Neue Pinakothek on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Neue Pinakothek (, ''New 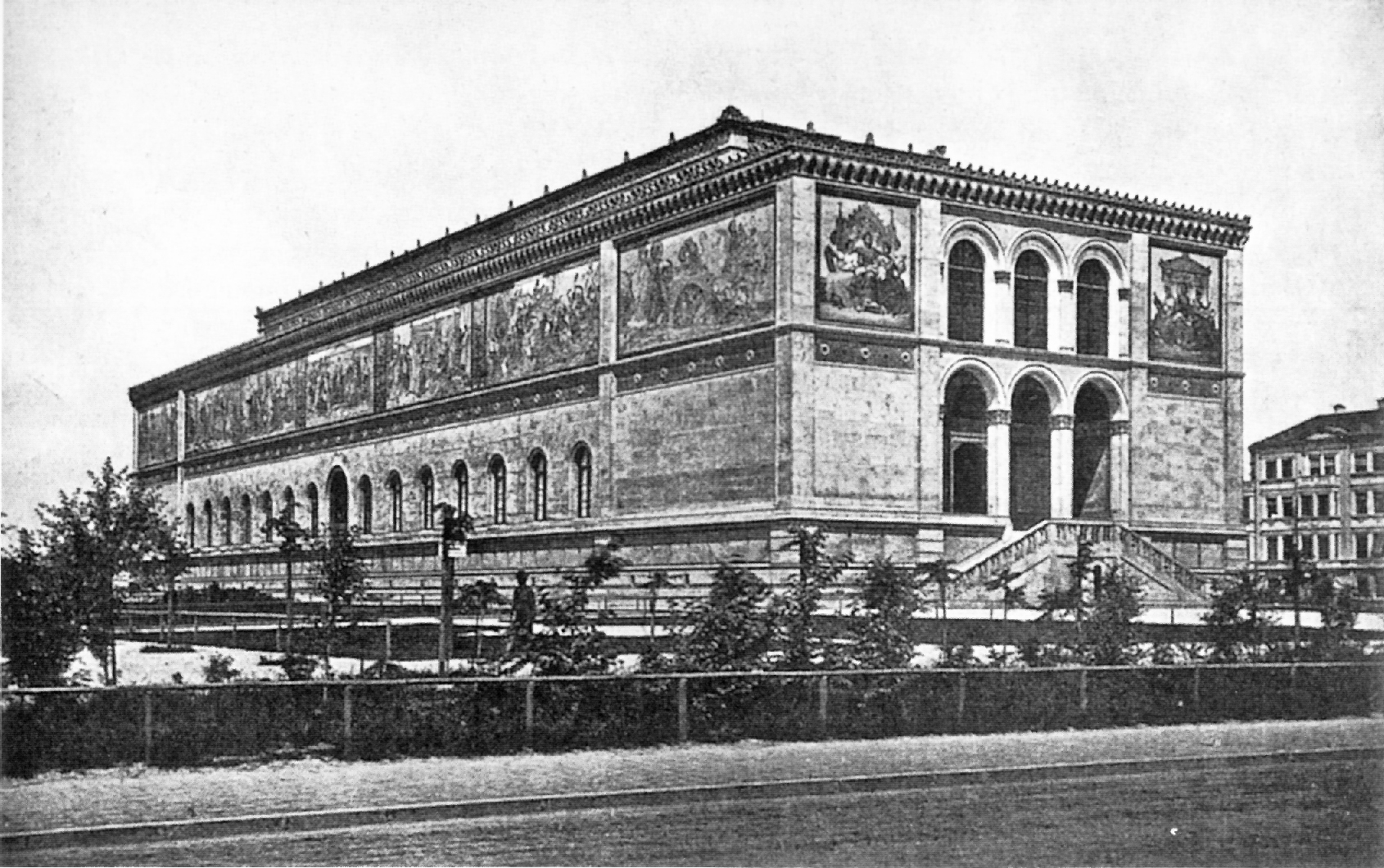
 * International paintings of the second half of the 18th century:
:Among others the gallery exhibits works of Francisco de Goya (''Plucked Turkey'') (''Don José Queraltó as a Spanish Army doctor''),
* International paintings of the second half of the 18th century:
:Among others the gallery exhibits works of Francisco de Goya (''Plucked Turkey'') (''Don José Queraltó as a Spanish Army doctor''),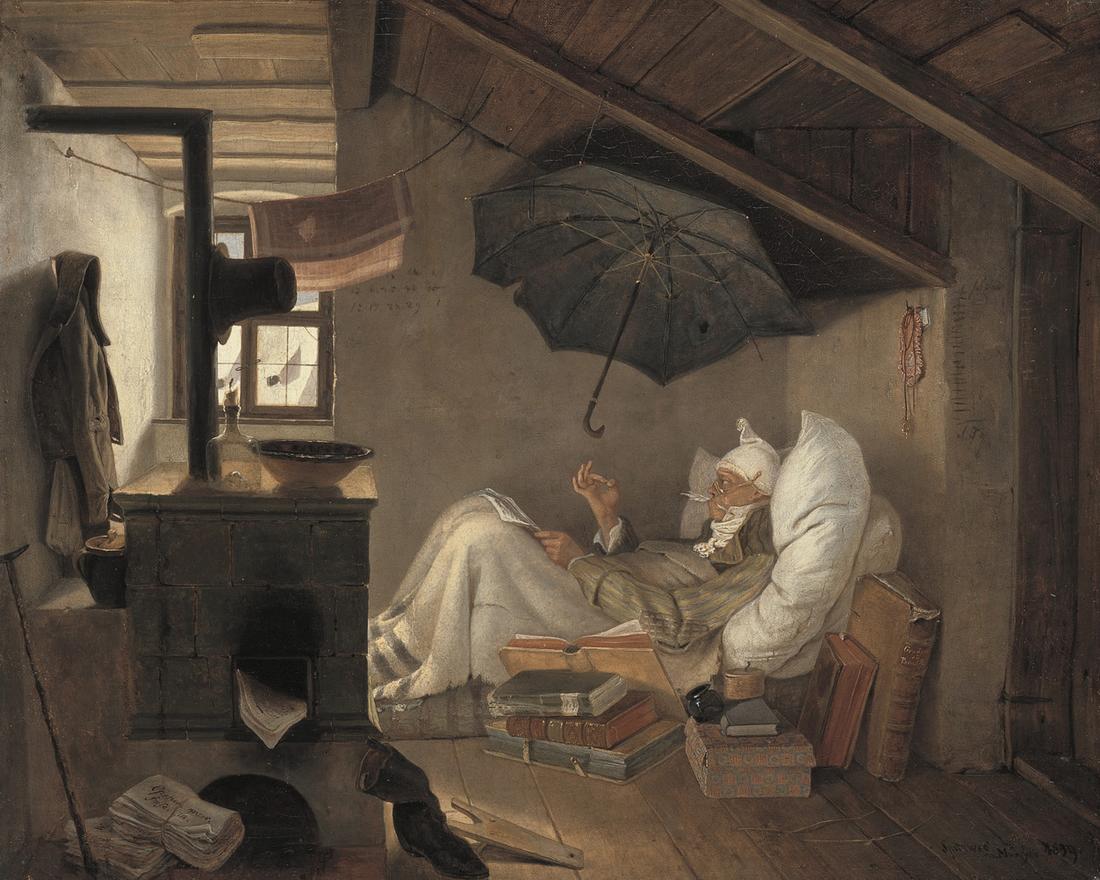  * Biedermeier
:represented by
* Biedermeier
:represented by  *French Impressionists
:One of the world's leading collections with masterpieces of
*French Impressionists
:One of the world's leading collections with masterpieces of
File:Goya - Don José Queraltó.jpg, Francisco de Goya —
''Don José Queraltó as a Spanish Army doctor'' File:David98.jpg,
''Anne-Marie-Louise Thélusson, Comtesse de Sorcy'' File:Gainsborough-Mrs. Thomas Hibbert.jpg,
''Mrs. Thomas Hibbert'' File:Olinde et Sophronia (Delacroix) Neue Pinakothek 13165.jpg,
'' Clorinda Rescues Olindo und Sophronia'' File:Peter von Hess - The Entry of King Othon of Greece in Athens - WGA11387.jpg, Peter von Hess —
'' The Entry of King Otto of Greece into Athens'' File:Max Liebermann Boys Bathing.jpg,
''Boys Bathing'' File:La Seine √Ý Argenteuil.jpg,
''The Bridge at
''Te tamari no atua'' File:Paul Cézanne 038.jpg,
''The railway cutting'' File:Le jeune Routy √Ý C√©leyran.jpg, Toulouse-Lautrec ‚Äî
''Le jeune Routy √Ý C√©leyran'' File:Edvard Munch - Woman in Red Dress (1902-03).jpg,
''Woman in Red Dress (Street in Åsgårdstrand)'' File:Don Quichotte Honoré Daumier.jpg,
'' Don Quichotte and Sancho Pansa'' c. 1868 File:Bertel Thorvaldsen Kopf eines Kriegers ca. 1812-18-1.jpg,
''Head of a warrior'' c. 1812 File:Auguste Rodin Der Mann mit der zerbrochenen Nase 1863-1.jpg,
''Man with broken nose'' c. 1863
Official website (in English)
(depending on your needs, forme
version
archived March 29, 2016, may be more useful)
website (in German)
* Lionel Gossman. “Making of a Romantic Icon: The Religious Context of Friedrich Overbeck’s ‘Italia und Germania.’” American Philosophical Society, 2007.
{{Authority control 1853 establishments in Bavaria Museums established in 1853 Art museums and galleries in Munich Ludwig I of Bavaria Postmodern architecture in Germany
Pinacotheca
A pinacotheca (Latin calque, borrowing from = + ) was a picture gallery in either ancient Greece or ancient Rome. The name is specifically used for the building containing pictures which formed the left wing of the Propylaea (Acropolis of Athen ...
'') is an art museum
An art museum or art gallery is a building or space for the display of art, usually from the museum's own Collection (artwork), collection. It might be in public or private ownership, be accessible to all, or have restrictions in place. Although ...
in Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
. Its focus is European Art
The art of Europe, also known as Western art, encompasses the history of visual art in Europe. European prehistoric art started as mobile Upper Paleolithic rock and cave painting and petroglyph art and was characteristic of the period betw ...
of the 18th and 19th centuries, and it is one of the most important museums of art of the nineteenth century in the world.
Together with the Alte Pinakothek
The Alte Pinakothek (, ''Old Pinakothek'') is an art museum located in the Kunstareal area in Munich, Germany. It is one of the oldest galleries in the world and houses a significant collection of Old Master paintings. The name Alte (Old) Pin ...
and the Pinakothek der Moderne
The Pinakothek der Moderne (, '' Pinakothek of the Modern'') is a modern art museum, situated in central Munich's '' Kunstareal''.
The building
Designed by German architect Stephan Braunfels, the Pinakothek der Moderne was inaugurated in Se ...
, the Neue Pinakothek is part of Munich's museum quarter ( Kunstareal).

The building
The Neue Pinakothek was completed in 1859 and was intended to be the first museum in Europe for the exhibition of contemporary paintings. The established schools of European painting were displayed. On the ground floor 186 plaster busts of contemporary celebrities were also displayed. The building was redeveloped in the late 20th century. Designed by architect Alexander von Branca in the new style ofPostmodernism
Postmodernism encompasses a variety of artistic, Culture, cultural, and philosophical movements that claim to mark a break from modernism. They have in common the conviction that it is no longer possible to rely upon previous ways of depicting ...
, the building opened in 1981. It combines a concrete construction with a stone facade design.
History
Ludwig I of Bavaria
Ludwig I or Louis I (; 25 August 1786 – 29 February 1868) was King of Bavaria from 1825 until the German revolutions of 1848–49, 1848 revolutions in the German states. When he was crown prince, he was involved in the Napoleonic Wars. As ki ...
began to collect contemporary art already as crown prince in 1809 and his collection was steadily enlarged. When the museum was founded, the separation to the old master
In art history, "Old Master" (or "old master")Old Masters De ...
s in the Alte Pinakothek was fixed with the period shortly before the turn of the 19th century, which has become a prototype for many galleries.
Owing to the personal preference of Ludwig I, the museum initially had a strong focus on paintings of German Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
and the Munich School. Also dynastic considerations played a role, as Greece had become a secundogeniture of Bavaria in 1832. In 1834 Carl Rottmann traveled to Greece to prepare for a commission from Ludwig I for a cycle of great Greek landscapes. These works were installed in the Neue Pinakothek, where the paintings were given their own hall.
The so-called Tschudi Contribution between 1905 and 1914 brought the Pinokathek an extraordinary collection of masterpieces of Impressionism
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by visible brush strokes, open Composition (visual arts), composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passage ...
and Post-Impressionism
Post-Impressionism (also spelled Postimpressionism) was a predominantly French art movement that developed roughly between 1886 and 1905, from the last Impressionist exhibition to the birth of Fauvism. Post-Impressionism emerged as a reaction a ...
. Hugo von Tschudi was dismissed by Wilhelm II, German Emperor
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia from 1888 until his abdication in 1918, which marked the end of the German Empire as well as the Hohenzollern dynasty ...
as a penalty for his exhibiting of Gauguin
Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin (; ; 7 June 1848 – 8 May 1903) was a French painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, and writer, whose work has been primarily associated with the Post-Impressionist and Symbolist movements. He was also an influ ...
's ''The Birth of Christ'' in Berlin's National Gallery. He became the director of the Pinokathek. As general director of the State Collections, Tschudi acquired 44 paintings, nine sculptures, and 22 drawings, mostly from emerging French artists. Since public funds could not be used to purchase these works, Tschudi’s associates raised the money from private contributions after his death in 1911.
The space dedicated to painters of the Modernity
Modernity, a topic in the humanities and social sciences, is both a historical period (the modern era) and the ensemble of particular Society, socio-Culture, cultural Norm (social), norms, attitudes and practices that arose in the wake of the ...
was fixed at ca. 1900 by including Henri Matisse
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse (; 31 December 1869 – 3 November 1954) was a French visual arts, visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a drawing, draughtsman, printmaking, printmaker, ...
and Expressionism
Expressionism is a modernist movement, initially in poetry and painting, originating in Northern Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. Its typical trait is to present the world solely from a subjective perspective, distorting it rad ...
. Consequentially a painting of Matisse, which was part of the "Tschudi Contribution" ,is now displayed in the Pinakothek der Moderne
The Pinakothek der Moderne (, '' Pinakothek of the Modern'') is a modern art museum, situated in central Munich's '' Kunstareal''.
The building
Designed by German architect Stephan Braunfels, the Pinakothek der Moderne was inaugurated in Se ...
.
In 1915, the Neue Pinakothek became the property of Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
. In 1938 the Nazi regime under Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
confiscated a self-portrait of Vincent van Gogh
Vincent Willem van Gogh (; 30 March 185329 July 1890) was a Dutch Post-Impressionist painter who is among the most famous and influential figures in the history of Western art. In just over a decade, he created approximately 2,100 artworks ...
, classifying the paintings as degenerate art.
Renovations
Since January 2019 the Neue Pinakothek has been closed for renovations. Originally, it was planned for the building to remain closed at least until 2025. The opening of the museum to visitors was delayed until 2029 in January 2022.Collection
The museum is under supervision of the Bavarian State Painting Collections, which houses an expanded collection of more than 3.000 European paintings fromclassicism
Classicism, in the arts, refers generally to a high regard for a classical period, classical antiquity in the Western tradition, as setting standards for taste which the classicists seek to emulate. In its purest form, classicism is an aesthe ...
to Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil¬Ýand Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and ...
. About 400 paintings and 50 sculptures of these are exhibited in the New Pinakothek.
 * International paintings of the second half of the 18th century:
:Among others the gallery exhibits works of Francisco de Goya (''Plucked Turkey'') (''Don José Queraltó as a Spanish Army doctor''),
* International paintings of the second half of the 18th century:
:Among others the gallery exhibits works of Francisco de Goya (''Plucked Turkey'') (''Don José Queraltó as a Spanish Army doctor''), Jacques-Louis David
Jacques-Louis David (; 30 August 1748 – 29 December 1825) was a French painter in the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical style, considered to be the preeminent painter of the era. In the 1780s, his cerebral brand of history painting marked a change in ...
(''Anne-Marie-Louise Thélusson, Comtesse de Sorcy''), Johann Friedrich August Tischbein
Johann Friedrich August Tischbein, known as the ''Leipziger Tischbein'' (9 March 1750, Maastricht - 21 June 1812, Heidelberg) was a German portrait painter from the Tischbein family of artists.
Biography
He received his first lessons from his ...
(''Nicolas Châtelain in the garden'') and Anton Graff (''Heinrich XIII, Graf Reuß'').
* English and Scottish paintings of 18th and early 19th centuries:
:It has masterpieces of Thomas Gainsborough
Thomas Gainsborough (; 14 May 1727 (baptised) – 2 August 1788) was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists o ...
(portraits of ''Mrs. Thomas Hibbert'' and of ''Thomas Hibbert'') (''Landscape with Shepherd and Flock''), William Hogarth
William Hogarth (; 10 November 1697 – 26 October 1764) was an English painter, engraving, engraver, pictorial social satire, satirist, editorial cartoonist and occasional writer on art. His work ranges from Realism (visual arts), realistic p ...
(''Richard Mounteney''), John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romanticism, Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedha ...
(''View of Dedham Vale from East Bergholt''), Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter who specialised in portraits. The art critic John Russell (art critic), John Russell called him one of the major European painters of the 18th century, while Lucy P ...
(''Captain Philemon Pownall''), David Wilkie (''Reading the Will''), Thomas Lawrence
Sir Thomas Lawrence (13 April 1769 – 7 January 1830) was an English people, English portrait painter and the fourth president of the Royal Academy. A child prodigy, he was born in Bristol and began drawing in Devizes, where his father was a ...
(''The Two Sons of the 1st Earl of Talbot''), George Romney (''Catherine Clements''), Richard Wilson (''View of Syon House Across the Thames near Richmond Gardens''), Henry Raeburn
Sir Henry Raeburn (; 4 March 1756 – 8 July 1823) was a Scottish portrait painter. He served as Portrait Painter to King George IV in Scotland.
Biography
Raeburn was born the son of a manufacturer in Stockbridge, on the Water of Leith: a f ...
(''Mrs. J. Campbell of Kilberry''), George Stubbs
George Stubbs (25 August 1724 – 10 July 1806) was an English painter, best known for his paintings of horses. Self-trained, Stubbs learnt his skills independently from other great artists of the 18th century such as Joshua Reynolds and Thoma ...
(''The pointer'') and J. M. W. Turner (''Ostende''). The Pinakothek owns five works by Thomas Gainsborough, more than any other European museum outside the British Isles.
* German artists of Classicism in Rome
:like Friedrich Overbeck (''Italia and Germania''), Friedrich Wilhelm von Schadow (''The Holy Family beneath the Portico''), Heinrich Maria von Hess (''Marchesa Marianna Florenzi''), Peter von Hess (''The Entry of King Othon of Greece into Nauplia'') and Peter von Cornelius (''The three Marys at the Tomb'').
*German Romanticism
German Romanticism () was the dominant intellectual movement of German-speaking countries in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, influencing philosophy, aesthetics, literature, and criticism. Compared to English Romanticism, the German vari ...
:with paintings of Caspar David Friedrich
Caspar David Friedrich (; 5 September 1774 – 7 May 1840) was a German Romanticism, German Romantic Landscape painting, landscape painter, generally considered the most important German artist of his generation, whose often symbolic, and anti ...
( ''The Garden Bower''), Karl Friedrich Schinkel
Karl Friedrich Schinkel (13 March 1781 – 9 October 1841) was a Prussian architect, urban planning, city planner and painter who also designed furniture and stage sets. Schinkel was one of the most prominent architects of Germany and designed b ...
(''Cathedral Towering over a Town''), Carl Blechen (''Building of the Devil's Bridge'') and others.
 * Biedermeier
:represented by
* Biedermeier
:represented by Franz Xaver Winterhalter
Franz Xaver Winterhalter (20 April 1805 – 8 July 1873) was a German painter and lithography, lithographer, known for his flattering portraits of royalty and upper-class society in the mid-19th century. His name has become associated with fashio ...
(''Graf Jenison-Walworth''), Carl Spitzweg ('' The Poor Poet''), Moritz von Schwind
image:Moritz von Schwind 2.jpg, 200px, Moritz von Schwind, c. 1860.
Moritz von Schwind (21 January 1804 – 8 February 1871) was an Austrian painter, born in Vienna. Schwind's genius was lyrical—he drew inspiration from chivalry, folklore, and t ...
(''A Symphony'') and Ferdinand Georg Waldmüller (''Young Peasant Woman with Three Children at the Window'').
* French Realism and French Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
:with Eugène Delacroix
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix ( ; ; 26 April 1798 – 13 August 1863) was a French people, French Romanticism, Romantic artist who was regarded as the leader of the French Romantic school.Noon, Patrick, et al., ''Crossing the Channel: ...
(''Clorinda Rescues Olindo and Sophronia''), Théodore Géricault
Jean-Louis André Théodore Géricault (; 26 September 1791 – 26 January 1824) was a French painter and lithographer, whose best-known painting is '' The Raft of the Medusa''. Despite his short life, he was one of the pioneers of the Romanti ...
(''Artillery Train Passing a Ravine''), Gustave Courbet
Jean Désiré Gustave Courbet ( ; ; ; 10 June 1819 – 31 December 1877) was a French painter who led the Realism movement in 19th-century French painting. Committed to painting only what he could see, he rejected academic convention and the ...
(''Landscape near Maizières''), Jean-François Millet (''Farmer Inserting a Graft on a Tree''), Honoré Daumier
Honoré-Victorin Daumier (; February 26, 1808 – February 10 or 11, 1879) was a French painter, sculptor, and printmaker, whose many works offer commentary on the social and political life in France, from the July Revolution, Revolution of 1830 ...
(''The Drama'') and others.
* Deutschrömer (or German-Romans)
:such as Hans von Marées (''Self-Portrait''), Arnold Böcklin (''Pan in the Reeds''), Anselm Feuerbach (''Medea'') and Hans Thoma (''Landscape in the Taunus'').
*History paintings
:with Wilhelm von Kaulbach ('' King Ludwig I surrounded by artists''), Karl Theodor von Piloty
Karl Theodor von Piloty (1 October 1826 – 21 July 1886) was a German painter, noted for his historical subjects, and recognised as the foremost representative of the realistic school in Germany.
Life and work
Piloty was born in Munich. His fath ...
(''Seni and Wallenstein''), Franz von Defregger (''Das letzte Aufgebot'') and Hans Makart (''Die Falknerin'').
* German Realism
:like Wilhelm Leibl (''Portrait of Frau Gedon''), Franz von Lenbach (''Aresing Village Street'') and Adolph Menzel (''Living-Room with the Artist's Sister'').
*German Impressionists
:especially Max Liebermann
Max Liebermann (20 July 1847 – 8 February 1935) was a German painter and printmaker, and one of the leading proponents of Impressionism in Germany and continental Europe. In addition to his activity as an artist, he also assembled an important ...
(''Boys Bathing''), Lovis Corinth (''Eduard, Count von Keyserling''), August von Brandis (''Durchblick'') and Max Slevogt (''The Day's Work Done'').
 *French Impressionists
:One of the world's leading collections with masterpieces of
*French Impressionists
:One of the world's leading collections with masterpieces of Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (; ; 25 February 1841 – 3 December 1919) was a French people, French artist who was a leading painter in the development of the Impressionism, Impressionist style. As a celebrator of beauty and especially femininity, fe ...
(''Portrait of a Young Woman''), Édouard Manet
Édouard Manet (, ; ; 23 January 1832 – 30 April 1883) was a French Modernism, modernist painter. He was one of the first 19th-century artists to paint modern life, as well as a pivotal figure in the transition from Realism (art movement), R ...
('' Luncheon in the Studio'') ('' Monet Painting on His Studio Boat''), Claude Monet
Oscar-Claude Monet (, ; ; 14 November 1840 – 5 December 1926) was a French painter and founder of Impressionism painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During his ...
(''The Bridge at Argenteuil''), Paul Cézanne
Paul Cézanne ( , , ; ; ; 19 January 1839 – 22 October 1906) was a French Post-Impressionism, Post-Impressionist painter whose work introduced new modes of representation, influenced avant-garde artistic movements of the early 20th century a ...
(''The Railway Cutting''), Paul Gauguin
Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin (; ; 7 June 1848 – 8 May 1903) was a French painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, and writer, whose work has been primarily associated with the Post-Impressionist and Symbolist movements. He was also an influ ...
('' The Birth - Te tamari no atua''), Edgar Degas
Edgar Degas (, ; born Hilaire-Germain-Edgar De Gas, ; 19 July 183427 September 1917) was a French Impressionist artist famous for his pastel drawings and oil paintings.
Degas also produced bronze sculptures, prints, and drawings. Degas is e ...
(''Woman Ironing''), Camille Pissarro (''Street in Upper Norwood''), Alfred Sisley
Alfred Sisley (; ; 30 October 1839 – 29 January 1899) was an Impressionist landscape painter who was born and spent most of his life in France, but retained British citizenship. He was the most consistent of the Impressionists in his dedic ...
(''The Road to Hampton Court''), Paul Sérusier (''The Laundresses'') and Vincent van Gogh
Vincent Willem van Gogh (; 30 March 185329 July 1890) was a Dutch Post-Impressionist painter who is among the most famous and influential figures in the history of Western art. In just over a decade, he created approximately 2,100 artworks ...
('' Sunflowers'') (''The Weaver'').
*Symbolism and Art Nouveau and early 20th century
:represented among others by Giovanni Segantini (''L'aratura''), Gustav Klimt (''Margaret Stonborough-Wittgenstein''), Paul Signac (''S.Maria della Salute''), Maurice Denis
Maurice Denis (; 25 November 1870 – 13 November 1943) was a French painter, decorative artist, and writer. An important figure in the transitional period between impressionism and modern art, he is associated with '' Les Nabis'', symbolism, ...
(''Gaulish Goddess of Herds and Flocks''), Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec
Count, ''Comte'' Henri Marie Raymond de Toulouse-Lautrec-Monfa (24 November 1864 – 9 September 1901), known as Toulouse-Lautrec (), was a French painter, printmaker, draughtsman, caricaturist, and illustrator whose immersion in the colour ...
(''Le jeune Routy √Ý C√©leyran''), James Ensor
James Sidney Edouard, Baron Ensor (13 April 1860 – 19 November 1949) was a Belgian painter and printmaker, an important influence on expressionism and surrealism who lived in Ostend for most of his life. He was associated with the artistic ...
(''Still Life in the Studio''), Édouard Vuillard
Jean-Édouard Vuillard (; 11 November 186821 June 1940) was a French painter, decorative artist, and printmaker. From 1891 through 1900, Vuillard was a member of the avant garde artistic group Les Nabis, creating paintings that assembled areas ...
(''Café Scene''), Ferdinand Hodler (''Tired of Life''), Franz von Stuck
Franz Ritter von Stuck (February 23, 1863 – August 30, 1928), born Franz Stuck, was a German painter, sculptor, printmaker, and architect. Stuck was best known for his paintings of ancient mythology, receiving substantial critical acclaim with ...
('' The Sin''), Edvard Munch
Edvard Munch ( ; ; 12 December 1863 – 23 January 1944) was a Norwegian painter. His 1893 work ''The Scream'' has become one of Western art's most acclaimed images.
His childhood was overshadowed by illness, bereavement and the dread of inher ...
(''Woman in Red Dress (Street in Aasgaardstrand)''), Walter Crane
Walter Crane (15 August 184514 March 1915) was an English artist and book illustrator. He is considered to be the most influential, and among the most prolific, children's book creators of his generation and, along with Randolph Caldecott and Ka ...
(''Neptune's horses''), Thomas Austen Brown (''Mademoiselle Plume rouge''), Pierre Bonnard (''Lady at the Mirror'') and Egon Schiele
Egon Leo Adolf Ludwig Schiele (; 12 June 1890 – 31 October 1918) was an Austrian Expressionist painters, painter. His work is noted for its intensity and its raw sexuality, and for the many self-portraits the artist produced, including nude sel ...
(''Agony'').
* Sculptures
:Also sculptures of the 19th century are exhibited, for example works of Bertel Thorvaldsen
Albert Bertel Thorvaldsen (; sometimes given as Thorwaldsen; 19 November 1770 – 24 March 1844) was a Danes, Danish-Icelanders, Icelandic Sculpture, sculptor and medallist, medalist of international fame, who spent most of his life (1797–183 ...
(''Adonis''), Antonio Canova
Antonio Canova (; 1 November 1757 – 13 October 1822) was an Italians, Italian Neoclassical sculpture, Neoclassical sculptor, famous for his marble sculptures. Often regarded as the greatest of the Neoclassical artists,. his sculpture was ins ...
(''Paris''), Rudolph Schadow (''Woman Tying Her Sandal''), Auguste Rodin
François Auguste René Rodin (; ; 12 November 184017 November 1917) was a French sculptor generally considered the founder of modern sculpture. He was schooled traditionally and took a craftsman-like approach to his work. Rodin possessed a u ...
(''Crouching Woman (La femme accroupie)''), Max Klinger
Max Klinger (18 February 1857 – 5 July 1920) was a German artist who produced significant work in painting, sculpture, prints and graphics, as well as writing a treatise articulating his ideas on art and the role of graphic arts and printmakin ...
(''Elsa Asenijeff''), Aristide Maillol (''La Flore''), Pablo Picasso
Pablo Diego José Francisco de Paula Juan Nepomuceno María de los Remedios Cipriano de la Santísima Trinidad Ruiz y Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, Ceramic art, ceramicist, and Scenic ...
(''Le Fou'') and others.
Gallery
''Don José Queraltó as a Spanish Army doctor'' File:David98.jpg,
Jacques-Louis David
Jacques-Louis David (; 30 August 1748 – 29 December 1825) was a French painter in the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical style, considered to be the preeminent painter of the era. In the 1780s, his cerebral brand of history painting marked a change in ...
—''Anne-Marie-Louise Thélusson, Comtesse de Sorcy'' File:Gainsborough-Mrs. Thomas Hibbert.jpg,
Thomas Gainsborough
Thomas Gainsborough (; 14 May 1727 (baptised) – 2 August 1788) was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists o ...
—''Mrs. Thomas Hibbert'' File:Olinde et Sophronia (Delacroix) Neue Pinakothek 13165.jpg,
Eugène Delacroix
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix ( ; ; 26 April 1798 – 13 August 1863) was a French people, French Romanticism, Romantic artist who was regarded as the leader of the French Romantic school.Noon, Patrick, et al., ''Crossing the Channel: ...
—'' Clorinda Rescues Olindo und Sophronia'' File:Peter von Hess - The Entry of King Othon of Greece in Athens - WGA11387.jpg, Peter von Hess —
'' The Entry of King Otto of Greece into Athens'' File:Max Liebermann Boys Bathing.jpg,
Max Liebermann
Max Liebermann (20 July 1847 – 8 February 1935) was a German painter and printmaker, and one of the leading proponents of Impressionism in Germany and continental Europe. In addition to his activity as an artist, he also assembled an important ...
‚Äî''Boys Bathing'' File:La Seine √Ý Argenteuil.jpg,
Claude Monet
Oscar-Claude Monet (, ; ; 14 November 1840 – 5 December 1926) was a French painter and founder of Impressionism painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During his ...
—''The Bridge at
Argenteuil
Argenteuil () is a Communes of France, commune in the northwestern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the Kilometre Zero, center of Paris. Argenteuil is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the Val-d'Oise Departments of France, ...
''
File:Paul Gauguin 062.jpg, Paul Gauguin
Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin (; ; 7 June 1848 – 8 May 1903) was a French painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, and writer, whose work has been primarily associated with the Post-Impressionist and Symbolist movements. He was also an influ ...
—''Te tamari no atua'' File:Paul Cézanne 038.jpg,
Paul Cézanne
Paul Cézanne ( , , ; ; ; 19 January 1839 – 22 October 1906) was a French Post-Impressionism, Post-Impressionist painter whose work introduced new modes of representation, influenced avant-garde artistic movements of the early 20th century a ...
‚Äî''The railway cutting'' File:Le jeune Routy √Ý C√©leyran.jpg, Toulouse-Lautrec ‚Äî
''Le jeune Routy √Ý C√©leyran'' File:Edvard Munch - Woman in Red Dress (1902-03).jpg,
Edvard Munch
Edvard Munch ( ; ; 12 December 1863 – 23 January 1944) was a Norwegian painter. His 1893 work ''The Scream'' has become one of Western art's most acclaimed images.
His childhood was overshadowed by illness, bereavement and the dread of inher ...
—''Woman in Red Dress (Street in Åsgårdstrand)'' File:Don Quichotte Honoré Daumier.jpg,
Honoré Daumier
Honoré-Victorin Daumier (; February 26, 1808 – February 10 or 11, 1879) was a French painter, sculptor, and printmaker, whose many works offer commentary on the social and political life in France, from the July Revolution, Revolution of 1830 ...
—'' Don Quichotte and Sancho Pansa'' c. 1868 File:Bertel Thorvaldsen Kopf eines Kriegers ca. 1812-18-1.jpg,
Bertel Thorvaldsen
Albert Bertel Thorvaldsen (; sometimes given as Thorwaldsen; 19 November 1770 – 24 March 1844) was a Danes, Danish-Icelanders, Icelandic Sculpture, sculptor and medallist, medalist of international fame, who spent most of his life (1797–183 ...
—''Head of a warrior'' c. 1812 File:Auguste Rodin Der Mann mit der zerbrochenen Nase 1863-1.jpg,
Auguste Rodin
François Auguste René Rodin (; ; 12 November 184017 November 1917) was a French sculptor generally considered the founder of modern sculpture. He was schooled traditionally and took a craftsman-like approach to his work. Rodin possessed a u ...
—''Man with broken nose'' c. 1863
References
External links
Official website (in English)
(depending on your needs, forme
version
archived March 29, 2016, may be more useful)
website (in German)
* Lionel Gossman. “Making of a Romantic Icon: The Religious Context of Friedrich Overbeck’s ‘Italia und Germania.’” American Philosophical Society, 2007.
{{Authority control 1853 establishments in Bavaria Museums established in 1853 Art museums and galleries in Munich Ludwig I of Bavaria Postmodern architecture in Germany