Number of humans that have ever lived on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This article lists current estimates of the
This article lists current estimates of the
 As a general rule, the confidence of estimates on historical world population decreases for the more distant past. Robust population data exist only for the last two or three centuries. Until the late 18th century, few governments had ever performed an accurate census. In many early attempts, such as in
As a general rule, the confidence of estimates on historical world population decreases for the more distant past. Robust population data exist only for the last two or three centuries. Until the late 18th century, few governments had ever performed an accurate census. In many early attempts, such as in
 Population estimates for world regions based on Maddison (2007),Angus Maddison, The World Economy: Historical Statistics, Statistical Appendix (2007, ggdc.net).
Estimates cited are for the beginning of the 1st millennium ("year 0"), the beginning of the 2nd millennium ("year 1000"), and for the beginning each century since the 16th (years 1820 and 1913 are given for the 19th and 20th century, respectively, as Maddison presents detailed estimates for these years), and a projection for the year 2030. in millions. The row showing total world population includes the average growth rate per year over the period separating each column from the preceding one.
Population estimates for world regions based on Maddison (2007),Angus Maddison, The World Economy: Historical Statistics, Statistical Appendix (2007, ggdc.net).
Estimates cited are for the beginning of the 1st millennium ("year 0"), the beginning of the 2nd millennium ("year 1000"), and for the beginning each century since the 16th (years 1820 and 1913 are given for the 19th and 20th century, respectively, as Maddison presents detailed estimates for these years), and a projection for the year 2030. in millions. The row showing total world population includes the average growth rate per year over the period separating each column from the preceding one.
Historical Estimates of World Population
–
 This article lists current estimates of the
This article lists current estimates of the world population
In demographics of the world, world demographics, the world population is the total number of humans currently alive. It was estimated by the United Nations to have exceeded eight billion in mid-November 2022. It took around 300,000 years of h ...
in history. In summary, estimates for the progression of world population since the Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
are in the following ranges:
Estimates for pre-modern times are necessarily fraught with great uncertainties, and few of the published estimates have confidence intervals; in the absence of a straightforward means to assess the error of such estimates, a rough idea of expert consensus can be gained by comparing the values given in independent publications. Population estimates cannot be considered accurate to more than two decimal digits; for example, the world population for the year 2012 was estimated at 7.02, 7.06, and 7.08 billion by the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
, the Population Reference Bureau
The Population Reference Bureau (PRB) is a private, nonprofit organization specializing in collecting and supplying statistics necessary for research and/or academic purposes focused on the environment, and health and structure of populations. The ...
, and the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Econ ...
, respectively, corresponding to a spread of estimates of the order of 0.8%.
Deep prehistory
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
and the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
, the focus was on counting merely a subset of the population for purposes of taxation or military service. Published estimates for the 1st century (" AD 1") suggest uncertainty of the order of 50% (estimates range between 150 and 330 million). Some estimates extend their timeline into deep prehistory, to "10,000
10,000 (ten thousand) is the natural number following 9,999 and preceding 10,001.
Name
Many languages have a specific word for this number: in Ancient Greek it is (the etymological root of the word myriad in English), in Aramaic , in Hebre ...
BC", i.e., the early Holocene, when world population estimates range roughly between 1 and 10 million (with an uncertainty of up to an order of magnitude).
Estimates for yet deeper prehistory, into the Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
, are of a different nature. At this time, human populations consisted entirely of non-sedentary hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
populations, with anatomically modern humans
Early modern human (EMH), or anatomically modern human (AMH), are terms used to distinguish ''Homo sapiens'' ( sometimes ''Homo sapiens sapiens'') that are anatomically consistent with the range of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans, from ...
existing alongside archaic human varieties, some of which are still ancestral to the modern human population due to interbreeding with modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories ...
. Estimates of the size of these populations are a topic of paleoanthropology
Paleoanthropology or paleo-anthropology is a branch of paleontology and anthropology which seeks to understand the early development of anatomically modern humans, a process known as hominization, through the reconstruction of evolutionary kinsh ...
. A late human population bottleneck
A population bottleneck or genetic bottleneck is a sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events such as famines, earthquakes, floods, fires, disease, and droughts; or human activities such as genocide, speciocide, wid ...
is postulated by some scholars at approximately 70,000 years ago, during the Toba catastrophe, when ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
'' population may have dropped to as low as between 1,000 and 10,000 individuals.
For the time of speciation of ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
'', some 200,000 years ago, an effective population size
The effective population size (''N'e'') is the size of an idealised population that would experience the same rate of genetic drift as the real population. Idealised populations are those following simple one- locus models that comply with ass ...
of the order of 10,000 to 30,000 individuals has been estimated, with an actual "census population" of early ''Homo sapiens'' of roughly 100,000 to 300,000 individuals.
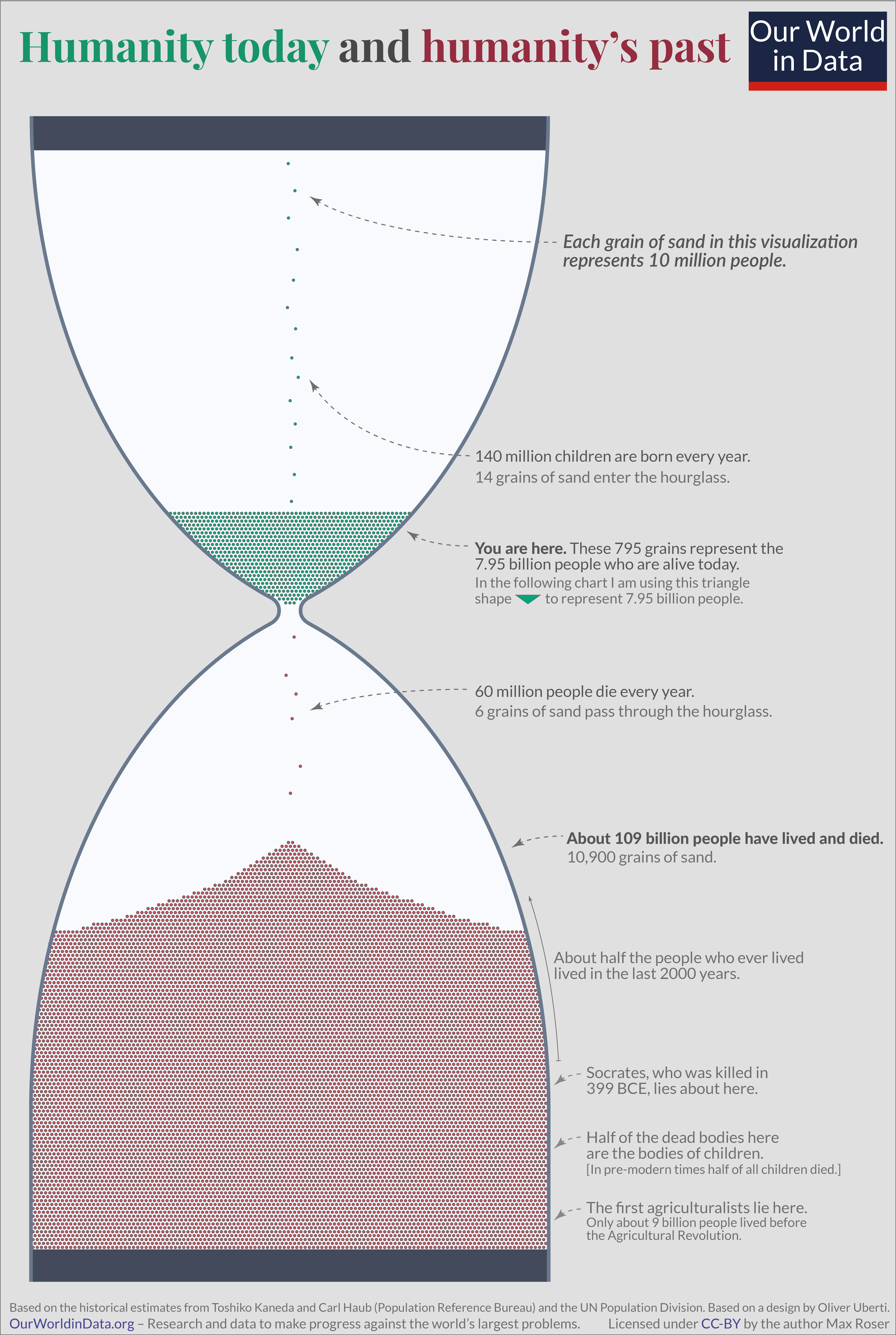
Estimates regarding the questions of "how many people have ever lived?" or "what percentage of people who have ever lived are alive today?" can be traced to the 1970s. The more dramatic phrasing of "the living outnumber the dead" also dates to the 1970s, a time of population explosion
Overpopulation or overabundance is a state in which the population of a species is larger than the carrying capacity of its environment. This may be caused by increased birth rates, lowered mortality rates, reduced predation or large scale migr ...
and growing fears of human overpopulation
Human overpopulation (or human population overshoot) is the idea that human populations may become too large to be sustainability, sustained by their environment or resources in the long term. The topic is usually discussed in the context of wor ...
in the wake of decolonization
Decolonization is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby Imperialism, imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholar ...
and before the adoption of China's one-child policy
The one-child policy ( zh, c=一孩政策, p=yī hái zhèngcè) was a population planning initiative in China implemented between 1979 and 2015 to curb the country's population growth by restricting many families to a single child. The progr ...
. The claim that "the living outnumber the dead" was never accurate. Arthur C. Clarke in ''2001: A Space Odyssey'' (1968) has the claim that "Behind every man now alive stand 30 ghosts, for that is the ratio by which the dead outnumber the living", which was roughly accurate at the time of writing.
Recent estimates of the "total number of people who have ever lived" are in the order of 100 billion. The answer depends on the definition of "people", i.e., whether only ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
'' are to be counted, or all of the genus ''Homo
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called ...
;'' due to the small population sizes in the Lower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3.3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears ...
, however, the order of magnitude of the estimate is not affected by the choice of cut-off date substantially more than by the uncertainty of estimates throughout the Neolithic to Iron Age. Importantly, the estimate is also affected by the estimate of infant mortalities vs. stillborn
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can often result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. T ...
infants, due to the very high rate of infant mortality throughout the pre-modern period. An estimate on the "total number of people who have ever lived" as of 1995 was calculated by Haub (1995) at "about 105 billion births since the dawn of the human race" with a cut-off date at 50,000 BC (beginning of the Upper Paleolithic), and inclusion of a high infant mortality rate throughout pre-modern history.
Historical population
Before 1950
The following table usesastronomical year numbering
Astronomical year numbering is based on AD/ CE year numbering, but follows normal decimal integer numbering more strictly. Thus, it has a year 0; the years before that are designated with negative numbers and the years after that are designated ...
for dates, negative numbers corresponding roughly to the corresponding year BC (strictly speaking, for example, −8,000 = 8,001 BC, etc.). The table starts counting approximately 10,000 years before present, or around 8,000 BC, during the middle Greenlandian
In the geologic time scale, the Greenlandian is the earliest age or lowest stage of the Holocene Epoch or Series, part of the Quaternary. Beginning in 11,650 BP (9701 BCE or 300 HE) and ending with the 8.2-kiloyear event (c. 8200–8300 B ...
, about 1,700 years after the end of the Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (YD, Greenland Stadial GS-1) was a period in Earth's geologic history that occurred circa 12,900 to 11,700 years Before Present (BP). It is primarily known for the sudden or "abrupt" cooling in the Northern Hemisphere, when the ...
and 1,800 years before the 8.2-kiloyear event.
From the beginning of the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
until the 20th century, world population has been characterized by a rapid growth. For the period of Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
to the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, roughly 500 BC to AD 1500, there was also a general tendency of growth (estimated at a factor 4 to 5 over the 2,000-year period), but not strictly monotonic
In mathematics, a monotonic function (or monotone function) is a function between ordered sets that preserves or reverses the given order. This concept first arose in calculus, and was later generalized to the more abstract setting of ord ...
: A noticeable dip in world population is assumed due to the Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
in the mid-14th century.
1950 to 2016
After , demographic data of some accuracy becomes available for a significant number of countries, and population estimates are often given as grand totals of numbers (typically given by country) of widely diverging accuracies. Some sources give these numbers rounded to the nearest million or the nearest thousand, while others give them without any rounding. Taking these numbers at face value would be false precision; in spite of being stated to four, seven, or even ten digits, they should not be interpreted as accurate to more than three digits at best (estimates by theUnited States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
and by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
differ by about 0.5–1.5%).
By world region
 Population estimates for world regions based on Maddison (2007),Angus Maddison, The World Economy: Historical Statistics, Statistical Appendix (2007, ggdc.net).
Estimates cited are for the beginning of the 1st millennium ("year 0"), the beginning of the 2nd millennium ("year 1000"), and for the beginning each century since the 16th (years 1820 and 1913 are given for the 19th and 20th century, respectively, as Maddison presents detailed estimates for these years), and a projection for the year 2030. in millions. The row showing total world population includes the average growth rate per year over the period separating each column from the preceding one.
Population estimates for world regions based on Maddison (2007),Angus Maddison, The World Economy: Historical Statistics, Statistical Appendix (2007, ggdc.net).
Estimates cited are for the beginning of the 1st millennium ("year 0"), the beginning of the 2nd millennium ("year 1000"), and for the beginning each century since the 16th (years 1820 and 1913 are given for the 19th and 20th century, respectively, as Maddison presents detailed estimates for these years), and a projection for the year 2030. in millions. The row showing total world population includes the average growth rate per year over the period separating each column from the preceding one.
World Population Estimates, 20 Countries and Regional Totals, AD 1–2000 (in thousands)
References
Further reading
* * *External links
Historical Estimates of World Population
–
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
{{Population
Estimates
In the Westminster system of government, the ''Estimates'' are an outline of government spending for the following fiscal year presented by the Cabinet (government), cabinet to parliament. The Estimates are drawn up by bureaucrats in the finance ...
Demographic history