Nanoemulsions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A miniemulsion (also known as nanoemulsion) is a particular type of 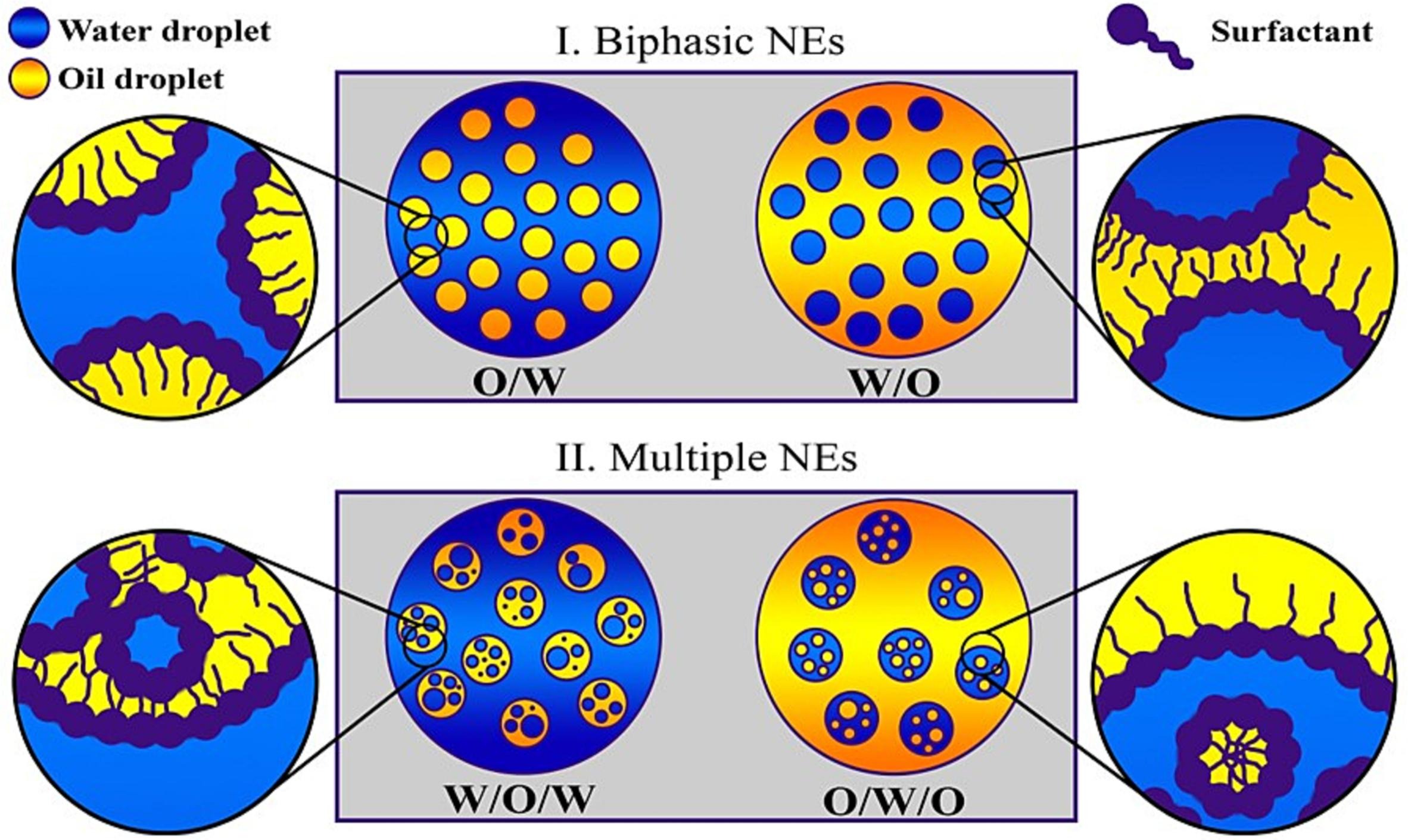
 A
A
emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally Miscibility, immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloi ...
. A miniemulsion is obtained by ultrasonicating a mixture comprising two immiscible
Miscibility () is the property of two chemical substance, substances to mix in all mixing ratio, proportions (that is, to fully dissolution (chemistry), dissolve in each other at any concentration), forming a homogeneity and heterogeneity, homoge ...
liquid phases (for example, oil and water), one or more surfactants
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word ''surfactant'' is a blend of "surface-active agent",
coined in 1950. As t ...
and, possibly, one or more co-surfactants (typical examples are hexadecane or cetyl alcohol). They usually have nanodroplets with uniform size distribution (20–500 nm) and are also known as sub-micron, mini-, and ultra-fine grain emulsions.

How to prepare a miniemulsion
# Selection of ingredients: The first step in creating a nanoemulsion is to select the ingredients, which include the oil, water, and emulsifying agent. The type and proportions of these ingredients will affect the stability and properties of the final emulsion. # Preparation of oil and aqueous phases: The oil and water phases are separately prepared, with any desired ingredients, such as surfactants or flavoring agents, added at this step. # Mixing oil and emulsifier with stirrer: Next, the oil and water phases are mixed in the presence of an emulsifying agent, typically using a high-shear mixing device such as a homogenizer or a high-pressure homogenizer. # Aging and stabilization: Theemulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally Miscibility, immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloi ...
is typically aged at room temperature to allow the droplets to stabilize, after which it can be cooled or heated as required.
# Optimizing and characterization: The droplet size and stability are then optimized by adjusting the ingredients and process parameters, such as temperature, pH, and mixing conditions. The nanoemulsion is also sterilized by filtration with 0.22μm. Several methods, such as DLS, TEM, and SEM, can characterize the final nanoemulsion's properties.
# Analyzing the quality of the particle sizer
Methods of preparing nanoemulsions/miniemulsions
There are two general types of methods for preparing miniemulsions: * High-energy methods - For the high-energy methods, the shearing proceeds usually via exposure to high powerultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
of the mixture or with a high-pressure homogenizer
A homogenizer is a laboratory or industrial device used to break down and evenly distribute particles within a liquid mixture, creating a stable and uniform emulsion, suspension, or solution. Homogenization (chemistry), Homogenization is a key pro ...
, which are high-shearing processes.
* Low-energy methods - For the low-energy methods, the water-in-oil emulsion is usually prepared and then transformed into an oil-in-water miniemulsion by changing either composition or temperature. The water-in-oil emulsion is diluted dropwise with water to an inversion point or gradually cooled to a phase inversion temperature. The emulsion inversion point and phase inversion temperature cause a significant decrease in the interfacial tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to ...
between two liquids, thereby generating very tiny oil droplets dispersed in the water.
Miniemulsions are kinetically stable but thermodynamically unstable. Oil and water are incompatible in nature, and the interface between them is not favored. Therefore, given a sufficient amount of time, the oil and water in miniemulsions separate again. Various mechanisms such as gravitational separation, flocculation
In colloidal chemistry, flocculation is a process by which colloidal particles come out of Suspension (chemistry), suspension to sediment in the form of floc or flake, either spontaneously or due to the addition of a clarifying agent. The actio ...
, coalescence
Coalesce, coalescence or coalescent can refer to:
Chemistry and physics
* Coalescence (chemistry), the process by which two or more separate masses of miscible substances seem to "pull" each other together should they make the slightest contac ...
, and Ostwald ripening
Ostwald ripening is a phenomenon observed in solid solutions and liquid sols that involves the change of an inhomogeneous structure over time, in that small crystals or sol particles first dissolve and then redeposit onto larger crystals or s ...
result in instability. In an ideal miniemulsion system, coalescence
Coalesce, coalescence or coalescent can refer to:
Chemistry and physics
* Coalescence (chemistry), the process by which two or more separate masses of miscible substances seem to "pull" each other together should they make the slightest contac ...
and Ostwald ripening
Ostwald ripening is a phenomenon observed in solid solutions and liquid sols that involves the change of an inhomogeneous structure over time, in that small crystals or sol particles first dissolve and then redeposit onto larger crystals or s ...
are suppressed thanks to the presence of the surfactant and co-surfactant.Mason TG, Wilking JN, Meleson K, Chang CB, Graves SM, "Nanoemulsions: formation, structure, and physical properties", Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2006, 18(41): R635-R666 With the addition of surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word ''surfactant'' is a Blend word, blend of "surface-active agent",
coined in ...
s, stable droplets
A drop or droplet is a small column of liquid, bounded completely or almost completely by free surfaces. A drop may form when liquid accumulates at the end of a tube or other surface boundary, producing a hanging drop called a pendant drop. Dro ...
are then obtained, which have typically a size between 50 and 500 nm.
Instruments needed in nanoemulsions
Sterile filter
A sterile filter is a device used to remove microorganisms and other contaminants from a liquid or gas, making it sterile. Sterile filters are commonly used in the medical, pharmaceutical, and biotech industries to ensure that the products produced are free of bacteria and other harmful organisms. There are different types of filters which include: *Membrane filter
Membrane technology encompasses the scientific processes used in the construction and application of membranes. Membranes are used to facilitate the transport or rejection of substances between mediums, and the mechanical separation of gas and liq ...
s: These filters use a porous membrane to block microorganisms and other particles physically. They are available in different pore sizes and materials, such as cellulose acetate, polypropylene, and nylon, to suit different applications.
* Depth filters: These filters use a matrix of fibers, beads, or powders to trap particles and microorganisms. Examples of depth filters include cellulose, glass fiber, and diatomaceous earth.
* Adsorptive filters: These filters use adsorbent materials, such as activated carbon, or specialized resins or beads, to remove certain types of contaminants by chemical adsorption.
Nanogenizer
A nanogenizer, also known as a high-pressurehomogenizer
A homogenizer is a laboratory or industrial device used to break down and evenly distribute particles within a liquid mixture, creating a stable and uniform emulsion, suspension, or solution. Homogenization (chemistry), Homogenization is a key pro ...
or a microfluidizer, is a device used to create small droplets or particles by applying high pressure to a liquid mixture. These devices can be used to produce nanoemulsions, as well as other types of emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally Miscibility, immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloi ...
s and suspensions. They work by passing the mixture through a small orifice under high pressure, which causes the liquid to be sheared and broken into small droplets or particles. The size of the droplets or particles can be controlled by adjusting the pressure and the design of the orifice.
Nanoparticle sizer
 A
A nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At ...
sizer, also known as a nanoparticle analyzer, is a device used to measure the size, size distribution, and concentration of nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At ...
s in a sample. The size of nanoparticles is typically in the range of 1 to 100 nanometers (nm), and they are much smaller than the particles that can be measured with conventional particle size analyzers.
Applications
Miniemulsions have wide application in the synthesis of nanomaterials and in the pharmaceutical and food industries. For example, miniemulsion-based processes are, therefore, particularly adapted for the generation ofnanomaterials
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, chemical substances or materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science ...
. There is a fundamental difference between traditional emulsion polymerisation and a miniemulsion polymerisation. Particle formation in the former is a mixture of micellar and homogeneous nucleation, particles formed via miniemulsion however are mainly formed by droplet nucleation. In the pharmaceutical industry, oil droplets act as tiny containers that carry water-insoluble drugs, and the water provides a mild environment that is compatible with the human body. Moreover, nanoemulsions that carry drugs allow the drugs to crystallize in a controlled size with a good dissolution rate. Finally, in the food industry, miniemulsions can not only be loaded with water-insoluble nutrients, such as beta-carotene and curcumin
Curcumin is a bright yellow chemical produced by plants of the ''Curcuma longa'' species. It is the principal curcuminoid of turmeric (''Curcuma longa''), a member of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is sold as a herbal supplement, cosmetic ...
, but also improve the nutrients' digestibility. Miniemulsions are also used in the creation of cannabinoid infused beverages and foods. Emulsifying cannabiniods has shown to increase bioavailability and digestion time.
References
{{reflist Colloidal chemistry Applied genetics fr:Miniémulsion