Operation Boardman on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Operation Avalanche was the codename for the Allied landings near the port of
 At Salerno the decision had been taken to assault without previous naval or aerial bombardment, in order to secure surprise. Tactical surprise was not achieved, as the naval commanders had predicted. As the first wave approached the shore at Paestum a loudspeaker from the landing area proclaimed in English, "Come on in and give up. We have you covered." The troops attacked nonetheless.
The Germans had established artillery and machine-gun posts and scattered tanks through the landing zones which made progress difficult, but the beach areas were successfully taken. Around 07:00 a concerted counterattack was made by the 16th Panzer division. It caused heavy casualties, but was beaten off with naval gunfire support. Both the British and the Americans made slow progress, and still had a 10-mile gap between them at the end of day one. They linked up by the end of day two and occupied 35–45 miles of coast line to a depth of six or seven miles.
General Montgomery had predicted ''Baytown'' would be a waste of effort because it assumed the Germans would give battle in Calabria; if they failed to do so, the diversion would not work. He was proved correct. After Baytown, the Eighth Army marched north to the Salerno area against no opposition other than engineer obstacles.
During September 12–14 the Germans organized a concerted counterattack with six divisions of motorised troops, hoping to throw the Salerno beachhead into the sea before it could link with the British 8th Army. Heavy casualties were inflicted, as the Allied troops were too thinly spread to be able to resist concentrated attacks. The outermost troops were therefore withdrawn in order to reduce the perimeter. The new perimeter was held with the assistance of 4,000 paratroopers from the 82nd and 509th PIB who air dropped near the hot spots, from strong naval gunfire support, and from well-served Fifth Army artillery. The German attacks reached almost to the beaches but ultimately failed. The heavy gunfire of Allied battleships practically immobilised counterattacking German units with their sheer firepower, forcing the Germans to halt their counteroffensive and regroup.
General Clark was awarded the Distinguished Service Cross, the second-highest US award for valor in combat, for his front-line leadership during this crisis. He was frequently seen in the most forward positions encouraging the troops. However, in the estimate of historian
At Salerno the decision had been taken to assault without previous naval or aerial bombardment, in order to secure surprise. Tactical surprise was not achieved, as the naval commanders had predicted. As the first wave approached the shore at Paestum a loudspeaker from the landing area proclaimed in English, "Come on in and give up. We have you covered." The troops attacked nonetheless.
The Germans had established artillery and machine-gun posts and scattered tanks through the landing zones which made progress difficult, but the beach areas were successfully taken. Around 07:00 a concerted counterattack was made by the 16th Panzer division. It caused heavy casualties, but was beaten off with naval gunfire support. Both the British and the Americans made slow progress, and still had a 10-mile gap between them at the end of day one. They linked up by the end of day two and occupied 35–45 miles of coast line to a depth of six or seven miles.
General Montgomery had predicted ''Baytown'' would be a waste of effort because it assumed the Germans would give battle in Calabria; if they failed to do so, the diversion would not work. He was proved correct. After Baytown, the Eighth Army marched north to the Salerno area against no opposition other than engineer obstacles.
During September 12–14 the Germans organized a concerted counterattack with six divisions of motorised troops, hoping to throw the Salerno beachhead into the sea before it could link with the British 8th Army. Heavy casualties were inflicted, as the Allied troops were too thinly spread to be able to resist concentrated attacks. The outermost troops were therefore withdrawn in order to reduce the perimeter. The new perimeter was held with the assistance of 4,000 paratroopers from the 82nd and 509th PIB who air dropped near the hot spots, from strong naval gunfire support, and from well-served Fifth Army artillery. The German attacks reached almost to the beaches but ultimately failed. The heavy gunfire of Allied battleships practically immobilised counterattacking German units with their sheer firepower, forcing the Germans to halt their counteroffensive and regroup.
General Clark was awarded the Distinguished Service Cross, the second-highest US award for valor in combat, for his front-line leadership during this crisis. He was frequently seen in the most forward positions encouraging the troops. However, in the estimate of historian
 The German 10th Army had come very close to overwhelming the Salerno beachhead. The Allies had been fortunate that at this time
The German 10th Army had come very close to overwhelming the Salerno beachhead. The Allies had been fortunate that at this time
 With the Salerno beachhead secure, the 5th Army could begin to attack northwest towards Naples. The 8th Army had been making quick progress from the "toe" in the face of German engineer delaying actions and linked with the 1st Airborne Division on the Adriatic coast. It united the left of its front with the 5th Army's right on 16 September, and advancing up the Adriatic coast captured the airfields near
With the Salerno beachhead secure, the 5th Army could begin to attack northwest towards Naples. The 8th Army had been making quick progress from the "toe" in the face of German engineer delaying actions and linked with the 1st Airborne Division on the Adriatic coast. It united the left of its front with the 5th Army's right on 16 September, and advancing up the Adriatic coast captured the airfields near
Print
* * * * – Total pages: 192 * – Total pages: 96 * * * * ·Salerno Remembered by Geoffrey Curtis. Published by The Queen's Royal Surrey Regimental Association 1988 ISBN 0 7110 1901 0
Salerno
Salerno (, ; ; ) is an ancient city and ''comune'' (municipality) in Campania, southwestern Italy, and is the capital of the namesake province, being the second largest city in the region by number of inhabitants, after Naples. It is located ...
, executed on 9 September 1943, part of the Allied invasion of Italy
The Allied invasion of Italy was the Allies of World War II, Allied Amphibious warfare, amphibious landing on mainland Italy that took place from 3 September 1943, during the Italian campaign (World War II), Italian campaign of World War II. T ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. The Italians withdrew from the war the day before the invasion, but the Allies landed in an area defended by German troops. Planned under the name ''Top Hat'', it was supported by the deception plan Operation ''Boardman''.
The landings were carried out by the U.S. Fifth Army, under Lieutenant General Mark W. Clark
Mark Wayne Clark (1 May 1896 – 17 April 1984) was a United States Army officer who fought in World War I, World War II, and the Korean War. He was the youngest four-star general in the U.S. Army during World War II.
During World War I, he wa ...
. It comprised the U.S. VI Corps, the British X Corps, and the U.S. 82nd Airborne Division
The 82nd Airborne Division is an Airborne forces, airborne infantry division (military), division of the United States Army specializing in Paratrooper, parachute assault operations into hostile areasSof, Eric"82nd Airborne Division" ''Spec Ops ...
, a total of about nine divisions
Division may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
* Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting of 10,000 t ...
. Its primary objectives were to seize the port of Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
to ensure resupply, and to cut across to the east coast, trapping the Axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
troops further south.
In order to draw troops away from the landing ground, Operation Baytown
Operation Baytown was an Allied amphibious landing on the mainland of Italy that took place on 3 September 1943, part of the Allied invasion of Italy, itself part of the Italian Campaign, during the Second World War.
Planning
The attack wa ...
was mounted. This was a landing by the British Eighth Army
The Eighth Army was a field army of the British Army during the Second World War. It was formed as the Western Army on 10 September 1941, in Egypt, before being renamed the Army of the Nile and then the Eighth Army on 26 September. It was cr ...
, under General Sir Bernard Montgomery, in Calabria
Calabria is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by the region Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian S ...
in the 'toe' of Italy, on 3 September. Simultaneous sea landings were made by the British 1st Airborne Division at the port of Taranto
Taranto (; ; previously called Tarent in English) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base.
Founded by Spartans ...
(Operation Slapstick
Operation Slapstick was the code name for a British landing from the sea at the Italian port of Taranto during the Second World War. The operation, one of three landings during the Allied invasion of Italy in September 1943, was undertaken by ai ...
).
The Salerno landings were carried out without previous naval or aerial bombardment in order to achieve surprise. Surprise was not achieved.
The Germans had established artillery and machine-gun posts and scattered tanks through the landing zones which made progress difficult, but the beach areas were captured. Around 07:00 a concerted counterattack was made by the 16th Panzer Division. It caused heavy casualties but was beaten off. Both the British and the Americans made slow progress, and still had a gap between them at the end of day one. They linked up by the end of day two and occupied of coastline to a depth of .
Over 12–14 September the Germans organized a concerted counterattack by six divisions of motorized troops, hoping to throw the Salerno beachhead into the sea before it could link with the British Eighth Army. Heavy casualties were inflicted, as the Allied troops were too thinly spread to be able to resist concentrated attacks. The outermost troops were therefore withdrawn in order to reduce the perimeter. The new perimeter was held with the assistance of naval and aerial support, although the German attacks reached almost to the beaches in places.
Background
Following the defeat of the Italian Forces and Afrika Korps inNorth Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, there was disagreement between the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
as to what the next step should be. Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
, the British Prime Minister
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet, and selects its ministers. Modern pri ...
, in particular wanted to invade Italy, which he called the "underbelly of Europe" (commonly misquoted as "soft underbelly"). Popular support in Italy for the war was declining, and he believed an invasion would remove Italy, and thus the influence of the Italian Navy (''Regia Marina
The , ) (RM) or Royal Italian Navy was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy () from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the birth of the Italian Republic (''Repubblica Italiana''), the changed its name to '' Marina Militare'' ("Military Navy").
Origin ...
'') in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
, opening it to Allied traffic. This would make it much easier to supply Allied forces in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
and Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
, and increase British and American supplies to the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. In addition, it would tie down German forces, keeping them away from the planned Allied invasion of Normandy – codenamed Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful liberation of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The ope ...
.
However, General George C. Marshall
George Catlett Marshall Jr. (31 December 1880 – 16 October 1959) was an American army officer and statesman. He rose through the United States Army to become Chief of Staff of the U.S. Army under presidents Franklin D. Roosevelt and Harry S. ...
, the Chief of Staff of the United States Army
The chief of staff of the Army (CSA) is a statutory position in the United States Army held by a general officer. As the highest-ranking officer assigned to serve in the Department of the Army, the chief is the principal military advisor and a ...
, and much of the American staff wanted to undertake no operations that might delay the Normandy invasion. When it became clear that Operation Overlord could not be undertaken in 1943, it was agreed forces in North Africa should be used to invade Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, with no commitment made to any follow-up operations.
Joint Allied Forces Headquarters (AFHQ) were operationally responsible for all Allied land forces in the Mediterranean theatre and it was they who planned and commanded the invasion of Sicily and the Italian mainland.
The Allied invasion of Sicily
The Allied invasion of Sicily, also known as the Battle of Sicily and Operation Husky, was a major campaign of World War II in which the Allies of World War II, Allied forces invaded the island of Sicily in July 1943 and took it from the Axis p ...
in July 1943, codenamed Operation Husky, was highly successful, although many of the Axis forces there were allowed to avoid capture and escape to the mainland. More importantly a coup deposed Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who, upon assuming office as Prime Minister of Italy, Prime Minister, became the dictator of Fascist Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 un ...
as head of the Italian government, which then began approaching the Allies to make peace. It was believed a quick invasion of Italy might hasten an Italian surrender and produce quick military victories over the German troops that would now be trapped fighting in a hostile country. However, Italian (and more so German) resistance proved relatively strong, and fighting in Italy continued even after the fall of Berlin. In addition, the invasion left the Allies in a position of supplying food and supplies to conquered territory, a burden that would otherwise have fallen on Germany. As well, Italy occupied by a hostile German army would have created additional problems for the German Commander-in-Chief Albrecht von Kesselring.
The plan
A diversion operation was designed to support the landings at Salerno, named Operation Boardman. The operation began on June 30, 1943, and ended on August 31, 1943. The plan for the operation was for theAbwehr
The (German language, German for ''resistance'' or ''defence'', though the word usually means ''counterintelligence'' in a military context) ) was the German military intelligence , military-intelligence service for the ''Reichswehr'' and the ...
to intercept radio transmissions which contained false plans for invasions of Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
, Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
, Apulia
Apulia ( ), also known by its Italian language, Italian name Puglia (), is a Regions of Italy, region of Italy, located in the Southern Italy, southern peninsular section of the country, bordering the Adriatic Sea to the east, the Strait of Ot ...
, Southern France
Southern France, also known as the south of France or colloquially in French as , is a geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi atlantique'', Atlas e ...
or Northwestern Italy, and finally Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
in that order. Essentially, the plan sought to weaken German and Italian forces in Southern and Central Italy
Central Italy ( or ) is one of the five official statistical regions of Italy used by the National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT), a first-level NUTS region with code ITI, and a European Parliament constituency. It has 11,704,312 inhabita ...
by shifting Axis focus away from those regions. Also part of this operation was the use of dummies previously used in Operation Waterfall. The dummies were refurbished and set up in Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika (, , after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between the 16th and 25th meridians east, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, als ...
in a way that would suggest an invasion of the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
.
The main landings were scheduled after the success at Sicily for September 9. The main force would land around Salerno
Salerno (, ; ; ) is an ancient city and ''comune'' (municipality) in Campania, southwestern Italy, and is the capital of the namesake province, being the second largest city in the region by number of inhabitants, after Naples. It is located ...
on the western coast in Operation Avalanche. It would consist of the U.S. Fifth Army under Lieutenant General Mark W. Clark, comprising the U.S. VI Corps under Major General Ernest J. Dawley
Major General Ernest Joseph "Mike" Dawley (17 February 1886 – 10 December 1973) was a senior officer of the United States Army, best known during World War II for commanding the VI Corps during Operation Avalanche, the Allied landings at ...
, the X British Corps under Lieutenant-General Richard McCreery
General Sir Richard Loudon McCreery, (1 February 1898 – 18 October 1967) was a career soldier of the British Army, who was decorated for leading one of the last cavalry actions in the First World War. During the Second World War, he was chief ...
, and the U.S. 82nd Airborne Division in reserve, a total of about nine divisions. Its primary objectives were to seize the port of Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
to ensure resupply, and to cut across to the east coast, trapping Axis
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics
*A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular:
** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system
*** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names ...
troops further south. The inclusion of the 82nd Airborne Division as a reserve force was possible only with the cancellation of Operation Giant II. The 1st British Airborne Division would be landed by sea near Taranto
Taranto (; ; previously called Tarent in English) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base.
Founded by Spartans ...
, on the "heel" of Italy in Operation Slapstick
Operation Slapstick was the code name for a British landing from the sea at the Italian port of Taranto during the Second World War. The operation, one of three landings during the Allied invasion of Italy in September 1943, was undertaken by ai ...
, as a diversion for Salerno. Their task was to capture the port and several nearby airfields and link with the Eighth Army before pressing north to join the Fifth Army near Foggia
Foggia (, ; ; ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) of Apulia, in Southern Italy, capital of the province of Foggia. In 2013, its population was 153,143. Foggia is the main city of a plain called Tavoliere delle Puglie, Tavoliere, also know ...
.
The plan was deeply flawed. The Fifth Army would be landing on a very broad 35-mile front, using only three assault divisions, and the two corps were widely separated both in distance and by a river. Furthermore, the terrain was highly favorable to the defender. A U.S. Army Ranger force under Colonel William Orlando Darby consisting of three Ranger battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of up to one thousand soldiers. A battalion is commanded by a lieutenant colonel and subdivided into several Company (military unit), companies, each typically commanded by a Major (rank), ...
s and two British Commando
The Commandos, also known as the British Commandos, were formed during the World War II, Second World War in June 1940, following a request from Winston Churchill, for special forces that could carry out Raid (military), raids against German-occ ...
units was tasked with holding the mountain passes leading to Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
, but no plan existed for linking the Ranger force with X Corps' follow-up units. Finally, Clark ordered that no naval preparatory bombardment take place, concerned that surprise would be lost and reinforcements summoned if a bombardment was made.
Approximately eight German divisions were positioned to cover possible landing sites, including the Hermann Goering Division, 26th and 16th ''Panzer
{{CatAutoTOC, numerals=no
Words and phrases
Germanic words and phrases
Words and phrases by language
la:Categoria:Verba Theodisca ...
'', the 15th and 29th ''Panzergrenadier'', and the 1st and 2nd ''Fallschirmjäger
The () were the airborne forces branch of the Luftwaffe before and during World War II. They were the first paratroopers to be committed in large-scale airborne operations. They were commanded by Kurt Student, the Luftwaffe's second-in-comman ...
''.
Order of battle
Allied
Allied Landing Forces : Embarked in Task Force 80: Western Naval Task Force :: Vice Admiral H. Kent Hewitt, USN :::US Fifth Army
The United States Army North (ARNORTH) is a formation of the United States Army. An Army Service Component Command (ASCC) subordinate to United States Northern Command (NORTHCOM), ARNORTH is the joint force land component of NORTHCOM.
(Lieutenant General Mark Wayne Clark
Mark Wayne Clark (1 May 1896 – 17 April 1984) was a United States Army officer who fought in World War I, World War II, and the Korean War. He was the youngest four-star general in the U.S. Army during World War II.
During World War I, he wa ...
, USA)
:::: British X Corps (Lt. Gen. Richard L. McCreery, BA)
:::: US VI Corps (Maj. Gen. Ernest J. Dawley
Major General Ernest Joseph "Mike" Dawley (17 February 1886 – 10 December 1973) was a senior officer of the United States Army, best known during World War II for commanding the VI Corps during Operation Avalanche, the Allied landings at ...
, USA)
Northern Landing Area (South of Salerno)
: Embarked in Task Force 85: Northern Landing Force
:: Commodore G.N. Oliver, RN
::: British X Corps (Lieutenant General Richard McCreery
General Sir Richard Loudon McCreery, (1 February 1898 – 18 October 1967) was a career soldier of the British Army, who was decorated for leading one of the last cavalry actions in the First World War. During the Second World War, he was chief ...
, BA)
::::* 46th Infantry Division (Maj.-Gen. John Hawkesworth)
::::* 56th (London) Infantry Division
The 56th (London) Infantry Division was a Territorial Army infantry division of the British Army, which served under several different titles and designations. The division served in the trenches of the Western Front during the First World Wa ...
(Maj.-Gen. Douglas Graham)
::::* 7th Armoured Division (Maj.-Gen. George Erskine
General Sir George Watkin Eben James Erskine, (23 August 1899 – 29 August 1965) was a British Army officer from Hascombe, Surrey. After he graduated from Royal Military College, Sandhurst, Erskine was commissioned into the King's Royal Rifle ...
)
::::* 3 US Ranger Battalions (Lt. Col. William O. Darby, USA)
::::* 2 Commando
A commando is a combatant, or operative of an elite light infantry or special operations force, specially trained for carrying out raids and operating in small teams behind enemy lines.
Originally, "a commando" was a type of combat unit, as oppo ...
Forces (Brig. Robert Laycock
Major-General Sir Robert Edward Laycock, (18 April 1907 – 10 March 1968) was a senior British Army officer best known for his influential role in the establishment and command of British Commandos during the Second World War.
Early life
La ...
)
Southern Landing Area (Paestum)
: Embarked in Task Force 81: Southern Landing Force
:: Rear Admiral John L. Hall Jr., USN
::: US VI Corps (Major General Ernest J. Dawley
Major General Ernest Joseph "Mike" Dawley (17 February 1886 – 10 December 1973) was a senior officer of the United States Army, best known during World War II for commanding the VI Corps during Operation Avalanche, the Allied landings at ...
, USA)
::::* 36th Infantry Division (Maj. Gen. Fred L. Walker, USA)
::::* 45th Infantry Division (Maj. Gen. Troy H. Middleton, USA)
Axis
Army Group CGeneralfeldmarschall
''Generalfeldmarschall'' (; from Old High German ''marahscalc'', "marshal, stable master, groom"; ; often abbreviated to ''Feldmarschall'') was a rank in the armies of several German states and the Holy Roman Empire, (''Reichsgeneralfeldmarsch ...
Albert Kesselring
Albert Kesselring (30 November 1885 – 16 July 1960) was a German military officer and convicted war crime, war criminal who served in the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II. In a career which spanned both world wars, Kesselring reached the ra ...
: Tenth Army
:General Heinrich von Vietinghoff
Heinrich Gottfried Otto Richard von Vietinghoff genannt Scheel (6 December 1887 – 23 February 1952) was a German general (''Generaloberst'') of the Wehrmacht during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with O ...
::XIV Panzer Corps
XIV Panzer Corps (also: XIV Army Corps or XIV. ''Armeekorps'') was a corps-level formation of the German Army which fought on both the Eastern Front and in the Italian Campaign.
History
The XIV Panzer Corps was originally formed as the XIV Moto ...
::General der Panzertruppen Hermann Balck
Georg Otto Hermann Balck (7 December 1893 – 29 November 1982) was a highly decorated officer of the German Army who served in both World War I and World War II, rising to the rank of General der Panzertruppe.
Early career
Balck was born in ...
:::''Deployed along coast from north to south of Naples:''
::* 15th Panzergrenadier Division
15th Panzergrenadier Division was a mobile division of the German Army in World War II.
Combat History Sicily
In July 1943 a new 15th Panzergrenadier Division, commanded by ''Generalleutnant'' Eberhard Rodt, was formed by redesignating the Sic ...
(Generalleutnant Eberhard Rodt)
::* Panzer Division ''Hermann Göring'' (Generalmajor Wilhelm Schmalz)
::* 16th Panzer Division (Generalleutnant Rudolf Sieckenius)
:: LXXVI Panzer Corps
::General der Panzertruppen Traugott Herr
Traugott Herr (16 September 1890 – 13 April 1976) was a German general during World War II who commanded the 14th Army and the 10th Army of the Wehrmacht. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords. ...
:::''Deployed in Calabria and Apulia:''
::* 26th Panzer Division
The German 23rd Infantry Division (''23. Infanterie-Division''), later the 26th Panzer Division, was a military unit operational during World War II. It was organized along standard lines for a German infantry division. It was non-motorised an ...
(Generalleutnant Smilo Freiherr von Lüttwitz
Smilo Walther Hinko Oskar Constantin Wilhelm Freiherr von Lüttwitz (23 December 1895 – 19 May 1975) was a German general during World War II and son of Walther von Lüttwitz. After World War II he joined the Bundeswehr in 1957 and served as th ...
)
::* 3rd Panzergrenadier Division (Generalleutnant Fritz-Hubert Gräser
__NOTOC__
Fritz-Hubert Gräser (3 January 1888 – 4 November 1960) was a German general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords.
Awards
* Iron Cross (1914) 2nd Cla ...
)
::* 29th Panzergrenadier Division (Generalleutnant Walter Fries)
Landings
 At Salerno the decision had been taken to assault without previous naval or aerial bombardment, in order to secure surprise. Tactical surprise was not achieved, as the naval commanders had predicted. As the first wave approached the shore at Paestum a loudspeaker from the landing area proclaimed in English, "Come on in and give up. We have you covered." The troops attacked nonetheless.
The Germans had established artillery and machine-gun posts and scattered tanks through the landing zones which made progress difficult, but the beach areas were successfully taken. Around 07:00 a concerted counterattack was made by the 16th Panzer division. It caused heavy casualties, but was beaten off with naval gunfire support. Both the British and the Americans made slow progress, and still had a 10-mile gap between them at the end of day one. They linked up by the end of day two and occupied 35–45 miles of coast line to a depth of six or seven miles.
General Montgomery had predicted ''Baytown'' would be a waste of effort because it assumed the Germans would give battle in Calabria; if they failed to do so, the diversion would not work. He was proved correct. After Baytown, the Eighth Army marched north to the Salerno area against no opposition other than engineer obstacles.
During September 12–14 the Germans organized a concerted counterattack with six divisions of motorised troops, hoping to throw the Salerno beachhead into the sea before it could link with the British 8th Army. Heavy casualties were inflicted, as the Allied troops were too thinly spread to be able to resist concentrated attacks. The outermost troops were therefore withdrawn in order to reduce the perimeter. The new perimeter was held with the assistance of 4,000 paratroopers from the 82nd and 509th PIB who air dropped near the hot spots, from strong naval gunfire support, and from well-served Fifth Army artillery. The German attacks reached almost to the beaches but ultimately failed. The heavy gunfire of Allied battleships practically immobilised counterattacking German units with their sheer firepower, forcing the Germans to halt their counteroffensive and regroup.
General Clark was awarded the Distinguished Service Cross, the second-highest US award for valor in combat, for his front-line leadership during this crisis. He was frequently seen in the most forward positions encouraging the troops. However, in the estimate of historian
At Salerno the decision had been taken to assault without previous naval or aerial bombardment, in order to secure surprise. Tactical surprise was not achieved, as the naval commanders had predicted. As the first wave approached the shore at Paestum a loudspeaker from the landing area proclaimed in English, "Come on in and give up. We have you covered." The troops attacked nonetheless.
The Germans had established artillery and machine-gun posts and scattered tanks through the landing zones which made progress difficult, but the beach areas were successfully taken. Around 07:00 a concerted counterattack was made by the 16th Panzer division. It caused heavy casualties, but was beaten off with naval gunfire support. Both the British and the Americans made slow progress, and still had a 10-mile gap between them at the end of day one. They linked up by the end of day two and occupied 35–45 miles of coast line to a depth of six or seven miles.
General Montgomery had predicted ''Baytown'' would be a waste of effort because it assumed the Germans would give battle in Calabria; if they failed to do so, the diversion would not work. He was proved correct. After Baytown, the Eighth Army marched north to the Salerno area against no opposition other than engineer obstacles.
During September 12–14 the Germans organized a concerted counterattack with six divisions of motorised troops, hoping to throw the Salerno beachhead into the sea before it could link with the British 8th Army. Heavy casualties were inflicted, as the Allied troops were too thinly spread to be able to resist concentrated attacks. The outermost troops were therefore withdrawn in order to reduce the perimeter. The new perimeter was held with the assistance of 4,000 paratroopers from the 82nd and 509th PIB who air dropped near the hot spots, from strong naval gunfire support, and from well-served Fifth Army artillery. The German attacks reached almost to the beaches but ultimately failed. The heavy gunfire of Allied battleships practically immobilised counterattacking German units with their sheer firepower, forcing the Germans to halt their counteroffensive and regroup.
General Clark was awarded the Distinguished Service Cross, the second-highest US award for valor in combat, for his front-line leadership during this crisis. He was frequently seen in the most forward positions encouraging the troops. However, in the estimate of historian Carlo D'Este
Carlo Winthrop D'Este (August 29, 1936 – November 22, 2020) was an American military historian and biographer, author of several books, especially on World War II. He was a decorated U.S. Army lieutenant colonel. In 2011, he was awarded the ...
, both Clark and Harold Alexander bore responsibility for the Salerno landings being a near-disaster.
The Salerno battle was also the site of a mutiny by about 600 men of the British 10th Corps, who on September 16 refused assignment to new units as replacements. They had previously understood that they would be returning to their own units from which they had been separated during the fighting in the North African Campaign
The North African campaign of World War II took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943, fought between the Allies and the Axis Powers. It included campaigns in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts (Western Desert campaign, Desert Wa ...
, mainly because they had been wounded. Eventually the Corps commander, McCreery, persuaded most of the men to follow their orders. The NCOs
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is an enlisted leader, petty officer, or in some cases warrant officer, who does not hold a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted rank ...
who led the mutiny were sentenced to death, but were eventually allowed to rejoin units and the sentence was not carried out.
German strategy changes
 The German 10th Army had come very close to overwhelming the Salerno beachhead. The Allies had been fortunate that at this time
The German 10th Army had come very close to overwhelming the Salerno beachhead. The Allies had been fortunate that at this time Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
had sided with the view of his Army Group commander in Northern Italy, Field Marshall Erwin Rommel
Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel (; 15 November 1891 – 14 October 1944), popularly known as The Desert Fox (, ), was a German '' Generalfeldmarschall'' (field marshal) during World War II. He served in the ''Wehrmacht'' (armed forces) of ...
, and decided that defending Italy south of Rome was not a strategic priority. As a result, the Army Group Commander in southern Italy, Field Marshall Albert Kesselring had been forbidden to call upon reserves from the northern Army Group. The subsequent success of the German 10th Army's defensive campaign in inflicting very heavy casualties on both U.S. 5th and British 8th Armies and Kesselring's strategic arguments that the Allies should be kept as far away from Germany as possible led Hitler to change his mind in October at which point he withdrew Rommel to oversee the build-up of defenses in northern France and gave Kesselring command of the whole of Italy with a remit to keep Rome in German hands for the longest time possible.
Aftermath
Casualties
General Clark in his book ''Calculated Risk'' reports that the X Corps suffered 531 killed in action, 1,915 wounded and 1,561 missing, while the VI Corps had 225 killed, 853 wounded and 589 missing. Clark also stated that most of the missing from both corps subsequently returned to the front lines. After a week long battle, the combined Allied losses were heavy, with 2,349 killed, 7,366 wounded and 4,100 missing. German losses numbered 840 killed, 2,002 wounded and 603 missing.Most of these losses were inflicted by Allied naval support fire and field guns.Further Allied advances
 With the Salerno beachhead secure, the 5th Army could begin to attack northwest towards Naples. The 8th Army had been making quick progress from the "toe" in the face of German engineer delaying actions and linked with the 1st Airborne Division on the Adriatic coast. It united the left of its front with the 5th Army's right on 16 September, and advancing up the Adriatic coast captured the airfields near
With the Salerno beachhead secure, the 5th Army could begin to attack northwest towards Naples. The 8th Army had been making quick progress from the "toe" in the face of German engineer delaying actions and linked with the 1st Airborne Division on the Adriatic coast. It united the left of its front with the 5th Army's right on 16 September, and advancing up the Adriatic coast captured the airfields near Foggia
Foggia (, ; ; ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) of Apulia, in Southern Italy, capital of the province of Foggia. In 2013, its population was 153,143. Foggia is the main city of a plain called Tavoliere delle Puglie, Tavoliere, also know ...
on 27 September. Foggia was a major Allied objective because the large airfield complex there would give the Allied air forces the ability to strike new targets in France, Germany and the Balkans. The 5th Army captured Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
on 1 October, and reached the line of the Volturno
The Volturno (ancient Latin name Volturnus, from ''volvere'', to roll) is a river in south-central Italy.
Geography
It rises in the Abruzzese central Apennines of Samnium near Castel San Vincenzo (province of Isernia, Molise) and flows southe ...
River on October 6. This provided a natural barrier, securing Naples, the Campanian Plain and the vital airfields on it from counterattack. Meanwhile, on the Adriatic coast, the British 8th Army had advanced to a line from Campobasso
Campobasso (, ; ) is a city and ''comune'' in southern Italy, the capital of the region of Molise and of the province of Campobasso. It is located in the high basin of the Biferno river, surrounded by Sannio and Matese mountains.
Campobas ...
to Larino
Larino (; ) is a town and ''comune'' of approximately 8,100 inhabitants in Molise, province of Campobasso, southern Italy. It is located in the fertile valley of the Biferno River.
The old town, seen from the mountains, is shaped like a bird' ...
and Termoli
Termoli ( Molisano: ''Térmëlë'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) on the south Adriatic coast of Italy, in the province of Campobasso, region of Molise. It has a population of around 32,000, having expanded quickly after World War II, and it is a ...
on the Biferno river.
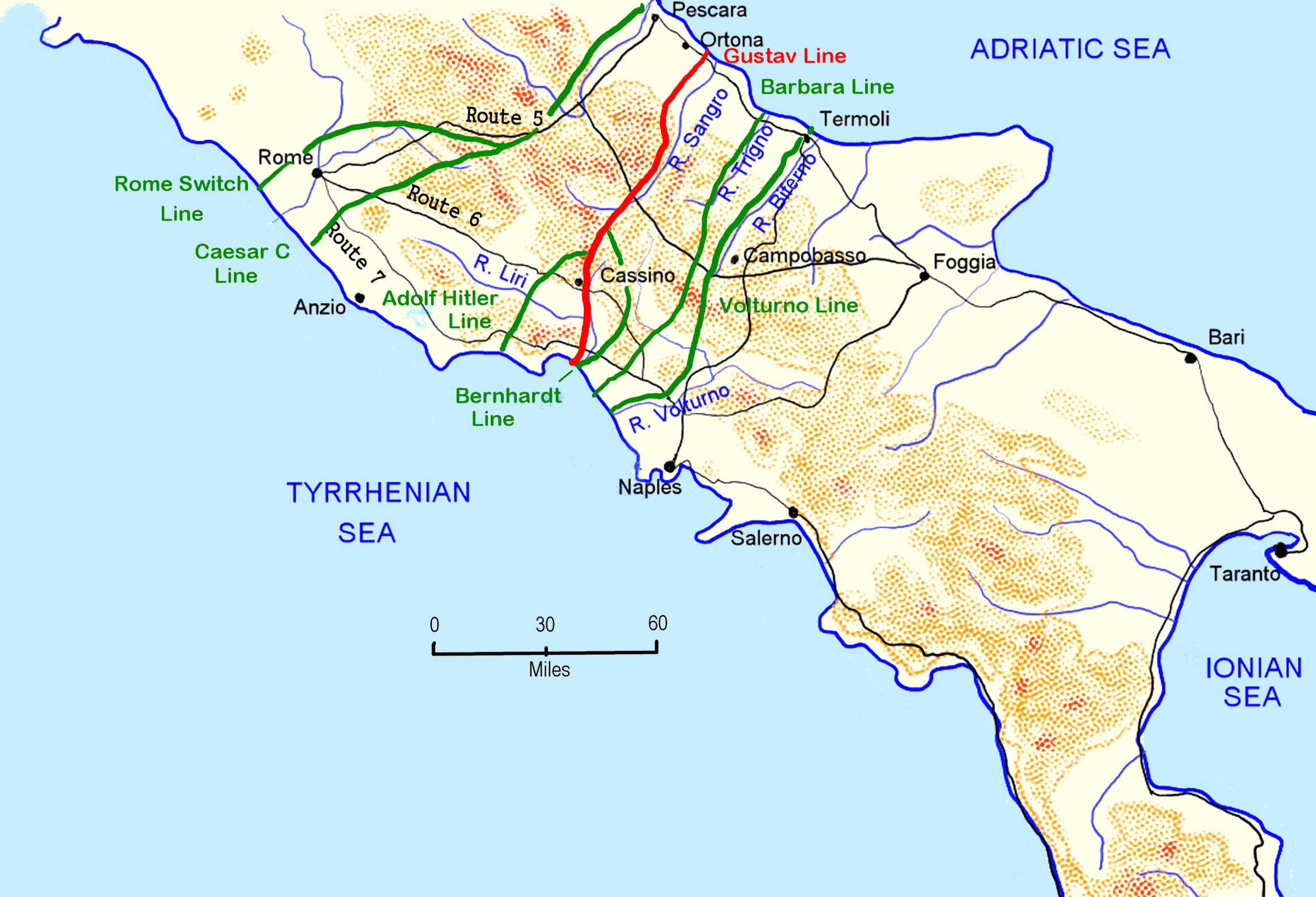
Thus, by early October, the whole of southern Italy was in Allied hands, and the Allied armies now stood facing the Volturno Line
The Volturno Line (also known as the Viktor Line; , ) was a German defensive position in Italy during the Italian Campaign of World War II.
The line ran from Termoli in the east, along the Biferno River through the Apennine Mountains to the ...
, the first of a series of prepared defensive lines running across Italy from which the Germans chose to fight delaying actions, giving ground slowly and buying time to complete their preparation of the Winter Line
The Winter Line was a series of German and Italian military fortifications in Italy, constructed during World War II by Organisation Todt and commanded by Albert Kesselring. The series of three lines was designed to defend a western section ...
, their strongest defensive line south of Rome. The next stage of the Italian Campaign became for the Allied armies a grinding and attritional slog against skillful, determined and well prepared defenses in terrain and weather conditions which favoured defense and hampered the Allied advantages in mechanised equipment and air superiority. It took until mid-January 1944 to fight through the Volturno, Barbara and Bernhardt lines to reach the Gustav Line, the backbone of the Winter Line defenses, setting the scene for the four Battles of Monte Cassino which took place between January and May 1944.
Notes
References
Bibliography
Filmography
*A Walk in the Sun (1945 film)
''A Walk in the Sun'' is a 1945 American war film based on the novel by Harry Brown, who was a writer for '' Yank, the Army Weekly'' based in England. The book was serialized in ''Liberty Magazine'' in October 1944.
The film was directed by Le ...
, directed by Lewis Milestone
Lewis Milestone (born Leib Milstein (Russian: Лейб Мильштейн); September 30, 1895 – September 25, 1980) was an American film director. Milestone directed '' Two Arabian Knights'' (1927) and '' All Quiet on the Western Front'' (1 ...
, US
{{DEFAULTSORT:Avalanche, Operation
Battles of World War II involving the United States
Invasions by the United Kingdom
World War II operations and battles of the Italian Campaign
Naval battles and operations of World War II involving the United Kingdom
Invasions by Canada
Invasions by the United States
Military history of Salerno
Military history of Campania
Airborne operations of World War II