Nichols Radiometer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
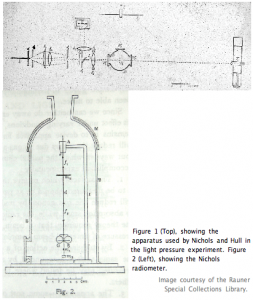 A Nichols radiometer was the apparatus used by Ernest Fox Nichols and Gordon Ferrie Hull in 1901 for the measurement of radiation pressure.
It consisted of a pair of small silvered glass
A Nichols radiometer was the apparatus used by Ernest Fox Nichols and Gordon Ferrie Hull in 1901 for the measurement of radiation pressure.
It consisted of a pair of small silvered glass
The Pressure due to Radiation
''The Astrophysical Journal'', Vol.17 No.5, p. 315-351 (1903) * *
Measuring the Pressure of Light: Pure Science at Dartmouth – Dartmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nichols Radiometer Electromagnetic radiation meters
 A Nichols radiometer was the apparatus used by Ernest Fox Nichols and Gordon Ferrie Hull in 1901 for the measurement of radiation pressure.
It consisted of a pair of small silvered glass
A Nichols radiometer was the apparatus used by Ernest Fox Nichols and Gordon Ferrie Hull in 1901 for the measurement of radiation pressure.
It consisted of a pair of small silvered glass mirror
A mirror, also known as a looking glass, is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror forms an image of whatever is in front of it, which is then focused through the lens of the eye or a camera ...
s suspended in the manner of a torsion balance by a fine quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
fibre within an enclosure in which the air pressure could be regulated. The torsion head to which the fiber was attached could be turned from the outside using a magnet. A beam of light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
was directed first on one mirror and then on the other, and the opposite deflections observed with mirror and scale. By turning the mirror system around to receive the light on the unsilvered side, the influence of the air in the enclosure could be ascertained. This influence was found to be of almost negligible value at an air pressure of about . The radiant energy
In physics, and in particular as measured by radiometry, radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic and gravitational radiation. As energy, its SI unit is the joule (J). The quantity of radiant energy may be calcul ...
of the incident beam was deduced from its heating effect upon a small blackened silver disk, which was found to be more reliable than the bolometer when it was first used. With this apparatus, the experimenters were able to obtain an agreement between observed and computed radiation pressures within about 0.6%.
The original apparatus is at the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase a ...
.
This apparatus is sometimes confused with the Crookes radiometer of 1873.
The original papers, with their historical context, have been re-printed in a chapter of the book ''Quantum Photonics: Pioneering Advances and Emerging Applications''.
See also
* Solar sailReferences
* * * E.F. Nichols and G.F. HullThe Pressure due to Radiation
''The Astrophysical Journal'', Vol.17 No.5, p. 315-351 (1903) * *
Measuring the Pressure of Light: Pure Science at Dartmouth – Dartmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nichols Radiometer Electromagnetic radiation meters