Ophellas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
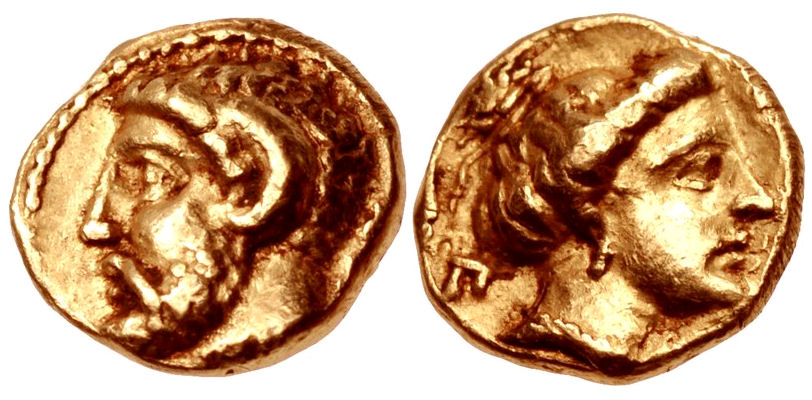

 Ophellas or Ophelas (
Ophellas or Ophelas (


 Ophellas or Ophelas (
Ophellas or Ophelas (fl.
''Floruit'' ( ; usually abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for 'flourished') denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indic ...
c. 350 – 308 BC) was an ancient Macedonia
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
n soldier and politician. Born in Pella
Pella () is an ancient city located in Central Macedonia, Greece. It served as the capital of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. Currently, it is located 1 km outside the modern town of Pella ...
in Macedonia, he was a member of the expeditionary army of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
in Asia, and later acted as Ptolemaic governor of Cyrene. His father's name was Seilenus.
India
Ophellas's name is first mentioned as atrierarch
Trierarch () was the title of officers who commanded a trireme (''triēres'') in the classical Greek world.
In Classical Athens, the title was associated with the trierarchy (τριηραρχία, ''triērarchia''), one of the public offices or ...
(commander of a trireme
A trireme ( ; ; cf. ) was an ancient navies and vessels, ancient vessel and a type of galley that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean Sea, especially the Phoenicians, ancient Greece, ancient Greeks and ancient R ...
) of the fleet of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
on the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
in 326 BC.
Governor of Cyrenaica (322 BC – c. 308 BC)
After the death of Alexander, he followed the fortunes ofPtolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (; , ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'', "Ptolemy the Savior"; 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian, and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the Ptolemaic Kingdom centered on Egypt. Pto ...
, by whom he was sent, in 322 BC, at the head of a considerable army, to take advantage of the civil war which had broken out in Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika (, , after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between the 16th and 25th meridians east, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, als ...
. This he successfully accomplished. Having totally defeated Thimbron and the party that supported him, he helped establish Ptolemaic control over Cyrene itself and its dependencies. The character of the new pro-Ptolemaic regime at Cyrene is illuminated by a lengthy constitutional document from Cyrene, preserved on stone, whose precise date remains controversial.
Ophellas' later career is somewhat obscure. Justin
Justin may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Justin (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Justin (historian), Latin historian who lived under the Roman Empire
* Justin I (c. 450–527) ...
styles Ophellas "''rex Cyrenarum''", king of Cyrene, but it seems improbable that he had really assumed the regal title. He was married to Eurydice of Athens, a descendant of Miltiades
Miltiades (; ; c. 550 – 489 BC), also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian statesman known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cimon Coalemos, a renowned ...
, and appears to have maintained friendly relations with Athens. It seems likely that he was left by Ptolemy as governor of Cyrene, which he presumably continued to hold on behalf of Ptolemy until 309/8 BC: his name is not mentioned in the account given by Diodorus of the revolt of the Cyrenaeans in 313 BC, which was rapidly suppressed by Ptolemy.
He is next heard of in 309/8 BC, when Agathocles
Agathocles ( Greek: ) is a Greek name. The most famous person called Agathocles was Agathocles of Syracuse, the tyrant of Syracuse. The name is derived from and .
Other people named Agathocles include:
*Agathocles, a sophist, teacher of Damon
...
of Syracuse
Syracuse most commonly refers to:
* Syracuse, Sicily, Italy; in the province of Syracuse
* Syracuse, New York, USA; in the Syracuse metropolitan area
Syracuse may also refer to:
Places
* Syracuse railway station (disambiguation)
Italy
* Provi ...
turned his attention towards Ophellas as likely to prove a useful ally in his war against the Carthaginians
The Punic people, usually known as the Carthaginians (and sometimes as Western Phoenicians), were a Semitic people, Semitic people who Phoenician settlement of North Africa, migrated from Phoenicia to the Western Mediterranean during the Iron ...
. In order to gain him over he promised to cede to him whatever conquests their combined forces might make in Africa, reserving to himself only the possession of Sicily. Ophellas gathered a powerful army from the homeland of his wife Euthydike where many citizens felt disgruntled after having lost their voting rights. Notwithstanding all the natural obstacles which presented themselves on his route, he succeeded in reaching the Carthaginian territories after a toilsome and perilous march of more than two months' duration. He was received by Agathocles with every demonstration of friendship, and the two armies encamped near each other: but not many days had elapsed when Agathocles betrayed his new ally, attacked the camp of the Cyrenaeans, and had Ophellas himself killed.Diodorus xx. 42.4-5; 43.3-4 The Cyrenean troops, left without a leader, went over to Agathocles.
Sometime after his death, the control of Cyrene was handed over to Magas of Cyrene
Magas of Cyrene (; born before 317 BC – 250 BC, ruled 276 BC – 250 BC) was a Greek King of Cyrenaica. Through his mother’s second marriage to Ptolemy I he became a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty. He managed to wrest independence for Cy ...
, who was first a governor for the province before claiming independence from the Ptolemaic Kingdom
The Ptolemaic Kingdom (; , ) or Ptolemaic Empire was an ancient Greek polity based in Ancient Egypt, Egypt during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 305 BC by the Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general Ptolemy I Soter, a Diadochi, ...
and becoming king in 276 BC.
References
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Ophellas 4th-century BC births 4th-century BC Macedonians Ancient Pellaeans Kings of Cyrene Ptolemaic generals Ptolemaic governors Trierarchs of Nearchus' fleet