Northeastern USA on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Northeastern United States (also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast) is one of the four census regions defined by the

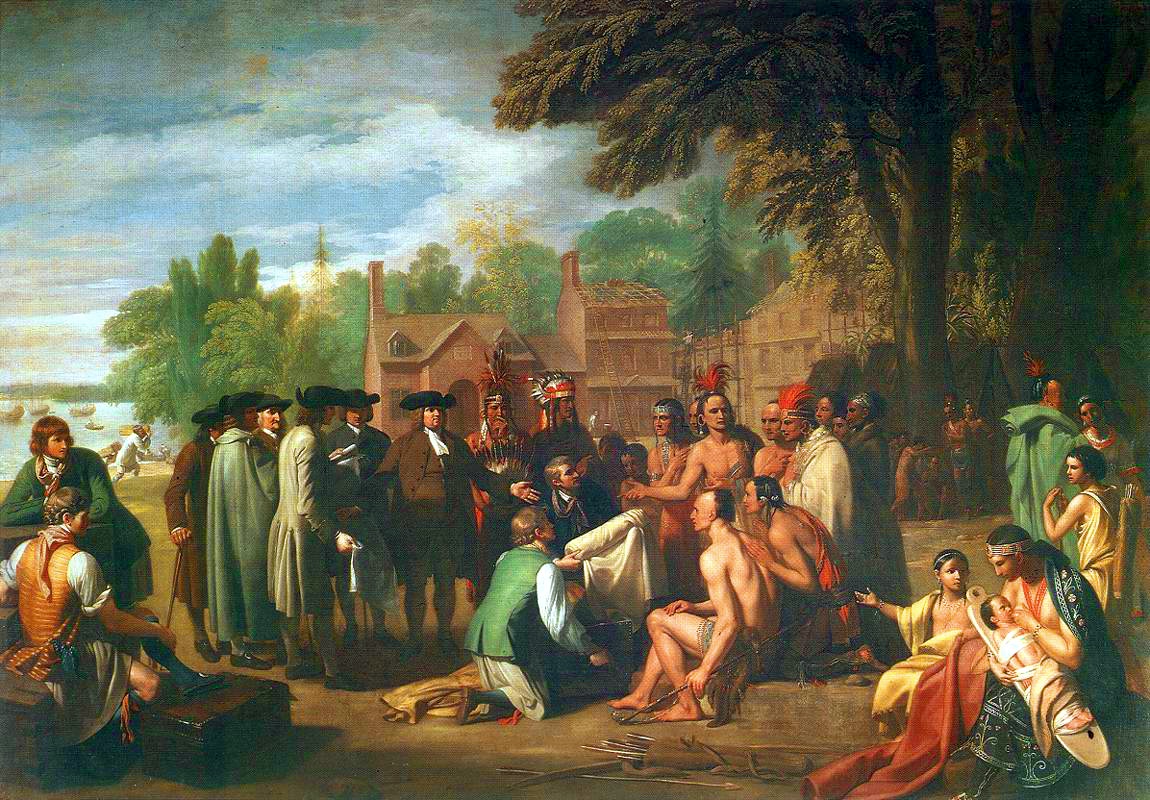 All of the
All of the
 The beginnings of the
The beginnings of the
 Following the Civil War, the Northeast would see a large economic boom and would become one of the most industrialized regions in the world. Many technological innovations would be made in the Northeast during this time. The
Following the Civil War, the Northeast would see a large economic boom and would become one of the most industrialized regions in the world. Many technological innovations would be made in the Northeast during this time. The


 The vast area from central
The vast area from central
 As of the 2020 U.S. census, the population of the region was 57,609,148, representing 17.38% of the nation's total population. With an average of 345.5 people per square mile, the Northeast is 2.5 times as densely populated as the second-most dense region, the
As of the 2020 U.S. census, the population of the region was 57,609,148, representing 17.38% of the nation's total population. With an average of 345.5 people per square mile, the Northeast is 2.5 times as densely populated as the second-most dense region, the
File:View of Empire State Building from Rockefeller Center New York City dllu.jpg, alt=Downtown NYC,
 , the
, the
 , the
, the
 The Northeast is served by
The Northeast is served by
 *
*
 The following table includes all airports categorized by the FAA as large or medium hubs located in the Northeastern states.
The following table includes all airports categorized by the FAA as large or medium hubs located in the Northeastern states.
 Many other minor highways exist in the Northeast, connecting cities. Major US Routes which run through the Northeast include
Many other minor highways exist in the Northeast, connecting cities. Major US Routes which run through the Northeast include
 *
*  Bulkeley Bridge (I-84) - Crosses the Connecticut River, connecting Hartford area traffic across the river. The oldest interstate crossing in the US. Opened in 1908.
*
Bulkeley Bridge (I-84) - Crosses the Connecticut River, connecting Hartford area traffic across the river. The oldest interstate crossing in the US. Opened in 1908.
*
 The Northeast has been a place for many firsts in transportation in the US, from the first commercial railroad in the US in
The Northeast has been a place for many firsts in transportation in the US, from the first commercial railroad in the US in
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
. Located on the Atlantic coast of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, the region borders Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
to its north, the Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is List of regions of the United States, census regions defined by the United States Cens ...
to its south, the Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
to its west, and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
to its east.
The Northeast is one of the four regions defined by the U.S. Census Bureau for the collection and analysis of statistics. The Census Bureau defines the region as including the six New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
states of Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
, Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
, and Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
, and three lower North-Eastern states of New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
, and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
. Some expanded definitions of the region include Mid-Atlantic locations such as Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Northern Virginia
Northern Virginia, locally referred to as NOVA or NoVA, comprises several County (United States), counties and independent city (United States), independent cities in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. ...
, and Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
The region is the base for the Northeast megalopolis
The Northeast megalopolis, also known as the Northeast Corridor, Acela Corridor, Boston–Washington corridor, BosWash, or BosNYWash, is the most populous megalopolis exclusively within the United States, with slightly over 50 million resident ...
, which includes many of the nation's largest metropolitan areas, including Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, and Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
. The megalopolis makes up 67% of the region's total population of 57,609,148. The gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
of the region was $5.1 trillion as of 2022 and contains some of the most developed states based on the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income i ...
, with every state above the national average. It is also the most densely populated region in the United States, with . The U.S. Census Bureau defines the Northeast United States as having a total area of , making it the smallest region of the United States by total area.
History
Indigenous people
Anthropologists recognize the "Northeastern Woodlands" as one of thecultural regions
In anthropology and geography, a cultural area, cultural region, cultural sphere, or culture area refers to a geography with one relatively homogeneous human activity or complex of activities (culture). Such activities are often associa ...
that existed in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the 180th meridian.- The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geopolitically, ...
at the time of European colonists in the 15th and later centuries. Most did not settle in North America until the 17th century. The cultural area, known as the " Northeastern Woodlands", in addition to covering the entire Northeast U.S., also covered much of what is now Canada and others regions of what is now the eastern United States
The Eastern United States, often abbreviated as simply the East, is a macroregion of the United States located to the east of the Mississippi River. It includes 17–26 states and Washington, D.C., the national capital.
As of 2011, the Eastern ...
.
Among the many tribes inhabiting this area were those that made up the Iroquois nations and the numerous Algonquian peoples
The Algonquians are one of the most populous and widespread North American indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous American groups, consisting of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages. They historically were prominent along the East ...
. In the United States of the 21st century, 18 federally recognized tribes
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes are legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United States.
reside in the Northeast. For the most part, the people of the Northeastern Woodlands, on whose lands European fishermen began camping to dry their codfish in the early 1600s, lived in villages, especially after being influenced by agricultural traditions of the Ohio and Mississippi valley societies.
Colonial history

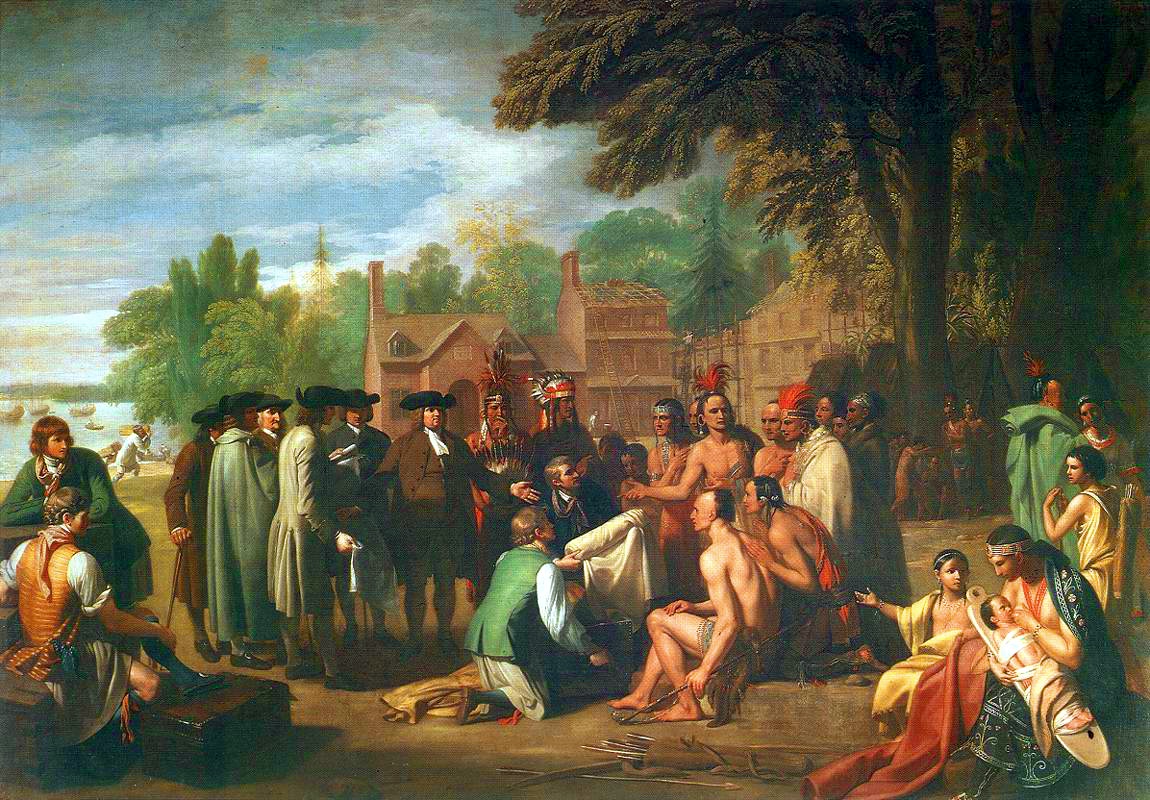 All of the
All of the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its so ...
s making up the Northeastern region were among the original Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
, though Maine and Vermont were part of other colonies before the United States became independent in the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
. The two cultural and geographic regions that form parts of the Northeastern region have distinct histories. The first European explorer known to have explored the Atlantic shoreline of the Northeast since the Norse was Giovanni da Verrazzano
Giovanni da Verrazzano ( , ; often misspelled Verrazano in English; 1491–1528) was an Italian ( Florentine) explorer of North America, who led most of his later expeditions, including the one to America, in the service of King Francis I of ...
in 1524. His ship ''La Dauphine'' explored the coast from what is now known as Florida to New Brunswick.
The first Europeans to settle and colonize New England were Pilgrims from England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, who landed in present-day Massachusetts in 1620. The Pilgrims arrived on the ship ''Mayflower
''Mayflower'' was an English sailing ship that transported a group of English families, known today as the Pilgrims, from England to the New World in 1620. After 10 weeks at sea, ''Mayflower'', with 102 passengers and a crew of about 30, reac ...
'' and founded Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes spelled Plimouth) was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on t ...
so they could practice religion freely. Ten years later, a larger group of Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
s settled north of Plymouth Colony in Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
to form Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1628–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around Massachusetts Bay, one of the several colonies later reorganized as the Province of M ...
. In 1636, colonists established Connecticut Colony
The Connecticut Colony, originally known as the Connecticut River Colony, was an English colony in New England which later became the state of Connecticut. It was organized on March 3, 1636, as a settlement for a Puritans, Puritan congregation o ...
and Providence Plantations.
Providence was founded by Roger Williams
Roger Williams (March 1683) was an English-born New England minister, theologian, author, and founder of the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Providence Plantations, which became the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Pl ...
, who was banished by Massachusetts for his beliefs in freedom of religion, and it was the first colony to guarantee all citizens freedom of worship. Anne Hutchinson
Anne Hutchinson (; July 1591 – August 1643) was an English-born religious figure who was an important participant in the Antinomian Controversy which shook the infant Massachusetts Bay Colony from 1636 to 1638. Her strong religious formal d ...
, who was also banished by Massachusetts, formed the town of Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Hampshire, England. Most of Portsmouth is located on Portsea Island, off the south coast of England in the Solent, making Portsmouth the only city in En ...
. Providence, Portsmouth and two other towns ( Newport and Warwick
Warwick ( ) is a market town, civil parish and the county town of Warwickshire in the Warwick District in England, adjacent to the River Avon, Warwickshire, River Avon. It is south of Coventry, and south-east of Birmingham. It is adjoined wit ...
) consolidated to form the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations
The Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations was an English colony on the eastern coast of America, founded in 1636 by Puritan minister Roger Williams after his exile from the Massachusetts Bay Colony. It became a haven for religious d ...
.
Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the Northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
explored the area of present-day New York in 1609 and claimed it for the Netherlands. His journey stimulated Dutch interest, and the area became known as New Netherland
New Netherland () was a colony of the Dutch Republic located on the East Coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva Peninsula to Cape Cod. Settlements were established in what became the states ...
. In 1625, the city of New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam (, ) was a 17th-century Dutch Empire, Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''Factory (trading post), fac ...
(the location of present-day New York City) was designated the capital of the province. The Dutch New Netherland settlement along the Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
and, for a time, the New Sweden
New Sweden () was a colony of the Swedish Empire between 1638 and 1655 along the lower reaches of the Delaware River in what is now Delaware, Maryland, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania. Established during the Thirty Years' War when Sweden was a g ...
settlement along the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and is the longest free-flowing (undammed) river in the Eastern United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock, New York, the river flows for a ...
divided the English settlements in the north and the south. In 1664, Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651 and King of England, Scotland, and King of Ireland, Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II was the eldest su ...
formally annexed New Netherland and incorporated it into the English colonial empire
The English overseas possessions comprised a variety of overseas territories that were colonised, conquered, or otherwise acquired by the Kingdom of England before 1707. (In 1707 the Acts of Union made England part of the Kingdom of Great Br ...
. The territory became the colonies of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
and New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
. New Jersey was originally split into East Jersey
The Province of East Jersey, along with the Province of West Jersey, between 1674 and 1702 in accordance with the Quintipartite Deed, were two distinct political divisions of the Province of New Jersey, which became the U.S. state of New Jersey. ...
and West Jersey
West Jersey and East Jersey were two distinct parts of the Province of New Jersey. The political division existed for 28 years, between 1674 and 1702. Determination of an exact location for a border between West Jersey and East Jersey was often ...
until the two were united as a royal colony in 1702.
New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
played a prominent role in early American education. Starting in the 17th century, the larger towns in New England opened grammar schools
A grammar school is one of several different types of school in the history of education in the United Kingdom and other English-speaking countries, originally a Latin school, school teaching Latin, but more recently an academically oriented Se ...
, the forerunner of the modern high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., ...
. The first public school in the English colonies was the Boston Latin School
The Boston Latin School is a Magnet school, magnet Latin schools, Latin Grammar schools, grammar State school, state school in Boston, Massachusetts. It has been in continuous operation since it was established on April 23, 1635. It is the old ...
, founded in 1635. In 1636, the colonial legislature of Massachusetts founded Harvard College
Harvard College is the undergraduate education, undergraduate college of Harvard University, a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Part of the Harvard Faculty of Arts and Scienc ...
, the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States.
In 1681, William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer, religious thinker, and influential Quakers, Quaker who founded the Province of Pennsylvania during the British colonization of the Americas, British colonial era. An advocate of democracy and religi ...
, who wanted to give Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestantism, Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally ...
a land of religious freedom, founded Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
and extended freedom of religion to all citizens.
Penn strongly desired access to the sea for the Province of Pennsylvania
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn, who received the land through a grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania was derived from ...
and leased what then came to be known as the "Lower Counties on the Delaware" from the Duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of Royal family, royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobi ...
. Penn established representative government and briefly combined his two possessions under one General Assembly in 1682.
By 1704, the province of Pennsylvania had grown so large that their representatives wanted to make decisions without the assent of the Lower Counties and the two groups of representatives began meeting on their own, one at Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, and the other at New Castle, Delaware
New Castle is a city in New Castle County, Delaware, United States. The city is located six miles (10 km) south of Wilmington, Delaware, Wilmington and is situated on the Delaware River. As of 2020, the city's population was 5,551. New Cast ...
. Penn and his heirs remained proprietors of both and always appointed the same person Governor for their province of Pennsylvania and their territory of the Lower Counties. The fact that Delaware and Pennsylvania shared the same governor was not unique. From 1703 to 1738, both New York and New Jersey shared a governor. Massachusetts and New Hampshire also shared a governor for some time.
American Revolution
 The beginnings of the
The beginnings of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
would be in the Northeast, specifically in Massachusetts. The Battles of Lexington and Concord
The Battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775 were the first major military actions of the American Revolutionary War between the Kingdom of Great Britain and Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot militias from America's Thirteen Co ...
in northeast of Boston would be the first military engagements between the Revolutionaries and the British. Many of the major battles of the revolution would be fought in the Northeast. The British would evacuate Boston in early-1776 and would move to capture New York City.
The revolutionaries were pushed to the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and is the longest free-flowing (undammed) river in the Eastern United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock, New York, the river flows for a ...
before suddenly moving forward against the British in the Battles of Trenton and Princeton
Princeton University is a private Ivy League research university in Princeton, New Jersey, United States. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the Unit ...
. A stalemate was reached in 1778, between the British and American Revolutionaries and continued until the end of the war in 1783. The war would move to southern states and eventually conclude with the Battle of Yorktown
The siege of Yorktown, also known as the Battle of Yorktown and the surrender at Yorktown, was the final battle of the American Revolutionary War. It was won decisively by the Continental Army, led by George Washington, with support from the Mar ...
in Virginia.
Formation of the United States of America
The idea of an independent United States of America, with the designs of its government would be created primarily in the Northeast in a series of declarations, constitutions, and documents. TheContinental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislature, legislative bodies, with some executive function, for the Thirteen Colonies of British America, Great Britain in North America, and the newly declared United States before, during, and after ...
es would meet in Philadelphia, which would produce the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the territory of another state or failed state, or are breaka ...
and the Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation, officially the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, was an agreement and early body of law in the Thirteen Colonies, which served as the nation's first frame of government during the American Revolutio ...
. Following the American Revolution, the capital of the newly formed United States would move around in the states of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, and New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
. It was based in New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
from 1785 until 1790, when it was moved to Congress Hall
Congress Hall, located in Philadelphia at the intersection of Chestnut and 6th Streets, served as the seat of the United States Congress from December 6, 1790, to May 14, 1800. During Congress Hall's duration as the capitol of the United State ...
in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, where it remained for a decade, until 1800, when the construction of the new national capital of Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
was completed.
The Constitutional Convention was held in Philadelphia, where the new United States Constitution was drafted in 1787. 6 of the first 13 states to ratify the new constitution would be in the Northeast, with the last of the original 13, Rhode Island, ratifying the constitution in 1790. Vermont would be admitted in 1791 as the 14th state. The first Congress would convene in Federal Hall
Federal Hall was the first capitol building of the United States under the Constitution. Serving as the meeting place of the First United States Congress and the site of George Washington's first presidential inauguration, the building existe ...
in New York City in March 1789.
Early and mid-19th century
Following the revolution the Northeast would see small skirmishes like theWhiskey Rebellion
The Whiskey Rebellion (also known as the Whiskey Insurrection) was a violent tax protest in the United States beginning in 1791 and ending in 1794 during the presidency of George Washington. The so-called "whiskey tax" was the first tax impo ...
in western parts of Pennsylvania. Partial preview
Partial may refer to:
Mathematics
*Partial derivative, derivative with respect to one of several variables of a function, with the other variables held constant
** ∂, a symbol that can denote a partial derivative, sometimes pronounced "partial ...
a Google Books. Many northeastern states would continue trading with the British and other European powers. Tensions between the United States and Europe (specifically Britain) would sour in the lead up to the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
.
This caused certain trade merchants to meet in Hartford to propose succeeding from the United States. The War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
would see less fighting in the Northeast and instead more fighting in western and southern areas. A failed invasion of Canada and the occupation of Maine would be some of the major conflicts during the war. The war would end in 1815 and most of the Northeast has not seen any major conflict since then.
The American Industrial Revolution was launched in Blackstone Valley
The Blackstone Valley or Blackstone River Valley is a region of Massachusetts and Rhode Island. It was a major factor in the American Industrial Revolution. It makes up part of the Blackstone River Valley National Heritage Corridor and Natio ...
in Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
and Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, where textile mills
Textile manufacturing or textile engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful good ...
spread across New England, and in eastern Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, where coal, steel, and industrialization launched the nation's manufacturing sector.
After the end of the War of 1812, industry boomed in the Northeast in the early and middle parts of the 19th century. With the construction of railroad and canals crossing the northeast and the rise of western territories and resources from the south, the Northeast experienced the development of new industries and a fast-growing population. Many of the coastal cities, including Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, and Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, served as ocean trade ports for American goods.
Cities, including Allentown Allentown may refer to:
Places
* Allentown, California, now called Toadtown, California
* Allentown, Georgia, a city in four counties in Georgia
* Allentown, Illinois, an unincorporated community in Tazewell County
* Allentown, New Jersey, a boroug ...
, Buffalo, Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of Un ...
, Rochester, and Syracuse
Syracuse most commonly refers to:
* Syracuse, Sicily, Italy; in the province of Syracuse
* Syracuse, New York, USA; in the Syracuse metropolitan area
Syracuse may also refer to:
Places
* Syracuse railway station (disambiguation)
Italy
* Provi ...
, were settled and emerged as major industrial centers.
By 1860, New York City, based on its present-day boundaries, was the first U.S. city to reach a population exceeding one million. Due to the settlement of the Midwest
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
and Great Plains
The Great Plains is a broad expanse of plain, flatland in North America. The region stretches east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. They are the western part of the Interior Plains, which include th ...
, agriculture would collapse in the Mid-Atlantic and New England, with many farms being abandoned by the end of the century, returning to rural forest.
Conflicts with the south over the spread of slavery would become a large factor in the start of the American Civil War, between the United States (western and Northeastern states) and the Confederacy (southeastern states). The admission of Maine as a free state in exchange for Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
becoming a slave state as part of the Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise (also known as the Compromise of 1820) was federal legislation of the United States that balanced the desires of northern states to prevent the expansion of slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand ...
in 1820 would settle the final boundaries of the Northeastern states.
The Mason-Dixon line would be established as the border of slavery, following the border of Pennsylvania and Delaware/Maryland. Abolitionist movements would start in the Northeast and Midwest and would become prominent towards the mid-19th century, these groups advocated the shrinking or banning of slavery in the United States. Some Northeastern states still had small amounts of slaves into the 1850s, though some would ban it during the decade.
The election of 1860 led to the start of the Civil War; southern states seceded from the United States in late-1860 and early-1861. States like Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
and Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
would remain in the union, even with slavery still legal. For the first two years, the eastern theater of the war would remain in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
and Maryland, but in 1863 the war would reach its northeastern most extent in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania
Gettysburg (; ) is a borough (Pennsylvania), borough in Adams County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the borough had a population of 7,106 people.
Gettysburg was the site of ...
. The Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was a three-day battle in the American Civil War, which was fought between the Union and Confederate armies between July 1 and July 3, 1863, in and around Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The battle, won by the Union, ...
is considered a turning point in the Civil War, seeing the end of the Confederate push northwards.
While all Northeastern states would remain in the United States during the war, conflicts did arise, like the New York draft riots in 1863. The war would end in 1865 with the United States taking back control of Southern states.
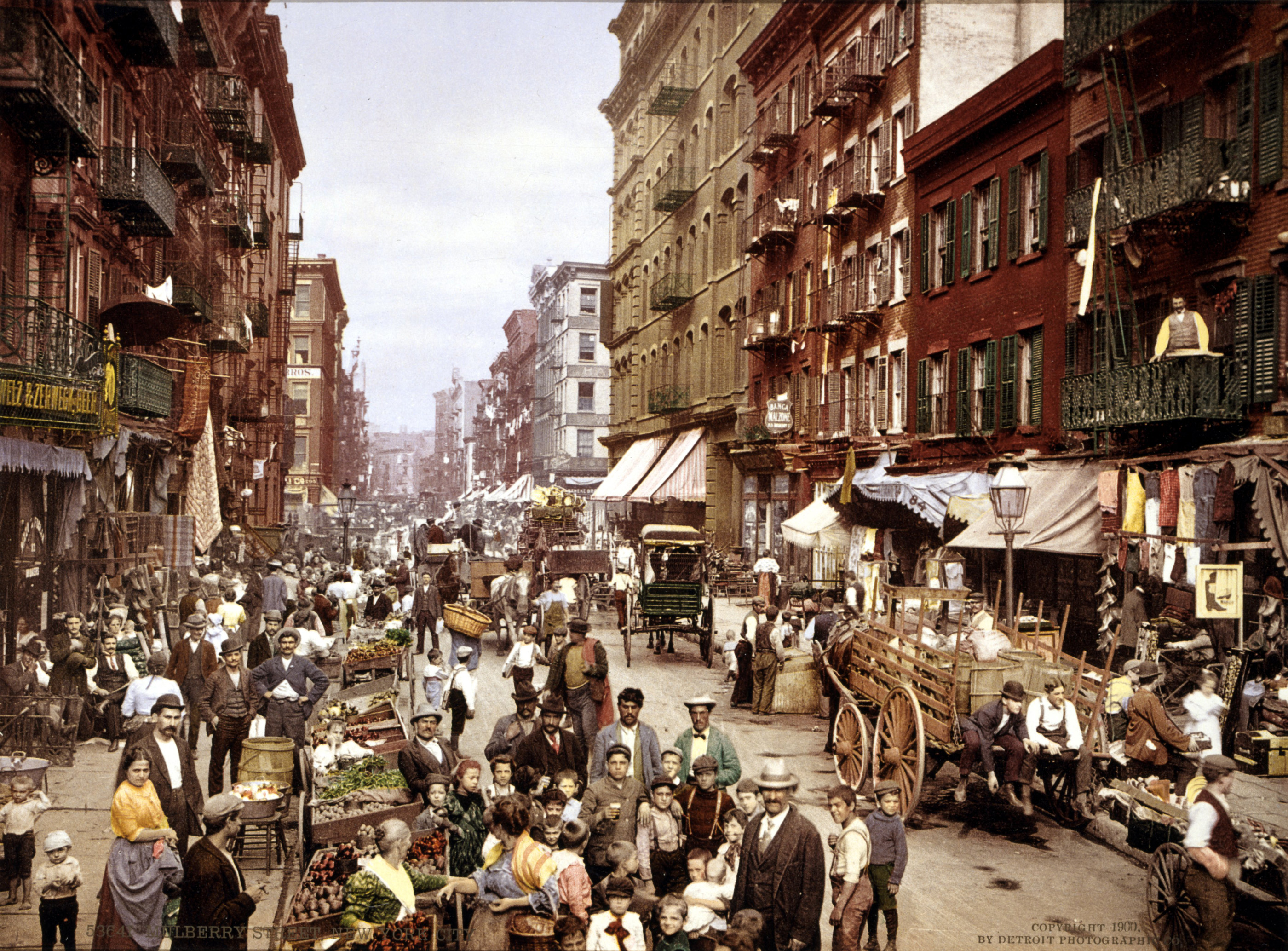
Industrial Revolution and modern times
 Following the Civil War, the Northeast would see a large economic boom and would become one of the most industrialized regions in the world. Many technological innovations would be made in the Northeast during this time. The
Following the Civil War, the Northeast would see a large economic boom and would become one of the most industrialized regions in the world. Many technological innovations would be made in the Northeast during this time. The Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid Discovery (observation), scientific discovery, standardisation, mass production and industrialisation from the late 19th century into the early ...
would see the northeast grow massively, even more so than before the Civil War. Many cities in the Northeast would explode in population, with cities like Philadelphia and New York climbing over one million people, while other cities like Buffalo, Boston, and Pittsburgh would rise above half a million during this time.
New York City eventually grew to become one of the largest cities in the world by 1900. With the American involvement in both World Wars, the Northeast would become a large base of war production, with the Brooklyn Naval Yard producing many navy ships. Many worker strikes would occur in the states, including the Homestead strike in 1892. Many of these cities would see a peak population and industrial output in the aftermath of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
in the 1950s.
Starting in the 1950s and continuing into the 21st century, a large industrial decline in the Northeast resulted in a depopulation of many Northeastern cities, many of which had not yet recovered from it into the 21st century. This led to the rise of programs of urban renewal
Urban renewal (sometimes called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address real or perceived urban decay. Urban renewal involves the clearing ...
and demolition of large parts of Northeastern cities during the mid and late 20th century. There has also been a large population shift to the Sun Belt states starting in the 1960s.
New York state
New York, also called New York State, is a state in the northeastern United States. Bordered by New England to the east, Canada to the north, and Pennsylvania and New Jersey to the south, its territory extends into both the Atlantic Ocean and ...
lost its claim to being the most populated state after it was surpassed by California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
in the 1970s. Some Northeastern cities, including New York City, have recovered from its decline in the mid-20th century. Many new information and service industries have risen in the northeast, which has led to a boom in the 21st century in some cities in the Northeast like Boston, New York, and Philadelphia. Some other cities like Hartford
Hartford is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The city, located in Hartford County, Connecticut, Hartford County, had a population of 121,054 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 ce ...
, Syracuse, and Buffalo still are declining though in the 21st century. Hurricane Sandy
Hurricane Sandy (unofficially referred to as Superstorm Sandy) was an extremely large and devastating tropical cyclone which ravaged the Caribbean and the coastal Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States in late ...
would impact much of the northeast in 2012, severely damaging much of the coast and causing flooding inland. The hurricane would directly impact New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
and caused large amounts of flooding in New York City.
Although the first settlers of New England were motivated by religion, since the 21st century, New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
had become one of the least religious parts of the United States. In a 2009 Gallup survey, less than half of residents in Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, and Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
reported religion as an important part of their daily life. In a 2010 Gallup survey, less than 30% of residents in Vermont, New Hampshire, Maine, and Massachusetts reported attending church weekly, giving them the lowest church attendance among U.S. states.
Geography


 The vast area from central
The vast area from central Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
to northern Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, and from western Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, from Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of Un ...
in the west to the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
in the east, have all been loosely grouped into the Northeast at one time or another.
The U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The U.S. Census Bureau is part of the U ...
's definition of the Northeast includes nine states: Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
, Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
.
The region is often subdivided into New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
, the six states east of New York state and the Mid-Atlantic states
The Mid-Atlantic is a region of the United States located in the overlap between the nation's Northeastern and Southeastern states. Traditional definitions include seven U.S. states: New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virg ...
of New Jersey, New York, and Pennsylvania. This definition has been essentially unchanged since 1880 and is widely used as a standard for data tabulation.
The U.S. Census Bureau has acknowledged the obvious limitations of this definition and the potential merits of a proposal created after the 1950 census, that would include changing regional boundaries to include Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, and Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
with the Mid-Atlantic states, but ultimately decided that "the new system did not win enough overall acceptance among data users to warrant adoption as an official new set of general-purpose State groupings. The previous development of many series of statistics, arranged and issued over long periods of time on the basis of the existing State groupings, favored the retention of the summary units of the current regions and divisions." The U.S. Census Bureau confirmed in 1994 that it would continue to "review the components of the regions and divisions to ensure that they continue to represent the most useful combinations of states and state equivalents."
Many organizations and reference works follow the Census Bureau's definition for the region. In the history of the United States, the Mason–Dixon line
The Mason–Dixon line, sometimes referred to as Mason and Dixon's Line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states: Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia. It was Surveying, surveyed between 1763 and 1767 by Charles Mason ...
between Pennsylvania ( the North) and Maryland ( the South) traditionally divided the regions, but in modern times, various entities define the Northeastern United States in somewhat different ways.
The Association of American Geographers
The American Association of Geographers (AAG) is a non-profit scientific and educational society aimed at advancing the understanding, study, and importance of geography and related fields. Its headquarters is located in Washington, D.C. The ...
divides the Northeast into two divisions: "New England", which is the same as the Census Bureau; and it has the same "Middle States" but adds Delaware. Similarly, the Geological Society of America
The Geological Society of America (GSA) is a nonprofit organization dedicated to the advancement of the geosciences.
History
The society was founded in Ithaca, New York, in 1888 by Alexander Winchell, John J. Stevenson, Charles H. Hi ...
defines the Northeast as these same states but with the addition of Maryland and the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
.
The narrowest definitions include only the states of New England. Other more restrictive definitions include New England and New York as part of the Northeast United States, but exclude Pennsylvania and New Jersey.
States beyond the Census Bureau definition are included in Northeast Region by various other entities:
* Various organizations include Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, and the national capital of Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
* The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on De ...
and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, ...
include in their Northeast Region Delaware, Maryland, and West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
.
* The United States Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is a List of federal agencies in the United States, U.S. federal government agency within the United States Department of the Interior which oversees the management of fish, wildlife, ...
includes in their Northeast Region: Delaware, Maryland, District of Columbia, West Virginia, and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
.
* The National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government, within the US Department of the Interior. The service manages all List ...
includes in their Northeast Region: Delaware, Maryland, West Virginia, and Virginia, though small parts are also in the National Capital Region.
Topography
While most of the Northeastern United States lie in the physiographic region of the Appalachian Highlands, some are also part of theAtlantic coastal plain
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
, which extends south to the southern tip of Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
. The coastal plain areas include Cape Cod
Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer months. The ...
in Massachusetts, Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated continental island in southeastern New York (state), New York state, extending into the Atlantic Ocean. It constitutes a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land are ...
in New York, and most of New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, and are generally low and flat with sandy soil and long tidal marsh waterways. The highlands, including the Piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
and the Appalachian Mountains, are heavily forested, ranging from rolling hills to summits greater than , and pocked with many lakes. The highest peak in the Northeast is Mount Washington
Mount Washington is an ultra-prominent mountain in the state of New Hampshire. It is the highest peak in the Northeastern United States at and the most topographically prominent mountain east of the Mississippi River.
The mountain is notorio ...
in New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
at .
Land use
, forest-use covered approximately 60% of the Northeastern states, including Delaware, Maryland, and Washington, D.C., about twice the national average. About 11% was cropland and another 4% grassland pasture or range. There is also more urbanized land in the Northeast (12%) than any other region in the U.S. Many parks on a state and national level cover the inland parts of the region. Large parks include theAdirondack Park
The Adirondack Park is a park in northeastern New York (state), New York protecting the Adirondack Mountains. The park was established in 1892 for "the free use of all the people for their health and pleasure", and for watershed protection. At , ...
in northeastern New York, Green Mountain National Forest
Green Mountain National Forest is a national forest located in Vermont, a temperate broadleaf and mixed forest typical of the New England/Acadian forests ecoregion. The forest supports a variety of wildlife, including beaver, moose, coyote, b ...
in Vermont, White Mountain Forest in northern New Hampshire, Baxter State Park in northern Maine, Acadia National Park
Acadia National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States located along the mid-section of the Maine coast, southwest of Bar Harbor, Maine, Bar Harbor. The park includes about half of Mount Desert ...
on the eastern coast of Maine, Allegheny National Forest
The Allegheny National Forest is a National Forest in Northwestern Pennsylvania, about 100 miles northeast of Pittsburgh. The forest covers of land. Within the forest is Kinzua Dam, which impounds the Allegheny River to form Allegheny Reserv ...
in northwestern Pennsylvania, and Catskill Park
The Catskill Park is in the Catskill Mountains in the U.S. state of New York. It consists of of land inside a Blue Line in four counties: Delaware, Greene, Sullivan, and Ulster. As of 2005, or 41 percent of the land within, is owned by ...
in southern New York. There are also some parks closer to the shore, though these are usually smaller and squeezed in-between urbanized areas. These include the Palisades Park in New Jersey, Fire Island
Fire Island is the large center island of the outer barrier islands parallel to the South Shore of Long Island in the U.S. state of New York.
In 2012, Hurricane Sandy once again divided Fire Island into two islands. Together, these two isl ...
in Long Island, and the Cape Cod shoreline in Massachusetts. The Northeast has 72 National Wildlife Refuge
The National Wildlife Refuge System (NWRS) is a system of protected areas of the United States managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS), an agency within the United States Department of the Interior, Department of the Interi ...
s, encompassing more than of habitat and designed to protect some of the 92 different threatened and endangered species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
living in the region.
Climate
The climate of the Northeastern United States varies from northernmost state ofMaine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
to its southernmost state in Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
. The region's climate is influenced by its positional western to eastern flow of weather in the lower middle latitudes in the United States. In summer the subtropical high (Bermuda High
The Azores High also known as North Atlantic (Subtropical) High/Anticyclone or the Bermuda- High, is a large subtropical semi-permanent centre of high atmospheric pressure typically found south of the Azores in the Atlantic Ocean, at the Horse lat ...
) moves toward the East Coast, this pumps warm and sultry air toward the Northeast (less so in the far northern areas of northern New York, Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine). Summers are normally warm in northern areas to hot in southern areas. Frequent (but brief) thundershowers are common on hot summer days from Connecticut south to Maryland.
In winter, the subtropical high retreats southeastward, and the polar jet stream moves south bringing colder air masses from up in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
and more frequent storm systems to the region. Winter often brings both rain and snow as well as surges of both warm and cold air. In the southern part of the Northeast from coastal Rhode Island southwest to eastern Maryland, the Appalachians partially protect these locations from the extreme cold coming from the west and the interior of North America.
The basic climate of the Northeast can be divided into a colder and snowier interior, including western Maryland, most of Pennsylvania, most of North Jersey
North Jersey, also known as Northern New Jersey, comprises the northern portions of the U.S. state of New Jersey between the upper Delaware River and the Atlantic Ocean. As a distinct toponym, North Jersey is a colloquial one rather than an a ...
, Upstate New York
Upstate New York is a geographic region of New York (state), New York that lies north and northwest of the New York metropolitan area, New York City metropolitan area of downstate New York. Upstate includes the middle and upper Hudson Valley, ...
, and most of New England, and a milder coastal plain region from Cape Cod
Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer months. The ...
and southern Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
southward, including Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated continental island in southeastern New York (state), New York state, extending into the Atlantic Ocean. It constitutes a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land are ...
, Southern Connecticut, New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, central and southern New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, part of the Pennsylvania portion of the Delaware Valley
The Philadelphia metropolitan area, also known as Greater Philadelphia and informally called the Delaware Valley, the Philadelphia tri-state area, and locally and colloquially Philly–Jersey–Delaware, is a major metropolitan area in the Nor ...
including Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
, and most of Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
.
In the latter region the hardiness zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely ...
ranges from 7a to 8a. Annual mean temperatures range from the low-to-mid 50s F from Maryland to southern Connecticut, to the 40s F in most of New York State, New England, and northern Pennsylvania.
Most of the Northeast has a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
(''Dfa/Dfb/occasional Dfc/Dc''). The northernmost portion of the humid subtropical
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between la ...
zone (''Cfa/Do'') begins at Martha's Vineyard
Martha's Vineyard, often simply called the Vineyard, is an island in the U.S. state of Massachusetts, lying just south of Cape Cod. It is known for being a popular, affluent summer colony, and includes the smaller peninsula Chappaquiddick Isla ...
and extreme SW Rhode Island and extends southwestward down the coastal plain to central and southern Maryland. The oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
zone (''Cfb/Do'') only exists on Block Island
Block Island is an island of the Outer Lands coastal archipelago in New England, located approximately south of mainland Rhode Island and east of Long Island's Montauk Point. The island is coterminous with the town of New Shoreham, Rhode Isl ...
and Nantucket
Nantucket () is an island in the state of Massachusetts in the United States, about south of the Cape Cod peninsula. Together with the small islands of Tuckernuck Island, Tuckernuck and Muskeget Island, Muskeget, it constitutes the Town and Co ...
. It is the only area of the Northeast where all months average between . Cape Cod
Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer months. The ...
borders this zone and warm-summer humid continental (''Dfb/Dc'').
Demographics
 As of the 2020 U.S. census, the population of the region was 57,609,148, representing 17.38% of the nation's total population. With an average of 345.5 people per square mile, the Northeast is 2.5 times as densely populated as the second-most dense region, the
As of the 2020 U.S. census, the population of the region was 57,609,148, representing 17.38% of the nation's total population. With an average of 345.5 people per square mile, the Northeast is 2.5 times as densely populated as the second-most dense region, the South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
. Since the last century, the U.S. population has been shifting away from the Northeast and Midwest
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
toward the South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
and West
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
.
The region's racial composition as of 2020 was 64.42% white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
, 11.51% African American, 0.51% Native American, 7.25% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 8.17% from other races, and 8.10% from two or more races. Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnici ...
or Latino of any race were 15.27% of the population. There were 22,418,883 households and 14,189,719 families in 2021. Of the 22,418,883 households, 27.7% included children under the age of 18.
In 2021, the region's the population's age distribution was 20.5% under age 18, 57.36% from 18 to 62, and 22.1% who were 62 years of age or older. The median age was 40.5 years. For every 100 females, there were 96.4 males. For every 100 women ages 18 and over, there were 94.3 men.
The median income for a household in the region in 2021 was $77,142, and the median income for a family was $97,347. About 11.9% of the population were below the poverty line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line, or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for ...
, including 16.0% of those under age 18 and 10.4% of those age 65 or over.
The two U.S. Census Bureau divisions in the Northeast, New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
and the Mid-Atlantic, rank second and first respectively among the 9 divisions in population density according to the 2013 population estimate. The South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for ...
region (233.1) was very close behind New England (233.2). Due to the faster growth of the South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for ...
region, it will take over the #2 division rank in population density in the next estimate, dropping New England to 3rd position. New England is projected to retain the number 3 rank for many, many years, as the only other lower-ranked division with even half the population density of New England is the East North Central division (192.1) and this region's population is projected to grow slowly.
New York City, New York
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on New York Harbor, one of the world's largest natural harb ...
is the most populated city in both the Northeast and the United States. Its population was 8,804,190 in 2020. Its metro area
Metro Area is a Brooklyn-based house and nu-disco duo formed in 1998 by Morgan Geist and Darshan Jesrani.
History
Geist grew up in Wayne, New Jersey, Spring Arts Clubs: Electro-Shock by Tricia Romano">village voice > nyclife > Spring Arts ...
has a population of 20,140,470.
File:Philadelphia skyline August 2007.jpg, alt=Downtown Philadelphia, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
is the second-most populated in the Northeast and sixth-most populous in the nation. Its population was 1,603,797 in 2020. Its metro area
Metro Area is a Brooklyn-based house and nu-disco duo formed in 1998 by Morgan Geist and Darshan Jesrani.
History
Geist grew up in Wayne, New Jersey, Spring Arts Clubs: Electro-Shock by Tricia Romano">village voice > nyclife > Spring Arts ...
population was 6,228,601.
File:Boston skyline from Longfellow Bridge September 2017 panorama 2.jpg, alt=Back Bay, Boston, Boston, Massachusetts
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
is the third-most populous city in the Northeast and 25th-most populous in the nation. Its population was 675,647 in 2020. Its metro area
Metro Area is a Brooklyn-based house and nu-disco duo formed in 1998 by Morgan Geist and Darshan Jesrani.
History
Geist grew up in Wayne, New Jersey, Spring Arts Clubs: Electro-Shock by Tricia Romano">village voice > nyclife > Spring Arts ...
had a population of 4,941,632.
File:Newark Skyline Northwest View.jpg, Newark, New Jersey
Newark ( , ) is the List of municipalities in New Jersey, most populous City (New Jersey), city in the U.S. state of New Jersey, the county seat of Essex County, New Jersey, Essex County, and a principal city of the New York metropolitan area. ...
is the fourth-most populous city in the Northeast and 64th-most populous in the U.S. Its population was 311,549 in 2020. Its metro area is combined with the New York area
The New York metropolitan area, also called the Tri-State area and sometimes referred to as Greater New York, is the largest metropolitan economy in the world, with a gross metropolitan product of over US$2.6 trillion. It is also the lar ...
.
File:Duquesne Incline (50076338942) (cropped).jpg, alt=downtown Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of Un ...
is the fifth most populous city in the Northeast and 68th-most populous in the nation. Pittsburgh is at the western frontier of the Northeast, a short drive from the Ohio border, and is widely regarded as the transition point between the Northeast and Midwest. Its population was 302,971 in 2020. Its metro area
Metro Area is a Brooklyn-based house and nu-disco duo formed in 1998 by Morgan Geist and Darshan Jesrani.
History
Geist grew up in Wayne, New Jersey, Spring Arts Clubs: Electro-Shock by Tricia Romano">village voice > nyclife > Spring Arts ...
has a population of 2,370,930.
File:Jersey City from a helicopter.jpg, alt=Newport area of Jersey City, Jersey City, New Jersey
Jersey City is the List of municipalities in New Jersey, second-most populous
is the sixth most populous-largest city in the Northeast and 70th-most populous in the nation. It had a population of 292,449 in 2020. It sits directly across the Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
from New York City.
File:Buffalo Skyline from Drone 1.jpg, alt=Downtown Buffalo, Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is a Administrative divisions of New York (state), city in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York and county seat of Erie County, New York, Erie County. It lies in Western New York at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of ...
is the seventh most populous city in the Northeast and 82nd-most populous in the U.S. Its population was 278,349 in 2020. Its metro area
Metro Area is a Brooklyn-based house and nu-disco duo formed in 1998 by Morgan Geist and Darshan Jesrani.
History
Geist grew up in Wayne, New Jersey, Spring Arts Clubs: Electro-Shock by Tricia Romano">village voice > nyclife > Spring Arts ...
had a population of 1,166,902.
File:View of Yonkers from the New Jersey Palisades (2).jpg, Yonkers, New York
Yonkers () is the List of municipalities in New York, third-most populous city in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York and the most-populous City (New York), city in Westchester County, New York, Westchester County. A centrally locate ...
is the eighth most populous city in the Northeast and 115th-most populous city in the U.S. It had a population of 211,569 in 2020. It borders the Bronx
The Bronx ( ) is the northernmost of the five Boroughs of New York City, boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. It shares a land border with Westchester County, New York, West ...
, a borough of New York City to its south.
File:Downtown Rochester, NY HDR by patrickashley.jpg, Rochester, New York
Rochester is a city in and the county seat, seat of government of Monroe County, New York, United States. It is the List of municipalities in New York, fourth-most populous city and 10th most-populated municipality in New York, with a populati ...
is the ninth most populous city in the Northeast and the 116th-most populous city in the United States. It had a population of 211,328 in 2020. The Rochester metro has a population of 1,090,135.
File:Downtown Worcester, Massachusetts.jpg, Worcester, Massachusetts
Worcester ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Massachusetts, second-most populous city in the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the list of United States cities by population, 113th most populous city in the United States. Named after Worcester ...
is the tenth most populous city in the Northeast and the 114th-most populous city in the United States. It had a population of 206,518 in the 2020 census. It is an edge city of Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston, the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England, and its surrounding areas, home to 4,941,632. The most s ...
and its metro is combined with it.
Economy
, the Northeast U.S. accounts for approximately 23% of the nation'sgross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
. Due to its vast population and diverse landscapes, the Northeast has a large and robust economy, ranging from financial services in Manhattan, to agriculture in Central Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania is the fifth-most populous state in the United States. Regions of Pennsylvania include:
Lehigh Valley
The Lehigh Valley, located in eastern Pennsylvania, is named for the Lehigh River, which flows through it. It is the state's thir ...
.
New York City
 , the
, the New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also called the Tri-State area and sometimes referred to as Greater New York, is the List of cities by GDP, largest metropolitan economy in the world, with a List of U.S. metropolitan areas by GDP, gross metropo ...
is estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product
Gross metropolitan product (GMP) is a monetary measure that calculates the total economic output of a statistical metropolitan unit during a specific time period. It represents the market value of all final goods and services produced within the u ...
(GMP) of $2.1 trillion US dollars, ranking it first in the U.S. If the New York metropolitan area were a sovereign state
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the ter ...
, it would have been the eighth-largest economy in the world. Manhattan
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the County statistics of the United States#Smallest, larg ...
is considered the world's financial center, with many large banks based in Manhattan
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the County statistics of the United States#Smallest, larg ...
and some of the largest stock exchanges on Wall Street
Wall Street is a street in the Financial District, Manhattan, Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs eight city blocks between Broadway (Manhattan), Broadway in the west and South Street (Manhattan), South Str ...
, like the New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District, Manhattan, Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is the List of stock exchanges, largest stock excha ...
, it is so prominent that the term "Wall Street" is usually synonymous with finance. Many other companies are based in New York City area, either in Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan, serving as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Building, the ...
, downtown Brooklyn
Downtown Brooklyn is the third-largest central business district in New York City (after Midtown Manhattan, Midtown and Lower Manhattan), and is located in the northwestern section of the borough (New York City), borough of Brooklyn. The neighb ...
, Long Island City
Long Island City (LIC) is a neighborhood within the New York City borough of Queens. It is bordered by Astoria to the north; the East River to the west; Sunnyside to the east; and Newtown Creek, which separates Queens from Greenpoint, Brook ...
, or the various suburbs, like Stamford or White Plains. Some of the largest companies based in New York City area include, Verizon
Verizon Communications Inc. ( ), is an American telecommunications company headquartered in New York City. It is the world's second-largest telecommunications company by revenue and its mobile network is the largest wireless carrier in the ...
, J.P. Morgan Chase, Citigroup
Citigroup Inc. or Citi (Style (visual arts), stylized as citi) is an American multinational investment banking, investment bank and financial services company based in New York City. The company was formed in 1998 by the merger of Citicorp, t ...
, MetLife
MetLife, Inc. is the Holding company, holding corporation for the Metropolitan Life Insurance Company (MLIC), better known as MetLife, and its affiliates. MetLife is among the largest global providers of insurance, Annuity (US financial produ ...
, PepsiCo
PepsiCo, Inc. is an American multinational corporation, multinational food, snack, and beverage corporation headquartered in Harrison, New York, in the hamlet of Purchase, New York, Purchase. PepsiCo's business encompasses all aspects of the f ...
, IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
, Time Warner
Warner Media, LLC ( doing business as WarnerMedia) was an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate owned by AT&T. It was headquartered at the 30 Hudson Yards complex in New York City.
It was established as Time Warne ...
, Goldman Sachs
The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. ( ) is an American multinational investment bank and financial services company. Founded in 1869, Goldman Sachs is headquartered in Lower Manhattan in New York City, with regional headquarters in many internationa ...
, and Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 184 ...
. Several technology companies have been founded in New York, or moved their headquarters to New York from other places.
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
is the nation's most populated city, and the New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also called the Tri-State area and sometimes referred to as Greater New York, is the List of cities by GDP, largest metropolitan economy in the world, with a List of U.S. metropolitan areas by GDP, gross metropo ...
including and surrounding it is the nation's most populated metropolitan region, contributing to a sizable shopping economy, including many large shopping malls and department stores based in the area, such as Macy's on 34th Street, Fifth Avenue
Fifth Avenue is a major thoroughfare in the borough (New York City), borough of Manhattan in New York City. The avenue runs south from 143rd Street (Manhattan), West 143rd Street in Harlem to Washington Square Park in Greenwich Village. The se ...
, and American Dream
The "American Dream" is a phrase referring to a purported national ethos of the United States: that every person has the freedom and opportunity to succeed and attain a better life. The phrase was popularized by James Truslow Adams during the ...
in East Rutherford, New Jersey
East Rutherford is a Borough (New Jersey), borough in Bergen County, New Jersey, Bergen County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. It is an inner suburb, inner-ring suburb of New York City, located west of Midtown Manhattan. As of the 2020 Unit ...
, the Palisades Center in West Nyack, New York
West Nyack is a hamlet and census-designated place in the town of Clarkstown, Rockland County, New York, United States. It is located north of Blauvelt, east of Nanuet, southwest of Valley Cottage, southeast of Bardonia, and west of Central ...
, and the SoNo Collection in Norwalk, Connecticut
Norwalk is a city in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. The city, part of the New York metropolitan area, New York Metropolitan Area, is the List of municipalities of Connecticut by population, sixth-most populous city in Connecticut ...
. The Port of New York and New Jersey
The Port of New York and New Jersey is the port district of the New York metropolitan area, New York-Newark metropolitan area, encompassing the region within approximately a radius of the Statue of Liberty National Monument.
It includes the sy ...
, one of the nation's largest ports, is located on New York Harbor
New York Harbor is a bay that covers all of the Upper Bay. It is at the mouth of the Hudson River near the East River tidal estuary on the East Coast of the United States.
New York Harbor is generally synonymous with Upper New York Bay, ...
.
Philadelphia
Philadelphia metropolitan area
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
is estimated to produce a GMP of $479 billion US dollars, making it the 9th largest economy in the United States. Many large companies are based in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, the nation's sixth-largest city, including AmerisourceBergen
Cencora, Inc., formerly known as AmerisourceBergen, is an American drug wholesale company and a contract research organization, that was formed by the merger of Bergen Brunswig and AmeriSource in 2001. It is one of the largest pharmaceutica ...
, Comcast
Comcast Corporation, formerly known as Comcast Holdings,Before the AT&T Broadband, AT&T merger in 2001, the parent company was Comcast Holdings Corporation. Comcast Holdings Corporation now refers to a subsidiary of Comcast Corporation, not th ...
, and DuPont
Dupont, DuPont, Du Pont, duPont, or du Pont may refer to:
People
* Dupont (surname) Dupont, also spelled as DuPont, duPont, Du Pont, or du Pont is a French surname meaning "of the bridge", historically indicating that the holder of the surname re ...
. The Philadelphia Mint
The Philadelphia Mint is a branch of the United States Mint in Philadelphia. It was built in 1792 following the Coinage Act of 1792, in order to establish a national identity and the needs of commerce in the United States, and is the first and ...
is also located in the city.
Boston
TheBoston metropolitan area
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston, the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England, and its surrounding areas, home to 4,941,632. The most s ...
is a major center for insurance, finance, and technology, serving as the global headquarters for General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) was an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1892, incorporated in the New York (state), state of New York and headquartered in Boston.
Over the year ...
, Liberty Mutual
Liberty Mutual Insurance Company is an American diversified global insurer and the sixth-largest Property insurance, property and Casualty insurance, casualty insurer in the world. It ranks 87th on the Fortune 100, ''Fortune'' 100 list of larges ...
, and other large companies.
Other regions
Rural regions and states, including most ofUpstate New York
Upstate New York is a geographic region of New York (state), New York that lies north and northwest of the New York metropolitan area, New York City metropolitan area of downstate New York. Upstate includes the middle and upper Hudson Valley, ...
, Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
, New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, and Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, rely more on agriculture, logging, mining, and tourism to help boost their local and statewide economies. Many national and state parks in the region generate lots of tourism, especially during fall months. The logging industry is especially prominent in Maine, making up a large part of Northern Maine's economy.
Many Northeastern states have very large economies and are highly developed. As of 2022, the per capita gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
s for these states are:
# New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
, US$2.1 trillion, per capita $105,226
# Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, US$931 billion, per capita $71,825
# New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, US$753 billion, per capita $81,307
# Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, US$693 billion, per capita $99,274
# Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
, US$323 billion, per capita $89,301
# New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, US$106 billion, per capita $76,008
# Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, US$85 billion, per capita $61,491
# Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
, US$72 billion per capita $65,879
# Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
, US$41 billion, per capita $63,275
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission
The United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with protecting public health and safety related to nuclear energy. Established by the Energy Reorganization Act of 1974, the ...
oversees 34 nuclear reactors, eight for research or testing and 26 for power production in the Northeastern United States.
Transportation
Rail systems
 The Northeast is served by
The Northeast is served by Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
trains, with the Northeast Regional
The ''Northeast Regional'' is an intercity rail service operated by Amtrak in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic United States. In the past it has been known as the ''NortheastDirect'', ''Acela Regional'', or ''Regional''. It is Amtrak's busie ...
and Acela
The ''Acela'' ( ; originally the ''Acela Express'' until September 2019) is Amtrak's flagship passenger train service along the Northeast Corridor (NEC) in the Northeastern United States between Washington, D.C. and Boston via 13 intermedia ...
, two of the busiest intercity rail lines running from Washington D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
in the south to Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
in the north. Other Amtrak Lines that serve the Northeast include the Downeaster, Empire Service
The ''Empire Service'' is an inter-city rail service operated by Amtrak within the state of New York in the United States. The brand name originated with the New York Central Railroad in 1967. Trains on the line provide frequent daily service ...
, Vermonter, Lake Shore Limited
The ''Lake Shore Limited'' is an Amtrak Long Distance, overnight passenger train operated by Amtrak between Chicago and the Northeastern United States, with sections to New York City and Boston. The central segment of the route runs along the s ...
, Pennsylvanian. Light rail
Light rail (or light rail transit, abbreviated to LRT) is a form of passenger urban rail transit that uses rolling stock derived from tram technology National Conference of the Transportation Research Board while also having some features from ...
, commuter rail
Commuter rail or suburban rail is a Passenger train, passenger rail service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting Commuting, commuters to a Central business district, central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter town ...
, and other subway systems are also available in the region.
Major stations
 *
* 30th Street Station
30th Street Station, officially William H. Gray III 30th Street Station, is a major intermodal passenger transport, intermodal transit station in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The station opened in 1933 as Pennsylvania Station– ...
in Philadelphia. Served by all SEPTA Regional Lines, Amtrak, NJ Transit's Atlantic City Line
The Atlantic City Line (ACL) is a commuter rail line operated by NJ Transit (NJT) in the United States between Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and Atlantic City, New Jersey, operating along the corridor of the White Horse Pike. It runs over trackage ...
, it is the third-busiest Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
station and 11th-busiest train station in North America with over four million passengers in 2019.
* Pennsylvania Station in New York City is served by some NJ Transit
New Jersey Transit Corporation, branded as NJ Transit or NJTransit and often shortened to NJT, is a state-owned public transportation system that serves the U.S. state of New Jersey and portions of the states of New York and Pennsylvania. I ...
lines, and some Long Island Rail Road
The Long Island Rail Road , or LIRR, is a Rail transport, railroad in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip of Suffolk County, New York, Suffolk County on Long Islan ...
and Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
trains. It is the busiest train station in North America, with over 10 million passengers in 2019, along with 27 million passengers from NJ Transit and 69 million from Long Island Rail in 2017.
* Grand Central Terminal
Grand Central Terminal (GCT; also referred to as Grand Central Station or simply as Grand Central) is a commuter rail terminal station, terminal located at 42nd Street (Manhattan), 42nd Street and Park Avenue in Midtown Manhattan, New York Ci ...
in New York City is served by Metro North and some Long Island Rail trains (beginning in January 2023). Grand Central Terminal had over 67 million annual passengers in 2017 and is the second-busiest train station in the nation and third-busiest in North America.
* Union Station
A union station, union terminal, joint station, or joint-use station is a railway station at which the tracks and facilities are shared by two or more separate railway company, railway companies, allowing passengers to connect conveniently bet ...
in New Haven, Connecticut
New Haven is a city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It is located on New Haven Harbor on the northern shore of Long Island Sound. With a population of 135,081 as determined by the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, New Haven is List ...
is served by New Haven Line
The New Haven Line is a commuter rail line operated by the Metro-North Railroad in the U.S. states of New York (state), New York and Connecticut. Running from New Haven, Connecticut, to New York City, the New Haven Line joins the Harlem Line ...
, Hartford Line, and Shoreline East along existing Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
train lines. It had 350,000 annual Amtrak passengers in 2017.
* South Station
South Station, officially The Governor Michael S. Dukakis Transportation Center at South Station, is the largest railroad station and intercity bus terminal in Greater Boston and New England's second-largest transportation center after Logan I ...
in Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
is served by southern MBTA commuter lines and Amtrak, and was the seventh-busiest train station in North America with nearly 29 million passengers as of 2017.
* North Station
North Station is a commuter rail and intercity rail terminal station in Boston, Massachusetts. It is served by four MBTA Commuter Rail lines – the Fitchburg Line, Haverhill Line, Lowell Line, and Newburyport/Rockport Line – and the Amtr ...
in Boston is served by northern MBTA commuter lines and the Downeaster on Amtrak. It had six million MBTA users in 2012 and 152,000 Amtrak passengers in 2021.
Airports
 The following table includes all airports categorized by the FAA as large or medium hubs located in the Northeastern states.
The following table includes all airports categorized by the FAA as large or medium hubs located in the Northeastern states.
Road
Many major highways cross the Northeast, connecting it to the rest of the nation.US 1
U.S. Route 1 or U.S. Highway 1 (US 1) is a major north–south United States Numbered Highway System, United States Numbered Highway that serves the East Coast of the United States. It runs from Key West, Florida, north to Fort ...
, US 2
U.S. Route 2 or U.S. Highway 2 (US 2) is an east–west United States Numbered Highway spanning across the northern continental United States. US 2 consists of two segments connected by various roadways in southern Canada. ...
, US 3
U.S. Route 3 (US 3) is a United States Numbered Highway running from Cambridge, Massachusetts, through New Hampshire, to the Canada–United States border near Third Connecticut Lake, where it connects to Quebec Route 257.
Massachu ...
, US 4, US 5
U.S. Route 5 (US 5) is a north–south United States Numbered Highway running through the New England states of Connecticut, Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, ...
, US 6
U.S. Route 6 (US 6) or U.S. Highway 6 (US 6), also called the Grand Army of the Republic Highway, honoring the Grand Army of the Republic, American Civil War veterans association, is a main route of the United States Numbere ...
, US 7
U.S. Route 7 (US 7) is a north–south United States Numbered Highway in western New England that runs for through the states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Vermont. The highway's southern terminus is at Interstate 95 (I-95) e ...
, US 9, US 11
U.S. Route 11 or U.S. Highway 11 (US 11) is a major north–south United States Numbered Highway extending across the eastern U.S. The southern terminus of the route is at US 90 in Bayou Sauvage National Wildlife Refu ...
, US 13, US 15
U.S. Route 15 or U.S. Highway 15 (US 15) is a United States Numbered Highway, serving the states of South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, and New York (state), New York. The route is signed north–sou ...
, US 19
U.S. Route 19 or U.S. Highway 19 (US 19) is a north–south United States Numbered Highway in the Eastern United States. Despite encroaching Interstate Highways, the route has remained a long-haul road, connecting the Gulf of Mex ...
, US 20
U.S. Route 20 or U.S. Highway 20 (US 20) is an east–west United States Highway, United States Numbered Highway that stretches from the Pacific Northwest east to New England. The "0" in its route number indicates that US 20 is a major ...
, US 22, US 30
U.S. Route 30 or U.S. Highway 30 (US 30) is an east–west main route of the United States Numbered Highway System, with the highway traveling across the Northern U.S. With a length of , it is the third-longest U.S. Highway, afte ...
, US 40
U.S. Route 40 or U.S. Highway 40 (US 40), also known as the Main Street of America (a nickname shared with U.S. Route 66), is a major east–west United States Highway traveling across the United States from the Mountain States to the Mid- ...
, US 44
U.S. Route 44 (US 44) is an east–west United States Numbered Highway that runs for through four states in the Northeastern United States. The western terminus is at US 209 and New York State Route 55 (NY 55) in Kerhonks ...
, US 46, US 62
U.S. Route 62 or U.S. Highway 62 (US 62) is an east–west United States Highway in the southern and northeastern United States. It runs from the Mexican border at El Paso, Texas, to Niagara Falls, New York, near the Canadian bo ...
, US 130, US 201, US 202
U.S. Route 202 (US 202) is a spur route of US 2. It follows a northeasterly and southwesterly direction stretching from Delaware in the south to Maine in the north and traveling through the states of Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Ne ...
, US 206, US 209
U.S. Route 209 (US 209) is a long U.S. Highway in the states of Pennsylvania and New York (state), New York. Although the route is a spur of U.S. Route 9, US 9, US 209 never intersects US 9, coming within five miles of ...
, US 219, US 220, US 222, US 224, US 302, US 322
U.S. Route 322 (US 322) is a , east–west United States Highway, traversing Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New Jersey. The road is a spur of US 22 and one of the original highways from 1926. A portion of it at one time was concurrent with the Lakes-t ...
, US 422
U.S. Route 422 (US 422) is a spur route of U.S. Route 22, US 22 split into two segments in the U.S. states of Ohio and Pennsylvania. The western segment of US 422 runs from downtown Cleveland, Ohio, east to Ebensburg, Penns ...
, US 522.
The Northeast has the highest amount of tolled roads/bridges in the nation with only two states in the Northeast having no tolls, Connecticut and Vermont. Notable turnpikes include the Pennsylvania Turnpike
The Pennsylvania Turnpike, sometimes shortened to Penna Turnpike or PA Turnpike, is a controlled-access toll road which is operated by the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission (PTC) in Pennsylvania. It runs for across the southern part of the st ...
(I-76/I-276/I-95), New Jersey Turnpike
The New Jersey Turnpike (NJTP) is a system of controlled-access highway, controlled-access toll roads in the U.S. state of New Jersey. The turnpike is maintained by the New Jersey Turnpike Authority (NJTA).The Garden State Parkway, although ma ...
(partially I-95), New York Thruway (I-87/I-90), Massachusetts Turnpike
The Massachusetts Turnpike (colloquially the "Mass Pike" or "the Pike") is a controlled-access toll road that runs concurrently with Interstate 90 (I-90) in the U.S. state of Massachusetts. It the longest Interstate Highway in Massachu ...
(I-90), Maine Turnpike
Interstate 95 (I-95) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs north–south from Miami, Florida to Houlton, Maine. The highway enters Maine from the New Hampshire state line in Kittery, Maine, Kittery and runs for to the Cana ...
(I-95), PA Turnpike Northeast Extension (I-476). The northeast also contains many tolled and non-tolled parkways, many of which are in New York City metro. Major parkways include the Garden State Parkway
The Garden State Parkway (GSP) is a Controlled-access highway, controlled-access toll road that stretches the north–south length of eastern New Jersey from the state's southernmost tip near Cape May, New Jersey, Cape May north to the New York ...
, Taconic State Parkway
The Taconic State Parkway (often called the Taconic or the TSP) is a limited-access parkway between Kensico Dam and Chatham, the longest in the U.S. state of New York. It follows a generally north–south route midway between the Hudson River ...
, Hutchinson River Parkway
The Hutchinson River Parkway (known colloquially as the Hutch) is a controlled-access highway, controlled-access Parkways in New York, parkway in southern New York (state), New York in the United States. It extends for from the Bruckner Interc ...
, Saw Mill River Parkway
The Saw Mill River Parkway (also known as the Saw Mill Parkway or the Saw Mill) is a limited-access road, limited-access Parkways in New York, parkway that extends for through Westchester County, New York, in the United States. It begins at the ...
, Lake Ontario State Parkway
The Lake Ontario State Parkway is a limited-access road, limited-access Parkways in New York, parkway along the southern shore of Lake Ontario in Western New York in the United States. The western end of the highway is at a partial interchange ...
, Niagara Scenic Parkway
The Niagara Scenic Parkway (known as the Robert Moses State Parkway until 2016) is a state parkway in western Niagara County, New York, in the United States. Its southern terminus is at the LaSalle Expressway on the east bank of the Niagara R ...
, Belt Parkway
The Belt Parkway is the name given to a series of controlled-access highway, controlled-access Parkways in New York, parkways that form a belt-like circle around the Borough (New York City), New York City boroughs of Brooklyn and Queens. The Belt ...
, Grand Central Parkway
The Grand Central Parkway (GCP) is a 14.61-mile (23.51 km) controlled-access parkway that stretches from the Triborough Bridge in New York City to the Queens– Nassau County line on Long Island. At the Nassau County line, it becomes t ...
, Northern State Parkway
The Northern State Parkway (also known as the Northern State or Northern Parkway) is a controlled-access parkway on Long Island in the U.S. state of New York. The western terminus is at the Queens– Nassau County line in Lake Success � ...
.
Major crossings
Delaware Memorial Bridge
The Delaware Memorial Bridge is a dual-span suspension bridge crossing the Delaware River. The toll bridges carry Interstate 295 and U.S. Route 40 and is also the link between Delaware and New Jersey. The bridge was designed by the firm o ...
(I-295
Interstate 295
is the designation for the following eight Interstate Highways in the United States, all of which are related to I-95:
*Interstate 295 (Delaware–Pennsylvania), a bypass of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
* Interstate 295 (Florida), a be ...
, NJ Turnpike) - Crosses the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States and is the longest free-flowing (undammed) river in the Eastern United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock, New York, the river flows for a ...
between Delaware and New Jersey, the southern most fixed crossing on the river. Eastbound span opened in 1951, westbound span opened in 1968.
* Walt Whitman Bridge
The Walt Whitman Bridge is a single-level suspension bridge spanning the Delaware River from Philadelphia in the west to Gloucester City in Camden County, New Jersey in the east. The bridge is named after American poet and essayist Walt Whi ...
(I-76) - Crosses the Delaware River, connecting southern Philadelphia to southern New Jersey suburbs. Opened in 1957.
* Benjamín Franklin Bridge ( I-676) - Connects downtown Philadelphia with Camden, New Jersey
Camden is a City (New Jersey), city in Camden County, New Jersey, Camden County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. It is part of the Delaware Valley metropolitan region. The city was incorporated on February 13, 1828.Snyder, John P''The Story of ...
and southern New Jersey. Opened in 1926.
* Delaware River Turnpike Toll Bridge (I-95, PA Turnpike) - Connects the PA Turnpike to the NJ Turnpike. I-95 was only designated in 2018, formerly was I-276. Opened in 1956.
* Driscoll Bridge
The Governor Alfred E. Driscoll Bridge, (Colloquialism, colloquially referred to as the Driscoll Bridge) is a bridge on the Garden State Parkway in the U.S. state of New Jersey, spanning the Raritan River near its mouth in Raritan Bay. The bridg ...
(Garden State Parkway
The Garden State Parkway (GSP) is a Controlled-access highway, controlled-access toll road that stretches the north–south length of eastern New Jersey from the state's southernmost tip near Cape May, New Jersey, Cape May north to the New York ...
) - Crosses the Raritan River
The Raritan River is a river of the U.S. state of New Jersey. Its Drainage basin, watershed drains much of the mountainous areas in the North Jersey, northern and Central Jersey, central sections of the state, emptying into the Raritan Bay near ...
near its mouth at Raritan Bay
Raritan Bay is a bay located at the southern portion of Lower New York Bay between the U.S. states of New York and New Jersey and is part of the New York Bight. The bay is bounded on the northwest by New York's Staten Island, on the west b ...
. Opened in 1954, the bridge is located within the heart of the state of New Jersey, providing access to the Jersey Shore
The Jersey Shore, commonly called the Shore by locals, is the coast, coastal region of the U.S. state of New Jersey. The term encompasses about of shore, oceanfront bordering the Atlantic Ocean, from Perth Amboy, New Jersey, Perth Amboy in the n ...
to the south and North Jersey
North Jersey, also known as Northern New Jersey, comprises the northern portions of the U.S. state of New Jersey between the upper Delaware River and the Atlantic Ocean. As a distinct toponym, North Jersey is a colloquial one rather than an a ...
to the north.
* Newark Bay Bridge (I-76, NJ Turnpike) - Crosses Newark Bay, connecting Newark to Jersey City and Bayonne
Bayonne () is a city in southwestern France near the France–Spain border, Spanish border. It is a communes of France, commune and one of two subprefectures in France, subprefectures in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques departments of France, departm ...
. Opened in 1956.
* Bayonne Bridge
The Bayonne Bridge is an Through arch bridge, arch bridge that spans the Kill Van Kull between Staten Island, New York (state), New York, and Bayonne, New Jersey, Bayonne, New Jersey, United States. It carries New York State Route 440 and ...
( NJ 440/ NY 440) - Crosses Arthur Kill
The Arthur Kill (sometimes referred to as the Staten Island Sound) is a tidal strait in the New York–New Jersey Harbor Estuary between Staten Island (also known as Richmond County), New York, and Union and Middlesex counties, New Jersey. It ...
, connecting Bayonne to Staten Island, New York
Staten Island ( ) is the southernmost of the boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County and situated at the southernmost point of New York (state), New York. The borough is separated from the ad ...
. Opened in 1931, raised in 2017.
* Verrazzano Narrows Bridge (I-278
Interstate 278 (I-278) is an auxiliary Interstate Highway in New Jersey and New York in the United States. The road runs from US Route 1/9 (US 1/9) in Linden, New Jersey, northeast to the Bruckner Interchange in the New Yo ...
) - Crosses New York Harbor
New York Harbor is a bay that covers all of the Upper Bay. It is at the mouth of the Hudson River near the East River tidal estuary on the East Coast of the United States.
New York Harbor is generally synonymous with Upper New York Bay, ...
to connect Staten Island to Brooklyn
Brooklyn is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the New York (state), State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelv ...
, double decked. Opened in 1964.
* Brooklyn-Battery Tunnel (I-478) - Crosses underneath the East River
The East River is a saltwater Estuary, tidal estuary or strait in New York City. The waterway, which is not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates Long Island, ...
to connect Lower Manhattan
Lower Manhattan, also known as Downtown Manhattan or Downtown New York City, is the southernmost part of the Boroughs of New York City, New York City borough of Manhattan. The neighborhood is History of New York City, the historical birthplace o ...
to Brooklyn. Opened in 1950.
* Brooklyn Bridge
The Brooklyn Bridge is a cable-stayed suspension bridge in New York City, spanning the East River between the boroughs of Manhattan and Brooklyn. Opened on May 24, 1883, the Brooklyn Bridge was the first fixed crossing of the East River. It w ...
, Manhattan Bridge
The Manhattan Bridge is a suspension bridge that crosses the East River in New York City, connecting Lower Manhattan at Canal Street with Downtown Brooklyn at the Flatbush Avenue Extension. Designed by Leon Moisseiff, the bridge has a tota ...
, Williamsburg Bridge
The Williamsburg Bridge is a suspension bridge across the East River in New York City, connecting the Lower East Side of Manhattan with the Williamsburg neighborhood of Brooklyn. Originally known as the East River Bridge, the Williamsburg Brid ...
- The bridges cross the East River to connect Lower Manhattan to Brooklyn. Opened in 1883, 1909, and 1903.
* PATH Hudson Tubes - Carries the PATH metro trains underneath the Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
to connect Newark, Jersey City, and Hoboken to Lower and Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan, serving as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Building, the ...
. The tubes opened up in 1908/1909.
* Holland Tunnel
The Holland Tunnel is a vehicular tunnel under the Hudson River that connects Hudson Square and Lower Manhattan in New York City in the east to Jersey City, New Jersey, in the west. The tunnel is operated by the Port Authority of New York an ...
(I-78) - Crosses underneath the Hudson River, connects road traffic from Jersey City and Newark to Lower Manhattan. Opened in 1927.
* Queens-Midtown Tunnel (I-495
Interstate 495 (I-495)
is the designation for the following five Interstate Highways in the United States, all of which are related to I-95:
* The Capital Beltway, a beltway around Washington, D.C., running through Virginia, Maryland, and a sliver ...
) - Crosses underneath the East River, connecting the Long Island Expressway to Manhattan. Opened in 1940.
* North River Tunnels
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' ...
(NJ Transit, Amtrak) Carries the Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston in the north to Washington, D.C., in the south, with major stops in Providence, Rhod ...
underneath the Hudson River, connecting rail traffic from New Jersey to Pennsylvania Station and New England. Opened in 1910.
* Lincoln Tunnel
The Lincoln Tunnel is an approximately tunnel under the Hudson River, connecting Weehawken, New Jersey, to the west with Midtown Manhattan in New York City to the east. It carries New Jersey Route 495 on the New Jersey side and the unsigned N ...
( NJ 495) - Crosses underneath the Hudson River to connect New Jersey to Midtown Manhattan. Opened in 1937.
* Queensboro Bridge
The Queensboro Bridge, officially the Ed Koch Queensboro Bridge, is a cantilever bridge over the East River in New York City. Completed in 1909, it connects the Long Island City neighborhood in the borough of Queens with the Midtown Manhattan ...
( NY 25) - Connects Midtown Manhattan to Long Island City. Opened in 1909.
* Triborough Bridge
The Robert F. Kennedy Bridge (RFK Bridge; also known by its previous name, the Triborough Bridge) is a complex of bridges and elevated expressway viaducts in New York City. The bridges link the boroughs of Manhattan, Queens, and the Bronx. Th ...
(I-278) - Crosses the East River and Harlem River
The Harlem River is an tidal strait in New York City, flowing between the Hudson River and the East River and separating the island of Manhattan from the Bronx on the United States mainland.
The northern stretch, also called the Spuyten Duyvi ...
, provides road connections to Upper Manhattan
Upper Manhattan is the northern section of the New York City borough of Manhattan. Its southern boundary has been variously defined, but some of the most common usages are 96th Street, 110th Street (the northern boundary of Central Park), 1 ...
, Queens, and the Bronx
The Bronx ( ) is the northernmost of the five Boroughs of New York City, boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. It shares a land border with Westchester County, New York, West ...
. Also crosses and connects Randalls Island
Randalls Island (sometimes called Randall's Island) and Wards Island are conjoined islands, collectively called Randalls and Wards Island, in New York City.
. Opened in 1936.
* Hell Gate Bridge
The Hell Gate Bridge (originally the New York Connecting Railroad Bridge) is a railroad bridge in New York City. The bridge carries two tracks of Amtrak's Northeast Corridor and one freight track between Astoria, Queens, and Port Morris, Bron ...
(Amtrak) - Crosses the East River and Bronx Kill
The Bronx Kill is a narrow strait in New York City delineating the southernmost extent of the Bronx. It separates the Bronx from Randalls Island. It connects the Harlem River to the East River.
History
Originally, the Bronx Kill was a sizeab ...
, provides a rail connection from Pennsylvania Station to the Bronx and Connecticut. Opened in 1917.
* George Washington Bridge
The George Washington Bridge is a double-decked suspension bridge spanning the Hudson River, connecting Fort Lee in Bergen County, New Jersey, with the Washington Heights neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. It is named after George W ...
(I-95) - Crosses the Hudson River, connecting New York and New England to New Jersey and cross-country I-80. One of the busiest crossings in the United States. Double Decked. Opened in 1931.
* Alexander Hamilton Bridge (I-95) - Crosses the Harlem River, connecting Manhattan and the GW Bridge to the Cross Bronx Expressway
The Cross Bronx Expressway is a major controlled-access highway, freeway in the New York City borough of the Bronx. It is mainly designated as part of Interstate 95 in New York, Interstate 95 (I-95), but also includes portions of Interstate ...
. Opened in 1963.
* Whitestone Bridge ( I-678) - Crosses the East River, connecting South Bronx
The South Bronx is an area of the Boroughs of New York City, New York City borough of the Bronx. The area comprises neighborhoods in the southern part of the Bronx, such as Concourse, Bronx, Concourse, Mott Haven, Bronx, Mott Haven, Melrose, B ...
to Queens. Opened in 1939.
* Throgs Neck Bridge
The Throgs Neck Bridge is a suspension bridge in New York City, carrying six lanes of Interstate 295 (New York), Interstate 295 (I-295) over the East River where it meets the Long Island Sound. The bridge connects the Throggs Neck section of t ...
(I-295
Interstate 295
is the designation for the following eight Interstate Highways in the United States, all of which are related to I-95:
*Interstate 295 (Delaware–Pennsylvania), a bypass of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
* Interstate 295 (Florida), a be ...
) Crosses the East River, connecting the Bronx and New England to the Queens and Long Island, northern most crossing of the East River. (no fixed crossings are in Long Island Sound) Opened in 1961.
* Tappan Zee Bridge (I-87, I-287) - Crosses the Hudson River, carrying NY Thruway and suburban traffic from Rockland and Westchester counties. Alternative to GW Bridge. Current span opened in 2017, former span opened in 1955.
* Newburgh-Beacon Bridge (I-84) - Crosses the Hudson River, carrying traffic from Pennsylvania and southeastern New York across the river to New England. Opened in 1963.
* Q Bridge (I-95) - Crosses the Quinnipiac River, carrying New Haven traffic along with traffic heading to New England or New York. Current span opened in 2012, original span opened in 1958.
* Baldwin Bridge (I-95) - Crosses the Connecticut River, carrying cross-state traffic and connecting Old Saybrook
Old Saybrook is a town in Middlesex County, Connecticut, United States. The town is part of the Lower Connecticut River Valley Planning Region. The population was 10,481 at the 2020 census. It contains the incorporated borough of Fenwick, an ...
to New London. Opened in 1948.
* Jamestown/ Newport Pell Bridges ( RI 138) - Crosses Narraganset Bay, connecting Newport, Rhode Island
Newport is a seaside city on Aquidneck Island in Rhode Island, United States. It is located in Narragansett Bay, approximately southeast of Providence, Rhode Island, Providence, south of Fall River, Massachusetts, south of Boston, and nort ...
to the rest of the state. Jamestown Bridge opened in 1992, Newport Pell opened in 1969.
* Charter Oak Bridge
The Charter Oak Bridge is one of the three highway bridges over the Connecticut River between Hartford, Connecticut, and East Hartford, Connecticut. The twin steel stringer bridge carries the Wilbur Cross Highway (U.S. Route 5 in Connecticut, U ...
( CT 15/US 5) - Crosses the Connecticut River
The Connecticut River is the longest river in the New England region of the United States, flowing roughly southward for through four states. It rises 300 yards (270 m) south of the U.S. border with Quebec, Canada, and discharges into Long Isl ...
, connecting southern Hartford and I-91 northbound to East Hartford
East Hartford is a town in Hartford County, Connecticut, United States. The population was 51,045 at the 2020 census. The town is located on the east bank of the Connecticut River, directly across from Hartford. It is home to aerospace manufactu ...
and I-84 eastbound. Opened in 1991.
*  Bulkeley Bridge (I-84) - Crosses the Connecticut River, connecting Hartford area traffic across the river. The oldest interstate crossing in the US. Opened in 1908.
*
Bulkeley Bridge (I-84) - Crosses the Connecticut River, connecting Hartford area traffic across the river. The oldest interstate crossing in the US. Opened in 1908.
* Ted Williams Tunnel
The Ted Williams Tunnel is a highway tunnel in Boston, Massachusetts. The third in the city to travel under Boston Harbor, with the Sumner Tunnel and the Callahan Tunnel, it carries the final segment of Interstate 90 (the Massachusetts Turnpi ...
(I-90) - Crosses underneath Boston Harbor
Boston Harbor is a natural harbor and estuary of Massachusetts Bay, located adjacent to Boston, Massachusetts. It is home to the Port of Boston, a major shipping facility in the Northeastern United States.
History 17th century
Since its dis ...
. Connects the Mass Pike and I-93 to East Boston
East Boston, nicknamed Eastie, is a Neighborhoods in Boston, neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, United States, which was annexed by the city of Boston in 1836. Neighboring communities include Winthrop, Massachusetts, Winthrop, Revere, Mas ...
and Logan Airport. Opened in 1995/2003.
* Zakim Bridge (I-93) - Crosses the Charles River
The Charles River (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ), sometimes called the River Charles or simply the Charles, is an river in eastern Massachusetts. It flows northeast from Hopkinton, Massachusetts, Hopkinton to Boston along a highly me ...
, carrying Boston traffic to the northern Massachusetts and Maine/New Hampshire. Opened in 2003.
* Piscataqua River Bridge
The Piscataqua River Bridge is a through arch bridge that crosses the Piscataqua River, connecting Portsmouth, New Hampshire with Kittery, Maine, United States. Carrying six lanes of Interstate 95, the bridge is the third modern span and first f ...
(I-95) - Crosses the Piscataqua River
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki language, Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River to the Atlant ...
, carrying traffic from New Hampshire and Massachusetts to Maine. Opened in 1972.
* Peace Bridge
The Peace Bridge is an international bridge over the Niagara River between Canada and the United States, located just north of the river's source at the east end of Lake Erie about upriver of Niagara Falls. It connects Buffalo, New York, in ...
(QEW
The Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW) is a 400-series highway in the Canadian province of Ontario linking Toronto with the Niagara Peninsula and Buffalo, New York. The highway begins at the Canada–United States border on the Peace Bridge in Fort ...
/I-190) - Crosses the Niagara River, carrying traffic from Buffalo, New York into Ontario. Opened in 1927.
* Rainbow Bridge (NY 384
New York State Route 384 (NY 384) is a state highway in Western New York in the United States. It is a north–south route extending from the city of Buffalo, New York, Buffalo, Erie County, New York, Erie County to the city of Niagara ...
/NY 104
New York State Route 104 (NY 104) is a east–west state highway in Upstate New York in the United States. It spans six counties and enters the vicinity of four cities—Niagara Falls, Lockport, Rochester, and Oswego—as it foll ...
) - Crosses the Niagara River, carrying traffic from Niagara Falls, New York
Niagara Falls is a City (New York), city in Niagara County, New York, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city had a total population of 48,671. It is adjacent to the Niagara River, across from the city of Niagar ...
into Niagara Falls, Ontario
Niagara Falls is a city in Ontario, Canada, adjacent to, and named after, Niagara Falls. As of the Canada 2021 Census, 2021 census, the city had a population of 94,415. The city is located on the Niagara Peninsula along the western bank of the ...
. Opened in 1941.
* Lewiston-Queenston Bridge ( I-190) Crosses the Niagara River
The Niagara River ( ) flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario, forming part of the border between Ontario, Canada, to the west, and New York, United States, to the east. The origin of the river's name is debated. Iroquoian scholar Bruce T ...
, carrying traffic from Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is a Administrative divisions of New York (state), city in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York and county seat of Erie County, New York, Erie County. It lies in Western New York at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of ...
into Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
. Opened in 1962.
History

Milton, Massachusetts
Milton is a town in Norfolk County, Massachusetts, United States. Milton is an immediate southern suburb of Boston, Massachusetts. The population was 28,630 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census.
Milton is located in the relatively hilly ...
(Granite Railway
The Granite Railway was one of the first railroads in the United States, built to carry granite from Quincy, Massachusetts, to a dock on the Neponset River in Milton. From there boats carried the heavy stone to Charlestown for construction ...
), first rapid transit system (MBTA Green Line
The Green Line is a light rail system run by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) in the Boston, Massachusetts, metropolitan area. It is the oldest MBTA subway line, and with tunnel sections dating from 1897, the oldest subway ...
), the first limited access road was the Bronx River Parkway
The Bronx River Parkway (sometimes abbreviated as the Bronx Parkway) is a limited-access Parkways in New York, parkway in downstate New York in the United States. It is named for the nearby Bronx River, which it parallels. The southern terminus ...
, opened in 1922, New York is also where the first urban freeway was built in the late-1930s. (FDR Drive
Franklin D. Roosevelt East River Drive, commonly known as the FDR Drive, is a controlled-access parkway on the east side of the New York City borough of Manhattan. It starts near South and Broad Streets, just north of the Battery Park Underpas ...
) The northeast would also be home to some of the first major freeway revolts in Greenwich Village
Greenwich Village, or simply the Village, is a neighborhood on the west side of Lower Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 14th Street (Manhattan), 14th Street to the north, Broadway (Manhattan), Broadway to the east, Houston Street to the s ...
, and would see the first major highway teardown ( Miller Highway) in the 1970s.
Before European settlement, most of the Northeast was loosely connected by Native American trails, some of which would be incorporated into early-European settlement roads and turnpikes. One major early road was the Boston Post Road
The Boston Post Road was a system of mail-delivery routes between New York City and Boston, Massachusetts, that evolved into one of the first major highways in the United States.
The three major alignments were the Lower Post Road (now U.S. Ro ...
, connecting New York City and Boston along the Connecticut and Rhode Island coasts. Later these roads would be included in the King's Highway, spanning most of the east coast. Smaller turnpikes would also connect cities across the northeast. These roads would prove essential to moving goods across the English colonies in the 18th century and would later play a large part in the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
.
The region saw a boom in canal-building in the early-19th century, with a major canal being the Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east–west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigability, navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, ...
, opened in 1825, connecting the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
to the Hudson River and Atlantic Ocean through Western New York
Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves "Western New Yorkers". Almost all so ...
. The first railroads would be built in the late-1820s and would explode in mileage in the mid to late 19th century. Places like Philadelphia, New York, Boston, Newark, and Pittsburgh would become large water and rail hubs during the Industrial Revolution and would see tremendous booms in population and use.
Many large rivers in the northeast like the Hudson and Delaware would be slowly crossed with bridges starting in the 1800s, with the first fixed crossing of the Hudson River south of Albany being the Poughkeepsie Railroad Bridge, opened in 1889. The Delair Bridge, which would connect Philadelphia with New Jersey was opened six years later in 1896. The first crossing of the Hudson River into New York City would be the series of Hudson River PATH tunnels, being opened in 1908 and 1909. The first major vehicle tunnel would be the Holland Tunnel, opened up in 1927.
The start of highway construction would be the Bronx River Parkway
The Bronx River Parkway (sometimes abbreviated as the Bronx Parkway) is a limited-access Parkways in New York, parkway in downstate New York in the United States. It is named for the nearby Bronx River, which it parallels. The southern terminus ...
and Long Island Motor Parkway
The Long Island Motor Parkway, also known as the Vanderbilt Parkway, Vanderbilt Motor Parkway, or Motor Parkway, was a limited-access parkway on Long Island, New York, United States. It was the first highway designed for automobile use only. Th ...
, both of which started construction in the early-1900s. The rise of Robert Moses
Robert Moses (December 18, 1888 – July 29, 1981) was an American urban planner and public official who worked in the New York metropolitan area during the early to mid-20th century. Moses is regarded as one of the most powerful and influentia ...
in New York would see the construction of many major road bridges and highways crossing the city and metro area. East River Drive (eventually renamed FDR Drive), was built along the corresponding river in Manhattan. The mid-20th century would see the rise of urban and suburban freeways
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms ...
and the decline of passenger and freight rail, with many lesser used tracks being abandoned or torn up during this time. It would also see the original Pennsylvania Station demolished in Midtown Manhattan during the mid-1960s. The construction of the Cross-Bronx Expressway in New York, Central Artery
The Central Artery (officially the John F. Fitzgerald Expressway) is the concurrent section of Interstate 93, US 1 and Route 3 through Downtown Boston, Massachusetts, United States. The modern-day Artery, built as part of the Big Dig from ...
in Boston, and the Vine Street Expressway in Philadelphia tore up many ethnic and minority neighborhoods in the name of urban renewal
Urban renewal (sometimes called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address real or perceived urban decay. Urban renewal involves the clearing ...
. Many other highways were proposed during this era, like the Lower Manhattan Expressway and the Inner Belt in Boston, which were not built due to fierce highway revolts and rising costs. After the major highway revolts and rise of environmental concerns, new highway and interstate projects were mostly cancelled or shortened in the Northeast by the 1990s.
Despite the lack of new major road projects in the Northeast, the region has still continued to grow in population, resulting in the rise of alternative forms of transport like HOV lanes
A high-occupancy vehicle lane (also known as an HOV lane, carpool lane, diamond lane, 2+ lane, and transit lane or T2 or T3 lanes) is a restricted traffic lane reserved for the exclusive use of vehicles with a driver and at least one passenger, ...
or commuter rail
Commuter rail or suburban rail is a Passenger train, passenger rail service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting Commuting, commuters to a Central business district, central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter town ...
s. This has led to the Northeast having one of the highest transit usage percentages in North America, with the Long Island Railroad being the most used commuter rail in the continent. One exception was the Big Dig
The Big Dig was a megaproject in Boston that rerouted the then elevated Central Artery of Interstate 93 that cut across Boston into the O'Neill Tunnel and built the Ted Williams Tunnel to extend Massachusetts Turnpike, Interstate 90 to Logan I ...
, a major road project that would tear down the former elevated Central Artery (I-93) and instead tunnel it (and widen). It would also construct a new Charles River bridge and the Ted Williams Tunnel
The Ted Williams Tunnel is a highway tunnel in Boston, Massachusetts. The third in the city to travel under Boston Harbor, with the Sumner Tunnel and the Callahan Tunnel, it carries the final segment of Interstate 90 (the Massachusetts Turnpi ...
(I-90). This would end up becoming one of the costliest construction projects in the world, costing $21 billion adjusted to 2020 inflation. The former highway's path would become the Rose Kennedy Greenway, a large public park. The Sheridan Expressway (former I-895) was also rebuilt into a boulevard in the late-2010s. Rochester, New York
Rochester is a city in and the county seat, seat of government of Monroe County, New York, United States. It is the List of municipalities in New York, fourth-most populous city and 10th most-populated municipality in New York, with a populati ...
has torn down the Inner Loop
In computer programs, an important form of control flow is the Loop (computing), loop which causes a block of code to be executed more than once. A common idiom is to have a loop Nested loop, nested inside another loop, with the contained loop be ...
due to low traffic and to reunify neighborhoods in downtown and to create developable space.
Culture
One geographer,Wilbur Zelinsky
Wilbur Zelinsky (21 December 1921 – 4 May 2013) was an American cultural geographer. He was most recently a professor emeritus at Pennsylvania State University. He also created the Zelinsky Model of Demographic Transition.
Background and educ ...
, asserts that the Northeast region lacks a unified cultural identity, but has served as a "culture hearth" for the rest of the nation. Several much smaller geographical regions within the Northeast have distinct cultural identities.
Landmarks
Almost half of theNational Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a National Register of Historic Places property types, building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the Federal government of the United States, United States government f ...
s maintained by the National Park Service are located in the Northeastern United States.
Religion
According to a 2009Gallup poll
Gallup, Inc. is an American multinational analytics and advisory company based in Washington, D.C. Founded by George Gallup in 1935, the company became known for its public opinion polls conducted worldwide. Gallup provides analytics and man ...
, the Northeastern states differ from most of the rest of the U.S. in religious affiliation, generally reflecting the descendants of immigration patterns of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with many Catholics arriving from Ireland, Italy, French Canada - Quebec, Portugal and east-central Europe. Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New York and New Jersey are the only states in the nation where Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
outnumber Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
s and other Christian denomination
A Christian denomination is a distinct Religion, religious body within Christianity that comprises all Church (congregation), church congregations of the same kind, identifiable by traits such as a name, particular history, organization, leadersh ...
s. More than 20% of respondents in Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont declared no religious identity. Compared to other U.S. regions, the Northeast, along with the Pacific Northwest, has had the lowest regular religious service attendance and the fewest people for whom religion is an important part of their daily lives as of 2015.
Sports
The Northeast region is home to numerous professional sports franchises in the "Big Four" leagues (NFL, NBA, NHL and MLB), with more than 100 championships collectively among them. Professional sports leagues such as theNational Football League
The National Football League (NFL) is a Professional gridiron football, professional American football league in the United States. Composed of 32 teams, it is divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National ...
(NFL), Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball league composed of 30 teams, divided equally between the National League (baseball), National League (NL) and the American League (AL), with 29 in the United States and 1 in Canada. MLB i ...
(MLB), National Basketball Association
The National Basketball Association (NBA) is a professional basketball league in North America composed of 30 teams (29 in the United States and 1 in Canada). The NBA is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Ca ...
(NBA), Women's National Basketball Association
The Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA) is a women's professional basketball league in the United States. The league comprises 13 teams (scheduled to expand to 15 in 2026). The WNBA is headquartered in Midtown Manhattan.
The WNBA w ...
(WNBA), National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; , ''LNH'') is a professional ice hockey league in North America composed of 32 teams25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. The NHL is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Cana ...
(NHL), Major League Soccer
Major League Soccer (MLS) is a professional Association football, soccer league in North America and the highest level of the United States soccer league system. It comprises 30 teams, with 27 in the United States and 3 in Canada, and is sanc ...
(MLS), and National Women's Soccer League
The National Women's Soccer League (NWSL) is a women's professional Association football, soccer league and the highest level of the United States soccer league system#Women's leagues, United States soccer league system (alongside the USL Supe ...
(NWSL), have team franchises in following Northeastern cities:
* New York metropolitan area: Giants
A giant is a being of human appearance, sometimes of prodigious size and strength, common in folklore.
Giant(s) or The Giant(s) may also refer to:
Mythology and religion
*Giants (Greek mythology)
* Jötunn, a Germanic term often translated as 'g ...
, Jets (NFL), Yankees, Mets
The New York Mets are an American professional baseball team based in the New York City borough of Queens. The Mets compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) East Division. They are one of two major l ...
(MLB), Knicks, Nets (NBA), Rangers
A ranger is typically someone in a law enforcement or military/paramilitary role specializing in patrolling a given territory, called "ranging" or "scouting". The term most often refers to:
* Park ranger or forest ranger, a person charged with prot ...
, Islanders, Devils
A devil is the personification of evil as it is conceived in many and various cultures and religious traditions.
Devil or Devils may also refer to:
* Satan
* Devil in Christianity
* Demon
* Folk devil
Art, entertainment, and media
Film and ...
(NHL), Red Bulls, City FC or Pigeons (MLS), Liberty
Liberty is the state of being free within society from oppressive restrictions imposed by authority on one's way of life, behavior, or political views. The concept of liberty can vary depending on perspective and context. In the Constitutional ...
(WNBA), Gotham or Bats (NWSL)
* Philadelphia: Eagles
Eagle is the common name for the golden eagle, bald eagle, and other birds of prey in the family of the Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of Genus, genera, some of which are closely related. True eagles comprise the genus ''Aquila ( ...
(NFL), Phillies
The Philadelphia Phillies are an American professional baseball team based in Philadelphia. The Phillies compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) East Division. Since 2004, the team's home stadium has ...
(MLB), 76ers (NBA), Flyers (NHL), Union (MLS)
* Boston: Patriots
A patriot is a person with the quality of patriotism.
Patriot(s) or The Patriot(s) may also refer to:
Political and military groups United States
* Patriot (American Revolution), those who supported the cause of independence in the American R ...
(NFL), Red Sox
The Boston Red Sox are an American professional baseball team based in Boston. The Red Sox compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East Division. Founded in as one of the American League's eight ch ...
(MLB), Celtics (NBA), Bruins (NHL), Revolution
In political science, a revolution (, 'a turn around') is a rapid, fundamental transformation of a society's class, state, ethnic or religious structures. According to sociologist Jack Goldstone, all revolutions contain "a common set of elements ...
(MLS)
* Pittsburgh: Steelers
The Pittsburgh Steelers are a professional American football team based in Pittsburgh. The Steelers compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the American Football Conference (AFC) North division. Founded in 1933, the Steeler ...
(NFL), Pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are call ...
(MLB), Penguins
Penguins are a group of aquatic flightless birds from the family Spheniscidae () of the order Sphenisciformes (). They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere. Only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is equatorial, with a sm ...
(NHL)
* Buffalo: Bills (NFL), Sabres
A sabre is a type of sword.
Sabre, Sabres, saber, or SABRE may also refer to:
Weapons and weapon systems
* Sabre (fencing), a sporting sword
* Sabre (tank), a modern British armoured reconnaissance vehicle
* Chinese sabre or ''dao'', a variet ...
(NHL)
* Uncasville: Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
(WNBA)
Notable golf tournaments in the Northeastern United States include The Northern Trust
The FedEx St. Jude Championship, founded as the Westchester Classic in 1967, is a professional golf tournament on the PGA Tour. The Championship has a partnership with St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, with the hospital serving as the tour ...
, Travelers Championship
The Travelers Championship is a professional golf tournament on the PGA Tour in Cromwell, Connecticut, a suburb south of Hartford. Since 1984 the tournament has been held at TPC River Highlands. It is managed by The Greater Hartford Community Fou ...
, and Atlantic City LPGA Classic. The US Open, held in New York, is one of the four Grand Slam tennis tournaments.
Notable Northeastern motorsports tracks include Watkins Glen International
Watkins Glen International, nicknamed "The Glen", is an automobile race track in the Northeastern United States, northeastern United States, located in Dix, New York, just southwest of the village of Watkins Glen, New York, Watkins Glen, at the ...
, Pocono Raceway
Pocono Raceway (formerly known as the Pocono International Raceway in early years) is a tri-oval track in Blakeslee, Pennsylvania. The track has held a variety of events since its opening in 1969, including NASCAR, IndyCar Series, and IMSA GT ...
, New Hampshire Motor Speedway
New Hampshire Motor Speedway (formerly known as the New Hampshire International Speedway from 1989 to 2007, the Bryar Motorsports Park from 1965 to 1989, and as the 106 Midway Raceway from 1961 to 1964) is a oval track in Loudon, New Hampshir ...
and Lime Rock Park
Lime Rock Park is a natural-terrain motorsport road racing venue located in Lakeville, Connecticut, United States, a hamlet in the town of Salisbury, Connecticut, Salisbury, in the state's northwest corner. Built in 1956, it is the nation's thi ...
, which have hosted Formula One
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one ...
, IndyCar
IndyCar, LLC (stylized as INDYCAR), is an auto racing sanctioning body for American open-wheel car racing headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana. The organization sanctions two racing series: the premier IndyCar Series with the Indianapolis ...
, NASCAR
The National Association for Stock Car Auto Racing, LLC (NASCAR) is an American auto racing sanctioning and operating company that is best known for stock car racing. It is considered to be one of the top ranked motorsports organizations in ...
and International Motor Sports Association
The International Motor Sports Association (IMSA) is a North American sports car racing sanctioning body based in Daytona Beach, Florida, under the jurisdiction of the ACCUS arm of the FIA. It was started by John Bishop, a former executive dir ...
races. Also, drag strips such as Englishtown, Epping and Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of symbols, often specifically those of a written language, by means of Visual perception, sight or Somatosensory system, touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifacete ...
have hosted NHRA
The National Hot Rod Association (NHRA) is a governing body which sets rules in drag racing and hosts events all over the United States and Canada. With over 40,000 drivers in its rosters, the NHRA claims to be the largest motorsport sanction ...
national events. Belmont Park
Belmont Park is a thoroughbred racing, thoroughbred horse racetrack in Elmont, New York, just east of New York City limits best known for hosting the Belmont Stakes, the final leg of the American Triple Crown of Thoroughbred Racing (United Stat ...
at New York hosts the Belmont Stakes
The Belmont Stakes is an American Graded stakes race, Grade I stakes Thoroughbred racing, race for three-year-old Thoroughbreds run at Belmont Park in Elmont, New York. It is run over the worldwide classic distance of . Colt (horseracing), Colt ...
horse races, which is part of the Triple Crown of Thoroughbred Racing (United States), Triple Crown of Thoroughbred Racing.
The region has also been noted for the prevalence of the traditionally Northeastern sports of ice hockey and lacrosse.
Politics
The Northeastern United States tended to vote Republican Party (United States), Republican in federal elections through the first half of the 20th century, but the region has since the 1990s shifted to become the most Democratic Party (United States), Democratic region in the nation, along with the West Coast of the United States, West Coast. Results from a 2008Gallup poll
Gallup, Inc. is an American multinational analytics and advisory company based in Washington, D.C. Founded by George Gallup in 1935, the company became known for its public opinion polls conducted worldwide. Gallup provides analytics and man ...
indicated that eight of the top ten Democratic states were located in the region, with every Northeastern state having a Democratic Party affiliation advantage of at least ten points. The following table demonstrates Democratic support in the Northeast as compared to the remainder of the nation.
The following table of United States presidential election results since 1920 illustrates that over the past eight presidential elections, only three Northeastern states supported a Republican candidate. New Hampshire voted for George W. Bush in 2000; Pennsylvania and Maine's 2nd congressional district voted for Donald Trump in 2016, Maine's 2nd district voted for Trump again in 2020, and 2024 saw Trump take back Pennsylvania and again hold on to Maine's 2nd district. 2004 is so far the only election in U.S. history in which the winner did not win any northeastern state. Bolded entries indicate that party's candidate also won the general election.
The following table shows the breakdown of party affiliation of governors, attorneys general, state legislative houses and U.S. congressional delegation for the Northeastern states for the upcoming term beginning in January 2025. (Demographics reflect registration-by-party figures from that state's registered voter statistics.)
See also
* List of online encyclopedias of U.S. states * Atlantic Northeast *Jersey Shore
The Jersey Shore, commonly called the Shore by locals, is the coast, coastal region of the U.S. state of New Jersey. The term encompasses about of shore, oceanfront bordering the Atlantic Ocean, from Perth Amboy, New Jersey, Perth Amboy in the n ...
* New England–Acadian forests
* Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston in the north to Washington, D.C., in the south, with major stops in Providence, Rhod ...
* Northeast megalopolis
The Northeast megalopolis, also known as the Northeast Corridor, Acela Corridor, Boston–Washington corridor, BosWash, or BosNYWash, is the most populous megalopolis exclusively within the United States, with slightly over 50 million resident ...
* Northeastern coastal forests
* Rust Belt
Notes
References
External links
{{Coord, 42, -73, region:US_dim:1000km, display=title Northeastern United States, Census regions of the United States Demographic history of the United States