naval gun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Naval artillery is
Naval artillery is
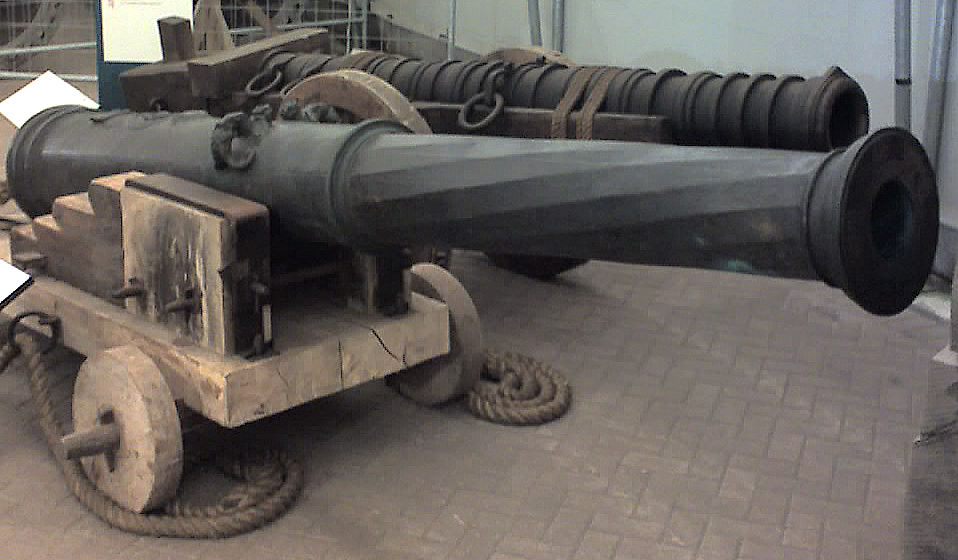 During rebuilding in 1536, ''Mary Rose'' had a second tier of carriage-mounted long guns fitted. Records show how the configuration of guns changed as gun-making technology evolved and new classifications were invented. In 1514, the armament consisted mostly of anti-personnel guns like the larger breech-loading iron ''murderers'' and the small ''serpentines'', ''demi-slings'' and stone guns. Only a handful of guns in the first inventory were powerful enough to hole enemy ships, and most would have been supported by the ship's structure rather than resting on carriages. The inventories of both the ''Mary Rose'' and the Tower had changed radically by 1540. There were now the new cast bronze ''cannons'', ''demi-cannons'', ''culverins'' and ''sakers'' and the wrought iron ''port pieces'' (a name that indicated they fired through ports), all of which required carriages, had longer range and were capable of doing serious damage to other ships.
Various types of ammunition could be used for different purposes: plain spherical shot of stone or iron smashed hulls, spiked bar shot and shot linked with chains would tear sails or damage rigging, and
During rebuilding in 1536, ''Mary Rose'' had a second tier of carriage-mounted long guns fitted. Records show how the configuration of guns changed as gun-making technology evolved and new classifications were invented. In 1514, the armament consisted mostly of anti-personnel guns like the larger breech-loading iron ''murderers'' and the small ''serpentines'', ''demi-slings'' and stone guns. Only a handful of guns in the first inventory were powerful enough to hole enemy ships, and most would have been supported by the ship's structure rather than resting on carriages. The inventories of both the ''Mary Rose'' and the Tower had changed radically by 1540. There were now the new cast bronze ''cannons'', ''demi-cannons'', ''culverins'' and ''sakers'' and the wrought iron ''port pieces'' (a name that indicated they fired through ports), all of which required carriages, had longer range and were capable of doing serious damage to other ships.
Various types of ammunition could be used for different purposes: plain spherical shot of stone or iron smashed hulls, spiked bar shot and shot linked with chains would tear sails or damage rigging, and
 Firing a naval cannon required a great amount of labour and manpower. The propellant was gunpowder, whose bulk had to be kept in a special storage area below deck for safety. ''Powder boys''- sometimes called Powder Monkeys- typically 10–14 years old, were enlisted to run powder from the armoury up to the gun decks of a vessel as required.
A typical firing procedure follows. A wet swab was used to mop out the interior of the barrel, extinguishing any embers from a previous firing which might set off the next charge of gunpowder prematurely.
Firing a naval cannon required a great amount of labour and manpower. The propellant was gunpowder, whose bulk had to be kept in a special storage area below deck for safety. ''Powder boys''- sometimes called Powder Monkeys- typically 10–14 years old, were enlisted to run powder from the armoury up to the gun decks of a vessel as required.
A typical firing procedure follows. A wet swab was used to mop out the interior of the barrel, extinguishing any embers from a previous firing which might set off the next charge of gunpowder prematurely.  The earlier method of firing a cannon was to apply a
The earlier method of firing a cannon was to apply a
 The muzzle-loading design and weight of the iron placed design constraints on the length and size of naval guns. Muzzle loading required the cannon muzzle to be positioned within the hull of the ship for loading. The hull is only so wide, with guns on both sides, and hatchways in the centre of the deck also limit the room available. Weight is always a great concern in ship design as it affects speed, stability, and buoyancy. The desire for longer guns for greater range and accuracy, and greater weight of shot for more destructive power, led to some interesting gun designs.
One unique naval gun was the long nine. It was a proportionately longer-barrelled 9-pounder. Its typical mounting as a bow or stern chaser, where it was not perpendicular to the keel, allowed room to operate this longer weapon. In a chase situation, the gun's greater range came into play. However, the desire to reduce weight in the ends of the ship and the relative fragility of the bow and stern portions of the hull limited this role to a 9-pounder, rather than one which used a 12 or 24 pound shot.
In the reign of Queen Elizabeth advances in manufacturing technology allowed the English Navy Royal to start using matched cannon firing standard ammunition,BBC: 'Superguns' of Elizabeth I's navy.
The muzzle-loading design and weight of the iron placed design constraints on the length and size of naval guns. Muzzle loading required the cannon muzzle to be positioned within the hull of the ship for loading. The hull is only so wide, with guns on both sides, and hatchways in the centre of the deck also limit the room available. Weight is always a great concern in ship design as it affects speed, stability, and buoyancy. The desire for longer guns for greater range and accuracy, and greater weight of shot for more destructive power, led to some interesting gun designs.
One unique naval gun was the long nine. It was a proportionately longer-barrelled 9-pounder. Its typical mounting as a bow or stern chaser, where it was not perpendicular to the keel, allowed room to operate this longer weapon. In a chase situation, the gun's greater range came into play. However, the desire to reduce weight in the ends of the ship and the relative fragility of the bow and stern portions of the hull limited this role to a 9-pounder, rather than one which used a 12 or 24 pound shot.
In the reign of Queen Elizabeth advances in manufacturing technology allowed the English Navy Royal to start using matched cannon firing standard ammunition,BBC: 'Superguns' of Elizabeth I's navy.
The wreck of an English full-rigged pinnace dating from around 1592 with 12 matched guns was discovered, and guns were recovered in 2009 allowing firing of coordinated broadsides (although that was more of a matter of improved training and discipline than of matched guns). Different types of shot were employed for various situations. Standard fare was the
New Principles in Gunnery
' (1742), which contains a description of his ballistic pendulum (see
Marshall's Practical Marine Gunnery
' in 1822. The book discusses the dimensions and apparatus necessary for the equipment of naval artillery. The book goes into further details regarding the distance of a shot on a ship based on the sound of the gun, which was found to fly at a rate of 1,142 feet or 381 yards in one second. According to Marshall's equation after seeing the flash of a cannon and hearing the blast the gunner would count the seconds until impact. This way a trained ear would know the distance a cannonball traveled and might gain information or return fire. The book example, outlines a 9-second scenario where the distance the cannon was fired from the gunner was approximately 10,278 feet or 3,426 yards.
 Explosive shell (projectile), shells had long been in use in ground warfare (in howitzers and mortars), but they were only fired at high angles and with relatively low velocities. Shells are inherently dangerous to handle, and no solution had been found to combine the explosive character of the shells with the high power and flatter trajectory of a high velocity gun.
However, high trajectories were not practical for marine combat and naval combat essentially required flat-trajectory guns in order to have some decent odds of hitting the target. Therefore, naval warfare had consisted for centuries of encounters between flat-trajectory cannon using inert cannonballs, which could inflict only local damage even on wooden hulls.
The first naval gun designed to fire explosive shells was the Paixhans gun, developed by the French general Henri-Joseph Paixhans in 1822–1823. He advocated using flat-trajectory shell guns against warships in 1822 in his ''Nouvelle force maritime et artillerie'', and developed a delaying mechanism which, for the first time, allowed shells to be fired safely in high-powered flat-trajectory guns. The effect of explosive shells lodging into wooden hulls and then detonating was potentially devastating. This was first demonstrated by Henri-Joseph Paixhans in trials against the two-decker French ship Pacificateur (1811), ''Pacificateur'' in 1824, in which he successfully broke up the ship. Two prototype Paixhans guns had been cast in 1823 and 1824 for this test. Paixhans reported the results in ''Experiences faites sur une arme nouvelle''. The shells were equipped with a fuse which ignited automatically when the gun was fired. The shell would then lodge itself in the wooden hull of the target before exploding a moment later.
The first Paixhans guns for the
Explosive shell (projectile), shells had long been in use in ground warfare (in howitzers and mortars), but they were only fired at high angles and with relatively low velocities. Shells are inherently dangerous to handle, and no solution had been found to combine the explosive character of the shells with the high power and flatter trajectory of a high velocity gun.
However, high trajectories were not practical for marine combat and naval combat essentially required flat-trajectory guns in order to have some decent odds of hitting the target. Therefore, naval warfare had consisted for centuries of encounters between flat-trajectory cannon using inert cannonballs, which could inflict only local damage even on wooden hulls.
The first naval gun designed to fire explosive shells was the Paixhans gun, developed by the French general Henri-Joseph Paixhans in 1822–1823. He advocated using flat-trajectory shell guns against warships in 1822 in his ''Nouvelle force maritime et artillerie'', and developed a delaying mechanism which, for the first time, allowed shells to be fired safely in high-powered flat-trajectory guns. The effect of explosive shells lodging into wooden hulls and then detonating was potentially devastating. This was first demonstrated by Henri-Joseph Paixhans in trials against the two-decker French ship Pacificateur (1811), ''Pacificateur'' in 1824, in which he successfully broke up the ship. Two prototype Paixhans guns had been cast in 1823 and 1824 for this test. Paixhans reported the results in ''Experiences faites sur une arme nouvelle''. The shells were equipped with a fuse which ignited automatically when the gun was fired. The shell would then lodge itself in the wooden hull of the target before exploding a moment later.
The first Paixhans guns for the
 William Armstrong, 1st Baron Armstrong, William Armstrong was awarded a contract by the British government in the 1850s to design a revolutionary new piece of artillery—the Armstrong Gun—produced at the Elswick Ordnance Company. This marked the birth of modern artillery both on land and at sea. The piece was rifled, which allowed for a much more accurate and powerful action. The necessary machinery to accurately rifle artillery was only available by the mid-19th century. The cast iron shell fired by the Armstrong gun was similar in shape to a Minié ball and had a thin lead coating which made it fractionally larger than the gun's bore and which engaged with the gun's rifling grooves to impart spin to the shell. This spin, together with the elimination of British ordnance terms#Windage, windage as a result of the tight fit, enabled the gun to achieve greater range and accuracy than existing smooth-bore muzzle-loaders with a smaller powder charge.
His gun was also a breech-loader. Although attempts at breech-loading mechanisms had been made since medieval times, the essential engineering problem was that the mechanism couldn't withstand the explosive charge. It was only with the advances in metallurgy and precision engineering capabilities during the Industrial Revolution that Armstrong was able to construct a viable solution. The gun combined all the properties that make up an effective artillery piece. The gun was mounted on a carriage in such a way as to return the gun to firing position after the recoil.
William Armstrong, 1st Baron Armstrong, William Armstrong was awarded a contract by the British government in the 1850s to design a revolutionary new piece of artillery—the Armstrong Gun—produced at the Elswick Ordnance Company. This marked the birth of modern artillery both on land and at sea. The piece was rifled, which allowed for a much more accurate and powerful action. The necessary machinery to accurately rifle artillery was only available by the mid-19th century. The cast iron shell fired by the Armstrong gun was similar in shape to a Minié ball and had a thin lead coating which made it fractionally larger than the gun's bore and which engaged with the gun's rifling grooves to impart spin to the shell. This spin, together with the elimination of British ordnance terms#Windage, windage as a result of the tight fit, enabled the gun to achieve greater range and accuracy than existing smooth-bore muzzle-loaders with a smaller powder charge.
His gun was also a breech-loader. Although attempts at breech-loading mechanisms had been made since medieval times, the essential engineering problem was that the mechanism couldn't withstand the explosive charge. It was only with the advances in metallurgy and precision engineering capabilities during the Industrial Revolution that Armstrong was able to construct a viable solution. The gun combined all the properties that make up an effective artillery piece. The gun was mounted on a carriage in such a way as to return the gun to firing position after the recoil.
 What made the gun really revolutionary lay in the technique of the construction of the gun barrel that allowed it to withstand much more powerful explosive forces. The "built-up gun, built-up" method involved assembling the barrel with wrought-iron (later mild steel was used) tubes of successively larger diameter. The next tube would be heated to allow it to expand and fit over the previous tube. When it cooled the tube would contract to a slightly smaller diameter, which allowed an even pressure along the walls of the gun which was directed inward against the outward forces that the gun firing exerted on the barrel. Built-up guns with rifling made cast cannon obsolete by 1880.
Armstrong's system was adopted in 1858, initially for "special service in the field" and initially he only produced smaller artillery pieces, 6-pounder (2.5 in/64 mm) mountain or light field guns, 9-pounder (3 in/76 mm) guns for horse artillery, and RBL 12 pounder 8 cwt Armstrong gun, 12-pounder (3 inches /76 mm) field guns.
However, despite the gun's advantages, an 1863 Ammunition, Ordnance Select committee (United Kingdom), Select committee decided to revert to muzzle-loading artillery pieces on the grounds of cost and efficiency.
Large-caliber Breech-loading weapon, breech-loading naval artillery became practical with French development of the interrupted screw Obturating ring, obturator by Charles Ragon de Bange in 1872. It was only after a serious accident on board in 1879 when the left muzzleloading gun in the forward turret exploded during practice firing in the Sea of Marmora killing 11 and injuring a further 35, that the Royal Navy decisively changed to breech loading guns. Improved loading and handling procedures were also adopted, and Thunderer herself was re-equipped with long-calibre 10" breech-loaders. Breech loading artillery overcame barrel length limitations of cast cannon imposed by the necessity of retracting the cannon into the hull for reloading through the muzzle. Simultaneous availability of longer barrels and slower burning brown powder increased projectile velocities to . Spin-stabilized elongated projectiles offered both reliable positioning of percussion fuzes and improved armor penetration through increased sectional density.
What made the gun really revolutionary lay in the technique of the construction of the gun barrel that allowed it to withstand much more powerful explosive forces. The "built-up gun, built-up" method involved assembling the barrel with wrought-iron (later mild steel was used) tubes of successively larger diameter. The next tube would be heated to allow it to expand and fit over the previous tube. When it cooled the tube would contract to a slightly smaller diameter, which allowed an even pressure along the walls of the gun which was directed inward against the outward forces that the gun firing exerted on the barrel. Built-up guns with rifling made cast cannon obsolete by 1880.
Armstrong's system was adopted in 1858, initially for "special service in the field" and initially he only produced smaller artillery pieces, 6-pounder (2.5 in/64 mm) mountain or light field guns, 9-pounder (3 in/76 mm) guns for horse artillery, and RBL 12 pounder 8 cwt Armstrong gun, 12-pounder (3 inches /76 mm) field guns.
However, despite the gun's advantages, an 1863 Ammunition, Ordnance Select committee (United Kingdom), Select committee decided to revert to muzzle-loading artillery pieces on the grounds of cost and efficiency.
Large-caliber Breech-loading weapon, breech-loading naval artillery became practical with French development of the interrupted screw Obturating ring, obturator by Charles Ragon de Bange in 1872. It was only after a serious accident on board in 1879 when the left muzzleloading gun in the forward turret exploded during practice firing in the Sea of Marmora killing 11 and injuring a further 35, that the Royal Navy decisively changed to breech loading guns. Improved loading and handling procedures were also adopted, and Thunderer herself was re-equipped with long-calibre 10" breech-loaders. Breech loading artillery overcame barrel length limitations of cast cannon imposed by the necessity of retracting the cannon into the hull for reloading through the muzzle. Simultaneous availability of longer barrels and slower burning brown powder increased projectile velocities to . Spin-stabilized elongated projectiles offered both reliable positioning of percussion fuzes and improved armor penetration through increased sectional density.
 The gun turret was independently invented by the Swedish inventor John Ericsson in America, although his design was technologically inferior to Coles'.
Ericsson designed in 1861. Its most prominent feature was a large cylindrical gun turret mounted amidships above the low-freeboard upper Hull (watercraft), hull, also called the "raft". This extended well past the sides of the lower, more traditionally shaped hull. A small armored pilot house was fitted on the upper deck towards the bow, however, its position prevented ''Monitor'' from firing her guns straight forward. One of Ericsson's prime goals in designing the ship was to present the smallest possible target to enemy gunfire.
The turret's rounded shape helped to deflect cannon shot. A pair of donkey engines rotated the turret through a set of gears; a full rotation was made in 22.5 seconds during testing on 9 February 1862. Fine control of the turret proved to be difficult as the engine would have to be placed in reverse if the turret overshot its mark or another full rotation could be made. Including the guns, the turret weighed approximately ; the entire weight rested on an iron spindle that had to be jacked up using a wedge before the turret could rotate.
The spindle was in diameter, which gave it ten times the strength needed in preventing the turret from sliding sideways. When not in use, the turret rested on a brass ring on the deck that was intended to form a watertight seal. In service, however, this proved to leak heavily, despite caulking by the crew. The gap between the turret and the deck proved to be a problem as debris and shell fragments entered the gap and jammed the turrets of several s, which used the same turret design, during the First Battle of Charleston Harbor in April 1863. Direct hits at the turret with heavy shot also had the potential to bend the spindle, which could also jam the turret.
The gun turret was independently invented by the Swedish inventor John Ericsson in America, although his design was technologically inferior to Coles'.
Ericsson designed in 1861. Its most prominent feature was a large cylindrical gun turret mounted amidships above the low-freeboard upper Hull (watercraft), hull, also called the "raft". This extended well past the sides of the lower, more traditionally shaped hull. A small armored pilot house was fitted on the upper deck towards the bow, however, its position prevented ''Monitor'' from firing her guns straight forward. One of Ericsson's prime goals in designing the ship was to present the smallest possible target to enemy gunfire.
The turret's rounded shape helped to deflect cannon shot. A pair of donkey engines rotated the turret through a set of gears; a full rotation was made in 22.5 seconds during testing on 9 February 1862. Fine control of the turret proved to be difficult as the engine would have to be placed in reverse if the turret overshot its mark or another full rotation could be made. Including the guns, the turret weighed approximately ; the entire weight rested on an iron spindle that had to be jacked up using a wedge before the turret could rotate.
The spindle was in diameter, which gave it ten times the strength needed in preventing the turret from sliding sideways. When not in use, the turret rested on a brass ring on the deck that was intended to form a watertight seal. In service, however, this proved to leak heavily, despite caulking by the crew. The gap between the turret and the deck proved to be a problem as debris and shell fragments entered the gap and jammed the turrets of several s, which used the same turret design, during the First Battle of Charleston Harbor in April 1863. Direct hits at the turret with heavy shot also had the potential to bend the spindle, which could also jam the turret.
 The turret was intended to mount a pair of smoothbore Dahlgren guns, but they were not ready in time and guns were substituted. Each gun weighed approximately . ''Monitor''s guns used the standard propellant charge of specified by the 1860 ordnance for targets "distant", "near", and "ordinary", established by the gun's designer Dahlgren himself. They could fire a round shot or shell up to a range of at an elevation of +15°.
HMS ''Thunderer'' represented the culmination of this pioneering work. An ironclad warship, ironclad turret ship designed by Edward James Reed, it was equipped with revolving turrets that used pioneering hydraulic turret machinery to maneouvre the guns. It was also the world's first mastless battleship, built with a central superstructure layout, and became the prototype for all subsequent warships. of 1871 was another pivotal design, and led directly to the modern battleship.
The turret was intended to mount a pair of smoothbore Dahlgren guns, but they were not ready in time and guns were substituted. Each gun weighed approximately . ''Monitor''s guns used the standard propellant charge of specified by the 1860 ordnance for targets "distant", "near", and "ordinary", established by the gun's designer Dahlgren himself. They could fire a round shot or shell up to a range of at an elevation of +15°.
HMS ''Thunderer'' represented the culmination of this pioneering work. An ironclad warship, ironclad turret ship designed by Edward James Reed, it was equipped with revolving turrets that used pioneering hydraulic turret machinery to maneouvre the guns. It was also the world's first mastless battleship, built with a central superstructure layout, and became the prototype for all subsequent warships. of 1871 was another pivotal design, and led directly to the modern battleship.
 During the late 1850s, the development and implementation of the ironclad warship carried wrought iron armor of considerable thickness. This armor was practically immune to both the round cast-iron cannonballs then in use and to the recently developed Artillery shell, explosive shell.
The first solution to this problem was effected by William Palliser, Major Sir W. Palliser. His Palliser shot, approved in 1867, was made of cast iron, the head being chilled in casting to harden it, using composite molds with a metal, water cooled portion for the head. At times there were defects that led to cracking in the projectiles but these were overcome with time. Bronze studs were installed into the outside of the projectile so as to engage the rifling grooves in the gun barrel. The base had a hollow pocket but was not filled with powder or explosive: the cavity was necessitated by difficulties in Casting (metalworking), casting large solid projectiles without their cracking when they cooled, because the nose and base of the projectiles cooled at different rates, and in fact a larger cavity facilitated a better quality casting.
At the Battle of Angamos (8 October 1879) the Chilean ironclad warships fired twenty 250-pound-Palliser gunshots against the Peruvian monitor , with devastating results. It was the first time that such piercing shells were used in actual combat.
These chilled iron shots proved very effective against wrought iron armor, but were not serviceable against compound and steel armor, which was first introduced in the 1880s. A new departure therefore had to be made, and Forging, forged steel rounds with points Hardening (metallurgy), hardened by water took the place of the Palliser shot. At first, these forged-steel rounds were made of ordinary carbon steel, but as armor improved in quality, the projectiles followed suit.
From the 1890s onwards, Cementation process, cemented steel armor became commonplace, initially only on the thicker armor of warships. To combat this, the projectile was formed of steel—forged or cast—containing both nickel and chromium. Another change was the introduction of a soft metal cap over the point of the shell – so called "Makarov tips" invented by Russian admiral Stepan Makarov. This "cap" increased penetration by cushioning some of the impact shock and preventing the armor-piercing point from being damaged before it struck the armor face, or the body of the shell from shattering. It could also help penetration from an oblique angle by keeping the point from deflecting away from the armor face. (See: APCBC ammunition)
Increased armor penetration became possible when projectile velocities of were obtained as smokeless powder propellants replaced gunpowder around the turn of the 20th century.
During the late 1850s, the development and implementation of the ironclad warship carried wrought iron armor of considerable thickness. This armor was practically immune to both the round cast-iron cannonballs then in use and to the recently developed Artillery shell, explosive shell.
The first solution to this problem was effected by William Palliser, Major Sir W. Palliser. His Palliser shot, approved in 1867, was made of cast iron, the head being chilled in casting to harden it, using composite molds with a metal, water cooled portion for the head. At times there were defects that led to cracking in the projectiles but these were overcome with time. Bronze studs were installed into the outside of the projectile so as to engage the rifling grooves in the gun barrel. The base had a hollow pocket but was not filled with powder or explosive: the cavity was necessitated by difficulties in Casting (metalworking), casting large solid projectiles without their cracking when they cooled, because the nose and base of the projectiles cooled at different rates, and in fact a larger cavity facilitated a better quality casting.
At the Battle of Angamos (8 October 1879) the Chilean ironclad warships fired twenty 250-pound-Palliser gunshots against the Peruvian monitor , with devastating results. It was the first time that such piercing shells were used in actual combat.
These chilled iron shots proved very effective against wrought iron armor, but were not serviceable against compound and steel armor, which was first introduced in the 1880s. A new departure therefore had to be made, and Forging, forged steel rounds with points Hardening (metallurgy), hardened by water took the place of the Palliser shot. At first, these forged-steel rounds were made of ordinary carbon steel, but as armor improved in quality, the projectiles followed suit.
From the 1890s onwards, Cementation process, cemented steel armor became commonplace, initially only on the thicker armor of warships. To combat this, the projectile was formed of steel—forged or cast—containing both nickel and chromium. Another change was the introduction of a soft metal cap over the point of the shell – so called "Makarov tips" invented by Russian admiral Stepan Makarov. This "cap" increased penetration by cushioning some of the impact shock and preventing the armor-piercing point from being damaged before it struck the armor face, or the body of the shell from shattering. It could also help penetration from an oblique angle by keeping the point from deflecting away from the armor face. (See: APCBC ammunition)
Increased armor penetration became possible when projectile velocities of were obtained as smokeless powder propellants replaced gunpowder around the turn of the 20th century.
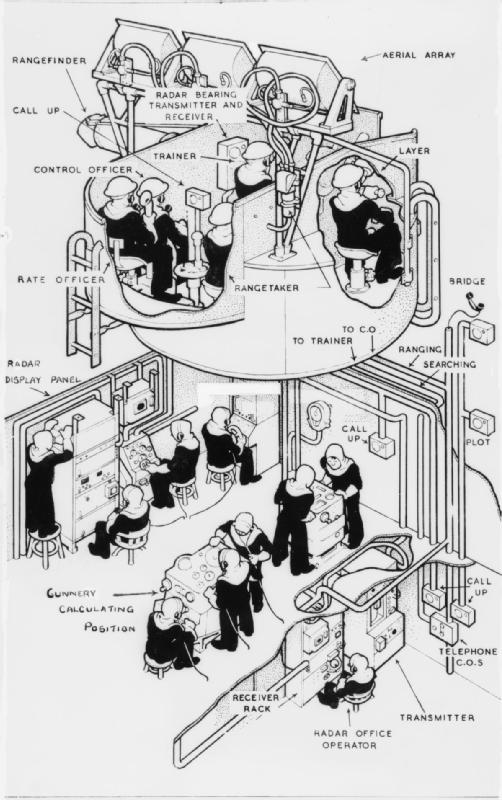 When gunnery ranges increased dramatically in the late 19th century, it was no longer a simple matter of calculating the proper aim point, given the flight times of the shells. Increasingly sophisticated analog computer, mechanical calculators were employed for proper Gun laying, gunlaying, typically with various spotters and distance measures being sent to a central plotting station deep within the ship. There the fire direction teams fed in the location, speed and direction of the ship and its target, as well as various adjustments for Coriolis effect, weather effects on the air, and other adjustments.
The resulting directions, known as a firing solution, would then be fed back out to the turrets for laying. If the rounds missed, an observer could work out how far they missed by and in which direction, and this information could be fed back into the computer along with any changes in the rest of the information and another shot attempted.
The situation for naval fire control was highly complex, due to the need to control the firing of several guns at once. In naval engagements both the firing guns and target are moving, and the variables are compounded by the greater distances and times involved. Rudimentary naval fire control systems were first developed around the time of World War I.
Arthur Pollen and Frederic Charles Dreyer independently developed the first such systems. Pollen began working on the problem after noting the poor accuracy of naval artillery at a gunnery practice near Malta in 1900. William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, Lord Kelvin, widely regarded as Britain's leading scientist, first proposed using an analogue computer to solve the equations which arise from the relative motion of the ships engaged in the battle and the time delay in the flight of the shell to calculate the required trajectory and therefore the direction and elevation of the guns.
Pollen aimed to produce a combined Calculating machine, mechanical computer and automatic plot of ranges and rates for use in centralised fire control. To obtain accurate data of the target's position and relative motion, Pollen developed a plotting unit (or plotter) to capture this data. He added a gyroscope to allow for the Yaw angle, yaw of the firing ship. Again this required substantial development of the, at the time, primitive gyroscope to provide continuous reliable correction. Trials were carried out in 1905 and 1906, which although completely unsuccessful showed promise. He was encouraged in his efforts by the rapidly rising figure of Admiral John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, Jackie Fisher, Admiral Arthur Knyvet Wilson and the Director of Naval Ordnance and Torpedoes (DNO), John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, John Jellicoe. Pollen continued his work, with tests carried out on Royal Navy warships intermittently.
Meanwhile, a group led by Dreyer designed a similar system. Although both systems were ordered for new and existing ships of the Royal Navy, the Dreyer system eventually found most favour with the Navy in its definitive Mark IV* form. The addition of director (military), director control facilitated a full, practicable fire control system for World War I ships, and most RN capital ships were so fitted by mid 1916. The director was high up over the ship where operators had a superior view over any gunlayer in the gun turret, turrets. It was also able to co-ordinate the fire of the turrets so that their combined fire worked together. This improved aiming and larger optical rangefinders improved the estimate of the enemy's position at the time of firing. The system was eventually replaced by the improved "Admiralty Fire Control Table" for ships built after 1927.
When gunnery ranges increased dramatically in the late 19th century, it was no longer a simple matter of calculating the proper aim point, given the flight times of the shells. Increasingly sophisticated analog computer, mechanical calculators were employed for proper Gun laying, gunlaying, typically with various spotters and distance measures being sent to a central plotting station deep within the ship. There the fire direction teams fed in the location, speed and direction of the ship and its target, as well as various adjustments for Coriolis effect, weather effects on the air, and other adjustments.
The resulting directions, known as a firing solution, would then be fed back out to the turrets for laying. If the rounds missed, an observer could work out how far they missed by and in which direction, and this information could be fed back into the computer along with any changes in the rest of the information and another shot attempted.
The situation for naval fire control was highly complex, due to the need to control the firing of several guns at once. In naval engagements both the firing guns and target are moving, and the variables are compounded by the greater distances and times involved. Rudimentary naval fire control systems were first developed around the time of World War I.
Arthur Pollen and Frederic Charles Dreyer independently developed the first such systems. Pollen began working on the problem after noting the poor accuracy of naval artillery at a gunnery practice near Malta in 1900. William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, Lord Kelvin, widely regarded as Britain's leading scientist, first proposed using an analogue computer to solve the equations which arise from the relative motion of the ships engaged in the battle and the time delay in the flight of the shell to calculate the required trajectory and therefore the direction and elevation of the guns.
Pollen aimed to produce a combined Calculating machine, mechanical computer and automatic plot of ranges and rates for use in centralised fire control. To obtain accurate data of the target's position and relative motion, Pollen developed a plotting unit (or plotter) to capture this data. He added a gyroscope to allow for the Yaw angle, yaw of the firing ship. Again this required substantial development of the, at the time, primitive gyroscope to provide continuous reliable correction. Trials were carried out in 1905 and 1906, which although completely unsuccessful showed promise. He was encouraged in his efforts by the rapidly rising figure of Admiral John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, Jackie Fisher, Admiral Arthur Knyvet Wilson and the Director of Naval Ordnance and Torpedoes (DNO), John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, John Jellicoe. Pollen continued his work, with tests carried out on Royal Navy warships intermittently.
Meanwhile, a group led by Dreyer designed a similar system. Although both systems were ordered for new and existing ships of the Royal Navy, the Dreyer system eventually found most favour with the Navy in its definitive Mark IV* form. The addition of director (military), director control facilitated a full, practicable fire control system for World War I ships, and most RN capital ships were so fitted by mid 1916. The director was high up over the ship where operators had a superior view over any gunlayer in the gun turret, turrets. It was also able to co-ordinate the fire of the turrets so that their combined fire worked together. This improved aiming and larger optical rangefinders improved the estimate of the enemy's position at the time of firing. The system was eventually replaced by the improved "Admiralty Fire Control Table" for ships built after 1927.
 Significant gunnery developments occurred in the late 1890s and the early 1900s, culminating with the launch of the revolutionary in 1906. Sir Percy Scott was given command of HMS ''Scylla'' in 1896, where he was able to implement his new theories on gunnery, scoring the unprecedented success of 80% during the 1897 gunnery trials. This was totally unprecedented, as the average in the Royal Navy was just 28%.
Scott noted that night time signalling between ships in the fleet was slow and inaccurate. He addressed this in two ways: he devised training aids and put his signallers under instruction and he devised a new more effective flashing lamp. The new efficiency of his ship's signalling was adopted by the whole Mediterranean fleet. He devised a new sub-calibre gun which involved fitting a one-inch-calibre rifled barrel inside the barrel of the main armament but which used the main gun's controls. He also came up with new sights employing telescope optics and new training targets. In the Navy's 1901 prize firing, ''Terrible'' achieved the same score of 80%, and Scott's gunnery practices were adopted by other ships in the fleet. Later, Scott taught at the naval gunnery school at Whale Island, Hampshire. a largely honorary role which he held until promotion to flag rank in 1905.
The development of the torpedo meant that it became necessary to engage an enemy at ranges outside torpedo range. This in turn meant that the old system whereby a gunlayer in each turret pointed and fired the turret guns independently could no longer be expected to achieve a significant hit rate on an opposing ship. Scott was instrumental in encouraging the development and installation of director firing, a system whereby the guns were all pointed, elevated and fired from a single point, usually at the top of the foremast. By firing all the guns simultaneously it was possible to observe the simultaneous splashes produced and correct the aim visually.
Significant gunnery developments occurred in the late 1890s and the early 1900s, culminating with the launch of the revolutionary in 1906. Sir Percy Scott was given command of HMS ''Scylla'' in 1896, where he was able to implement his new theories on gunnery, scoring the unprecedented success of 80% during the 1897 gunnery trials. This was totally unprecedented, as the average in the Royal Navy was just 28%.
Scott noted that night time signalling between ships in the fleet was slow and inaccurate. He addressed this in two ways: he devised training aids and put his signallers under instruction and he devised a new more effective flashing lamp. The new efficiency of his ship's signalling was adopted by the whole Mediterranean fleet. He devised a new sub-calibre gun which involved fitting a one-inch-calibre rifled barrel inside the barrel of the main armament but which used the main gun's controls. He also came up with new sights employing telescope optics and new training targets. In the Navy's 1901 prize firing, ''Terrible'' achieved the same score of 80%, and Scott's gunnery practices were adopted by other ships in the fleet. Later, Scott taught at the naval gunnery school at Whale Island, Hampshire. a largely honorary role which he held until promotion to flag rank in 1905.
The development of the torpedo meant that it became necessary to engage an enemy at ranges outside torpedo range. This in turn meant that the old system whereby a gunlayer in each turret pointed and fired the turret guns independently could no longer be expected to achieve a significant hit rate on an opposing ship. Scott was instrumental in encouraging the development and installation of director firing, a system whereby the guns were all pointed, elevated and fired from a single point, usually at the top of the foremast. By firing all the guns simultaneously it was possible to observe the simultaneous splashes produced and correct the aim visually.
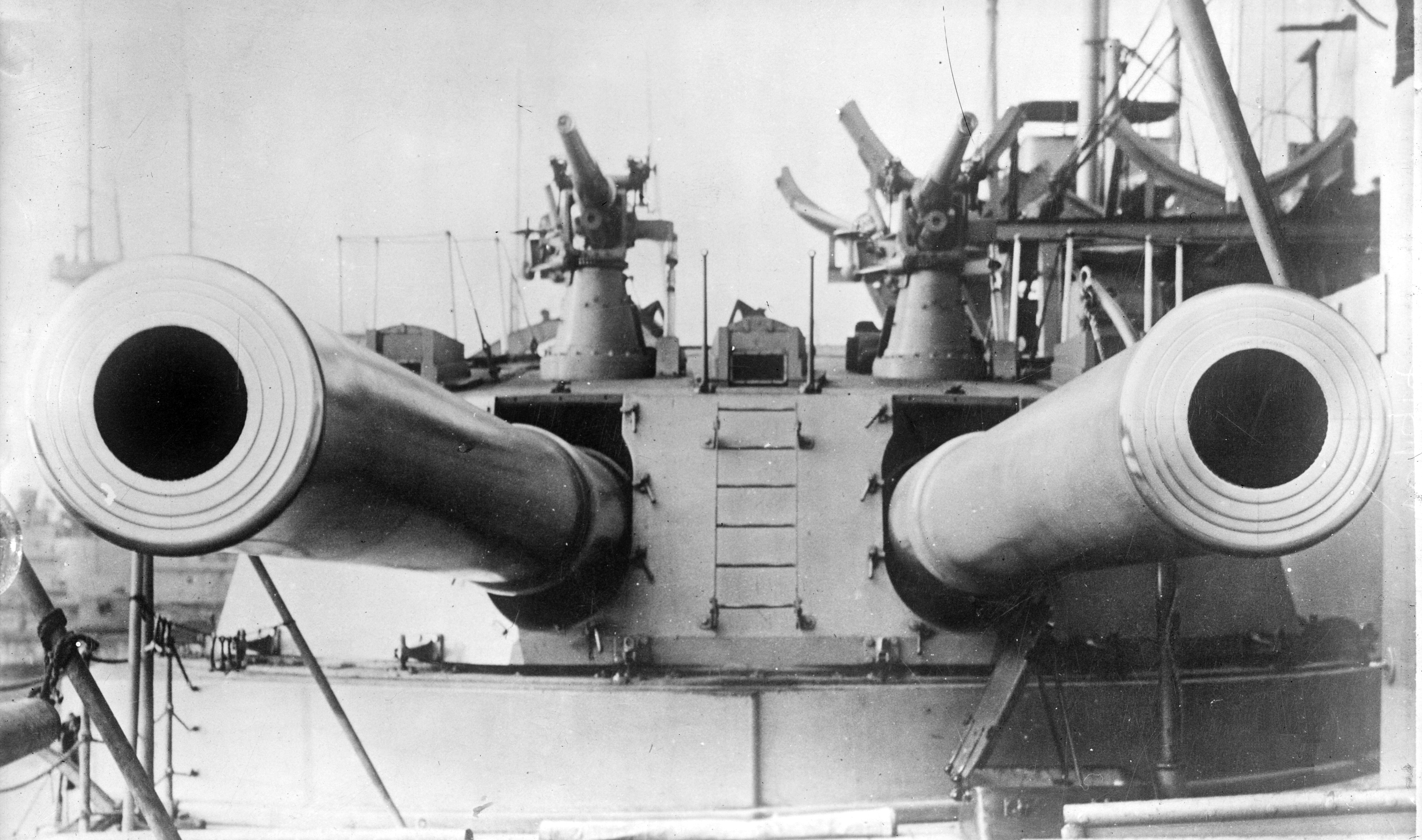 As battle ranges were pushed out to an unprecedented , the distance was great enough to force gunners to wait for the shells to arrive before applying corrections for the next salvo. A related problem was that the shell splashes from the more numerous smaller weapons tended to obscure the splashes from the bigger guns. Either the smaller-Caliber, calibre guns would have to hold their fire to wait for the slower-firing heavies, losing the advantage of their faster rate of fire, or it would be uncertain whether a splash was due to a heavy or a light gun, making ranging and aiming unreliable. Italian naval architect Vittorio Cuniberti first argued for the concept of an all-big-gun battleship in 1903, proposing an "ideal" future British battleship of , with a main battery of a dozen 12-inch guns in eight turrets, 12 inches of belt armour, and a speed of .
First Sea Lord John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, Sir John Fisher pushed through the Board of Admiralty a decision to arm the next battleship with 12-inch guns and that it would have a speed no less than . The result was HMS ''Dreadnought'', which rendered all previous ships immediately obsolete on its launch in 1906. The ship mounted the 45-caliber (artillery), calibre BL 12 inch Mk X naval gun, BL 12-inch Mark X gun in five twin gun turrets. These could deliver a broadside of a maximum of eight guns and could be elevated up to +13.5°. They fired projectiles at a muzzle velocity of ; at 13.5°, this provided a maximum range of with Armor-piercing shot and shell, armour-piercing (AP) 2 List of British ordnance terms#C.R.H., crh shells. At 16° elevation, the range was extended to using the more aerodynamic, but slightly heavier 4 crh AP shells. The rate of fire of these guns was one to two rounds per minute. The ships carried 80 rounds per gun.
As battle ranges were pushed out to an unprecedented , the distance was great enough to force gunners to wait for the shells to arrive before applying corrections for the next salvo. A related problem was that the shell splashes from the more numerous smaller weapons tended to obscure the splashes from the bigger guns. Either the smaller-Caliber, calibre guns would have to hold their fire to wait for the slower-firing heavies, losing the advantage of their faster rate of fire, or it would be uncertain whether a splash was due to a heavy or a light gun, making ranging and aiming unreliable. Italian naval architect Vittorio Cuniberti first argued for the concept of an all-big-gun battleship in 1903, proposing an "ideal" future British battleship of , with a main battery of a dozen 12-inch guns in eight turrets, 12 inches of belt armour, and a speed of .
First Sea Lord John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, Sir John Fisher pushed through the Board of Admiralty a decision to arm the next battleship with 12-inch guns and that it would have a speed no less than . The result was HMS ''Dreadnought'', which rendered all previous ships immediately obsolete on its launch in 1906. The ship mounted the 45-caliber (artillery), calibre BL 12 inch Mk X naval gun, BL 12-inch Mark X gun in five twin gun turrets. These could deliver a broadside of a maximum of eight guns and could be elevated up to +13.5°. They fired projectiles at a muzzle velocity of ; at 13.5°, this provided a maximum range of with Armor-piercing shot and shell, armour-piercing (AP) 2 List of British ordnance terms#C.R.H., crh shells. At 16° elevation, the range was extended to using the more aerodynamic, but slightly heavier 4 crh AP shells. The rate of fire of these guns was one to two rounds per minute. The ships carried 80 rounds per gun.
 Within five years of the commissioning of ''Dreadnought'', a new generation of more powerful "super-dreadnoughts" was being built. The arrival of the super-dreadnought is commonly believed to have started with the British . What made them 'super' was the unprecedented 2,000-ton jump in displacement, the introduction of the heavier BL 13.5 inch /45 naval gun, 13.5-inch (343 mm) gun, and the placement of all the main armament on the centerline. In the four years between ''Dreadnought'' and ''Orion'', displacement had increased by 25%, and weight of broadside had doubled.
In comparison to the rapid advancement of the preceding half-century, naval artillery changed comparatively little through World War I and World War II. Battleships remained similar to ''Dreadnought'', torpedo boats evolved into destroyers, and ships of intermediate size were called cruisers. All ship types became larger as the calibre of heavy guns increased (to a maximum of 40 cm/45 Type 94 naval gun, in the
Within five years of the commissioning of ''Dreadnought'', a new generation of more powerful "super-dreadnoughts" was being built. The arrival of the super-dreadnought is commonly believed to have started with the British . What made them 'super' was the unprecedented 2,000-ton jump in displacement, the introduction of the heavier BL 13.5 inch /45 naval gun, 13.5-inch (343 mm) gun, and the placement of all the main armament on the centerline. In the four years between ''Dreadnought'' and ''Orion'', displacement had increased by 25%, and weight of broadside had doubled.
In comparison to the rapid advancement of the preceding half-century, naval artillery changed comparatively little through World War I and World War II. Battleships remained similar to ''Dreadnought'', torpedo boats evolved into destroyers, and ships of intermediate size were called cruisers. All ship types became larger as the calibre of heavy guns increased (to a maximum of 40 cm/45 Type 94 naval gun, in the
 Although naval artillery had been designed to perform within the classical broadside tactics of the age of sail, World War I demonstrated the need for naval artillery mounts capable of greater elevation for anti-aircraft gun, defending against aircraft. High-velocity naval artillery intended to puncture side armor at close range was theoretically capable of hitting targets miles away with the aid of fire control directors; but the maximum elevation of guns mounted within restrictive armored casemates prevented reaching those ranges.
The QF 4 inch Mk V naval gun was one of the first artillery pieces to be adapted as an anti-aircraft gun and mounted on ships for defence. It was first used in 1914 as a secondary armament on s in a high-angle anti-aircraft role.
Most naval artillery on ships built after World War I was capable of elevating to at least 45°, and some guns as large as 20 cm/50 3rd Year Type naval gun#Type E, were capable of elevating to 70° for potential use against aircraft. The Japanese used their large caliber guns for anti-aircraft defense when employing San Shiki (anti-aircraft shell), San Shiki "beehive" shells.
Dual purpose guns were devised to protect ships against both torpedo boats and aircraft, and for WWII they comprised the primary armament on frigates and destroyers, and the secondary armament on cruisers and battleships. Dual purpose guns such as the US Navy's 5"/38 caliber gun, 5-inch (127 mm) /38 caliber guns functioned as heavy anti-aircraft artillery, firing VT shells (proximity fuzed-shells) that would detonate when they came close to an enemy aircraft, and could also aim into the water to create waterspouts which could bring down low flying aircraft such as torpedo planes. The light anti-aircraft artillery typically consisted of autocannons such as the Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60, Bofors 40 mm anti-aircraft guns and 65 single Oerlikon 20 mm cannon.
As destroyers began to assume Anti-submarine warfare, ASW roles to include protection of the fleet from submarines, they were fitted with high-angle
Although naval artillery had been designed to perform within the classical broadside tactics of the age of sail, World War I demonstrated the need for naval artillery mounts capable of greater elevation for anti-aircraft gun, defending against aircraft. High-velocity naval artillery intended to puncture side armor at close range was theoretically capable of hitting targets miles away with the aid of fire control directors; but the maximum elevation of guns mounted within restrictive armored casemates prevented reaching those ranges.
The QF 4 inch Mk V naval gun was one of the first artillery pieces to be adapted as an anti-aircraft gun and mounted on ships for defence. It was first used in 1914 as a secondary armament on s in a high-angle anti-aircraft role.
Most naval artillery on ships built after World War I was capable of elevating to at least 45°, and some guns as large as 20 cm/50 3rd Year Type naval gun#Type E, were capable of elevating to 70° for potential use against aircraft. The Japanese used their large caliber guns for anti-aircraft defense when employing San Shiki (anti-aircraft shell), San Shiki "beehive" shells.
Dual purpose guns were devised to protect ships against both torpedo boats and aircraft, and for WWII they comprised the primary armament on frigates and destroyers, and the secondary armament on cruisers and battleships. Dual purpose guns such as the US Navy's 5"/38 caliber gun, 5-inch (127 mm) /38 caliber guns functioned as heavy anti-aircraft artillery, firing VT shells (proximity fuzed-shells) that would detonate when they came close to an enemy aircraft, and could also aim into the water to create waterspouts which could bring down low flying aircraft such as torpedo planes. The light anti-aircraft artillery typically consisted of autocannons such as the Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60, Bofors 40 mm anti-aircraft guns and 65 single Oerlikon 20 mm cannon.
As destroyers began to assume Anti-submarine warfare, ASW roles to include protection of the fleet from submarines, they were fitted with high-angle
 The Royal Navy continually advanced their technology and techniques necessary to conduct effective bombardments in the face of the German defenders—firstly refining aerial reconnaissance techniques, then experimenting with night-bombardment and moving on to adopt indirect fire. Finally, in the summer of 1918, monitors were equipped with Gyro Director Training gear, which effectively provided the Director with a gyro-stabilised Artificial Line of Sight, and thereby enabled a ship to carry out Indirect Bombardment while underway. This was a very significant advance, and established a firm foundation for naval bombardment as practiced by the Royal Navy and United States Navy during World War II.
The practice reached its zenith during World War II, when the availability of man-portable radio systems and sophisticated relay networks allowed forward observers to transmit targeting information and provide almost instant accuracy reports—once troops had landed. Battleships, cruisers and destroyers would pound shore installations, sometimes for days, in the hope of reducing fortifications and attriting defending forces. Obsolete battleships unfit for combat against other ships were often used as floating gun platforms expressly for this purpose. However, given the relatively primitive nature of the fire control computers and radar of the era combined with the high velocity of naval gunfire, accuracy was poor until troops landed and were able to radio back reports to the ship.
Naval gunfire could reach as far as inland, and was often used to supplement land-based artillery. The heavy-calibre guns of some eighteen battleships and cruisers were used to stop German Panzer counterattack at Salerno. Naval gunfire was used extensively throughout Operation Overlord, Normandy, although initially the surprise nature of the landings themselves precluded a drawn-out bombardment which could have reduced the Atlantic Wall defences sufficiently, a process that fell to Hobart's Funnies, specialist armoured vehicles instead.
The Royal Navy continually advanced their technology and techniques necessary to conduct effective bombardments in the face of the German defenders—firstly refining aerial reconnaissance techniques, then experimenting with night-bombardment and moving on to adopt indirect fire. Finally, in the summer of 1918, monitors were equipped with Gyro Director Training gear, which effectively provided the Director with a gyro-stabilised Artificial Line of Sight, and thereby enabled a ship to carry out Indirect Bombardment while underway. This was a very significant advance, and established a firm foundation for naval bombardment as practiced by the Royal Navy and United States Navy during World War II.
The practice reached its zenith during World War II, when the availability of man-portable radio systems and sophisticated relay networks allowed forward observers to transmit targeting information and provide almost instant accuracy reports—once troops had landed. Battleships, cruisers and destroyers would pound shore installations, sometimes for days, in the hope of reducing fortifications and attriting defending forces. Obsolete battleships unfit for combat against other ships were often used as floating gun platforms expressly for this purpose. However, given the relatively primitive nature of the fire control computers and radar of the era combined with the high velocity of naval gunfire, accuracy was poor until troops landed and were able to radio back reports to the ship.
Naval gunfire could reach as far as inland, and was often used to supplement land-based artillery. The heavy-calibre guns of some eighteen battleships and cruisers were used to stop German Panzer counterattack at Salerno. Naval gunfire was used extensively throughout Operation Overlord, Normandy, although initially the surprise nature of the landings themselves precluded a drawn-out bombardment which could have reduced the Atlantic Wall defences sufficiently, a process that fell to Hobart's Funnies, specialist armoured vehicles instead.
1943 article on the history of naval cannons
''Popular Science'' {{Use dmy dates, date=May 2017 Naval artillery, Naval bombing operations and battles, *
 Naval artillery is
Naval artillery is artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
mounted on a warship
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is used for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the navy branch of the armed forces of a nation, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations. As well as b ...
, originally used only for naval warfare
Naval warfare is combat in and on the sea, the ocean, or any other battlespace involving a major body of water such as a large lake or wide river.
The Military, armed forces branch designated for naval warfare is a navy. Naval operations can be ...
and then subsequently used for more specialized roles in surface warfare such as naval gunfire support
Naval gunfire support (NGFS), also known as naval surface fire support (NSFS), or shore bombardment, is the use of naval artillery to provide fire support for amphibious assault and other troops operating within their range. NGFS is one of seve ...
(NGFS) and anti-aircraft warfare
Anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) is the counter to aerial warfare and includes "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It encompasses surface-based, subsurface (Submarine#Armament, submarine-lau ...
(AAW) engagements. The term generally refers to powder-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes self-propelled projectiles such as torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such ...
es, rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
s, and missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this ...
s and those simply dropped overboard such as depth charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon designed to destroy submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited ...
s and naval mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive weapon placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Similar to anti-personnel mine, anti-personnel and other land mines, and unlike purpose launched naval depth charges, they are ...
s.
Origins
The idea of ship-borne artillery dates back to the classical era.Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
wrote about the Roman navy
The naval forces of the Ancient Rome, ancient Roman state () were instrumental in the Roman conquest of the Mediterranean Basin, but it never enjoyed the prestige of the Roman legions. Throughout their history, the Romans remained a primarily land ...
's usage of ship-borne catapults against Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', , ), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were the Celtic people who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age until the High Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh, ...
ashore in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico
''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (; ), also ''Bellum Gallicum'' (), is Julius Caesar's first-hand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it, Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine yea ...
''. The dromons of the Byzantine Empire carried catapults and Greek fire
Greek fire was an incendiary weapon system used by the Byzantine Empire from the seventh to the fourteenth centuries. The recipe for Greek fire was a closely-guarded state secret; historians have variously speculated that it was based on saltp ...
.
From the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
onwards, warships began to carry cannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during th ...
s of various calibres. In the Battle of Tangdao in 1161, the Southern Song
The Song dynasty ( ) was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending ...
general Li Bao used huopao (a type of gunpowder weapons, possibly cannons
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during t ...
) and fire arrows against the Jin dynasty fleets.
The Mongol invasion of Java
The Yuan dynasty under Kublai Khan attempted in 1293 to invade Java, an island in modern Indonesia, with 20,000 to 30,000 soldiers. This was intended as a punitive expedition against Kertanegara of Singhasari, who had refused to pay tribute to ...
introduced cannons, to be used in Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
naval general warfare (e.g.Cetbang
Cetbang (originally known as bedil, also known as warastra or meriam coak) were cannons produced and used by the Majapahit Empire (1293–1527) and other kingdoms in the Indonesian archipelago. There are 2 main types of cetbang: the eastern- ...
by Majapahit
Majapahit (; (eastern and central dialect) or (western dialect)), also known as Wilwatikta (; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia based on the island o ...
). The Battle of Arnemuiden
The Battle of Arnemuiden was a naval battle fought on 23 September 1338 at the start of the Hundred Years' War between England and France. It was the first naval battle of the Hundred Years' War and the first recorded European naval battle usi ...
, fought between England and France in 1338 at the start of the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
, was the first recorded European naval battle using artillery. The English ship ''Christopher'' was armed with three cannons and one hand gun. In Asia naval artillery are recorded from the Battle of Lake Poyang
The Battle of Lake Poyang () was a naval battle which took place (30 August – 4 October 1363) between the rebel forces of Zhu Yuanzhang and Chen Youliang during the Red Turban Rebellion which led to the fall of the Yuan dynasty. Chen Youlia ...
in 1363 and in considerable quantities at the Battle of Jinpo in 1380 with cannon made by Ch'oe Mu-sŏn. 80 Koryo warships successfully repelled 500 Japanese pirates referred to as Wokou
''Wokou'' ( zh, c=, p=Wōkòu; ; Hepburn romanization, Hepburn: ; ; literal Chinese translation: "dwarf bandits"), which translates to "Japanese pirates", were pirates who raided the coastlines of China and Korea from the 13th century to the 17 ...
using long range cannon fire.
By the 15th century, most Mediterranean powers were utilising heavy cannon mounted on the bow or stern of a vessel and designed to bombard fortresses on shore. By mid-century some vessels also carried smaller broadside cannon for bombarding other vessels immediately prior to an attempted boarding. These small guns were anti-personnel weapons and were fired at point blank range to accompany engagement with muskets or bows.
In the 1470s, the Portuguese and Venetian navies were experimenting with ship mounted cannons as anti-ship weapons. King John II of Portugal
John II (; ; 3 May 1455 – 25 October 1495), called the Perfect Prince (), was King of Portugal from 1481 until his death in 1495, and also for a brief time in 1477. He is known for reestablishing the power of the Portuguese monarchy, reinvigo ...
, while still a prince in 1474, is credited with pioneering the introduction of a reinforced deck on the old Henry-era caravel
The caravel (Portuguese language, Portuguese: , ) is a small sailing ship developed by the Portuguese that may be rigged with just lateen sails, or with a combination of lateen and Square rig, square sails. It was known for its agility and s ...
to allow the mounting of heavy guns for this purpose.Rodrigues and Tevezes (2009: p. 193) These were initially wrought iron breech-loading weapon
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition from the breech end of the barrel (i.e., from the rearward, open end of the gun's barrel), as opposed to a muzzleloader, in which the user loads the ammunition from the ( muzzle ...
s known as basilisks. In 1489 he further contributed to the development of naval artillery by establishing the first standardized teams of trained naval gunners (''bombardeiros'').
Use of naval artillery expanded toward the end of the 15th century, with ships purpose-built to carry dozens of small bore breech-loading anti-personnel guns. English examples of these types include Henry VII's ''Regent'' and ''Sovereign'', with 141 and 225 guns respectively. Elsewhere in late medieval Northern Europe, the Dutch-built flagship of the Danish-Norwegian King Hans, ''Gribshunden
''Gribshunden'' or ''Griffen'' (English language, English: "Griffin-Hound" or "Griffin"), also known by several variant names including ''Gribshund'', ''Gripshunden'', ''Gripshund'', ''Griff'', and ''Griffone'', was a Denmark, Danish warship, th ...
'', carried 68 guns. Eleven gun beds from ''Gribshunden''muzzleloader
A muzzleloader is any firearm in which the user loads the bullet, projectile and the propellant charge into the Muzzle (firearms), muzzle end of the gun (i.e., from the forward, open end of the gun's barrel). This is distinct from the modern desi ...
s, cast in bronze and capable of firing balls or stones weighing up to .
Age of Sail
The 16th century was an era of transition in naval warfare. Since ancient times, war at sea had been fought much like that on land: with melee weapons and bows and arrows, but on floating wooden platforms rather than battlefields. Though the introduction of guns was a significant change, it only slowly changed the dynamics of ship-to-ship combat. As guns became heavier and able to take more powerful gunpowder charges, they needed to be placed lower in the ship, closer to the water line. Heavy artillery ongalley
A galley is a type of ship optimised for propulsion by oars. Galleys were historically used for naval warfare, warfare, Maritime transport, trade, and piracy mostly in the seas surrounding Europe. It developed in the Mediterranean world during ...
s was mounted in the bow, which aligned easily with the long-standing tactical tradition of attacking head on, bow first. The ordnance on galleys was heavy from its introduction in the 1480s, and capable of quickly demolishing the high, thin medieval stone walls that still prevailed in the 16th century. This temporarily upended the strength of older seaside fortresses, which had to be rebuilt to cope with gunpowder weapons. The addition of guns also improved the amphibious abilities of galleys as they could make assaults supported with heavy firepower, and were even more effectively defended when beached stern-first.
The broadside
Gunports cut in the hull of ships were introduced as early as 1501, about a decade before the famousTudor era
In England and Wales, the Tudor period occurred between 1485 and 1603, including the Elizabethan era during the reign of Elizabeth I (1558–1603). The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in England, which began with ...
ship, the ''Mary Rose
The ''Mary Rose'' was a carrack in the English Tudor navy of Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII. She was launched in 1511 and served for 34 years in several wars against France, Scotland, and Brittany. After being substantially rebuilt in ...
'', was built. This made broadsides, coordinated volleys from all the guns on one side of a ship, possible for the first time in history, at least in theory.
Ships such as ''Mary Rose'' carried a mixture of cannon of different types and sizes, many designed for land use, and using incompatible ammunition at different ranges and rate of fire. ''Mary Rose'', like other ships of the time, was built during a period of rapid development of heavy artillery, and her armament was a mix of old designs and innovations. The heavy armament was a mix of older-type wrought iron and cast bronze guns, which differed considerably in size, range and design. The large iron guns were made up of staves or bars welded into cylinders and then reinforced by shrinking iron hoops and breech loaded, and equipped with simpler gun-carriages made from hollowed-out elm logs with only one pair of wheels, or without wheels entirely. The bronze guns were cast in one piece and rested on four-wheel carriages which were essentially the same as those used until the 19th century. The breech-loaders were cheaper to produce and both easier and faster to reload, but could take less powerful charges than cast bronze guns. Generally, the bronze guns used cast iron shot and were more suited to penetrate hull sides while the iron guns used stone shot that would shatter on impact and leave large, jagged holes, but both could also fire a variety of ammunition intended to destroy rigging and light structure or injure enemy personnel.
The majority of the guns were small iron guns with short range that could be aimed and fired by a single person. The two most common were ''bases'', breech-loading swivel guns, most likely placed in the castles, and ''hailshot pieces'', small muzzle-loaders with rectangular bores and fin-like protrusions that were used to support the guns against the railing and allow the ship structure to take the force of the recoil. Though the design is unknown, there were two ''top pieces'' in a 1546 inventory (finished after the sinking) which was probably similar to a base, but placed in one or more of the fighting tops.
 During rebuilding in 1536, ''Mary Rose'' had a second tier of carriage-mounted long guns fitted. Records show how the configuration of guns changed as gun-making technology evolved and new classifications were invented. In 1514, the armament consisted mostly of anti-personnel guns like the larger breech-loading iron ''murderers'' and the small ''serpentines'', ''demi-slings'' and stone guns. Only a handful of guns in the first inventory were powerful enough to hole enemy ships, and most would have been supported by the ship's structure rather than resting on carriages. The inventories of both the ''Mary Rose'' and the Tower had changed radically by 1540. There were now the new cast bronze ''cannons'', ''demi-cannons'', ''culverins'' and ''sakers'' and the wrought iron ''port pieces'' (a name that indicated they fired through ports), all of which required carriages, had longer range and were capable of doing serious damage to other ships.
Various types of ammunition could be used for different purposes: plain spherical shot of stone or iron smashed hulls, spiked bar shot and shot linked with chains would tear sails or damage rigging, and
During rebuilding in 1536, ''Mary Rose'' had a second tier of carriage-mounted long guns fitted. Records show how the configuration of guns changed as gun-making technology evolved and new classifications were invented. In 1514, the armament consisted mostly of anti-personnel guns like the larger breech-loading iron ''murderers'' and the small ''serpentines'', ''demi-slings'' and stone guns. Only a handful of guns in the first inventory were powerful enough to hole enemy ships, and most would have been supported by the ship's structure rather than resting on carriages. The inventories of both the ''Mary Rose'' and the Tower had changed radically by 1540. There were now the new cast bronze ''cannons'', ''demi-cannons'', ''culverins'' and ''sakers'' and the wrought iron ''port pieces'' (a name that indicated they fired through ports), all of which required carriages, had longer range and were capable of doing serious damage to other ships.
Various types of ammunition could be used for different purposes: plain spherical shot of stone or iron smashed hulls, spiked bar shot and shot linked with chains would tear sails or damage rigging, and canister shot
Canister shot is a kind of anti-personnel artillery ammunition. It has been used since the advent of gunpowder-firing artillery in Western armies, and saw particularly frequent use on land and at sea in the various wars of the 18th and 19th cent ...
packed with sharp flints produced a devastating shotgun
A shotgun (also known as a scattergun, peppergun, or historically as a fowling piece) is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed to shoot a straight-walled cartridge (firearms), cartridge known as a shotshell, which discharges numerous small ...
effect. Trials made with replicas of culverins and port pieces showed that they could penetrate wood the same thickness of the ''Mary Rose's'' hull planking, indicating a stand-off range of at least 90 m (295 ft). The port pieces proved particularly efficient at smashing large holes in wood when firing stone shot and were a devastating anti-personnel weapon when loaded with flakes or pebbles.
A perrier threw a stone projectile three quarters of a mile (1.2 km), while a cannon threw a 32-pound ball
A ball is a round object (usually spherical, but sometimes ovoid) with several uses. It is used in ball games, where the play of the game follows the state of the ball as it is hit, kicked or thrown by players. Balls can also be used for s ...
a full mile (1.6 km), and a culverin
A culverin was initially an ancestor of the hand-held arquebus, but the term was later used to describe a type of medieval and Renaissance cannon. The word is derived from the antiquated "culuering" and the French (from " grass snake", follo ...
a 17-pound ball a mile and a quarter (2 km). Swivel gun
A swivel gun (or simply swivel) is a small cannon mounted on a swiveling stand or fork which allows a very wide arc of movement. Another type of firearm referred to as a swivel gun was an early flintlock combination gun with two barrels that rot ...
s and smaller cannon were often loaded with grapeshot
In artillery, a grapeshot is a type of ammunition that consists of a collection of smaller-caliber round shots packed tightly in a canvas bag and separated from the gunpowder charge by a metal wadding, rather than being a single solid projectile ...
for antipersonnel use at closer ranges, while the larger cannon might be loaded with a single heavy cannonball to cause structural damage.
In Portugal, the development of the heavy galleon removed even the necessity of bringing carrack firepower to bear in most circumstances. One of them became famous in the conquest of Tunis in 1535, and could carry 366 bronze cannon (a possible exaggeration – or possibly not – of the various European chroniclers of the time, that reported this number; or also possibly counting the weapons in reserve). This ship had an exceptional capacity of fire for its time, illustrating the evolution that was operating at the time, and for this reason, it became known as ''Botafogo
Botafogo (local/standard alternative Brazilian Portuguese pronunciation: ) is a beachfront neighborhood (''bairro'') in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It is a mostly upper middle class and small commerce community, and is located between the hills of M ...
'', meaning literally ''fire maker'', ''torcher'' or ''spitfire'' in popular Portuguese.
Maturation
Naval artillery and tactics stayed relatively constant during the period 1571–1862, with large, sail-powered wooden naval warships mounting a great variety of different types and sizes of cannon as their main armament. By the 1650s, the line of battle had developed as a tactic that could take advantage of the broadside armament. This method became the heart of naval warfare during theAge of Sail
The Age of Sail is a period in European history that lasted at the latest from the mid-16th (or mid-15th) to the mid-19th centuries, in which the dominance of sailing ships in global trade and warfare culminated, particularly marked by the int ...
, with navies adapting their strategies and tactics in order to get the most broadside-on fire. Cannon were mounted on multiple decks to maximise broadside effectiveness. Numbers and calibre differed somewhat with preferred tactics. France and Spain attempted to immobilize ships by destroying rigging with long-range, accurate fire from their swifter and more maneuverable ships, while England and the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
favoured rapid fire at close range to shatter a ship's hull and disable its crew.
A typical broadside of a Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
ship of the late 18th century could be fired 2-3 times in approximately 5 minutes, depending on the training of the crew, a well trained one being essential to the simple yet detailed process of preparing to fire. French and Spanish crews typically took twice as long to fire an aimed broadside. An 18th-century ship of the line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactics in the Age of Sail, naval tactic known as the line of battl ...
typically mounted 32-pounder or 36-pounder long gun
The 36-pounder long gun was the largest piece of naval artillery in the Age of Sail, artillery mounted on French warships of the Age of Sail. They were also used for Coastal defense and fortification. They largely exceeded the heaviest guns fielded ...
s on a lower deck, and 18- or 24-pounders on an upper deck, with some 12-pounders on the forecastle and quarterdeck. From the late sixteenth century it was routine for naval ships to carry a master gunner, responsible for overseeing the operation of the cannon on board. Originally a prestigious position, its status declined throughout the Age of Sail as responsibility for gunnery strategy was devolved to midshipmen or lieutenants. By the eighteenth century the master gunner had become responsible only for the maintenance of the guns and their carriages, and for overseeing supplies of gunpowder and shot. In status the master gunner remained equal to the boatswain
A boatswain ( , ), bo's'n, bos'n, or bosun, also known as a deck boss, or a qualified member of the deck department, or the third hand on a fishing vessel, is the most senior Naval rating, rate of the deck department and is responsible for the ...
and ship's carpenter as senior warrant officer
Warrant officer (WO) is a Military rank, rank or category of ranks in the armed forces of many countries. Depending on the country, service, or historical context, warrant officers are sometimes classified as the most junior of the commissioned ...
s, and was entitled to the support of one or more gunner's mates. In the Royal Navy, the master gunner also directed the "quarter gunners" able seamen with the added responsibility of managing the rate and direction of fire from any set of four gun crews.
The British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, department of the Government of the United Kingdom that was responsible for the command of the Royal Navy.
Historically, its titular head was the Lord High Admiral of the ...
did not see fit to provide additional powder to captains to train their crews, generally only allowing 1/3 of the powder loaded onto the ship to be fired in the first six months of a typical voyage, barring hostile action. Instead of live fire practice, most captains exercised their crews by "running" the guns in and out—performing all the steps associated with firing but for the actual discharge. Some wealthy captains—those who had made money capturing prizes or from wealthy families—were known to purchase powder with their own funds to enable their crews to fire real discharges at real targets.
Firing
 Firing a naval cannon required a great amount of labour and manpower. The propellant was gunpowder, whose bulk had to be kept in a special storage area below deck for safety. ''Powder boys''- sometimes called Powder Monkeys- typically 10–14 years old, were enlisted to run powder from the armoury up to the gun decks of a vessel as required.
A typical firing procedure follows. A wet swab was used to mop out the interior of the barrel, extinguishing any embers from a previous firing which might set off the next charge of gunpowder prematurely.
Firing a naval cannon required a great amount of labour and manpower. The propellant was gunpowder, whose bulk had to be kept in a special storage area below deck for safety. ''Powder boys''- sometimes called Powder Monkeys- typically 10–14 years old, were enlisted to run powder from the armoury up to the gun decks of a vessel as required.
A typical firing procedure follows. A wet swab was used to mop out the interior of the barrel, extinguishing any embers from a previous firing which might set off the next charge of gunpowder prematurely. Gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
, either loose or in a cloth or parchment cartridge pierced by a metal 'pricker' through the touch hole, was placed in the barrel and followed by a cloth wad (typically made from canvas and old rope), then rammed home with a rammer. Next the shot was rammed in, followed by another wad (to prevent the cannonball from rolling out of the barrel if the muzzle was depressed.) The gun in its carriage was then 'run out'—men heaved on the gun tackles until the front of the gun carriage
A gun carriage is a frame or a mount that supports the gun barrel of an artillery piece, allowing it to be maneuvered and fired. These platforms often had wheels so that the artillery pieces could be moved more easily. Gun carriages are also use ...
was hard up against the ship's bulwark, and the barrel protruding out of the gun port. This took the majority of the guncrew manpower as the total weight of a large cannon in its carriage could reach over two tons, and the ship would probably be rolling.
The touch hole in the rear ('breech') of the cannon was primed with finer gunpowder ('priming powder'), or a 'quill' (from a porcupine or such, or the skin-end of a feather) pre-filled with priming powder, then ignited.
 The earlier method of firing a cannon was to apply a
The earlier method of firing a cannon was to apply a linstock
A linstock (also called a lintstock) is a staff with a fork at one end to hold a lighted slow match. The name was adapted from the Dutch ''lontstok'', "match stick". Linstocks were used for discharging cannons in the early days of artillery; th ...
—a wooden staff holding a length of smoldering match at the end—to the touch-hole of the gun. This was dangerous and made accurate shooting from a moving ship difficult, as the gun had to be fired from the side, to avoid its recoil, and there was a noticeable delay between the application of the linstock and the gun firing. In 1745, the British began using ''gunlocks'' (flintlock mechanism
The flintlock mechanism is a type of lock (firearm), lock used on muskets, rifles, and pistols from the early 17th to the mid-19th century. It is commonly referred to as a "flintlock" (without the word ''mechanism''). The term is also used for th ...
s fitted to cannon).
The gunlock was operated by pulling a cord, or lanyard
A lanyard is a length of cord, webbing, or strap that may serve any of various functions, which include a means of attachment, restraint, retrieval, activation, and deactivation. A lanyard is also a piece of rigging used to secure or lowe ...
. The gun-captain could stand behind the gun, safely beyond its range of recoil, and sight along the barrel, firing when the roll of the ship lined the gun up with the enemy and so avoid the chance of the shot hitting the sea or flying high over the enemy's deck. Despite their advantages, gunlocks spread gradually as they could not be retrofitted to older guns. The British adopted them faster than the French, who had still not generally adopted them by the time of the Battle of Trafalgar (1805), placing them at a disadvantage as they were in general use by the Royal Navy at this time. After the introduction of gunlocks, linstocks were retained, but only as a backup means of firing.
The linstock slow match, or the spark from the flintlock, ignited the priming powder, which in turn set off the main charge, which propelled the shot out of the barrel. When the gun discharged, the recoil sent it backwards until it was stopped by the breech rope—a sturdy rope made fast to ring bolts set into the bulwarks, and a turn taken about the gun's cascabel, the knob at the end of the gun barrel.
Artillery and shot
The types of artillery used varied from nation and time period. The more important types included the demi-cannon, theculverin
A culverin was initially an ancestor of the hand-held arquebus, but the term was later used to describe a type of medieval and Renaissance cannon. The word is derived from the antiquated "culuering" and the French (from " grass snake", follo ...
and demi-culverin, and the carronade
A carronade is a short, smoothbore, cast-iron cannon which was used by the Royal Navy. It was first produced by the Carron Company, an ironworks in Falkirk, Scotland, and was used from the last quarter of the 18th century to the mid-19th cen ...
. One descriptive characteristic which was commonly used was to define guns by their 'pound' rating: theoretically, the weight of a single solid iron shot fired by that bore of cannon. Common sizes were 42-pounders, 36-pounders, 32-pounders, 24-pounders, 18-pounders, 12-pounders, 9-pounders, 8-pounders, 6-pounders, and various smaller calibres. French ships used standardized guns of 36-pound, 24-pound and 12-pound calibres, augmented by smaller pieces. In general, larger ships carrying more guns carried larger ones as well.
 The muzzle-loading design and weight of the iron placed design constraints on the length and size of naval guns. Muzzle loading required the cannon muzzle to be positioned within the hull of the ship for loading. The hull is only so wide, with guns on both sides, and hatchways in the centre of the deck also limit the room available. Weight is always a great concern in ship design as it affects speed, stability, and buoyancy. The desire for longer guns for greater range and accuracy, and greater weight of shot for more destructive power, led to some interesting gun designs.
One unique naval gun was the long nine. It was a proportionately longer-barrelled 9-pounder. Its typical mounting as a bow or stern chaser, where it was not perpendicular to the keel, allowed room to operate this longer weapon. In a chase situation, the gun's greater range came into play. However, the desire to reduce weight in the ends of the ship and the relative fragility of the bow and stern portions of the hull limited this role to a 9-pounder, rather than one which used a 12 or 24 pound shot.
In the reign of Queen Elizabeth advances in manufacturing technology allowed the English Navy Royal to start using matched cannon firing standard ammunition,BBC: 'Superguns' of Elizabeth I's navy.
The muzzle-loading design and weight of the iron placed design constraints on the length and size of naval guns. Muzzle loading required the cannon muzzle to be positioned within the hull of the ship for loading. The hull is only so wide, with guns on both sides, and hatchways in the centre of the deck also limit the room available. Weight is always a great concern in ship design as it affects speed, stability, and buoyancy. The desire for longer guns for greater range and accuracy, and greater weight of shot for more destructive power, led to some interesting gun designs.
One unique naval gun was the long nine. It was a proportionately longer-barrelled 9-pounder. Its typical mounting as a bow or stern chaser, where it was not perpendicular to the keel, allowed room to operate this longer weapon. In a chase situation, the gun's greater range came into play. However, the desire to reduce weight in the ends of the ship and the relative fragility of the bow and stern portions of the hull limited this role to a 9-pounder, rather than one which used a 12 or 24 pound shot.
In the reign of Queen Elizabeth advances in manufacturing technology allowed the English Navy Royal to start using matched cannon firing standard ammunition,BBC: 'Superguns' of Elizabeth I's navy.The wreck of an English full-rigged pinnace dating from around 1592 with 12 matched guns was discovered, and guns were recovered in 2009 allowing firing of coordinated broadsides (although that was more of a matter of improved training and discipline than of matched guns). Different types of shot were employed for various situations. Standard fare was the
round shot
A round shot (also called solid shot or simply ball) is a solid spherical projectile without explosive charge, launched from a gun. Its diameter is slightly less than the bore of the barrel from which it is shot. A round shot fired from a lar ...
, which is spherical cast-iron shot used for smashing through the enemy's hull, holing his waterline, smashing gun carriages and breaking masts and yards, with a secondary effect of sending large wooden splinters flying about to maim and kill the enemy crew. At very close range, two round shots could be loaded in one gun and fired together. "Double-shotting", as it was called, lowered the effective range and accuracy of the gun, but could be devastating within pistol shot range.
Canister shot
Canister shot is a kind of anti-personnel artillery ammunition. It has been used since the advent of gunpowder-firing artillery in Western armies, and saw particularly frequent use on land and at sea in the various wars of the 18th and 19th cent ...
consisted of metallic canisters which broke open upon firing, each of which was filled with hundreds of lead musket balls for clearing decks like a giant shotgun
A shotgun (also known as a scattergun, peppergun, or historically as a fowling piece) is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed to shoot a straight-walled cartridge (firearms), cartridge known as a shotshell, which discharges numerous small ...
blast; it is commonly mistakenly called "grapeshot", both today and in historic accounts (typically those of landsmen). Although canister shot could be used aboard ship, it was more traditionally an army artillery projectile for clearing fields of infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
. Grapeshot
In artillery, a grapeshot is a type of ammunition that consists of a collection of smaller-caliber round shots packed tightly in a canvas bag and separated from the gunpowder charge by a metal wadding, rather than being a single solid projectile ...
was similar in that it also consisted of multiple (usually 9–12) projectiles that separated upon firing, except that the shot was larger (at least 1 inch in diameter, up to 3 inches or larger for heavier guns), and it either came in bundles held together by lengths of rope wrapped around the balls and wedged between, with wooden bases to act as wadding when rammed down the muzzles, or in canvas sacks wrapped about with rope. The name "grapeshot" comes from the former's apparent resemblance to a bunch of grapes
In viticulture, the grape cluster (also bunch of grapes) is a fertilized inflorescence of the grapevine, the primary part of this plant used for food (grape leaves are also used in some culinary traditions). The size of the grape bunch greatly va ...
. When fired, the inertial forces would cause the bundle to disintegrate, and the shot would spread out to hit numerous targets. Grapeshot was a naval weapon, and existed for almost as long as naval artillery. The larger size of the grapeshot projectiles was desirable because it was more capable of cutting thick cordage and smashing equipment than the relatively smaller musket balls of a canister shot, although it could rarely penetrate a wooden hull. Although grapeshot won great popular fame as a weapon used against enemy crew on open decks (especially when massed in great numbers, such as for a boarding attempt), it was originally designed and carried primarily for cutting up enemy rigging.
A more specialized shot for similar use was the chain-shot, which consisted of two iron balls joined together with a chain, and was particularly designed for cutting large swaths of rigging
Rigging comprises the system of ropes, cables and chains, which support and control a sailing ship or sail boat's masts and sails. ''Standing rigging'' is the fixed rigging that supports masts including shrouds and stays. ''Running rigg ...
, such as boarding nets and sail
A sail is a tensile structure, which is made from fabric or other membrane materials, that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may b ...
s. It was far more effective than other projectiles in this use, but was of little use for any other purpose. ''Bar shot'' was similar, except that it used a solid bar to join the two balls; the bar could sometimes also extend upon firing. Series of long chain links were also used in a similar way. Bags of junk, such as scrap metal, bolts, rocks, gravel, or old musket balls, were known as 'langrage', and were fired to injure enemy crews (although this was not common, and when it was used, it was generally aboard non-commissioned vessels such as privateer
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign o ...
s, actual pirate ships
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are call ...
, merchantmen, and others who couldn't afford real ammunition).
In China and other parts of Asia, fire arrows were thick, dartlike, rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
-propelled incendiary projectiles with barbed points, wrapped with pitch-soaked canvas which took fire when the rocket was launched, which could either be from special launching racks or from a cannon barrel (see '' Chongtong'', '' Bō hiya''.) The point stuck in sails, hulls or spars and set fire to the enemy ship. In Western naval warfare, shore forts sometimes heated iron shot red-hot in a special furnace before loading it (with water-soaked wads to prevent it from setting off the powder charge prematurely.) The hot shot lodging in a ship's dry timbers would set the ship afire. Because of the danger of fire aboard (and the difficulty of heating and transporting the red-hot shot aboard ship), heated shot was seldom used from ship-mounted cannon, as the danger to the vessel deploying it was almost as great as to the enemy; fire was the single greatest fear of all men sailing in wooden ships. Consequently, for men aboard these vessels, going up against shore artillery firing heated shot was a terrifying experience, and typically wooden fleets were not expected to brave such fire except in cases of great emergency, as a single heated shot could easily destroy the entire ship and crew, while the same ship could typically be expected to survive numerous hits from normal solid shot.
Bomb ketch
The bomb ketch was developed as a wooden sailingnaval ship
A naval ship (or naval vessel) is a military ship (or sometimes boat, depending on classification) that is used by a navy. Naval ships are differentiated from civilian ships by construction and purpose. Generally, naval ships are damage resili ...
with its primary armament
A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime (e.g., murder), law e ...
as mortars
Mortar may refer to:
* Mortar (weapon), an indirect-fire infantry weapon
* Mortar (masonry), a material used to fill the gaps between blocks and bind them together
* Mortar and pestle, a tool pair used to crush or grind
* Mortar, Bihar, a village i ...
mounted forward near the bow and elevated to a high angle, and projecting their fire in a ballistic arc. Explosive shells or carcasses were employed rather than solid shot. Bomb vessels were specialized ships designed for bombarding (hence the name) fixed positions on land.
The first recorded deployment of bomb vessels by the English was for the Siege of Calais in 1347 when Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after t ...
deployed single deck ships with Bombardes and other artillery.
The first specialised bomb vessels were built towards the end of the 17th century, based on the designs of Bernard Renau d'Eliçagaray, and used by the French Navy
The French Navy (, , ), informally (, ), is the Navy, maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the four military service branches of History of France, France. It is among the largest and most powerful List of navies, naval forces i ...
. Five such vessels were used to shell Algiers in 1682 destroying the land forts, and killing some 700 defenders. Two years later the French repeated their success at Genoa. The early French bomb vessels had two forward-pointing mortars fixed side-by-side on the foredeck. To aim these weapons, the entire ship was rotated by letting out or pulling in a spring anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal, used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ', which itself comes from the Greek ().
Anch ...
. The range was usually controlled by adjusting the gunpowder charge.
The Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
continued to refine the class over the next century or more, after Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
exiles brought designs over to England and the United Provinces. The side-by-side, forward-pointing mortars were replaced in the British designs by mortars mounted on the centerline on revolving platforms. These platforms were supported by strong internal wooden framework to transmit the forces of firing the weapons to the hull. The interstices of the framework were used as storage areas for ammunition. Early bomb vessels were rigged as ketch
A ketch is a two- masted sailboat whose mainmast is taller than the mizzen mast (or aft-mast), and whose mizzen mast is stepped forward of the rudder post. The mizzen mast stepped forward of the rudder post is what distinguishes the ketch f ...
es with two masts. They were awkward vessels to handle, in part because bomb ketches typically had the masts stepped farther aft than would have been normal in other vessels of similar rig, in order to accommodate the mortars forward and provide a clear area for their forward fire. As a result, the 19th century British bomb vessels were designed as full-rigged ship
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing ship, sailing vessel with a sail plan of three or more mast (sailing), masts, all of them square rig, square-rigged. Such a vessel is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged, with each mas ...
s with three masts, and two mortars, one between each neighboring pair of masts.
Scientific gunnery
The art of gunnery was put on a scientific basis in the mid-18th century. British military engineer Benjamin Robins usedNewtonian mechanics
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows:
# A body r ...
to calculate the projectile trajectory while taking the air resistance
In fluid dynamics, drag, sometimes referred to as fluid resistance, is a force acting opposite to the direction of motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers, two solid surfaces, or b ...
into account. He also carried out an extensive series of experiments in gunnery, embodying his results in his famous treatise on New Principles in Gunnery
' (1742), which contains a description of his ballistic pendulum (see
chronograph
A chronograph is a specific type of watch that is used as a stopwatch combined with a display watch. A basic chronograph has hour and minute hands on the main dial to tell the time, a small seconds hand to tell that the watch is running, and ...
).
Robins also made a number of important experiments on the resistance of the air to the motion of projectiles, and on the force of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
, with computation of the velocities thereby communicated to projectiles. He compared the results of his theory with experimental determinations of the ranges of mortars and cannon, and gave practical maxims for the management of artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
. He also made observations on the flight of rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
s and wrote on the advantages of rifled gun barrels.
Robins argued for the use of larger bore cannon and the importance of tightly fitting cannonballs. His work on gunnery was translated into German by Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler ( ; ; ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss polymath who was active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, logician, geographer, and engineer. He founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made influential ...
and was heavily influential on the development of naval weaponry across Europe.
Another significant scientific gunnery book was written by Warrant Officer George Marshall
George Catlett Marshall Jr. (31 December 1880 – 16 October 1959) was an American army officer and statesman. He rose through the United States Army to become Chief of Staff of the United States Army, Chief of Staff of the U.S. Army under pres ...
, a Master Gunner in the United Navy. He wrote Marshall's Practical Marine Gunnery
' in 1822. The book discusses the dimensions and apparatus necessary for the equipment of naval artillery. The book goes into further details regarding the distance of a shot on a ship based on the sound of the gun, which was found to fly at a rate of 1,142 feet or 381 yards in one second. According to Marshall's equation after seeing the flash of a cannon and hearing the blast the gunner would count the seconds until impact. This way a trained ear would know the distance a cannonball traveled and might gain information or return fire. The book example, outlines a 9-second scenario where the distance the cannon was fired from the gunner was approximately 10,278 feet or 3,426 yards.
Technical innovations
file:Carronade (schematics).jpg, Thecarronade
A carronade is a short, smoothbore, cast-iron cannon which was used by the Royal Navy. It was first produced by the Carron Company, an ironworks in Falkirk, Scotland, and was used from the last quarter of the 18th century to the mid-19th cen ...
was a small gun, devastating at short range
By the outbreak of the French Revolutionary Wars in 1793, a series of technical innovations over the course of the late 18th century combined to give the British fleet a distinct superiority over the ships of the French and Spanish navies.
The carronade
A carronade is a short, smoothbore, cast-iron cannon which was used by the Royal Navy. It was first produced by the Carron Company, an ironworks in Falkirk, Scotland, and was used from the last quarter of the 18th century to the mid-19th cen ...
was a short-barrelled gun which threw a heavy ball developed by the Carron Company, a Scottish ironworks, in 1778. Because of irregularities in the size of cannonballs and the difficulty of boring out gun barrels, there was usually a considerable gap between the ball and the bore—often as much as a quarter of an inch—with a consequent loss of efficiency. This gap was known as the "windage". The manufacturing practices introduced by the Carron Company reduced the windage considerably, enabling the ball to be fired with less powder and hence a smaller and lighter gun. The carronade was half the weight of an equivalent long gun, but could throw a heavy ball over a limited distance. The light weight of the carronade meant that the guns could be added to the forecastle and quarterdeck of frigates and ships of the line, increasing firepower without affecting the ship's sailing qualities. It became known as the "Smasher" and gave ships armed with carronades a great advantage at short range. The mounting, attached to the side of the ship on a pivot, took the recoil on a slider. The reduced recoil did not alter the alignment of the gun. The smaller gunpowder charge reduced the guns' heating in action. The pamphlet advocated the use of woollen cartridges, which, although more expensive, eliminated the need for wadding
Wadding is a disc of material used in guns to seal gas behind a projectile (a bullet or ball), or to separate the propellant from loosely packed shots.
Wadding can be crucial to a gun's efficiency, since any gas that leaks past a projectile ...
and worming. Simplifying gunnery for comparatively untrained merchant seamen in both aim and reloading was part of the rationale for the gun. The replacement of trunnions by a bolt underneath, to connect the gun to the mounting, reduced the width of the carriage enhancing the wide angle of fire. A carronade weighed a quarter as much and used a quarter to a third of the gunpowder charge for a long gun firing the same cannonball. Its invention is variously ascribed to Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the battlefield, who was norma ...
Robert Melvill
General Robert Melvill (or Melville) LLD (12 October 1723 – 29 August 1809) was a Scottish soldier in the British Army, antiquary, botanist, inventor, and slave plantation owner. He was owner of the Marigot, Dominica, Melville Hall (Dominica ...
e in 1759, or to Charles Gascoigne, manager of the Carron Company from 1769 to 1779. Carronades initially became popular on British merchant ships during the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
. A lightweight gun that needed only a small gun crew and was devastating at short range was a weapon well suited to defending merchant ships against French and American privateer
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign o ...
s. In the Action of 4 September 1782
The action of 4 September 1782 was a small naval engagement fought off the Île de Batz between a French naval frigate, , and a Royal Naval frigate, . This battle was notable as the first proper use of a carronade, and so effective was this ...
, the impact of a single carronade broadside fired at close range by the frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuvera ...
HMS ''Rainbow'' under Henry Trollope caused a wounded French captain to capitulate and surrender the ''Hebe'' after a short fight.
file:12-pdrShrapnel.jpg, A 12-pounder U.S. shrapnel shell ca. 1865
Flintlock firing mechanisms for cannon were suggested by Captain Sir Charles Douglas (admiral), Charles Douglas and introduced during the American War of Independence in place of the traditional matches. Flintlocks enabled a higher rate of fire and greater accuracy as the gun captain could choose the exact moment of firing. Prior to this the Royal Navy introduced the use of goose quills filled with powder during the Seven Years' War giving an almost instantaneous burn time compared with earlier methods of detonation.
Douglas also innovated a system that greatly increased the field of fire. By the simple expedient of attaching the gun ropes at a greater distance from the gunports, the range through which each cannon could be traversed was greatly improved. The new system was first tested at the Battle of the Saintes in 1782, where the ''Duke'', ''Formidable',' and ''Arrogant'', and perhaps other British ships, had adopted Douglas's new system.
The shrapnel shell was developed in 1784, by Major General Henry Shrapnel of the Royal Artillery. Canister shot
Canister shot is a kind of anti-personnel artillery ammunition. It has been used since the advent of gunpowder-firing artillery in Western armies, and saw particularly frequent use on land and at sea in the various wars of the 18th and 19th cent ...
was already in widespread use at the time; a tin or canvas container filled with small iron or lead balls burst open when fired, giving the effect of an oversized shotgun shell. Shrapnel's innovation was to combine the multi-projectile shotgun effect of canister shot, with a Artillery fuze#Time fuzes, time fuze to open the canister and disperse the bullets it contained at some distance along the canister's trajectory from the gun. His shell was a hollow cast-iron sphere filled with a mixture of balls and powder, with a crude time fuze. If the fuze was set correctly then the shell would break open, either in front or above the intended target, releasing its contents (of musket balls). The shrapnel balls would carry on with the "remaining velocity" of the shell. In addition to a denser pattern of musket balls, the retained velocity could be higher as well, since the shrapnel shell as a whole would likely have a higher ballistic coefficient than the individual musket balls (see external ballistics).
Industrial era and the Age of Steamships
The Industrial Revolution introduced steam-powered ironclad warships seemingly impervious to casting, cast cannon. The inadequacy of naval artillery caused the naval ram to reappear as a means of sinking armored warships.Breyer 1973, pp. 28–38. The rapidity of innovation through the last half of the 19th century caused some ships to be obsolete before they were launched. Maximum projectile velocity obtainable with gunpowder in cast cannon was approximately . Increased projectile weight through increased caliber was the only method of improving armor penetration with this velocity limitation. Some ironclads carried extremely heavy, slow-firing guns of calibres up to . These guns were the only weapons capable of piercing the ever-thicker iron armour on the later ironclads, but required steam powered machinery to assist loading cannonballs too heavy for men to lift.Explosive shells
 Explosive shell (projectile), shells had long been in use in ground warfare (in howitzers and mortars), but they were only fired at high angles and with relatively low velocities. Shells are inherently dangerous to handle, and no solution had been found to combine the explosive character of the shells with the high power and flatter trajectory of a high velocity gun.
However, high trajectories were not practical for marine combat and naval combat essentially required flat-trajectory guns in order to have some decent odds of hitting the target. Therefore, naval warfare had consisted for centuries of encounters between flat-trajectory cannon using inert cannonballs, which could inflict only local damage even on wooden hulls.
The first naval gun designed to fire explosive shells was the Paixhans gun, developed by the French general Henri-Joseph Paixhans in 1822–1823. He advocated using flat-trajectory shell guns against warships in 1822 in his ''Nouvelle force maritime et artillerie'', and developed a delaying mechanism which, for the first time, allowed shells to be fired safely in high-powered flat-trajectory guns. The effect of explosive shells lodging into wooden hulls and then detonating was potentially devastating. This was first demonstrated by Henri-Joseph Paixhans in trials against the two-decker French ship Pacificateur (1811), ''Pacificateur'' in 1824, in which he successfully broke up the ship. Two prototype Paixhans guns had been cast in 1823 and 1824 for this test. Paixhans reported the results in ''Experiences faites sur une arme nouvelle''. The shells were equipped with a fuse which ignited automatically when the gun was fired. The shell would then lodge itself in the wooden hull of the target before exploding a moment later.
The first Paixhans guns for the
Explosive shell (projectile), shells had long been in use in ground warfare (in howitzers and mortars), but they were only fired at high angles and with relatively low velocities. Shells are inherently dangerous to handle, and no solution had been found to combine the explosive character of the shells with the high power and flatter trajectory of a high velocity gun.
However, high trajectories were not practical for marine combat and naval combat essentially required flat-trajectory guns in order to have some decent odds of hitting the target. Therefore, naval warfare had consisted for centuries of encounters between flat-trajectory cannon using inert cannonballs, which could inflict only local damage even on wooden hulls.
The first naval gun designed to fire explosive shells was the Paixhans gun, developed by the French general Henri-Joseph Paixhans in 1822–1823. He advocated using flat-trajectory shell guns against warships in 1822 in his ''Nouvelle force maritime et artillerie'', and developed a delaying mechanism which, for the first time, allowed shells to be fired safely in high-powered flat-trajectory guns. The effect of explosive shells lodging into wooden hulls and then detonating was potentially devastating. This was first demonstrated by Henri-Joseph Paixhans in trials against the two-decker French ship Pacificateur (1811), ''Pacificateur'' in 1824, in which he successfully broke up the ship. Two prototype Paixhans guns had been cast in 1823 and 1824 for this test. Paixhans reported the results in ''Experiences faites sur une arme nouvelle''. The shells were equipped with a fuse which ignited automatically when the gun was fired. The shell would then lodge itself in the wooden hull of the target before exploding a moment later.
The first Paixhans guns for the French Navy
The French Navy (, , ), informally (, ), is the Navy, maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the four military service branches of History of France, France. It is among the largest and most powerful List of navies, naval forces i ...
were manufactured in 1841. The barrel of the guns weighed about 10,000 lbs. (4.5 metric tons), and proved accurate to about two miles. In the 1840s, Britain, Russia and the United States adopted the new naval guns. The effect of the guns in an operational context was decisively demonstrated during the Crimean War. The incendiary ammunition, incendiary properties of exploding shells demonstrated the obsolescence of wooden warships in the 1853 Battle of Sinop; but detonation effectiveness was limited by use of gunpowder bursting charges. Early high explosives used in torpedo warheads would detonate during the acceleration of firing from a gun. After brief use of dynamite guns aboard , picric acid became widely used in conventional naval artillery shells during the 1890s.
Breech-loading, rifled artillery
 William Armstrong, 1st Baron Armstrong, William Armstrong was awarded a contract by the British government in the 1850s to design a revolutionary new piece of artillery—the Armstrong Gun—produced at the Elswick Ordnance Company. This marked the birth of modern artillery both on land and at sea. The piece was rifled, which allowed for a much more accurate and powerful action. The necessary machinery to accurately rifle artillery was only available by the mid-19th century. The cast iron shell fired by the Armstrong gun was similar in shape to a Minié ball and had a thin lead coating which made it fractionally larger than the gun's bore and which engaged with the gun's rifling grooves to impart spin to the shell. This spin, together with the elimination of British ordnance terms#Windage, windage as a result of the tight fit, enabled the gun to achieve greater range and accuracy than existing smooth-bore muzzle-loaders with a smaller powder charge.
His gun was also a breech-loader. Although attempts at breech-loading mechanisms had been made since medieval times, the essential engineering problem was that the mechanism couldn't withstand the explosive charge. It was only with the advances in metallurgy and precision engineering capabilities during the Industrial Revolution that Armstrong was able to construct a viable solution. The gun combined all the properties that make up an effective artillery piece. The gun was mounted on a carriage in such a way as to return the gun to firing position after the recoil.
William Armstrong, 1st Baron Armstrong, William Armstrong was awarded a contract by the British government in the 1850s to design a revolutionary new piece of artillery—the Armstrong Gun—produced at the Elswick Ordnance Company. This marked the birth of modern artillery both on land and at sea. The piece was rifled, which allowed for a much more accurate and powerful action. The necessary machinery to accurately rifle artillery was only available by the mid-19th century. The cast iron shell fired by the Armstrong gun was similar in shape to a Minié ball and had a thin lead coating which made it fractionally larger than the gun's bore and which engaged with the gun's rifling grooves to impart spin to the shell. This spin, together with the elimination of British ordnance terms#Windage, windage as a result of the tight fit, enabled the gun to achieve greater range and accuracy than existing smooth-bore muzzle-loaders with a smaller powder charge.
His gun was also a breech-loader. Although attempts at breech-loading mechanisms had been made since medieval times, the essential engineering problem was that the mechanism couldn't withstand the explosive charge. It was only with the advances in metallurgy and precision engineering capabilities during the Industrial Revolution that Armstrong was able to construct a viable solution. The gun combined all the properties that make up an effective artillery piece. The gun was mounted on a carriage in such a way as to return the gun to firing position after the recoil.
 What made the gun really revolutionary lay in the technique of the construction of the gun barrel that allowed it to withstand much more powerful explosive forces. The "built-up gun, built-up" method involved assembling the barrel with wrought-iron (later mild steel was used) tubes of successively larger diameter. The next tube would be heated to allow it to expand and fit over the previous tube. When it cooled the tube would contract to a slightly smaller diameter, which allowed an even pressure along the walls of the gun which was directed inward against the outward forces that the gun firing exerted on the barrel. Built-up guns with rifling made cast cannon obsolete by 1880.
Armstrong's system was adopted in 1858, initially for "special service in the field" and initially he only produced smaller artillery pieces, 6-pounder (2.5 in/64 mm) mountain or light field guns, 9-pounder (3 in/76 mm) guns for horse artillery, and RBL 12 pounder 8 cwt Armstrong gun, 12-pounder (3 inches /76 mm) field guns.
However, despite the gun's advantages, an 1863 Ammunition, Ordnance Select committee (United Kingdom), Select committee decided to revert to muzzle-loading artillery pieces on the grounds of cost and efficiency.
Large-caliber Breech-loading weapon, breech-loading naval artillery became practical with French development of the interrupted screw Obturating ring, obturator by Charles Ragon de Bange in 1872. It was only after a serious accident on board in 1879 when the left muzzleloading gun in the forward turret exploded during practice firing in the Sea of Marmora killing 11 and injuring a further 35, that the Royal Navy decisively changed to breech loading guns. Improved loading and handling procedures were also adopted, and Thunderer herself was re-equipped with long-calibre 10" breech-loaders. Breech loading artillery overcame barrel length limitations of cast cannon imposed by the necessity of retracting the cannon into the hull for reloading through the muzzle. Simultaneous availability of longer barrels and slower burning brown powder increased projectile velocities to . Spin-stabilized elongated projectiles offered both reliable positioning of percussion fuzes and improved armor penetration through increased sectional density.
What made the gun really revolutionary lay in the technique of the construction of the gun barrel that allowed it to withstand much more powerful explosive forces. The "built-up gun, built-up" method involved assembling the barrel with wrought-iron (later mild steel was used) tubes of successively larger diameter. The next tube would be heated to allow it to expand and fit over the previous tube. When it cooled the tube would contract to a slightly smaller diameter, which allowed an even pressure along the walls of the gun which was directed inward against the outward forces that the gun firing exerted on the barrel. Built-up guns with rifling made cast cannon obsolete by 1880.
Armstrong's system was adopted in 1858, initially for "special service in the field" and initially he only produced smaller artillery pieces, 6-pounder (2.5 in/64 mm) mountain or light field guns, 9-pounder (3 in/76 mm) guns for horse artillery, and RBL 12 pounder 8 cwt Armstrong gun, 12-pounder (3 inches /76 mm) field guns.
However, despite the gun's advantages, an 1863 Ammunition, Ordnance Select committee (United Kingdom), Select committee decided to revert to muzzle-loading artillery pieces on the grounds of cost and efficiency.
Large-caliber Breech-loading weapon, breech-loading naval artillery became practical with French development of the interrupted screw Obturating ring, obturator by Charles Ragon de Bange in 1872. It was only after a serious accident on board in 1879 when the left muzzleloading gun in the forward turret exploded during practice firing in the Sea of Marmora killing 11 and injuring a further 35, that the Royal Navy decisively changed to breech loading guns. Improved loading and handling procedures were also adopted, and Thunderer herself was re-equipped with long-calibre 10" breech-loaders. Breech loading artillery overcame barrel length limitations of cast cannon imposed by the necessity of retracting the cannon into the hull for reloading through the muzzle. Simultaneous availability of longer barrels and slower burning brown powder increased projectile velocities to . Spin-stabilized elongated projectiles offered both reliable positioning of percussion fuzes and improved armor penetration through increased sectional density.
Gun turrets
Before the development of large-calibre, long-range guns in the mid-19th century, the classic battleship design used rows of port-mounted guns on each side of the ship, often mounted in casemates. Firepower was provided by a large number of guns which could only be aimed in a limited arc from one side of the ship. Due to instability, fewer larger and heavier guns can be carried on a ship. Also, the casemates often sat near the waterline, which made them vulnerable to flooding and restricted their use to calm seas. Gun turret, Turrets were weapon mounts designed to protect the crew and mechanism of the artillery, artillery piece and with the capability of being aimed and fired in many directions as a rotating weapon platform. This platform can be mounted on a fortification, fortified building or structure such as an anti-naval land battery, or on a combat vehicle, anaval ship
A naval ship (or naval vessel) is a military ship (or sometimes boat, depending on classification) that is used by a navy. Naval ships are differentiated from civilian ships by construction and purpose. Generally, naval ships are damage resili ...
, or a military aviation, military aircraft.
During the Crimean War, Captain Cowper Phipps Coles constructed a raft with guns protected by a 'cupola' and used the raft, named Siege of Taganrog, ''Lady Nancy'', to shell the Russian town of Taganrog in the Black Sea. ''Lady Nancy'' "proved a great success", and Coles patented his rotating turret after the war. Following Coles' patenting, the British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, department of the Government of the United Kingdom that was responsible for the command of the Royal Navy.
Historically, its titular head was the Lord High Admiral of the ...
ordered a prototype of Coles' design in 1859, which was installed in the floating battery vessel, , for trials in 1861, becoming the first warship to be fitted with a revolving gun turret. Coles' design aim was to create a ship with the greatest possible all round arc of fire, as low in the water as possible to minimise the target.
The Admiralty accepted the principle of the turret gun as a useful innovation, and incorporated it into other new designs. Coles submitted a design for a ship having ten domed turrets each housing two large guns. The design was rejected as impractical, although the Admiralty remained interested in turret ships and instructed its own designers to create better designs. Coles enlisted the support of Albert, Prince Consort, Prince Albert, who wrote to the first Lord of the Admiralty, the Duke of Somerset, supporting the construction of a turret ship. In January 1862, the Admiralty agreed to construct a ship, , which had four turrets and a low freeboard, intended only for coastal defence. Coles was allowed to design the turrets, but the ship was the responsibility of the chief Constructor Isaac Watts (naval architect), Isaac Watts.
Another of Coles' designs, , was completed in August 1864. Its existing broadside guns were replaced with four turrets on a flat deck and the ship was fitted with of armour in a belt around the waterline. Early ships like ''Monitor'' and ''Royal Sovereign'' had little sea-keeping qualities, being limited to coastal waters. Coles, in collaboration with Sir Edward James Reed, went on to design and build , the first seagoing warship to carry her guns in turrets. Laid down in 1866 and completed in June 1869, it carried two turrets, although the inclusion of a forecastle and poop prevented the guns firing fore and aft.
 The gun turret was independently invented by the Swedish inventor John Ericsson in America, although his design was technologically inferior to Coles'.
Ericsson designed in 1861. Its most prominent feature was a large cylindrical gun turret mounted amidships above the low-freeboard upper Hull (watercraft), hull, also called the "raft". This extended well past the sides of the lower, more traditionally shaped hull. A small armored pilot house was fitted on the upper deck towards the bow, however, its position prevented ''Monitor'' from firing her guns straight forward. One of Ericsson's prime goals in designing the ship was to present the smallest possible target to enemy gunfire.
The turret's rounded shape helped to deflect cannon shot. A pair of donkey engines rotated the turret through a set of gears; a full rotation was made in 22.5 seconds during testing on 9 February 1862. Fine control of the turret proved to be difficult as the engine would have to be placed in reverse if the turret overshot its mark or another full rotation could be made. Including the guns, the turret weighed approximately ; the entire weight rested on an iron spindle that had to be jacked up using a wedge before the turret could rotate.
The spindle was in diameter, which gave it ten times the strength needed in preventing the turret from sliding sideways. When not in use, the turret rested on a brass ring on the deck that was intended to form a watertight seal. In service, however, this proved to leak heavily, despite caulking by the crew. The gap between the turret and the deck proved to be a problem as debris and shell fragments entered the gap and jammed the turrets of several s, which used the same turret design, during the First Battle of Charleston Harbor in April 1863. Direct hits at the turret with heavy shot also had the potential to bend the spindle, which could also jam the turret.
The gun turret was independently invented by the Swedish inventor John Ericsson in America, although his design was technologically inferior to Coles'.
Ericsson designed in 1861. Its most prominent feature was a large cylindrical gun turret mounted amidships above the low-freeboard upper Hull (watercraft), hull, also called the "raft". This extended well past the sides of the lower, more traditionally shaped hull. A small armored pilot house was fitted on the upper deck towards the bow, however, its position prevented ''Monitor'' from firing her guns straight forward. One of Ericsson's prime goals in designing the ship was to present the smallest possible target to enemy gunfire.
The turret's rounded shape helped to deflect cannon shot. A pair of donkey engines rotated the turret through a set of gears; a full rotation was made in 22.5 seconds during testing on 9 February 1862. Fine control of the turret proved to be difficult as the engine would have to be placed in reverse if the turret overshot its mark or another full rotation could be made. Including the guns, the turret weighed approximately ; the entire weight rested on an iron spindle that had to be jacked up using a wedge before the turret could rotate.
The spindle was in diameter, which gave it ten times the strength needed in preventing the turret from sliding sideways. When not in use, the turret rested on a brass ring on the deck that was intended to form a watertight seal. In service, however, this proved to leak heavily, despite caulking by the crew. The gap between the turret and the deck proved to be a problem as debris and shell fragments entered the gap and jammed the turrets of several s, which used the same turret design, during the First Battle of Charleston Harbor in April 1863. Direct hits at the turret with heavy shot also had the potential to bend the spindle, which could also jam the turret.
 The turret was intended to mount a pair of smoothbore Dahlgren guns, but they were not ready in time and guns were substituted. Each gun weighed approximately . ''Monitor''s guns used the standard propellant charge of specified by the 1860 ordnance for targets "distant", "near", and "ordinary", established by the gun's designer Dahlgren himself. They could fire a round shot or shell up to a range of at an elevation of +15°.
HMS ''Thunderer'' represented the culmination of this pioneering work. An ironclad warship, ironclad turret ship designed by Edward James Reed, it was equipped with revolving turrets that used pioneering hydraulic turret machinery to maneouvre the guns. It was also the world's first mastless battleship, built with a central superstructure layout, and became the prototype for all subsequent warships. of 1871 was another pivotal design, and led directly to the modern battleship.
The turret was intended to mount a pair of smoothbore Dahlgren guns, but they were not ready in time and guns were substituted. Each gun weighed approximately . ''Monitor''s guns used the standard propellant charge of specified by the 1860 ordnance for targets "distant", "near", and "ordinary", established by the gun's designer Dahlgren himself. They could fire a round shot or shell up to a range of at an elevation of +15°.
HMS ''Thunderer'' represented the culmination of this pioneering work. An ironclad warship, ironclad turret ship designed by Edward James Reed, it was equipped with revolving turrets that used pioneering hydraulic turret machinery to maneouvre the guns. It was also the world's first mastless battleship, built with a central superstructure layout, and became the prototype for all subsequent warships. of 1871 was another pivotal design, and led directly to the modern battleship.
Armour-piercing shot
 During the late 1850s, the development and implementation of the ironclad warship carried wrought iron armor of considerable thickness. This armor was practically immune to both the round cast-iron cannonballs then in use and to the recently developed Artillery shell, explosive shell.
The first solution to this problem was effected by William Palliser, Major Sir W. Palliser. His Palliser shot, approved in 1867, was made of cast iron, the head being chilled in casting to harden it, using composite molds with a metal, water cooled portion for the head. At times there were defects that led to cracking in the projectiles but these were overcome with time. Bronze studs were installed into the outside of the projectile so as to engage the rifling grooves in the gun barrel. The base had a hollow pocket but was not filled with powder or explosive: the cavity was necessitated by difficulties in Casting (metalworking), casting large solid projectiles without their cracking when they cooled, because the nose and base of the projectiles cooled at different rates, and in fact a larger cavity facilitated a better quality casting.
At the Battle of Angamos (8 October 1879) the Chilean ironclad warships fired twenty 250-pound-Palliser gunshots against the Peruvian monitor , with devastating results. It was the first time that such piercing shells were used in actual combat.
These chilled iron shots proved very effective against wrought iron armor, but were not serviceable against compound and steel armor, which was first introduced in the 1880s. A new departure therefore had to be made, and Forging, forged steel rounds with points Hardening (metallurgy), hardened by water took the place of the Palliser shot. At first, these forged-steel rounds were made of ordinary carbon steel, but as armor improved in quality, the projectiles followed suit.
From the 1890s onwards, Cementation process, cemented steel armor became commonplace, initially only on the thicker armor of warships. To combat this, the projectile was formed of steel—forged or cast—containing both nickel and chromium. Another change was the introduction of a soft metal cap over the point of the shell – so called "Makarov tips" invented by Russian admiral Stepan Makarov. This "cap" increased penetration by cushioning some of the impact shock and preventing the armor-piercing point from being damaged before it struck the armor face, or the body of the shell from shattering. It could also help penetration from an oblique angle by keeping the point from deflecting away from the armor face. (See: APCBC ammunition)
Increased armor penetration became possible when projectile velocities of were obtained as smokeless powder propellants replaced gunpowder around the turn of the 20th century.
During the late 1850s, the development and implementation of the ironclad warship carried wrought iron armor of considerable thickness. This armor was practically immune to both the round cast-iron cannonballs then in use and to the recently developed Artillery shell, explosive shell.
The first solution to this problem was effected by William Palliser, Major Sir W. Palliser. His Palliser shot, approved in 1867, was made of cast iron, the head being chilled in casting to harden it, using composite molds with a metal, water cooled portion for the head. At times there were defects that led to cracking in the projectiles but these were overcome with time. Bronze studs were installed into the outside of the projectile so as to engage the rifling grooves in the gun barrel. The base had a hollow pocket but was not filled with powder or explosive: the cavity was necessitated by difficulties in Casting (metalworking), casting large solid projectiles without their cracking when they cooled, because the nose and base of the projectiles cooled at different rates, and in fact a larger cavity facilitated a better quality casting.
At the Battle of Angamos (8 October 1879) the Chilean ironclad warships fired twenty 250-pound-Palliser gunshots against the Peruvian monitor , with devastating results. It was the first time that such piercing shells were used in actual combat.
These chilled iron shots proved very effective against wrought iron armor, but were not serviceable against compound and steel armor, which was first introduced in the 1880s. A new departure therefore had to be made, and Forging, forged steel rounds with points Hardening (metallurgy), hardened by water took the place of the Palliser shot. At first, these forged-steel rounds were made of ordinary carbon steel, but as armor improved in quality, the projectiles followed suit.
From the 1890s onwards, Cementation process, cemented steel armor became commonplace, initially only on the thicker armor of warships. To combat this, the projectile was formed of steel—forged or cast—containing both nickel and chromium. Another change was the introduction of a soft metal cap over the point of the shell – so called "Makarov tips" invented by Russian admiral Stepan Makarov. This "cap" increased penetration by cushioning some of the impact shock and preventing the armor-piercing point from being damaged before it struck the armor face, or the body of the shell from shattering. It could also help penetration from an oblique angle by keeping the point from deflecting away from the armor face. (See: APCBC ammunition)
Increased armor penetration became possible when projectile velocities of were obtained as smokeless powder propellants replaced gunpowder around the turn of the 20th century.
Quick-firing artillery
Underwater hull damage possible withtorpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such ...
es encouraged development of small, inexpensive torpedo boats capable of sinking the largest warships. By the end of the 19th century, all warships required a defensive battery of quick-firing guns capable of hitting fast, maneuverable torpedo boats.
The Royal Navy first introduced the QF 4.7 inch Gun Mk I–IV, quick-firing 4.7-inch gun in HMS ''Sharpshooter'' in 1889, and the QF 6 inch /40 naval gun, quick-firing 6-inch MK 1 in , launched 1891. Other navies followed suit; the French Navy installed quick-firing weapons on its ships completed in 1894–95.
Quick-firing guns were a key characteristic of the pre-dreadnought battleship, the dominant design of the 1890s. The quick-firing guns, while unable to penetrate thick armour, were intended to destroy the superstructure of an opposing battleship, start fires, and kill or distract the enemy's gun crews. The development of heavy guns and their increasing rate of fire meant that the quick-firer lost its status as the decisive weapon of naval combat in the early 1900s, though quick-firing guns were vital to defend battleships from attack by torpedo boats and destroyers, and formed the main armament of smaller vessels.
Most late-19th-century warships mounted naval artillery of more than one caliber because of uncertainty about the relative destruction possible from a few large shells (which might miss) in comparison to the increased hit probability of a larger number of less damaging small-caliber shells fired within the same time period. Quick-firing guns were initially breech-loading weapons firing ammunition small enough to be loaded by hand. Later substitution of brass cartridge (firearms), cartridges for silk powder bags allowed increased rates of fire using Rifled breech loader#Krupp sliding block, sliding wedge breech blocks. Increasing mechanization ultimately enabled similar rates of fire from naval artillery calibers up to 8"/55 caliber gun#Mark 16, .
Fire control
 When gunnery ranges increased dramatically in the late 19th century, it was no longer a simple matter of calculating the proper aim point, given the flight times of the shells. Increasingly sophisticated analog computer, mechanical calculators were employed for proper Gun laying, gunlaying, typically with various spotters and distance measures being sent to a central plotting station deep within the ship. There the fire direction teams fed in the location, speed and direction of the ship and its target, as well as various adjustments for Coriolis effect, weather effects on the air, and other adjustments.
The resulting directions, known as a firing solution, would then be fed back out to the turrets for laying. If the rounds missed, an observer could work out how far they missed by and in which direction, and this information could be fed back into the computer along with any changes in the rest of the information and another shot attempted.
The situation for naval fire control was highly complex, due to the need to control the firing of several guns at once. In naval engagements both the firing guns and target are moving, and the variables are compounded by the greater distances and times involved. Rudimentary naval fire control systems were first developed around the time of World War I.
Arthur Pollen and Frederic Charles Dreyer independently developed the first such systems. Pollen began working on the problem after noting the poor accuracy of naval artillery at a gunnery practice near Malta in 1900. William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, Lord Kelvin, widely regarded as Britain's leading scientist, first proposed using an analogue computer to solve the equations which arise from the relative motion of the ships engaged in the battle and the time delay in the flight of the shell to calculate the required trajectory and therefore the direction and elevation of the guns.
Pollen aimed to produce a combined Calculating machine, mechanical computer and automatic plot of ranges and rates for use in centralised fire control. To obtain accurate data of the target's position and relative motion, Pollen developed a plotting unit (or plotter) to capture this data. He added a gyroscope to allow for the Yaw angle, yaw of the firing ship. Again this required substantial development of the, at the time, primitive gyroscope to provide continuous reliable correction. Trials were carried out in 1905 and 1906, which although completely unsuccessful showed promise. He was encouraged in his efforts by the rapidly rising figure of Admiral John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, Jackie Fisher, Admiral Arthur Knyvet Wilson and the Director of Naval Ordnance and Torpedoes (DNO), John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, John Jellicoe. Pollen continued his work, with tests carried out on Royal Navy warships intermittently.
Meanwhile, a group led by Dreyer designed a similar system. Although both systems were ordered for new and existing ships of the Royal Navy, the Dreyer system eventually found most favour with the Navy in its definitive Mark IV* form. The addition of director (military), director control facilitated a full, practicable fire control system for World War I ships, and most RN capital ships were so fitted by mid 1916. The director was high up over the ship where operators had a superior view over any gunlayer in the gun turret, turrets. It was also able to co-ordinate the fire of the turrets so that their combined fire worked together. This improved aiming and larger optical rangefinders improved the estimate of the enemy's position at the time of firing. The system was eventually replaced by the improved "Admiralty Fire Control Table" for ships built after 1927.
When gunnery ranges increased dramatically in the late 19th century, it was no longer a simple matter of calculating the proper aim point, given the flight times of the shells. Increasingly sophisticated analog computer, mechanical calculators were employed for proper Gun laying, gunlaying, typically with various spotters and distance measures being sent to a central plotting station deep within the ship. There the fire direction teams fed in the location, speed and direction of the ship and its target, as well as various adjustments for Coriolis effect, weather effects on the air, and other adjustments.
The resulting directions, known as a firing solution, would then be fed back out to the turrets for laying. If the rounds missed, an observer could work out how far they missed by and in which direction, and this information could be fed back into the computer along with any changes in the rest of the information and another shot attempted.
The situation for naval fire control was highly complex, due to the need to control the firing of several guns at once. In naval engagements both the firing guns and target are moving, and the variables are compounded by the greater distances and times involved. Rudimentary naval fire control systems were first developed around the time of World War I.
Arthur Pollen and Frederic Charles Dreyer independently developed the first such systems. Pollen began working on the problem after noting the poor accuracy of naval artillery at a gunnery practice near Malta in 1900. William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, Lord Kelvin, widely regarded as Britain's leading scientist, first proposed using an analogue computer to solve the equations which arise from the relative motion of the ships engaged in the battle and the time delay in the flight of the shell to calculate the required trajectory and therefore the direction and elevation of the guns.
Pollen aimed to produce a combined Calculating machine, mechanical computer and automatic plot of ranges and rates for use in centralised fire control. To obtain accurate data of the target's position and relative motion, Pollen developed a plotting unit (or plotter) to capture this data. He added a gyroscope to allow for the Yaw angle, yaw of the firing ship. Again this required substantial development of the, at the time, primitive gyroscope to provide continuous reliable correction. Trials were carried out in 1905 and 1906, which although completely unsuccessful showed promise. He was encouraged in his efforts by the rapidly rising figure of Admiral John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, Jackie Fisher, Admiral Arthur Knyvet Wilson and the Director of Naval Ordnance and Torpedoes (DNO), John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, John Jellicoe. Pollen continued his work, with tests carried out on Royal Navy warships intermittently.
Meanwhile, a group led by Dreyer designed a similar system. Although both systems were ordered for new and existing ships of the Royal Navy, the Dreyer system eventually found most favour with the Navy in its definitive Mark IV* form. The addition of director (military), director control facilitated a full, practicable fire control system for World War I ships, and most RN capital ships were so fitted by mid 1916. The director was high up over the ship where operators had a superior view over any gunlayer in the gun turret, turrets. It was also able to co-ordinate the fire of the turrets so that their combined fire worked together. This improved aiming and larger optical rangefinders improved the estimate of the enemy's position at the time of firing. The system was eventually replaced by the improved "Admiralty Fire Control Table" for ships built after 1927.
Big-gun battleships
 Significant gunnery developments occurred in the late 1890s and the early 1900s, culminating with the launch of the revolutionary in 1906. Sir Percy Scott was given command of HMS ''Scylla'' in 1896, where he was able to implement his new theories on gunnery, scoring the unprecedented success of 80% during the 1897 gunnery trials. This was totally unprecedented, as the average in the Royal Navy was just 28%.
Scott noted that night time signalling between ships in the fleet was slow and inaccurate. He addressed this in two ways: he devised training aids and put his signallers under instruction and he devised a new more effective flashing lamp. The new efficiency of his ship's signalling was adopted by the whole Mediterranean fleet. He devised a new sub-calibre gun which involved fitting a one-inch-calibre rifled barrel inside the barrel of the main armament but which used the main gun's controls. He also came up with new sights employing telescope optics and new training targets. In the Navy's 1901 prize firing, ''Terrible'' achieved the same score of 80%, and Scott's gunnery practices were adopted by other ships in the fleet. Later, Scott taught at the naval gunnery school at Whale Island, Hampshire. a largely honorary role which he held until promotion to flag rank in 1905.
The development of the torpedo meant that it became necessary to engage an enemy at ranges outside torpedo range. This in turn meant that the old system whereby a gunlayer in each turret pointed and fired the turret guns independently could no longer be expected to achieve a significant hit rate on an opposing ship. Scott was instrumental in encouraging the development and installation of director firing, a system whereby the guns were all pointed, elevated and fired from a single point, usually at the top of the foremast. By firing all the guns simultaneously it was possible to observe the simultaneous splashes produced and correct the aim visually.
Significant gunnery developments occurred in the late 1890s and the early 1900s, culminating with the launch of the revolutionary in 1906. Sir Percy Scott was given command of HMS ''Scylla'' in 1896, where he was able to implement his new theories on gunnery, scoring the unprecedented success of 80% during the 1897 gunnery trials. This was totally unprecedented, as the average in the Royal Navy was just 28%.
Scott noted that night time signalling between ships in the fleet was slow and inaccurate. He addressed this in two ways: he devised training aids and put his signallers under instruction and he devised a new more effective flashing lamp. The new efficiency of his ship's signalling was adopted by the whole Mediterranean fleet. He devised a new sub-calibre gun which involved fitting a one-inch-calibre rifled barrel inside the barrel of the main armament but which used the main gun's controls. He also came up with new sights employing telescope optics and new training targets. In the Navy's 1901 prize firing, ''Terrible'' achieved the same score of 80%, and Scott's gunnery practices were adopted by other ships in the fleet. Later, Scott taught at the naval gunnery school at Whale Island, Hampshire. a largely honorary role which he held until promotion to flag rank in 1905.
The development of the torpedo meant that it became necessary to engage an enemy at ranges outside torpedo range. This in turn meant that the old system whereby a gunlayer in each turret pointed and fired the turret guns independently could no longer be expected to achieve a significant hit rate on an opposing ship. Scott was instrumental in encouraging the development and installation of director firing, a system whereby the guns were all pointed, elevated and fired from a single point, usually at the top of the foremast. By firing all the guns simultaneously it was possible to observe the simultaneous splashes produced and correct the aim visually.
 As battle ranges were pushed out to an unprecedented , the distance was great enough to force gunners to wait for the shells to arrive before applying corrections for the next salvo. A related problem was that the shell splashes from the more numerous smaller weapons tended to obscure the splashes from the bigger guns. Either the smaller-Caliber, calibre guns would have to hold their fire to wait for the slower-firing heavies, losing the advantage of their faster rate of fire, or it would be uncertain whether a splash was due to a heavy or a light gun, making ranging and aiming unreliable. Italian naval architect Vittorio Cuniberti first argued for the concept of an all-big-gun battleship in 1903, proposing an "ideal" future British battleship of , with a main battery of a dozen 12-inch guns in eight turrets, 12 inches of belt armour, and a speed of .
First Sea Lord John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, Sir John Fisher pushed through the Board of Admiralty a decision to arm the next battleship with 12-inch guns and that it would have a speed no less than . The result was HMS ''Dreadnought'', which rendered all previous ships immediately obsolete on its launch in 1906. The ship mounted the 45-caliber (artillery), calibre BL 12 inch Mk X naval gun, BL 12-inch Mark X gun in five twin gun turrets. These could deliver a broadside of a maximum of eight guns and could be elevated up to +13.5°. They fired projectiles at a muzzle velocity of ; at 13.5°, this provided a maximum range of with Armor-piercing shot and shell, armour-piercing (AP) 2 List of British ordnance terms#C.R.H., crh shells. At 16° elevation, the range was extended to using the more aerodynamic, but slightly heavier 4 crh AP shells. The rate of fire of these guns was one to two rounds per minute. The ships carried 80 rounds per gun.
As battle ranges were pushed out to an unprecedented , the distance was great enough to force gunners to wait for the shells to arrive before applying corrections for the next salvo. A related problem was that the shell splashes from the more numerous smaller weapons tended to obscure the splashes from the bigger guns. Either the smaller-Caliber, calibre guns would have to hold their fire to wait for the slower-firing heavies, losing the advantage of their faster rate of fire, or it would be uncertain whether a splash was due to a heavy or a light gun, making ranging and aiming unreliable. Italian naval architect Vittorio Cuniberti first argued for the concept of an all-big-gun battleship in 1903, proposing an "ideal" future British battleship of , with a main battery of a dozen 12-inch guns in eight turrets, 12 inches of belt armour, and a speed of .
First Sea Lord John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, Sir John Fisher pushed through the Board of Admiralty a decision to arm the next battleship with 12-inch guns and that it would have a speed no less than . The result was HMS ''Dreadnought'', which rendered all previous ships immediately obsolete on its launch in 1906. The ship mounted the 45-caliber (artillery), calibre BL 12 inch Mk X naval gun, BL 12-inch Mark X gun in five twin gun turrets. These could deliver a broadside of a maximum of eight guns and could be elevated up to +13.5°. They fired projectiles at a muzzle velocity of ; at 13.5°, this provided a maximum range of with Armor-piercing shot and shell, armour-piercing (AP) 2 List of British ordnance terms#C.R.H., crh shells. At 16° elevation, the range was extended to using the more aerodynamic, but slightly heavier 4 crh AP shells. The rate of fire of these guns was one to two rounds per minute. The ships carried 80 rounds per gun.
 Within five years of the commissioning of ''Dreadnought'', a new generation of more powerful "super-dreadnoughts" was being built. The arrival of the super-dreadnought is commonly believed to have started with the British . What made them 'super' was the unprecedented 2,000-ton jump in displacement, the introduction of the heavier BL 13.5 inch /45 naval gun, 13.5-inch (343 mm) gun, and the placement of all the main armament on the centerline. In the four years between ''Dreadnought'' and ''Orion'', displacement had increased by 25%, and weight of broadside had doubled.
In comparison to the rapid advancement of the preceding half-century, naval artillery changed comparatively little through World War I and World War II. Battleships remained similar to ''Dreadnought'', torpedo boats evolved into destroyers, and ships of intermediate size were called cruisers. All ship types became larger as the calibre of heavy guns increased (to a maximum of 40 cm/45 Type 94 naval gun, in the
Within five years of the commissioning of ''Dreadnought'', a new generation of more powerful "super-dreadnoughts" was being built. The arrival of the super-dreadnought is commonly believed to have started with the British . What made them 'super' was the unprecedented 2,000-ton jump in displacement, the introduction of the heavier BL 13.5 inch /45 naval gun, 13.5-inch (343 mm) gun, and the placement of all the main armament on the centerline. In the four years between ''Dreadnought'' and ''Orion'', displacement had increased by 25%, and weight of broadside had doubled.
In comparison to the rapid advancement of the preceding half-century, naval artillery changed comparatively little through World War I and World War II. Battleships remained similar to ''Dreadnought'', torpedo boats evolved into destroyers, and ships of intermediate size were called cruisers. All ship types became larger as the calibre of heavy guns increased (to a maximum of 40 cm/45 Type 94 naval gun, in the High-angle artillery (dual purpose, anti-aircraft and anti-surface)
 Although naval artillery had been designed to perform within the classical broadside tactics of the age of sail, World War I demonstrated the need for naval artillery mounts capable of greater elevation for anti-aircraft gun, defending against aircraft. High-velocity naval artillery intended to puncture side armor at close range was theoretically capable of hitting targets miles away with the aid of fire control directors; but the maximum elevation of guns mounted within restrictive armored casemates prevented reaching those ranges.
The QF 4 inch Mk V naval gun was one of the first artillery pieces to be adapted as an anti-aircraft gun and mounted on ships for defence. It was first used in 1914 as a secondary armament on s in a high-angle anti-aircraft role.
Most naval artillery on ships built after World War I was capable of elevating to at least 45°, and some guns as large as 20 cm/50 3rd Year Type naval gun#Type E, were capable of elevating to 70° for potential use against aircraft. The Japanese used their large caliber guns for anti-aircraft defense when employing San Shiki (anti-aircraft shell), San Shiki "beehive" shells.
Dual purpose guns were devised to protect ships against both torpedo boats and aircraft, and for WWII they comprised the primary armament on frigates and destroyers, and the secondary armament on cruisers and battleships. Dual purpose guns such as the US Navy's 5"/38 caliber gun, 5-inch (127 mm) /38 caliber guns functioned as heavy anti-aircraft artillery, firing VT shells (proximity fuzed-shells) that would detonate when they came close to an enemy aircraft, and could also aim into the water to create waterspouts which could bring down low flying aircraft such as torpedo planes. The light anti-aircraft artillery typically consisted of autocannons such as the Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60, Bofors 40 mm anti-aircraft guns and 65 single Oerlikon 20 mm cannon.
As destroyers began to assume Anti-submarine warfare, ASW roles to include protection of the fleet from submarines, they were fitted with high-angle
Although naval artillery had been designed to perform within the classical broadside tactics of the age of sail, World War I demonstrated the need for naval artillery mounts capable of greater elevation for anti-aircraft gun, defending against aircraft. High-velocity naval artillery intended to puncture side armor at close range was theoretically capable of hitting targets miles away with the aid of fire control directors; but the maximum elevation of guns mounted within restrictive armored casemates prevented reaching those ranges.
The QF 4 inch Mk V naval gun was one of the first artillery pieces to be adapted as an anti-aircraft gun and mounted on ships for defence. It was first used in 1914 as a secondary armament on s in a high-angle anti-aircraft role.
Most naval artillery on ships built after World War I was capable of elevating to at least 45°, and some guns as large as 20 cm/50 3rd Year Type naval gun#Type E, were capable of elevating to 70° for potential use against aircraft. The Japanese used their large caliber guns for anti-aircraft defense when employing San Shiki (anti-aircraft shell), San Shiki "beehive" shells.
Dual purpose guns were devised to protect ships against both torpedo boats and aircraft, and for WWII they comprised the primary armament on frigates and destroyers, and the secondary armament on cruisers and battleships. Dual purpose guns such as the US Navy's 5"/38 caliber gun, 5-inch (127 mm) /38 caliber guns functioned as heavy anti-aircraft artillery, firing VT shells (proximity fuzed-shells) that would detonate when they came close to an enemy aircraft, and could also aim into the water to create waterspouts which could bring down low flying aircraft such as torpedo planes. The light anti-aircraft artillery typically consisted of autocannons such as the Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60, Bofors 40 mm anti-aircraft guns and 65 single Oerlikon 20 mm cannon.
As destroyers began to assume Anti-submarine warfare, ASW roles to include protection of the fleet from submarines, they were fitted with high-angle depth charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon designed to destroy submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited ...
mortar (weapon), mortars (called Y-guns, K-guns or squid (weapon), squid).
Naval bombardment
Battleships were used in support of amphibious landing, amphibious operations since the late 19th century in the form of naval gunfire support, naval bombardment. Under international law such bombardments are regulated by the general law of war and the "Hague Conventions (1907), Bombardment by Naval Forces in Time of War (Hague Convention IX)"; 18 October 1907. At the beginning of World War I, its principal practitioner was theRoyal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
. During the War RN ships fired against targets at Gallipoli campaign, Gallipoli, the Salonika front and along the Belgian Coast. In the Aegean Sea, Aegean, the problems were not especially challenging, and enemy coastal defences (forts, shore-batteries etc.) were fairly unsophisticated; but along the Belgian Coast the German Empire, Germans constructed an extensive, well-equipped and well-coordinated system of gun-batteries to defend the coast. Ports, such as Ostend and Zeebrugge were of major importance to the U-boat Campaign (World War I), U-boat campaign and were frequently bombarded by British monitor (warship), monitors operating from Dover and Dunkirk.
 The Royal Navy continually advanced their technology and techniques necessary to conduct effective bombardments in the face of the German defenders—firstly refining aerial reconnaissance techniques, then experimenting with night-bombardment and moving on to adopt indirect fire. Finally, in the summer of 1918, monitors were equipped with Gyro Director Training gear, which effectively provided the Director with a gyro-stabilised Artificial Line of Sight, and thereby enabled a ship to carry out Indirect Bombardment while underway. This was a very significant advance, and established a firm foundation for naval bombardment as practiced by the Royal Navy and United States Navy during World War II.
The practice reached its zenith during World War II, when the availability of man-portable radio systems and sophisticated relay networks allowed forward observers to transmit targeting information and provide almost instant accuracy reports—once troops had landed. Battleships, cruisers and destroyers would pound shore installations, sometimes for days, in the hope of reducing fortifications and attriting defending forces. Obsolete battleships unfit for combat against other ships were often used as floating gun platforms expressly for this purpose. However, given the relatively primitive nature of the fire control computers and radar of the era combined with the high velocity of naval gunfire, accuracy was poor until troops landed and were able to radio back reports to the ship.
Naval gunfire could reach as far as inland, and was often used to supplement land-based artillery. The heavy-calibre guns of some eighteen battleships and cruisers were used to stop German Panzer counterattack at Salerno. Naval gunfire was used extensively throughout Operation Overlord, Normandy, although initially the surprise nature of the landings themselves precluded a drawn-out bombardment which could have reduced the Atlantic Wall defences sufficiently, a process that fell to Hobart's Funnies, specialist armoured vehicles instead.
The Royal Navy continually advanced their technology and techniques necessary to conduct effective bombardments in the face of the German defenders—firstly refining aerial reconnaissance techniques, then experimenting with night-bombardment and moving on to adopt indirect fire. Finally, in the summer of 1918, monitors were equipped with Gyro Director Training gear, which effectively provided the Director with a gyro-stabilised Artificial Line of Sight, and thereby enabled a ship to carry out Indirect Bombardment while underway. This was a very significant advance, and established a firm foundation for naval bombardment as practiced by the Royal Navy and United States Navy during World War II.
The practice reached its zenith during World War II, when the availability of man-portable radio systems and sophisticated relay networks allowed forward observers to transmit targeting information and provide almost instant accuracy reports—once troops had landed. Battleships, cruisers and destroyers would pound shore installations, sometimes for days, in the hope of reducing fortifications and attriting defending forces. Obsolete battleships unfit for combat against other ships were often used as floating gun platforms expressly for this purpose. However, given the relatively primitive nature of the fire control computers and radar of the era combined with the high velocity of naval gunfire, accuracy was poor until troops landed and were able to radio back reports to the ship.
Naval gunfire could reach as far as inland, and was often used to supplement land-based artillery. The heavy-calibre guns of some eighteen battleships and cruisers were used to stop German Panzer counterattack at Salerno. Naval gunfire was used extensively throughout Operation Overlord, Normandy, although initially the surprise nature of the landings themselves precluded a drawn-out bombardment which could have reduced the Atlantic Wall defences sufficiently, a process that fell to Hobart's Funnies, specialist armoured vehicles instead.
Artillery ranges
The effective range of naval artillery evolved over the course of its history.Decline
By the mid-20th century, aircraft began to replace naval artillery as more effective weapons against ships, especially during World War II. This was particularly true of the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II, Pacific Ocean theater where there ended up being far fewer engagements between surface combatants, including only two "battleship-versus-battleship" meetings. Most of the decisive battles in the Pacific were carrier-versus-carrier, included Battle of the Coral Sea, Coral Sea, the first battle in which the opposing ships neither sighted nor fired directly upon one another, followed by Battle of Midway, Midway, the Battle of the Eastern Solomons, Eastern Solomons, and the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands, Santa Cruz Islands in 1942; and the Battle of the Philippine Sea, Philippine Sea in 1944. Larger surface combatants (cruisers, battleships) thus employed their large caliber naval guns mostly for shore bombardment. Also, the Japanese fired San Shiki (anti-aircraft shell), San Shiki "beehive" shells for anti-aircraft defense, as did the German battleship ''German battleship Tirpitz, Tirpitz'', but this largely proved ineffective against attacking aircraft. Naval artillery calibers greater than were not installed on most new ships after World War II. With the progression of ship design away from heavy caliber guns, nearly all main gun armaments developed since then are of Dual-purpose gun, dual-purpose nature. Ships who remained in service equipped with old large-caliber artillery were used only for naval gunfire support, as the anti-ship missile has supplanted naval guns for ship-versus-ship combat. USS Missouri (BB-63), USS ''Missouri'', the last active battleship with large-caliber guns () was decommissioned in 1992. Submarines shed their deck guns as a handicap in modern naval tactics. After World War II, Missile, guided missiles were retrofitted to certain surface combatants. New classes of vessels were designed with guided missiles as the primary weaponry, notably the Royal Navy's Type 22 frigate whose Batch 1 and Batch 2 subclasses lacked a main gun while only carrying a pair of Bofors 40 mm L/60 gun, 40 mm anti-aircraft guns although the Batch 3 was redesigned to include a 4.5-inch Mark 8 naval gun, 4.5-inch Mark 8 Dual-purpose gun, dual-purpose main gun. Modern cruisers, destroyers, andfrigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuvera ...
s often carry 1-2 dual-purpose guns, as a backup to missile systems for anti-aircraft defense and capable of land fire support, ranging from 3 inch to 5.1 inch (76 to 130 mm) calibre. Many modern warships also carry a Close-in weapon system such as the 20 mm Phalanx CIWS as a last ditch short-range defence against anti-ship missiles or aircraft that got through the other defense systems.
Modern naval artillery is nevertheless still capable of impressive performances. For example, the Italian 127 mm (~5 inch) Otobreda 127/54 Compact can fire 40 rounds a minute at a range of over , or up to when using rocket-boosted, terminal guided "Vulcano GLR" rounds.
Smaller, multi-role vessels are also seeing a resurgence. The Ukrainian Gyurza-M-class gunboat, Gyurza M-Class Gunboat is an example, armed with 2 turrets built by Mykolayiv Mechanical Repair Plant.
In the early 21st century the use of railguns mounted on ships is under development and study.
See also
* * *Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * Guilmartin, John Francis, ''Gunpowder and Galleys: Changing Technology and Mediterranean Warfare at Sea in the Sixteenth Century.'' Cambridge University Press, London. 1974. * * * * * * * * * * * Garcia de Resende, Vida e feitos d' el-rey Dom João Segundo, 1545 *External links
1943 article on the history of naval cannons
''Popular Science'' {{Use dmy dates, date=May 2017 Naval artillery, Naval bombing operations and battles, *