Nano-I-beam on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nano-I-beams are 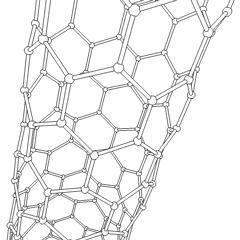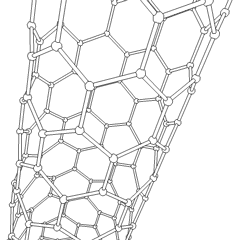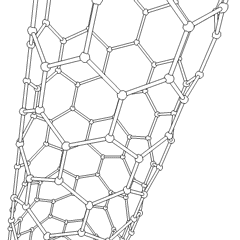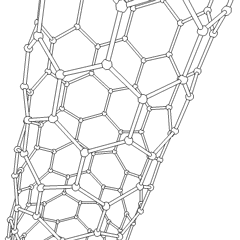
 Compared to traditional
Compared to traditional
nanostructure
A nanostructure is a structure of intermediate size between microscopic and molecular structures. Nanostructural detail is microstructure at nanoscale.
In describing nanostructures, it is necessary to differentiate between the number of dimen ...
s characterized by their -shaped cross-section
Cross section may refer to:
* Cross section (geometry)
** Cross-sectional views in architecture and engineering 3D
* Cross section (geology)
* Cross section (electronics)
* Radar cross section, measure of detectability
* Cross section (physics)
...
, resembling the letter in macroscopic scale. They are typically made from hybrid organic/inorganic
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''.
Inor ...
materials and have unique properties that make them suitable for various applications in structural nano-mechanics.

carbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range ( nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized:
* ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''S ...
s, nano-I-beams exhibit higher structural stiffness, reduced induced stress, and longer service life. They have the potential to outperform carbon nanotubes in various applications, offering enhanced mechanical properties and improved functionality. The Wide Flange Nano-I-beam variation has been found to provide even higher structural stiffness and longer service life compared to the Equal Flange & Web Nano-I-beam.
Origin of the name
Nano-I-beams are named after theI-beam
An I-beam is any of various structural members with an - (serif capital letter 'I') or H-shaped cross section (geometry), cross-section. Technical terms for similar items include H-beam, I-profile, universal column (UC), w-beam (for "wide flang ...
s used in construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
and structural engineering
Structural engineering is a sub-discipline of civil engineering in which structural engineers are trained to design the 'bones and joints' that create the form and shape of human-made Structure#Load-bearing, structures. Structural engineers also ...
. The I-beam, also known as the H-beam or universal beam, is a widely used structural element due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and structural stability. The shape of the I-beam, with its central vertical web and horizontal flanges, provides excellent load-bearing capabilities and resistance to bending and torsion.
Inspired by the structural properties of I-beams, the nano-I-beam was developed as a nanoscale counterpart, utilizing the same I-shaped cross-section. The nano-I-beam inherits the geometric characteristics of the macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenome ...
I-beam, but at a much smaller scale, making it suitable for applications in the realm of nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing propertie ...
Kinetics and growth of nano-I-beam
The Ritz method, based on the shell theory, is frequently utilised for dynamic analysis of carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The Ritz method, connected toHamilton's principle
In physics, Hamilton's principle is William Rowan Hamilton's formulation of the principle of stationary action. It states that the dynamics of a physical system are determined by a variational problem for a functional based on a single funct ...
, is employed to determine the equilibrium state and minimize the energy functional of a conservative structural system undergoing kinematically admissible growth or deformation. Hamilton's principle considers the interplay of different energy elements, including the kinetic energy (T), strain energy (U), and potential energy (WP). By applying the Ritz method based on Hamilton's principle, the strain energy ''U'' of Single & Multi-Walled Nano-I-beams (SWNT) is formulated as:
When considering the kinetic energy, observations are often made in a moving frame of reference. To account for this, the time derivative of the observed variables in the fixed frame of reference (ρ, θ, z) is utilized. As a result, the formulation of the kinetic energy, denoted as T, takes into account these considerations.
Application and suitability
Both CNTs and I-beams have distinct properties and advantages, and their suitability depends on the specific application and requirements. CNTs offer exceptional mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and stiffness. They have a high strength-to-weight ratio, making them lightweight yet strong. CNTs also exhibit excellentelectrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
and thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low ...
, making them suitable for applications in electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
and energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an Accumulator (energy), accumulator or Batte ...
. However, challenges in large-scale production, potential toxicity concerns, and difficulties in achieving uniform dispersion within materials are some drawbacks associated with CNTs.
Among the variations of the Hybrid Organic/Inorganic Nano-I-beam, research highlights the good performance of the Wide Flange Nano-I-Beam. It demonstrates decent structural stiffness, reduced induced stress, and an extended service life when compared to the Equal Flange & Web Nano-I-Beam. This distinction makes the Wide Flange variation particularly desirable for various applications, including nano-heat engines and sensors as an attractive option for cost-effective and high-performance material.
Ultimately, the choice between CNTs and Nano-I-beams depends on the specific requirements of the application, considering factors such as scale, performance needs, and cost-effectiveness. Each material has its own strengths and limitations, and the selection should be based on a careful evaluation of the desired properties and constraints of the project at hand.
References
{{reflist Nanomaterials