Official Bank Rate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the United Kingdom, the official bank rate is the rate that the

Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
charges banks and financial institutions for loans with a maturity of 1 day. It is the Bank of England's key interest rate for enacting monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
. It is more analogous to the US discount rate than to the federal funds rate
In the United States, the federal funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions (banks and credit unions) lend reserve balances to other depository institutions overnight on an collateral (finance), uncollateralized basis ...
. The security for the lending can be any of a list of eligible securities (commonly gilts
Gilt-edged securities, also referred to as gilts, are bonds issued by the UK Government. The term is of British origin, and referred to the debt securities issued by the Bank of England on behalf of His Majesty's Treasury, whose paper certific ...
) and the transactions are overnight repurchase agreements. Changes are recommended by the Monetary Policy Committee
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is a committee of the Bank of England, which meets for three and a half days, eight times a year, to decide the official interest rate in the United Kingdom (the Bank of England Base Rate).
It is also respo ...
and enacted by the Governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
.
On 2 August 2018 the Bank of England base rate was increased to 0.75%, but then cut to 0.25% on 11 March 2020, and shortly thereafter to an all-time low of 0.1% on 19 March, as emergency measures during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
. On 15 December 2021, the Monetary Policy Committee voted 8-1 to increase the bank rate to 0.25%, and subsequently increased it thirteen more times to 5.25% on 02 August 2023. As of 21 August 2024 the bank rate sits at 5%.
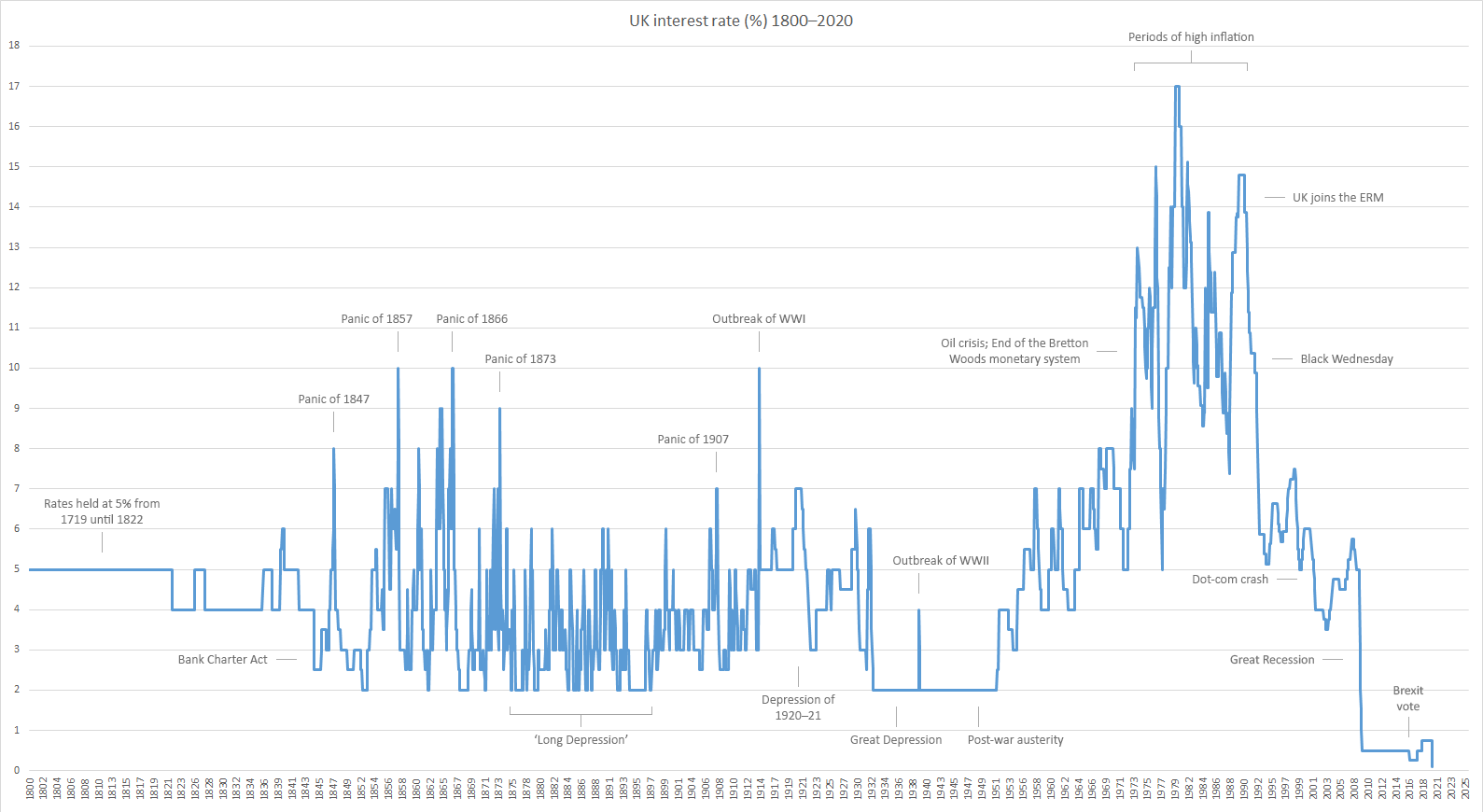
History
The official bank rate has existed in various forms since 1694 and has ranged from 0.1% to 17%. The name and meaning (depositing vs lending) of this key interest rate has changed over the years. The current name, Official Bank Rate, was introduced in 2006 and replaced the previous Repo Rate (repo is short forrepurchase agreement
A repurchase agreement, also known as a repo, RP, or sale and repurchase agreement, is a form of secured short-term borrowing, usually, though not always using government securities as collateral. A contracting party sells a security to a lend ...
) in use since 1997. Previously (between 1981 and 1997) the name was Minimum Band 1 Dealing Rate and prior to that the Minimum Lending Rate.


See also
*Bank rate
Bank rate, also known as discount rate in American English, and (familiarly) the base rate in British English, is the rate of interest which a central bank charges on its loans and advances to a commercial bank. The bank rate is known by a numb ...
* Implied repo rate
* Repo rate
References
Bank of England Interest rates Banking terms {{bank-stub