Nesians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hittites () were an Anatolian

Indo-European people
Indo-European is a major language family of Europe, parts of West and Central Asia, and South Asia.
Indo-European may also refer to:
* Proto-Indo-European language, the reconstructed common ancestor of all Indo-European languages
* Proto-Indo-Euro ...
who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
in West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, they settled in modern-day Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
in the early 2nd millennium BC
File:2nd millennium BC montage.jpg, 400x400px, From top left clockwise: Hammurabi, Babylonian king, best known for his Code of Hammurabi, code of laws; The gold Mask of Tutankhamun, funerary mask of Tutankhamun has become a symbol of ancient Egypt ...
. The Hittites formed a series of polities
A polity is a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of political institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources.
A polity can be any group of people organized for governance ...
in north-central Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, including the kingdom of Kussara
Kussara (''Kuššar'') was a Middle Bronze Age kingdom in Anatolia. The kingdom, though apparently important at one time, is mostly remembered today as the origin of the dynasty that would form the Old Hittite Kingdom.
Location
Kussara is occasion ...
(before 1750 BC), the Kanesh or Nesha Kingdom (–1650 BC), and an empire centered on their capital, Hattusa
Hattusa, also Hattuşa, Ḫattuša, Hattusas, or Hattusha, was the capital of the Hittites, Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age during two distinct periods. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey (originally Boğazköy) within the great ...
(around 1650 BC). Known in modern times as the Hittite Empire, it reached its peak during the mid-14th century BC under Šuppiluliuma I
Šuppiluliuma I, also Suppiluliuma () or Suppiluliumas (died c. 1322 BC) () was an ancient Hittite king (r. –1322 BC).Bryce 2005: xv, 154; Freu 2007b: 311 dates the reign to c. 1350–c. 1319 BC; Kuhrt 1995: 230 dates him within the range 1370 ...
, when it encompassed most of Anatolia and parts of the northern Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia constitutes the Upland and lowland, uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the regio ...
, bordering the rival empires of the Hurri-Mitanni and Assyrians.
Between the 15th and 13th centuries BC, the Hittites were one of the dominant powers of the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
, coming into conflict with the New Kingdom of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also called the Egyptian Empire, refers to ancient Egypt between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC. This period of History of ancient Egypt, ancient Egyptian history covers the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth, ...
, the Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. ...
, and the Empire of Mitanni
Mitanni (–1260 BC), earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, ; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat in Assyrian records, or in Ancient Egypt, Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian language, Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria (region), Syria an ...
. By the 12th century BC, much of the Hittite Empire had been annexed by the Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. ...
, with the remainder being sacked by Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; , ''Phrygía'') was a kingdom in the west-central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River.
Stories of the heroic age of Greek mythology tell of several legendary Ph ...
n newcomers to the region. From the late 12th century BC, during the Late Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a period of societal collapse in the Mediterranean basin during the 12th century BC. It is thought to have affected much of the Eastern Mediterranean and Near East, in particular Egypt, Anatolia, the Aegea ...
, the Hittites splintered into several small independent states, some of which survived until the eighth century BC before succumbing to the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East and parts of South Caucasus, Nort ...
; lacking a unifying continuity, their descendants scattered and ultimately merged into the modern populations of the Levant and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
.
The Hittite language
Hittite (, or ), also known as Nesite (Nešite/Neshite, Nessite), is an extinct Indo-European language that was spoken by the Hittites, a people of Bronze Age Anatolia who created an empire centred on Hattusa, as well as parts of the northern ...
—referred to by its speakers as , "the language of Nesa"—was a distinct member of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
; along with the closely related Luwian language
Luwian (), sometimes known as Luvian or Luish, is an ancient language, or group of languages, within the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. The ethnonym Luwian comes from ''Luwiya'' (also spelled ''Luwia'' or ''Luvia'') – ...
, it is the oldest historically attested Indo-European language. The history of the Hittite civilization is known mostly from cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
texts found in their former territories, and from diplomatic and commercial correspondence found in the various archives of Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
, Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
and the broader Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
; the decipherment of these texts was a key event in the history of Indo-European studies
Indo-European studies () is a field of linguistics and an interdisciplinary field of study dealing with Indo-European languages, both current and extinct. The goal of those engaged in these studies is to amass information about the hypothetical p ...
.
Scholars once attributed the development of iron-smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron-making, iron, copper extraction, copper ...
to the Hittites, who were believed to have monopolized ironworking
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and its alloys. The earliest surviving prehistoric iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ...
during the Bronze Age. This theory has been increasingly contested in the 21st century, with the Late Bronze Age collapse, and subsequent Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
, seeing the slow, comparatively continuous spread of ironworking technology across the region. While there are some iron objects from Bronze Age Anatolia
The prehistory of Anatolia stretches from the Paleolithic era through to the appearance of classical civilization in the middle of the 1st millennium BC. It is generally regarded as being divided into three ages reflecting the dominant materia ...
, the number is comparable to that of iron objects found in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
and in other places from the same period; and only a small number of these objects are weapons. X-ray fluorescence spectrometry suggests that most or all irons from the Bronze Age are derived from meteorite
A meteorite is a rock (geology), rock that originated in outer space and has fallen to the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical ...
s. The Hittite military also made successful use of chariots
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Ru ...
.
Modern interest in the Hittites increased with the founding of the Republic of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
in 1923. The Hittites attracted the attention of Turkish archaeologists such as Halet Çambel
Halet Çambel (27 August 1916 – 12 January 2014) was a Turkish archaeologist and Olympic fencer. She was the first woman with a Muslim background to compete in the Olympic Games.
Biography
Çambel was born in Berlin, German Empire on 27 ...
and Tahsin Özgüç
Tahsin Özgüç (1916–2005) was an eminent Turkish field archaeologist. The careers of Tahsin Özgüç and his wife, Nimet Özgüç, began after World War II and lasted for nearly 60 years. He was said to be the doyen of Anatolian archaeology ...
. During this period, the new field of Hittitology
Hittitology is the study of the Hittites, an ancient Anatolian people that established an empire around Hattusa in the 2nd millennium BCE. It combines aspects of the archaeology, history, philology, and art history of the Hittite civilisation.
Ther ...
also influenced the naming of Turkish institutions, such as the state-owned ''Etibank
Etibank A.Ş is a defunct Turkish bank. Founded in 1935 as a state bank focussed on financing the electricity sector, it launched commercial banking activities in 1955. The commercial banking division was separated out in 1993 (from what would bec ...
'' ("Hittite bank"), and the foundation of the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations
The Museum of Anatolian Civilizations () is located on the south side of Ankara Castle in the Atpazarı area in Ankara, Turkey. It consists of the old Ottoman Mahmut Paşa bazaar storage building, and the Kurşunlu Han. Because of Atatürk's ...
in Ankara
Ankara is the capital city of Turkey and List of national capitals by area, the largest capital by area in the world. Located in the Central Anatolia Region, central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5,290,822 in its urban center ( ...
, built west of the Hittite capital of Hattusa, which houses the world's most comprehensive exhibition of Hittite art
Hittite art was produced by the Hittite civilization in ancient Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey, and also stretching into Syria during the second millennium BCE from the nineteenth century up until the twelfth century BCE. This period falls under ...
and artifacts.
Etymology
The Hittites called their kingdom ''Hattusa'' (''Hatti'' in Akkadian), a name received from theHattians
The Hattians () were an ancient Bronze Age people that inhabited the land of ''Hatti'', in central Anatolia (modern Turkey). They spoke a distinctive Hattian language, which was neither Semitic languages, Semitic nor Indo-European languages, In ...
, an earlier people who had inhabited and ruled the central Anatolian region until the beginning of the second millennium BC, and who spoke an unrelated language known as Hattic. The modern conventional name "Hittites" is due to the initial identification of the people of Hattusa with the Biblical Hittites
The Hittites, also spelled Hethites, were a group of people mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. Under the names (''bny-ḥt'' "children of Heth", who was the son of Canaan) and (''ḥty'' "native of Heth") they are described several times as living ...
by 19th-century archaeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
. The Hittites would have called themselves something closer to "Neshites" or "Neshians" after the city of Nesha, which flourished for some two hundred years until a king named Labarna renamed himself Hattusili I Ḫattušili (''Ḫattušiliš'' in the inflected nominative case) was the regnal name of three Hittite kings:
* Hattusili I (Labarna II)
* Hattusili II
*Hattusili III Ḫattušili (''Ḫattušiliš'' in the inflected nominative case) was the regnal ...
(meaning "the man of Hattusa") sometime around 1650 BC and established his capital city at Hattusa.
Archeological discovery

Biblical background
Before the archeological discoveries that revealed the Hittite civilization, the only source of information about the Hittites had been the Hebrew Bible.Francis William Newman
Francis William Newman (27 June 1805 – 4 October 1897) was an English classical scholar and moral philosopher, prolific miscellaneous writer and activist for vegetarianism and other causes.
He was the younger brother of John Henry Newman. Th ...
expressed the critical view, common in the early 19th century, that, "no Hittite king could have compared in power to the King of Judah
The Kings of Judah were the monarchs who ruled over the ancient Kingdom of Judah, which was formed in about 930 BC, according to the Hebrew Bible, when the United Kingdom of Israel split, with the people of the northern Kingdom of Israel rejecti ...
...".
As the discoveries in the second half of the 19th century revealed the scale of the Hittite kingdom, Archibald Sayce
Archibald Henry Sayce (25 September 18454 February 1933) was a pioneer British Assyriologist and linguist, who held a chair as Professor of Assyriology at the University of Oxford from 1891 to 1919. He was able to write in at least twenty anci ...
asserted that, rather than being compared to Judah, the Anatolian civilization " asworthy of comparison to the divided Kingdom of Egypt", and was "infinitely more powerful than that of Judah". Sayce and other scholars also noted that Judah and the Hittites were never enemies in the Hebrew texts; in the Book of Kings Book of Kings may refer to:
* Books of Kings in the Bible
* ''Shahnameh'', an 11th-century epic Persian poem
* ''Pararaton'', the Javanese Book of Kings, a 16th-century Javanese history of southeast Asia
* ''The Book of Kings'', a 1999 World War II ...
, they supplied the Israelites with cedar, chariots, and horses, and in the Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek language, Greek ; ; ) is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its incipit, first word, (In the beginning (phrase), 'In the beginning'). Genesis purpor ...
were friends and allies to Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
. Uriah the Hittite
Uriah the Hittite ( ''ʾŪrīyyā haḤīttī'') is a minor figure in the Hebrew Bible, mentioned in the Books of Samuel, an elite soldier in the army of David, king of Israel and Judah, and the husband of Bathsheba, the daughter of Eliam. While ...
was a captain in King David
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament.
The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Dam ...
's army and counted as one of his "mighty men" in 1 Chronicles
The Book of Chronicles ( , "words of the days") is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Chronicles) in the Christian Old Testament. Chronicles is the final book of the Hebrew Bible, concluding the third section of the Jewish Tan ...
11.
Initial discoveries
French scholarCharles Texier
Félix Marie Charles Texier (22 August 1802, Versailles – 1 July 1871, Paris) was a French historian, architect and archaeologist. Texier published a number of significant works involving personal travels throughout Asia Minor and the Middle Eas ...
found the first Hittite ruins in 1834 but did not identify them as such.
The first archaeological evidence for the Hittites appeared in tablets found at the '' karum'' of Kanesh (now called Kültepe
Kültepe ( Turkish: ), also known under its ancient name Kaneš (Kanesh, sometimes also Kaniš/Kanish) or Neša (Nesha), is an archaeological site in Kayseri Province, Turkey. It was already a major settlement at the beginning of the 3rd mille ...
), containing records of trade between Assyrian merchants and a certain "land of ''Hatti''". Some names in the tablets were neither Hattic nor Assyrian, but clearly Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
.
The script on a monument at Boğazkale
Boğazkale ("Gorge Fortress") is a town of Çorum Province in the Black Sea region of Turkey, located from the city of Çorum. It is the seat of Boğazkale District.William Wright in 1884 was found to match peculiar
 The Hittite kingdom was centered on the lands surrounding Hattusa and Neša (Kültepe), known as "the land Hatti" (). After Hattusa was made the capital, the area encompassed by the bend of the
The Hittite kingdom was centered on the lands surrounding Hattusa and Neša (Kültepe), known as "the land Hatti" (). After Hattusa was made the capital, the area encompassed by the bend of the
 The Hittite state was formed from many small polities in North-Central Anatolia, at the banks of the
The Hittite state was formed from many small polities in North-Central Anatolia, at the banks of the
 The founding of the Hittite Kingdom is attributed to either Labarna I or
The founding of the Hittite Kingdom is attributed to either Labarna I or
 The last monarch of the Old Kingdom, Telepinu, reigned until about 1500 BC. Telepinu's reign marked the end of the "Old Kingdom" and the beginning of the lengthy weak phase known as the "Middle Kingdom". The period of the 15th century BC is largely unknown with few surviving records. Part of the reason for both the weakness and the obscurity is that the Hittites were under constant attack, mainly from the Kaskians, a non-
The last monarch of the Old Kingdom, Telepinu, reigned until about 1500 BC. Telepinu's reign marked the end of the "Old Kingdom" and the beginning of the lengthy weak phase known as the "Middle Kingdom". The period of the 15th century BC is largely unknown with few surviving records. Part of the reason for both the weakness and the obscurity is that the Hittites were under constant attack, mainly from the Kaskians, a non-
 After this date, the power of both the Hittites and Egyptians began to decline yet again because of the power of the Assyrians. The Assyrian king
After this date, the power of both the Hittites and Egyptians began to decline yet again because of the power of the Assyrians. The Assyrian king
 By 1160 BC, the political situation in Asia Minor looked vastly different from that of only 25 years earlier. In that year, the Assyrian king
By 1160 BC, the political situation in Asia Minor looked vastly different from that of only 25 years earlier. In that year, the Assyrian king


 The Hittite language is recorded fragmentarily from about the 19th century BC (in the
The Hittite language is recorded fragmentarily from about the 19th century BC (in the
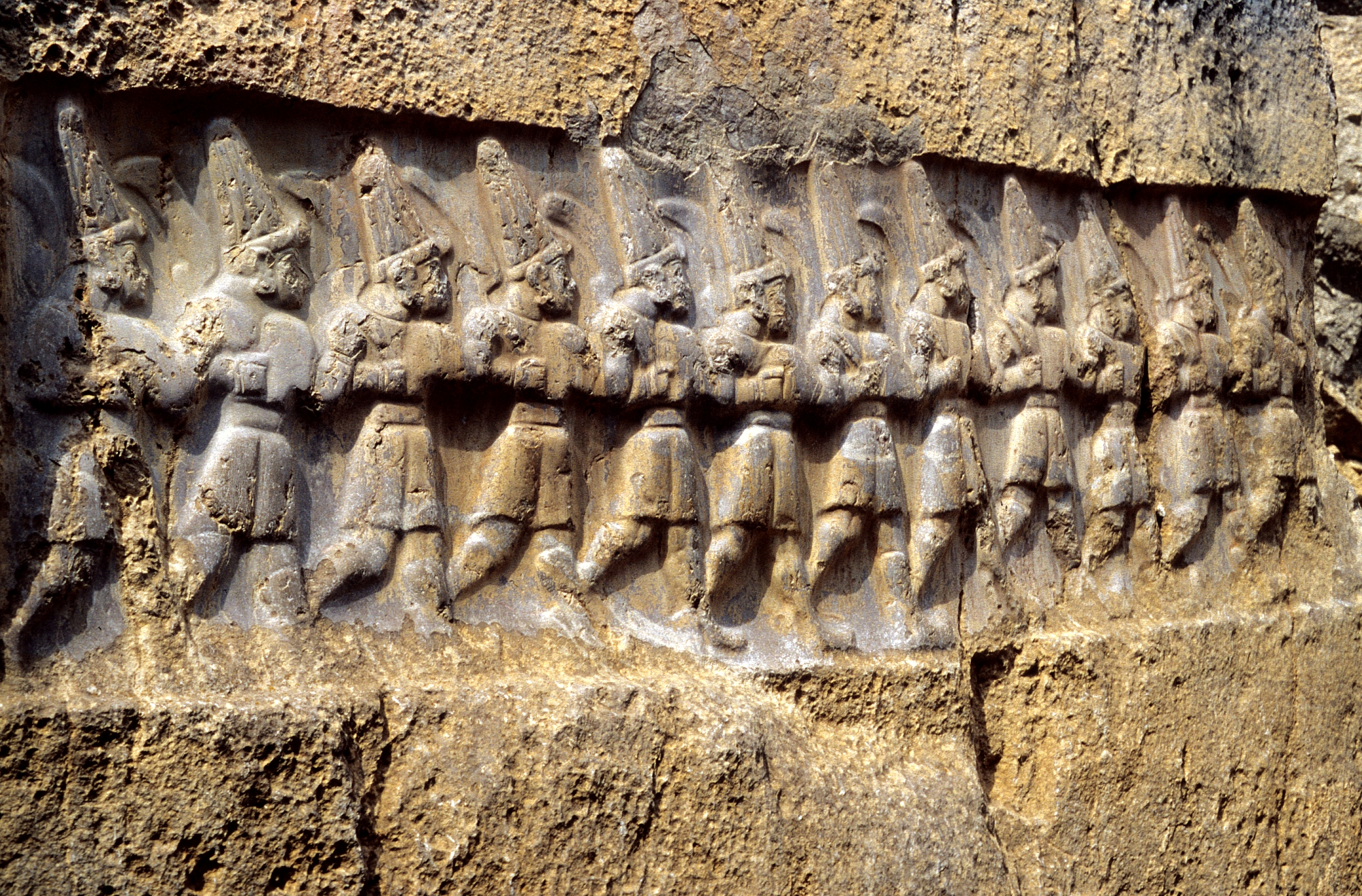
 Given the size of the empire, there are relatively few remains of Hittite art. These include some impressive monumental carvings, a number of
Given the size of the empire, there are relatively few remains of Hittite art. These include some impressive monumental carvings, a number of
hieroglyphic
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs ( ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined ideographic, logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with more than 1,000 distinct characters. ...
scripts from Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
and Hama
Hama ( ', ) is a city on the banks of the Orontes River in west-central Syria. It is located north of Damascus and north of Homs. It is the provincial capital of the Hama Governorate. With a population of 996,000 (2023 census), Hama is one o ...
in Northern Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
. In 1887, excavations at Amarna
Amarna (; ) is an extensive ancient Egyptian archaeological site containing the ruins of Akhetaten, the capital city during the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and a ...
in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
uncovered the diplomatic correspondence of Pharaoh Amenhotep III
Amenhotep III ( , ; "Amun is satisfied"), also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent or Amenhotep the Great and Hellenization, Hellenized as Amenophis III, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. According to d ...
and his son, Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton ( ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning 'Effective for the Aten'), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eig ...
. Two of the letters from a "kingdom of ''Kheta''"—apparently located in the same general region as the Mesopotamian references to "land of ''Hatti''"—were written in standard Akkadian cuneiform, but in an unknown language; although scholars could interpret its sounds, no one could understand it. Shortly after this, Sayce proposed that ''Hatti'' or ''Khatti'' in Anatolia was identical with the "kingdom of ''Kheta''" mentioned in these Egyptian texts, as well as with the biblical Hittites. Others, such as Max Müller
Friedrich Max Müller (; 6 December 1823 – 28 October 1900) was a German-born British comparative philologist and oriental studies, Orientalist. He was one of the founders of the Western academic disciplines of Indology and religious s ...
, agreed that ''Khatti'' was probably ''Kheta'', but proposed connecting it with Biblical Kittim
Kittim was a settlement in present-day Larnaca on the east coast of Cyprus, known in ancient times as Kition, or (in Latin) Citium. On this basis, the whole island became known as "Kittim" in Hebrew, including the Hebrew Bible. However the name s ...
rather than with the Biblical Hittites
The Hittites, also spelled Hethites, were a group of people mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. Under the names (''bny-ḥt'' "children of Heth", who was the son of Canaan) and (''ḥty'' "native of Heth") they are described several times as living ...
. Sayce's identification came to be widely accepted over the course of the early 20th century; and the name "Hittite" has become attached to the civilization uncovered at Boğazköy.
During sporadic excavations at Boğazköy (Hattusa
Hattusa, also Hattuşa, Ḫattuša, Hattusas, or Hattusha, was the capital of the Hittites, Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age during two distinct periods. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey (originally Boğazköy) within the great ...
) that began in 1906, the archaeologist Hugo Winckler
Hugo Winckler (4 July 1863 – 19 April 1913) was a German orientalist, archaeologist, and historian who uncovered the capital of the Hittite Empire (Hattusa) at Boğazkale, Turkey.
A student of the languages of the ancient Middle East, he ...
found a royal archive with 10,000 tablets, inscribed in cuneiform Akkadian and the same unknown language as the Egyptian letters from ''Kheta''—thus confirming the identity of the two names. He also proved that the ruins at Boğazköy were the remains of the capital of an empire that, at one point, controlled northern Syria.
Under the direction of the German Archaeological Institute
The German Archaeological Institute (, ''DAI'') is a research institute in the field of archaeology (and other related fields). The DAI is a "federal agency" under the Federal Foreign Office, Federal Foreign Office of Germany.
Status, tasks and ...
, excavations at Hattusa have been under way since 1907, with interruptions during the world wars. Kültepe was successfully excavated by Professor Tahsin Özgüç
Tahsin Özgüç (1916–2005) was an eminent Turkish field archaeologist. The careers of Tahsin Özgüç and his wife, Nimet Özgüç, began after World War II and lasted for nearly 60 years. He was said to be the doyen of Anatolian archaeology ...
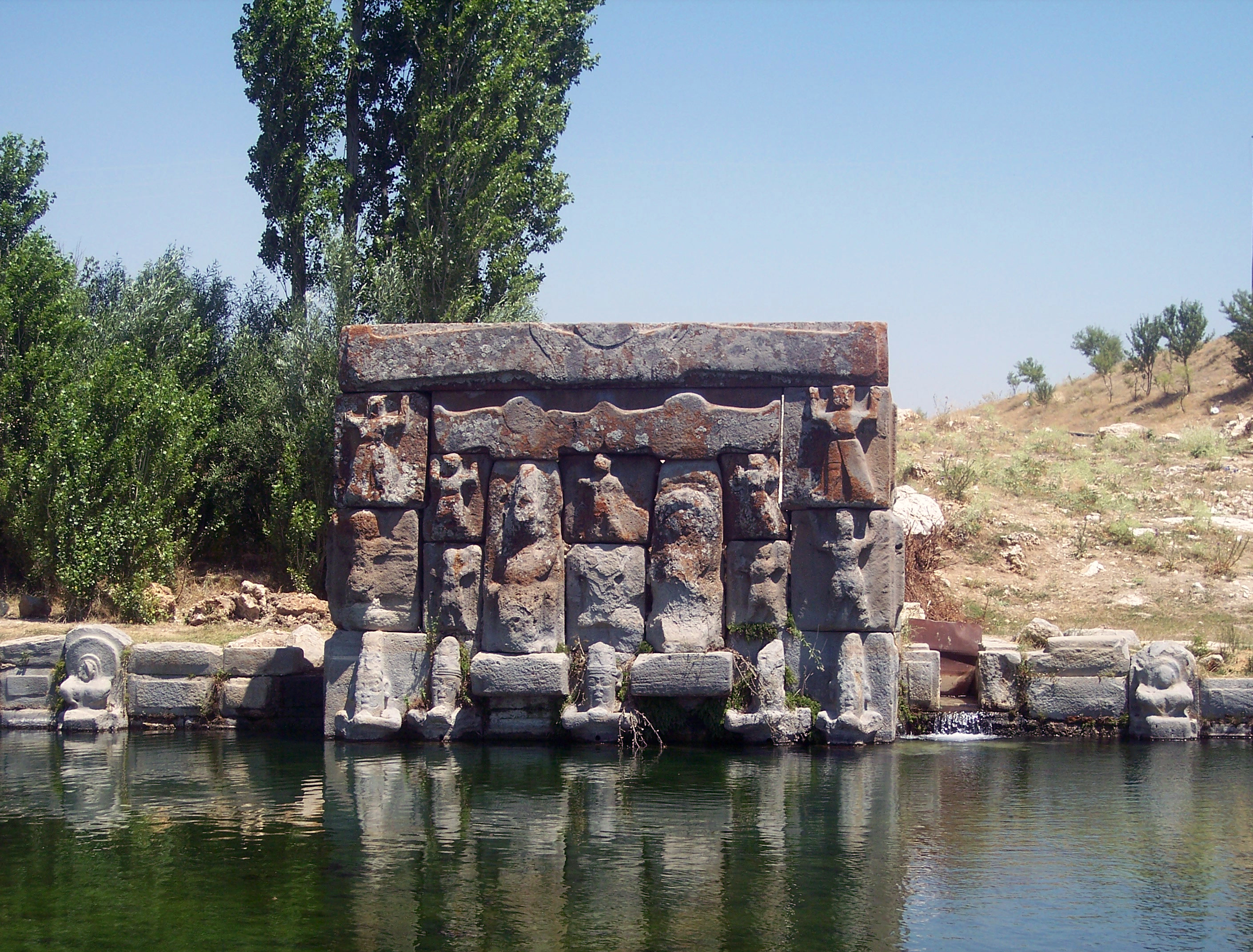
from 1948 until his death in 2005. Smaller scale excavations have also been carried out in the immediate surroundings of Hattusa, including the rock sanctuary of Yazılıkaya
:'' Yazılıkaya, Eskişehir, also called Midas City, is a village with Phrygian ruins.''
Yazılıkaya () was a sanctuary of Hattusa, the capital city of the Hittite Empire, today in the Çorum Province, Turkey. Rock reliefs are a prominent aspec ...
, which contains numerous rock relief
A rock relief or rock-cut relief is a relief, relief sculpture carved on solid or "living rock" such as a cliff, rather than a detached piece of stone. They are a category of rock art, and sometimes found as part of, or in conjunction ...
s portraying the Hittite rulers and the gods of the Hittite pantheon.
Writings
The Hittites used a variation of cuneiform calledHittite cuneiform
Hittite cuneiform is the implementation of cuneiform script used in writing the Hittite language. The surviving corpus of Hittite texts is preserved in cuneiform on clay tablets dating to the 2nd millennium BC (roughly spanning the 17th to 1 ...
. Archaeological expeditions to Hattusa have discovered entire sets of royal archives on cuneiform tablets, written either in Akkadian, the diplomatic language of the time, or in the various dialects of the Hittite confederation.
Museums
TheMuseum of Anatolian Civilizations
The Museum of Anatolian Civilizations () is located on the south side of Ankara Castle in the Atpazarı area in Ankara, Turkey. It consists of the old Ottoman Mahmut Paşa bazaar storage building, and the Kurşunlu Han. Because of Atatürk's ...
in Ankara
Ankara is the capital city of Turkey and List of national capitals by area, the largest capital by area in the world. Located in the Central Anatolia Region, central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5,290,822 in its urban center ( ...
, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
houses the richest collection of Hittite and Anatolian artifacts.
Geography
 The Hittite kingdom was centered on the lands surrounding Hattusa and Neša (Kültepe), known as "the land Hatti" (). After Hattusa was made the capital, the area encompassed by the bend of the
The Hittite kingdom was centered on the lands surrounding Hattusa and Neša (Kültepe), known as "the land Hatti" (). After Hattusa was made the capital, the area encompassed by the bend of the Kızılırmak River
The Kızılırmak (, Turkish language, Turkish for "Red River"), once known as the Halys River () and Alis River, is the longest river flowing entirely within Turkey. It is a source of hydroelectric power and is not used for navigation.
Geogra ...
(Hittite ''Marassantiya,'' Greek ''Halys'') was considered the core of the Empire, and some Hittite laws make a distinction between "this side of the river" and "that side of the river". For example, the bounty for an escaped slave who had fled beyond the river is higher than for a slave caught on the near side.
To the west and south of the core territory lay the region known as ''Luwiya
The Luwians (also known as Luvians) were an ancient people in Anatolia who spoke the Luwian language. During the Bronze Age, Luwians formed part of the population of the Hittite Empire and adjoining states such as Kizzuwatna. During the Hittite Ne ...
'' in the earliest Hittite texts. This terminology was replaced by the names Arzawa
Arzawa was a region and political entity in Western Anatolia during the Late Bronze Age. In Hittite texts, the term is used to refer both to a particular kingdom and to a loose confederation of states. The chief Arzawan state, whose capital wa ...
and Kizzuwatna
Kizzuwatna (or Kizzuwadna; in Ancient Egyptian ''Kode'' or ''Qode'') was an ancient Anatolian kingdom, attested in written sources from the end of the 16th century BC onwards, but though its origins are still obscure, the Middle Bronze Age in Cili ...
with the rise of those kingdoms. Nevertheless, the Hittites continued to refer to the language that originated in these areas as Luwian
Luwian (), sometimes known as Luvian or Luish, is an ancient language, or group of languages, within the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. The ethnonym Luwian comes from ''Luwiya'' (also spelled ''Luwia'' or ''Luvia'') – ...
. Prior to the rise of Kizzuwatna, the heart of that territory in Cilicia
Cilicia () is a geographical region in southern Anatolia, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilician plain (). The region inclu ...
was first referred to by the Hittites as Adaniya. Upon its revolt from the Hittites during the reign of Ammuna
Ammuna was a King of the Hittites ca. 1550–1530 BC (middle chronology) or 1486–1466 BC (short chronology timeline). The land seems to have suffered badly during his reign, and he lost a considerable amount of territory.
Biography Family ...
, it assumed the name of Kizzuwatna and successfully expanded northward to encompass the lower Anti-Taurus Mountains
The Anti-Taurus Mountains (from ) or Aladaglar are a mountain range in southern and eastern Turkey, curving northeast from the Taurus Mountains.
At , Mount Erciyes ( Turkish: Erciyes Dağı) is the highest peak not just in the range but in ce ...
as well. To the north lived the mountain people called the Kaskians
The Kaska (also Kaška, later Tabal (state), Tabalian Kasku and Gasga) were a loosely affiliated Bronze Age non-Indo-European tribal people, who spoke the unclassified Kaskian language and lived in mountainous East Pontus (region), Pontic Anatolia ...
. To the southeast of the Hittites lay the Hurrian empire of Mitanni
Mitanni (–1260 BC), earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, ; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat in Assyrian records, or in Ancient Egypt, Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian language, Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria (region), Syria an ...
.
At its peak during the reign of Muršili II
Mursili II (also spelled Mursilis II) was a king of the Hittite Empire (New kingdom) –1295 BC (middle chronology) or 1321–1295 BC (short chronology).
Early Life
Mursili was the third born son of King Suppiluliuma I, one of the most powerful ...
, the Hittite empire stretched from Arzawa in the west to Mitanni in the east, and included many of the Kaskian territories north as far as Hayasa-Azzi
Hayasa-Azzi or Azzi-Hayasa (, ) was a Late Bronze Age confederation in the Armenian Highlands and/or Pontic region of Asia Minor. The Hayasa-Azzi confederation was in conflict with the Hittite Empire in the 14th century BC, leading up to the ...
in the far north-east, as well as south into Canaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
near the southern border of Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
.
History

Origins
The ancestors of the Hittites came intoAnatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
between 4400 and 4100 BC, when the Anatolian language family split from (Proto)-Indo-European. Recent genetic and archaeological research has indicated that Proto-Anatolian speakers arrived in this region sometime between 5000 and 3000 BC. The Proto-Hittite language developed around 2100 BC, and the Hittite language itself is believed to have been in use in Central Anatolia between the 20th and 12th centuries BC.
The Hittites are first associated with the kingdom of Kussara
Kussara (''Kuššar'') was a Middle Bronze Age kingdom in Anatolia. The kingdom, though apparently important at one time, is mostly remembered today as the origin of the dynasty that would form the Old Hittite Kingdom.
Location
Kussara is occasion ...
sometime prior to 1750 BC.
Hittites in Anatolia during the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
coexisted with Hattians
The Hattians () were an ancient Bronze Age people that inhabited the land of ''Hatti'', in central Anatolia (modern Turkey). They spoke a distinctive Hattian language, which was neither Semitic languages, Semitic nor Indo-European languages, In ...
and Hurrians
The Hurrians (; ; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri) were a people who inhabited the Ancient Near East during the Bronze Age. They spoke the Hurrian language, and lived throughout northern Syria, upper Mesopotamia and southeaste ...
, either by means of conquest or by gradual assimilation.. In archaeological terms, relationships of the Hittites to the Ezero culture of the Balkans and Maykop culture
The Maykop culture or Maikop culture (, , scientific transliteration: ''Majkop,''), c. 3700 BC–3000 BC, is a major Bronze Age archaeological culture in the western Caucasus region.
It extends along the area from the Taman Peninsula at the Ker ...
of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
had previously been considered within the migration framework.
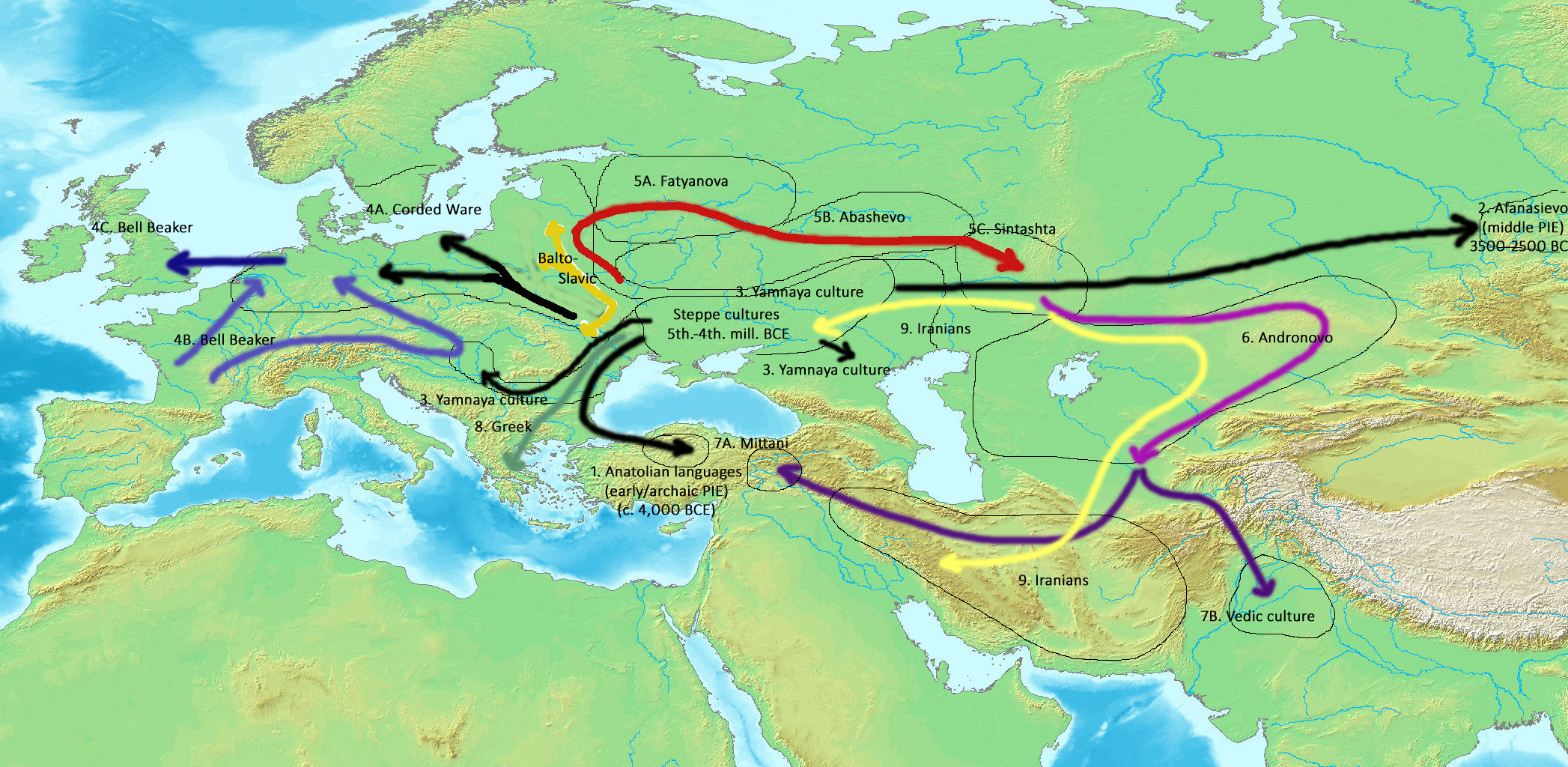
Analyses by David W. Anthony in 2007 concluded that steppe herders who were archaic Indo-European speakers spread into the lower Danube valley about 4200–4000 BC, either causing or taking advantage of the collapse of Old Europe. He thought their languages "probably included archaic Proto-Indo-European dialects of the kind partly preserved later in Anatolian," and that their descendants later moved into Anatolia at an unknown time but maybe as early as 3000 BC.
J. P. Mallory
James Patrick Mallory (born October 25, 1945) is an American archaeologist and Indo-Europeanist. Mallory is an emeritus professor at Queen's University, Belfast; a member of the Royal Irish Academy, and the former editor of the '' Journal of ...
also thought it was likely that the Anatolians reached the Near East from the north either via the Balkans or the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
in the 3rd millennium BC. According to Parpola, the appearance of Indo-European speakers from Europe into Anatolia, and the appearance of Hittite, was related to later migrations of Proto-Indo-European speakers from the Yamnaya culture into the Danube Valley at c. 2800 BC, which was in line with the "customary" assumption that the Anatolian Indo-European language was introduced into Anatolia sometime in the third millennium BC.
However, Petra Goedegebuure has shown that the Hittite language has borrowed many words related to agriculture from cultures on their eastern borders, which is evidence of having taken a route across the Caucasus.
A team at the David Reich Lab
The David Reich Lab is a research laboratory located within the Department of Genetics at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts. Led by population geneticist David Reich, the lab is known for industrializing the fields of ancient DNA, p ...
demonstrated that the Hittite route must have been via the Caucasus and not the Balkans, since Yamnaya expansion into the Balkans carried a component of Eastern Hunter Gatherer ancestry that does not exist in any ancient Anatolian DNA samples, which indicates also that Hittites and their cousin groups split off from the Proto Indo Europeans before the formation of the Yamnaya which did admix with Eastern Hunter Gatherers.
The dominant indigenous inhabitants in central Anatolia were Hurrians and Hattians who spoke non-Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
. Some have argued that Hattic was a Northwest Caucasian language
The Northwest Caucasian languages, also called West Caucasian, Abkhazo-Adyghean, Abkhazo-Circassian, Circassic, or sometimes Pontic languages (from Ancient Greek, ''pontos'', referring to the Black Sea, in contrast to the Northeast Caucasian l ...
, but its affiliation remains uncertain, whilst the Hurrian language
Hurrian is an extinct Hurro-Urartian language spoken by the Hurrians (Khurrites), a people who entered northern Mesopotamia around 2300 BC and had mostly vanished by 1000 BC. Hurrian was the language of the Mitanni kingdom in northern Mesopotami ...
was a near- isolate (i.e. it was one of only two or three languages in the Hurro-Urartian family). There were also Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n colonies in the region during the Old Assyrian Empire
The Old Assyrian period was the second stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of the city of Assur from its rise as an independent city-state under Puzur-Ashur I 2025 BC to the foundation of a larger Assyrian territorial state after th ...
(2025–1750 BC); it was from the Assyrian speakers of Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia constitutes the Upland and lowland, uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the regio ...
that the Hittites adopted the cuneiform script
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
. It took some time before the Hittites established themselves following the collapse of the Old Assyrian Empire in the mid-18th century BC, as is clear from some of the texts included here. For several centuries there were separate Hittite groups, usually centered on various cities. But then strong rulers with their center in Hattusa (modern Boğazkale) succeeded in bringing these together and conquering large parts of central Anatolia to establish the Hittite kingdom.
Early period
 The Hittite state was formed from many small polities in North-Central Anatolia, at the banks of the
The Hittite state was formed from many small polities in North-Central Anatolia, at the banks of the Kızılırmak River
The Kızılırmak (, Turkish language, Turkish for "Red River"), once known as the Halys River () and Alis River, is the longest river flowing entirely within Turkey. It is a source of hydroelectric power and is not used for navigation.
Geogra ...
, during the Middle Bronze Age (ca. 1900–1650 BC). The early history of the Hittite kingdom is known through four "cushion-shaped" tablets, (classified as KBo 3.22, KBo 17.21+, KBo 22.1, and KBo 22.2), not made in Ḫattuša, but probably created in Kussara
Kussara (''Kuššar'') was a Middle Bronze Age kingdom in Anatolia. The kingdom, though apparently important at one time, is mostly remembered today as the origin of the dynasty that would form the Old Hittite Kingdom.
Location
Kussara is occasion ...
, Nēša, or another site in Anatolia, that may first have been written in the 18th century BC, in Old Hittite language, and three of them using the so-called "Old Script" (OS); although most of the remaining tablets survived only as Akkadian copies made in the 14th and 13th centuries BC. These reveal a rivalry within two branches of the royal family up to the Middle Kingdom; a northern branch first based in Zalpuwa Zalpa (also called Zalba, Zalpah, Zalpuwa) were ancient regions mentioned in Assyrian, Mari and Hittite records. The toponyms appear in a variety of forms and contexts and likely refer to multiple similarly named regions. They have been located on ...
and secondarily Hattusa
Hattusa, also Hattuşa, Ḫattuša, Hattusas, or Hattusha, was the capital of the Hittites, Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age during two distinct periods. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey (originally Boğazköy) within the great ...
, and a southern branch based in Kussara
Kussara (''Kuššar'') was a Middle Bronze Age kingdom in Anatolia. The kingdom, though apparently important at one time, is mostly remembered today as the origin of the dynasty that would form the Old Hittite Kingdom.
Location
Kussara is occasion ...
(still not found) and the former Assyrian colony of Kanesh. These are distinguishable by their names; the northerners retained language isolate Hattian names, and the southerners adopted Indo-European Hittite and Luwian names.
Zalpuwa first attacked Kanesh under Uhna in 1833 BC. And during this kārum period, when the merchant colony of the Old Assyrian Empire was flourishing in the site, and before the conquest of Pithana, the following local kings reigned in Kaneš: Ḫurmili (prior to 1790 BC), Paḫanu (a short time in 1790 BC), Inar (–1775 BC), and Waršama (–1750 BC).
One set of tablets, known collectively as the Anitta Anitta may refer to:
*Anitta (king), Hittite king
*Anitta (singer)
Larissa de Macedo Machado (born 30 March 1993), known professionally as Anitta (), is a Brazilian singer, songwriter, dancer, actress, and occasional television host. One of Br ...
text, begin by telling how Pithana the king of Kussara
Kussara (''Kuššar'') was a Middle Bronze Age kingdom in Anatolia. The kingdom, though apparently important at one time, is mostly remembered today as the origin of the dynasty that would form the Old Hittite Kingdom.
Location
Kussara is occasion ...
conquered neighbouring Neša ( Kanesh), this conquest took place around 1750 BC. However, the real subject of these tablets is Pithana's son Anitta ( BC), who continued where his father left off and conquered several northern cities: including Hattusa, which he cursed, and also Zalpuwa. This was likely propaganda for the southern branch of the royal family, against the northern branch who had fixed on Hattusa as capital. Another set, the Tale of Zalpuwa, supports Zalpuwa and exonerates the later Ḫattušili I
Hattusili I (''Ḫattušili'' I) was a Hittite king, king of the Hittite Old Kingdom. He reigned ca. 1650–1620 BC (middle chronology), or ca. 1640–1610 BC (low middle chronology).
Family
Ḫattušili was possibly a nephew of his predecess ...
from the charge of sacking Kanesh.
Anitta was succeeded by Zuzzu ( BC); but sometime in 1710–1705 BC, Kanesh was destroyed, taking the long-established Assyrian merchant trading system with it. A Kussaran noble family survived to contest the Zalpuwan/Hattusan family, though whether these were of the direct line of Anitta is uncertain.
Meanwhile, the lords of Zalpa lived on. Huzziya I( the "elder" Huzziya), descendant of a Huzziya of Zalpa, took over Hatti. His son-in-law Labarna I
Labarna was the traditional first king of the Hittites, (middle chronology), the most accepted chronology nowadays. He was the traditional founder of the Hittite Old Kingdom (fl. c. 1680(?)-1650 BC). His wife was Tawannanna.
The existence of La ...
, a southerner from Hurma usurped the throne but made sure to adopt Huzziya's grandson Ḫattušili as his own son and heir. The location of the land of Hurma is believed to be in the mountains south of Kussara
Kussara (''Kuššar'') was a Middle Bronze Age kingdom in Anatolia. The kingdom, though apparently important at one time, is mostly remembered today as the origin of the dynasty that would form the Old Hittite Kingdom.
Location
Kussara is occasion ...
.
Old Kingdom
 The founding of the Hittite Kingdom is attributed to either Labarna I or
The founding of the Hittite Kingdom is attributed to either Labarna I or Hattusili I Ḫattušili (''Ḫattušiliš'' in the inflected nominative case) was the regnal name of three Hittite kings:
* Hattusili I (Labarna II)
* Hattusili II
*Hattusili III Ḫattušili (''Ḫattušiliš'' in the inflected nominative case) was the regnal ...
(the latter might also have had Labarna as a personal name), who conquered the area south and north of Hattusa. Hattusili I campaigned as far as the Semitic Amorite
The Amorites () were an ancient Northwest Semitic-speaking Bronze Age people from the Levant. Initially appearing in Sumerian records c. 2500 BC, they expanded and ruled most of the Levant, Mesopotamia and parts of Egypt from the 21st century BC ...
kingdom of Yamkhad
Yamhad (Yamḫad) was an ancient Semitic-speaking kingdom centered on Ḥalab (Aleppo) in Syria. The kingdom emerged at the end of the 19th century BC and was ruled by the Yamhad dynasty, who counted on both military and diplomacy to expand th ...
in Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, where he attacked, but did not capture, its capital of Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
. Hattusili I did eventually capture Hattusa and was credited for the foundation of the Hittite Empire. "Hattusili was king, and his sons, brothers, in-laws, family members, and troops were all united. Wherever he went on campaign he controlled the enemy land with force. He destroyed the lands one after the other, took away their power, and made them the borders of the sea. When he came back from campaign, however, each of his sons went somewhere to a country, and in his hand the great cities prospered. But, when later the princes' servants became corrupt, they began to devour the properties, conspired constantly against their masters, and began to shed their blood."This excerpt from ''The Edict of Telepinu'', dating to the 16th century BC, is supposed to illustrate the unification, growth, and prosperity of the Hittites under his rule. It also illustrates the corruption of "the princes", believed to be his sons. The lack of sources leads to uncertainty of how the corruption was addressed. On Hattusili I's deathbed, he chose his grandson,
Mursili I
Mursili I (also known as Mursilis; sometimes transcribed as Murshili) was a king of the Hittites 1620-1590 BC, as per the middle chronology, the most accepted chronology in our times (or alternatively c. 1556–1526 BC, short chronology), and was ...
(or Murshilish I), as his heir.
Mursili continued the conquests of Hattusili I. In 1595 BC (middle chronology
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Com ...
) or 1587 BC (low middle chronology), Mursili I conducted a great raid down the Euphrates River, bypassing Assyria and sacking Mari and Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
, ejecting the Amorite rulers of the Old Babylonian Empire
The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to , and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The chronology of the first dynasty of Babylon ...
in the process. Rather than incorporate Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
into Hittite domains, Mursili seems to have instead turned control of Babylonia over to his Kassite
The Kassites () were a people of the ancient Near East. They controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire from until (short chronology).
The Kassites gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon in 1531 B ...
allies, who were to rule it for the next four centuries. Due to fear of revolts at home, he did not remain in Babylon for long. This lengthy campaign strained the resources of Hatti, and left the capital in a state of near-anarchy. Mursili was assassinated by his brother-in-law Hantili I
Hantili I was a king of the Hittites during the Hittite Old Kingdom. His reign lasted for 30 years, from c. 1590 to c. 1560 BC (middle chronology).
Biography
Rise to power
According to the Telepinu Proclamation, Hantili was the royal cup-bearer ...
during his journey back to Hattusa or shortly after his return home, and the Hittite Kingdom was plunged into chaos. Hantili took the throne. He was able to escape multiple murder attempts on himself, however, his family did not. His wife, Harapsili and her son were murdered. In addition, other members of the royal family were killed by Zidanta I
Zidanta I was a king of the Hittites (Old Kingdom), ruling for 10 years, ca. 1560–1550 BC (middle chronology) or 1496–1486 BC (short chronology timeline). According to the Telepinu Proclamation, this king became a ruler by murder.
Family
Zida ...
, who was then murdered by his own son, Ammuna
Ammuna was a King of the Hittites ca. 1550–1530 BC (middle chronology) or 1486–1466 BC (short chronology timeline). The land seems to have suffered badly during his reign, and he lost a considerable amount of territory.
Biography Family ...
. All of the internal unrest among the Hittite royal family led to a decline of power. The Hurrians, a people living in the mountainous region along the upper Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabia ...
and Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
rivers in modern south east Turkey, took advantage of the situation to seize Aleppo and the surrounding areas for themselves, as well as the coastal region of Adaniya, renaming it Kizzuwatna (later Cilicia
Cilicia () is a geographical region in southern Anatolia, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilician plain (). The region inclu ...
). Throughout the remainder of the 16th century BC, the Hittite kings were held to their homelands by dynastic quarrels and warfare with the Hurrians. The Hurrians became the center of power in Anatolia. The campaigns into Amurru and southern Mesopotamia may be responsible for the reintroduction of cuneiform writing into Anatolia, since the Hittite script is quite different from that of the preceding Assyrian colonial period.
The Hittites entered a weak phase of obscure records, insignificant rulers, and reduced domains. This pattern of expansion under strong kings followed by contraction under weaker ones, was to be repeated over and over through the Hittite Kingdom's 500-year history, making events during the waning periods difficult to reconstruct. The political instability of these years of the Old Hittite Kingdom can be explained in part by the nature of the Hittite kingship at that time. During the Old Hittite Kingdom prior to 1400 BC, the king of the Hittites was not viewed by his subjects as a "living god" like the pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty ( ...
s of Egypt, but rather as a first among equals. Only in the later period from 1400 BC until 1200 BC did the Hittite kingship become more centralized and powerful. Also in earlier years the succession was not legally fixed, enabling "War of the Roses"-style rivalries between northern and southern branches.
The next monarch of note following Mursili I was Telepinu
Telipinu was the last king of the Hittites Old Kingdom, reigning in middle chronology. At the beginning of his reign, the Hittite Empire had contracted to its core territories, having long since lost all of its conquests, made in the former era ...
(), who won a few victories to the southwest, apparently by allying himself with one Hurrian state (Kizzuwatna) against another. Telepinu also attempted to secure the lines of succession.
Middle Kingdom
 The last monarch of the Old Kingdom, Telepinu, reigned until about 1500 BC. Telepinu's reign marked the end of the "Old Kingdom" and the beginning of the lengthy weak phase known as the "Middle Kingdom". The period of the 15th century BC is largely unknown with few surviving records. Part of the reason for both the weakness and the obscurity is that the Hittites were under constant attack, mainly from the Kaskians, a non-
The last monarch of the Old Kingdom, Telepinu, reigned until about 1500 BC. Telepinu's reign marked the end of the "Old Kingdom" and the beginning of the lengthy weak phase known as the "Middle Kingdom". The period of the 15th century BC is largely unknown with few surviving records. Part of the reason for both the weakness and the obscurity is that the Hittites were under constant attack, mainly from the Kaskians, a non-Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
people settled along the shores of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
. The capital once again went on the move, first to Sapinuwa
Sapinuwa (sometimes Shapinuwa; Hittite language, Hittite: ''Šapinuwa'') was a Bronze Age Hittites, Hittite city at the location of modern Ortaköy, Çorum, Ortaköy in the province Çorum in Turkey about 70 kilometers east of the Hittite capital ...
and then to Samuha. There is an archive in Sapinuwa, but it has not been adequately translated to date.
It segues into the "Hittite Empire period" proper, which dates from the reign of Tudhaliya I Tudḫaliya is the name of several Hittite kings or royals. It is not clear how many kings bore that name, and numbering schemes vary from source to source.
*Tudḫaliya (sometimes called Tudḫaliya I) is deduced from his early placement in a lat ...
from .
One innovation that can be credited to these early Hittite rulers is the practice of conducting treaties and alliances with neighboring states; the Hittites were thus among the earliest known pioneers in the art of international politics and diplomacy. This is also when the Hittite religion adopted several gods and rituals from the Hurrians.
New Kingdom
With the reign of Tudhaliya I (who may actually not have been the first of that name; see alsoTudhaliya Tudḫaliya is the name of several Hittite kings or royals. It is not clear how many kings bore that name, and numbering schemes vary from source to source.
*Tudḫaliya (sometimes called Tudḫaliya I) is deduced from his early placement in a lat ...
), the Hittite Kingdom re-emerged from the fog of obscurity and entered the "Hittite Empire period". Many changes were afoot during this time, not the least of which was a strengthening of the kingship. Settlement of the Hittites progressed in the Empire period. However, the Hittite people tended to settle in the older lands of south Anatolia rather than the lands of the Aegean. As this settlement progressed, treaties were signed with neighboring peoples. During the Hittite Empire period the kingship became hereditary and the king took on a "superhuman aura" and began to be referred to by the Hittite citizens as "My Sun". The kings of the Empire period began acting as a high priest for the whole kingdommaking an annual tour of the Hittite holy cities, conducting festivals and supervising the upkeep of the sanctuaries.
During his reign (), King Tudhaliya I, again allied with Kizzuwatna, then vanquished the Hurrian states of Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
and Mitanni, and expanded to the west at the expense of Arzawa (a Luwian state).
Another weak phase followed Tudhaliya I, and the Hittites' enemies from all directions were able to advance even to Hattusa and raze it. However, the kingdom recovered its former glory under Šuppiluliuma I
Šuppiluliuma I, also Suppiluliuma () or Suppiluliumas (died c. 1322 BC) () was an ancient Hittite king (r. –1322 BC).Bryce 2005: xv, 154; Freu 2007b: 311 dates the reign to c. 1350–c. 1319 BC; Kuhrt 1995: 230 dates him within the range 1370 ...
(), who again conquered Aleppo. Mitanni was reduced to vassalage by the Assyrians under his son-in-law, and he defeated Carchemish
Carchemish ( or ), also spelled Karkemish (), was an important ancient capital in the northern part of the region of Syria. At times during its history the city was independent, but it was also part of the Mitanni, Hittite and Neo-Assyrian ...
, another Amorite city-state. With his own sons placed over all of these new conquests and Babylonia still in the hands of the allied Kassites
The Kassites () were a people of the ancient Near East. They controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire from until (short chronology).
The Kassites gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon in 1531 B ...
, this left Šuppiluliuma the supreme power broker in the known world, alongside Assyria and Egypt, and it was not long before Egypt was seeking an alliance by marriage of another of his sons with the widow of Tutankhamen
Tutankhamun or Tutankhamen, (; ), was an Egyptian pharaoh who ruled during the late Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Born Tutankhaten, he instituted the restoration of the traditional polytheistic form of ancient Egyptian religion, undo ...
. That son was evidently murdered before reaching his destination, and this alliance was never consummated. However, the Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. ...
(1365–1050 BC) once more began to grow in power with the ascension of Ashur-uballit I
Ashur-uballit I ''(Aššur-uballiṭ I)'', who reigned between 1363 and 1328 BC, was the first king of the Middle Assyrian Empire. After his father Eriba-Adad I had broken Mitanni influence over Assyria, Ashur-uballit I's defeat of the Mitanni ...
in 1365 BC. Ashur-uballit I attacked and defeated Mattiwaza
Shattiwaza or Šattiwaza, alternatively referred to as Kurtiwaza or ''Mattiwaza'', was a king of the Hurrian kingdom of Mitanni, who reigned 1330-1305 BC.
Biography
Shattiwaza was the son of king Tushratta. His Hurrian name was ''Kili-Tešup''. ...
the Mitanni king despite attempts by the Hittite king Šuppiluliuma I, now fearful of growing Assyrian power, attempting to preserve his throne with military support. The lands of the Mitanni and Hurrians were duly appropriated by Assyria, enabling it to encroach on Hittite territory in eastern Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, and Adad-nirari I
Adad-nārārī I (1305–1274 BC or 1295–1263 BC short chronology) was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian Empire. He is the earliest Assyrian king whose annals survive in any detail, and achieved major military victories that further s ...
annexed Carchemish and northeast Syria from the control of the Hittites.
While Šuppiluliuma I reigned, the Hittite Empire was devastated by an epidemic of tularemia
Tularemia, also known as rabbit fever, is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium '' Francisella tularensis''. Symptoms may include fever, skin ulcers, and enlarged lymph nodes. Occasionally, a form that results in pneumonia or a throat ...
. The epidemic afflicted the Hittites for decades and tularemia killed Šuppiluliuma I and his successor, Arnuwanda II
Arnuwanda II was a Hittite great king who reigned in the late 14th century BC, perhaps in c. 1322–1321 BC. His reign was a briefly interlude between those of his father Šuppiluliuma I and younger brother Muršili II.
Early Life
Arnuwanda ...
. After Šuppiluliuma I's rule, and the brief reign of his eldest son, Arnuwanda II, another son, Mursili II There were three Hittite kings called Mursili:
* Mursili I, ca. 1556–1526 BCE ( short chronology), and was likely a grandson of his predecessor, Hattusili I. His sister was Ḫarapšili and his wife was queen Kali.
* Mursili II, (also spelled Mur ...
, became king (). Having inherited a position of strength in the east, Mursili was able to turn his attention to the west, where he attacked Arzawa. At a point when the Hittites were weakened by the tularemia epidemic, the Arzawans attacked the Hittites, who repelled the attack by sending infected rams to the Arzawans. This was the first recorded use of biological warfare
Biological warfare, also known as germ warfare, is the use of biological toxins or Pathogen, infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, insects, and Fungus, fungi with the intent to kill, harm or incapacitate humans, animals or plants as an ...
. Mursili also attacked a city known as Millawanda (Miletus
Miletus (Ancient Greek: Μίλητος, Mílētos) was an influential ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in present day Turkey. Renowned in antiquity for its wealth, maritime power, and ex ...
), which was under the control of Ahhiyawa
The Achaeans or Akhaians (; , "the Achaeans" or "of Achaea") is one of the names in Homer which is used to refer to the Greeks collectively.
The term "Achaean" is believed to be related to the Hittite term Ahhiyawa and the Egyptian term Ekwe ...
. More recent research based on new readings and interpretations of the Hittite texts, as well as of the material evidence for Mycenaean contacts with the Anatolian mainland, came to the conclusion that Ahhiyawa referred to Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainla ...
, or at least to a part of it.
Battle of Kadesh
Hittite prosperity was mostly dependent on control of the trade routes and metal sources. Because of the importance of Northern Syria to the vital routes linking theCilician gates
The Cilician Gates or Gülek Pass is a pass through the Taurus Mountains connecting the low plains of Cilicia to the Anatolian Plateau, by way of the narrow gorge of the Gökoluk River. Its highest elevation is about 1000m.
The Cilician Gates ...
with Mesopotamia, defense of this area was crucial, and was soon put to the test by Egyptian expansion under Pharaoh Ramesses II
Ramesses II (sometimes written Ramses or Rameses) (; , , ; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was an Pharaoh, Egyptian pharaoh. He was the third ruler of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty. Along with Thutmose III of th ...
. The outcome of the Battle of Kadesh
The Battle of Kadesh took place in the 13th century BC between the New Kingdom of Egypt, Egyptian Empire led by pharaoh Ramesses II and the Hittites, Hittite Empire led by king Muwatalli II. Their armies engaged each other at the Orontes River, ...
is uncertain, though it seems that the timely arrival of Egyptian reinforcements prevented total Hittite victory. The Egyptians forced the Hittites to take refuge in the fortress of Kadesh
Qadesh, Qedesh, Qetesh, Kadesh, Kedesh, Kadeš and Qades come from the common Semitic root "Q-D-Š", which means "sacred."
Kadesh and variations may refer to:
Ancient/biblical places
* Kadesh (Syria) or Qadesh, an ancient city of the Levant, on ...
, but their own losses prevented them from sustaining a siege. This battle took place in the 5th year of Ramesses ( by the most commonly used chronology).
Downfall and demise of the kingdom
 After this date, the power of both the Hittites and Egyptians began to decline yet again because of the power of the Assyrians. The Assyrian king
After this date, the power of both the Hittites and Egyptians began to decline yet again because of the power of the Assyrians. The Assyrian king Shalmaneser I
Shalmaneser I (𒁹𒀭𒁲𒈠𒉡𒊕 md''sál-ma-nu-SAG'' ''Salmanu-ašared''; 1273–1244 BC or 1265–1235 BC) was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian Empire. He was the son and successor of Adad-nirari I.
Reign
Year 1: According ...
had seized the opportunity to vanquish Hurria and Mitanni, occupy their lands, and expand up to the head of the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
, while Muwatalli was preoccupied with the Egyptians. The Hittites had vainly tried to preserve the Mitanni Kingdom with military support. Assyria now posed just as great a threat to Hittite trade routes as Egypt ever had. Muwatalli's son, Urhi-Teshub, took the throne and ruled as king for seven years as Mursili III There were three Hittite kings called Mursili:
*Mursili I, ca. 1556–1526 BCE (short chronology), and was likely a grandson of his predecessor, Hattusili I. His sister was Ḫarapšili and his wife was queen Kali.
*Mursili II, (also spelled Mursil ...
before being ousted by his uncle, Hattusili III Ḫattušili (''Ḫattušiliš'' in the inflected nominative case) was the regnal name of three Hittite kings:
* Hattusili I (Labarna II)
* Hattusili II
* Hattusili III
It was also the name of two Neo-Hittite kings:
* Hattusili I (Kummuh)
* Hattus ...
after a brief civil war. In response to increasing Assyrian annexation of Hittite territory, he concluded a peace and alliance with Ramesses II (also fearful of Assyria), presenting his daughter's hand in marriage to the Pharaoh. The Treaty of Kadesh
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention ...
, one of the oldest completely surviving treaties in history, fixed their mutual boundaries in southern Canaan, and was signed in the 21st year of Rameses (c. 1258 BC). Terms of this treaty included the marriage of one of the Hittite princesses to Ramesses.
Hattusili's son, Tudhaliya IV Tudḫaliya is the name of several Hittite kings or royals. It is not clear how many kings bore that name, and numbering schemes vary from source to source.
*Tudḫaliya (sometimes called Tudḫaliya I) is deduced from his early placement in a lat ...
, was the last strong Hittite king able to keep the Assyrians out of the Hittite heartland to some degree at least, though he too lost much territory to them, and was heavily defeated by Tukulti-Ninurta I
Tukulti-Ninurta I (meaning: "my trust is in he warrior godNinurta"; reigned 1243–1207 BC) was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian Empire. He is known as the first king to use the title "King of Kings".
Reign
Tukulti-Ninurta I succeed ...
of Assyria in the Battle of Nihriya
The Battle of Niḫriya was the culminating point of the hostilities between the Hittites and the Assyrians for control over the remnants of the former empire of Mitanni in Upper Mesopotamia, in the second half of the 13th Century BC.
When Hittit ...
. He even temporarily annexed the island of Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, before that too fell to Assyria. The last king, Šuppiluliuma II
Šuppiluliuma II (), the son of Tudḫaliya IV, was the last certain great king of the New Kingdom of the Hittite Empire, contemporary with Tukulti-Ninurta I of the Middle Assyrian Empire. His reign began around 1207 BC (short chronology) and en ...
also managed to win some victories, including a naval battle against Alashiya
Alashiya ( ''Alašiya'' -la-ši-ia ''ẢLṮY''; Linear B: 𐀀𐀨𐀯𐀍 ''Alasios'' -ra-si-jo Hieratic "'irs3"), also spelled Alasiya, also known as the Kingdom of Alashiya, was a state which existed in the Middle and Late Bronze Ages, a ...
off the coast of Cyprus.Horst Nowacki, Wolfgang Lefèvre ''Creating Shapes in Civil and Naval Architecture: A Cross-Disciplinary Comparison'' Brill, 2009
Bryce sees the Great Kingdom's end as a gradual disintegration. Pointing to the death of Hattusili as a starting point. Tudhaliya would have to put down rebellions and plots against his rule. This was not abnormal. However the Hittite military were stretched thin, due to a lack of manpower and hits to the population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and pl ...
of the Empire. Putting down revolts and civil wars with brute force was not something Hatti could do to the same extent anymore. Every soldier was also a worker away from the economy
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
, such as food production. Thus, casualties from war became ever more costly and unsustainable.
The Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples were a group of tribes hypothesized to have attacked Ancient Egypt, Egypt and other Eastern Mediterranean regions around 1200 BC during the Late Bronze Age. The hypothesis was proposed by the 19th-century Egyptology, Egyptologis ...
had already begun their push down the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
coastline, starting from the Aegean, and continuing all the way to Canaan, founding the state of Philistia
Philistia was a confederation of five main cities or pentapolis in the Southwest Levant, made up of principally Gaza, Ashkelon, Ashdod, Ekron, Gath, and for a time, Jaffa (part of present-day Tel Aviv-Yafo).
Scholars believe the Philist ...
taking Cilicia
Cilicia () is a geographical region in southern Anatolia, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilician plain (). The region inclu ...
and Cyprus away from the Hittites en route and cutting off their coveted trade routes. This left the Hittite homelands vulnerable to attack from all directions, and Hattusa was burnt to the ground sometime around 1180 BC following a combined onslaught from new waves of invaders: the Kaskians, Phrygians
The Phrygians (Greek: Φρύγες, ''Phruges'' or ''Phryges'') were an ancient Indo-European speaking people who inhabited central-western Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) in antiquity.
Ancient Greek authors used "Phrygian" as an umbrella term t ...
and Bryges
Bryges or Briges () is the historical name given to a people of the ancient Balkans. They are generally considered to have been related to the Phrygians, who during classical antiquity lived in western Anatolia. Both names, ''Bryges'' and ''Phryg ...
. The Hittite Kingdom thus vanished from historical records, much of the territory being seized by Assyria. Alongside these attacks, many internal issues also led to the end of the Hittite Kingdom. The end of the kingdom was part of the larger Bronze Age Collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a period of societal collapse in the Mediterranean basin during the 12th century BC. It is thought to have affected much of the Eastern Mediterranean and Near East, in particular Egypt, Anatolia, the Aege ...
. A study of tree rings of juniper trees growing in the region showed a change to drier conditions from the 13th century BC into the 12th century BC with drought for three consecutive years in 1198, 1197 and 1196 BC.
Post-Hittite period
 By 1160 BC, the political situation in Asia Minor looked vastly different from that of only 25 years earlier. In that year, the Assyrian king
By 1160 BC, the political situation in Asia Minor looked vastly different from that of only 25 years earlier. In that year, the Assyrian king Tiglath-Pileser I
Tiglath-Pileser I (; from the Hebraic form of , "my trust is in the son of Ešarra") was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian period (1114–1076 BC). According to Georges Roux, Tiglath-Pileser was "one of the two or three great Assyri ...
was defeating the ''Mushki
The Mushki (sometimes transliterated as Muški) were an Iron Age people of Anatolia who appear in sources from Assyria but not from the Hittites. Several authors have connected them with the Moschoi (Μόσχοι) of Greek sources and the Geor ...
'' (Phrygians) who had been attempting to press into Assyrian colonies in southern Anatolia from the Anatolian highlands, and the Kaska people, the Hittites' old enemies from the northern hill-country between Hatti and the Black Sea, seem to have joined them soon after. The Phrygians had apparently overrun Cappadocia
Cappadocia (; , from ) is a historical region in Central Anatolia region, Turkey. It is largely in the provinces of Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde. Today, the touristic Cappadocia Region is located in Nevşehir ...
from the West, with recently discovered epigraphic evidence confirming their origins as the Balkan "Bryges" tribe, forced out by the Macedonians.
Although the Hittite Kingdom disappeared from Anatolia at this point, there emerged a number of so-called Syro-Hittite states
The states called Neo-Hittite, Syro-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works) were Luwian and Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwestern parts of ...
in Anatolia and northern Syria. They were the successors of the Hittite Kingdom. The most notable Syro-Hittite kingdoms were those at Carchemish
Carchemish ( or ), also spelled Karkemish (), was an important ancient capital in the northern part of the region of Syria. At times during its history the city was independent, but it was also part of the Mitanni, Hittite and Neo-Assyrian ...
and Melid
Arslantepe, also known as Melid, was an ancient city on the Tohma River, a tributary of the upper Euphrates rising in the Taurus Mountains. It has been identified with the modern archaeological site of Arslantepe near Malatya, Turkey.
It was na ...
. With the ruling family in Carchemish believed to have been a cadet branch
A cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets (realm, titles, fiefs, property and incom ...
of the then defunct central ruling Hittite line. These Syro-Hittite states gradually fell under the control of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East and parts of South Caucasus, Nort ...
(911–608 BC). Carchemish and Melid were made vassals of Assyria under Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III (''Šulmānu-ašarēdu'', "the god Shulmanu is pre-eminent") was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 859 BC to 824 BC.
His long reign was a constant series of campaigns against the eastern tribes, the Babylonians, the nations o ...
(858–823 BC), and fully incorporated into Assyria during the reign of Sargon II
Sargon II (, meaning "the faithful king" or "the legitimate king") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III (745–727), Sargon is generally believed to have be ...
(722–705 BC).
A large and powerful state known as Tabal Tabal may refer to:
* Tabal (region), a region of southern Central Anatolia during the Iron Age.
* Tabal (state), a Luwian-speaking Syro-Hittite petty kingdom that existed during the Iron Age.
{{disambiguation ...
occupied much of southern Anatolia. Known as Greek '' Tibarenoi'' (), Latin ''Tibareni'', ''Thobeles'' in Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of pr ...
, their language may have been Luwian, testified to by monuments written using Anatolian hieroglyphs
Anatolian hieroglyphs are an indigenous logographic script native to central Anatolia, consisting of some 500 signs. They were once commonly known as Hittite hieroglyphs, but the language they encode proved to be Luwian language, Luwian, not Hitt ...
. This state too was conquered and incorporated into the vast Neo-Assyrian Empire.
Ultimately, both Luwian hieroglyphs and cuneiform were rendered obsolete by an innovation, the alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from a ...
, which seems to have entered Anatolia simultaneously from the Aegean (with the Bryges, who changed their name to Phrygians), and from the Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
ns and neighboring peoples in Syria.
Government
The earliest knownconstitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
was developed by the Hittites.
The head of the Hittite state was the king, followed by the heir-apparent. The king was the supreme ruler of the land, in charge of being a military commander, judicial authority, as well as a high priest. However, some officials exercised independent authority over various branches of the government. One of the most important of these posts in the Hittite society was that of the ''gal mesedi
The ''gal mesedi'' was a Hittite military and administrative title literally meaning "chief of the royal bodyguards". He was in charge of the Mesedi, the personal bodyguard of the Hittite king.Burney p.234-235 It is considered to be one of the mo ...
'' (Chief of the Royal Bodyguards). It was superseded by the rank of the ''gal gestin
The ''gal gestin'' was a Hittite military and administrative title literally meaning "chief of the wine stewards". It is considered to be one of the most important and prestigious posts of the Hittite Kingdom.
History
As a ''gal gestin'' a comm ...
'' (chief of the wine stewards), who, like the ''gal mesedi'', was generally a member of the royal family. The kingdom's bureaucracy was headed by the ''gal dubsar The ''gal dubsar'' was a Hittite administrative title literally meaning "chief of the scribes". It is considered to be one of the most important and prestigious posts of the Hittite Empire as the ''gal dubsar'' was the head of the government.
His ...
'' (chief of the scribes), whose authority did not extend over the ''lugal dubsar'', the king's personal scribe.
Egyptian monarchs engaged in diplomacy with two chief Hittite seats, located at Kadesh (a city located on the Orontes River
The Orontes (; from Ancient Greek , ) or Nahr al-ʿĀṣī, or simply Asi (, ; ) is a long river in Western Asia that begins in Lebanon, flowing northwards through Syria before entering the Mediterranean Sea near Samandağ in Hatay Province, Turk ...
) and Carchemish (located on the Euphrates river in Southern Anatolia).

Religion of the early Hittites
In the Central Anatolian settlement ofAnkuwa Ankuwa was an ancient Hattian and Hittite settlement in central Anatolia. Along with Hattusa and Katapa, it was one of the capitals from which the Hittite kings reigned during the year. Travelling from Hattusa, the royal entourage would arrive at ...
, home of the pre-Hittite goddess Kattaha and the worship of other Hattic deities illustrates the ethnic differences in the areas the Hittites tried to control. Kattaha was originally given the name Hannikkun. The usage of the term Kattaha over Hannikkun, according to Ronald Gorny (head of the Alisar regional project in Turkey), was a device to downgrade the pre-Hittite identity of this female deity, and to bring her more in touch with the Hittite tradition. Their reconfiguration of gods throughout their early history such as with Kattaha was a way of legitimizing their authority and to avoid conflicting ideologies in newly included regions and settlements. By transforming local deities to fit their own customs, the Hittites hoped that the traditional beliefs of these communities would understand and accept the changes to become better suited for the Hittite political and economic goals.
The Pankus
KingTelipinu
Telipinu was the last king of the Hittites Old Kingdom, reigning in middle chronology. At the beginning of his reign, the Hittite Empire had contracted to its core territories, having long since lost all of its conquests, made in the former era ...
(reigned BC) is considered to be the last king of the Old Kingdom of the Hittites. He seized power during a dynastic power struggle. During his reign, he wanted to take care of lawlessness and regulate royal succession. He thus issued the '' Edict of Telipinus''. In this edict, he designated the Pankus, which was a general assembly, as the high court for constitutional crimes. Crimes such as murder were observed and judged by the Pankus. Kings themselves were also subject to jurisdiction under the Pankus. The Pankus also served as an advisory council for the king. The rules and regulations set out by the edict, and the establishment of the Pankus proved to be very successful and lasted all the way through to end of the New Kingdom.
The Pankus established a legal code where violence was not a punishment for a crime. Crimes such as a murder and theft, which at the time were punishable by death, in other southwest Asian kingdoms, were not capital crime
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in s ...
s under the Hittite law code. Most criminal penalties involved restitution. For example, in cases of thievery, the punishment of that crime would to be to repay what was stolen in equal value.
Foreign Policy and Wars
The Hittite Great Kingdom frequently took booty people during its wars, which were an important source of labor in food production and replacement ofpopulation
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and pl ...
losses. While they had frequent dealings with foreign powers, such as, Bryce thinks they may have had an non-aggression pact
A non-aggression pact or neutrality pact is a treaty between two or more states/countries that includes a promise by the signatories not to engage in military action against each other. Such treaties may be described by other names, such as a t ...
with Ahhiyawa
The Achaeans or Akhaians (; , "the Achaeans" or "of Achaea") is one of the names in Homer which is used to refer to the Greeks collectively.
The term "Achaean" is believed to be related to the Hittite term Ahhiyawa and the Egyptian term Ekwe ...
, having taken then traded back Millawanda in negotiations. While the Hittites had a troubled relationship with Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, culminating in the famous battle of Kadesh
The Battle of Kadesh took place in the 13th century BC between the New Kingdom of Egypt, Egyptian Empire led by pharaoh Ramesses II and the Hittites, Hittite Empire led by king Muwatalli II. Their armies engaged each other at the Orontes River, ...
Hittite Queens often were influential wielders of power in foreign policy, such as via establishment of marriage alliances. An example of this is Queen Puduhepa. With the Hittites internationally being part of the Club of great powers
The Great Powers' Club or The Club of Great Powers is a term used by historians to refer to a collection of empires in the ancient Near East and Egypt between 1500 and 1100 BC, or the Late Bronze Age. These powers were Assyria, Babylon, Egyptian E ...
with Hatti maintaining an alliance with Egypt after the Egyptian–Hittite peace treaty
The Egyptian–Hittite peace treaty, also known as the Eternal Treaty or the Silver Treaty, was concluded between Ramesses II of the Egyptian Empire and Ḫattušili III of the Hittite Empire around 1259 BC. It is the oldest known surviving pea ...
. Hatti's northern and eastern frontiers were often unstable as evidenced by Battle of Ganuvara and Hittite Wars of Survival
The Wars of Survival were a series of wars between the Hittite Empire and its neighbours including Arzawa, Kaška, and Hayasa-Azzi. The wars, which lasted from c. 1400 BC to 1350 BC proved to be an existential period for the Hittites, whose capita ...
. While its relationship with Assyria was often troublesome, like around the time of Battle of Nihriya
The Battle of Niḫriya was the culminating point of the hostilities between the Hittites and the Assyrians for control over the remnants of the former empire of Mitanni in Upper Mesopotamia, in the second half of the 13th Century BC.
When Hittit ...
or to its south with Battles of Alashiya
The Battles of Alashiya were a series of two naval engagements and one joint land and naval operation fought between the Hittite Navy and the Hittite Army of the Hittite Empire and the Alashiyan Navy and Alashiyan Army of the Kingdom of Alashiy ...
.
Economy
The Hittite economy was an Agro-Pastoral one, growing fruits and vegetables with cattle and sheep being common. Grain silos where usually placed in administrative centers such as Hattusa. In theory the land was owned by the gods, while in practice the King controlled the best lands, with a variety of other ownership forms after this. Land could be granted to you for military service by the King. The workforce working in food production was critical to the economy, thus wars taking men away from this could impact the food output of the Great Kingdom. Temples were an important part of the economy. Shekels, minas and talents where the standard form of 'currency'. They were weights in either, copper, bronze, silver or gold. With the ratio being 40 Shekels equaling 1 Mina, which is different from other great kingdoms where it could be 60 to 1. One shekel being 8.3gram
The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a Physical unit, unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth of a kilogram.
Originally defined in 1795 as "the absolute Mass versus weight, weight of a volume ...
. A silver shekel being worth 150l of wheat, you could buy 3,600 square meters land plot for 2-3 shekels silver, with an similar sized vineyard going up to 40 shekels of silver. An male laborer could earn one silver shekel per month, with women half that. You could also be payed in-kind, taking a part of the harvest, this could be more profitable to a wage. Bryce notes that men also did the most physically demanding work.
Population
Bryce, citing in his book a previous population estimate of 9,000-15,000 for Hattuša, but stating that recent research by Jürgen Seeher now suggest the city would have had a population of 2,300-4,600, with a peak of 5,000 during special occasions at maximum. While the total population of the Kingdom estimated at 140,000-150,000 by Zsolt Simon and Bryce himself giving a figure of 200,000+. Noting that Hatti was able to muster 47,500 thousand troops for Kadesh and could in total have mustered all-in-all ~100,000 for military service, not all necessarily participated in battle or in campaigns, but some may have provided labour service. Thus military campaigns that were costly in lives resulted in difficulties maintaining Hittite food production and economy. With 'booty-people' taken from foreign lands during campaigns would've been important in covering losses in population. The book discusses these figures in relation to the Empire during the reign ofHattusili III Ḫattušili (''Ḫattušiliš'' in the inflected nominative case) was the regnal name of three Hittite kings:
* Hattusili I (Labarna II)
* Hattusili II
* Hattusili III
It was also the name of two Neo-Hittite kings:
* Hattusili I (Kummuh)
* Hattus ...
, even if Bryce doesn't give exact dates for when these population numbers were actual, they should be understood for this reign.
Language
Kültepe
Kültepe ( Turkish: ), also known under its ancient name Kaneš (Kanesh, sometimes also Kaniš/Kanish) or Neša (Nesha), is an archaeological site in Kayseri Province, Turkey. It was already a major settlement at the beginning of the 3rd mille ...
texts, see ''Ishara
Ishara may refer to:
* Išḫara, a Hurrian deity
*Ishara, a small town in Ogun State
Ogun State is a state in southwestern Nigeria. It is bordered to the south by Lagos State and the Bight of Benin, to the east by Ondo State, and to the n ...
''). It remained in use until about 1100 BC. Hittite is the best attested member of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family, and the Indo-European language for which the earliest surviving written attestation exists, with isolated Hittite loanwords and numerous personal names appearing in an Old Assyrian context from as early as the 20th century BC.
The language of the Hattusa tablets was eventually deciphered by a Czech linguist, Bedřich Hrozný
Bedřich Hrozný (; 6 May 1879 – 12 December 1952), also known as , was a Czechs, Czech Oriental studies, orientalist and linguist. He contributed to the decipherment of the ancient Hittite language, identified it as an Indo-European language, ...
(1879–1952), who, on 24 November 1915, announced his results in a lecture at the Near Eastern Society of Berlin. His book about the discovery was printed in Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Ge ...
in 1917, under the title ''The Language of the Hittites; Its Structure and Its Membership in the Indo-European Linguistic Family''. The preface of the book begins with:
:"The present work undertakes to establish the nature and structure of the hitherto mysterious language of the Hittites, and to decipher this language ..It will be shown that Hittite is in the main an Indo-European language."
The decipherment famously led to the confirmation of the laryngeal theory
The laryngeal theory is a theory in historical linguistics positing that the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) language included a number of laryngeal consonants that are not linguistic reconstruction, reconstructable by direct application of the com ...
in Indo-European linguistics, which had been predicted several decades before. Due to its marked differences in its structure and phonology, some early philologists
Philology () is the study of language in Oral tradition, oral and writing, written historical sources. It is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics with strong ties to etymology. Philology is also de ...
, most notably Warren Cowgill
Warren Crawford Cowgill ( ; December 19, 1929 – June 20, 1985) was an American linguist. He was a professor of linguistics at Yale University and the Encyclopædia Britannica's authority on Indo-European linguistics. Two separate Indo-Europea ...
, had even argued that it should be classified as a sister language to Indo-European languages (Indo-Hittite
In Indo-European linguistics, the term Indo-Hittite (also Indo-Anatolian) refers to Edgar Howard Sturtevant's 1926 hypothesis that the Anatolian languages split off a Pre-Proto-Indo-European language considerably earlier than the separation o ...
), rather than a daughter language. By the end of the Hittite Empire, the Hittite language had become a written language of administration and diplomatic correspondence. The population of most of the Hittite Empire by this time spoke Luwian, another Indo-European language of the Anatolian family that had originated to the west of the Hittite region.
According to Craig Melchert
Harold Craig Melchert (born April 5, 1945) is an American linguist known particularly for his work on the Anatolian branch of Indo-European.
Biography
He received his B.A. in German from Michigan State University in 1967 and his Ph.D. in Lingui ...
, the current tendency is to suppose that Proto-Indo-European evolved, and that the "prehistoric speakers" of Anatolian became isolated "from the rest of the PIE speech community, so as not to share in some common innovations." Hittite, as well as its Anatolian cousins, split off from Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Euro ...
at an early stage, thereby preserving archaisms that were later lost in the other Indo-European languages.
In Hittite there are many loanwords, particularly religious vocabulary, from the non-Indo-European Hurrian
The Hurrians (; ; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri) were a people who inhabited the Ancient Near East during the Bronze Age. They spoke the Hurro-Urartian language, Hurrian language, and lived throughout northern Syria (region) ...
and Hattic languages. The latter was the language of the Hattians, the local inhabitants of the land of Hatti before being absorbed or displaced by the Hittites. Sacred and magical texts from Hattusa were often written in Hattic, Hurrian, and Luwian, even after Hittite became the norm for other writings.
Art
 Given the size of the empire, there are relatively few remains of Hittite art. These include some impressive monumental carvings, a number of
Given the size of the empire, there are relatively few remains of Hittite art. These include some impressive monumental carvings, a number of rock relief
A rock relief or rock-cut relief is a relief, relief sculpture carved on solid or "living rock" such as a cliff, rather than a detached piece of stone. They are a category of rock art, and sometimes found as part of, or in conjunction ...
s, as well as metalwork, in particular the Alaca Höyük bronze standards Alaca () may refer to the following places in Turkey:
* Alaca, Çorum, a large district in Çorum Province
** Alaca Dam
* Alaca, Borçka, a village in Artvin Province
* Alaca, Beşiri, a village in Batman Province
* Alaca, Elâzığ, a village in E ...
, carved ivory, and ceramics, including the Hüseyindede vases. The Sphinx Gates of Alaca Höyük
Alacahöyük or Alaca Höyük (sometimes also spelled as ''Alacahüyük'', ''Euyuk'', or ''Evuk'') is the site of a Neolithic Age, Neolithic and Hittites, Hittite settlement and is an important archaeological site. It is situated near the villag ...
and Hattusa, with the monument at the spring of Eflatun Pınar
Eflatun Pınar (, ) is the name given to a spring, which rises up from the ground, and the stone-built pool monument built at the time of the Hittite Empire. The spring lies inside the Lake Beyşehir National Park, west of Konya, and drains int ...
, are among the largest constructed sculptures, along with a number of large recumbent lions, of which the ''Lion of Babylon'' statue at Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
is the largest, if it is indeed Hittite. Nearly all are notably worn. Rock reliefs include the Hanyeri relief
The Hanyeri relief (or ''Gezbeli relief'') is a Hittite rock relief near Hanyeri on the road from Tufanbeyli to Develi in Tufanbeyli district in Adana Province, about 80 km southeast of Kayseri, in Turkey. In Hittite times, the route over t ...
, and Hemite relief
The Hemite relief is a Hittite rock relief at Gökçedam (formerly ''Hemite'') in the central district of Osmaniye Province in Turkey, about 20 km northwest of the provincial capital of Osmaniye. Rock reliefs are a prominent aspect of Hittit ...
. The Niğde Stele
The Niğde Stele is a Neo-Hittite monument from the modern Turkish city of Niğde, which dates from the end of the 8th century BC.
Discovery
The stele was found on 24 September 1975 near the citadel of Niğde in the Çelebi Hüsamettin Bey Mo ...
from the end of the 8th century BC is a Luwian monument, from the Post-Hittite period, found in the modern Turkish city of Niğde
Niğde (; ; Hittite: Nahita, Naxita) is a city and is located in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey. It is the seat of Niğde Province and Niğde District.
Hittite religion and mythology were heavily influenced by their Hattic,
 While different translations of laws can be seen throughout the history of the empire, the Hittite outlook of law was originally founded on religion and were intended to preserve the authority of the state. Additionally, punishments had the goal of crime prevention and the protection of individual property rights. The goals of crime prevention can be seen in the severity of the punishments issued for certain crimes. Capital punishment and torture are specifically mentioned as punishment for more severe crimes against religion and harsh fines for the loss of private property or life. The tablets also describe the ability of the king to pardon certain crimes, but specifically prohibit an individual being pardoned for murder.
At some point in the 16th or 15th century BC, Hittite law codes move away from torture and capital punishment and to more humanitarian forms of punishments, such as fines. Where the old law system was based on retaliation and retribution for crimes, the new system saw punishments that were much more mild, favoring monetary compensation over physical or capital punishment. Why these drastic reforms happened is not exactly clear, but it is likely that punishing murder with execution was deemed not to benefit any individual or family involved. These reforms were not just seen in the realm of capital punishment. Where major fines were to be paid, a severe reduction in penalty can be seen. For example, prior to these major reforms, the payment to be made for the theft of an animal was thirty times the animal's value; after the reforms, the penalty was reduced to half the original fine. Simultaneously, attempts to modernize the language and change the verbiage used in the law codes can be seen during this period of reform.
While different translations of laws can be seen throughout the history of the empire, the Hittite outlook of law was originally founded on religion and were intended to preserve the authority of the state. Additionally, punishments had the goal of crime prevention and the protection of individual property rights. The goals of crime prevention can be seen in the severity of the punishments issued for certain crimes. Capital punishment and torture are specifically mentioned as punishment for more severe crimes against religion and harsh fines for the loss of private property or life. The tablets also describe the ability of the king to pardon certain crimes, but specifically prohibit an individual being pardoned for murder.
At some point in the 16th or 15th century BC, Hittite law codes move away from torture and capital punishment and to more humanitarian forms of punishments, such as fines. Where the old law system was based on retaliation and retribution for crimes, the new system saw punishments that were much more mild, favoring monetary compensation over physical or capital punishment. Why these drastic reforms happened is not exactly clear, but it is likely that punishing murder with execution was deemed not to benefit any individual or family involved. These reforms were not just seen in the realm of capital punishment. Where major fines were to be paid, a severe reduction in penalty can be seen. For example, prior to these major reforms, the payment to be made for the theft of an animal was thirty times the animal's value; after the reforms, the penalty was reduced to half the original fine. Simultaneously, attempts to modernize the language and change the verbiage used in the law codes can be seen during this period of reform.
website
last updated on 29 May 2020. * * *
New research suggests drought accelerated Hittite Empire collapse - Phys.org February 8, 2023
* ttp://www.pbase.com/dosseman/bogazkale Pictures of Boğazköy, one of a group of important sites
Pictures of Yazılıkaya, one of a group of important sites
Tahsin Ozguc
Hittites.info
Hethitologieportal Mainz, by the Akademie der Wissenschaften, Mainz, corpus of texts and extensive bibliographies on all things Hittite
*
Map of Hittite Anatolia
{{Authority control States and territories established in the 17th century BC States and territories disestablished in the 12th century BC Ancient peoples of Anatolia Ancient Syria History of the Mediterranean Former kingdoms Former empires
Mesopotamian
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary o ...
, Canaanite, and Hurrian
The Hurrians (; ; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri) were a people who inhabited the Ancient Near East during the Bronze Age. They spoke the Hurro-Urartian language, Hurrian language, and lived throughout northern Syria (region) ...
counterparts. In earlier times, Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
elements may still be clearly discerned.
Storm gods
A weather god or goddess, also frequently known as a storm god or goddess, is a deity in mythology associated with weather phenomena such as thunder, snow, lightning, rain, wind, storms, tornadoes, and hurricanes. Should they only be in charge of ...
were prominent in the Hittite pantheon. Tarhunt (Hurrian
The Hurrians (; ; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri) were a people who inhabited the Ancient Near East during the Bronze Age. They spoke the Hurro-Urartian language, Hurrian language, and lived throughout northern Syria (region) ...
's Teshub) was referred to as 'The Conqueror', 'The king of Kummiya', 'King of Heaven', 'Lord of the land of Hatti'. He was chief among the gods and his symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
is the bull. As Teshub he was depicted as a bearded man astride two mountains and bearing a club. He was the god of battle and victory, especially when the conflict involved a foreign power. Teshub was also known for his conflict with the serpent Illuyanka
In Hittite mythology, Illuyanka was a serpentine dragon slain by Tarḫunz (), the Hittite incarnation of the Hurrian god of sky and storm. It is known from Hittite cuneiform tablets found at Çorum-Boğazköy, the former Hittite capital Hat ...
.
The Hittite gods are also honoured with festivals, such as Puruli
Puruli () was a Hattian spring festival, held at Nerik, dedicated to the earth goddess Hannahanna, who is married to a new king.
The central ritual of the Puruli festival is dedicated to the destruction of the dragon Illuyanka by the storm god ...
in the spring, the ''nuntarriyashas'' festival in the autumn, and the KI.LAM festival of the gate house where images of the Storm God and up to thirty other idols were paraded through the streets.
Law
Hittite laws, much like other records of the empire, are recorded oncuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
tablets made from baked clay. What is understood to be the Hittite Law Code comes mainly from two clay tablets, each containing 186 articles, and are a collection of practiced laws from across the early Hittite Kingdom. In addition to the tablets, monuments bearing Hittite cuneiform inscriptions can be found in central Anatolia describing the government and law codes of the empire. The tablets and monuments date from the Old Hittite Kingdom (1650–1500 BC) to what is known as the New Hittite Kingdom (1500–1180 BC). Between these time periods, different translations can be found that modernize the language and create a series of legal reforms in which many crimes are given more humane punishments. These changes could possibly be attributed to the rise of new and different kings throughout the history empire or to the new translations that change the language used in the law codes. In either case, the law codes of the Hittites provide very specific fines or punishments that are to be issued for specific crimes and have many similarities to Biblical laws found in the books of Exodus and Deuteronomy
Deuteronomy (; ) is the fifth book of the Torah (in Judaism), where it is called () which makes it the fifth book of the Hebrew Bible and Christian Old Testament.
Chapters 1–30 of the book consist of three sermons or speeches delivered to ...
. In addition to criminal punishments, the law codes also provide instruction on certain situations such as inheritance and death.
Use of laws
The law articles used by the Hittites most often outline very specific crimes or offenses, either against the state or against other individuals, and provide a sentence for these offenses. The laws carved in the tablets are an assembly of established social conventions from across the empire. Hittite laws at this time have a prominent lack of equality in punishments in many cases, distinct punishments or compensations for men and women are listed. Free men most often received more compensation for offenses against them than free women did. Slaves, male or female, had very few rights, and could easily be punished or executed by their masters for crimes. Most articles describe destruction of property and personal injury, to which the most common sentence was payment for compensation of the lost property. Again, in these cases men oftentimes receive a greater amount of compensation than women. Other articles describe how marriage of slaves and free individuals should be handled. In any case of separation or estrangement, the free individual, male or female, would keep all but one child that resulted from the marriage. Cases in which capital punishment is recommended in the articles most often seem to come from pre-reform sentences for severe crimes and prohibited sexual pairings. Many of these cases include public torture and execution as punishment for serious crimes against religion. Most of these sentences would begin to go away in the later stages of the Hittite Empire as major law reforms began to occur.Law reform
 While different translations of laws can be seen throughout the history of the empire, the Hittite outlook of law was originally founded on religion and were intended to preserve the authority of the state. Additionally, punishments had the goal of crime prevention and the protection of individual property rights. The goals of crime prevention can be seen in the severity of the punishments issued for certain crimes. Capital punishment and torture are specifically mentioned as punishment for more severe crimes against religion and harsh fines for the loss of private property or life. The tablets also describe the ability of the king to pardon certain crimes, but specifically prohibit an individual being pardoned for murder.
At some point in the 16th or 15th century BC, Hittite law codes move away from torture and capital punishment and to more humanitarian forms of punishments, such as fines. Where the old law system was based on retaliation and retribution for crimes, the new system saw punishments that were much more mild, favoring monetary compensation over physical or capital punishment. Why these drastic reforms happened is not exactly clear, but it is likely that punishing murder with execution was deemed not to benefit any individual or family involved. These reforms were not just seen in the realm of capital punishment. Where major fines were to be paid, a severe reduction in penalty can be seen. For example, prior to these major reforms, the payment to be made for the theft of an animal was thirty times the animal's value; after the reforms, the penalty was reduced to half the original fine. Simultaneously, attempts to modernize the language and change the verbiage used in the law codes can be seen during this period of reform.
While different translations of laws can be seen throughout the history of the empire, the Hittite outlook of law was originally founded on religion and were intended to preserve the authority of the state. Additionally, punishments had the goal of crime prevention and the protection of individual property rights. The goals of crime prevention can be seen in the severity of the punishments issued for certain crimes. Capital punishment and torture are specifically mentioned as punishment for more severe crimes against religion and harsh fines for the loss of private property or life. The tablets also describe the ability of the king to pardon certain crimes, but specifically prohibit an individual being pardoned for murder.
At some point in the 16th or 15th century BC, Hittite law codes move away from torture and capital punishment and to more humanitarian forms of punishments, such as fines. Where the old law system was based on retaliation and retribution for crimes, the new system saw punishments that were much more mild, favoring monetary compensation over physical or capital punishment. Why these drastic reforms happened is not exactly clear, but it is likely that punishing murder with execution was deemed not to benefit any individual or family involved. These reforms were not just seen in the realm of capital punishment. Where major fines were to be paid, a severe reduction in penalty can be seen. For example, prior to these major reforms, the payment to be made for the theft of an animal was thirty times the animal's value; after the reforms, the penalty was reduced to half the original fine. Simultaneously, attempts to modernize the language and change the verbiage used in the law codes can be seen during this period of reform.
Examples of laws
Under both the old and reformed Hittite law codes, three main types of punishment can be seen: Death, torture, or compensation/fines. The articles outlined on the cuneiform tablets provide very specific punishments for crimes committed against the Hittite religion or against individuals. In many, but not all cases, articles describing similar laws are grouped together. More than a dozen consecutive articles describe what are known to be permitted and prohibited sexual pairings. These pairings mostly describe men (sometimes specifically referred to as free men, sometimes just men in general) having relations, be they consensual or not, with animals, step-family, relatives of spouses, or concubines. Many of these articles do not provide specific punishments but, prior to the law reforms, crimes against religion were most often punishable by death. These include incestuous marriages and sexual relations with certain animals. For example, one article states, "If a man has sexual relations with a cow, it is an unpermitted sexual pairing: he will be put to death." Similar relations with horses and mules were not subject to capital punishment, but the offender could not become a priest afterwards. Actions at the expense of other individuals most often see the offender paying some sort of compensation, be it in the form money, animals, or land. These actions could include the destruction of farmlands, death or injury of livestock, or assault of an individual. Several articles also specifically mention acts of the gods. If an animal were to die by certain circumstances, the individual could claim that it died by the hand of a god. Swearing that what they claim was true, it seems that they were exempt from paying compensation to the animal's owner. Injuries inflicted upon animals owned by another individual are almost always compensated with either direct payment, or trading the injured animal with a healthy one owned by the offender. Not all laws prescribed in the tablets deal with criminal punishment. For example, the instructions of how the marriage of slaves and division of their children are given in a group of articles, "The slave woman shall take most of the children, with the male slave taking one child." Similar instructions are given to the marriage of free individuals and slaves. Other actions include how breaking of engagements are to be handled.Biblical Hittites
The Bible refers to people as "Hittites" in several passages. The relationship between these peoples and the Bronze Age Hittite Empire is unclear. In some passages, the Biblical Hittites appear to have their own kingdoms, apparently located outside geographic Canaan, and were powerful enough to defeat Syrian armies in battle. In these passages, the Biblical Hittites appear to refer to the Iron AgeSyro-Hittite states
The states called Neo-Hittite, Syro-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works) were Luwian and Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwestern parts of ...
. However, in most of their appearances, the Biblical Hittites are depicted as a people living among the IsraelitesAbraham purchases the Patriarchal burial-plot of Machpelah from Ephron the Hittite Ephron is a Jewish surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Ephron (biblical figure), Hittite who sold a cave to Abraham according to the Bible
*A family of American writers:
** Henry Ephron (1911–1992), father
** Phoebe Ephron (1914 ...
and Hittites serve as high military officers in David
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament.
The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Dam ...
's army. The nature of this ethnic group is unclear, but has sometimes been interpreted as a local Canaanite tribe who had absorbed Hittite cultural influence from the Syro-Hittite kingdoms to the north.
Other biblical scholars (following Max Müller
Friedrich Max Müller (; 6 December 1823 – 28 October 1900) was a German-born British comparative philologist and oriental studies, Orientalist. He was one of the founders of the Western academic disciplines of Indology and religious s ...
) have argued that the Bronze Age Hittites appear in Hebrew Bible literature and apocrypha as "Kittim
Kittim was a settlement in present-day Larnaca on the east coast of Cyprus, known in ancient times as Kition, or (in Latin) Citium. On this basis, the whole island became known as "Kittim" in Hebrew, including the Hebrew Bible. However the name s ...
", a people said to be named for a son of Javan
Javan () was the fourth son of Noah's son Japheth according to the "Generations of Noah" (Book of Genesis, chapter 10) in the Hebrew Bible. Josephus states the traditional belief that this individual was the ancestor of the Greeks.
Also servi ...
.
In ancient Greek mythology
One single mention of a Trojan ally named ''Keteians'' () is made byHomer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
in the Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; ) is one of two major epics of ancient Greek literature attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest surviving works of literature and remains popular with modern audiences. Like the ''Iliad'', the ''Odyssey'' is divi ...
. Some scholars have proposed that the Homeric Keteians correspond to the Bronze Age Hittites.
See also
*Hittite plague
The Hittite Plague or Hand of Nergal was an epidemic, possibly of tularemia, which occurred in the mid-to-late 14th century BC.
Background
The Hittite Empire stretched from Turkey to Syria. The plague was likely an outbreak of ''Francisella tu ...
* List of Hittite kings
The dating and sequence of Hittite Empire, Hittite kings is compiled by scholars from fragmentary records, supplemented by the finds in Hattusa, Ḫattuša and other administrative centers of cuneiform tablets and more than 3,500 seal impressions ...
* List of artifacts significant to the Bible
The following is a list of inscribed Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, items made or given shape by humans, that are significant to biblical archaeology.
Selected artifacts significant to biblical chronology
This table lists inscriptions which ...
* Short chronology timeline
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Com ...
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Listed as "to appear" on hiwebsite
last updated on 29 May 2020. * * *
Studien zu den Bogazkoy-Texten Studien zu den Bogazköy-Texten (abbreviated StBoT; lit. Studies in the Bogazköy (Hattusa) Texts) edited by the German ''Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur'' (Academy of Sciences and Literature), Mainz, since 1965, is a series of editio ...
18.
*
*
*
* Studien zu den Bogazkoy-Texten Studien zu den Bogazköy-Texten (abbreviated StBoT; lit. Studies in the Bogazköy (Hattusa) Texts) edited by the German ''Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur'' (Academy of Sciences and Literature), Mainz, since 1965, is a series of editio ...
49.
*
*
*
Further reading
* * Jacques Freu et Michel Mazoyer, Des origines à la fin de l'ancien royaume hittite, Les Hittites et leur histoire Tome 1, Collection Kubaba, L'Harmattan, Paris, 2007 * Jacques Freu et Michel Mazoyer, Les débuts du nouvel empire hittite, Les Hittites et leur histoire Tome 2, Collection Kubaba, L'Harmattan, Paris, 2007 * Jacques Freu et Michel Mazoyer, L'apogée du nouvel empire hittite, Les Hittites et leur histoire Tome 3, Collection Kubaba, L'Harmattan, Paris, 2008 * Jacques Freu et Michel Mazoyer, Le déclin et la chute de l'empire Hittite, Les Hittites et leur histoire Tome 4, Collection Kubaba, L'Harmattan, Paris, 2010 * Jacques Freu et Michel Mazoyer, Les royaumes Néo-Hittites, Les Hittites et leur histoire Tome 5, Collection Kubaba, L'Harmattan, Paris, 2012 * Imparati, Fiorella. "Aspects De L'organisation De L'État Hittite Dans Les Documents Juridiques Et Administratifs." Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient 25, no. 3 (1982): 225–67. * * Stone, Damien. The Hittites: Lost Civilizations. United Kingdom, Reaktion Books, 2023.External links
New research suggests drought accelerated Hittite Empire collapse - Phys.org February 8, 2023
* ttp://www.pbase.com/dosseman/bogazkale Pictures of Boğazköy, one of a group of important sites
Pictures of Yazılıkaya, one of a group of important sites
Tahsin Ozguc
Hittites.info
Hethitologieportal Mainz, by the Akademie der Wissenschaften, Mainz, corpus of texts and extensive bibliographies on all things Hittite
*
Map of Hittite Anatolia
{{Authority control States and territories established in the 17th century BC States and territories disestablished in the 12th century BC Ancient peoples of Anatolia Ancient Syria History of the Mediterranean Former kingdoms Former empires