Nochnitsa Restoration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Nochnitsa'' is an extinct
 The only known
The only known
 Although incompletely known, the holotype specimen of ''Nochnitsa'' contains part of the postcranial elements with the skull, including the
Although incompletely known, the holotype specimen of ''Nochnitsa'' contains part of the postcranial elements with the skull, including the
 ''Nochnitsa'' is currently the most basal gorgonopsian known, and its position is justified by several
''Nochnitsa'' is currently the most basal gorgonopsian known, and its position is justified by several
 ''Nochnitsa'' is known from the Kotelnich locality, which consists of a series of Permian red bed exposures along the banks of the Vyatka River in Russia. It is specifically from the Vanyushonki Member, which is the oldest rock unit in the Kotelnich succession, consisting of pale or brown
''Nochnitsa'' is known from the Kotelnich locality, which consists of a series of Permian red bed exposures along the banks of the Vyatka River in Russia. It is specifically from the Vanyushonki Member, which is the oldest rock unit in the Kotelnich succession, consisting of pale or brown
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of gorgonopsian
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of Saber-toothed predator, sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle Permian, Middle to the Upper Permian, roughly between 270 and 252 million years ago. ...
therapsids who lived during an uncertain stage of the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
in what is now European Russia
European Russia is the western and most populated part of the Russia, Russian Federation. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the country's sparsely populated and vastly larger eastern part, Siberia, which is situated in Asia ...
. Only one species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
is known, ''N. geminidens'', described in 2018 from a single specimen including a complete skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
and some postcranial remains, discovered in the red beds
A bed is a piece of furniture that is used as a place to sleep, rest, and relax.
Most modern beds consist of a soft, cushioned mattress on a bed frame. The mattress rests either on a solid base, often wood slats, or a sprung base. Many be ...
of Kotelnich
Kotelnich (; ) is a river port town in Kirov Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Vyatka River near its confluence with the Moloma, along the route of the Trans-Siberian Railway, southwest of Kirov. Population:
History
The loca ...
, Kirov Oblast
Kirov Oblast ( rus, Кировская область, p=ˈkʲirəfskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) located in Eastern Europe. Its administrative center is the city of Kirov. As of the 2010 census, the population ...
. The genus is named in reference to Nocnitsa
In Slavic mythology, notsnitsa (, , , , , , , ), often referred in plural, is a nightmare spirit or demon that torments people and especially children at night. Other names for notsnitsa in East Slavic languages include kriksy, plaksy, plachky, p ...
, a nocturnal creature from Slavic mythology
Slavic paganism, Slavic mythology, or Slavic religion refer to the Religion, religious beliefs, myths, and ritual practices of the Slavs before Christianisation of the Slavs, Christianisation, which occurred at various stages between the 8th and ...
. This name is intended as a parallel to the Gorgon
The Gorgons ( ; ), in Greek mythology, are three monstrous sisters, Stheno, Euryale, and Medusa, said to be the daughters of Phorcys and Ceto. They lived near their sisters the Graeae, and were able to turn anyone who looked at them to sto ...
s, which are named after many genera among gorgonopsians, as well as for the nocturnal behavior inferred for the animal. The only known specimen of ''Nochnitsa'' is one of the smallest gorgonopsians identified to date, with a skull measuring close to in length. The rare postcranial elements indicate that the animal's skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal fra ...
should be particularly slender.
Phylogenetic analyzes published since its official description consider it as the most basal gorgonopsian known, due to several anatomical characteristics wo are not present in more or less derived genera. The Vanyushonki Member, the exact site from which ''Nochnitsa'' was discovered, would have been a moist, well-vegetated landscape, which would have been periodically flooded. The site contains numerous taxa of contemporary tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
s, including other various therapsids. The presence of large therocephalian
Therocephalia is an extinct clade of therapsids (mammals and their close extinct relatives) from the Permian and Triassic periods. The therocephalians ("beast-heads") are named after their large skulls, which, along with the structure of their te ...
s and the smaller size of ''Nochnitsa'' and its close relative '' Viatkogorgon'' indicate that the latter occupied comparatively small predatory roles.
Discovery and naming
 The only known
The only known specimen
Specimen may refer to:
Science and technology
* Sample (material), a limited quantity of something which is intended to be similar to and represent a larger amount
* Biological specimen or biospecimen, an organic specimen held by a biorepository f ...
of ''Nochnitsa'', cataloged KPM 310, was discovered in 1994 by the Russian paleontologist Albert J. Khlyupin in the Red Beds of Kotelnich
Kotelnich (; ) is a river port town in Kirov Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Vyatka River near its confluence with the Moloma, along the route of the Trans-Siberian Railway, southwest of Kirov. Population:
History
The loca ...
, located along the Vyatka River
The Vyatka is a river in Kirov Oblast and Tatarstan in Russia. It is a right tributary of the Kama.Kirov Oblast
Kirov Oblast ( rus, Кировская область, p=ˈkʲirəfskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) located in Eastern Europe. Its administrative center is the city of Kirov. As of the 2010 census, the population ...
, European Russia
European Russia is the western and most populated part of the Russia, Russian Federation. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the country's sparsely populated and vastly larger eastern part, Siberia, which is situated in Asia ...
. This specimen was found more precisely in the Vanyushonki Member
Member may refer to:
* Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon
* Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set
* In object-oriented programming, a member of a class
** Field (computer science), entries in ...
, a site already known for the discovery of other contemporary therapsids, including the gorgonopsian
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of Saber-toothed predator, sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle Permian, Middle to the Upper Permian, roughly between 270 and 252 million years ago. ...
'' Viatkogorgon''. The datation of this site is not clear, but it seems to date to the latest Guadalupian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle Series (stratigraphy), series/Epoch (geology), epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico an ...
or early Lopingian
The Lopingian is the uppermost series/last epoch of the Permian. It is the last epoch of the Paleozoic. The Lopingian was preceded by the Guadalupian and followed by the Early Triassic.
The Lopingian is often synonymous with the informal te ...
epochs. After this discovery, the specimen was subsequently prepared in the by Olga Masyutina.
In 2018, paleontologists Christian F. Kammerer and Vladimir Masyutin named new genera of gorgonopsians and therocephalia
Therocephalia is an extinct clade of therapsids (mammals and their close extinct relatives) from the Permian and Triassic periods. The therocephalians ("beast-heads") are named after their large skulls, which, along with the structure of their te ...
ns discovered at Kotelnitch in two articles in the scientific journal
In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication designed to further the progress of science by disseminating new research findings to the scientific community. These journals serve as a platform for researchers, schola ...
''PeerJ
''PeerJ'' is an open access peer-reviewed scientific mega journal covering research in the biological and medical sciences. It officially launched in June 2012, started accepting submissions on December 3, 2012, and published its first articles ...
''. In their paper focusing on gorgonopsians, the specimen KPM 310 is identified as the holotype of a new genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
and species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, which they name ''Nochnitsa geminidens''.
''Nochnitsa'' is named after the Nocnitsa
In Slavic mythology, notsnitsa (, , , , , , , ), often referred in plural, is a nightmare spirit or demon that torments people and especially children at night. Other names for notsnitsa in East Slavic languages include kriksy, plaksy, plachky, p ...
, a nocturnal hag-like creature from Slavic mythology
Slavic paganism, Slavic mythology, or Slavic religion refer to the Religion, religious beliefs, myths, and ritual practices of the Slavs before Christianisation of the Slavs, Christianisation, which occurred at various stages between the 8th and ...
. Its name was intended as a parallel to the Gorgon
The Gorgons ( ; ), in Greek mythology, are three monstrous sisters, Stheno, Euryale, and Medusa, said to be the daughters of Phorcys and Ceto. They lived near their sisters the Graeae, and were able to turn anyone who looked at them to sto ...
s, similarly hag-like creatures from Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
, which are the namesake of many genera within Gorgonopsia and the clade as a whole. The name also reflects the nocturnal habits inferred for the genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
. The type species name, ''geminidens'', means "twin tooth" and refers to one of the autapomorphies of the species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, postcanine teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
arranged in pairs.
Description
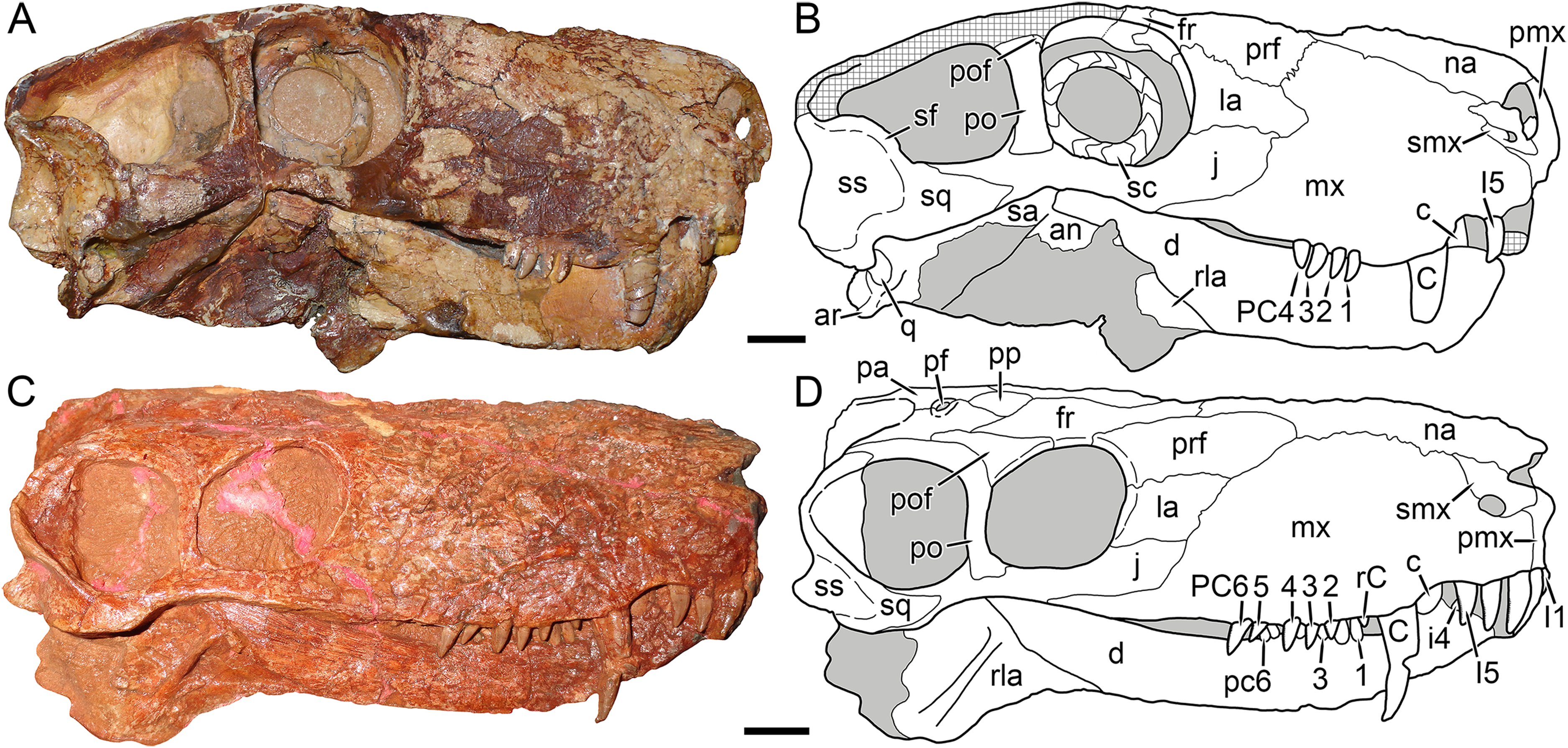
Skull
''Nochnitsa'' is small for a gorgonopsian, with a skull only long. It had a relatively long snout with five incisors, a canine, and six postcanine teeth on each side. The postcanine teeth are autapomorphic for the genus in being arranged in three pairs of closely placed teeth separated by longer diastemata. In each pair, the posterior tooth is larger. The mandible is relatively slender and lacks a strong "chin", unlike other gorgonopsians.Postcranial skeleton
 Although incompletely known, the holotype specimen of ''Nochnitsa'' contains part of the postcranial elements with the skull, including the
Although incompletely known, the holotype specimen of ''Nochnitsa'' contains part of the postcranial elements with the skull, including the cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
, some dorsal vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the ce ...
, and associated rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs () are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ...
s. The right forelimb
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages ( limbs) attached on the cranial (anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used inst ...
is also preserved and partially articulated.
In the cervical vertebrae, the axial spine is broadly rounded and similar in morphology to that of other gorgonopsians. The dorsal vertebrae are preserved as central and transverse process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
* Business process, activities that produce a specific s ...
fragments interspersed by the ribs. The ribs are also simple and elongated. The scapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side ...
is elongated, narrow and weakly curved, comparable to that of other gorgonopsians of similar size like ''Cyonosaurus
''Cyonosaurus'' is a genus of gorgonopsian therapsids from the late Permian of South Africa. Some skulls have been reported from Early Triassic strata, but further investigation revealed that these reports were erroneous. ''Cyonosaurus'' was in ...
'', but different from the anteroposteriorly broadened scapular spines of ''Inostrancevia
''Inostrancevia'' is an extinction, extinct genus of large carnivorous therapsids which lived during the Late Permian in what is now European Russia and Southern Africa. The first-known fossils of this gorgonopsian were discovered in the context ...
''.
The humerus
The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extrem ...
is relatively slender, having a short, poorly developed delto-pectoral ridge, where the muscles attach to the upper arm. The radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is th ...
and ulna
The ulna or ulnar bone (: ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the Radius (bone), radius, the forearm's other long ...
, have a distinct distal curvature, and the distal tip of the radius forms a discrete differentiated rim of the shaft
Shaft may refer to:
Rotating machine elements
* Shaft (mechanical engineering), a rotating machine element used to transmit power
* Line shaft, a power transmission system
* Drive shaft, a shaft for transferring torque
* Axle, a shaft around whi ...
. No olecranon
The olecranon (, ), is a large, thick, curved bony process on the proximal, posterior end of the ulna. It forms the protruding part of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit (trochlear notch). The olecranon serves as a lever ...
process is visible on the ulna, but it is possible that this is the result of a lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
. The preserved proximal carpal
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The terms "carpus" and "carpal" are derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In huma ...
elements consist of the radial, the ulnar and two smaller, irregular elements that would probably represent the centralia. The ulnar is the longest carpus on the proximodistal side and is widened at its proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
and distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
ends. The radial is a shorter and more rounded element. The possible centralia, although poorly preserved, appear to be weakly curved. The concave surface of the centralia would presumably have been articulated with the radial, based on the conditions of other gorgonopsians. Several small irregular bones between the proximal carpals and the metacarpals
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular skeleton, appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones (wrist, wris ...
probably represent distal carpals, but these elements are too poorly preserved to be further identified. Based on their great length relative to the other manual elements, the two best preserved elements probably represent the third and fourth metacarpals, which are the longest of all other gorgonopsians for which the manus
Manus may refer to:
Relating to locations around New Guinea
*Manus Island, a Papua New Guinean island in the Admiralty Archipelago
** Manus languages, languages spoken on Manus and islands close by
** Manus Regional Processing Centre, an offshore ...
are known. A shorter but still elongated element may represent the fifth metacarpal. A semi-articulated set of poorly preserved bones appear to represent finger
A finger is a prominent digit (anatomy), digit on the forelimbs of most tetrapod vertebrate animals, especially those with prehensile extremities (i.e. hands) such as humans and other primates. Most tetrapods have five digits (dactyly, pentadact ...
s, one potentially ending in the ungual
An ungual (from Latin ''unguis'', i.e. ''nail'') is a highly modified distal toe bone which ends in a hoof, claw, or nail. Elephants and ungulates have ungual phalanges, as did the sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; ...
. Based on the size of the phalanx
The phalanx (: phalanxes or phalanges) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar polearms tightly packed together. The term is particularly used t ...
-like elements, these probably correspond to the third and fourth fingers, disarticulated from the third and fourth metacarpals. These elements are too poor for a definitive count of the phalanges, and there is no clear evidence of the reduced disc-shaped phalanges commonly present in gorgonopsians.
Classification
 ''Nochnitsa'' is currently the most basal gorgonopsian known, and its position is justified by several
''Nochnitsa'' is currently the most basal gorgonopsian known, and its position is justified by several plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, an ...
criteria, such as the lowered mandibular symphysis
In human anatomy, the facial skeleton of the skull the external surface of the mandible is marked in the median line by a faint ridge, indicating the mandibular symphysis (Latin: ''symphysis menti'') or line of junction where the two lateral ha ...
, the low and inclined front of the dentary bone
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
(similar to those of therocephalians), as well as a surface and a row of elongated teeth. These mentioned features are not present in derived genera. The 2018 analysis by Kammerer and Masyutin, although derived from a previous analysis conducted by one of the two authors, is a major revision of the phylogeny of the gorgonopsians, discovering that the derived representatives are divided into two groups, of Russian and African origin. The basal position of ''Nochnitsa'' in phylogenetic analysis of gorgonopsians is still recognized in later published studies.
The following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
showing the position of ''Nochnitsa'' within Gorgonopsia follows Kammerer and Rubidge (2022):
Paleoecology
Paleoenvironment
 ''Nochnitsa'' is known from the Kotelnich locality, which consists of a series of Permian red bed exposures along the banks of the Vyatka River in Russia. It is specifically from the Vanyushonki Member, which is the oldest rock unit in the Kotelnich succession, consisting of pale or brown
''Nochnitsa'' is known from the Kotelnich locality, which consists of a series of Permian red bed exposures along the banks of the Vyatka River in Russia. It is specifically from the Vanyushonki Member, which is the oldest rock unit in the Kotelnich succession, consisting of pale or brown mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from ''shale'' by its lack of fissility.Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, ...
s (clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
and silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension (chemistry), suspension with water. Silt usually ...
s, with some fine-grained sand) as well as gray mudstone, and dark red mudstone at the base of this exposure. These mudstones were possibly deposited from suspension in standing water bodies on floodplains or shallow ephemeral lakes, that remained flooded for short periods of time, but the exact environment has not yet been determined, due to the lack of a primary structure of the sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
s. The presence of rootlets, roots and tree stumps would show that the landscape represented by the member of Vanyushonki would be relatively humid and well vegetated. Although the age of the Kotelnitch faunal complex is uncertain, it may date to the same age as those found in South Africa, which date from either the Late Middle Permian or the Early Late Permian.
The Vanyushonki Member contains abundant fossils of tetrapods contemporary to Nochnitsa, most including numerous fossils often consisting of articulated and complete skeletons. Apart from its close relative ''Viatkogorgon'', other therapsids from the locality include the anomodont
Anomodontia is an extinct group of non-mammalian therapsids from the Permian and Triassic periods. By far the most speciose group are the dicynodonts, a clade of beaked, tusked herbivores. Anomodonts were very diverse during the Middle Pe ...
''Suminia
''Suminia'' is an extinct genus of basal anomodont that lived during the Tatarian age of the late Permian, spanning approximately from 268–252 Ma.Rybczynski N. 2000. Cranial anatomy and phylogenetic position of Suminia getmanovi, a basal anomod ...
'' and the therocephalians ''Chlynovia
''Chlynovia'' is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids from the Late Permian of Russia. The type species is ''C. serridentatus'', named in 2000. ''Chlynovia'' was originally classified within Scaloposauria, a group of therocephalians c ...
'', ''Gorynychus
''Gorynychus'' is a genus of therocephalian from the mid-Permian from Kotelnich, Russia. The genus contains two species, ''G. masyutinae'' and ''G. sundyrensis''. It was named after the three-headed dragon Zmey Gorynych (Змей Горыны� ...
'', '' Karenites'', '' Perplexisaurus'', ''Scalopodon
''Scalopodon'' is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids from the Late Permian of Russia. The type species ''Scalopodon tenuisfrons'' was named in 1999 from the Kotelnichsky District of Kirov Oblast. ''Scalopodon'' is known from a singl ...
'', '' Scalopodontes'', and ''Viatkosuchus
''Viatkosuchus'' is an extinct genus of therocephalians known from the Late Capitanian–Wuchiapingian Deltavjatia Assemblage Zone.
See also
* List of therapsids
This list of therapsids is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all ...
''. The pareiasaur
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with osteoderms which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Per ...
''Deltavjatia
''Deltavjatia'' is an extinct species of pareiasauromorph procolophonoid from the Tatarian stage of the Permian time period. It had a large body of about in length. ''Deltavjatia'' was an herbivore and lived in what is now Russia. The first sp ...
'' is particularly abundant there, and the parareptile
Parareptilia ("near-reptiles") is an extinct group of Basal (phylogenetics), basal Sauropsida, sauropsids ("Reptile, reptiles"), traditionally considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds ...
''Emeroleter
''Emeroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile known from the early Late Permian of European Russia. It was a long-legged lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to ...
'' is present. Fossil ostracods
Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea (class Ostracoda), sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 33,000 species (only 13,000 of which are extant) have been identified,Brandão, S.N.; Antonietto, L.S; Nery, D.G.; Santos, S.G.; Karano ...
have also been found.
Ecological niche
As the fossil record shows, the fauna of Kotelnitch was mainly dominated by the large therocephalians, and more specifically by ''Gorynychus'' and ''Viatkosuchus''. These two taxa being much larger than ''Nochnitsa'' and ''Viatkogorgon'', this indicates that the gorgonopsians occupied smaller predatory roles than the large therocephalians. This is further confirmed by the fact that several gorgonopsians having appeared after the extinction of the end of the Guadalupian reach considerably larger sizes than the two previously mentioned genera. This type ofecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of Resource (biology), resources an ...
is also similar to that seen in the ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone in the Karoo Basin
The Karoo Supergroup is the most widespread stratigraphic unit in Africa south of the Kalahari Desert. The supergroup consists of a sequence of units, mostly of nonmarine origin, deposited between the Late Carboniferous and Early Jurassic, a per ...
, South Africa, prior to the main round of gorgonopsian diversification there. However, he noted that some Guadalupian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle Series (stratigraphy), series/Epoch (geology), epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico an ...
gorgonopsians, notably ''Phorcys
In Greek mythology, Phorcys or Phorcus (; ) is a primordial sea god, generally cited (first in Hesiod) as the son of Pontus and Gaia (Earth). Classical scholar Karl Kerenyi conflated Phorcys with the similar sea gods Nereus and Proteus. His w ...
'', are already larger in size, indicating that not all genera shared similar roles.
See also
* '' Viatkogorgon'', another gorgonopsian from the Vanyushonki Member.Notes
References
External links
* {{Taxonbar, from=Q55625337 Gorgonopsia Prehistoric therapsid genera Guadalupian synapsids of Europe Lopingian synapsids of Europe Permian Russia Fossils of Russia Fossil taxa described in 2018