Norepinephrine Structure on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an

 Inside the brain norepinephrine functions as a
Inside the brain norepinephrine functions as a
 Norepinephrine is the main neurotransmitter used by the sympathetic nervous system, which consists of about two dozen
Norepinephrine is the main neurotransmitter used by the sympathetic nervous system, which consists of about two dozen
 The noradrenergic neurons in the brain form a
The noradrenergic neurons in the brain form a
 Norepinephrine has been reported to exist in a wide variety of animal species, including
Norepinephrine has been reported to exist in a wide variety of animal species, including
organic chemical
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a Carbon–hydrogen bond, carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. F ...
in the catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA), most typically a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine.
Cate ...
family that functions in the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
and body
Body may refer to:
In science
* Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space
* Body (biology), the physical material of an organism
* Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of anim ...
as a hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
, neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
and neuromodulator
Neuromodulation is the physiological process by which a given neuron uses one or more chemicals to regulate diverse populations of neurons. Neuromodulators typically bind to metabotropic, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) to initiate a secon ...
. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
'' ad'', "near", and '' ren'', "kidney") is more commonly used in the United Kingdom and the rest of the world, whereas "norepinephrine" (from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
ἐπῐ́ (''epí''), "upon", and νεφρός (''nephrós''), "kidney") is usually preferred in the United States. "Norepinephrine" is also the international nonproprietary name given to the drug. Regardless of which name is used for the substance itself, parts of the body that produce or are affected by it are referred to as noradrenergic.
The general function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in the so-called fight-or-flight response
The fight-or-flight or the fight-flight-freeze-or-fawn (also called hyperarousal or the acute stress response) is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to a perceived harmful event, attack, or threat to survival. It was first describ ...
. In the brain, norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ...
and blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
, triggers the release of glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
from energy stores, increases blood flow
Hemodynamics American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or haemodynamics are the Fluid dynamics, dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostasis, homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydrau ...
to skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are a ...
, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and inhibits voiding of the bladder and gastrointestinal motility
Gastrointestinal physiology is the branch of Human body, human physiology that addresses the physical function of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The function of the GI tract is to process ingested food by mechanical ...
.
In the brain, noradrenaline is produced in nuclei that are small yet exert powerful effects on other brain areas. The most important of these nuclei is the locus coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system in the reticular ...
, located in the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
. Outside the brain, norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia
The sympathetic ganglia, or paravertebral ganglia, are autonomic ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. Ganglia are 20,000 to 30,000 afferent and efferent nerve cell bodies that run along on either side of the spinal cord. Afferent nerve cel ...
located near the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
or in the abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
, as well as Merkel cells
Merkel cells, also known as Merkel–Ranvier cells or tactile epithelial cells, are oval-shaped mechanoreceptors essential for light touch sensation and found in the skin of vertebrates. They are abundant in highly sensitive skin like that of the ...
located in the skin. It is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer adrenal corte ...
s. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating adrenergic receptor
The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like b ...
s located on the cell surface.
A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of noradrenaline systems. Noradrenaline
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The name "noradrenaline" (from ...
itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Stimulants
Stimulants (also known as central nervous system stimulants, or psychostimulants, or colloquially as uppers) are a class of drugs that increase alertness. They are used for various purposes, such as enhancing attention, motivation, cognitio ...
often increase, enhance, or otherwise act as agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ...
s of norepinephrine. Drugs such as cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
and methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
act as reuptake inhibitors of norepinephrine, as do some antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
s, such as those in the SNRI class. One of the more notable drugs in the stimulant class is amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
, which acts as a dopamine and norepinephrine analog, reuptake inhibitor, as well as an agent that increases the amount of global catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA), most typically a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine.
Cate ...
signaling throughout the nervous system by reversing transporters in the synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending o ...
s. Beta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention ...
s, which counter some of the effects of noradrenaline by blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, are sometimes used to treat glaucoma, migraines and a range of cardiovascular diseases. β1Rs preferentially bind epinephrine, along with norepinephrine to a lesser extent and mediates some of their cellular effects in cardiac myocytes such as increased positive inotropy and lusitropy. β-blockers exert their cardioprotective effects through decreasing oxygen demand in cardiac myocytes; this is accomplished via decreasing the force of contraction during systole (negative inotropy) and decreasing the rate of relaxation during diastole (negative lusitropy), thus reducing myocardial energy demand which is useful in treating cardiovascular disorders accompanied by inadequate myocardial oxygen supply. Alpha blocker
Alpha blockers, also known as α-blockers or α-adrenoreceptor antagonists, are a class of pharmacological agents that act as antagonists on α-adrenergic receptors ( α-adrenoceptors).
Historically, alpha-blockers were used as a tool for p ...
s, which counter the effects of noradrenaline on alpha-adrenergic receptors, are occasionally used to treat hypertension and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating and antihypertensive effect and are commonly used as anesthesia enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence
Alcohol dependence is a previous (DSM-IV and ICD-10) psychiatric diagnosis in which an individual is physically or psychologically dependent upon alcohol (also chemically known as ethanol).
In 2013, it was reclassified as alcohol use disorder ...
. For reasons that are still unclear, some Alpha-2 agonists, such as guanfacine
Guanfacine, sold under the brand name Tenex ( immediate-release) and Intuniv ( extended-release) among others, is an oral alpha-2a agonist medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and high blood pressure.
Co ...
, have also been shown to be effective in the treatment of anxiety disorders and ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple ...
. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on noradrenaline systems in the brain, resulting in effects that may be helpful or harmful.
Structure
Norepinephrine is acatecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA), most typically a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine.
Cate ...
and a phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace ami ...
. Its structure differs from that of epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
only in that epinephrine has a methyl group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated a ...
attached to its nitrogen, whereas the methyl group is replaced by a hydrogen atom in norepinephrine. The prefix ''nor-
In chemical nomenclature, nor- is a prefix to name a structural analog that can be derived from a parent compound by the removal of one carbon atom along with the accompanying hydrogen atoms. The nor-compound can be derived by removal of a , , or ...
'' is derived as an abbreviation of the word "normal", used to indicate a demethylated
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen at ...
compound. Norepinephrine consists of a catechol moiety (a benzene ring with two adjoining hydroxyl groups in the ''meta''-''para'' position), and an ethylamine side chain consisting of a hydroxyl group bonded in the benzylic position.
Biochemical mechanisms
Biosynthesis
Norepinephrine is synthesized from theamino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
by a series of enzymatic steps in the adrenal medulla
The adrenal medulla () is the inner part of the adrenal gland. It is located at the center of the gland, being surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It is the innermost part of the adrenal gland, consisting of chromaffin cells that secrete catecho ...
and postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
, while the norepinephrine that functions as a neurotransmitter in the brain is produced in the locus coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system in the reticular ...
, located in the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
of the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
.
While the conversion of tyrosine to dopamine occurs predominantly in the cytoplasm, the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine by dopamine β-monooxygenase occurs predominantly inside neurotransmitter vesicles. The metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell (biology), cell. The reactants, products, and Metabolic intermediate, intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are ...
is:
:Phenylalanine → Tyrosine → L-DOPA → Dopamine → Norepinephrine
Thus the direct precursor of norepinephrine is dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
, which is synthesized indirectly from the essential amino acid phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
or the non-essential amino acid tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is ...
. These amino acids are found in nearly every protein and, as such, are provided by ingestion of protein-containing food, with tyrosine being the most common.
Phenylalanine is converted into tyrosine by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) () is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of the aromatic side-chain of phenylalanine to generate tyrosine. PAH is one of three members of the biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylases, a clas ...
, with molecular oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
(O2) and tetrahydrobiopterin
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4, THB), also known as sapropterin ( INN), is a cofactor of the three aromatic amino acid hydroxylase enzymes, used in the metabolism of amino acid phenylalanine and in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotoni ...
as cofactors
Cofactor may also refer to:
* Cofactor (biochemistry), a substance that needs to be present in addition to an enzyme for a certain reaction to be catalysed
* A domain parameter in elliptic curve cryptography, defined as the ratio between the order ...
. Tyrosine is converted into L-DOPA by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase
Tyrosine hydroxylase or tyrosine 3-monooxygenase is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of the amino acid L-tyrosine to L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA). It does so using molecular oxygen (O2), as well as iron (Fe2+) and ...
, with tetrahydrobiopterin
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4, THB), also known as sapropterin ( INN), is a cofactor of the three aromatic amino acid hydroxylase enzymes, used in the metabolism of amino acid phenylalanine and in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotoni ...
, O2, and probably ferrous iron
In chemistry, iron(II) refers to the element iron in its +2 oxidation state. The adjective ''ferrous'' or the prefix ''ferro-'' is often used to specify such compounds, as in ''ferrous chloride'' for iron(II) chloride (). The adjective ''ferr ...
(Fe2+) as cofactors. Conversion of tyrosine to L-DOPA is inhibited by Metyrosine, a tyrosine analog. L-DOPA is converted into dopamine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (also known as DOPA decarboxylase), with pyridoxal phosphate
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependen ...
as a cofactor. Dopamine is then converted into norepinephrine by the enzyme dopamine β-monooxygenase (formerly known as ''dopamine β-hydroxylase''), with O2 and ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula , originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent.
Asco ...
as cofactors.
Norepinephrine itself can further be converted into epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
by the enzyme phenylethanolamine ''N''-methyltransferase with ''S''-adenosyl-L-methionine as cofactor.
Degradation
In mammals, norepinephrine is rapidly degraded to variousmetabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
s. The initial step in the breakdown can be catalyzed by either of the enzymes monoamine oxidase
Monoamine oxidases (MAO) () are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, employing oxygen to clip off their amine group. They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types of the body. The fi ...
(mainly monoamine oxidase A
Monoamine oxidase A, also known as MAO-A, is an enzyme ( E.C. 1.4.3.4) that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOA'' gene. This gene is one of two neighboring gene family members that encode mitochondrial enzymes which catalyze the oxidative dea ...
) or COMT
Catechol-''O''-methyltransferase (COMT; ) is one of several enzymes that degrade catecholamines (neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine), catecholestrogens, and various drugs and substances having a catechol struc ...
. From there, the breakdown can proceed by a variety of pathways. The principal end products are either Vanillylmandelic acid
Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) is a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of artificial vanilla flavorings and is an end-stage metabolite of the catecholamines (epinephrine, and norepinephrine). It is produced via intermediary metabolites.
Chemica ...
or a conjugated form of MHPG
3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol (MHPG, MOPEG) is a metabolite of norepinephrine degradation. In the brain, it is the principal norepinephrine metabolite. It is released into the blood and cerebrospinal fluid, and a blood sample of it may therefo ...
, both of which are thought to be biologically inactive and are excreted in the urine.
Functions
Cellular effects
Like many other biologically active substances, norepinephrine exerts its effects by binding to and activatingreceptors
Receptor may refer to:
*Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds ...
located on the surface of cells. Two broad families of norepinephrine receptors have been identified, known as alpha and beta-adrenergic receptors. Alpha receptors are divided into subtypes α1 and α2; beta receptors into subtypes β1, β2, and β3. All of these function as G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related ...
s, meaning that they exert their effects via a complex second messenger system
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first me ...
. Alpha-2 receptors usually have inhibitory effects, but many are located pre-synaptically (i.e., on the surface of the cells that release norepinephrine), so the net effect of alpha-2 activation is often a decrease in the amount of norepinephrine released. Alpha-1 receptors and all three types of beta receptors usually have excitatory effects.
Storage, release, and reuptake
 Inside the brain norepinephrine functions as a
Inside the brain norepinephrine functions as a neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
and neuromodulator
Neuromodulation is the physiological process by which a given neuron uses one or more chemicals to regulate diverse populations of neurons. Neuromodulators typically bind to metabotropic, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) to initiate a secon ...
, and is controlled by a set of mechanisms common to all monoamine neurotransmitter
Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
All monoamines ...
s. After synthesis, norepinephrine is transported from the cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
into synaptic vesicles
In a neuron, synaptic vesicles (or neurotransmitter vesicles) store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impul ...
by the vesicular monoamine transporter
The vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) is a transport protein integrated into the membranes of synaptic vesicles of presynaptic neurons. It transports monoamine neurotransmitters – such as dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, epinephrin ...
(VMAT). VMAT can be inhibited by Reserpine
Reserpine is a drug that is used for the treatment of hypertension, high blood pressure, usually in combination with a thiazide diuretic or vasodilator. Large clinical trials have shown that combined treatment with reserpine plus a thiazide diur ...
causing a decrease in neurotransmitter stores. Norepinephrine is stored in these vesicles until it is ejected into the synaptic cleft
Chemical synapses are biological junctions through which neurons' signals can be sent to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in neuromuscular junction, muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form biological neural ...
, typically after an action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
causes the vesicles to release their contents directly into the synaptic cleft through a process called exocytosis
Exocytosis is a term for the active transport process that transports large molecules from cell to the extracellular area. Hormones, proteins and neurotransmitters are examples of large molecules that can be transported out of the cell. Exocytosis ...
.
Once in the synapse, norepinephrine binds to and activates receptors. After an action potential, the norepinephrine molecules quickly become unbound from their receptors. They are then absorbed back into the presynaptic cell, via reuptake
Reuptake is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by a neurotransmitter transporter located along the plasma membrane of an axon terminal (i.e., the pre-synaptic neuron at a synapse) or glial cell after it has performed its function of transmi ...
mediated primarily by the norepinephrine transporter
The norepinephrine transporter (NET), also known as noradrenaline transporter (NAT), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the solute carrier family 6 member 2 (SLC6A2) gene.
NET is a monoamine transporter and is responsible for the sodium ...
(NET). Once back in the cytosol, norepinephrine can either be broken down by monoamine oxidase
Monoamine oxidases (MAO) () are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, employing oxygen to clip off their amine group. They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types of the body. The fi ...
or repackaged into vesicles by VMAT, making it available for future release.
Sympathetic nervous system
 Norepinephrine is the main neurotransmitter used by the sympathetic nervous system, which consists of about two dozen
Norepinephrine is the main neurotransmitter used by the sympathetic nervous system, which consists of about two dozen sympathetic chain ganglia
The sympathetic ganglia, or paravertebral ganglia, are autonomic ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. Ganglia are 20,000 to 30,000 afferent and efferent nerve cell bodies that run along on either side of the spinal cord. Afferent nerve cel ...
located next to the spinal cord, plus a set of prevertebral ganglia
Prevertebral ganglia (or collateral ganglia, or preaortic ganglia) are sympathetic ganglia situated along the midline, anterior to the aorta and the vertebral column. The prevertebral ganglia are the celiac ganglia (including the aorticorenal g ...
located in the chest and abdomen. These sympathetic ganglia are connected to numerous organs, including the eyes, salivary glands, heart, lungs, liver, gallbladder, stomach, intestines, kidneys, urinary bladder, reproductive organs, muscles, skin, and adrenal glands. Sympathetic activation of the adrenal glands causes the part called the adrenal medulla
The adrenal medulla () is the inner part of the adrenal gland. It is located at the center of the gland, being surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It is the innermost part of the adrenal gland, consisting of chromaffin cells that secrete catecho ...
to release norepinephrine (as well as epinephrine) into the bloodstream, from which, functioning as a hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
, it gains further access to a wide variety of tissues.
Broadly speaking, the effect of norepinephrine on each target organ is to modify its state in a way that makes it more conducive to active body movement, often at a cost of increased energy use and increased wear and tear. This can be contrasted with the acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
-mediated effects of the parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulat ...
, which modifies most of the same organs into a state more conducive to rest, recovery, and digestion of food, and usually less costly in terms of energy expenditure.
The sympathetic effects of norepinephrine include:
* In the eyes, an increase in the production of tears, making the eyes more moist, and pupil dilation through contraction of the iris dilator.
* In the heart, an increase in the amount of blood pumped.
* In brown adipose tissue
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) or brown fat makes up the adipose organ together with white adipose tissue (or white fat). Brown adipose tissue is found in almost all mammals.
Classification of brown fat refers to two distinct cell populations with si ...
, an increase in calories burned to generate body heat (thermogenesis
Thermogenesis is the process of heat production in organisms. It occurs in all warm-blooded animals, and also in a few species of thermogenic plants such as the Eastern skunk cabbage, the Voodoo lily ('' Sauromatum venosum''), and the giant w ...
).
* Multiple effects on the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
. The sympathetic nervous system is the primary path of interaction between the immune system and the brain, and several components receive sympathetic inputs, including the thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus ...
, spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
, and lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s. However, the effects are complex, with some immune processes activated while others are inhibited.
* In the arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
, constriction of blood vessels causes an increase in blood pressure.
* In the kidneys
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retro ...
, release of renin
Renin ( etymology and pronunciation), also known as an angiotensinogenase, is an aspartic protease protein and enzyme secreted by the kidneys that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)—also known as the reni ...
and retention of sodium in the bloodstream.
* In the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, an increase in production of glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
, either by glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanis ...
after a meal or by gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In verte ...
when food has not recently been consumed. Glucose is the body's main energy source in most conditions.
* In the pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
, increased release of glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a Glucagon (medic ...
, a hormone whose main effect is to increase the production of glucose by the liver.
* In skeletal muscles, an increase in glucose uptake.
* In adipose tissue
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
(i.e., fat cells), an increase in lipolysis
Lipolysis is the metabolic pathway through which lipid triglycerides are hydrolysis, hydrolyzed into a glycerol and free fatty acids. It is used to mobilize stored energy during fasting or exercise, and usually occurs in Adipose tissue, fat adip ...
, that is, conversion of fat to substances that can be used directly as energy sources by muscles and other tissues.
* In the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
and intestines, a reduction in digestive activity. This results from a generally inhibitory effect of norepinephrine on the enteric nervous system
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the others being the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). It consists of a mesh-like system of neurons th ...
, causing decreases in gastrointestinal mobility, blood flow, and secretion of digestive substances.
Noradrenaline and ATP are sympathetic co-transmitters. It is found that the endocannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found primarily in the ''Cannabis'' plant or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoact ...
anandamide
Anandamide (ANA), also referred to as ''N''-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA) is a fatty acid neurotransmitter belonging to the fatty acid derivative group known as N-acylethanolamine (NAE). Anandamide takes its name from the Sanskrit word ''ananda ...
and the cannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found primarily in the ''Cannabis'' plant or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoact ...
WIN 55,212-2
WIN 55,212-2 is a chemical described as an aminoalkylindole derivative, which produces effects similar to those of cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) but has an entirely different chemical structure.
WIN 55,212-2 is a potent cannab ...
can modify the overall response to sympathetic nerve stimulation, which indicates that prejunctional CB1 receptors mediate the sympatho-inhibitory action. Thus cannabinoids can inhibit both the noradrenergic and purinergic
Purinergic receptors, also known as purinoceptors, are a family of plasma membrane molecules that are found in almost all mammalian tissues. Within the field of purinergic signalling, these receptors have been implicated in learning and memory, ...
components of sympathetic neurotransmission
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron ...
.
Central nervous system
 The noradrenergic neurons in the brain form a
The noradrenergic neurons in the brain form a neurotransmitter system
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotransmitters are rele ...
, that, when activated, exerts effects on large areas of the brain. The effects are manifested in alertness, arousal
Arousal is the physiology, physiological and psychology, psychological state of being awoken or of Five senses, sense organs stimulated to a point of perception. It involves activation of the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) in the hu ...
, and readiness for action.
Noradrenergic
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The name "noradrenaline" (from L ...
neurons (i.e., neurons whose primary neurotransmitter is norepinephrine) are comparatively few in number, and their cell bodies are confined to a few relatively small brain areas, but they send projections to many other brain areas and exert powerful effects on their targets. These noradrenergic cell groups
Noradrenergic cell groups refers to collections of neurons in the central nervous system that have been demonstrated by histochemical fluorescence to contain the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (noradrenalin). They are named
* Noradrenergic cell g ...
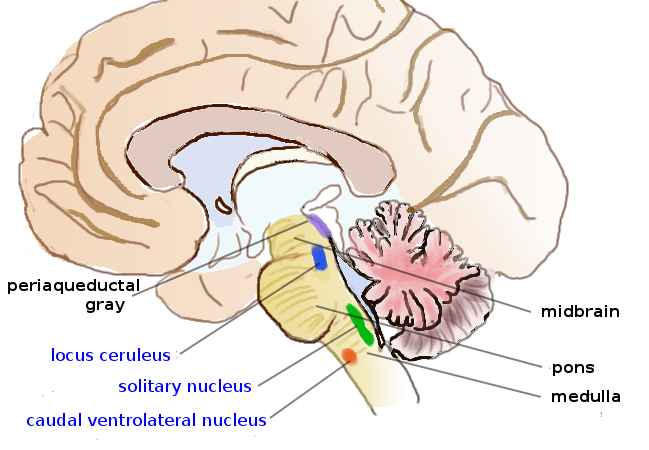
were first mapped in 1964 by Annica Dahlström and Kjell Fuxe, who assigned them labels starting with the letter "A" (for "aminergic"). In their scheme, areas A1 through A7 contain the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (A8 through A14 contain dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
). Noradrenergic cell group A1
Noradrenergic cell group A1 is a group of cells in the vicinity of the lateral reticular nucleus of the medullary reticular formation that label for norepinephrine in primates and rodents. They are found in the ventrolateral medulla in conjunct ...
is located in the caudal ventrolateral part of the medulla, and plays a role in the control of body fluid metabolism. Noradrenergic cell group A2
Noradrenergic cell group A2 is a group of cells in the vicinity of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve in the medulla that label for norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic ...
is located in a brainstem area called the solitary nucleus
The solitary nucleus (SN) (nucleus of the solitary tract, nucleus solitarius, or nucleus tractus solitarii) is a series of neurons whose cell bodies form a roughly vertical column of grey matter in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. Their a ...
; these cells have been implicated in a variety of responses, including control of food intake and responses to stress. Cell groups A5 and A7 project mainly to the spinal cord.
The most important source of norepinephrine in the brain is the locus coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system in the reticular ...
, which contains noradrenergic cell group A6
Noradrenergic cell group A6 is a group of cells fluorescent for noradrenaline that are identical with the locus ceruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem in ...
and adjoins cell group A4. The locus coeruleus is quite small in absolute terms—in primates, it is estimated to contain around 15,000 neurons, less than one-millionth of the neurons in the brain—but it sends projections to every major part of the brain and also to the spinal cord.
The level of activity in the locus coeruleus correlates broadly with vigilance and speed of reaction. LC activity is low during sleep and drops to virtually nothing during the REM (dreaming) state. It runs at a baseline level during wakefulness, but increases temporarily when a person is presented with any sort of stimulus that draws attention. Unpleasant stimuli such as pain, difficulty breathing, bladder distension, heat or cold generate larger increases. Extremely unpleasant states such as intense fear or intense pain are associated with very high levels of LC activity.
Norepinephrine released by the locus coeruleus affects brain function in several ways. It enhances processing of sensory inputs, enhances attention, enhances formation and retrieval of both long-term and working memory, and enhances the ability of the brain to respond to inputs by changing the activity pattern in the prefrontal cortex and other areas. The control of arousal level is strong enough that drug-induced suppression of the LC has a powerful sedating effect.
There is a great similarity between situations that activate the locus coeruleus in the brain and situations that activate the sympathetic nervous system in the periphery: the LC essentially mobilizes the brain for action while the sympathetic system mobilizes the body. It has been argued that this similarity arises because both are to a large degree controlled by the same brain structures, particularly a part of the brainstem called the nucleus gigantocellularis.
Skin
Norepinephrine is also produced byMerkel cell
Merkel cells, also known as Merkel–Ranvier cells or tactile epithelial cells, are oval-shaped mechanoreceptors essential for light touch sensation and found in the skin of vertebrates. They are abundant in highly sensitive skin like that of th ...
s which are part of the somatosensory system. It activates the afferent sensory neuron.
Pharmacology
A large number of important drugs exert their effects by interacting with norepinephrine systems in the brain or body. Their uses include treatment of cardiovascular problems, shock, and a variety of psychiatric conditions. These drugs are divided into: sympathomimetic drugs which mimic or enhance at least some of the effects of norepinephrine released by the sympathetic nervous system;sympatholytic
A sympatholytic (sympathoplegic) drug is a medication that opposes the downstream effects of postganglionic nerve firing in effector organs innervated by the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). They are indicated for various functions; for example, t ...
drugs, in contrast, block at least some of the effects. Both of these are large groups with diverse uses, depending on exactly which effects are enhanced or blocked.
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
itself is classified as a sympathomimetic drug: its effects when given by intravenous injection of increasing heart rate and force and constricting blood vessels make it very useful for treating medical emergencies that involve critically low blood pressure. Surviving Sepsis Campaign
The Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC) is a global initiative to bring together professional organizations in reducing mortality from sepsis. The purpose of the SSC is to create an international collaborative effort to improve the treatment of sepsis ...
recommended norepinephrine as first line agent in treating septic shock
Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International C ...
which is unresponsive to fluid resuscitation
Fluid replacement or fluid resuscitation is the medical practice of replenishing bodily fluid lost through sweating, bleeding, fluid shifts or other pathologic processes. Fluids can be replaced with oral rehydration therapy (drinking), intravenous ...
, supplemented by vasopressin
Mammalian vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the ''AVP'' gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It ...
and epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
. Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
usage is restricted only to highly selected patients.Antagonists
Beta blockers
These aresympatholytic
A sympatholytic (sympathoplegic) drug is a medication that opposes the downstream effects of postganglionic nerve firing in effector organs innervated by the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). They are indicated for various functions; for example, t ...
drugs that block the effects of beta adrenergic receptor
The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like bet ...
s while having little or no effect on alpha receptors. They are sometimes used to treat high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
, atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
, and congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically pr ...
, but recent reviews have concluded that other types of drugs are usually superior for those purposes. Beta blockers may be a viable choice for other cardiovascular conditions, though, including angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of parti ...
and Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
. They are also widely used to treat glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of ...
, most commonly in the form of eyedrops. Because of their effects in reducing anxiety symptoms and tremor, they have sometimes been used by entertainers, public speakers, and athletes to reduce performance anxiety
Stage fright or performance anxiety is the anxiety, fear, or persistent phobia that may be aroused in an individual by the requirement to perform in front of an audience, real or imagined, whether actually or potentially (for example, when perf ...
, although they are not medically approved for that purpose and are banned by the International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; , CIO) is the international, non-governmental, sports governing body of the modern Olympic Games. Founded in 1894 by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas, it is based i ...
.
However, the usefulness of beta blockers is limited by a range of serious side effects, including slowing of heart rate, a drop in blood pressure, asthma, and reactive hypoglycemia
Reactive hypoglycemia, postprandial hypoglycemia, or sugar crash is a term describing recurrent episodes of symptomatic hypoglycemia occurring within four hours"Hypoglycemia." It can also be referred to as "sugar crash" or "glucose crash." Nati ...
. The negative effects can be particularly severe in people with diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
.
Alpha blockers
These aresympatholytic
A sympatholytic (sympathoplegic) drug is a medication that opposes the downstream effects of postganglionic nerve firing in effector organs innervated by the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). They are indicated for various functions; for example, t ...
drugs that block the effects of adrenergic alpha receptors while having little or no effect on beta receptors. Drugs belonging to this group can have very different effects, however, depending on whether they primarily block alpha-1 receptors, alpha-2 receptors, or both. Alpha-2 receptors, as described elsewhere in this article, are frequently located on norepinephrine-releasing neurons themselves and have inhibitory effects on them; consequently, blockage of alpha-2 receptors usually results in an increase in norepinephrine release. Alpha-1 receptors are usually located on target cells and have excitatory effects on them; consequently, blockage of alpha-1 receptors usually results in blocking some of the effects of norepinephrine. Drugs such as phentolamine
Phentolamine, sold under the brand name Regitine among others, is a reversible nonselective α- adrenergic antagonist.
Mechanism
Its primary action is vasodilation due to α1 blockade.
Non-selective α-blockers can cause a much more pronounced ...
that act on both types of receptors can produce a complex combination of both effects. In most cases when the term "alpha blocker" is used without qualification, it refers to a selective alpha-1 antagonist.
Selective alpha-1 blocker
Alpha-1 blockers (also called alpha-adrenergic blocking agents or alpha-1 antagonists) constitute a variety of drugs that block the effect of catecholamines on alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, alpha-1-adrenergic receptors. They are mainly used to tr ...
s have a variety of uses. Since one of their effects is to inhibit the contraction of the smooth muscle in the prostate, they are often used to treat symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, urinary retention, inability t ...
. Alpha-blockers also likely help people pass their kidney stones. Their effects on the central nervous system make them useful for treating generalized anxiety disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is an anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable and often irrational worry about events or activities. Worry often interferes with daily functioning. Individuals with GAD are often overly con ...
, panic disorder
Panic disorder is a mental disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder, characterized by reoccurring unexpected panic attacks. Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, shortness of breath ...
, and posttraumatic stress disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental disorder that develops from experiencing a Psychological trauma, traumatic event, such as sexual assault, domestic violence, child abuse, warfare and its associated traumas, natural disaster ...
. They may, however, have significant side effects, including a drop in blood pressure.
Some antidepressants function partly as selective alpha-2 blocker
Alpha-2 blockers (or α2 blockers) are a subset of the alpha blocker class of drugs and are antagonists to the α2 adrenergic receptor. They are mainly used in research, having found limited clinical application in human medicine. They are exten ...
s, but the best-known drug in that class is yohimbine
Yohimbine, also known as quebrachine, is an indole alkaloid derived from the bark of the African tree '' Pausinystalia johimbe'' (yohimbe); also from the bark of the unrelated South American tree '' Aspidosperma quebracho-blanco''. Yohimbine is ...
, which is extracted from the bark of the African yohimbe
''Corynanthe johimbe'', synonym ''Pausinystalia johimbe'', common name yohimbe, is a plant species in the family Rubiaceae native to western and central Africa (Nigeria, Cabinda, Cameroon, Congo-Brazzaville, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea).
Extrac ...
tree. Yohimbine acts as a male potency enhancer, but its usefulness for that purpose is limited by serious side-effects including anxiety and insomnia. Overdoses can cause a dangerous increase in blood pressure. Yohimbine is banned in many countries, but in the United States, because it is extracted from a plant rather than chemically synthesized, it is sold over the counter
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medicines sold directly to a consumer without a requirement for a prescription from a healthcare professional, as opposed to prescription drugs, which may be supplied only to consumers possessing a valid pres ...
as a nutritional supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement a person's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources, or that are synthetic ( ...
.
Alpha-2 agonists
These are sympathomimetic drugs that activatealpha-2 receptor
The alpha-2 (α2) adrenergic receptor (or adrenoceptor) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) associated with the Gi heterotrimeric G-protein. It consists of three highly homologous subtypes, including α2A-, α2B-, and α2C-adrenergic. Som ...
s or enhance their effects. Because alpha-2 receptors are inhibitory and many are located presynaptically on norepinephrine-releasing cells, the net effect of these drugs is usually to reduce the amount of norepinephrine released. Drugs in this group that are capable of entering the brain often have strong sedating effects, due to their inhibitory effects on the locus coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system in the reticular ...
. Clonidine
Clonidine, sold under the brand name Catapres among others, is an α2A-adrenergic receptor agonist medication used to treat high blood pressure, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), drug withdrawal (e.g., alcohol, opioids, or nic ...
and guanfacine
Guanfacine, sold under the brand name Tenex ( immediate-release) and Intuniv ( extended-release) among others, is an oral alpha-2a agonist medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and high blood pressure.
Co ...
, for example, are used for the treatment of anxiety disorders and insomnia, and also as a sedative premedication
Premedication is using medication before some other therapy (usually surgery or chemotherapy) to prepare for that forthcoming therapy. Typical examples include premedicating with a sedative or analgesic before surgery; using prophylactic (preven ...
for patients about to undergo surgery. Xylazine
Xylazine is a structural analog of clonidine and an α2-adrenergic receptor, α2-adrenergic receptor agonist, sold under many trade names worldwide, most notably the Bayer brand name Rompun, as well as Anased, Sedazine and Chanazine.
Xylazine ...
, another drug in this group, is also a powerful sedative and is often used in combination with ketamine
Ketamine is a cyclohexanone-derived general anesthetic and NMDA receptor antagonist with analgesic and hallucinogenic properties, used medically for anesthesia, depression, and pain management. Ketamine exists as its S- (esketamine) a ...
as a general anaesthetic
General anaesthetics (or anesthetics) are often defined as compounds that induce a loss of consciousness in humans or loss of righting reflex in animals. Clinical definitions are also extended to include an induced coma that causes lack of awaren ...
for veterinary surgery
Veterinary surgery is surgery performed on non-human animals by veterinarians, whereby the procedures fall into three broad categories: orthopaedics (bones, joints, muscles), soft tissue surgery (skin, body cavities, cardiovascular system, GI/u ...
—in the United States it has not been approved for use in humans.
Stimulants and antidepressants
These are drugs whose primary effects are thought to be mediated by different neurotransmitter systems (dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
for stimulant
Stimulants (also known as central nervous system stimulants, or psychostimulants, or colloquially as uppers) are a class of drugs that increase alertness. They are used for various purposes, such as enhancing attention, motivation, cognition, ...
s, serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
for antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
s), but many also increase levels of norepinephrine in the brain. Amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
, for example, is a stimulant that increases release of norepinephrine as well as dopamine. Monoamine oxidase A inhibitors (MAO-A) are antidepressants that inhibit the metabolic degradation of norepinephrine as well as serotonin and dopamine. In some cases it is difficult to distinguish the norepinephrine-mediated effects from the effects related to other neurotransmitters.
Diseases and disorders
A number of important medical problems involve dysfunction of the norepinephrine system in the brain or body.Sympathetic hyperactivation
Hyperactivation of thesympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
is not a recognized condition in itself, but it is a component of a number of conditions, as well as a possible consequence of taking sympathomimetic drugs. It causes a distinctive set of symptoms including aches and pains, rapid heartbeat, elevated blood pressure, sweating, palpitations, anxiety, headache, paleness, and a drop in blood glucose. If sympathetic activity is elevated for an extended time, it can cause weight loss and other stress-related body changes.
The list of conditions that can cause sympathetic hyperactivation includes severe brain injury, spinal cord damage, heart failure, high blood pressure, kidney disease, and various types of stress.
Pheochromocytoma
Apheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of the adrenal medulla composed of chromaffin cells and is part of the paraganglioma (PGL) family of tumors, being defined as an intra-adrenal PGL. These neuroendocrine tumors can be sympathetic, where they relea ...
is a rarely occurring tumor of the adrenal medulla
The adrenal medulla () is the inner part of the adrenal gland. It is located at the center of the gland, being surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It is the innermost part of the adrenal gland, consisting of chromaffin cells that secrete catecho ...
, caused either by genetic factors or certain types of cancer. The consequence is a massive increase in the amount of norepinephrine and epinephrine released into the bloodstream. The most obvious symptoms are those of sympathetic hyperactivation, including particularly a rise in blood pressure that can reach fatal levels. The most effective treatment is surgical removal of the tumor.
Stress
Stress, to a physiologist, means any situation that threatens the continued stability of the body and its functions. Stress affects a wide variety of body systems: the two most consistently activated are the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the norepinephrine system, including both thesympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
and the locus coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system in the reticular ...
-centered system in the brain. Stressors of many types evoke increases in noradrenergic activity, which mobilizes the brain and body to meet the threat. Chronic stress, if continued for a long time, can damage many parts of the body. A significant part of the damage is due to the effects of sustained norepinephrine release, because of norepinephrine's general function of directing resources away from maintenance, regeneration, and reproduction, and toward systems that are required for active movement. The consequences can include slowing of growth (in children), sleeplessness, loss of libido, gastrointestinal problems, impaired disease resistance, slower rates of injury healing, depression, and increased vulnerability to addiction.
ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple con ...
is a neurodevelopmental condition involving problems with attention, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness. It is most commonly treated using stimulant
Stimulants (also known as central nervous system stimulants, or psychostimulants, or colloquially as uppers) are a class of drugs that increase alertness. They are used for various purposes, such as enhancing attention, motivation, cognition, ...
drugs such as methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
(Ritalin), whose primary effect is to increase dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
levels in the brain, but drugs in this group also generally increase brain levels of norepinephrine, and it has been difficult to determine whether these actions are involved in their clinical value. There is also substantial evidence that many people with ADHD show biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
s involving altered norepinephrine processing. Several drugs whose primary effects are on norepinephrine, including guanfacine
Guanfacine, sold under the brand name Tenex ( immediate-release) and Intuniv ( extended-release) among others, is an oral alpha-2a agonist medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and high blood pressure.
Co ...
, clonidine
Clonidine, sold under the brand name Catapres among others, is an α2A-adrenergic receptor agonist medication used to treat high blood pressure, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), drug withdrawal (e.g., alcohol, opioids, or nic ...
, and atomoxetine
Atomoxetine, formerly sold under the brand name Strattera, is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (sNRI) medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and, to a lesser extent, cognitive disengagement syndr ...
, have been tried as treatments for ADHD, and found to have effects comparable to those of stimulants.
Autonomic failure
Several conditions, includingParkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, and so-called pure autonomic failure
Pure autonomic failure (PAF) is an uncommon, sporadic neurodegenerative condition marked by a steadily declining autonomic regulation. Bradbury and Eggleston originally described pure autonomic failure in 1925.
Patients usually present with orthos ...
, can cause a loss of norepinephrine-secreting neurons in the sympathetic nervous system. The symptoms are widespread, the most serious being a reduction in heart rate and an extreme drop in resting blood pressure, making it impossible for severely affected people to stand for more than a few seconds without fainting. Treatment can involve dietary changes or drugs.
REM sleep deprivation
Norepinephrine preventsREM sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals (including humans) and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the s ...
, and lack of REM sleep increases noradrenaline secretion as a result of the locus coeruleus not ceasing producing it. It causes neurodegeneration if its loss is sustained for several days.
Comparative biology and evolution
protozoa
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically ...
, placozoa
Placozoa ( ; ) is a phylum of free-living (non-parasitic) marine invertebrates. They are blob-like animals composed of aggregations of cells. Moving in water by ciliary motion, eating food by Phagocytosis, engulfment, reproducing by Fission (biol ...
and cnidaria
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in fresh water, freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroid (zoology), hydroids, ...
(jellyfish and related species), but not in ctenophore
Ctenophora (; : ctenophore ) is a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they ar ...
s (comb jellies), whose nervous systems differ greatly from those of other animals. It is generally present in deuterostome
Deuterostomes (from Greek: ) are bilaterian animals of the superphylum Deuterostomia (), typically characterized by their anus forming before the mouth during embryonic development. Deuterostomia comprises three phyla: Chordata, Echinodermata, ...
s (vertebrates, etc.), but in protostome
Protostomia () is the clade of animals once thought to be characterized by the formation of the organism's mouth before its anus during embryonic development. This nature has since been discovered to be extremely variable among Protostomia's memb ...
s (arthropods, molluscs, flatworms, nematodes, annelids, etc.) it is replaced by octopamine
Octopamine (OA), also known as ''para''-octopamine and norsynephrine among synonyms, is an organic chemical closely related to norepinephrine, and synthesized biologically by a homologous pathway. Octopamine is often considered the major "fig ...
, a closely related chemical with a closely related synthesis pathway. In insects, octopamine has alerting and activating functions that correspond (at least roughly) with the functions of norepinephrine in vertebrates. It has been argued that octopamine evolved to replace norepinephrine rather than ''vice versa''; however, the nervous system of amphioxus
The lancelets ( ), also known as amphioxi (: amphioxus ), consist of 32 described species of somewhat fish-like benthic filter feeding chordates in the subphylum Cephalochordata, class Leptocardii, and family Branchiostomatidae.
Lancelets div ...
(a primitive chordate) has been reported to contain octopamine but not norepinephrine, which presents difficulties for that hypothesis.
History
Early in the twentieth centuryWalter Cannon
Walter Bradford Cannon (October 19, 1871 – October 1, 1945) was an American physiologist, professor and chairman of the Department of Physiology at Harvard Medical School. He coined the term " fight or flight response", and developed the theory ...
, who had popularized the idea of a sympathoadrenal system
The sympathoadrenal system is a physiological connection between the sympathetic nervous system and the adrenal medulla and is crucial in an organism's physiological response to outside stimuli. When the body receives sensory information, the sympa ...
preparing the body for fight and flight, and his colleague Arturo Rosenblueth
Arturo Rosenblueth Stearns (October 2, 1900 Chihuahua – September 20, 1970 Mexico City) was a Mexican researcher, physician and physiologist, who is known as one of the pioneers of cybernetics.
Biography
Rosenblueth was born in 1900 in Ciu ...
developed a theory of two ''sympathins'', ''sympathin E'' (excitatory) and ''sympathin I'' (inhibitory), responsible for these actions. The Belgian pharmacologist Zénon Bacq as well as Canadian and U.S. pharmacologists between 1934 and 1938 suggested that noradrenaline might be a sympathetic transmitter. In 1939, Hermann Blaschko and Peter Holtz independently identified the biosynthetic mechanism for norepinephrine in the vertebrate body. In 1945 Ulf von Euler
Ulf Svante von Euler (7 February 1905 – 9 March 1983) was a Swedish physiologist and pharmacologist. He shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1970 for his work on neurotransmitters.
Life
Ulf Svante von Euler-Chelpin was born in S ...
published the first of a series of papers that established the role of norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter. He demonstrated the presence of norepinephrine in sympathetically innervated tissues and brain, and adduced evidence that it is the ''sympathin'' of Cannon and Rosenblueth.
Stanley Peart
Sir William Stanley Peart (31 March 1922 – 14 March 2019) was a British medical doctor and clinical researcher who was first to demonstrate the release of noradrenaline after the stimulation of sympathetic nerves. One or more of the preceding ...
was the first to demonstrate the release of noradrenaline after the stimulation of sympathetic nerves.
References
External links
* {{Authority control TAAR1 agonists Amphetamine Alpha-adrenergic agonists Beta-adrenergic agonists Neurotransmitters Hormones Biology of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder Catecholamines Peripherally selective drugs Phenylethanolamines Stress hormones