Neutral Third on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A neutral third is a musical interval wider than a
A neutral third is a musical interval wider than a

 A neutral third is a musical interval wider than a
A neutral third is a musical interval wider than a minor third
In music theory, a minor third is a interval (music), musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing three staff positions (see: interval (music)#Number, interval numb ...
but narrower than a major third
In music theory, a third is a Interval (music), musical interval encompassing three staff positions (see Interval (music)#Number, Interval number for more details), and the major third () is a third spanning four Semitone, half steps or two ...
, named by Jan Pieter Land in 1880. Land makes reference to the neutral third attributed to Zalzal (8th c.), described by Al-Farabi
file:A21-133 grande.webp, thumbnail, 200px, Postage stamp of the USSR, issued on the 1100th anniversary of the birth of Al-Farabi (1975)
Abu Nasr Muhammad al-Farabi (; – 14 December 950–12 January 951), known in the Greek East and Latin West ...
(10th c.) as corresponding to a ratio of 27:22 (354.5 cents) and by Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian ...
(Ibn Sina, 11th c.) as 39:32 (342.5 cents). The Zalzalian third may have been a mobile interval.
Three distinct intervals may be termed neutral thirds:
* The ''undecimal neutral third'' has a ratio of 11:9 between the frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
of the two tones, or about 347.41 cents . This ratio is the mathematical mediant of the major third
In music theory, a third is a Interval (music), musical interval encompassing three staff positions (see Interval (music)#Number, Interval number for more details), and the major third () is a third spanning four Semitone, half steps or two ...
5/4 and the minor third
In music theory, a minor third is a interval (music), musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing three staff positions (see: interval (music)#Number, interval numb ...
6/5, and as such, has the property that if harmonic notes of frequency ''f'' and (11/9) ''f'' are played together, the beat frequency of the 5th harmonic of the lower pitch against the 4th of the upper, i.e. , is the same as the beat frequency of the 6th harmonic of the lower pitch against the 5th of the upper, i.e. . In this sense, it is the unique ratio which is equally well-tuned as a major and minor third.
* A ''tridecimal neutral third'' has a ratio of 16:13 between the frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
of the two tones, or about 359.47 cents. This is the largest neutral third, and occurs infrequently in music, as little music utilizes the 13th harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
. It is the mediant
In music, the mediant (''Latin'': "being in the middle") is the third scale degree () of a diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant.Benward & Saker (2003), p.32. In the movable do solfège system, the mediant no ...
of the septimal major third 9/7 and septimal minor third
Septimal may refer to:
*Septimal chromatic semitone, the interval 21:20, about 84.47 cents
*Septimal comma, a small musical interval in just intonation divisible by 7
*Septimal diatonic semitone, the interval 15:14, about 119.44 cents
*S ...
7/6, and as such, enjoys an analogous property with regard to the beating of the corresponding harmonics as above. That is, .
* An '' equal-tempered neutral third'' is characterized by a difference of 350 cents between the two tones, slightly wider than the 11:9 ratio, and exactly half of an equal-tempered perfect fifth.
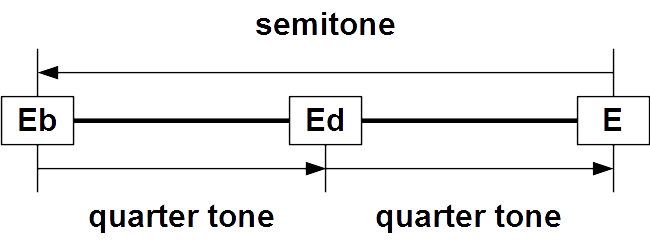
These intervals are all within about 12 cents and are difficult for most people to distinguish by ear. Neutral thirds are roughly a quarter tone
A quarter tone is a pitch halfway between the usual notes of a chromatic scale or an interval about half as wide (orally, or logarithmically) as a semitone, which itself is half a whole tone. Quarter tones divide the octave by 50 cents each, a ...
sharp from 12 equal temperament
12 equal temperament (12-ET) is the musical system that divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are Equal temperament, equally tempered (equally spaced) on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the Twelfth root of two, 12th root of 2 ...
minor thirds and a quarter tone flat from 12-ET major thirds. In just intonation, as well as in tunings such as 31-ET, 41-ET, or 72-ET, which more closely approximate just intonation, the intervals are closer together.
In addition to the above examples, a ''square root neutral third'' can be characterized by a ratio of between two frequencies, being exactly half of a just perfect fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the Interval (music), musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitch (music), pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so.
In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval f ...
of 3/2 and measuring about 350.98 cents. Such a definition stems from the two thirds traditionally making a fifth-based triad.
A triad formed by two neutral thirds is neither major nor minor, thus the neutral thirds triad is ambiguous. While it is not found in twelve tone equal temperament it is found in others such as the quarter tone scale and 31-tet .
Occurrence in human music
In infants' song
Infants experiment with singing, and a few studies of individual infants' singing found that neutral thirds regularly arise in their improvisations. In two separate case studies of the progression and development of these improvisations, neutral thirds were found to arise in infants' songs after major and minor seconds and thirds, but before intervals smaller than asemitone
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically.
It is defined as the interval between ...
and also before intervals as large as a perfect fourth
A fourth is a interval (music), musical interval encompassing four staff positions in the music notation of Western culture, and a perfect fourth () is the fourth spanning five semitones (half steps, or half tones). For example, the ascending int ...
or larger.
In modern classical Western music
The neutral third has been used by a number of modern composers, includingCharles Ives
Charles Edward Ives (; October 20, 1874May 19, 1954) was an American modernist composer, actuary and businessman. Ives was among the earliest renowned American composers to achieve recognition on a global scale. His music was largely ignored d ...
, James Tenney, and Gayle Young.
In traditional music
Claudius Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine, Islamic, and ...
describes an "even diatonic" tuning which uses two justly tuned neutral thirds in ''Harmonikon'' built off the 12:11 and 11:10 neutral seconds in compound intervals with 9:8 and 10:9 whole tones, forming the intervals: (12/11)*(9/8) = 27/22, (11/10)*(10/9) = 11/9. The latter of these is an interval found in the harmonic series as the interval between partials 9 and 11.
The equal-tempered neutral third may be found in the quarter tone scale and in some traditional Arab music
Arabic music () is the music of the Arab world with all its diverse List of music styles, music styles and genres. Arabic countries have many rich and varied styles of music and also many linguistic Varieties of Arabic, dialects, with each countr ...
(see also Arab tone system). Undecimal neutral thirds appear in traditional Georgian music. Neutral thirds are also found in American folk music.
In contemporary popular music
Blue notes (a note found incountry music
Country (also called country and western) is a popular music, music genre originating in the southern regions of the United States, both the American South and American southwest, the Southwest. First produced in the 1920s, country music is p ...
, blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
, and some rock music
Rock is a Music genre, genre of popular music that originated in the United States as "rock and roll" in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of styles from the mid-1960s, primarily in the United States and the United Kingdo ...
) on the third note of a scale can be seen as a variant of a neutral third with the tonic, as they fall in between a major third and a minor third. Similarly the blue note on the seventh note of the scale can be seen as a neutral third with the dominant.
In equal temperaments
Two steps of seven-tone equal temperament form an interval of 342.8571 cents, which is within 5 cents of 347.4079 for the undecimal (11:9) neutral third. This is an equal temperament in reasonably common use, at least in the form of "near seven equal", as it is a tuning used for Thai music as well as the Ugandan Chopi tradition of music. The neutral third also has good approximations in other commonly used equal temperaments including 24-ET (7 steps, 350 cents) and similarly by all multiples of 24 equal steps such as 48-ET and 72-ET, 31-ET (9 steps, 348.39), 34-ET (10 steps, 352.941 cents), 41-ET (12 steps, 351.22 cents), and slightly less closely by 53-ET (15 steps, 339.62 cents). Close approximations to the tridecimal neutral third (16:13) appear in 53-ET and 72-ET. Both of these temperaments distinguish between the tridecimal (16:13) and undecimal (11:9) neutral thirds. All the other tuning systems mentioned above fail to distinguish between these intervals; they temper out the comma 144:143.See also
* List of pitch intervals * Microtonal musicReferences
{{Intervals Neutral intervals Quarter tones Thirds (music)