Namib on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Namib ( ; ) is a coastal

 The Namib Desert is one of the 500 distinct physiographic provinces of the South African Platform physiographic division. It occupies an area of around , stretching from the Uniab River (north) to the town of Lüderitz (south) and from the
The Namib Desert is one of the 500 distinct physiographic provinces of the South African Platform physiographic division. It occupies an area of around , stretching from the Uniab River (north) to the town of Lüderitz (south) and from the
 The Namib's aridity is caused by the descent of dry air of the
The Namib's aridity is caused by the descent of dry air of the 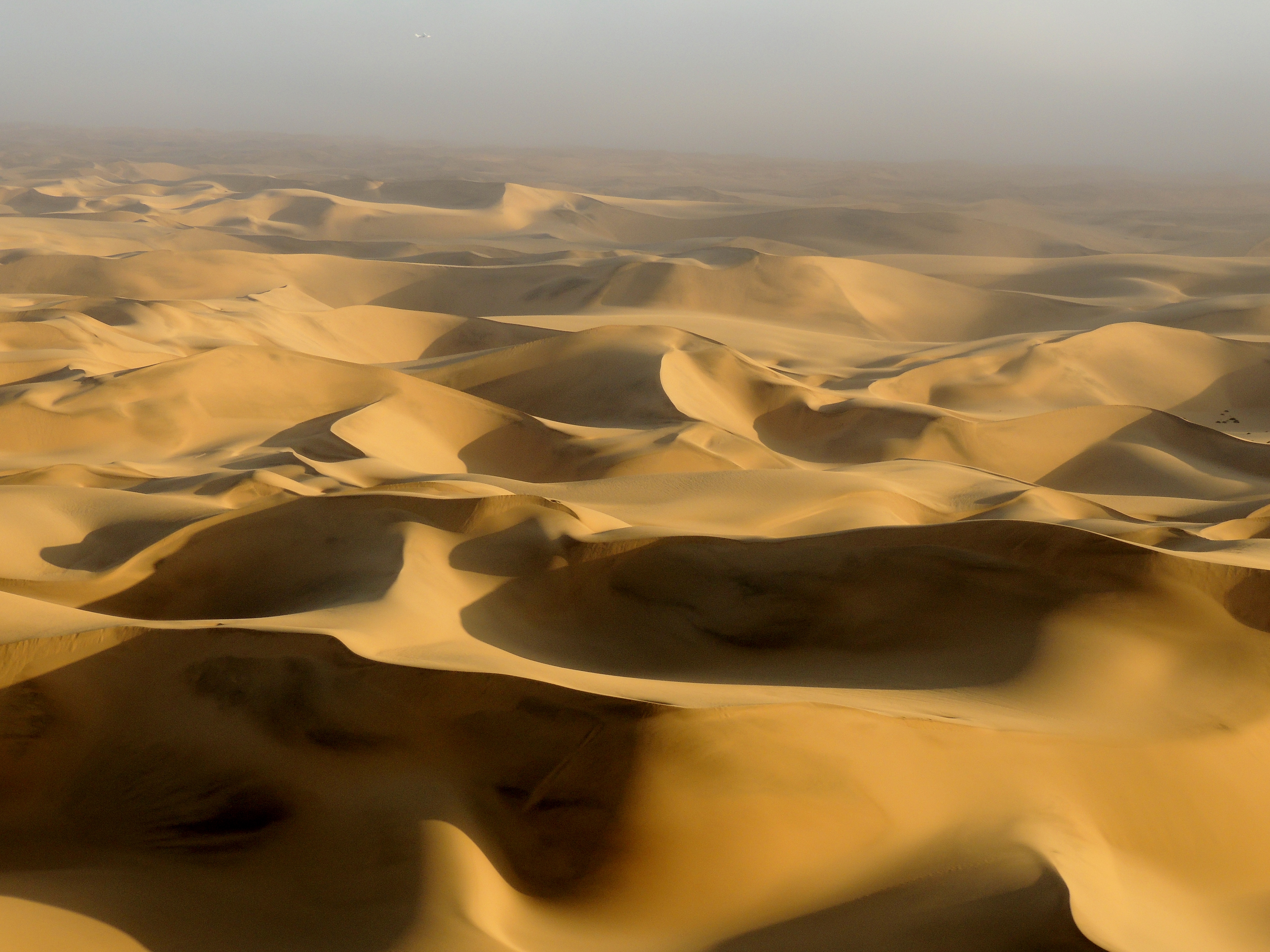 The dry climate of Namib reflects the almost complete lack of bodies of water on the surface. Most rivers flow underground and/or are dry for most of the year. Even when they are not, they usually drain into
The dry climate of Namib reflects the almost complete lack of bodies of water on the surface. Most rivers flow underground and/or are dry for most of the year. Even when they are not, they usually drain into
 The Namib fauna mostly comprises
The Namib fauna mostly comprises
 Before the 20th century, some San roamed the Namib, gathering edible plants on the shore, hunting in the interior, and drinking the juice of the tsamma melon for water. Today, some Herero still herd their livestock in the Kaokoveld in the Namib and take them from waterhole to waterhole. A few Nama
Before the 20th century, some San roamed the Namib, gathering edible plants on the shore, hunting in the interior, and drinking the juice of the tsamma melon for water. Today, some Herero still herd their livestock in the Kaokoveld in the Namib and take them from waterhole to waterhole. A few Nama
Namib Naukluft Park photo gallery
{{Authority control Deserts of Namibia Deserts of South Africa Afrotropical ecoregions Ergs of Africa Physiographic provinces World Heritage Sites in Namibia Namib-Naukluft National Park First 100 IUGS Geological Heritage Sites
desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
in Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of Africa. No definition is agreed upon, but some groupings include the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations geoscheme, the intergovernmental Southern African Development Community, and ...
. According to the broadest definition, the Namib stretches for more than along the Atlantic coasts of Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c ...
, Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country on the west coast of Southern Africa. Its borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south; in the no ...
, and northwest South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, extending southward from the Carunjamba River in Angola, through Namibia and to the Olifants River in Western Cape, South Africa. The Namib's northernmost portion, which extends from the Angola-Namibia border, is known as Moçâmedes Desert, while its southern portion approaches the neighboring Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semiarid climate, semiarid sandy savanna in Southern Africa covering including much of Botswana as well as parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African ...
. From the Atlantic coast eastward, the Namib gradually ascends in elevation, reaching up to inland to the foot of the Great Escarpment. Annual precipitation ranges from in the aridest regions to at the escarpment, making the Namib the only true desert in southern Africa. Having endured arid
Aridity is the condition of geographical regions which make up approximately 43% of total global available land area, characterized by low annual precipitation, increased temperatures, and limited water availability.Perez-Aguilar, L. Y., Plata ...
or semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a aridity, dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below Evapotranspiration#Potential evapotranspiration, potential evapotranspiration, but not as l ...
conditions for roughly 55–80 million years, the Namib may be the oldest desert in the world and contains some of the world's driest regions, with only western South America's Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert () is a desert plateau located on the Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast of South America, in the north of Chile. Stretching over a strip of land west of the Andes Mountains, it covers an area of , which increases to if the barre ...
to challenge it for age and aridity benchmarks. Most of Namibia's share of the Namib Desert is protected under the environmental protection included in the constitution of the country.
The desert geology consists of sand seas near the coast, while gravel plains and scattered mountain outcrops occur further inland. The sand dunes, some of which are high and span long, are the second-largest in the world after the Badain Jaran Desert
The Badain Jaran Desert () is a desert in China which spans the provinces of Gansu, Ningxia and Inner Mongolia. It covers an area of . By size it is the third largest desert in China.
This desert is home to some of the tallest stationary dunes o ...
dunes in China. Temperatures along the coast are stable and generally range between annually, while temperatures further inland are variable—summer daytime temperatures can exceed while nights can be freezing. Fogs that originate offshore from the collision of the cold Benguela Current
The Benguela Current is the broad, northward flowing ocean current that forms the eastern portion of the South Atlantic Ocean gyre. The current extends from roughly Cape Point in the south, to the position of the Angola-Benguela Front in the no ...
and warm air from the Hadley cell
The Hadley cell, also known as the Hadley circulation, is a global-scale tropical atmospheric circulation that features air rising near the equator, flowing poleward near the tropopause at a height of above the Earth's surface, cooling and des ...
create a fog belt that frequently envelops parts of the desert. Coastal regions can experience more than 180 days of thick fog a year. While this has proved a major hazard to ships—more than a thousand wrecks litter the Skeleton Coast—it is a vital source of moisture for desert life.
The Namib is almost completely uninhabited by humans except for several small settlements and indigenous pastoral groups, including the Ovahimba and Obatjimba Herero in the north, and the Topnaar Nama in the central region. Owing to its antiquity, the Namib may be home to more endemic species
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
than any other desert in the world. Most of the desert wildlife is arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s and other small animals that live on little water, although larger animals inhabit the northern regions. Near the coast, the cold ocean water is rich in fishery resources and supports populations of brown fur seal
The brown fur seal (''Arctocephalus pusillus''), also known as the Cape fur seal, and Afro-Australian fur seal, is a species of fur seal.
Description
The brown fur seal is the largest and most robust member of the fur seals. It has a large an ...
s and shorebirds, which serve as prey for the Skeleton Coast's lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the ...
s. Further inland, the Namib-Naukluft National Park
The Namib-Naukluft National Park is a national park in western Namibia, situated between the coast of the Atlantic Ocean and the edge of the Great Escarpment. It encompasses part of the Namib Desert (considered the world's oldest desert), the ...
supports population of mountain zebra
The mountain zebra (''Equus zebra'') is a zebra species in the family Equidae, native to southwestern Africa. There are two subspecies, the Cape mountain zebra (''E. z. zebra'') found in South Africa and Hartmann's mountain zebra (''E. z. hartma ...
s, and other large mammals. Further north near the Skeleton Coast, lions, elephants
Elephants are the Largest and heaviest animals, largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian ele ...
and rhinos can be found. Although the outer Namib is largely barren of vegetation, lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), m ...
s and succulents are found in coastal areas, while grasses, shrubs, and ephemeral plants thrive near the escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
Due to the similarity, the term '' scarp'' may mistakenly be incorrectly used inte ...
. Several types of trees are also able to survive the extremely arid climate.
Etymology
The name is of Khoekhoegowab (or Nama language) origin, and has been variously reported to mean "vast place" and "an area where there is nothing".Geography and geology
 The Namib Desert is one of the 500 distinct physiographic provinces of the South African Platform physiographic division. It occupies an area of around , stretching from the Uniab River (north) to the town of Lüderitz (south) and from the
The Namib Desert is one of the 500 distinct physiographic provinces of the South African Platform physiographic division. It occupies an area of around , stretching from the Uniab River (north) to the town of Lüderitz (south) and from the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
(west) to the Namib Escarpment (east). It is about long from north to south and its east–west width varies from . To the north, the desert leads into the Kaokoveld; the dividing line between these two regions is roughly at the latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
of the city of Walvis Bay
Walvis Bay (; ; ) is a city in Namibia and the name of the bay on which it lies. It is the List of cities in Namibia, second largest city in Namibia and the largest coastal city in the country. The city covers an area of of land.
The bay is a ...
, and it consists in a narrow strip of land (about 50 km wide) that is the driest place in Southern Africa. To the south, the Namib borders the South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
n Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe Khoemana (also known as !Orakobab or Korana) word is a semidesert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its extent is ...
semi-desert.
Southern Namib (between Lüderitz and the Kuiseb River) comprises a vast dune sea with some of the tallest and most spectacular dunes in the world, ranging in color from pink to vivid orange. In the Sossusvlei area, several dunes exceed in height. The complexity and regularity of dune patterns in its dune sea have attracted the attention of geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the structure, composition, and History of Earth, history of Earth. Geologists incorporate techniques from physics, chemistry, biology, mathematics, and geography to perform research in the Field research, ...
s for decades, but it remains poorly understood.
The source of the unconsolidated sand (the most recent sand sea) is dominantly from the Orange River, which drains into the Atlantic south of the Namib Sand Sea, with minor contributions in the east from the (now ephemeral) rivers that drain into the sand sea. For this reason, the Namib Sand Sea has been referred to as the "wind displaced delta of the Orange River."
Moving north from Sossusvlei, the sand gradually gives way to a rocky desert that extends from Sossusvlei to the Swakop river. This area is traversed by the Tropic of Capricorn
The Tropic of Capricorn (or the Southern Tropic) is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point at the December (or southern) solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. It also reach ...
and is mostly flat, although some scenic canyons and elevations are found in some areas, for example in the Moon Valley system. While most of the soil is rocky, sand dunes are still occasionally found in this region; for example, sand dunes occupy much of the coastline between Walvis Bay and Swakopmund.
The Namib desert is an important location for the mining of tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
, salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
, and diamonds
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of electricity, and insol ...
.
Several rivers and streams run through the Namib, although all of the rivers south of the Cunene River
The Cunene (Portuguese spelling) or Kunene (common Namibian spelling) is a river in Southern Africa. It flows from the Angola highlands southwards to the border with Namibia. It then flows in a westerly direction along the border until it reaches ...
and north of the Orange River
The Orange River (from Afrikaans/Dutch language, Dutch: ''Oranjerivier'') is a river in Southern Africa. It is the longest river in South Africa. With a total length of , the Orange River Basin extends from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibi ...
are ephemeral
Ephemerality (from the Greek word , meaning 'lasting only one day') is the concept of things being transitory, existing only briefly. Academically, the term ephemeral constitutionally describes a diverse assortment of things and experiences, fr ...
and rarely or never reach the ocean. These rivers arise in the interior mountains of Namibia and flow after summer rain storms.
Climate
Hadley cell
The Hadley cell, also known as the Hadley circulation, is a global-scale tropical atmospheric circulation that features air rising near the equator, flowing poleward near the tropopause at a height of above the Earth's surface, cooling and des ...
, cooled by the cold Benguela Current
The Benguela Current is the broad, northward flowing ocean current that forms the eastern portion of the South Atlantic Ocean gyre. The current extends from roughly Cape Point in the south, to the position of the Angola-Benguela Front in the no ...
along the coast. It has less than of rain annually and is almost completely barren. Besides rain being scarce, it is also unpredictable. Western Namib gets less rain (5 mm) than eastern Namib (85 mm). This is due to several factors. Winds coming from the Indian Ocean lose part of their humidity when passing the Drakensberg
The Drakensberg (Zulu language, Zulu: uKhahlamba, Sotho language, Sotho: Maloti, Afrikaans: Drakensberge) is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, Southern Africa, Great Escarpment, which encloses the central South Africa#Geography, Sout ...
mountains, and are essentially dry when they reach the Namib Escarpment at the eastern end of the desert. On the other hand, winds coming from the Atlantic Ocean are pressed down by hot air from the east; their humidity thus forms clouds and fog. Morning fogs coming from the ocean and pushing inwards into the desert are a regular phenomenon along the coast, and much of the life cycle of animals and plants in the Namib relies on these fogs as the main source of water.
endorheic
An endorheic basin ( ; also endoreic basin and endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water (e.g. rivers and oceans); instead, the water drainage flows into permanent ...
basins, without reaching the sea. The Swakop and the Omaruru are the only rivers that occasionally drain into the ocean.
All along the coast, but mostly in the northernmost part of it, the interaction between the water-laden air coming from the sea via southerly wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heatin ...
s, some of the strongest of any coastal desert, and the dry air of the desert causes immense fogs and strong currents. It causes sailors to lose their way; this is testified by the remnants of several shipwreck
A shipwreck is the wreckage of a ship that is located either beached on land or sunken to the bottom of a body of water. It results from the event of ''shipwrecking'', which may be intentional or unintentional. There were approximately thre ...
s that can be found along the Skeleton Coast, in northern Namib. Some of these wrecked ships (such as that of the '' Eduard Bolen'', can be found as much as 400m inland, as the desert slowly moves westwards into the sea, reclaiming land over many years.
Benguela's El Niño (similar to the Pacific event in its environmental change in the seas) spreads from the Kunene estuary southward to, on occasion, south of Luderitz. Warm waters with depth and associated water flow from the northwest were first fully catalogued by Sea Fisheries researchers, in Cape Town (L V Shannon ''et al.''). The research noted the positive effect of Benguela's El Niño on the rainfall of the interior. Rainfall records also show positive values variously across the Namib, Desert Research Station, and Gobabeb for instance. This event recurs approximately mid-decade (recent examples are 1974, 1986, 1994, 1995, and 2006).
Plants and animals
Flora
Several unusualspecies
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
of plants and animals are found in this desert, many of which are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
and highly adapted to the specific climate of the area.
One of the most well-known endemic plants of the Namib is the welwitchia plant, a shrub-like plant, it grows two long strap-shaped leaves continuously throughout its lifetime. These leaves may be several meters long, gnarled, and twisted from the desert winds. The taproot
A taproot is a large, central, and dominant root from which other roots sprout laterally. Typically a taproot is somewhat straight and very thick, is tapering in shape, and grows directly downward. In some plants, such as the carrot, the taproot ...
of the plant develops into a flat, concave disc in age. ''Welwitschia'' is notable for its survival in the extremely arid Namib conditions, made possible by its ability to capture moisture from coastal sea fogs. Areas where ''Welwitschias'' are a common sight include the eponymous Welwitschia Plains, which are adjacent to the Husab uranium mine, one of the largest of its kind in the world.
" Fairy circles", which are circular patches of land barren of plants, varying between in diameter and often encircled by a ring of stimulated growth of grass, are found in the Namib, such as those near the Wolwedans desert camp.
Fauna
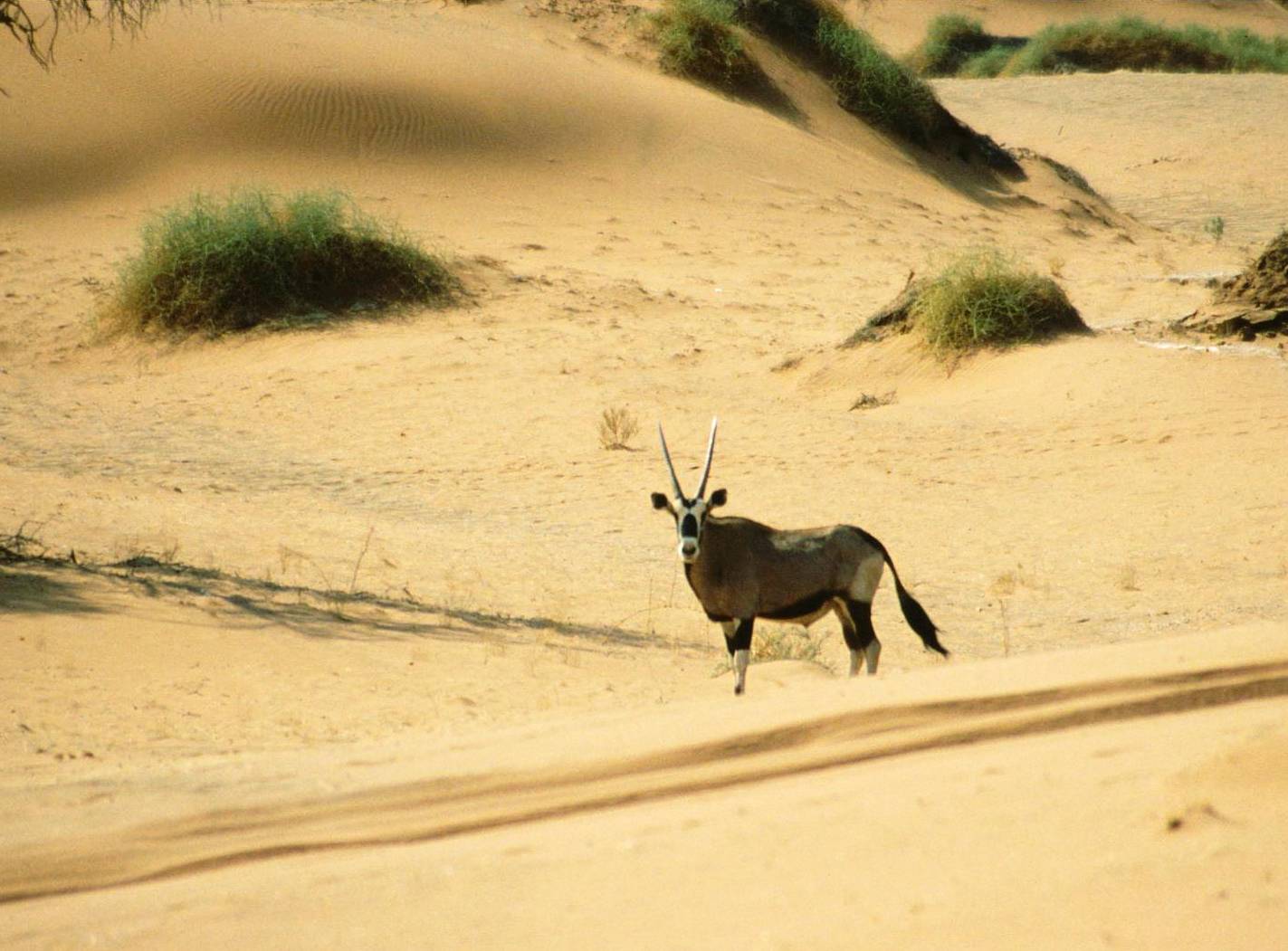
 The Namib fauna mostly comprises
The Namib fauna mostly comprises arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s and other small animals that can live on little water, but a few species of bigger animals are also found, including antelope
The term antelope refers to numerous extant or recently extinct species of the ruminant artiodactyl family Bovidae that are indigenous to most of Africa, India, the Middle East, Central Asia, and a small area of Eastern Europe. Antelopes do ...
s (such as gemsboks and springbok
The springbok or springbuck (''Antidorcas marsupialis'') is an antelope found mainly in south and southwest Africa. The sole member of the genus (biology), genus ''Antidorcas'', this bovid was first Species description, described by the Germa ...
s), common ostrich
The common ostrich (''Struthio camelus''), or simply ostrich, is a species of flightless bird native to certain areas of Africa. It is one of two extant species of ostriches, the only living members of the genus ''Struthio'' in the ratite group ...
es, and in some areas even desert elephants or lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the ...
s. All these species have developed techniques to survive in the Namib environment. Several endemic darkling beetle
Darkling beetle is the common name for members of the beetle family Tenebrionidae, comprising over 20,000 species in a cosmopolitan distribution.
Taxonomy
''Tenebrio'' is the Latin generic name that Carl Linnaeus assigned to some flour beetles ...
s species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
have different methods of collecting water droplets from morning fog; they are collectively known as "fog beetles". For example, one beetle, '' Onymacris unguicularis,'' has smooth elytron
An elytron (; ; : elytra, ) is a modified, hardened forewing of beetles (Coleoptera), though a few of the true bugs (Hemiptera) such as the family Schizopteridae are extremely similar; in true bugs, the forewings are called hemelytra (sometimes ...
s that cause humidity from the morning fogs to condense into droplets, which roll down the beetle's back to its mouth. Another beetle, the ''Lepidochora discoidalis'', builds "water-capturing" webs. Black-backed jackal
The black-backed jackal (''Lupulella mesomelas'') is a medium-sized Caninae, canine native to East Africa, eastern and southern Africa. These regions are separated by roughly .
One region includes the southernmost tip of the continent, includin ...
s lick humidity from stones. Gemsboks (also known as the South African oryx) can raise the temperature of their bodies to 40 °C in the hottest hours of the day. The desert is also home to meerkat
The meerkat (''Suricata suricatta'') or suricate is a small mongoose found in southern Africa. It is characterised by a broad head, large eyes, a pointed snout, long legs, a thin tapering tail, and a brindled coat pattern. The head-and-body ...
s and several species of lizards.
Human activity
 Before the 20th century, some San roamed the Namib, gathering edible plants on the shore, hunting in the interior, and drinking the juice of the tsamma melon for water. Today, some Herero still herd their livestock in the Kaokoveld in the Namib and take them from waterhole to waterhole. A few Nama
Before the 20th century, some San roamed the Namib, gathering edible plants on the shore, hunting in the interior, and drinking the juice of the tsamma melon for water. Today, some Herero still herd their livestock in the Kaokoveld in the Namib and take them from waterhole to waterhole. A few Nama Khoikhoi
Khoikhoi (Help:IPA/English, /ˈkɔɪkɔɪ/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''KOY-koy'') (or Khoekhoe in Namibian orthography) are the traditionally Nomad, nomadic pastoralist Indigenous peoples, indigenous population of South Africa. They ...
still graze their livestock on the banks of the Kuiseb River
The Kuiseb River is an ephemeral river in western-central Namibia. Its source is in the Khomas Highland west of Windhoek. From there it flows westwards through the Namib-Naukluft National Park and the Namib desert to Walvis Bay. Several settlement ...
in the desert. Most of the native people have left, leaving the vast majority of the desert uninhabited.
The steppes in the southern half of the desert are mostly made up of ranches run by Europeans, who raise Karakul sheep
Karakul or Qaraqul (named after Qorakoʻl, a city in Bukhara Region in Uzbekistan) is a breed of domestic fat-tailed sheep which originated in Central Asia. Some archaeological evidence points to Karakul sheep being raised there continuously sinc ...
with local help and send the pelts of the lambs to Europe for use in fur coats. Most of the rest of the desert is set aside for conservation. A vast portion of the desert, called the Sperrgebiet, was access-restricted due to the presence of diamonds, which are mined in the area at the mouth of the Orange River
The Orange River (from Afrikaans/Dutch language, Dutch: ''Oranjerivier'') is a river in Southern Africa. It is the longest river in South Africa. With a total length of , the Orange River Basin extends from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibi ...
. Although the desert is largely unpopulated and inaccessible, there are year-round settlements at Sesriem, close to the Sossusvlei area, and other small outposts in other locations. Moçâmedes in Angola, and Lüderitz, Walvis Bay
Walvis Bay (; ; ) is a city in Namibia and the name of the bay on which it lies. It is the List of cities in Namibia, second largest city in Namibia and the largest coastal city in the country. The city covers an area of of land.
The bay is a ...
, and Swakopmund
Swakopmund ("Mouth of the Swakop River, Swakop") is a city on the coast of western Namibia, west of the Namibian capital Windhoek via the B2 road (Namibia), B2 main road. It is the capital of the Erongo Region, Erongo administrative district. It ...
in Namibia, bordering on the desert, are the main settlements in the area.
The 2015 film '' Mad Max: Fury Road'' was filmed here.
In 2019 the Namibian-German artist Max Siedentopf created an installation in the Namib consisting of a ring of large white blocks atop of which sit six speakers attached to a solar-powered MP3 player
A portable media player (PMP) or digital audio player (DAP) is a portable consumer electronics device capable of storing and playing digital media such as audio, images, and video files. Normally they refer to small, battery-powered devices ...
configured to continuously play the 1982 song "Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
" by the American band Toto. The exact location of the installation has not been disclosed.
Since 2021, a livestream has operated from the an artificial watering hole on the inland edge of the desert.
Namib-Naukluft National Park
The Namib-Naukluft National Park, which extends over a large part of the Namib Desert, is the largest game reserve inAfrica
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
and one of the largest in the world at 49,768 sq km (19,215 sq mi). While most of the park is hardly accessible, several well-known visitor attraction
A tourist attraction is a place of interest that tourists visit, typically for its inherent or exhibited natural or cultural value, historical significance, natural or built beauty, offering leisure and amusement.
Types
Places of natural beaut ...
s are found in the desert. The prominent attraction is the Sossusvlei area, where high orange sand dunes surround vivid white salt pans, creating a fascinating landscape.
Access to the park is either by gravel road
A gravel road is a type of unpaved road surfaced with gravel that has been brought to the site from a quarry or stream bed. Gravel roads are common in less-developed nations, and also in the rural areas of developed nations such as Canada and ...
s or dust roads (except for 60 km of concrete road from the Sesriem gate to Sossusvlei) or by light aircraft from Windhoek
Windhoek (; ; ) is the capital and largest city of Namibia. It is located in central Namibia in the Khomas Highland plateau area, at around above sea level, almost exactly at the country's geographical centre. The population of Windhoek, which ...
(the capital of Namibia, about northeast of the centre of the desert), or Swakopmund
Swakopmund ("Mouth of the Swakop River, Swakop") is a city on the coast of western Namibia, west of the Namibian capital Windhoek via the B2 road (Namibia), B2 main road. It is the capital of the Erongo Region, Erongo administrative district. It ...
and Walvis Bay
Walvis Bay (; ; ) is a city in Namibia and the name of the bay on which it lies. It is the List of cities in Namibia, second largest city in Namibia and the largest coastal city in the country. The city covers an area of of land.
The bay is a ...
at the north end of the desert.
Notable places
* Bogenfels * Sesriem * Skeleton Coast *Solitaire
Solitaire may refer to:
Film and television
*'' Le Solitaire'', a 1987 French film
* ''Solitaire'' (1991 film), a Canadian drama film
* ''Solitaire'' (2008 film), a drama film
*''Solitaire'', 2016 Lebanese comedy film with Bassam Kousa
*"Solit ...
* Sossusvlei
** Deadvlei
** Dune 45
* Spitzkoppe
The Spitzkoppe (from German language, German for "pointed dome"; also referred to as Spitzkop, Groot Spitzkop, or the "Matterhorn of Namibia") is a group of bald granite peaks or inselbergs located between Usakos and Swakopmund in the Nami ...
* Swakopmund
Swakopmund ("Mouth of the Swakop River, Swakop") is a city on the coast of western Namibia, west of the Namibian capital Windhoek via the B2 road (Namibia), B2 main road. It is the capital of the Erongo Region, Erongo administrative district. It ...
See also
* '' Animals Are Beautiful People'', a nature documentary set in the Namib *List of deserts by area
This is a list of the largest deserts in the world by area. It includes all deserts above .
See also
* Desert
* Desertification
* List of deserts, List of deserts by continent
* Polar desert
* Tundra
* United Nations Convention to Combat D ...
Notes
References
* ''National Geographic'', January 1992, pp. 54–85. * Mary Seely: ''The Namib: Natural History of an Ancient Desert'', 3rd ed., Windhoek: Desert Research Foundation of Namibia 2004, .Further reading
* * *External links
*Namib Naukluft Park photo gallery
{{Authority control Deserts of Namibia Deserts of South Africa Afrotropical ecoregions Ergs of Africa Physiographic provinces World Heritage Sites in Namibia Namib-Naukluft National Park First 100 IUGS Geological Heritage Sites