Nursing Administration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
online article – see documents link at left
Nightingale believed that nursing was a social freedom and mission for women. She believed that any educated woman could help improve the care of the ill. Her '' Notes on Nursing'' (1859) was a popular call to action. The Nightingale model of nursing education led to one of the first schools of nursing to be connected to a hospital and medical school. It spread widely in Europe and North America after 1870. Nightingale included five factors that helped nurses in her time who worked amidst poor sanitation and little education. These factors include fresh air, clean water, a working drainage system, cleanliness, and good light. Nightingale believed that a clean working environment was important in caring for patients. In the 19th century, this theory was ideal for helping patients, providing a guide for nurses to alter the environment around patients for the betterment of their health. Nightingale's recommendations built upon the successes of Jamaican "doctresses" such as
 In the 19th and early 20th century, nursing was considered a woman's profession, just as doctoring was a profession for men. With increasing expectations of workplace equality during the late 20th century, nursing became an officially gender-neutral profession, though in practice the percentage of male nurses remained well below that of female
In the 19th and early 20th century, nursing was considered a woman's profession, just as doctoring was a profession for men. With increasing expectations of workplace equality during the late 20th century, nursing became an officially gender-neutral profession, though in practice the percentage of male nurses remained well below that of female  The development of undergraduate and post-graduate nursing degrees came after the war. Nursing research and a desire for association and organization led to the formation of professional organizations and
The development of undergraduate and post-graduate nursing degrees came after the war. Nursing research and a desire for association and organization led to the formation of professional organizations and
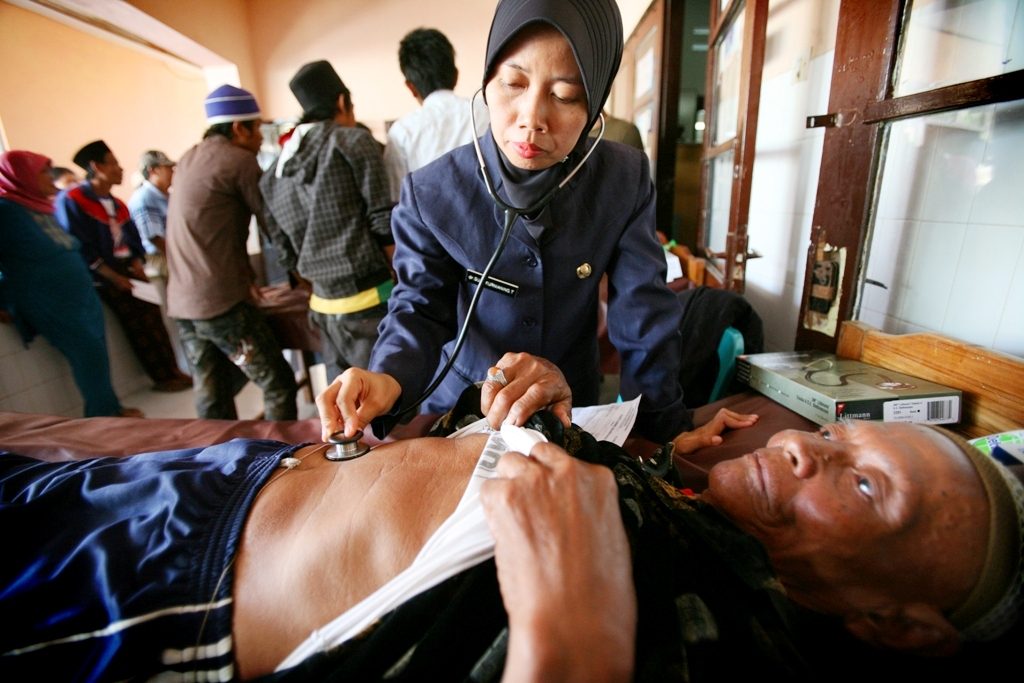 The practice of nursing is based upon a
The practice of nursing is based upon a
Retrieved August 2007 Multiple educational paths lead to becoming a professional nurse; these vary by jurisdiction; all involve extensive study of
/ref> The list of regulated nursing professions is held in the regulated professions database.
UNCG Library Betty H. Carter Women Veterans Historical Project: Nurse
* {{Authority control Military supporting service occupations Rehabilitation team Health care occupations Hospital staff Occupational safety and health Articles containing video clips
health care
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physic ...
profession that "integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alleviation of suffering through compassionate presence". Nurses practice in many specialties with varying levels of certification and responsibility. Nurses comprise the largest component of most healthcare environments. There are shortages of qualified nurses in many countries.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis ...
, therapist
A therapist is a person who offers any kinds of therapy. Therapists are trained professionals in the field of any types of services like psychologists, social workers, counselors, etc. They are helpful in counseling individuals for various mental ...
s, patients, patients' families, and other team members that focuses on treating illness to improve quality of life.
In the United Kingdom and the United States, clinical nurse specialists and nurse practitioners diagnose health problems and prescribe medications and other therapies, depending on regulations that vary by state. Nurses may help coordinate care performed by other providers or act independently as nursing professionals. In addition to providing care and support, nurses educate the public and promote health and wellness.
In the U.S., nurse practitioners are nurses with a graduate degree in advanced practice nursing, and are permitted to prescribe medications. They practice independently in a variety of settings in more than half of the United States. In the postwar
A post-war or postwar period is the interval immediately following the end of a war. The term usually refers to a varying period of time after World War II, which ended in 1945. A post-war period can become an interwar period or interbellum, ...
period, nurse education has diversified, awarding advanced and specialized credentials, and many traditional regulations and roles are changing.
History
Premodern
Nursing historians face challenges of determining whether care provided to the sick or injured in antiquity is called nursing care. In the fifth century BC, for example, the Hippocratic Collection in places described skilled care and observation of patients by male "attendants," who may have provided care now provided by nurses. Around 600 BC in India, it is recorded in ''Sushruta Samhita
The ''Sushruta Samhita'' (, ) is an ancient Sanskrit text on medicine and one of the most important such treatises on this subject to survive from the ancient world. The ''Compendium of Sushruta, Suśruta'' is one of the foundational texts of ...
'', Book 3, Chapter V about the role of the nurse as "the different parts or members of the body as mentioned before including the skin, cannot be correctly described by one who is not well versed in anatomy. Hence, anyone desirous of acquiring a thorough knowledge of anatomy should prepare a dead body and carefully, observe, by dissecting it, and examining its different parts."
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, members of religious orders
A religious order is a subgroup within a larger confessional community with a distinctive high-religiosity lifestyle and clear membership. Religious orders often trace their lineage from revered teachers, venerate their founders, and have a d ...
such as nuns
A nun is a woman who vows to dedicate her life to religious service and contemplation, typically living under vows of Evangelical counsels, poverty, chastity, and obedience in the Enclosed religious orders, enclosure of a monastery or convent.' ...
and monks often provided nursing-like care. Examples exist in Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
, Islamic
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, and other traditions. The biblical figure of Phoebe is described in many sources as "the first visiting nurse". These traditions were influential in the development of the ethos
''Ethos'' is a Greek word meaning 'character' that is used to describe the guiding beliefs or ideals that characterize a community, nation, or ideology; and the balance between caution and passion. The Greeks also used this word to refer to the ...
of modern nursing. Its religious roots remain in evidence in many countries. One example in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
is the use of the historical title "sister" to refer to a senior nurse.
During the Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
, Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
reformers shut down monasteries and convents, allowing a few hundred municipal hospices to remain in operation in northern Europe. Nuns who had been serving as nurses were given pensions or told to marry and stay home. Nursing care went to the inexperienced as traditional caretakers, rooted in the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, were removed from their positions. The nursing profession in Europe was extinguished for approximately 200 years.
19th century
During theCrimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
, Grand Duchess Elena Pavlovna called for women to join the Order of Exaltation of the Cross (''Krestodvizhenskaya Obshchina'') for a year of service in military hospitals. The first section of twenty-eight "sisters", headed by Aleksandra Petrovna Stakhovich, the Directress of the Order, reached Crimea early in November 1854.
Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale (; 12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English Reform movement, social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during th ...
laid the foundations of professional nursing after the Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
, in light of a comprehensive statistical study she made of sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
in India, leading her to emphasize the importance of sanitation. "After 10 years of sanitary reform, in 1873, Nightingale reported that mortality among the soldiers in India had declined from 69 to 18 per 1,000". (alternative pagination depending on country of sale: 98–107, bibliography on p. 114online article – see documents link at left
Nightingale believed that nursing was a social freedom and mission for women. She believed that any educated woman could help improve the care of the ill. Her '' Notes on Nursing'' (1859) was a popular call to action. The Nightingale model of nursing education led to one of the first schools of nursing to be connected to a hospital and medical school. It spread widely in Europe and North America after 1870. Nightingale included five factors that helped nurses in her time who worked amidst poor sanitation and little education. These factors include fresh air, clean water, a working drainage system, cleanliness, and good light. Nightingale believed that a clean working environment was important in caring for patients. In the 19th century, this theory was ideal for helping patients, providing a guide for nurses to alter the environment around patients for the betterment of their health. Nightingale's recommendations built upon the successes of Jamaican "doctresses" such as
Mary Seacole
Mary Jane Seacole (;Anionwu, E. N. (2012), "Mary Seacole: nursing care in many lands". ''British Journal of Healthcare Assistants'' 6(5), pp. 244–248. 23 November 1805 – 14 May 1881) was a British Nursing, nurse and Women in business ...
, who like Nightingale, served in the Crimean War. Seacole practised hygiene and the use of herbs in healing wounded soldiers and those suffering from diseases in the 19th century in the Crimea, Central America, and Jamaica. Her predecessors had great success as healers in the Colony of Jamaica
The Crown Colony of Jamaica and Dependencies was a British colony from 1655, when it was Invasion of Jamaica (1655), captured by the The Protectorate, English Protectorate from the Spanish Empire. Jamaica became a British Empire, British colon ...
in the 18th century, and they included Seacole's mother (Mrs. Grant), Sarah Adams, Cubah Cornwallis, and Grace Donne, the mistress and doctress to Jamaica's wealthiest planter, Simon Taylor.
Other important nurses in the development of the profession include:
* Agnes Hunt from Shropshire
Shropshire (; abbreviated SalopAlso used officially as the name of the county from 1974–1980. The demonym for inhabitants of the county "Salopian" derives from this name.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the West M ...
was the first orthopedic nurse and was pivotal in the emergence of the orthopedic hospital, the Robert Jones & Agnes Hunt Hospital in Oswestry
Oswestry ( ; ) is a market town, civil parish and historic railway town in Shropshire, England, close to the England–Wales border, Welsh border. It is at the junction of the A5 road (Great Britain), A5, A483 road, A483 and A495 road, A495 ro ...
, Shropshire.
* Valérie de Gasparin opened, with her husband Agénor de Gasparin, the world's first nursing school: , in Lausanne
Lausanne ( , ; ; ) is the capital and largest List of towns in Switzerland, city of the Swiss French-speaking Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Vaud, in Switzerland. It is a hilly city situated on the shores of Lake Geneva, about halfway bet ...
, Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
.
*Agnes Jones
Agnes Elizabeth Jones (1832 – 1868) of Fahan, County Donegal, Ireland became the first trained Nursing Superintendent of Liverpool Workhouse Infirmary. She gave all her time and energy to her patients and died at the age of 35 from typhus ...
established a nurse training regime at Brownlow Hill infirmary, Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
, in 1865.
* Linda Richards established nursing schools in the United States and Japan, and was officially the first professionally trained nurse in the US, graduating in 1873 from the '' New England Hospital for Women and Children'' in Boston.
* Clarissa Harlowe "Clara" Barton was a pioneer American teacher, patent clerk, nurse, and humanitarian, and the founder of the American Red Cross
The American National Red Cross is a Nonprofit organization, nonprofit Humanitarianism, humanitarian organization that provides emergency assistance, disaster relief, and disaster preparedness education in the United States. Clara Barton founded ...
.
* Saint Marianne Cope was a Sister of St. Francis who opened and operated some of the first general hospitals in the United States, instituting cleanliness standards that influenced the development of America's hospital system.
Red Cross
The organized International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 16million volunteering, volunteers, members, and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ...
chapters, which began appearing after the establishment of the International Committee of the Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) is a humanitarian organization based in Geneva, Switzerland, and is a three-time Nobel Prize laureate. The organization has played an instrumental role in the development of rules of war and ...
in 1863, offered employment and professionalization opportunities for nurses (despite Nightingale's initial objections). Catholic orders such as Little Sisters of the Poor, Sisters of Mercy
The Sisters of Mercy is a religious institute for women in the Catholic Church. It was founded in 1831 in Dublin, Ireland, by Catherine McAuley. In 2019, the institute had about 6,200 Religious sister, sisters worldwide, organized into a number ...
, Sisters of St. Mary, St. Francis Health Services, Inc. and Sisters of Charity
Many religious communities have the term Sisters of Charity in their name. Some ''Sisters of Charity'' communities refer to the Vincentian tradition alone, or in America to the tradition of Saint Elizabeth Ann Seton (whose sisters are also of ...
built hospitals and provided nursing services during this period. The modern deaconess
The ministry of a deaconess is a ministry for women in some Protestant, Oriental Orthodox, and Eastern Orthodox churches to provide pastoral care, especially for other women, and which may carry a liturgical role. The word comes from the Greek ...
movement began in Germany in 1836. Within a half century, over 5,000 deaconesses had surfaced in Europe.
Formal use of nurses in the military began in the latter half of the nineteenth century. Nurses saw active duty in the First Boer War
The First Boer War (, ), was fought from 16 December 1880 until 23 March 1881 between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and Boers of the Transvaal (as the South African Republic was known while under British ad ...
, the Egyptian Campaign (1882), and the Sudan Campaign (1883).
20th century
 In the 19th and early 20th century, nursing was considered a woman's profession, just as doctoring was a profession for men. With increasing expectations of workplace equality during the late 20th century, nursing became an officially gender-neutral profession, though in practice the percentage of male nurses remained well below that of female
In the 19th and early 20th century, nursing was considered a woman's profession, just as doctoring was a profession for men. With increasing expectations of workplace equality during the late 20th century, nursing became an officially gender-neutral profession, though in practice the percentage of male nurses remained well below that of female physician
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the Medical education, study, Med ...
s in the 21st century.
Hospital-based training became standard in the US in the early 1900s, with an emphasis on practical experience. The Nightingale-style school began to disappear. Hospitals and physicians saw women in nursing as a source of free/inexpensive labor. Exploitation of nurses was not uncommon by employers, physicians, and education providers.
Many nurses saw active duty in the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, but the profession transformed again during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. British nurses of the Army Nursing Service were part of every overseas campaign. More nurses volunteered for service in the US Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
and Navy
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the military branch, branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral z ...
than any other occupation. The Nazis had their own Brown Nurses, numbering 40,000. Two dozen German Red Cross nurses were awarded the Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the in ...
for heroism under fire.
 The development of undergraduate and post-graduate nursing degrees came after the war. Nursing research and a desire for association and organization led to the formation of professional organizations and
The development of undergraduate and post-graduate nursing degrees came after the war. Nursing research and a desire for association and organization led to the formation of professional organizations and academic journals
An academic journal (or scholarly journal or scientific journal) is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. They serve as permanent and transparent forums for the dissemination, scr ...
. Nursing became recognized as a distinct academic discipline, initially tasked to define the theoretical basis for practice.
Shortages
Nurses are perceived to be in short supply around the world, particularly in South East Asia and Africa. A global survey byMcKinsey & Company
McKinsey & Company (informally McKinsey or McK) is an American multinational strategy and management consulting firm that offers professional services to corporations, governments, and other organizations. Founded in 1926 by James O. McKinse ...
in 2022 found that between 28% and 38% of nurse respondents in the United States, the United Kingdom, Singapore, Japan, and France said they were likely to leave their role in direct patient care in the next year. The top five factors which they said would make them stay were:
*Safe working environment
*Work-life balance
*Caring and trusting team-mates
*Meaningful work
*Flexible work schedule
Pay ranked eighth on the list. A 2023 American survey found that around 30% were considering leaving patient care.
Definition
According to the traditional interpretation physicians are concerned with curing or treating medical conditions, while nurses focus on care. In healthcare settings this line is often blurred, complicating the task of distinguishing the professions. Although nursing practice varies both through its various specialties and countries, nursing organizations offer the following definitions:Professional nursing
social contract
In moral and political philosophy, the social contract is an idea, theory, or model that usually, although not always, concerns the legitimacy of the authority of the state over the individual. Conceptualized in the Age of Enlightenment, it ...
that delineates professional rights and responsibilities as well as accountability mechanisms. In almost all countries, nursing practice is defined and governed by law, and entrance to the profession is regulated at the national or state level.
The nursing community worldwide aims for professional nurses to ensure quality care, while maintaining their credentials, code of ethics
Ethics is the philosophy, philosophical study of Morality, moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates Normativity, normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches inclu ...
, standards, and competencies, and continuing their education.International Council of NursesRetrieved August 2007 Multiple educational paths lead to becoming a professional nurse; these vary by jurisdiction; all involve extensive study of
nursing theory
Nursing theory is defined as "a creative and conscientious structuring of ideas that project a tentative, purposeful, and systematic view of phenomena". Through systematic inquiry, whether in nursing research or practice, nurses are able to develop ...
and practice as well as training in clinical skills.
Nurses provide care based on the individual's physical, emotional, psychological, intellectual, social, and spiritual needs. The profession combines physical science, social science, nursing theory, and technology.
Nurses typically hold one or more formal credentials. Roles and responsibilities follow the level of education. For example, in the United States, Licensed Practical Nurse
A licensed practical nurse (LPN), in much of the United States and Canada, is a nurse who provides direct nursing care for people who are sick, injured, convalescent, or disabled. In the United States, LPNs work under the direction of physicia ...
s (LPN) have less education than Registered Nurse
A registered nurse (RN) is a healthcare professional who has graduated or successfully passed a nursing program from a recognized nursing school and met the requirements outlined by a country, state, province or similar government-authorized ...
s (RN) and accordingly, a narrower scope of practice.
Diversity
Nursing is a female-dominated profession in many countries; according to the WHO's 2020 ''State of the World's Nursing,'' approximately 90% of the nursing workforce is female. For instance, the male-to-female ratio of nurses is approximately 1:19 in Canada and the United States. This ratio is matched in many other countries. Notable exceptions includeFrancophone Africa
African French () is the umbrella grouping of varieties of the French language spoken throughout Francophone Africa. Used mainly as a secondary language or ''lingua franca'', it is spoken by an estimated 320 million people across 34 coun ...
, which includes the countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Chad, Congo, Côte d'Ivoire
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire and officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital city of Yamoussoukro is located in the centre of the country, while its largest city and ...
, the Democratic Republic of Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
, Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
, Guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
, Gabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and ...
, Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, Mauritania
Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Maghreb, Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to Mauritania–Western Sahara border, the north and northwest, ...
, Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
, Rwanda
Rwanda, officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator, Rwanda is bordered by ...
, Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
, and Togo
Togo, officially the Togolese Republic, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to Ghana–Togo border, the west, Benin to Benin–Togo border, the east and Burkina Faso to Burkina Faso–Togo border, the north. It is one of the le ...
, which all have more male than female nurses. In Europe, in countries such as Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
and Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, over 20% of nurses are male. As of 2016, 11% of nurses and midwives registered with the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) in the UK were male. The number of male nurses in the United States doubled between 1980 and 2000. On average, male nurses in the US receive more pay than female nurses.
Theory and process
Nursing practice is the actual provision of nursing care. In providing care, nurses implement anursing care plan
Nursing is a health care profession that "integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alle ...
defined using the nursing process. This is based around a specific nursing theory
Nursing theory is defined as "a creative and conscientious structuring of ideas that project a tentative, purposeful, and systematic view of phenomena". Through systematic inquiry, whether in nursing research or practice, nurses are able to develop ...
that is selected based on the care setting and the population served. In providing nursing care, the nurse uses both nursing theory and best practice derived from nursing research Nursing research is research that provides evidence used to support nursing practices. Nursing, as an evidence-based area of practice, has been developing since the time of Florence Nightingale to the present day, where many nurses now work as resea ...
. Many nursing theories are in use. Like other disciplines, the profession has developed multiple theories derived from reflecting varying philosophical beliefs and paradigm
In science and philosophy, a paradigm ( ) is a distinct set of concepts or thought patterns, including theories, research methods, postulates, and standards for what constitute legitimate contributions to a field. The word ''paradigm'' is Ancient ...
s or worldview
A worldview (also world-view) or is said to be the fundamental cognitive orientation of an individual or society encompassing the whole of the individual's or society's knowledge, culture, and Perspective (cognitive), point of view. However, whe ...
s.
In general terms, the nursing process is the method used to assess and diagnose needs, plan outcomes and interventions, implement interventions, and evaluate outcomes. The nursing process as defined by the American Nurses Association
The American Nurses Association (ANA) is a 501(c)(6) professional organization to advance and protect the profession of nursing. It started in 1896 as the Nurses Associated Alumnae and was renamed the American Nurses Association in 1911. It is b ...
comprises five steps: 1) evaluate, 2) implement, 3) plan, 4) diagnose, and 5) assess.
Healthcare staffing platforms
Digital health platforms connect nurses and nurse assistants with job openings in healthcare facilities such as skilled nursing homes, home health agencies, and hospitals. Platforms offer an app to facilitate communication and allow nurses to find work opportunities based on their preferences. Healthcare partners and facilities benefit from access to qualified nurses. In 2017, the UK's National Health Service began trialing such a platform. Platforms such asUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
–based ConnectRN, Nomad Health, Gale Healthcare solutions or Lantum add resources, career development tools, and networking opportunities.
Nursing as a science
Florence Nightingale's seminal epidemiological study examining mortality among British soldiers during theCrimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont fro ...
was published in 1858. With the exception of her works, nursing practice remained an oral tradition until the mid-20th century. The inaugural issue of ''Nursing Research Nursing research is research that provides evidence used to support nursing practices. Nursing, as an evidence-based area of practice, has been developing since the time of Florence Nightingale to the present day, where many nurses now work as resea ...
'', the first scientific journal specialized in nursing, came in in 1952. During the 1960s, interest in attaining PhDs increased among nurses in the US, but nursing remained a fledgling area of research, with few journals until the 1970s. Nursing research is increasingly presented as a valid discipline, although lacking a prevailing definition. The question is further complicated by the numerous interpretations of nursing's defining essence.
Evidence-based practice
During the 1980s there was an increased focus on research utilization (RU). Nursing research took an interest in clinical issues and US nursing schools began teaching research methods to facilitate interpretation and integration of scientific findings in routine practice. Several RU initiatives were active during the late 20th century, but the RU movement was superseded by evidence-based practice in the 1990s. Evidence-based practice (EBP) is about using research, but unlike RU it allows for the integration of research findings with clinical expertise and patient preferences. The EBP movement had originated in the field ofmedicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
with Archie Cochrane
Archibald Leman Cochrane (12 January 1909 – 18 June 1988) was a Scottish physician noted for his book, ''Effectiveness and Efficiency: Random Reflections on Health Services'', which advocated the use of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) t ...
publishing ''Effectiveness and Efficiency'' in 1972, leading up to the founding of the Cochrane Collaboration
Cochrane is a British international charitable organisation formed to synthesize medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes ...
in 1993. The emerging area of evidence-based medicine also applies to nursing. Common barriers to the study and integration of research findings into clinical decision making include: a lack of opportunity, inexperience, and the rapid pace of evidence accumulation.
Scope of activities
Nurses perform a variety of different tasks. Their activities vary based on their level of training and their specialty. For example, operating room nurses work in surgical settings and perform tasks that other nurses do not. Nurses may receive additional training and certifications to perform a variety of tasks. For example, in the United States, RN first assists (RNFAs) perform basic surgical procedures.Assessment
Assessment is an essential nursing skill. Nurses assess patients' physical and mental health. In hospital settings, nurses regularly perform assessments to notice any acute changes in their patients. Nurses also assess a patient's response to medication or other treatments, such as physical activity and blood transfusions. Nurses may also take health histories. Nurses also must assess a patient's understanding of their health status and their medications. Critical thinking is an important skill for nurses to have: in emergency situations, nurses must quickly assess a patient and determine the best course of action.Medication
Medication management and administration are common hospital nursing roles, although prescribing authority varies across jurisdictions. In many areas, RNs administer and manage medications prescribed by others. Nurses are responsible for evaluating patients throughout their care – including before and after medication administration – adjustments to medications are often made through a collaborative effort between the prescriber and the nurse. Regardless of the prescriber, nurses are legally responsible for the drugs they administer. Legal implications may accompany an error in a prescription, and the nurse may be expected to note and report the error. In the United States, nurses have the right to refuse to administer medication that they deem to be potentially harmful. Some nurses take additional training that allows them to prescribe medications within their scope of practice.Patient education
Effective patient/family education leads to better outcomes. Nurses explain procedures, recovery, and ongoing care, while helping everyone cope with the medical situation. Many times, nurses are busy, leaving little time to educate patients. Patients' families needs similar education.Taylor, C. R., Lillis, C., LeMone, P., Lynn, P. (2011) Fundamentals of nursing: The art and science of nursing care. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, page 468. Educating both patients and their families increases the chance for a better outcome. Nurses have to communicate in a way that can be understood by patients. Education techniques encompass conversations, visuals, reading materials, and demonstrations.Daily living assistance
Nurses manage and coordinate care to support activities of daily living (ADL) such as hygiene and toileting. This includes assisting in patient mobility, such as moving an activity intolerant patient within a bed. They often delegate such care to nursing assistants.Specialties
Nursing is the most diverse of all health care professions. Nurses practice in a wide range of settings, but generally follows the needs of their patients. The major specialties are: *communities
A community is a Level of analysis, social unit (a group of people) with a shared socially-significant characteristic, such as place (geography), place, set of Norm (social), norms, culture, religion, values, Convention (norm), customs, or Ide ...
/public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the de ...
*family/individual care
*adult-gerontology
Gerontology ( ) is the study of the social, culture, cultural, psychology, psychological, cognitive, and biology, biological aspects of aging. The word was coined by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov in 1903, from the Ancient Greek, Greek ('), meaning "o ...
*pediatrics
Pediatrics (American English) also spelled paediatrics (British English), is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, Adolescence, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, pediatrics covers many o ...
*obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a su ...
*neonatal
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
*women's health/gender-related
*mental health
Mental health is often mistakenly equated with the absence of mental illness. However, mental health refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and how t ...
*informatics
Informatics is the study of computational systems. According to the Association for Computing Machinery, ACM Europe Council and Informatics Europe, informatics is synonymous with computer science and computing as a profession, in which the centra ...
( eHealth)
*acute care
* ambulatory settings (physician offices, urgent care settings, camps, etc.)
*school
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the Educational architecture, building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most co ...
/college/institutional infirmaries
*military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
* cardiac care
* orthopedic care
*palliative care
Palliative care (from Latin root "to cloak") is an interdisciplinary medical care-giving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating or reducing suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Man ...
* perioperative
*oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis, and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's Etymology, etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγ ...
* telenursing
*radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide treatment within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but tod ...
*emergency care
Emergency medicine is the medical specialty concerned with the care of illnesses or injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians (or "ER doctors") specialize in providing care for unscheduled and undifferentiated pa ...
Nurses with additional degrees allow for specialization. Nursing professions can be separated into categories by care type, age, gender, certain age group, practice setting, individually or in combination.
Settings
Nurses practice in a wide range of settings, including hospitals, privatehomes
A home, or domicile, is a space used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for one or more human occupants, and sometimes various companion animals. Homes provide sheltered spaces, for instance rooms, where domestic activity can be p ...
, schools
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of ...
, and pharmaceutical companies
The pharmaceutical industry is a Medicine, medical industry that discovers, develops, produces, and markets pharmaceutical goods such as medications and medical devices. Medications are then administered to (or Self-medicate, self-administered b ...
. Nurses work in occupational health
Occupational safety and health (OSH) or occupational health and safety (OHS) is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work (i.e., while performing duties required by one's occupation). OSH is re ...
settings (also called industrial health settings), free-standing clinics, physician offices, nurse-led clinics, long-term care
Long-term care (LTC) is a variety of services which help meet both the medical and non-medical needs of people with a chronic illness or disability who cannot care for themselves for long periods. Long-term care is focused on individualized and ...
facilities and camps. They work on cruise ships
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports of call, where passengers may go on tours known as " ...
, military bases, and in combat settings.
Nurses act as advisers and consultants to the health care and insurance industries. Many nurses also work in health advocacy and patient advocacy
Patient advocacy is a process in health care concerned with advocacy for patients, survivors, and caregivers. The patient advocate may be an individual or an organization, concerned with healthcare standards or with one specific group of disor ...
, helping in clinical and administrative domains. Some are attorneys and others work with attorneys as legal nurse consultants, reviewing patient records to assure that adequate care was provided and testifying in court.
Nurses can work on a temporary basis, which involves doing shifts without a contract in a variety of settings, sometimes known as ''per diem nursing'', ''agency nursing'' or ''travel nursing''. Nurses work as researchers in laboratories, universities, and research institutions
A research institute, research centre, or research organization is an establishment founded for doing research. Research institutes may specialize in basic research or may be oriented to applied research. Although the term often implies natural sc ...
. Nurses work in informatics, acting as consultants to the creation of computerized charting programs and other software. Nurse authors publish articles and books to provide essential reference materials.
Occupational hazards
The international nursing shortage is in part due to their work environment. In a recent review of the literature specific to nursing performance, nurses were found to work in generally poor environmental conditions. Some jurisdictions have legislation specifying acceptable nurse-to-patient ratios. The fast-paced and unpredictable nature of health care places nurses at risk for injuries and illnesses, including highoccupational stress
Occupational stress is psychological stress related to one's job. Occupational stress refers to a chronic condition. Occupational stress can be managed by understanding what the stressful conditions at work are and taking steps to remediate tho ...
. Nurses consistently identify stress as a major work-related concern and have among the highest levels of occupational stress among all professions. This stress is caused by the environment, psychosocial stressors, and the demands of nursing, including mastering new technology, emotional labor, physical labor, shift work
Shift work is an employment practice designed to keep a service or production line operational at all times. The practice typically sees the day divided into shifts, set periods of time during which different groups of workers perform their ...
, and high workload. This stress puts nurses at risk for short-term and long-term health problems, including sleep disorders
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder affecting an individual's sleep patterns, sometimes impacting physical, mental, social, and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sle ...
, depression, mortality, psychiatric disorders, stress-related illnesses, and overall poor health. Nurses are at risk of developing compassion fatigue and moral distress, which can damage mental health. They have high rates of occupational burnout
The ICD-11 of the World Health Organization (WHO) describes occupational burnout as a work-related phenomenon resulting from chronic workplace stress that has not been successfully managed. According to the WHO, symptoms include "feelings of e ...
(40%) and emotional exhaustion
Emotional exhaustion is a symptom of burnout, a chronic state of physical and emotional depletion that results from excessive work or personal demands, or continuous stress. It describes a feeling of being emotionally overextended and exhausted b ...
(43.2%). Burnout and exhaustion increase the risk for illness, medical error, and suboptimal care provision.
Patient handling
Healthcare has consistently ranked among the industries with the highest rates of musculoskeletal injuries, largely related to patient handling. Anywhere from 30 to 70% of reported musculoskeletal injuries are related to patient handling. Nurses are routinely tasked with lifting, repositioning, and mobilizing patients. According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) the single greatest factor in overexertion injuries is the manual lifting, moving and repositioning of patients. These tasks present unique ergonomic hazards that result in a high rate of acute and cumulative musculoskeletal injuries. The most frequently injured body part is the back, with up to 72% of nurses reporting non-specificlow back pain
Low back pain or wiktionary:lumbago#Etymology, lumbago is a common musculoskeletal disorders, disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back, in between the lower edge of the ribs and the lower fold of the buttocks. Pain can var ...
. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that for 2021-2022 the rate of overexertion injuries leading to days away from work for nurses was 45.4 per 10,000 full time employees, while nursing aids came in at 145.5 compared to the average for all industries of 26.1.
Traditionally, nurses are trained in manual patient handling techniques. The body of evidence has demonstrated, however, that such interventions are ineffective.
Workplace violence
Nurses are at risk for workplace violence and abuse. Violence is typically perpetrated by non-staff (e.g. patients or family), whereas abuse is typically perpetrated by hospital personnel. In the US in 2011, 57% of nurses reported that they had been threatened at work; 17% were physically assaulted. The three types of workplace violence that nurses can experience are: physical violence (hitting, kicking, beating, punching, biting, and using objects); psychological violence (threats or coercion); sexual violence (attempted/completed non-consensual sex act). Workplace violence can be viewed in another way: interpersonal violence and organizational coercion. Interpersonal violence is committed by workers or patients and their families. Its predominant form is verbal abuse. Organizational coercion may include excessive workloads, mandatory shifts, involuntary placement in another part of the workplace, low salaries, denial of benefits/overtime, poor working environment, and other stressors. These issues affectquality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
. Managers who lack understanding of the severity of these problems and do not support workers increase worker stress.
Many factors contribute to workplace violence. These factors can be divided into environmental, organizational, and individual psychosocial. The environmental factors can include the specific setting (for example the emergency department), long patient wait times, frequent interruptions, uncertainty regarding patients' treatment, and heavy workloads. Organizational factors can include inefficient teamwork, organizational injustice, lack of aggression- and stress-management programs, and distrust between colleagues. Individual psychosocial factors may include nurses being young and inexperienced, previous experiences with violence, and a lack of communication skills. Misunderstandings may also occur due to the communication barrier between nurses and patients. An example of this could be patients' conditions being affected by medications, pain, or anxiety.
Workplace violence has many causes. The most common perpetrators of harassment or bullying of nursing students were registered nurses including preceptors, mentors, and clinical facilitators. However, the main perpetrators of workplace violence against nurses were patients. 80% of serious violent incidents in health care centers were committed by patients.
Workplace violence has many effects. It has negative emotional and physical impacts on nurses. They feel depersonalized, dehumanized, worn out, and stressed out. Nurses have reported burn-out due to frequent exposure to this violence.
Interventions
Interventions can mitigate these occupational hazards. They can be individual-focused or organization-focused. Individual-focused interventions includestress management
Stress management consists of a wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapy, psychotherapies aimed at controlling a person's level of psychological stress, especially chronic stress, generally for the purpose of improving the function of everyda ...
programs, which can be customized to individuals. Stress management programs can reduce anxiety, sleep disorders, and other symptoms of stress. Organizational interventions focus on reducing stressful aspects of the work environment by identifying stress generators and developing solutions to them. Combining organizational and individual interventions is most effective at reducing stress. In some Japanese hospitals, powered exoskeletons are used to reduce physical loads. Lumbar supports (i.e. back belts) have been trialed.
Nursing ethics
Professional abuse Professional abuse is "a pattern of conduct in which a person abuses, violates, or takes advantage of a victim within the context of the abuser's profession." This typically involves a violation of the relevant professional organization's code of et ...
by nurses can be mitigated by nursing ethics
Nursing ethics is a branch of applied ethics that concerns itself with activities in the field of nursing. Nursing ethics shares many principles with medical ethics, such as beneficence, non-maleficence, and respect for autonomy. It can be distin ...
and professional responsibility
Professional responsibility is a set of duties within the concept of professional ethics for those who exercise a unique set of knowledge and skill as professionals.
Professional responsibility applies to those professionals making judgments, a ...
.
By country
Africa
Kenya
South Africa
Americas
United States
Canada
Latin America/Caribbean
Latin American nursing is based on three levels of training: (a) professional/registered, (b) technical, and (c) auxiliary. Nursing education inLatin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
and the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
includes the principles and values of universal health and primary health care. These principles are based on critical and complex thinking development, problem-solving, evidence-based clinical decision-making, and lifelong learning.
Europe
European Union
In the European Union, the profession of nurse requires a specific professional qualification. The qualification of nurses responsible for general care in the EU is regulated inDirective 2005/36/EC
Directive 2005/36/EC on the recognition of professional qualifications provides for a system of recognition of professional experience and promotes automatic recognition of professional experience across the European Union (EU). It covers the Eu ...
.Directive 2005/36/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 7 September 2005 on the recognition of professional qualifications, Official Journal of the European Union, 30.9.2005/ref> The list of regulated nursing professions is held in the regulated professions database.
= Germany
== Spain
=United Kingdom
Asia
India
Hong Kong
Japan
Pakistan
Philippines
Taiwan
InTaiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, the Ministry of Health and Welfare regulates nursing. The Taiwan Union of Nurses Association (TUNA) organizes nurses.
Australia
Middle East
Iran
Islam
Historically, female nurses during the era of slavery in the Muslim world where often slaves, a tradition which continued in Saudi Arabia until the abolition ofslavery in Saudi Arabia
Legal chattel slavery existed in Saudi Arabia from antiquity until its abolition in the 1960s.
Hejaz (the western region of modern day Saudi Arabia), which encompasses approximately 12% of the total land area of Saudi Arabia, was under th ...
in 1962, where nursing was considered a dishonorable profession.Drake, M. (2010). A Us Feminist in Saudi Arabia: 1980-1982. Storbritannien: iUniverse. p. 66
Israel
Nurses inIsrael
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
has responsibilities including hospital care, patient education, wound care, prenatal and other monitoring, midwifery, and well-baby clinics.
Nurses and midwives are regulated by the Israeli Ministry of Health.
Nursing in Israeli Jewish culture traces its origins to Shifra and Puah, two Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
midwives depicted in the Book of Exodus
The Book of Exodus (from ; ''Šəmōṯ'', 'Names'; ) is the second book of the Bible. It is the first part of the narrative of the Exodus, the origin myth of the Israelites, in which they leave slavery in Biblical Egypt through the strength of ...
helping women in ancient Egypt give birth and keep their infants safe.
Modern-day nursing was established by nurses sent to Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine was a British Empire, British geopolitical entity that existed between 1920 and 1948 in the Palestine (region), region of Palestine, and after 1922, under the terms of the League of Nations's Mandate for Palestine.
After ...
and later Israel by the Hadassah organization, as well as at a nursing school founded by Henrietta Szold in 1918. The United Kingdom regulated midwifery in Mandatory Palestine, but nurses were not mentioned in the regulation decree.
See also
* Advanced practice registered nurse *History of nursing
The word "nurse" originally came from the Latin word "nutricius", meaning to nourish,to protect and to sustain, referring to a wet-nurse; only in the late 16th century did it attain its modern meaning of a person who cares for the infirm.
From t ...
* History of Nursing in the United Kingdom
*History of nursing in the United States
The history of nursing in the United States focuses on the professionalization of Nursing in the United States since the Civil War.
Origins
Before the 1870s "women working in North American urban hospitals typically were untrained, working class ...
* History of Philippine nurses in the United States
*Index of nursing articles
This is an index of nursing articles on Wikipedia.
A
B
C
H
I
L
M
N
P
R
S
T
U
W
{{Nursing
Indexes of science articles, Nursing
Nursing, * ...
*Licensed practical nurse
A licensed practical nurse (LPN), in much of the United States and Canada, is a nurse who provides direct nursing care for people who are sick, injured, convalescent, or disabled. In the United States, LPNs work under the direction of physicia ...
*List of nurses
This is a list of famous nurses in history. To be listed here, the nurse must already have a Wiki biography article. For background information see History of nursing and Timeline of nursing history. For nurses in art, film and literature see lis ...
*List of nursing specialties
This is a list of different nursing specialities. In recent decades, the number of non-bedside nursing roles has increased. Professional organizations or certifying boards issue voluntary Nursing board certification, certification in many of the ...
*Men in nursing
Nursing is a profession which is staffed unproportionately by women in most parts of the world. According to the World Health Organization's (WHO) 2020 ''State of the World's Nursing,'' approximately 10% of the worldwide nursing workforce is ma ...
*Nightingale Pledge
The Nightingale Pledge, named in honour of Florence Nightingale, is a modified version of the Hippocratic Oath. Lystra Gretter and a Committee for the Farrand Training School Grace for Nurses in Detroit, Michigan created the pledge in 1893. Gr ...
* Nurse uniform
* Nurse–client relationship
*Nurse scheduling problem
The nurse scheduling problem (NSP), also called the nurse rostering problem (NRP), is the operations research problem of finding an optimal way to assign nurses to shifts, typically with a set of hard constraints which all valid solutions must fol ...
*Nursing care plan
Nursing is a health care profession that "integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alle ...
*Nursing school
Nursing is a health care profession that "integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alle ...
*Nurse stereotypes
A stereotype is a widely held and fixed notion of a specific type of person and is often oversimplified and can be offensive. Stereotypes of people and groups are harmful, especially when they lack factual information. Nursing as a profession has ...
*Nursing theory
Nursing theory is defined as "a creative and conscientious structuring of ideas that project a tentative, purposeful, and systematic view of phenomena". Through systematic inquiry, whether in nursing research or practice, nurses are able to develop ...
*Registered nurse
A registered nurse (RN) is a healthcare professional who has graduated or successfully passed a nursing program from a recognized nursing school and met the requirements outlined by a country, state, province or similar government-authorized ...
* Transcultural nursing
References
Book sources
* * *Journal articles
* * * *External links
UNCG Library Betty H. Carter Women Veterans Historical Project: Nurse
* {{Authority control Military supporting service occupations Rehabilitation team Health care occupations Hospital staff Occupational safety and health Articles containing video clips