North Koreans on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The demographics of North Korea are determined through national
The demographics of North Korea are determined through national
Famine in North Korea: Causes and Cures
, ''Institute for International Economics''. A 2011 U.S. Census Bureau report put the likely number of excess deaths during 1993 to 2000 at from 500,000 to 600,000.
 The figures disclosed by the government reveal an unusually low proportion of males to females: in 1980 and 1987, the male-to-female ratios were 86.2 to 100, and 84.2 to 100, respectively. Low male-to-female ratios are usually the result of a war, but these figures were lower than the sex ratio of 88.3 males per 100 females recorded for 1953, the last year of the
The figures disclosed by the government reveal an unusually low proportion of males to females: in 1980 and 1987, the male-to-female ratios were 86.2 to 100, and 84.2 to 100, respectively. Low male-to-female ratios are usually the result of a war, but these figures were lower than the sex ratio of 88.3 males per 100 females recorded for 1953, the last year of the
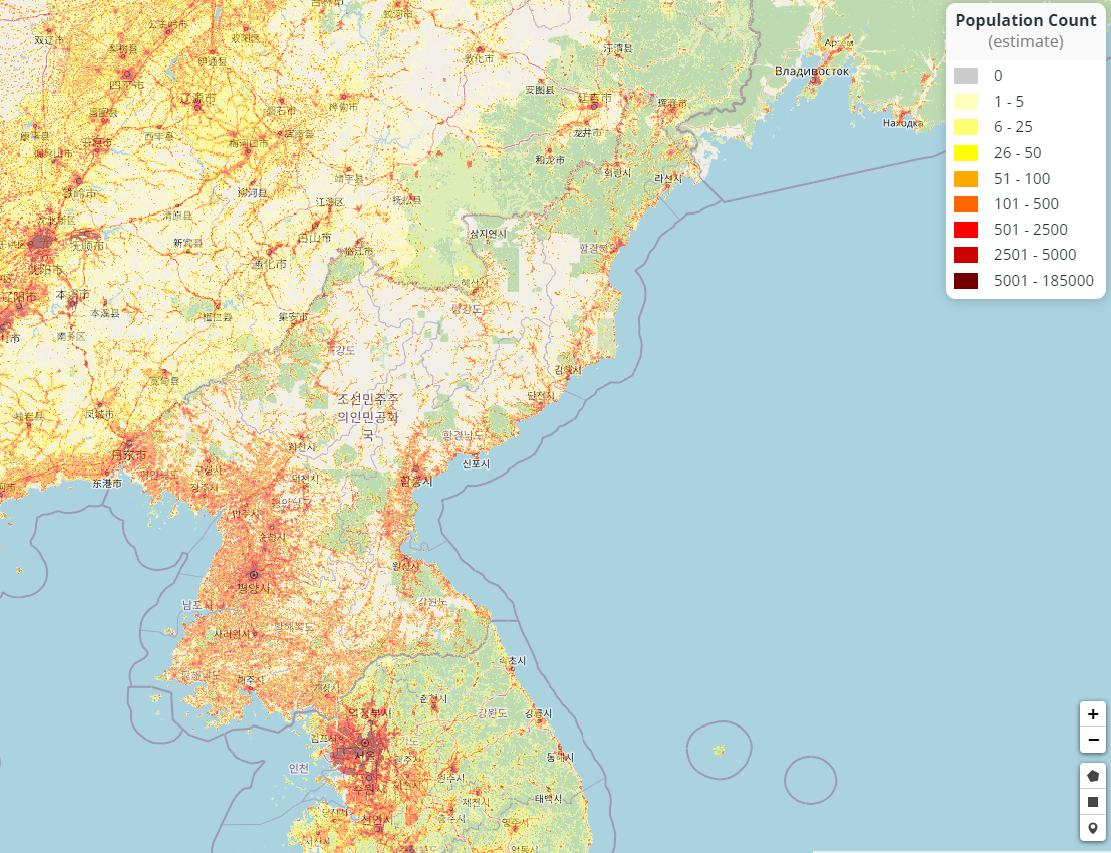 North Korea's population is concentrated in the plains and lowlands. The least populated regions are the mountainous Chagang and Yanggang provinces adjacent to the Chinese border. The largest concentrations of population are in North Pyongan and South Pyongan provinces, in the municipal district of Pyongyang, and in
North Korea's population is concentrated in the plains and lowlands. The least populated regions are the mountainous Chagang and Yanggang provinces adjacent to the Chinese border. The largest concentrations of population are in North Pyongan and South Pyongan provinces, in the municipal district of Pyongyang, and in
N. Korean defector says best to leave North alone for now.
/ref>
 The following demographic statistics are from the ''
The following demographic statistics are from the ''
''0–14 years:'' 20.97% (male 2,678,638/female 2,588,744)
''15–24 years:'' 15.88% (male 2,009,360/female 1,977,942)
''25–54 years:'' 44.22% (male 5,567,682/female 5,537,077)
''55–64 years:'' 9.19% (male 1,090,739/female 1,218,406)
''65 years and over:'' 9.74% (male 840,003/female 1,606,720) (2016 est.) Population growth rate
1.02% (1991 est.)
0.31% (1996 est.)
0.87% (2006 est.)
0.42% (2009 est.)
0.53% (2016 est.) Birth rate
20.01 births/1,000 population (1991 est.)
17.58 births/1,000 population (1996 est.)
14.61 births/1,000 population (2006 est.)
14.61 births/1,000 population (2008 est.)
14.60 births/1,000 population (2016 est.) Death rate
8.94 deaths/1,000 population (1991 est.)
9.52 deaths/1,000 population (1996 est.)
7.29 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.)
7.29 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.)
9.30 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.) Net migration rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.) Sex ratio
''at birth:'' 1.05 male(s)/female
''0–14 years:'' 1.03 male(s)/female
''15–24 years:'' 1.02 male(s)/female
''25–54 years:'' 1.01 male(s)/female
''55–64 years:'' 0.9 male(s)/female
''65 years and over:'' 0.53 male(s)/female
''total population:'' 0.94 male(s)/female (2016 est.) Infant mortality rate
total: 22.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)
 Life expectancy at birth
Life expectancy at birth
''total population:'' 70.4 years
''male:'' 66.6 years
''female:'' 74.5 years (2016 est.) Total fertility rate
2.09 children born/woman (2006 est.)
1.94 children born/woman (2010 est.)
1.96 children born/woman (2016 est.)
1.91 children born/woman (2021 est.) Nationality
''noun:'' Korean(s)
''adjective:'' Korean Ethnic groups
racially homogeneous:
''definition:'' age 15 and over can read and write Korean using the Korean script
''total population:'' 100%
''male:'' 100%
''female:'' 100% (2015 est.)
census
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of stati ...
es and international estimates. The Central Bureau of Statistics of North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
conducted the most recent census in 2008, where the population reached 24 million inhabitants. The population density is 199.54 inhabitants per square kilometre, and the 2014 estimated life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
is 69.81 years. In 1980, the population rose at a near consistent, but low, rate (0.84% from the two censuses). Since 2000, North Korea's birth rate
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live childbirth, human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registr ...
has exceeded its death rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
; the natural growth is positive. In terms of age structure, the population is dominated by the 15–64-year-old segment (68.09%). The median age of the population is 32.9 years, and the gender ratio is 0.95 males to 1.00 female. Since the early 1990s, the birth rate has been fairly stable, with an average of 2 children per woman, down from an average of 3 in the early 1980s.
According to ''The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a Reference work, reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The off ...
'', North Korea is racially homogeneous and contains a small Chinese community and a few ethnic Japanese. Data currently from the 2016 archive The 2008 census listed two ethnicities: Korean (%) and Other (%). Korea was annexed by the Empire of Japan in 1910, in which the Korean Peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
was occupied by Japanese. In 1945, when Japan was defeated in World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Korea was divided into two occupied zones: north occupied by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
and the south by the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. Negotiations on unification failed, and in 1948 two separate countries were formed: North and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
.
Korean is the official language of North Korea. ''The World Factbook'' states "traditionally Buddhist and Confucianist, some Christian and syncretic Chondogyo" in regards to religion, but also states "autonomous religious activities now almost nonexistent; government-sponsored religious groups exist to provide illusion of religious freedom". , 8.86% of the population older than 5 years old have attained academic degrees
An academic degree is a qualification awarded to a student upon successful completion of a course of study in higher education, usually at a college or university. These institutions often offer degrees at various levels, usually divided into un ...
. In 2000, North Korea spent 38.2% of its expenditures on education, social insurance, and social security. Estimates show that, in 2012, gross domestic product (GDP) per capita was $1,800. The most significant sources of employment were machine building and manufacturing of metallurgical products, military products, and textiles. In 2006, the unemployment rate
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work d ...
was between 14.7% and 36.5%. The 2008 census enumerated 5,887,471 households, averaging 3.9 persons per house. Average urbanization rate was 60.3% in 2011.
During the North Korean famine
The North Korean famine (), dubbed by the government as the Arduous March (), was a period of mass starvation together with a general economic crisis from 1995 to 2000 in North Korea. During this time there was an increase in defection from N ...
of 1994–1998 somewhere between 240,000 and 3,500,000 North Koreans died from starvation or hunger-related illnesses, with the deaths peaking in 1997.Noland, Marcus, Sherman Robinson and Tao WangFamine in North Korea: Causes and Cures
, ''Institute for International Economics''. A 2011 U.S. Census Bureau report put the likely number of excess deaths during 1993 to 2000 at from 500,000 to 600,000.
History of reporting demographics
Until the release of official data in 1989, the 1963 edition of the North Korea Central Yearbook was the last official publication to disclose population figures.. After 1963, demographers used varying methods to estimate the population. They either totaled the number of delegates elected to the Supreme People's Assembly (each delegate representing 50,000 people before 1962 and 30,000 people afterward) or relied on official statements that a certain number of persons, or percentage of the population, was engaged in a particular activity. Thus, on the basis of remarks made by PresidentKim Il Sung
Kim Il Sung (born Kim Song Ju; 15 April 1912 – 8 July 1994) was a North Korean politician and the founder of North Korea, which he led as its first Supreme Leader (North Korean title), supreme leader from North Korea#Founding, its establishm ...
in 1977 concerning school attendance, the population that year was calculated at 17.2 million persons.. During the 1980s, health statistics, including life expectancy and causes of mortality, were gradually made available to the outside world.
In 1989, the Central Bureau of Statistics released demographic data to the United Nations Fund for Population Activities (UNFPA) to secure the UNFPA's assistance in holding North Korea's first nationwide census since the establishment of the DPRK in 1946. Although the figures given to the United Nations (UN) might have been purposely distorted, it appears that in line with other attempts to open itself to the outside world, the North Korean regime has also opened somewhat in the demographic realm. Although the country lacks trained demographers, accurate data on household registration, migration, and births and deaths are available to North Korean authorities.
According to the United States scholar Nicholas Eberstadt and demographer Judith Banister, vital statistics and personal information on residents are kept by agencies on the ''ri'', or ''ni'' (: village, the local administrative unit) level in rural areas and the ''dong'' (: district or block) level in urban areas.
The next census was scheduled for 2018, but was cancelled.
Size and growth rate
In their 1992 monograph, ''The Population of North Korea'', Eberstadt and Banister use the data given to the UNFPA and make their own assessments. They place the total population at 21.4 million persons in mid-1990, consisting of 10.6 million males and 10.8 million females. This figure is close to an estimate of 21.9 million persons for mid-1988 cited in the 1990 edition of the ''Demographic Yearbook'' published by the UN. ''Korean Review'', a book by Pang Hwan-ju published by the Foreign Languages Publishing House in 1987, gives a figure of 19.1 million persons for 1986.Male-female ratio
 The figures disclosed by the government reveal an unusually low proportion of males to females: in 1980 and 1987, the male-to-female ratios were 86.2 to 100, and 84.2 to 100, respectively. Low male-to-female ratios are usually the result of a war, but these figures were lower than the sex ratio of 88.3 males per 100 females recorded for 1953, the last year of the
The figures disclosed by the government reveal an unusually low proportion of males to females: in 1980 and 1987, the male-to-female ratios were 86.2 to 100, and 84.2 to 100, respectively. Low male-to-female ratios are usually the result of a war, but these figures were lower than the sex ratio of 88.3 males per 100 females recorded for 1953, the last year of the Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was s ...
. The male-to-female ratio would be expected to rise to a normal level with the passage of years, as happened between 1953 and 1970, when the figure was 95.1 males per 100 females. After 1970, however, the ratio declined. Eberstadt and Banister suggest that before 1970 male and female population figures included the whole population, yielding ratios in the ninetieth percentile, but that after that time the male military population was excluded from population figures.
Based on the figures provided by the Central Statistics Bureau, Eberstadt and Banister estimate that the actual size of the "hidden" male North Korean military had reached 1.2 million by 1986 and that the actual male-to-female ratio was 97.1 males to 100 females in 1990.. If their estimates are correct, 6.1 percent of North Korea's total population was in the military, numerically the world's fourth largest active military force as of 2021.
A survey in 2017 found that the famine had skewed North Korea's demography, impacting particularly on male infants. Women aged 20–24 made up 4% of the population, while men in the same age group made up only 2.5%.
Growth rate
The annual population growth rate in 1960 was 2.7 percent, rising to a high of 3.6 percent in 1970, and falling to 1.9 percent in 1975. This fall reflected a dramatic decline in the fertility rate: the average number of children born to women decreased from 6.5 in 1966 to 2.5 in 1988. Assuming the data is reliable, reasons for falling growth rates and fertility rates probably include late marriage,urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
, limited housing space, and the expectation that women would participate equally in work hours in the labor force. The experience of other socialist countries suggests that widespread labor force participation by women often goes hand-in-hand with more traditional role expectations; in other words, they are still responsible for housework and childrearing. The high percentage of males age 17 to 26 may have contributed to the low fertility
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate ...
rate.
According to Eberstadt and Banister's data, the annual population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The World population, global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025. Actual global human population growth amounts to aroun ...
rate in 1991 was 1.9 percent. However, the CIA ''World Factbook'' estimated that North Korea's annual population growth rate was 1.0% in 1991 and that it has since declined to 0.4% by 2009.
Promoting population growth
The North Korean government seems to perceive its population as too small in relation to that of South Korea. In its public pronouncements, Pyongyang has called for accelerated population growth and encouraged large families. According to oneKorean American
Korean Americans () are Americans of full or partial Korean ethnic descent. While the broader term Overseas Korean in America () may refer to all ethnic Koreans residing in the United States, the specific designation of Korean American impli ...
scholar who visited North Korea in the early 1980s, the country has no birth control policies; parents are encouraged to have as many as six children. The state provides ''tagaso'' (nurseries) to lessen the burden of childrearing for parents and offers a 77-day paid leave after childbirth.
Eberstadt and Banister suggest, however, that authorities at the local level make contraceptive
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only be ...
information readily available to parents and that intrauterine devices are the most commonly adopted birth control method. An interview with a former North Korean resident in the early 1990s revealed that such devices are distributed free at clinics.
Population structure and projections
Demographers determine the age structure of a given population by dividing it into five-year age-groups and arranging them chronologically in a pyramid-like structure that "bulges" or recedes in relation to the number of persons in a given age cohort. Many poor,developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed Secondary sector of the economy, industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. ...
have a broad base and steadily tapering higher levels, which reflects a large number of births and young children but much smaller age cohorts in later years as a result of relatively short life expectancies.. North Korea does not entirely fit this pattern; data reveal a "bulge" in the lower ranges of adulthood. In 1991, life expectancy at birth was approximately 66 years for males, almost 73 for females.
It is likely that annual population growth rates will increase, as well as difficulties in employing the many young men and women entering the labor force in a socialist economy already suffering from stagnant growth. Eberstadt and Banister project that the population will stabilize (that is, cease to grow) at 34 million persons in 2045 and will then experience a gradual decline..
Settlement patterns and urbanization
 North Korea's population is concentrated in the plains and lowlands. The least populated regions are the mountainous Chagang and Yanggang provinces adjacent to the Chinese border. The largest concentrations of population are in North Pyongan and South Pyongan provinces, in the municipal district of Pyongyang, and in
North Korea's population is concentrated in the plains and lowlands. The least populated regions are the mountainous Chagang and Yanggang provinces adjacent to the Chinese border. The largest concentrations of population are in North Pyongan and South Pyongan provinces, in the municipal district of Pyongyang, and in South Hamgyong
South Hamgyong Province (, ''Hamgyŏngnamdo''; ) is a Administrative divisions of North Korea, province of North Korea. The province was formed in 1896 from the southern half of the former Hamgyong Province, Hamgyong Province, remained a provin ...
Province, which includes the Hamhung
Hamhŭng (''Hamhŭng-si''; ) is North Korea's List of cities in North Korea, second-most populous city, the capital of South Hamgyong, South Hamgyŏng Province and the 16th largest city in the Korea, Korean Peninsula. Located in the southern part ...
-Hungnam urban area. Eberstadt and Banister calculate the average population density at 167 persons per square kilometer, ranging from 1,178 persons per square kilometer in Pyongyang Municipality to 44 persons per square kilometer in Yanggang Province. By contrast, South Korea had an average population density of 425 persons per square kilometer in 1989.
Like South Korea, North Korea has experienced significant urban migration since the end of the Korean War. Official statistics reveal that 59.6 percent of the total population was classified as urban in 1987. This figures compares with only 17.7 percent in 1953. It is not entirely clear, however, what standards are used to define urban populations. Eberstadt and Banister suggest that although South Korean statisticians do not classify settlements of under 50,000 as urban, their North Korean counterparts include settlements as small as 20,000 in this category. And, in North Korea, people who engage in agricultural pursuits inside municipalities sometimes are not counted as urban.
Urbanization in North Korea seems to have proceeded most rapidly between 1953 and 1960, when the urban population grew between 12 and 20 percent annually. Subsequently, the increase slowed to about 6 percent annually in the 1960s and between 1 and 3 percent from 1970 to 1987.
In 1987, North Korea's largest cities were Pyongyang
Pyongyang () is the Capital city, capital and largest city of North Korea, where it is sometimes labeled as the "Capital of the Revolution" (). Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River about upstream from its mouth on the Yellow Sea. Accordi ...
, with approximately 2.3 million inhabitants; Hamhung
Hamhŭng (''Hamhŭng-si''; ) is North Korea's List of cities in North Korea, second-most populous city, the capital of South Hamgyong, South Hamgyŏng Province and the 16th largest city in the Korea, Korean Peninsula. Located in the southern part ...
, 701,000; Chongjin
Chŏngjin (; ) is the capital of North Korea's North Hamgyong Province (함경북도) and the country's List of cities in North Korea, third-largest city. Sometimes called the City of Iron, it is located in the northeast of the country.
History ...
, 520,000; Nampo
Nampo (North Korean official spelling: Nampho; ), also spelled Namp'o, is a major city in North Korea which is the country's List of cities in North Korea, fourth-largest by population. The city is an important seaport in the country as it lies ...
, 370,000; Sunchon
Sunch'ŏn () is a city in South Pyongan province, North Korea. It has a population of 297,317, and is home to various manufacturing plants. The city is on the Taedong River.
History
In 1413, the name of the city became Sunchon, due to a rena ...
, 356,000; and Sinuiju
Sinŭiju (; ) is a city in North Korea which faces Dandong, Liaoning, China, across the international border of the Yalu River. It is the capital of North Pyongan Province, North P'yŏngan province. Part of the city is included in the Sinuiju Spe ...
, 289,000. In 1987, the total national population living in Pyongyang was 11.5 percent. The government restricts and monitors migration to cities and ensures a relatively balanced distribution of population in provincial centers in relation to Pyongyang.
Vital statistics
Source: Population Division of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social AffairsTotal and percent distribution of population by single year of age (census 2008)
Source: Central Bureau of StatisticsKoreans living overseas
Large-scale emigration from Korea began around 1904 and continued until the end of World War II. During the Japanese colonial occupation (1910–1945), many Koreans emigrated to: China (particularlyNortheast China
Northeast China () is a geographical region of China, consisting officially of three provinces Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang. The heartland of the region is the Northeast China Plain, the largest plain in China with an area of over . The regi ...
), the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, and the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
.. People from Korea's northern provinces went primarily to Manchuria, China, and Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
; many of those from the southern provinces went to Japan. Most emigrants left for economic reasons because employment opportunities were scarce; many Korean farmers had lost their land after the Japanese colonial government introduced a system of private land tenure, imposed higher land taxes, and promoted the growth of an absentee landlord class charging exorbitant rents.
In the 1980s, more than 4 million ethnic Koreans lived outside the peninsula. The largest group, about 1.7 million people, lived in China (''see Koreans in China
Koreans in China include both ethnic Koreans with Chinese nationality and non-Chinese nationalities such as South Korean ( zh, s=在华韩国人·韩裔) and North Korean ( zh, s=在华朝鲜人·朝鲜裔) people living in China. For this re ...
''); most had assumed Chinese citizenship. Approximately 1 million Koreans, almost exclusively from South Korea, lived in North America (''see Korean Americans
Korean Americans () are Americans of full or partial Korean ethnicity, Korean ethnic descent. While the broader term Overseas Korean in America () may refer to all ethnic Koreans residing in the United States, the specific designation of Kore ...
''). About 389,000 ethnic Koreans resided in the former Soviet Union (''see Koryosaram and Sakhalin Koreans
Sakhalin Koreans (; ) are Russian citizens and residents of Korean descent living on Sakhalin Island, who can trace their roots to the immigrants from the Gyeongsang Province, Gyeongsang and Jeolla Province, Jeolla provinces of Korea during th ...
''). One observer noted that Koreans have been so successful in running collective farms in Soviet Central Asia that being Korean is often associated by other citizens with being rich. As a result, there is growing antagonism against Koreans. Smaller groups of Koreans are found in Central America and South America (85,000), the Middle East (62,000), Europe (40,000), Asia (27,000), and Africa (25,000).
Many of Japan's approximately 680,000 Koreans have below average standards of living. This is partly because of discrimination by the Japanese. Many resident Koreans, loyal to North Korea, remain separate from, and often hostile to, the Japanese social mainstream. The pro-North Korean Chongryon (General Association of Korean Residents in Japan) initially was more successful than the pro-South Korean Mindan (Association for Korean Residents in Japan) in attracting adherents. However, the widening disparity between the political and economic conditions of the two Koreas has since made Mindan the larger and certainly the less politically controversial faction. In addition, third- and fourth-generation Zainichi Chosenjin have largely given up active participation or loyalty to the Chongryon ideology. Reasons stated for this increased disassociation include widespread mainstream tolerance of Koreans by Japanese in recent years, greatly reducing the need to rely on Chongryon and the increasing unpopularity of Kim Jong Il
Kim Jong Il (born Yuri Kim; 16 February 1941 or 1942 – 17 December 2011) was a North Korean politician who was the second Supreme Leader (North Korean title), supreme leader of North Korea from Death and state funeral of Kim Il Sung, the de ...
even among loyal members of Chongryon.
Between 1959 and 1982, Chongryon encouraged the repatriation of Korean residents in Japan to North Korea. More than 93,000 Koreans left Japan, the majority (80,000 persons) in 1960 and 1961. Thereafter, the number of repatriates declined, apparently because of reports of hardships suffered by their compatriots. Approximately 6,637 Japanese wives accompanied their husbands to North Korea, of whom about 1,828 retained Japanese citizenship in the early 1990s. Pyongyang had originally promised that the wives could return home every two or three years to visit their relatives. In fact, however, they are not allowed to do so, and few have had contact with their families in Japan. In normalization talks between North Korean and Japanese officials in the early 1990s, the latter urged unsuccessfully that the wives be allowed to make home visits. According to a defector, himself a former returnee, many petitioned to be returned to Japan and in response were sent to political prison camps. Japanese research puts the number of Zainichi Korean returnees condemned to prison camps at around 10,000./ref>
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
CIA World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print ve ...
'', unless otherwise indicated:
Population: 25,115,311 (July 2016 est.)
Age structure''0–14 years:'' 20.97% (male 2,678,638/female 2,588,744)
''15–24 years:'' 15.88% (male 2,009,360/female 1,977,942)
''25–54 years:'' 44.22% (male 5,567,682/female 5,537,077)
''55–64 years:'' 9.19% (male 1,090,739/female 1,218,406)
''65 years and over:'' 9.74% (male 840,003/female 1,606,720) (2016 est.) Population growth rate
1.02% (1991 est.)
0.31% (1996 est.)
0.87% (2006 est.)
0.42% (2009 est.)
0.53% (2016 est.) Birth rate
20.01 births/1,000 population (1991 est.)
17.58 births/1,000 population (1996 est.)
14.61 births/1,000 population (2006 est.)
14.61 births/1,000 population (2008 est.)
14.60 births/1,000 population (2016 est.) Death rate
8.94 deaths/1,000 population (1991 est.)
9.52 deaths/1,000 population (1996 est.)
7.29 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.)
7.29 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.)
9.30 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.) Net migration rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.) Sex ratio
''at birth:'' 1.05 male(s)/female
''0–14 years:'' 1.03 male(s)/female
''15–24 years:'' 1.02 male(s)/female
''25–54 years:'' 1.01 male(s)/female
''55–64 years:'' 0.9 male(s)/female
''65 years and over:'' 0.53 male(s)/female
''total population:'' 0.94 male(s)/female (2016 est.) Infant mortality rate
total: 22.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)

''total population:'' 70.4 years
''male:'' 66.6 years
''female:'' 74.5 years (2016 est.) Total fertility rate
2.09 children born/woman (2006 est.)
1.94 children born/woman (2010 est.)
1.96 children born/woman (2016 est.)
1.91 children born/woman (2021 est.) Nationality
''noun:'' Korean(s)
''adjective:'' Korean Ethnic groups
racially homogeneous:
Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
; small Chinese community, a few ethnic Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
, ethnic Japanese, Singaporeans
Singaporeans are the citizens and nationals of the sovereign island city-state of Singapore. Singapore is home to a people of a variety of ethno-racial-religious origins, with the city-state itself being a multi-racial, multi-cultural, m ...
, ethnic Thai, Indian, African, Americans
Americans are the Citizenship of the United States, citizens and United States nationality law, nationals of the United States, United States of America.; ; Law of the United States, U.S. federal law does not equate nationality with Race (hu ...
and ethnic Vietnamese
The Vietnamese people (, ) or the Kinh people (), also known as the Viet people or the Viets, are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to modern-day northern Vietnam and southern China who speak Vietnamese, the most widely spoken Austr ...
Religion:
no statistics available; predominantly Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, Shamanism
Shamanism is a spiritual practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into ...
, Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, Religious Confucianism, religion, theory of government, or way of li ...
, and Cheondoism
Cheondoism (Hanja: 天道敎; spelled Chondoism in North Korea) is a Korean indigenous religion that emerged as a continuation and development of Donghak, which was founded by Choe Je-u (Su-un) in 1860 during the late Joseon Dynasty as an anti ...
(see "religion in North Korea
There are no known official statistics of religions in North Korea. Officially, North Korea is an state atheism, atheist state, although its constitution guarantees free exercise of religion, provided that religious practice does not introduce ...
")
Language: Korean
Literacy''definition:'' age 15 and over can read and write Korean using the Korean script
Hangul
The Korean alphabet is the modern writing system for the Korean language. In North Korea, the alphabet is known as (), and in South Korea, it is known as (). The letters for the five basic consonants reflect the shape of the speech organs ...
''total population:'' 100%
''male:'' 100%
''female:'' 100% (2015 est.)
See also
* 1993 North Korea Census *2008 North Korea Census
The 2008 North Korean census () was the second North Korea national census. The reference day used for the census was October 1, 2008. This census conducted by the Central Bureau of Statistics from 1 to 15 October 2008 throughout the DPRK. The ce ...
* Ethnic minorities in North Korea
While North Korea is ethnically and linguistically homogeneous, some minorities in North Korea exist. They include groups of repatriated Koreans, small religious communities, and migrants from neighboring China and Japan.
The historical Jaegase ...
* Demographics of South Korea
demography, Demographic features of the population of South Korea include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religion in South Korea, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the populatio ...
Citations
General and cited references
* * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of North Korea Society of North Korea pt:Coreia do Norte#Demografia