Naval Aircraft Factory PN on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Naval Aircraft Factory PN was a series of open cockpit American
 The PN-7 was a 1925 development with an improved thicker section, shorter-span wings with a more modern
The PN-7 was a 1925 development with an improved thicker section, shorter-span wings with a more modern
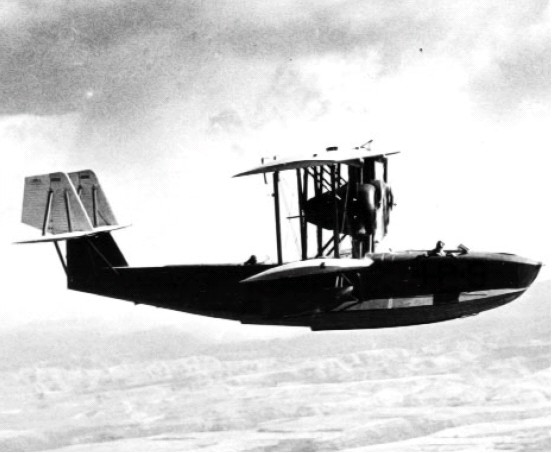


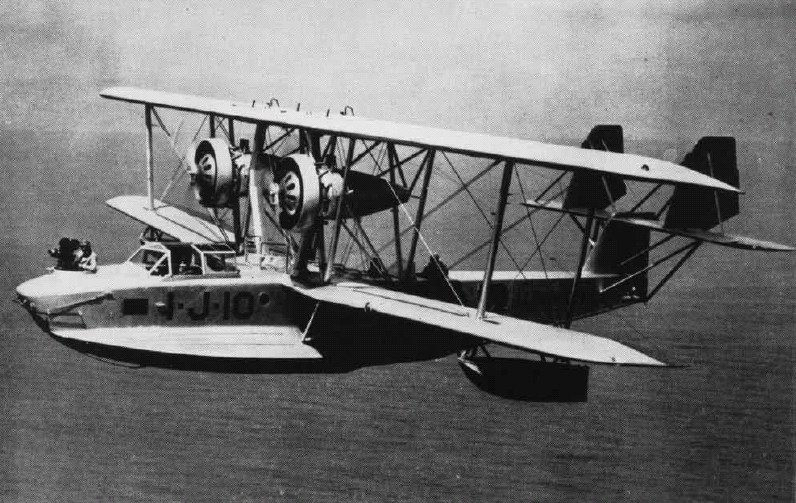
 ;PN-5
:Redesignated
;PN-5
:Redesignated

navy.mil
{{AvN aircraft designations Flying boats Naval Aircraft Factory PN01 P1N Biplanes Twin piston-engined tractor aircraft
flying boat
A flying boat is a type of seaplane with a hull, allowing it to land on water. It differs from a floatplane in having a fuselage that is purpose-designed for flotation, while floatplanes rely on fuselage-mounted floats for buoyancy.
Though ...
s of the 1920s and 1930s. A development of the Felixstowe F5L
The twin-engine F5L was one of the Felixstowe F series of flying boats developed by John Cyril Porte at the Seaplane Experimental Station, Felixstowe, England, during the First World War for production in America.
A civilian version of the ai ...
flying boat of the World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, variants of the PN were built for the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
by Douglas
Douglas may refer to:
People
* Douglas (given name)
* Douglas (surname)
Animals
* Douglas (parrot), macaw that starred as the parrot ''Rosalinda'' in Pippi Longstocking
* Douglas the camel, a camel in the Confederate Army in the American Civil ...
, Keystone and Martin Martin may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Martin Peninsula, Marie Byrd Land
* Port Martin, Adelie Land
* Point Martin, South Orkney Islands
Europe
* Martin, Croatia, a village
* Martin, Slovakia, a city
* Martín del Río, Aragón, Spain
* M ...
.
Development and design
The PN flying boats were twin-enginebiplane
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While ...
s with their engines mounted in nacelles between the fabric-covered wings. Other than on the PN-11 which had a different hull form, the hull had large chines running back to the first step similar to those on the F.5L. It had a standard crew of five, but was capable of carrying a relief crew for long patrols. Early machines had wood hulls and wings, with the wings covered in fabric, while various versions replaced these with metal components. A wide variety of V-12 and radial engines were fitted, due to problems with several of the engines chosen, with later versions generally using radial engines.
At the end of World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
was operating the Curtiss H.16 and the Felixstowe F5L
The twin-engine F5L was one of the Felixstowe F series of flying boats developed by John Cyril Porte at the Seaplane Experimental Station, Felixstowe, England, during the First World War for production in America.
A civilian version of the ai ...
Long-range patrol flying boat
A flying boat is a type of seaplane with a hull, allowing it to land on water. It differs from a floatplane in having a fuselage that is purpose-designed for flotation, while floatplanes rely on fuselage-mounted floats for buoyancy.
Though ...
s, which had been developed in collaboration with the British. The F.5L was a license-built version of the British Felixstowe F.5
The Felixstowe F.5 was a British First World War flying boat designed by Lieutenant Commander John Cyril Porte, Royal Navy, RN of the Seaplane Experimental Station in Felixstowe.
Design and development
Porte designed a better hull for the large ...
using the American Liberty engine
The Liberty L-12 is an American water-cooled 45° V-12 engine, displacing and making , designed for a high power-to-weight ratio and ease of mass production. It was designed principally as an aircraft engine and saw wide use in aero applicat ...
. The series of Felixstowe flying boats, developed by the Seaplane Experimental Station
The Seaplane Experimental Station, formerly RNAS Felixstowe, was a British aircraft design unit during the early part of the 20th century.
Creation
During June 1912, surveys began for a suitable site for a base for Naval hydro-aeroplanes, with ...
, had started with improving the hull of the Curtiss America.
PN-5 was the new designation assigned to F.5Ls built by the Naval Aircraft Factory
The Naval Aircraft Factory (NAF) was established by the United States Navy in 1918 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was created to help solve aircraft supply issues which the United States Department of the Navy, Navy Department faced upon the ...
after 1922, although identical aircraft built before then retained the F.5L designation. Under the new designation system, P indicated that the role was Patrol, and N denoted aircraft built by the US Navy's Naval Aircraft Factory. Numbers 1-4 were skipped.
The PN-6 was had an enlarged curved fin with an unbalanced rudder. The first two examples had been ordered as the final two F.5Ls, and had been designated as F.6Ls, with the new PN-6 designation coming into effect in 1922. Some F.5L/PN-5s were later upgraded to PN-6 standard. Neither the PN-5 or the PN-6 designation was used outside of official paperwork, and these aircraft were simply referred to as F.5Ls.
 The PN-7 was a 1925 development with an improved thicker section, shorter-span wings with a more modern
The PN-7 was a 1925 development with an improved thicker section, shorter-span wings with a more modern airfoil
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is a streamlined body that is capable of generating significantly more Lift (force), lift than Drag (physics), drag. Wings, sails and propeller blades are examples of airfoils. Foil (fl ...
section, and were powered by two experimental Wright T-2 V-12 engine
A V12 engine is a twelve-cylinder piston engine where two banks of six cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V12 engines are more common than V10 engines. However, they are less common than V8 engines.
The f ...
s.Swanborough & Bowers 1976, p.334 Two were built.
The PN-8 was developed due to problems with the wooden hull, which quickly absorbed hundreds of pounds of water and was maintenance intensive, so two aircraft with a metal hull of the same shape as the F.5Ls, and fitted with the new wing, were built. Due to reliability problems with the Wright T-2, they were powered by two V-12 Packard 1A-2500
The Packard 1A-2500 is an American V-12 liquid-cooled aircraft engine designed by Packard in 1924 as a successor to the World War I-era Liberty L-12. Five aero variants were produced, of which the 3A-2500 was the most numerous. Three marine v ...
engines.
The two PN-9s were converted from PN-8s, after being fitted with a redesigned broad-chord tail to fix a vibration problem.
Four PN-10s were built, and while similar to the PN-9, each was given a different engine as the Packard 1A-2500 engines were disappointing. One was fitted with Packard 1A-1500 and another with a Packard 3A-1500, both V-12 water-cooled engines and one each was fitted with the Wright R-1820
The Wright R-1820 Cyclone 9 is an American radial engine developed by Curtiss-Wright, widely used on aircraft in the 1930s through 1950s. It was produced under license in France as the Hispano-Suiza 9V or Hispano-Wright 9V, and in the Soviet Uni ...
and Pratt & Whitney R-1690
The Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet was a widely used American aircraft engine. Developed by Pratt & Whitney, 2,944 were produced from 1926 through 1942. It first flew in 1927. It was a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design. Displaceme ...
radial engines. The wings of the first two Packard powered aircraft had a wood structure, while the second pair with the radial engines had wings with a metal structure, both with a fabric covering.
The four PN-11s had a new metal hull with a round turtle deck and lacking the previously characteristic enlarged chines and had a new empennage with twin fins and rudders. One aircraft was fitted with two Wright R-1750
Wright Cyclone was the name given to a family of air-cooled radial piston engines designed by the Wright Aeronautical Corporation and used in numerous American aircraft in the 1930s, 1940s and 1950s.
Background
The Wright Aeronautical Corporation ...
radial engines, while one aircraft were fitted with two Pratt & Whitney R-1690
The Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet was a widely used American aircraft engine. Developed by Pratt & Whitney, 2,944 were produced from 1926 through 1942. It first flew in 1927. It was a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design. Displaceme ...
radial engines as the XPN-11, which was later redesignated as the XP4N-1. Two aircraft were fitted with Wright R-1820
The Wright R-1820 Cyclone 9 is an American radial engine developed by Curtiss-Wright, widely used on aircraft in the 1930s through 1950s. It was produced under license in France as the Hispano-Suiza 9V or Hispano-Wright 9V, and in the Soviet Uni ...
radial engines and while ordered as an XP4N-1 were designated as the XP4N-2 when they entered service.
The two metal wing radial-engine powered PN-10s were redesignated as PN-12s, which combined the revised wings of the PN-7 but reverted to the metal hull of the PN-8 with the enlarged chines and was fitted with the more reliable radial engines. The fin was further enlarged, with a straight leading edge. It would see extensive production to re-equip the Navy's patrol squadrons.Swanborough & Bowers 1976, p.335
As the production capacity of the Naval Aircraft Factory was limited, production was contracted out to several aircraft companies, with versions being built by Douglas
Douglas may refer to:
People
* Douglas (given name)
* Douglas (surname)
Animals
* Douglas (parrot), macaw that starred as the parrot ''Rosalinda'' in Pippi Longstocking
* Douglas the camel, a camel in the Confederate Army in the American Civil ...
as the PD-1, by Keystone as the PK-1 and by Martin Martin may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Martin Peninsula, Marie Byrd Land
* Port Martin, Adelie Land
* Point Martin, South Orkney Islands
Europe
* Martin, Croatia, a village
* Martin, Slovakia, a city
* Martín del Río, Aragón, Spain
* M ...
as the PM-1 and PM-2. These each had their own differences from the PN-12, as the Keystone PK-1 and Martin PM-2 the twin fins and rudders of the PN-11, while the PM-1 and PM-2 also had an enclosed cockpit, and the PK-1 had a modified hull form with a sharper bow.
These also formed the basis for the Hall PH
The Hall PH was an American flying boat of the 1930s. It was a twin-engined biplane, developed from the Naval Aircraft Factory PN and could hence trace its lineage back to the Felixstowe flying boats of World War I. The PH was purchased in small n ...
flying boats, with a different hull fitted with an enclosed cockpit, and some of these remained in service until World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
Operational history
The early prototypes of PN sea planes were used in a series of long-distance flights. During the afternoon of 31 August 1925, an attempt was made to fly a pair of PN-9 planes non-stop fromSan Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
to Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, a distance of nearly 2,400 miles (3,864 km) — a trip anticipated to take 26 hours to complete."Flight to Hawaiian Islands," in James Langland (ed.), ''The Chicago Daily News Almanac and Year-Book for 1926.'' Chicago: Chicago Daily News Company, 1925; pg. 629. The first plane to start was forced to land outside of San Francisco due to a failure of oil pressure, with the crew rescued by the destroyer USS ''William Jones'' and the aircraft towed back to port.
The second PN-9 to depart, captained by U.S. Navy Commander John Rodgers, flew before running out of fuel when anticipated tailwinds that would have slowed gasoline consumption did not materialize. The plane was unable to make contact with the naval airplane tender USS ''Aroostook'', a ship stationed along the PN-9's flight path and was forced to land at sea when both engines stopped functioning. With power lost, the plane was unable to send or receive radio signals. Although this was at the time a new distance record for seaplane
A seaplane is a powered fixed-wing aircraft capable of takeoff, taking off and water landing, landing (alighting) on water.Gunston, "The Cambridge Aerospace Dictionary", 2009. Seaplanes are usually divided into two categories based on their tech ...
s, the plane remained hundreds of miles short of the nearest landfall and the situation of the crew, with limited quantities of food and water, appeared dire.
Since seas were moderate, the decision was made to attempt to sail the plane to Hawaii. The crew then rigged crude sails made from fabric torn from the aircraft's wings and sailed the aircraft a further , finally being spotted on the ninth day about off the southeast coast of the Hawaiian island of Kauai
Kauai (), anglicized as Kauai ( or ), is one of the main Hawaiian Islands.
It has an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), making it the fourth-largest of the islands and the 21st-largest island in the United States. Kauai lies 73 m ...
. In the aftermath of the headline-grabbing rescue, Commander Rogers was promoted to the position of Assistant Chief of the Navy's Bureau of Aeronautics. PN-9 No. 1, the same plane sailed to Hawaii, did not fare as well, later ditching in the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba ...
during an attempted long-distance flight to South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
and subsequently sunk as a navigation hazard.
The two PN-12s were also used to set various records, including range and speed over circuit records.
The various production derivatives of the PN-12 entered service with the US Navy from 30 April 1928, when VP-7D received its first Douglas PD-1, remaining in service until July 1938, when the last Keystone PK-1 was retired.
Three Martin PM-1s were also supplied to the Brazilian Navy
The Brazilian Navy () is the navy, naval service branch of the Brazilian Armed Forces, responsible for conducting naval warfare, naval operations.
The navy was involved in War of Independence of Brazil#Naval action, Brazil's war of independence ...
in 1930, and used in bombing raids during the 1932 revolution.
Variants



 ;PN-5
:Redesignated
;PN-5
:Redesignated Felixstowe F5L
The twin-engine F5L was one of the Felixstowe F series of flying boats developed by John Cyril Porte at the Seaplane Experimental Station, Felixstowe, England, during the First World War for production in America.
A civilian version of the ai ...
;PN-6
:Redesignated F-6L. Last two Naval Aircraft Factory F5Ls, modified with revised tail surfaces.
;PN-7
:Modified version with new wings with high-lift thick aerofoil section and wingspan reduced from 103 ft 9 in to 72 ft 10 in (from 32 m to 22 m). Powered by two Wright T-2 engines. Two built.
;PN-8
:PN-7 with metal hull. Powered by two Packard 1A-2500
The Packard 1A-2500 is an American V-12 liquid-cooled aircraft engine designed by Packard in 1924 as a successor to the World War I-era Liberty L-12. Five aero variants were produced, of which the 3A-2500 was the most numerous. Three marine v ...
V-12 engines. Two built.
;PN-9
:Converted from PN-8 with redesigned engine nacelle
A nacelle ( ) is a streamlined container for aircraft parts such as Aircraft engine, engines, fuel or equipment. When attached entirely outside the airframe, it is sometimes called a pod, in which case it is attached with a Hardpoint#Pylon, pylo ...
s. One converted.
;PN-10
:Similar to PN-8. Powered by two Packard 1A-2500
The Packard 1A-2500 is an American V-12 liquid-cooled aircraft engine designed by Packard in 1924 as a successor to the World War I-era Liberty L-12. Five aero variants were produced, of which the 3A-2500 was the most numerous. Three marine v ...
. Two built.
;PN-11
:New hull eliminating sponsons, fitted with twin vertical tail surfaces. Four built, one with two Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet
The Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet was a widely used American aircraft engine. Developed by Pratt & Whitney, 2,944 were produced from 1926 through 1942. It first flew in 1927. It was a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design. Displaceme ...
engines, and remaining three powered by two Wright R-1750D Cyclone.
;XP4N-1
:Improved PN-11; three aircraft ordered, originally designated XP2N but redesignated XP4N-1 before delivery. Last two aircraft completed as XP4N-2s.Johnson 2011, p.147.
;XP4N-2
:Improved XP4N-1 with additional fuel capacity.Johnson 2011, p.147.
;PN-12
:Development of PN-10 powered by radial engines. Two built. One powered by two Pratt & Whitney Hornet
The Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet was a widely used American aircraft engine. Developed by Pratt & Whitney, 2,944 were produced from 1926 through 1942. It first flew in 1927. It was a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design. Displaceme ...
engines, with the other powered by two Wright R-1750 Cyclone engines.
;Douglas PD-1
:Developed production version of PN-12. Two Wright R-1750 Cyclone engines. 25 built by Douglas
Douglas may refer to:
People
* Douglas (given name)
* Douglas (surname)
Animals
* Douglas (parrot), macaw that starred as the parrot ''Rosalinda'' in Pippi Longstocking
* Douglas the camel, a camel in the Confederate Army in the American Civil ...
.
;Keystone PK-1
:Production version of PN-12. Twin tails. Two Wright R-1820 Cyclone
The Wright R-1820 Cyclone 9 is an American radial engine developed by Curtiss-Wright, widely used on aircraft in the 1930s through 1950s. It was produced under license in France as the Hispano-Suiza 9V or Hispano-Wright 9V, and in the Soviet Uni ...
engines. 18 built by Keystone.
;Martin PM-1
:Production derivative of PN-12. Two Wright R-1750 Cyclone engines. 27 built for US Navy by Martin Martin may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Martin Peninsula, Marie Byrd Land
* Port Martin, Adelie Land
* Point Martin, South Orkney Islands
Europe
* Martin, Croatia, a village
* Martin, Slovakia, a city
* Martín del Río, Aragón, Spain
* M ...
.
;Martin PM-1B
:Export version of PM-1 for Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. Three built.
;Martin PM-2
:Improved derivative of PM-1 with more powerful Wright R-1820 Cyclone
The Wright R-1820 Cyclone 9 is an American radial engine developed by Curtiss-Wright, widely used on aircraft in the 1930s through 1950s. It was produced under license in France as the Hispano-Suiza 9V or Hispano-Wright 9V, and in the Soviet Uni ...
engines and twin tails. 25 built.
;P1M
:Brazilian Navy
The Brazilian Navy () is the navy, naval service branch of the Brazilian Armed Forces, responsible for conducting naval warfare, naval operations.
The navy was involved in War of Independence of Brazil#Naval action, Brazil's war of independence ...
designation of the Martin PM.
Operators
; *Brazilian Naval Aviation
The Brazilian Naval Aviation () is the air component of the Brazilian Navy, currently called ''Força Aeronaval''. Most of its air structure is subordinated to the Naval Air Force Command (''Comando da Força Aeronaval'', ComForAerNav), the milita ...
;
*United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
Specifications (PN-12)

See also
*Boeing XPB
The Boeing XPB (company Model 50) was an American twin-engined biplane long-range patrol flying boat of the 1920s. A single example was built for the United States Navy.
Design and development
In September 1924, the Naval Aircraft Factory was ...
* Earl Schuyler Kleinhans
References
* *External links
*https://web.archive.org/web/20071013194609/http://bluejacket.com/usn-usmc_avi_image_vintage_g-z.htm#P *http://www.cofe.ru/avia/N/N-31.htmnavy.mil
{{AvN aircraft designations Flying boats Naval Aircraft Factory PN01 P1N Biplanes Twin piston-engined tractor aircraft