Nakhichivan Autonomous Republic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic (, ) is a
Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
with a population of 459,600. It is bordered by
The Library of CongressAndrew Andersen, Ph
/ref>Croissant. ''Armenia–Azerbaijan Conflict'', p. 16. Nakhchivan is homogeneously Azerbaijani today besides a small population of
in the ''Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary'', St. Petersburg, Russia: 1890–1907. The older form of the name is ''Naxčawan'' (). According to philologist Heinrich Hübschmann, the name was originally borne by the namesake city (modern Nakhchivan) and later given to the region. Hübschmann believed the name to be composed of ''Naxič'' or ''Naxuč'' (probably a personal name) and ''awan'', an Armenian word (ultimately of Iranian origin) meaning "place, town". In the Armenian tradition, the name of the region and its namesake city is connected with the Biblical narrative of Noah's Ark and interpreted as meaning "place of the first descent" or "first resting place" (as if deriving from and ) due to it being regarded as the site where
by Bill Crouse
 The oldest material culture artifacts found in the region date back to the
The oldest material culture artifacts found in the region date back to the
 In 189 BC, Nakhchivan became part of the new Kingdom of Armenia established by
In 189 BC, Nakhchivan became part of the new Kingdom of Armenia established by
Atlas of Conflicts: Armenia: Nation Building and Territorial Disputes: 1918–1920
/ref> In December 1918, with the support of Azerbaijan's Musavat Party,
 Facilities improved during Soviet times. Education and public health especially began to see some major changes. In 1913, Nakhchivan only had two hospitals with a total of 20 beds. The region was plagued by widespread diseases including
Facilities improved during Soviet times. Education and public health especially began to see some major changes. In 1913, Nakhchivan only had two hospitals with a total of 20 beds. The region was plagued by widespread diseases including
The Library of Congress Nakhchivan became a scene of conflict during the
The Washington Post. May 23, 1992Background Paper on the Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict
Council of Europe. The Armenians claimed that the attack was in response to cross-border shelling of Armenian villages by Azeri forces from Nakhchivan.The Toronto Star
May 20, 1992 David Zadoyan, a 42-year-old Armenian physicist and mayor of the region, said that the Armenians lost patience after months of firing by the Azeris. "If they were sitting on our hilltops and harassing us with gunfire, what do you think our response should be?" he asked.Armenian Siege of Azeri Town Threatens Turkey, Russia, Iran
The Baltimore Sun. June 3, 1992 The government of Nakhchivan denied these charges and instead asserted that the Armenian assault was unprovoked and specifically targeted the site of a bridge between Turkey and Nakhchivan. "The Armenians do not react to diplomatic pressure," Nakhchivan foreign minister Rza Ibadov told the ITAR-Tass news agency, "It's vital to speak to them in a language they understand." Speaking to the agency from the Turkish capital
, wire carried by the Globe and Mail (Canada) on May 20, 1992. pg. A.10 According to Human Rights Watch, hostilities broke out after three people were killed when Armenian forces began shelling the region.Overview of Areas of Armed Conflict in the former Soviet Union
The Salt Lake Tribune. September 4, 1993. pg. A1. The tension reached its peak, when Turkish heavy artillery shelled the Nakhchivan side of the Nakhchivan-Armenian border, from the Turkish border for two hours. Iran also reacted to Armenia's attacks by conducting military maneuvers along its border with Nakhchivan in a move widely interpreted as a warning to Armenia.
The Library of Congress However, Armenia did not launch any further attacks on Nakhchivan and the presence of Russia's military warded off any possibility that Turkey might play a military role in the conflict. After a period of political instability, the Parliament of Azerbaijan turned to Heydar Aliyev and invited him to return from exile in Nakhchivan to lead the country in 1993.
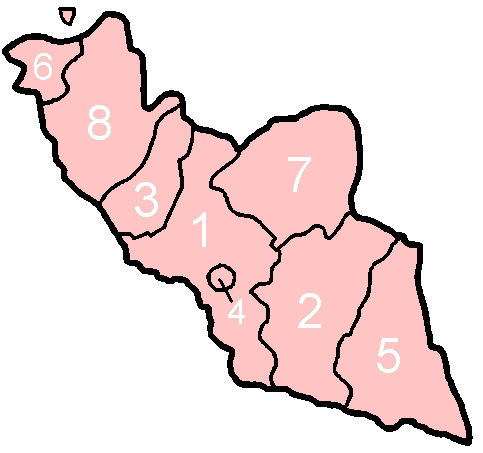 Nakhchivan is subdivided into eight
Nakhchivan is subdivided into eight
 Nakhchivan is a semi-desert region that is separated from the main portion of Azerbaijan by Armenia. The
Nakhchivan is a semi-desert region that is separated from the main portion of Azerbaijan by Armenia. The

File:Qarabağlar türbə kompleksinin ümumi görünüşü.jpg,
Archaeological Treasures Of Nakhchivan
– OpEd – Eurasia Review 2016

Image:Momine Fragment.jpg, Brickwork and faience pattern on the Momine Khatun mausoleum
Image:Nakhichevan02.JPG, Medieval-period ram-shaped grave monuments collected near the Momine Khatun mausoleum
Image:Nakhichevan04.JPG, Ram-shaped grave monument embedded in concrete
Image:Batabat Mountains.jpg, The Batabat region of Shakhbuz
Image:Nakhichevan05.jpg, General view of
Official website of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
Nakhchivan Guide
Silent Erasure
- A Satellite Investigation of the Destruction of Armenian Cultural Heritage in Nakhchivan, Azerbaijan {{coord, 39, 20, N, 45, 30, E, region:AZ_type:adm1st, display=title Subdivisions of Azerbaijan Autonomous republics Enclaves and exclaves States and territories established in 1990 Armenia–Azerbaijan border Azerbaijan–Turkey border Azerbaijan–Iran border Mount Ararat Countries and territories where Azerbaijani is an official language
landlocked
A landlocked country is a country that has no territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie solely on endorheic basins. Currently, there are 44 landlocked countries, two of them doubly landlocked (Liechtenstein and Uzbekistan), and t ...
exclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is s ...
of the Republic of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russi ...
. The region covers Official portal of Nakhchivan Autonomous RepublicNakhchivan Autonomous Republic
with a population of 459,600. It is bordered by
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
to the east and north, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
to the southwest, and Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
to the west. It is the sole autonomous republic of Azerbaijan, governed by its own elected legislature.
The republic, especially the capital city of Nakhchivan, has a long history dating back to about 1500 BC. ''Nakhijevan'' was one the cantons
A canton is a type of administrative division of a country. In general, cantons are relatively small in terms of area and population when compared with other administrative divisions such as counties, departments, or provinces. Internationally, th ...
of the historical Armenian province of Vaspurakan in the Kingdom of Armenia. Historically, the Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
, Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
, Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
, and Turks all competed for the region. The area that is now Nakhchivan became part of Safavid Iran
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the begi ...
in the 16th century. The semi-autonomous Nakhchivan Khanate was established there in the mid-18th century. In 1828, after the last Russo-Persian War and the Treaty of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay (; ) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–1828). It was second of the series of treaties (the first was the 1813 Treaty of Gulistan and the last, the ...
, the Nakhchivan Khanate passed from Iranian into Imperial Russian possession.
After the 1917 February Revolution
The February Revolution (), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and sometimes as the March Revolution or February Coup was the first of Russian Revolution, two revolutions which took place in Russia ...
, Nakhchivan and its surrounding region were under the authority of the Special Transcaucasian Committee of the Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was a provisional government of the Russian Empire and Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately after the abdication of Nicholas II on 2 March, O.S. New_Style.html" ;"title="5 ...
and subsequently of the short-lived Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic
The Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic (TDFR; 22 April – 28 May 1918) was a short-lived sovereign state, state in the Caucasus that included most of the territory of the present-day Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia (coun ...
. When the TDFR was dissolved in May 1918, Nakhchivan, Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh (, ; ) is a region in Azerbaijan, covering the southeastern stretch of the Lesser Caucasus mountain range. Part of the greater region of Karabakh, it spans the area between Lower Karabakh and Syunik Province, Syunik. Its ter ...
, Syunik, and Qazakh were heavily contested between the newly formed and short-lived states of the First Republic of Armenia
The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia, was an independent History of Armenia, Armenian state that existed from May (28th ''de jure'', 30th ''de facto'') 1918 to 2 December 1920 in ...
and the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic (), also known as the Azerbaijan People's Republic (; ), was the first secular democracy, democratic republic in the Turkic peoples, Turkic and Muslim worlds.
*Tadeusz Swietochowski. ''Russia and Azerbaijan: ...
(ADR). In June 1918, the region came under Ottoman occupation. Under the terms of the Armistice of Mudros
The Armistice of Mudros () ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between Ottoman Turkey and the Allies of World War I. It was signed on 30 October 1918 by the Ottoman Minister of Marine Affairs Rauf Bey and British Admiral Somerset ...
, the Ottomans agreed to pull their troops out of the Transcaucasus to make way for British occupation at the close of the First World War. The British placed Nakhchivan under Armenian administration in April 1919, although an Azerbaijani revolt prevented Armenia from establishing full control over the territory.
In July 1920, the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
occupied the region. In November of that year, Bolshevik Russia and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
both promised that Nakhchivan, alongside neighboring Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh (, ; ) is a region in Azerbaijan, covering the southeastern stretch of the Lesser Caucasus mountain range. Part of the greater region of Karabakh, it spans the area between Lower Karabakh and Syunik Province, Syunik. Its ter ...
and Zangezur, was an "integral part" of Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
.De Waal. ''Black Garden'', p. 129. However, on March 16, 1921, in accordance with the results of a referendum, the Bolshevik government declared the Nakhchivan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, which went on to become an autonomous republic ''within'' the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic
The Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic, also referred to as the Azerbaijani Soviet Socialist Republic, Azerbaijan SSR, Azerbaijani SSR, AzSSR, Soviet Azerbaijan or simply Azerbaijan, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent re ...
in 1924. In January 1990, Nakhchivan declared independence from the USSR to protest against the suppression of the national movement in Azerbaijan and became the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic within the newly independent Republic of Azerbaijan a year later.
Though a mixed Azerbaijani-Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
region as late as a century ago,Ian Bremmer
Ian Arthur Bremmer (born November 12, 1969) is an American political scientist, author, and entrepreneur focused on global political risk. He is the founder and president of Eurasia Group, a political risk research and consulting firm. He is al ...
and Ray Taras. ''New States, New Politics: Building Post-Soviet Nations'', p. 484. Armenia: A Country Study: The New NationalismThe Library of CongressAndrew Andersen, Ph
/ref>Croissant. ''Armenia–Azerbaijan Conflict'', p. 16. Nakhchivan is homogeneously Azerbaijani today besides a small population of
Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
.
Etymology
Variations of the name Nakhchivan include Nakhichevan, Naxcivan, Naxçivan, Nakhijevan, Nakhchawan, Nakhitchevan,Elisabeth Bauer, ''Armenia: Past and Present'', p.99 (ISBN B0006EXQ9C). Nakhjavan, and Nakhdjevan. Nakhchivan is mentioned inPtolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
's ''Geography'' and by other classical writers as "Naxuana"."Nakhichevan"in the ''Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary'', St. Petersburg, Russia: 1890–1907. The older form of the name is ''Naxčawan'' (). According to philologist Heinrich Hübschmann, the name was originally borne by the namesake city (modern Nakhchivan) and later given to the region. Hübschmann believed the name to be composed of ''Naxič'' or ''Naxuč'' (probably a personal name) and ''awan'', an Armenian word (ultimately of Iranian origin) meaning "place, town". In the Armenian tradition, the name of the region and its namesake city is connected with the Biblical narrative of Noah's Ark and interpreted as meaning "place of the first descent" or "first resting place" (as if deriving from and ) due to it being regarded as the site where
Noah
Noah (; , also Noach) appears as the last of the Antediluvian Patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5–9), the Quran and Baháʼí literature, ...
descended and settled after the landing of the Ark on nearby Mount Ararat
Mount Ararat, also known as Masis or Mount Ağrı, is a snow-capped and dormant compound volcano in Eastern Turkey, easternmost Turkey. It consists of two major volcanic cones: Greater Ararat and Little Ararat. Greater Ararat is the highest p ...
. It was probably under the influence of this tradition that the name changed in Armenian from the older ''Naxčawan'' to ''Naxijewan''. Although this is a folk etymology, William Whiston
William Whiston (9 December 166722 August 1752) was an English theologian, historian, natural philosopher, and mathematician, a leading figure in the popularisation of the ideas of Isaac Newton. He is now probably best known for helping to inst ...
believed Nakhchivan/Nakhijevan to be the ''Apobatērion'' ("place of descent") mentioned by the first-century Jewish historian Flavius Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing ''The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Judaea ...
in connection with Noah's Ark, which would make the tradition connecting the name with the Biblical figure Noah very old, predating Armenia's conversion to Christianity in the early fourth century.''Noah's Ark: Its Final Berth''by Bill Crouse
History
Early history
Neolithic Age
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wid ...
. On the other hand, Azerbaijani archaeologists have found that the history of Nakhchivan dates back to the Stone Age (Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
). As a result of archaeological diggings, archaeologists discovered a great number of Stone-Age materials in different regions of Nakhchivan. These materials were useful to study the Paleolithic age in Azerbaijan. Pollen analysis conducted in Gazma Cave (Sharur District) suggests that humans in the Middle Palaeolithic (Mousterian
The Mousterian (or Mode III) is an Industry (archaeology), archaeological industry of Lithic technology, stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and with the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and We ...
) lived not only in the mountain forests but also in the dry woodlands found in Nakhchivan. Several archaeological sites dating from the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
and Chalcolithic
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in di ...
periods have also been found in Nakhchivan, including the ancient towns of Nakhchivan Tepe
Nakhchivan Tepe (Naxçıvantəpə) is a Chalcolithic settlement in Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, Nakhchivan, Azerbaijan. It is located in Nakhchivan (city), Nakhchivan and is dated to around 5000 BC. It is on the right bank of the Nakhchivança ...
(near the city of Nakhchivan) and Ovchular Tepesi. Some of the oldest salt mines in the world have also been discovered.
The region was part of the states of Urartu
Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around the Armenian highlands between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan. The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Armenia.Kleiss, Wo ...
and later Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Means of communication, tools and channels used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Interactive media, media that is inter ...
.Нахичеванская Автономная Советская Социалистическая РеспубликаGreat Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; , ''BSE'') is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Great Russian Enc ...
It became part of the Satrapy of Armenia under Achaemenid Persia c. 521 BC. After the death of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
in 323 BC several generals of the Macedonian army, including Neoptolemus
In Greek mythology, Neoptolemus (; ), originally called Pyrrhus at birth (; ), was the son of the mythical warrior Achilles and the princess Deidamia, and the brother of Oneiros. He became the progenitor of the ruling dynasty of the Molossian ...
, attempted but failed to take control of the region, and it was ruled by the native Armenian dynasty of Orontids until Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
was conquered by Antiochus III the Great
Antiochus III the Great (; , ; 3 July 187 BC) was the sixth ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 223 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of West Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to th ...
(ruled 222–187 BC).
 In 189 BC, Nakhchivan became part of the new Kingdom of Armenia established by
In 189 BC, Nakhchivan became part of the new Kingdom of Armenia established by Artaxias I
Artaxias I (from ) was the founder of the Artaxiad dynasty of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenia, ruling from 189 BC to 160 BC. Artaxias was a member of a branch of the Orontid dynasty, the earlier ruling dynasty of Armenia. He expanded his ...
.Ayvazyan, Argam. ''The Historical Monuments Of Nakhichevan'', pp. 10–12. Within the kingdom, the region of present-day Nakhchivan was part of the Ayrarat, Vaspurakan and Syunik provinces. According to the early medieval Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi
Movses Khorenatsi ( 410–490s AD; , ) was a prominent Armenians, Armenian historian from late antiquity and the author of the ''History of Armenia (book), History of the Armenians''.
Movses's ''History of the Armenians'' was the first attempt at ...
, from the third to second centuries, the region belonged to the Muratsyan '' nakharar'' family but after disputes with central power, King Artavazd I massacred the family and seized the lands and formally attached it to the kingdom. The area's status as a major trade center allowed it to prosper; as a result, many foreign powers coveted it. According to the Armenian historian Faustus of Byzantium (5th century), when the Sassanid Persians invaded Armenia, Sassanid King Shapur II
Shapur II ( , 309–379), also known as Shapur the Great, was the tenth King of Kings (List of monarchs of the Sasanian Empire, Shahanshah) of Sasanian Iran. He took the title at birth and held it until his death at age 70, making him the List ...
(310–380) removed 2,000 Armenian and 16,000 Jewish families in 360–370. In 428, the Armenian Arshakuni monarchy was abolished and Nakhchivan was annexed by Sassanid Persia. In 623, possession of the region passed to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
but was soon left to its own rule. Sebeos referred to the area as Tachkastan. According to the 5th-century Armenian author Koriun, Nakhchivan was the place where the Armenian scholar Mesrop Mashtots
Mesrop Mashtots (; , ' 362February 17, 440 AD) was an Armenians, Armenian Linguistics, linguist, composer, Christian theology, theologian, Politician, statesman, and Hymnology, hymnologist. He is venerated as a saint in the Armenian Apostolic C ...
finished the creation of the Armenian alphabet
The Armenian alphabet (, or , ) or, more broadly, the Armenian script, is an alphabetic writing system developed for Armenian and occasionally used to write other languages. It is one of the three historical alphabets of the South Caucasu ...
and opened the first Armenian schools. This occurred in the province of Goghtan, which corresponds to Nakhchivan's modern Ordubad district.
From 640 on, the Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
invaded Nakhchivan and undertook many campaigns in the area, crushing all resistance and attacking Armenian nobles who remained in contact with the Byzantines or who refused to pay tribute. In 705, after suppressing an Armenian revolt, Arab viceroy Muhammad ibn Marwan decided to eliminate the Armenian nobility.David Marshall Lang
David Marshall Lang (6 May 1924 – 20 March 1991), was a Professor of Caucasian Studies, School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London. He was one of the most productive British scholars who specialized in Georgian, Armenian and ...
, ''Armenia: Cradle of Civilization'', p. 178 . In Nakhchivan, several hundred Armenian nobles were locked up in churches and burnt, while others were crucified.
The violence caused many Armenian princes to flee to the neighboring Kingdom of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia (), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a Middle Ages, medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in Anno Domini, AD. It reached Georgian Golden Age, its Golden Age of political and economic strength during the reign ...
or the Byzantine Empire. Meanwhile, Nakhchivan itself became part of the autonomous Principality of Armenia under Arab control.Mark Whittow. ''The Making of Byzantium, 600–1025''. Berkeley: University of California
The University of California (UC) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university, research university system in the U.S. state of California. Headquartered in Oakland, California, Oakland, the system is co ...
Press, 1996, p. 210. In the eighth century, Nakhchivan was one of the scenes of an uprising against the Arabs led by Persian revolutionary Babak Khorramdin of the Iranian Khorram-Dinān ("those of the joyous religion" in Persian). Nakhchivan was finally released from Arab rule in the tenth century by Bagratuni King Smbat I and handed over to the princes of Syunik. This region also was taken by Sajids in 895 and between 909 and 929, Sallarid
The Sallarid dynasty (), (also known as the Musafirids or Langarids) was a Muslim dynasty of Daylami origin, which ruled in Tarom, Samiran, Daylam, Gilan and subsequently Azerbaijan, Arran, and some districts in Eastern Armenia in the 2nd half o ...
between 942 and 971 and Shaddadid
The Shaddadids were a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Kurdish origin. who ruled in various parts of Armenia and Arran from 951 to 1199 AD. They were established in Dvin. Through their long tenure in Armenia, they often intermarried with the Bagratuni ...
between 971 and 1045.
About 1055, the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turks, Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate society, Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persi ...
took over the region. In the 12th century, the city of Nakhchivan became the capital of the state of Atabegs of Azerbaijan
Atabeg, Atabek, or Atabey is a hereditary title of nobility of Turkic origin, indicating a governor of a nation or province who was subordinate to a monarch and charged with raising the crown prince. The first instance of the title's use was wi ...
, also known as Ildegizid state, which included most of Iranian Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan or Azarbaijan (, , ), also known as Iranian Azerbaijan, is a historical region in northwestern Iran that borders Iraq and Turkey to the west and Armenia, Azerbaijan, and the Azerbaijani exclave of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republ ...
and a significant part of the South Caucasus. The magnificent 12th-century mausoleum of Momine Khatun, the wife of Ildegizid ruler, Great Atabeg
Atabeg, Atabek, or Atabey is a hereditary title of nobility of Turkic language, Turkic origin, indicating a governor of a nation or province who was subordinate to a monarch and charged with raising the crown prince. The first instance of the ti ...
Jahan Pehlevan, is the main attraction of modern Nakhchivan. At its heyday, the Ildegizid authority in Nakhchivan and some other areas of South Caucasus was contested by Georgia. The Armeno-Georgian princely house of Zacharids frequently raided the region when the Atabeg state was in decline in the early years of the 13th century. It was then plundered by invading Mongols in 1220 and Khwarezmians in 1225 and became part of Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
in 1236 when the Caucasus was invaded by Chormaqan. In the 13th century, during the reign of the Mongol horde ruler Güyük Khan
Güyük Khan or Güyüg Khagan, mononymously Güyüg ( 19 March 1206 – 20 April 1248), was the third Khagan of the Mongol Empire, the eldest son of Ögedei Khan and a grandson of Genghis Khan. He reigned from 1246 to 1248. He started his mili ...
, Christians were allowed to build churches in the strongly Muslim town of Nakhchivan; however, the conversion to Islam of Gazan khan brought about a reversal of this favor. The 14th century saw the rise of Armenian Catholicism in Nakhchivan, though by the 15th century the territory became part of the states of Kara Koyunlu
The Qara Qoyunlu or Kara Koyunlu (, ; ), also known as the Black Sheep Turkomans, were a culturally Persianate, Muslim Turkoman "Kara Koyunlu, also spelled Qara Qoyunlu, Turkish Karakoyunlular, English Black Sheep, Turkmen tribal federation th ...
and Ak Koyunlu.
Iranian rule
In the16th century
The 16th century began with the Julian calendar, Julian year 1501 (represented by the Roman numerals MDI) and ended with either the Julian or the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian year 1600 (MDC), depending on the reckoning used (the Gregorian calend ...
, control of Nakhchivan passed to the Safavid dynasty
The Safavid dynasty (; , ) was one of Iran's most significant ruling dynasties reigning from Safavid Iran, 1501 to 1736. Their rule is often considered the beginning of History of Iran, modern Iranian history, as well as one of the gunpowder em ...
. Until the demise of the Safavids, it remained as an administrative jurisdiction of the Erivan Province (also known as Chokhur-e Sa'd). Because of its geographic position, it frequently suffered during the wars between the Safavids and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, from the 16th to 18th centuries. Turkish historian İbrahim Peçevi described the passing of the Ottoman army from the Ararat plain to Nakhchivan:
In 1604, Shah Abbas I
Abbas I (; 27 January 1571 – 19 January 1629), commonly known as Abbas the Great (), was the fifth Safavid shah of Iran from 1588 to 1629. The third son of Shah Mohammad Khodabanda, he is generally considered one of the most important rulers ...
of Iran, concerned that the skilled peoples of Nakhchivan, its natural resources, and the surrounding areas could get in danger due to its relatively close proximity to the Ottoman-Persian frontline, decided to institute a scorched earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy of destroying everything that allows an enemy military force to be able to fight a war, including the deprivation and destruction of water, food, humans, animals, plants and any kind of tools and i ...
policy. He forcefully deported the entire hundreds of thousands of local population—Muslims, Jews, and Armenians alike—to leave their homes and move to the provinces south of the Aras River
The Aras is a transboundary river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, fin ...
.Lang. ''Armenia: Cradle of Civilization'', pp. 210–1.
Many of the Armenian deportees were settled in the neighborhood of Isfahan
Isfahan or Esfahan ( ) is a city in the Central District (Isfahan County), Central District of Isfahan County, Isfahan province, Iran. It is the capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is located south of Tehran. The city ...
that was named New Julfa
New Julfa (, ''Now Jolfā'', or , ''Jolfâ-ye Now''; , ''Nor Jugha'') is the Armenians, Armenian quarter of Isfahan, Iran, located along the south bank of the Zayanderud.
Established and named after the Gülüstan, Nakhchivan, older city of Julf ...
since most of the residents were from the original Julfa. The Turkic Kangerli tribe was later permitted to move back under Shah Abbas II (1642–1666) to repopulate the frontier region of his realm. In the 17th century, Nakhchivan was the scene of a peasant movement led by Köroğlu against foreign invaders and "native exploiters". In 1747, the Nakhchivan Khanate emerged in the region after the death of Nader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar (; 6 August 1698 or 22 October 1688 – 20 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian history, ruling as shah of Iran (Persia) from 1736 to 1747, when he was a ...
Afshar.
Passing to Imperial Russian rule
After the last Russo-Persian War and theTreaty of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay (; ) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–1828). It was second of the series of treaties (the first was the 1813 Treaty of Gulistan and the last, the ...
, the Nakhchivan Khanate passed into Russian possession in 1828 due to Iran's forced ceding as a result of the outcome of the war and treaty. With the onset of Russian rule, the Tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, цар, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the Euro ...
ist authorities encouraged resettlement of Armenians to Nakhchivan and other areas of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
from the Persian and Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
s. Special clauses of the Turkmenchay and Adrianople
Edirne (; ), historically known as Orestias, Adrianople, is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the Edirne Province, province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, Edirne was the second c ...
treaties allowed for this. Alexandr Griboyedov, the Russian envoy to Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, stated that by the time Nakhchivan came under Russian rule, there had been 290 native Armenians families in the province excluding the city of Nakhchivan, the number of Muslim families was 1,632, and the number of the Armenian immigrant families was 943. The same numbers in the city of Nakhchivan were 114, 392, and 285 respectively. With such a dramatic influx of Armenian immigrants, Griboyedov noted friction arising between the Armenian and Muslim populations. He requested Russian army commander Count Ivan Paskevich to give orders on resettlement of some of the arriving people further to the region of Daralayaz to quiet the tensions.
The Nakhchivan Khanate was dissolved in 1828 the same year it came into Russian possession, and its territory was merged with the territory of the Erivan khanate
The Erivan Khanate (), also known as , was a Khanates of the Caucasus, khanate (i.e., province) that was established in Afsharid dynasty, Afsharid Iran in the 18th century. It covered an area of roughly 19,500 km2, and corresponded to most o ...
and the area became the Nakhichevan uezd
The Nakhichevan ''uezd'' was a county (''uezd'') of the Erivan Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty (1801–1917), Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire. It bordered the governorate's Sharur-Daralayaz uezd to the north, the Zangezur uez ...
of the new Armenian oblast, which later became the Erivan Governorate in 1849. According to official statistics of the Russian Empire, by the turn of the 20th century Tatars (later known as Azerbaijanis
Azerbaijanis (; , ), Azeris (, ), or Azerbaijani Turks (, ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group living mainly in the Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan region of northwestern Iran and the Azerbaijan, Republic of Azerbaijan. They are predomin ...
) made up roughly 57% of the ''uezd''Russian Revolution of 1905
The Russian Revolution of 1905, also known as the First Russian Revolution, was a revolution in the Russian Empire which began on 22 January 1905 and led to the establishment of a constitutional monarchy under the Russian Constitution of 1906, t ...
, conflict erupted between the Armenians and the Tatars, culminating in the Armenian-Tatar massacres which saw violence in Nakhchivan in May of that year.Michael P. Croissant. ''The Armenia-Azerbaijan Conflict: Causes and Implications'', p. 9.
War and revolution
In the final year ofWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, Nakhchivan was the scene of more bloodshed between Armenians and Azerbaijanis, who both laid claim to the area. By 1914, the Armenian population had decreased slightly to 40% while the Azeri population increased to roughly 60%. After the February Revolution
The February Revolution (), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and sometimes as the March Revolution or February Coup was the first of Russian Revolution, two revolutions which took place in Russia ...
, the region was under the authority of the Special Transcaucasian Committee of the Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was a provisional government of the Russian Empire and Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately after the abdication of Nicholas II on 2 March, O.S. New_Style.html" ;"title="5 ...
and subsequently of the short-lived Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic
The Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic (TDFR; 22 April – 28 May 1918) was a short-lived sovereign state, state in the Caucasus that included most of the territory of the present-day Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia (coun ...
. When the TDFR was dissolved in May 1918, Nakhchivan, Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh (, ; ) is a region in Azerbaijan, covering the southeastern stretch of the Lesser Caucasus mountain range. Part of the greater region of Karabakh, it spans the area between Lower Karabakh and Syunik Province, Syunik. Its ter ...
, Zangezur (today the Armenian province of Syunik), and Qazakh were heavily contested between the newly formed and short-lived states of the Republic of Armenia and the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic (), also known as the Azerbaijan People's Republic (; ), was the first secular democracy, democratic republic in the Turkic peoples, Turkic and Muslim worlds.
*Tadeusz Swietochowski. ''Russia and Azerbaijan: ...
(ADR). In June 1918, the region came under Ottoman occupation. The Ottomans proceeded to massacre 10,000 Armenians and razed 45 of their villages. Under the terms of the Armistice of Mudros
The Armistice of Mudros () ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between Ottoman Turkey and the Allies of World War I. It was signed on 30 October 1918 by the Ottoman Minister of Marine Affairs Rauf Bey and British Admiral Somerset ...
, the Ottomans agreed to pull their troops out of the Transcaucasus to make way for the forthcoming British military presence.Croissant. ''Armenia-Azerbaijan Conflict'', p. 15.
Under British occupation, Sir Oliver Wardrop, British Chief Commissioner in the South Caucasus, made a border proposal to solve the conflict. According to Wardrop, Armenian claims against Azerbaijan should not go beyond the administrative borders of the former Erivan Governorate (which under prior Imperial Russian rule encompassed Nakhchivan), while Azerbaijan was to be limited to the governorates of Baku
Baku (, ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Azerbaijan, largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and in the Caucasus region. Baku is below sea level, which makes it the List of capital ci ...
and Elizavetpol. This proposal was rejected by both Armenians (who did not wish to give up their claims to Qazakh, Zangezur and Karabakh) and Azeris (who found it unacceptable to give up their claims to Nakhchivan). As disputes between both countries continued, it soon became apparent that the fragile peace under British occupation would not last.Dr. Andrew Andersen, PhAtlas of Conflicts: Armenia: Nation Building and Territorial Disputes: 1918–1920
/ref> In December 1918, with the support of Azerbaijan's Musavat Party,
Jafargulu Khan Nakhchivanski
Jafargulu Khan Nakhchivanski (; ; 5 February 1859 – 1929) was a Russian officer and later an Azerbaijani statesman. He was the brother of General-Adjutant Huseyn Khan Nakhchivanski and father of Major General Jamshid Nakhchivanski.
Early li ...
declared the Republic of Aras in the Nakhchivan uyezd of the former Erivan Governorate assigned to Armenia by Wardrop. The Armenian government did not recognize the new state and sent its troops into the region to take control of it. The conflict soon erupted into the violent Aras War. British journalist C. E. Bechhofer Roberts described the situation in April 1920:
By mid-June 1919, however, Armenia succeeded in establishing control over Nakhchivan and the whole territory of the self-proclaimed republic. The fall of the Aras republic triggered an invasion by the regular Azerbaijani army and by the end of July, the Armenian administration was ousted from Nakhchivan. Again, more violence erupted leaving some ten thousand Armenians dead and forty-five Armenian villages destroyed. Meanwhile, feeling the situation to be hopeless and unable to maintain any control over the area, the British decided to withdraw from the region in mid-1919.Croissant. ''Armenia-Azerbaijan Conflict'', p. 16. Still, fighting between Armenians and Azeris continued and after a series of skirmishes that took place throughout the Nakhchivan district, a cease-fire agreement was concluded. However, the cease-fire lasted only briefly, and by early March 1920, more fighting broke out, primarily in Karabakh between Karabakh Armenians and Azerbaijan's regular army. This triggered conflicts in other areas with mixed populations, including Nakhchivan.
Following the adoption of the name of "Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
" by the newly established Azerbaijan Democratic Republic, a naming dispute arose with Qajar Iran
The Guarded Domains of Iran, alternatively the Sublime State of Iran and commonly called Qajar Iran, Qajar Persia or the Qajar Empire, was the Iranian state under the rule of the Qajar dynasty, which was of Turkic peoples, Turkic origin,Cyrus G ...
, with the latter protesting this decision. In tandem with this naming controversy, however, the young Azerbaijan Republic also faced a threat from the nascent Soviets in Moscow and the Armenians. In order to escape the possibility of a Soviet invasion and an even greater imminent threat of an Armenian invasion, Muslim Nakhchivan proposed being annexed to Iran. The then pro-British government in Tehran led by Vossug ed Dowleh made endeavours amongst Baku's leadership to join Iran. In order to promote this idea, Vosugh ed Dowleh dispatched two separate Iranian delegations; one to Baku and one to the Paris Peace Conference in 1919. The delegation at Baku, at the behest of Zia ol Din Tabatabaee, held intensive negotiations with the leadership of the Musavat party during the increasing chaos and instability in the city. During the closing stages, an accord was reached between them; however, before the idea was presented to Vossug ed Dowleh in Tehran, the Communists took over Baku and terminated the Musavat-Ottoman rule. The Iranian delegation at Paris, which was headed by foreign minister Firouz Nosrat-ed-Dowleh III, reached a unity negotiation with the delegation from Baku and signed a confederation agreement. In the end, these efforts proved to be of no avail, with the Soviets taking over the entirety of Transcaucasia.
Sovietization
In July 1920, the 11th Soviet Red Army invaded and occupied the region and on July 28, declared the Nakhchivan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic with "close ties" to theAzerbaijan SSR
The Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic, also referred to as the Azerbaijani Soviet Socialist Republic, Azerbaijan SSR, Azerbaijani SSR, AzSSR, Soviet Azerbaijan or simply Azerbaijan, was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union be ...
. In November, on the verge of taking over Armenia, the Bolsheviks, to attract public support, promised they would allot Nakhchivan to Armenia, along with Karabakh and Zangezur. Nariman Narimanov
Nariman Karbalayi Najaf oghlu Narimanov (, ; – 19 March 1925) was an Azerbaijanis, Azerbaijani Bolsheviks, Bolshevik revolutionary, writer, publicist, politician and statesman. For just over one year, beginning in May 1920, Narimanov headed th ...
, leader of Bolshevik Azerbaijan, issued a declaration celebrating the "victory of Soviet power in Armenia" and proclaimed that both Nakhchivan and Zangezur should be awarded to the Armenian people as a sign of the Azerbaijani people's support for Armenia's fight against the former Armenian government:
Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...
, while welcoming this act of "great Soviet fraternity" where "boundaries had no meaning among the family of Soviet peoples", did not agree with the motion and instead called for the people of Nakhchivan to be consulted in a referendum. According to the formal figures of this referendum, held at the beginning of 1921, 90% of Nakhchivan's population wanted to be included in the Azerbaijan SSR "with the rights of an autonomous republic".Tim Potier. ''Conflict in Nagorno-Karabakh, Abkhazia, and South Ossetia: A Legal Appraisal'', p. 4. The decision to make Nakhchivan a part of modern-day Azerbaijan was cemented on March 16, 1921, in the Treaty of Moscow between Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
and the newly founded Republic of Turkey.Ian Bremmer and Ray Taras. ''New States, New Politics: Building Post-Soviet Nations'', p. 444. The agreement between Soviet Russia and Turkey also called for attachment of the former Sharur-Daralagezsky Uyezd (which had a solid Azeri majority) to Nakhchivan, thus allowing Turkey to share a border with the Azerbaijan SSR. This deal was reaffirmed on October 13, in the Treaty of Kars. Article V of the treaty stated the following:
Thus, on February 9, 1924, the Soviet Union officially established the Nakhchivan ASSR. Its constitution was adopted on April 18, 1926.
In the Soviet Union
As a constituent part of the Soviet Union, tensions lessened over the ethnic composition of Nakhchivan or any territorial claims regarding it. Instead, it became an important point of industrial production with particular emphasis on the mining of minerals such as salt. Under Soviet rule, it was once a major junction on the Moscow-Tehran
Tehran (; , ''Tehrân'') is the capital and largest city of Iran. It is the capital of Tehran province, and the administrative center for Tehran County and its Central District (Tehran County), Central District. With a population of around 9. ...
railway lineDe Waal. ''Black Garden'', p. 271. as well as the Baku
Baku (, ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Azerbaijan, largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and in the Caucasus region. Baku is below sea level, which makes it the List of capital ci ...
-Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev ...
railway. It also served as an important strategic area during the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, sharing borders with both Turkey (a NATO member state) and Iran (a close ally of the West until the Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution (, ), also known as the 1979 Revolution, or the Islamic Revolution of 1979 (, ) was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1979. The revolution led to the replacement of the Impe ...
of 1979).
 Facilities improved during Soviet times. Education and public health especially began to see some major changes. In 1913, Nakhchivan only had two hospitals with a total of 20 beds. The region was plagued by widespread diseases including
Facilities improved during Soviet times. Education and public health especially began to see some major changes. In 1913, Nakhchivan only had two hospitals with a total of 20 beds. The region was plagued by widespread diseases including trachoma
Trachoma is an infectious disease caused by bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. The infection causes a roughening of the inner surface of the eyelids. This roughening can lead to pain in the eyes, breakdown of the outer surface or cornea ...
and typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
. Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, which mostly came from the adjoining Aras River, brought serious harm to the region. At any one time, between 70% and 85% of Nakhchivan's population was infected with malaria, and in the region of Norashen (present-day Sharur) almost 100% were struck with the disease. This situation improved dramatically under Soviet rule. Malaria was sharply reduced and trachoma, typhus, and relapsing fever were eliminated.
During the Soviet era, Nakhchivan saw a great demographic shift. In 1926, 15% of the region's population was Armenian, but by 1979, this number had shrunk to 1.4%. Azeris made up 85% in 1926, but 96% in 1979 (leaving the small remainder mixed or other). Three factors were involved: the emigration of Armenians to the Armenian SSR
The Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic (ArSSR), also known as Soviet Armenia, or simply Armenia, was one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union, located in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Soviet Armenia bordered the Soviet republics ...
, the immigration of Azeris from Armenia, and the birth rate of Azeris being higher than that of Armenians.
Armenians in Nagorno-Karabakh noted similar though slower demographic trends and feared an eventual "de-Armenianization" of the area. When tensions between Armenians and Azeris were reignited in the late-1980s by the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, Azerbaijan's Popular Front managed to pressure the Azerbaijan SSR to instigate a partial railway and air blockade against Armenia, while another reason for the disruption of rail service to Armenia were attacks of Armenian forces on the trains entering the Armenian territory from Azerbaijan, which resulted in railroad personnel refusing to enter Armenia. This effectively crippled Armenia's economy, as 85% of the cargo and goods arrived through rail traffic. In response, Armenia closed the railway to Nakhchivan, thereby strangling the exclave's only link to the rest of the Soviet Union.
December 1989 saw unrest in Nakhchivan as its Azeri inhabitants moved to physically dismantle the Soviet border with Iran to flee the area and meet their ethnic Azeri cousins in northern Iran. This action was angrily denounced by the Soviet leadership and the Soviet media accused the Azeris of "embracing Islamic fundamentalism
Islamic fundamentalism has been defined as a revivalist and reform movement of Muslims who aim to return to the founding scriptures of Islam. The term has been used interchangeably with similar terms such as Islamism, Islamic revivalism, Qut ...
".De Waal, ''Black Garden'', p. 88–89.
Declaring independence
On Saturday, January 20, 1990, theSupreme Soviet
The Supreme Soviet () was the common name for the legislative bodies (parliaments) of the Soviet socialist republics (SSR) in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR). These soviets were modeled after the Supreme Soviet of the USSR, establ ...
of the Nakhchivan ASSR issued a declaration stating the intention for Nakhchivan to secede
Secession is the formal withdrawal of a group from a political entity. The process begins once a group proclaims an act of secession (such as a declaration of independence). A secession attempt might be violent or peaceful, but the goal is the c ...
from the USSR to protest the Soviet Union's actions during Black January. Iranian Press Agency, IRNA, reported that upon its independence, Nakhchivan asked Turkey, Iran, and the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
to come to its aid. It was the first part of the Soviet Union to declare independence, preceding Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
's declaration by only a few weeks. Subsequently, Nakhchivan was independent from Moscow and Baku but was then brought under control by the clan of Heydar Aliyev
Heydar Alirza oghlu Aliyev (10 May 1923 – 12 December 2003) was an Azerbaijani politician who was a Soviet party boss in the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic from 1969 to 1982, and the third president of Azerbaijan from October 1993 to ...
.
In the post-Soviet era
Heydar Aliyev
Heydar Alirza oghlu Aliyev (10 May 1923 – 12 December 2003) was an Azerbaijani politician who was a Soviet party boss in the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic from 1969 to 1982, and the third president of Azerbaijan from October 1993 to ...
, the future president of Azerbaijan, returned to his birthplace of Nakhchivan in 1990, after being ousted from his position in the Politburo
A politburo () or political bureau is the highest organ of the central committee in communist parties. The term is also sometimes used to refer to similar organs in socialist and Islamist parties, such as the UK Labour Party's NEC or the Poli ...
by Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the last leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
in 1987. Soon after returning to Nakhchivan, Aliyev was elected to the Supreme Soviet by an overwhelming majority. Aliyev subsequently resigned from the CPSU
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU),. Abbreviated in Russian as КПСС, ''KPSS''. at some points known as the Russian Communist Party (RCP), All-Union Communist Party and Bolshevik Party, and sometimes referred to as the Soviet ...
, and after the failed August 1991 coup against Gorbachev, he called for complete independence for Azerbaijan and denounced Ayaz Mütallibov for supporting the coup. In late 1991, Aliyev consolidated his power base as chairman of the Nakhchivan Supreme Soviet and asserted Nakhchivan's near-total independence from Baku
Baku (, ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Azerbaijan, largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and in the Caucasus region. Baku is below sea level, which makes it the List of capital ci ...
.Azerbaijan: A Country Study: Aliyev and the Presidential Election of October 1993The Library of Congress Nakhchivan became a scene of conflict during the
First Nagorno-Karabakh War
The First Nagorno-Karabakh War was an ethnic conflict, ethnic and territorial conflict that took place from February 1988 to May 1994, in the enclave of Nagorno-Karabakh in southwestern Azerbaijan, between the majority ethnic Armenians of Nag ...
. On May 4, 1992, Armenian forces shelled the raion
A raion (also spelt rayon) is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet states. The term is used for both a type of subnational entity and a division of a city. The word is from the French (meaning 'honeycomb, department'), and is c ...
of Sadarak.Russia Plans Leaner, More Open MilitaryThe Washington Post. May 23, 1992Background Paper on the Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict
Council of Europe. The Armenians claimed that the attack was in response to cross-border shelling of Armenian villages by Azeri forces from Nakhchivan.The Toronto Star
May 20, 1992 David Zadoyan, a 42-year-old Armenian physicist and mayor of the region, said that the Armenians lost patience after months of firing by the Azeris. "If they were sitting on our hilltops and harassing us with gunfire, what do you think our response should be?" he asked.Armenian Siege of Azeri Town Threatens Turkey, Russia, Iran
The Baltimore Sun. June 3, 1992 The government of Nakhchivan denied these charges and instead asserted that the Armenian assault was unprovoked and specifically targeted the site of a bridge between Turkey and Nakhchivan. "The Armenians do not react to diplomatic pressure," Nakhchivan foreign minister Rza Ibadov told the ITAR-Tass news agency, "It's vital to speak to them in a language they understand." Speaking to the agency from the Turkish capital
Ankara
Ankara is the capital city of Turkey and List of national capitals by area, the largest capital by area in the world. Located in the Central Anatolia Region, central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5,290,822 in its urban center ( ...
, Ibadov said that Armenia's aim in the region was to seize control of Nakhchivan.Reuters News Agency, wire carried by the Globe and Mail (Canada) on May 20, 1992. pg. A.10 According to Human Rights Watch, hostilities broke out after three people were killed when Armenian forces began shelling the region.Overview of Areas of Armed Conflict in the former Soviet Union
Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. Headquartered in New York City, the group investigates and reports on issues including War crime, war crimes, crim ...
, Helsinki Report
The heaviest fighting took place on May 18, when the Armenians captured Nakhchivan's exclave of Karki, a tiny territory through which Armenia's main north–south highway passes. The exclave presently remains under Armenian control.Azerbaijan: Seven Years Of Conflict In Nagorno-KarabakhHuman Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. Headquartered in New York City, the group investigates and reports on issues including War crime, war crimes, crim ...
, Helsinki Report After the fall of Shusha
Shusha (, ) or Shushi () is a city in Azerbaijan, in the region of Nagorno-Karabakh. Situated at an altitude of 1,400–1,800 metres (4,600–5,900 ft) in the Karabakh mountains, the city was a mountain resort in the Soviet Union, Soviet ...
, the Mütallibov government of Azerbaijan accused Armenia of moving to take the whole of Nakhchivan (a claim that was denied by Armenian government officials). However, Heydar Aliyev declared a unilateral ceasefire on May 23 and sought to conclude a separate peace with Armenia. Armenian President Levon Ter-Petrossian expressed his willingness to sign a cooperation treaty with Nakhchivan to end the fighting, and subsequently a cease-fire was agreed upon.
The conflict in the area caused a harsh reaction from Turkey. Turkish Prime Minister Tansu Çiller announced that any Armenian advance on the main territory of Nakhchivan would result in a declaration of war against Armenia. Russian military leaders declared that "third party intervention into the dispute could trigger a Third World War
World War III, also known as the Third World War, is a hypothetical future global conflict subsequent to World War I (1914–1918) and World War II (1939–1945). It is widely predicted that such a war would involve all of the great powers, l ...
". Thousands of Turkish troops were sent to the border between Turkey and Armenia in early September. Russian military forces in Armenia countered their movements by increasing troop levels along the Armenian-Turkish frontier and bolstering defenses in a tense period where war between the two seemed inevitable.Turkey Orders Armenians to Leave Azerbaijan, Moves Troops to the BorderThe Salt Lake Tribune. September 4, 1993. pg. A1. The tension reached its peak, when Turkish heavy artillery shelled the Nakhchivan side of the Nakhchivan-Armenian border, from the Turkish border for two hours. Iran also reacted to Armenia's attacks by conducting military maneuvers along its border with Nakhchivan in a move widely interpreted as a warning to Armenia.
The Library of Congress However, Armenia did not launch any further attacks on Nakhchivan and the presence of Russia's military warded off any possibility that Turkey might play a military role in the conflict. After a period of political instability, the Parliament of Azerbaijan turned to Heydar Aliyev and invited him to return from exile in Nakhchivan to lead the country in 1993.
Recent times
Today, Nakhchivan retains its autonomy as the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, and is internationally recognized as a constituent part of Azerbaijan governed by its own elected legislative assembly.Richard Plunkett and Tom Masters. ''Lonely Planet: Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan'', p. 243. A new constitution for Nakhchivan was approved in a referendum on November 12, 1995. The constitution was adopted by the republic's assembly on April 28, 1998, and has been in force since January 8, 1999. However, the republic remains isolated, not only from the rest of Azerbaijan, but practically from the entireSouth Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
region. From 1995 until his resignation in December 2022, the region was ruled by Vasif Talibov, who is related by marriage to Azerbaijan's ruling family, the Aliyevs. He was known for his authoritarian and largely corrupt rule of the region. Most residents prefer to watch Turkish television as opposed to Nakhchivan television, which one Azerbaijani journalist criticised as "a propaganda vehicle for Talibov and the Aliyevs."
Economic hardships and energy shortages plague the area. There have been many cases of migrant workers
A migrant worker is a person who Human migration, migrates within a home country or outside it to pursue work. Migrant workers usually do not have an intention to stay permanently in the country or region in which they work.
Migrant workers ...
seeking jobs in neighboring Turkey. "Emigration rates to Turkey," one analyst said, "are so high that most of the residents of the Besler district in Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
are Nakhchivanis." In 2007, an agreement was struck with Iran to obtain more gas exports, and a new bridge on the Aras River between the two countries was inaugurated in October 2007; the Azerbaijani president, Ilham Aliyev and the first vice-president of Iran, Parviz Davoodi also attended the opening ceremony.
As part of the 2020 ceasefire agreement which ended the Second Nagorno-Karabakh War
The Second Nagorno-Karabakh War was an armed conflict in 2020 that took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh and the Armenian-occupied territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh, surrounding occupied territories. It was a major esca ...
, Armenia, in the context of all economic and transport connections in the region to be unblocked, agreed "to guarantee the security of transport connections between the western regions of the Republic of Azerbaijan and the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic in order to arrange unobstructed movement of persons, vehicles and cargo in both directions". As part of the agreement, these transport communications are to be patrolled by Border Service of the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation.
Administrative divisions
 Nakhchivan is subdivided into eight
Nakhchivan is subdivided into eight administrative divisions
Administrative divisions (also administrative units, administrative regions, subnational entities, or constituent states, as well as many similar generic terms) are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divi ...
. Seven of these are ''raion
A raion (also spelt rayon) is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet states. The term is used for both a type of subnational entity and a division of a city. The word is from the French (meaning 'honeycomb, department'), and is c ...
s''. The capital city (şəhər) of Nakhchivan City is treated separately.
Demographics
As of 2019 census, Nakhchivan's population was estimated to be 457,619. Most of the population areAzerbaijanis
Azerbaijanis (; , ), Azeris (, ), or Azerbaijani Turks (, ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group living mainly in the Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan region of northwestern Iran and the Azerbaijan, Republic of Azerbaijan. They are predomin ...
, who constituted 99.72% of the population in 2019, while Kurds
Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syri ...
constituted the largest minority with a 0.25% of the population.
The Kurds of Nakhchivan are mainly found in the districts of Sadarak and Teyvaz. The remaining Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
were expelled by Azerbaijani forces during the conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh as part of the forceful exchange of population between Armenia and Azerbaijan. According to a 1932 Soviet estimate, 85% of the area's population was rural, while only 15% was urban. This urban percentage increased to 18% by 1939 and 27% by 1959. As of 2011, 127,200 people of Nakhchivan's total population of 435,400 live in urban areas, making the urban percentage 29.2%.
Nakhchivan enjoys a high Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income i ...
; its socio-economic prowess far exceeds that of the neighbouring countries except for Turkey, as well as Azerbaijan itself. According to the report of Nakhchivan AR Committee of Statistics on June 30, 2014, for the end of 2013, some socio-economical data, including the following, are unveiled:
Making use of the Human Development Index calculation method according to the new UNHD 2014 method, the above values change into these:
Further, the value of the HDI becomes to
:
Were it a country, Nakhchivan would be ranked between Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
( 62nd) and Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
(63rd) for its HDI. Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
's HDI is 0.749 (75th), Turkey's 0.759 (69th), and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
's 0.747 (76th).
Geography
 Nakhchivan is a semi-desert region that is separated from the main portion of Azerbaijan by Armenia. The
Nakhchivan is a semi-desert region that is separated from the main portion of Azerbaijan by Armenia. The Zangezur Mountains
The Zangezur Mountains (, ) are a mountain range that defines the border between Armenia's southern provinces of Syunik, Vayots Dzor, and Azerbaijan's Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The Zangezur region has the second-largest tract of forests ...
make up its border with Armenia while the Aras River
The Aras is a transboundary river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, fin ...
defines its border with Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. The Araz reservoir located on that river supplies water for agricultural needs and the hydroelectric dam
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
generates power for both Azerbaijan and Iran.
Nakhchivan is arid
Aridity is the condition of geographical regions which make up approximately 43% of total global available land area, characterized by low annual precipitation, increased temperatures, and limited water availability.Perez-Aguilar, L. Y., Plata ...
and mountainous. Its highest peak is Mount Kapudzhukh and its most distinctive is İlandağ (Snake Mountain) , which is visible from Nakhchivan City. According to legend, the cleft in its summit was formed by the keel of Noah's Ark as the floodwaters abated.Plunkett and Masters. ''Lonely Planet'', p. 246. Qazangödağ is another major peak.
Both the absolute minimum temperature () and the absolute maximum temperature () were observed in Julfa and Ordubad
Ordubad is the second largest city of Azerbaijan's Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic and the capital of an eponymous district. Ordubad is a medieval city of the Caucasus and in its current capacity of a town was founded in the 18th century. The town ...
.
Economy
Industry
Nakhchivan's major industries include the mining of minerals such as salt,molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
, and lead. Dryland farming
Drylands are defined by a scarcity of water. Drylands are zones where precipitation is balanced by evaporation from surfaces and by transpiration by plants (evapotranspiration). The United Nations Environment Program defines drylands as tropical ...
, developed during the Soviet years, has allowed the region to expand into the growing of wheat (mostly cultivated on the plains of the Aras River
The Aras is a transboundary river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, fin ...
), barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
, cotton, tobacco, orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit tree, fruit- or nut (fruit), nut-producing trees that are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also so ...
fruits, mulberries, and grapes for producing wine. Other industries include cotton ginning/cleaning, silk spinning, fruit canning, meatpacking, and, in the drier regions, sheep farming
Sheep farming or sheep husbandry is the raising and breeding of domestic sheep. It is a branch of animal husbandry. Sheep are raised principally for their meat (lamb and mutton), milk (sheep's milk), and fiber (wool). They also yield sheepskin ...
. Processing of minerals, salt, radio engineering
Broadcast engineering or radio engineering is the field of electrical engineering, and now to some extent computer engineering and information technology, which deals with radio and television broadcasting. Audio engineering and RF engineering ...
, farm ginning, preserving, silk products, meat, and dairy, bottling of mineral water
Mineral water is water from a mineral spring that contains various minerals, such as salts and sulfur compounds. It is usually still, but may be sparkling ( carbonated/ effervescent).
Traditionally, mineral waters were used or consumed at t ...
s, clothing, and furniture are the principal branches of Nakhchivan's industry. The Nakhchivan Automobile Plant (, abbr. NAZ), is a prominent automobile manufacturer in the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The economy suffered a severe blow in 1988 with the loss of access to both raw material
A raw material, also known as a feedstock, unprocessed material, or primary commodity, is a basic material that is used to produce goods, finished goods, energy, or intermediate materials/Intermediate goods that are feedstock for future finished ...
s and markets, due to the First Nagorno-Karabakh War
The First Nagorno-Karabakh War was an ethnic conflict, ethnic and territorial conflict that took place from February 1988 to May 1994, in the enclave of Nagorno-Karabakh in southwestern Azerbaijan, between the majority ethnic Armenians of Nag ...
. Although new markets are emerging in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and Turkey, this isolation still persists to this day, impairing development. The economy of Nakhchivan is based on agriculture, mining, and food processing
Food processing is the transformation of agricultural products into food, or of one form of food into other forms. Food processing takes many forms, from grinding grain into raw flour, home cooking, and complex industrial methods used in the mak ...
, however, 75% of the republic's budget is supplied by the central government in Baku
Baku (, ; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Azerbaijan, largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and in the Caucasus region. Baku is below sea level, which makes it the List of capital ci ...
.
The Republic is rich in minerals. Nakhchivan possesses deposits of marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
, lime, and gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate Hydrate, dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, drywall and blackboard or sidewalk ...
. The deposits of the rock salt
Halite ( ), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pi ...
are exhausted in Nehram, Nakhchivan, and Sustin. The important molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
mines are currently closed as a consequence of the exclave's isolation. There are a lot of mineral spring
Mineral springs are naturally occurring springs that produce hard water, water that contains dissolved minerals. Salts, sulfur compounds, and gases are among the substances that can be dissolved in the spring water during its passage un ...
s such as Badamli, Sirab, Nagajir, Kiziljir where water contains arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
. About 90% of the agricultural land is now in private hands. However, agriculture has become a poorly capitalized, backyard
A backyard, or back yard (known in the United Kingdom as a back garden or just garden), is a Yard (land), yard at the back of a house, common in suburban developments in the Western world.
It is typically a residential garden located at the ...
activity. Production has dropped sharply and large-scale commercial agriculture has declined. Over two-thirds of the land are rocky slopes and desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
s, therefore the area of arable lands is quite limited. The main crops – cotton and tobacco – are cultivated in the PriAraz plain, near Sharur and Nakhchivan City. Three-quarters of the grain production, especially winter wheat
Winter wheat (usually ''Common wheat, Triticum aestivum'') are strains of wheat that are planted in the autumn to germinate and develop into young plants that remain in the vegetative phase during the winter and resume growth in early spring. C ...
is concentrated on the irrigated lands of the Sharur plain and in the basin of the Nakhchivan river. Vine growing in Nakhchivan has an ancient tradition, in the Araz valley and foothills. Very hot summers and long warm autumns make it possible to grow such highly saccharine grapes as bayan-shiraz, tebrizi, shiraz
Shiraz (; ) is the List of largest cities of Iran, fifth-most-populous city of Iran and the capital of Fars province, which has been historically known as Pars (Sasanian province), Pars () and Persis. As of the 2016 national census, the popu ...
. Wines such as "Nakhchivan" "Shahbuz", " Abrakunis", at " Aznaburk" are of reasonable quality and very popular. Fruit production is quite important, mainly of quince
The quince (; ''Cydonia oblonga'') is the sole member of the genus ''Cydonia'' in the Malinae subtribe (which contains apples, pears, and other fruits) of the Rosaceae family. It is a deciduous tree that bears hard, aromatic bright golden-yel ...
, pear, peach, apricot, fig, almonds, and pomegranate
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punica, Punicoideae, that grows between tall. Rich in symbolic and mythological associations in many cultures, it is thought to have o ...
. Cattle ranching is another traditional branch of Nakhchivan farming. Due to the dry climate, pastures in Nakhchivan are unproductive, therefore sheep breeding prevails over other livestock production. Winter pastures stretch on the PriAraz plain, on the foothills and mountainsides to the altitude of . But the summer pastures go up on the high-mountain area to an altitude of . The most widespread sheep variety is "balbas". These sheep are distinguished by their productivity and snow-white silky wool which is widely used in the manufacture of carpets. Horned and small cattle are bred everywhere, especially in the environs of Sharur and Nakhchivan. Buffaloes are also bred here.
Although intentions to facilitate tourism have been declared by the government, it is still at best incipient. Until 1997 tourists needed special permission to visit, which has now been abolished, making travel easier. Facilities are very basic and heating fuel is hard to find in the winter, but the arid mountains bordering Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
and Iran are magnificent. In terms of services, Nakhchivan offers very basic facilities and lacks heating fuel during the winter.
In 2007 the Poldasht-Shah Takhti Bridge, which connects Poldasht, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, and Shah Takhti in Nakhchivan, was completed, allowing residents of the republic to access Azerbaijan proper via Iran without having to cross Armenian territory.
International issues
Destruction of Armenian cultural monuments
The number of named Armenian churches known to have existed in the Nakhchivan region is over 280. As early as 1648, French traveller Alexandre de Rhodes reported seeing more than ten thousand Armenian tombstones made of marble in Julfa. The number of ecclesiastical monuments still standing in Nakhchivan in the 1980s is estimated to be between 59 and 100. The author and journalist Sylvain Besson believe them to have all been subsequently destroyed as part of a campaign by the Government of Azerbaijan to erase all traces of Armenian culture on its soil. When the 14th-century church of St. Stephanos at Abrakunis was visited in 2005, it was found to have been recently destroyed, with its site reduced to a few bricks sticking out of loose, bare earth. Similar complete destruction had happened to the 16th century St. Hakop-Hayrapet church in Shurut. The Armenian churches in Norashen, Kırna and Gah that were standing in the 1980s had also vanished. The most publicised case of mass destruction concerns gravestones at a medieval cemetery in Julfa, with photographic, video and satellite evidence supporting the charges. In April 2006 British ''The Times'' wrote about the destruction of the cemetery in the following way:A Medieval cemetery regarded as one of the wonders of the Caucasus has been erased from the Earth in an act of cultural vandalism likened to the Taleban blowing up the Bamiyan Buddhas in Afghanistan in 2001. The Jugha cemetery was a unique collection of several thousand carved stone crosses on Azerbaijan's southern border with Iran. But after 18 years of conflict between Azerbaijan and its western neighbour, Armenia, it has been confirmed that the cemetery has vanished."Armenians have long sounded the alarm that the Azerbaijanis intend to eliminate all evidence of Armenian presence in Nakhchivan and to this end, have been carrying out massive and irreversible destruction of Armenian cultural traces. "The irony is that this destruction has taken place not during a time of war but at a time of peace," Armenian Foreign Minister Vartan Oskanian told The Times. Azerbaijan has consistently denied these accusations. For example, according to the Azerbaijani ambassador to the US, Hafiz Pashayev, the videos and photographs "show some unknown people destroying mid-size stones", and "it is not clear of what nationality those people are", and the reports are Armenian propaganda designed to divert attention from what he claimed was a "state policy (by Armenia) to destroy the historical and cultural monuments in the occupied Azeri territories". A number of international organizations have confirmed the complete destruction of the cemetery. The
Institute for War and Peace Reporting
The Institute for War & Peace Reporting (IWPR) is an independent nonprofit organization that trains and provide publishing opportunities for professional and citizen journalists. IWPR is registered in the UK as a charity (charity reg. no: 1027201, ...
reported on April 19, 2006, that "there is nothing left of the celebrated stone crosses of Jugha."
According to the International Council on Monuments and Sites
The International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS; ) is a professional association that works for the conservation and protection of cultural heritage places around the world. Now headquartered in Charenton-le-Pont, France, ICOMOS was fou ...
(Icomos), the Azerbaijan government removed 800 khachkars in 1998. Though the destruction was halted following protests from UNESCO, it resumed four years later. By January 2003 "the 1,500-year-old cemetery had completely been flattened" according to Icomos. On December 8, 2010, the American Association for the Advancement of Science
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is a United States–based international nonprofit with the stated mission of promoting cooperation among scientists, defending scientific freedom, encouraging scientific responsib ...
released a report entitled "Satellite Images Show Disappearance of Armenian Artifacts in Azerbaijan". The report contained the analysis of high resolution satellite images of the Julfa cemetery, which verified the destruction of the khachkars.
The European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
has formally called on Azerbaijan to stop the demolition as a breach of the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Convention. According to its resolution regarding cultural monuments in the South Caucasus, the European Parliament "condemns strongly the destruction of the Julfa cemetery as well as the destruction of all sites of historical importance that has taken place on Armenian or Azerbaijani territory, and condemns any such action that seeks to destroy cultural heritage." In 2006, Azerbaijan barred a Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (PACE) mission from inspecting and examining the ancient burial site, stating that it would only accept a delegation if it also visited Armenian-occupied territory. "We think that if a comprehensive approach is taken to the problems that have been raised," said Azerbaijani foreign ministry spokesman Tahir Tagizade, "it will be possible to study Christian monuments on the territory of Azerbaijan, including in the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic."
A renewed attempt was planned by PACE inspectors for August 29 – September 6, 2007, led by British MP Edward O'Hara. As well as Nakhchivan, the delegation would visit Baku, Yerevan, Tbilisi, and Nagorno Karabakh. The inspectors planned to visit Nagorno Karabakh via Armenia; however, on August 28, the head of the Azerbaijani delegation to PACE released a demand that the inspectors must enter Nagorno Karabakh via Azerbaijan. On August 29, PACE Secretary-General Mateo Sorinas announced that the visit had to be cancelled because of the difficulty in accessing Nagorno Karabakh using the route required by Azerbaijan. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Armenia issued a statement saying that Azerbaijan had stopped the visit "due solely to their intent to veil the demolition of Armenian monuments in Nakhijevan".
In 2022, the Cornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson W ...
-led monitoring group Caucasus Heritage Watch released a report detailing the "complete destruction of Armenian cultural heritage" in Nakhchivan starting the 1990s. According the report, out of 110 medieval and early modern Armenian monasteries, churches and cemeteries identified from archival sources, 108 were deliberately and systematically destroyed between 1997 and 2011. In some cases, such as the Saint Thomas Monastery in Yukhari Aylis (Agulis), mosques or other civic buildings were built on the site of the destroyed buildings.
Recognition of the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
In the late 1990s the Supreme Assembly issued a non-binding declaration recognising thesovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
of the self-proclaimed
Self-proclaimed describes a legal title that is recognized by the declaring person but not necessarily by any recognized legal authority. It can be the status of a noble title or the status of a nation. The term is used informally for anyone declar ...
Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus, officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC), is a '' de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. It is recognised only by Turkey, and its territory is considered by all o ...
(TRNC) and calling upon Azerbaijan to do so. While sympathetic to the TRNC, Azerbaijan has not followed suit because doing so could prompt the Republic of Cyprus to recognise the self-proclaimed Nagorno-Karabakh Republic
Artsakh ( ), officially the Republic of Artsakh or the Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh ( ), was a list of states with limited recognition, breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory was internationally recognised as part of Azerbai ...
. Close relations between Nakhchivan and Turkey probably initiated this recognition.
Culture
Nakhchivan is one of the cultural centers of Azerbaijan. In 1923, a musical subgroup was organized at the State Drama Theater (renamed the Nakhchivan Music and Drama Theater in 1965). The Aras Song and Dance Ensemble (established in 1959) is another famous group. Dramatic performances staged by an amateur dance troupe were held in Nakhchivan in the late 19th century. Theatrical art also greatly contributed to Nakhchivan's culture. The creative work ofJalil Mammadguluzadeh
Jalil Huseyngulu oghlu Mammadguluzadeh (, ; 22 February 1869 – 4 January 1932), was an Azerbaijani people, Azerbaijani List of satirists and satires, satirist and writer. He was the founder of Molla Nasraddin (magazine), ''Molla Nasraddin'', a ...
, Huseyn Javid, and Huseyn Arablinski (the first Azerbaijani theatre director) stemmed from Nakhchivan. The region has also produced noteworthy Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
artists, too, such as Soviet actress Hasmik Agopyan. Nakhchivan has also at times been mentioned in works of literature. World-renowned Soviet composer Aram Khatchaturian, the Armenian Hovnatanian
The Hovnatanyan family (, ''Hovnat'anyanner'') was a prominent Armenian family of painters. They include five generations from 17th to 19th centuries. Hovnatanyans are originally from the village of Shorot, Yernjak district in Nakhichevan (now ...
painter family, as well as the actor Yervand Manaryan, have shaped the cultural wealth of Nakchivan, too. Nizami, the Persian poet, once wrote:
::که تا جایگه یافتی نخچوان
::''Oh Nakhchivan, respect you've attained,''
::بدین شاه شد بخت پیرت جوان
::''With this King in luck you'll remain.''
Garabaghlar Mausoleum
The Karabakhlar Mausoleum () is a mausoleum located in Qarabağlar, Nakhchivan, Garabaghlar village of Kangarli District of Azerbaijan, about 30 kilometers far from the north-western part of Nakhichivan Autonomous Republic, Nakhchivan.
History
T ...
File:Palace of Nakhchivan Khans.jpg, Palace of Nakhchivan Khans
File:Ordubad cümə məscidi ümumi görünüş.jpg, Juma Mosque, Ordubad
File:Mömünəxatun türbəsi 2018.jpg, Momine Khatun Mausoleum
File:Nakhichevan Mausoleum.jpg, Yusif ibn Kuseyir Mausoleum
File:Gülüstan türbəsi bərpadan sonra.jpg, Juma Mosque, Ordubad
File:Şeyx Xorasan türbəsin.jpg, Khanegah tomb
Media
Radio broadcasting in Nakhchivan began on 1 April 1932 under Soviet rule. Television broadcasting began later on 12 March 1963, with the launch of Nakhchivan TV. State-owned radio and television broadcasting in the autonomous republic is managed by the State Committee for Television and Radio Broadcasting of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The Nukhchikhan Information Agency was founded in 2018. Under the Ministry of Communications and New Technologies, the Voice of Nakhchivan radio network was founded in 2001 and the Kanal 35 television station was founded in 2004. Both ceased operations in May 2023.Archaeology
The very early Kura-Araxes culture flourished in Nakhchivan before spreading to many other areas, as far as Palestine. This region reveals the genesis and chronology of thisChalcolithic
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in di ...
and Early Bronze Age culture. Kültəpə
Kültəpə (also rendered as ''Kultepe, Aşağı Gültəpə, Gültəpə, Kyul'tepe, Kul'tepe'', and ''Kultepe-1'') is a settlement dating from the Neolithic, a village and municipality in the Babek District of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, ...
is an important early Chalcolithic site in Nakhchivan. Another such site is Makhta Kultepe
Maxta (also, ''Makhta'', ''Makhta Kultepe'') is a village and municipality in the Sharur District of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, Azerbaijan. It is located 7 km in the north-west from the district center, on the plain. Its population is ...
. Recent excavations at Ovcular Tepesi allow the dating of the initial stage of formation of Kura-Araxes culture to 4200–3400 BC.
The Naxçivan Archaeological Project is the first-ever joint American-Azerbaijani program of surveys and excavations, that was active since 2006. In 2010–11, they have excavated the large Iron Age fortress of Oğlanqala.
In Nakhchivan, there are also numerous archaeological monuments of the early Iron Age, and they shed a lot of light on the cultural, archaeological and agricultural developments of that era. There are important sites such as Ilikligaya, Irinchoy, and the Sanctuary of Iydali Piri in Kangarli region.– OpEd – Eurasia Review 2016
Notable people

Political leaders
*Heydar Aliyev
Heydar Alirza oghlu Aliyev (10 May 1923 – 12 December 2003) was an Azerbaijani politician who was a Soviet party boss in the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic from 1969 to 1982, and the third president of Azerbaijan from October 1993 to ...
, former President of Azerbaijan
The president of the Republic of Azerbaijan is the head of state of the Azerbaijan, Republic of Azerbaijan. The Constitution of Azerbaijan, Constitution states that the president is the embodiment of Executive (government), executive power, co ...
(1993–2003).
* Abulfaz Elchibey, former President of Azerbaijan (1992–1993).
* Rasul Guliyev, former speaker of the National Assembly of Azerbaijan (1993–1996) and opposition leader.
* Christapor Mikaelian, founding member of the Armenian Revolutionary Federation
The Armenian Revolutionary Federation (, abbr. ARF (ՀՅԴ) or ARF-D), also known as Dashnaktsutyun (Armenians, Armenian: Դաշնակցություն, Literal translation, lit. "Federation"), is an Armenian nationalism, Armenian nationalist a ...
.
* Stepan Sapah-Gulian, leader of the Armenian Social Democrat Hunchakian Party (19th–20th century).
* Garegin Nzhdeh, famous Armenian revolutionary, military leader and political thinker.
* Vasif Talibov, chairman of the Supreme Assembly of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic from 1995 to 2022.
Religious leaders
* Alexander Jughaetsi (Alexander I of Jugha),Catholicos of All Armenians
The Catholicos of All Armenians () is the chief bishop and spiritual leader of Armenia's national church, the Armenian Apostolic Church, and the worldwide Armenian diaspora. The Armenian Catholicos (plural Catholicoi) is also known as the Armenian ...
(1706–1714).
Military leaders
* Abdurahman Fatalibeyli, Soviet army major who defected to the German forces during World War II. * Ehsan Khan Nakhchivanski, Russian military general. * Huseyn Khan Nakhchivanski, Russiancavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
general and the only Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
to serve as General-Adjutant of the Russian Tsar.
* Ismail Khan Nakhchivanski, Russian military general.
* Kelbali Khan Nakhchivanski, Russian military general.
* Jamshid Khan Nakhchivanski, Soviet and Azerbaijani military general.
* Yusif Mirzayev, National Hero of Azerbaijan.
* Maharram Seyidov, National Hero of Azerbaijan.
* Kerim Kerimov
Lieutenant General Kerim Abbasali oghlu Kerimov (, ; November 14, 1917March 29, 2003) was a Soviet and Russian engineer of Azerbaijani ethnicity and a general in Soviet Army, who is regarded as one of the key scientists and founders in the Sovi ...
, National Hero of Azerbaijan.
* Sayavush Hasanov, National Hero of Azerbaijan.
* Mirasgar Seyidov, National Hero of Azerbaijan.
* Ali Mammadov, National Hero of Azerbaijan.
* Ibrahim Mammadov, National Hero of Azerbaijan.
* Amiraslan Aliyev, National Hero of Azerbaijan.
Writers and poets
* Huseyn Javid Rasizade, poet and playwright. *Jalil Mammadguluzadeh
Jalil Huseyngulu oghlu Mammadguluzadeh (, ; 22 February 1869 – 4 January 1932), was an Azerbaijani people, Azerbaijani List of satirists and satires, satirist and writer. He was the founder of Molla Nasraddin (magazine), ''Molla Nasraddin'', a ...
, writer and satirist.
* Mammed Said Ordubadi, writer.
* Mammad Araz, poet.
Scientists
* Alec (Alirza) Rasizade, an American professor of history and political science, the author of the Rasizade's algorithm. * Ruben Orbeli, Soviet archaeologist, historian and jurist, who was renowned as the founder of Soviet underwater archaeology.Others
* Bahruz Kangarli, Azerbaijani painter. * Haji Aliyev, Wrestling, World and European champion. * Vladimir Makogonov, chessInternational Master
FIDE titles are awarded by the international chess governing body FIDE (''Fédération Internationale des Échecs'') for outstanding performance. The highest such title is Grandmaster (GM). Titles generally require a combination of Elo rating and ...
and Grandmaster.
* Ajami Nakhchivani, architect and founder of the Nakhchivan school of architecture.
* Gaik Ovakimian, Soviet Armenian spy.
* Ibrahim Safi, Turkish artist.
* Natavan Gasimova, volleyball player
* Rza Tahmasib, Azerbaijani film director.
Gallery
Ordubad
Ordubad is the second largest city of Azerbaijan's Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic and the capital of an eponymous district. Ordubad is a medieval city of the Caucasus and in its current capacity of a town was founded in the 18th century. The town ...
with a range of high mountains in neighboring Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
in the distance
Image:Nakhichevan06.jpg, Houses in Ordubad photographed near the east bank of Ordubad-chay (also known as the Dubendi stream)
Image:Nakhichevan07.jpg, Narrow streets in Ordubad
Image:Nakhichevan08.jpg, A mosque in a quarter of Ordubad
Image:Jolfa-Aras2.jpg, Aras River
The Aras is a transboundary river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, fin ...
on the Iranian border near Julfa
Image:Nakhichevan09.jpg, Mountainous terrain of Nakhchivan
Image:Julfa-khachkars.jpg, Armenian khachkar
A ''khachkar'' (also spelled as ''khatchkar'') or Armenian cross-stone (, , խաչ ''xačʿ'' "cross" + քար ''kʿar'' "stone") is a carved, memorial stele bearing a cross, and often with additional motifs such as rosette (design), rosettes ...
cemetery at Julfa
See also
* List of Chairmen of the Supreme Majlis of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic * Nakhchivan Memorial Museum * Nakhchivan culture * Nakhchivan Garrison, theAzerbaijani Armed Forces
The Azerbaijani Armed Forces () is the military of the Azerbaijan, Republic of Azerbaijan. It was re-established according to the country's Law of the Armed Forces on 9 October 1991. The original Azerbaijan Democratic Republic's armed forces were ...
stationed in Nakhchivan (also referred to as the Nakhchivan Army)
* Thamanin in southeast Turkey
References
;Notes ;ReferencesSources
*Further reading
*External links
Official website of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
Nakhchivan Guide
Silent Erasure
- A Satellite Investigation of the Destruction of Armenian Cultural Heritage in Nakhchivan, Azerbaijan {{coord, 39, 20, N, 45, 30, E, region:AZ_type:adm1st, display=title Subdivisions of Azerbaijan Autonomous republics Enclaves and exclaves States and territories established in 1990 Armenia–Azerbaijan border Azerbaijan–Turkey border Azerbaijan–Iran border Mount Ararat Countries and territories where Azerbaijani is an official language