injuries,tumours
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
and infections of the sinonasal region or complications after surgery.
Orbital emphysema develops after an orbital fracture in a three-step process. After the fracture has occurred on one of the orbital walls, a sino-orbital communication is established. The communication will allow air to be forced from the sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoi ...
into the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
in the presence of a pressure gradient from forceful expiratory efforts, nose-blowing
Nose-blowing is the act of expelling nasal mucus by exhaling forcefully through the nose. This is usually done into a facial tissue or handkerchief, facial tissues being more hygienic as they are disposed of after each use while handkerchiefs are ...
or even a sneeze
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth a ...
. Orbital emphysema is typically a harmless disorder because air escapes as quickly as it enters the fracture site, and the increase in intraorbital pressure is usually transient, lasting for as long as the sneeze
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth a ...
or nose blowing. However, when orbital soft tissues, such as fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
, falls back on the sino-orbital communication, a one-way ball valve will be created, leading to the entrapment of air. When sufficient air accumulates, it will result in acute compartment syndrome and vascular compromise, causing complications including proptosis
Exophthalmos (also called exophthalmus, exophthalmia, proptosis, or exorbitism) is a bulging of the eye anteriorly out of the orbit. Exophthalmos can be either bilateral (as is often seen in Graves' disease) or unilateral (as is often seen in ...
, visual impairment
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
, central retinal artery occlusion
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a disease of the eye where the flow of blood through the central retinal artery is blocked (occluded). There are several different causes of this occlusion; the most common is carotid artery atheroscle ...
, compressive optic neuropathy
Optic neuropathy is damage to the optic nerve from any cause. The optic nerve is a bundle of millions of fibers in the retina that sends visual signals to the brain.
Damage and death of these nerve cells, or neurons, leads to characteristic featu ...
, and other severe complications caused by orbital compartment syndrome.
There are three variations of orbital emphysema, namely palpebral emphysema, true orbital emphysema, and orbitopalpebral emphysema.
Palpebral emphysema
Palpebral emphysema refers to emphysema of the eyelids alone. It is a rare kind of orbital emphysema which is usually caused by fractures of thelacrimal bone
The lacrimal bones are two small and fragile bones of the facial skeleton; they are roughly the size of the little fingernail and situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. They each have two surfaces and four borders. Several bon ...
. The lacrimal sac
The lacrimal sac or lachrymal sac is the upper dilated end of the nasolacrimal duct, and is lodged in a deep groove formed by the lacrimal bone and frontal process of the maxilla. It connects the lacrimal canaliculi, which drain tears from th ...
ruptures as a result of the fracture, allowing air from the nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nas ...
to enter the tissues of the eyelid. Alternatively, facial subcutaneous air may simply pass into the eyelids along fascial plane to produce palpebral emphysema. As long as the orbital septum
In anatomy, the orbital septum (palpebral fascia) is a membranous sheet that acts as the anterior (frontal) boundary of the orbit. It extends from the orbital rims to the eyelids. It forms the fibrous portion of the eyelids.
Structure
In the ...
is intact, air is confined in the eyelids.
True orbital emphysema
True orbital emphysema occurs when there is air behind an intactorbital septum
In anatomy, the orbital septum (palpebral fascia) is a membranous sheet that acts as the anterior (frontal) boundary of the orbit. It extends from the orbital rims to the eyelids. It forms the fibrous portion of the eyelids.
Structure
In the ...
. This condition arises due to a fracture of more than one bony orbital walls of paranasal sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphe ...
and tearing of adjacent sinus mucosa, and communication of a sinus with the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
is established. This fracture usually involves the ethmoid
The ethmoid bone (; from ) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbit (anatomy), orbits. The cubical (cube-shaped) bone is lightweight due to a sp ...
, and sometimes involves frontal, sphenoid, and maxillary sinus
The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus (or antrum of Nathaniel Highmore (surgeon), Highmore) is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, located in the maxilla. It drains into the middle meatus of the noseHuman Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 209- ...
es. The air usually enters the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
when the pressure within the upper respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory ...
is increased due to expiratory efforts, nose blowing or sneezing
A sneeze (also known as sternutation) is a semi-autonomous, convulsive expulsion of air from the lungs through the nose and mouth, usually caused by foreign particles irritating the nasal mucosa. A sneeze expels air forcibly from the mouth a ...
.
Orbitopalperbal emphysema
Orbitopalpebral emphysema refers to the trapping of air inside both the soft tissues of theorbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
and the eyelid
An eyelid ( ) is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. "Palpebral ...
. It is usually a sequelae of a true orbital emphysema. When too much air accumulates inside the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
, the orbital septum
In anatomy, the orbital septum (palpebral fascia) is a membranous sheet that acts as the anterior (frontal) boundary of the orbit. It extends from the orbital rims to the eyelids. It forms the fibrous portion of the eyelids.
Structure
In the ...
ruptures due to high intraorbital pressure. Air may then pass freely from the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
into the eyelid
An eyelid ( ) is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. "Palpebral ...
s through the break in the orbital septum
In anatomy, the orbital septum (palpebral fascia) is a membranous sheet that acts as the anterior (frontal) boundary of the orbit. It extends from the orbital rims to the eyelids. It forms the fibrous portion of the eyelids.
Structure
In the ...
.
Stages
There are four stages of orbital emphysema.Stage I
Stage I orbital emphysema can only be diagnosed with radiological films. There is only a small amount of intraorbital air, and the patient does not show any clinical signs or symptoms.Stage II
Stage II orbital emphysema develops as the intraorbital air volume increases, causing theeye
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
ball to displace horizontally or vertically (globe dystopia) or to protrude anteriorly (proptosis
Exophthalmos (also called exophthalmus, exophthalmia, proptosis, or exorbitism) is a bulging of the eye anteriorly out of the orbit. Exophthalmos can be either bilateral (as is often seen in Graves' disease) or unilateral (as is often seen in ...
). The patient may experience diplopia
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occ ...
as a result of the globe displacement.
Stage III
Stage III orbital emphysema develops when the limits of spontaneous decompression are exceeded. The pressure will be transmitted to orbital tissues and then to the globe, resulting in an increase inintraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the fluid pressure inside the eye. Tonometry is the method eye care professionals use to determine this. IOP is an important aspect in the evaluation of patients at risk of glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated t ...
which may cause visual loss
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
when the nutrient vessels supplying the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
are compressed.
Stage IV
Stage IV orbital emphysema develops when the intraorbital air mass results in anintraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the fluid pressure inside the eye. Tonometry is the method eye care professionals use to determine this. IOP is an important aspect in the evaluation of patients at risk of glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated t ...
of more than 60 to 70 mmHg. The significantly elevated intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the fluid pressure inside the eye. Tonometry is the method eye care professionals use to determine this. IOP is an important aspect in the evaluation of patients at risk of glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated t ...
will lead to central retinal artery occlusion
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a disease of the eye where the flow of blood through the central retinal artery is blocked (occluded). There are several different causes of this occlusion; the most common is carotid artery atheroscle ...
, which may result in permanent and irreversible damage to the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
.
Clinical Diagnosis
The diagnosis of orbital emphysema is usually made byphysical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
of the eyelids, and, or by computer tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
(CT).
Physical examination
Physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
of the eyelid
An eyelid ( ) is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. "Palpebral ...
can be done by the palpation
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine ...
for the pathognomonic cracking, crepitation, and tense tissue on the upper and lower eyelid
An eyelid ( ) is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. "Palpebral ...
s. The findings of the examination are supported with the medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
of the patient and confirmed with orbital CT.
Computed tomography (CT)


Computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
is effective and sensitive in the diagnosis of orbital emphysema, as it can confirm the anatomical location and size of air, bony defects, indentation of the eyeball, and the condition of the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
, as well as the presence of any extraocular muscle entrapment and herniation of preorbital fat into the sinus cavities. The location of the orbital emphysema is present near the site of the fracture. The scans are usually taken along the transverse plane
A transverse plane is a plane that is rotated 90° from two other planes.
Anatomy
The transverse plane is an anatomical plane that is perpendicular to the sagittal plane and the dorsal plane. It is also called the axial plane or horizonta ...
. Transverse images allow the evaluation of fractures in medial and lateral orbital walls. By reformatting these transverse images or taking coronal images, the examination of orbital floor and roof is permitted. Helical scanning is preferred as it has a lower imaging time and radiation dose comparing to conventional scanning, especially when reforming transverse helical scans into coronal images. The staging of orbital emphysema can then be determined with visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye ...
examination and ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part ...
. A disadvantage of using a CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
is that when detecting air after orbital trauma, the presence of a wooden foreign object can give a false positive result of orbital emphysema. The wooden object can mimic the presence of orbital emphysema. Therefore, patients’ medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
is crucial in making the correct diagnosis.
Other tests
Conventionalradiography
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiog ...
is commonly employed for imaging orbital injuries and identifying orbital fractures. It can be used to diagnose orbital emphysema because it shows the presence of air in the orbit best while the patient is standing upright. Skull films of posterior-anterior, lateral projections, and orbital rim views are recommended to show fractures in orbital rims and walls
Walls may refer to:
*The plural of wall, a structure
* Walls (surname), a list of notable people with the surname
Places
* Walls, Louisiana, United States
* Walls, Mississippi, United States
*Walls, Ontario
Perry is a township (Canada), ...
. However, CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
is better than conventional radiography in the diagnosis of the condition, as it has a lower high false-negative rate and non-diagnostic rate.
Orbital emphysema can also be diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Although MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
has a low sensitivity for detecting orbital fractures, it can be used to evaluate rectus muscle pathology, optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
pathology, and brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
pathology, as well as vascular injury.
Treatment
Orbital emphysema on its own is a mild and self-limiting disease. The majority of cases of orbital emphysema are self-resolving and do not need treatment. The underlying causes and injuries that caused orbital emphysema, on the other hand, may be serious, necessitating urgent intervention including surgery. If related visual symptoms or other acute orbital compression symptoms are present, lateral canthotomy or cantholysis, orbital decompression by needle aspiration, and bone decompression may be required to relieve orbital pressure and preserve vision. Prophylactic oral antibiotics may be needed to prevent secondary infection.Reference list
{{Reflist Ophthalmology