Ooidal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ooids (, ) are small (commonly ≤2 mm in diameter),
Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks: Analysis, Interpretation and Application
', 2nd ed.
Springer
pp. 242–244. . Accessed 2014-06-23. Wilson, M.A., Cooke, A.M., Judge, S.A. and Palmer, T.J. 2021. Ooimmuration: Enhanced fossil preservation by ooids, with examples from the Middle Jurassic of southwestern Utah, USA. ''Palaios'' 36: 326-329. https://doi.org/10.2110/palo.2021.036
spheroid
A spheroid, also known as an ellipsoid of revolution or rotational ellipsoid, is a quadric surface (mathematics), surface obtained by Surface of revolution, rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with t ...
al, "coated" (layered) sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock formed by the cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedime ...
grains, usually composed of calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
, but sometimes made up of iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
- or phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
-based minerals. Ooids usually form on the sea floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as seabeds.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
, most commonly in shallow tropical seas (around the Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of its population. ...
, for example, or in the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
). After being buried under additional sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
, these ooid grains can be cemented together to form a sedimentary rock called an ''oolite
Oolite or oölite () is a sedimentary rock formed from ooids, spherical grains composed of concentric layers. Strictly, oolites consist of ooids of diameter 0.25–2 millimetres; rocks composed of ooids larger than 2 mm are called pis ...
''. Oolites usually consist of calcium carbonate; these belong to the limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
rock family. Pisoids are similar to ooids, but are larger than 2 mm in diameter, often considerably larger, as with the pisoids in the hot springs at Carlsbad (Karlovy Vary
Karlovy Vary (; , formerly also spelled ''Carlsbad'' in English) is a spa town, spa city in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 49,000 inhabitants. It is located at the confluence of the Ohře and Teplá (river), Teplá ri ...
) in the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
. Ooids have been the subject of scientific research for centuries.https://www.geological-digressions.com/the-mineralogy-of-carbonates-non-skeletal-grains/
Formation
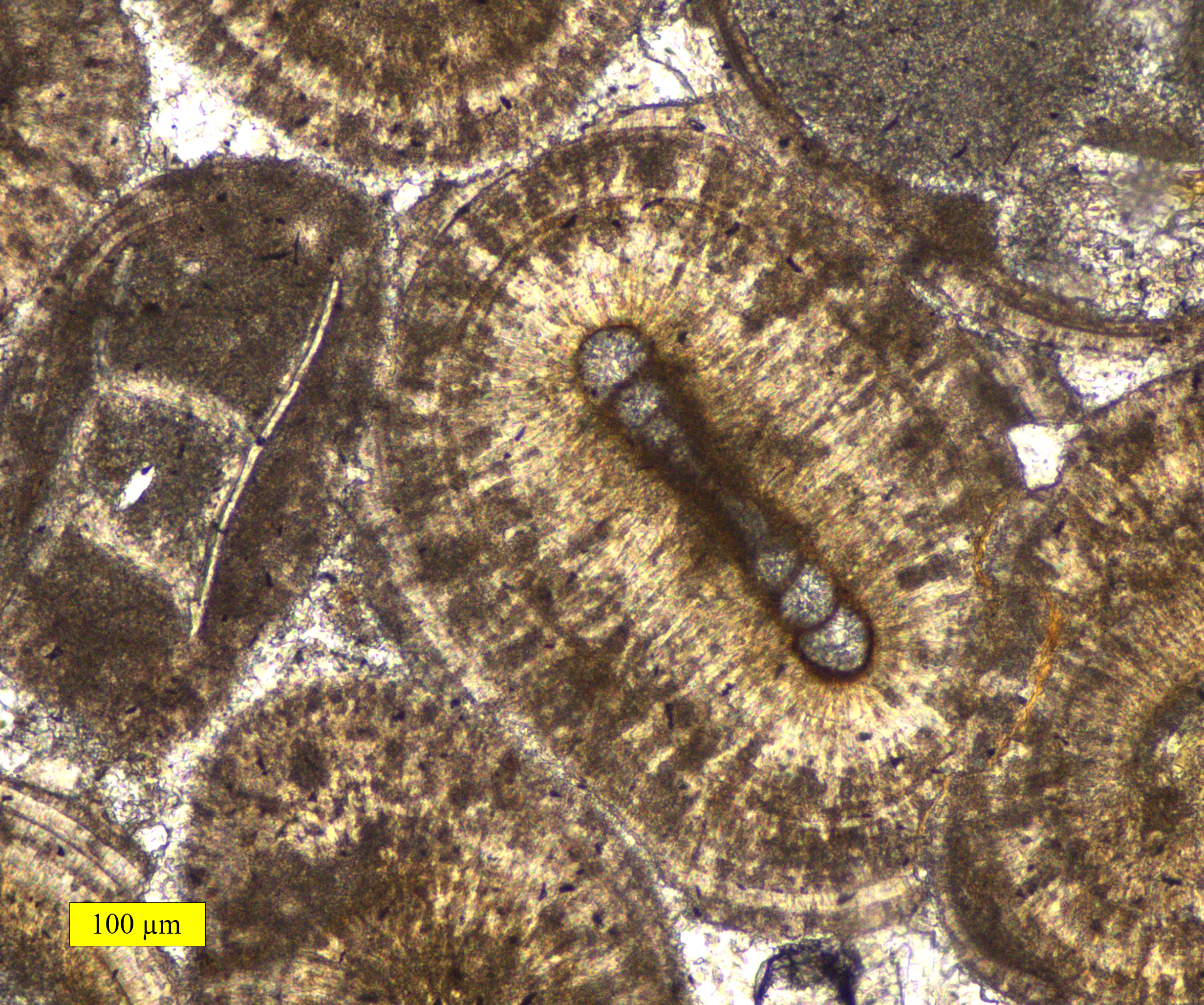
An ooid forms as a series of concentric layers around a nucleus. The layers contain crystals arranged radially, tangentially or randomly. The nucleus can be a shell fragment, quartz grain or any other small fragment. Most modern ooids arearagonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral and one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate (), the others being calcite and vaterite. It is formed by biological and physical processes, including precipitation fr ...
, a polymorph of calcium carbonate; some are composed of high-magnesium calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
, and some are bimineralic (layers of calcite and aragonite). Ancient ooids can be calcitic, either originally precipitated as calcite (as in calcite seas
A calcite sea is a sea in which low-magnesium calcite is the primary inorganic marine calcium carbonate precipitate. An aragonite sea is the alternate seawater chemistry in which aragonite and high-magnesium calcite are the primary inorganic carbo ...
), or formed by alteration (neomorphic replacement) of aragonitic ooids (or the aragonite layers in originally bimineralic ooids). Moldic ooids (or molds later filled in by calcite cement) occur in both young and ancient rocks, indicating the removal of a soluble polymorph (usually aragonite).
Variation
Whether ooids become calcitic or aragonitic can be linked tostrontium
Strontium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, it is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to ...
/calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
substitution within the crystalline structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat ...
. This has been shown in some examples to be due to temperature fluctuations in marine environment
A marine habitat is a habitat that supports marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term ''marine'' comes from the Latin ''mare'', meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmen ...
s, which affects salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
levels, which in turn facilitate the substitution. Marine calcitic ooids were typically formed during calcite sea
A calcite sea is a sea in which low-magnesium calcite is the primary inorganic marine calcium carbonate precipitate. An aragonite sea is the alternate seawater chemistry in which aragonite and high-magnesium calcite are the primary inorganic carb ...
intervals, especially during the Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
and the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
Periods. The geochemistry of these seas was a function of seafloor spreading
Seafloor spreading, or seafloor spread, is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
History of study
Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener ...
and fluctuating Mg/Ca ratios. Low Mg/Ca ratios favor the precipitation of low-magnesium calcite.
Growth mode
Ooids with radial crystals (such as the aragonitic ooids in theGreat Salt Lake
The Great Salt Lake is the largest saltwater lake in the Western Hemisphere and the eighth-largest terminal lake in the world. It lies in the northern part of the U.S. state of Utah and has a substantial impact upon the local climate, partic ...
, Utah, US) grow by ions extending the lattices of the radial crystals. The mode of growth of ooids with tangential (usually minute needle-like) crystals is less clear. They may be accumulated in a "snowball" fashion from tiny crystals in the sediment or water, or they may crystallize in place on the ooid surface. A hypothesis of growth by accretion (like a snowball) from the polymineralic sediment of fine aragonite, high-magnesium calcite (HMC) and low-magnesium calcite (LMC), must explain how only aragonite needles are added to the ooid cortex. Both in tangential and in radial ooids, the cortex is composed of many very fine increments of growth. Some modern (and ancient) ooids partially or totally lack clear layering and have a micritic (very fine grained) texture. Examination of such micritic ooids by scanning electron microscopy often shows evidence of microbial borings later filled by fine cement.
Growth factors
There are several factors that affect ooid growth:supersaturation
In physical chemistry, supersaturation occurs with a solution (chemistry), solution when the concentration of a solute exceeds the concentration specified by the value of solubility at Solubility equilibrium, equilibrium. Most commonly the term ...
of the water with respect to calcium carbonate, the availability of nuclei, agitation of the ooids, water depth, and the role of microbes
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in ...
.

Ooimmuration
Sometimesfossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
are included in ooids, often forming the nuclei. This taphonomic
Taphonomy is the study of how organisms decay and become fossilized or preserved in the paleontological record. The term ''taphonomy'' (from Greek , 'burial' and , 'law') was introduced to paleontology in 1940 by Soviet scientist Ivan Efremov ...
process is termed ''ooimmuration'' (Wilson et al., 2021). The formation of the ooid cortex around the test or shell protects it from abrasion, fragmentation and bioerosion. Ooimmuration also retains fine organic remains that would ordinarily be winnowed away by currents.
References
Flügel, Erik (2010),Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks: Analysis, Interpretation and Application
', 2nd ed.
Springer
pp. 242–244. . Accessed 2014-06-23. Wilson, M.A., Cooke, A.M., Judge, S.A. and Palmer, T.J. 2021. Ooimmuration: Enhanced fossil preservation by ooids, with examples from the Middle Jurassic of southwestern Utah, USA. ''Palaios'' 36: 326-329. https://doi.org/10.2110/palo.2021.036
References
External links
*{{webarchive , url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130620192517/http://www.geologyrocks.co.uk/tutorials/ooid_formation , date=20 June 2013 , title= Ooid Formation Sedimentary rocks Limestone Petrology