Nablus Military Police Base on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nablus ( ; , ) is a
''Anthropology and Global Counterinsurgency,''
pp.125-136 p.126. Nablus is under the administration of the
 ('new city of the emperor
('new city of the emperor  Conflict among the Christian population of Neapolis emerged in 451. By this time, Neapolis was within the
Conflict among the Christian population of Neapolis emerged in 451. By this time, Neapolis was within the
 Neapolis, along with most of Palestine, was conquered by the Muslims under
Neapolis, along with most of Palestine, was conquered by the Muslims under
p. 55
He also noted that it was nicknamed "Little
– Nablus, At the Foot of the Holy Mountain
Med Cooperation, p.6. At the time, the linen produced in Nablus was well known throughout the
 Crusader rule came to an end in 1187, when the
Crusader rule came to an end in 1187, when the
511
��515 After its recapture by the Muslims, the Great Mosque of Nablus, which had become a church under Crusader rule, was restored as a mosque by the Ayyubids, who also built a
 In the mid-18th century,
In the mid-18th century,
 In 1831–32 Khedivate Egypt, then led by
In 1831–32 Khedivate Egypt, then led by
 Between 19 September and 25 September 1918, in the last months of the
Between 19 September and 25 September 1918, in the last months of the
 The 1967
The 1967
 Jurisdiction over the city was handed over to the
Jurisdiction over the city was handed over to the
''Building a Palestinian State: The Incomplete Revolution,''
Indiana University Press, 1997 p.57. and, located between two mountains, was closed off at both ends of the valley by Israeli checkpoints. For several years, movements in and out of the city were highly restricted. Nablus produced more List of Palestinian suicide attacks, suicide bombers than any other city during the Second Intifada. The city and the Palestinian refugee camps, refugee camps of Balata and Askar constituted the center of "knowhow" for the production and operation of the rockets in the West Bank. According to the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, 522 residents of Nablus and surrounding refugee camps, including civilians, were killed and 3,104 injured during IDF military operations from 2000 to 2005. In April 2002, following the Passover massacre—an attack by Palestinian militants that killed 30 Israeli civilians attending a Passover Seder, seder dinner at the Park Hotel in Netanya—Israel launched Operation Defensive Shield, a major Battle of Nablus, military operation targeting in particular Nablus and Jenin. At least 80 Palestinians were killed in Nablus during the operation and several houses were destroyed or severely damaged. The operation also resulted in severe damage to the historic core of the city, with 64 heritage buildings being heavily damaged or destroyed. IDF forces reentered Nablus during Operation Determined Path in June 2002, remaining inside the city until the end of September. Over those three months, there had been more than 70 days of full 24-hour curfews. According to Gush Shalom, IDF bulldozers damaged the al-Khadra Mosque, the Great Mosque, the al-Satoon Mosque and the Greek Orthodox Church in 2002. Some 60 houses were destroyed, and parts of the stone-paving in the old city were damaged. The al-Shifa ''Turkish bath, hammam'' was hit by three rockets from Apache helicopters. The eastern entrance of the Khan al-Wikala (old market) and three soap factories were destroyed in F-16 Fighting Falcon, F-16 bombings. The cost of the damage was estimated at $80 million US. In August 2016, the Old City of Nablus became a site of August 2016 Nablus clashes, fierce clashes between a militant group vs Palestinian police. On 18 August, two Palestinian Civil Police Force, Palestinian Police servicemen were killed in the city. Shortly after the raid of police on the suspected areas in the Old City deteriorated into a gun battle, in which three armed militia men were killed, including one killed by beating following his arrest. The person beaten to death was the suspected “mastermind” behind the August 18 shooting - Ahmed Izz Halaweh, a senior member of the armed wing of the Fatah movement the al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades. His death was branded by the UN and Palestinian factions as a part of “extrajudicial executions.” A widespread manhunt for multiple gunmen was initiated by the police as a result, concluding with the arrest of one suspect Salah al-Kurdi on 25 August.
 Nablus lies in a strategic position at a junction between two ancient commercial roads; one linking the Sharon plain, Sharon coastal plain to the Jordan Valley (Middle East), Jordan valley, the other linking Nablus to the
Nablus lies in a strategic position at a junction between two ancient commercial roads; one linking the Sharon plain, Sharon coastal plain to the Jordan Valley (Middle East), Jordan valley, the other linking Nablus to the
– Nablus, At the Foot of the Holy Mountain
Med Cooperation, p.17. There are six (
Nablus Website.
Mohammed Assadi, July 18, 2009, Malaysia Star. Traditional industries such as the production of soap, olive oil, and Palestinian handicrafts continue to operate in Nablus. Other industries include furniture production, tile production, stone quarrying, textile manufacturing and leather tanning. The city is widely known for sweets like kunafah, olive oil, soap and ice-cream. The Vegetable Oil Industry Co. is a Nablus factory that produces olive oil, and vegetable butter which is exported to
'Palestinian ice cream's big comeback,'
at Haaretz, 3 August 2012.'They buy the ingredients mainly from Israeli suppliers .' Before 2000, 13.4% of Nablus' residents worked in Israel, with the figure dropping to 4.7% in 2004. The city's manufacturing sector made up 15.7% of the economy in 2004, a drop from 21% in 2000. Since 2000, most of the workforce has been employed in agriculture and local trade. In the wake of the Intifada, unemployment rates rose from 14.2% in 1997 to 60% in 2004. According to an OCHA report in 2008, one of the reasons for the high unemployment was a ring of checkpoints around the city, leading to the relocation of many businesses. Since the removal of the Huwara, Hawara roadblock, the casbah has become a vibrant marketplace. Nablus is home to the Palestine Securities Exchange (PSE) and the al-Quds Financial Index, housed in the al-Qasr building in the Rafidia suburb of the city. The PSE's first trading session took place on 19 February 1997. In 2007, the capitalization of the PSE topped 3.5 million Jordanian dinars.
an
Hospitals
Nablus Municipality Guides. In addition to that, in 2001, Nablus Speciality Hospital was built, in which it is specialized in open heart surgery, angiograms and angioplasty, angioplasties. Rafidia Surgical Hospital is located in the city.
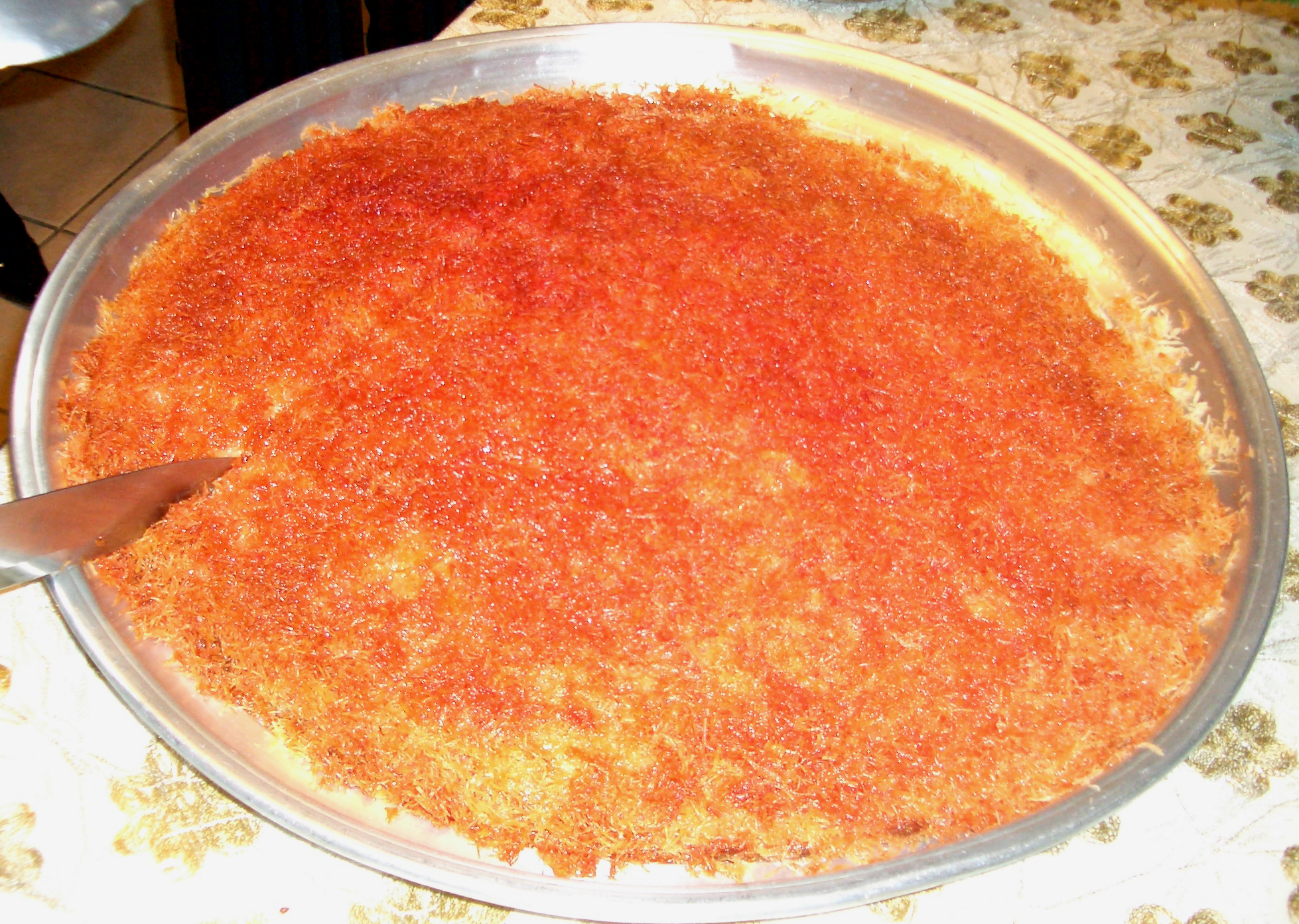 Nablus is one of the Palestinian cities that sustained elite classes, fostering the development of a culture of "high cuisine", such as that of
Nablus is one of the Palestinian cities that sustained elite classes, fostering the development of a culture of "high cuisine", such as that of

 There are three cultural centers in Nablus. The Child Cultural Center (CCC), founded in 1998 and built in a renovated historic building, operates an art and drawing workshop, a stage for play performances, a music room, a children's library and a multimedia lab. The Children Happiness Center (CHC) was also established in 1998. Its main activities include promoting Palestinian culture through social events, ''dabke'' classes and field trips. In addition to national culture, the CHC has a football (soccer), football and chess team. The Nablus municipal government established its own cultural center in 2003, called the Nablus Municipality Cultural Center (NMCC) aimed at establishing and developing educational facilities.
There are three cultural centers in Nablus. The Child Cultural Center (CCC), founded in 1998 and built in a renovated historic building, operates an art and drawing workshop, a stage for play performances, a music room, a children's library and a multimedia lab. The Children Happiness Center (CHC) was also established in 1998. Its main activities include promoting Palestinian culture through social events, ''dabke'' classes and field trips. In addition to national culture, the CHC has a football (soccer), football and chess team. The Nablus municipal government established its own cultural center in 2003, called the Nablus Municipality Cultural Center (NMCC) aimed at establishing and developing educational facilities.
 In 1997, 99.7% of Nablus' 18,003 households were connected to electricity through a public network. Prior to its establishment in 1957, electricity came from private generators. Today, the majority of the inhabitants of 18 nearby towns, in addition to the city's inhabitants, are connected to the Nablus network.
The majority of households are connected to a public sewage system (93%), with the remaining 7% connected through cesspits.Occupied Housing Units by Locality and Connection to Electricity Network in Housing Unit
In 1997, 99.7% of Nablus' 18,003 households were connected to electricity through a public network. Prior to its establishment in 1957, electricity came from private generators. Today, the majority of the inhabitants of 18 nearby towns, in addition to the city's inhabitants, are connected to the Nablus network.
The majority of households are connected to a public sewage system (93%), with the remaining 7% connected through cesspits.Occupied Housing Units by Locality and Connection to Electricity Network in Housing Unit
Occupied Housing Units by Locality and Connection to Sewage System in Housing Unit
Occupied Housing Units by Locality and Connection to Water Network in Housing Unit
Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics. Statistic from a 1997 census. The sewage system, established n the early 1950s, also connects the refugee camps of Balata, Askar and Ein Beit al-Ma'. Pipe water is provided for 100% of the city's households, primarily through a public network (99.3%), but some residents receive water through a private system (0.7%). The water network was established in 1932 by the British authorities and is fed by water from four nearby wells: Deir Sharaf, Far'a, al-Badan and Audala.
 The Nablus football (soccer), football stadium has a capacity of 8,000. The stadium is home to the city's football club al-Ittihad (Nablus), al-Ittihad, which is in the main league of the Palestinian Territories. The club participated in the Middle East Mediterranean Scholar Athlete Games in 2000.
The Nablus football (soccer), football stadium has a capacity of 8,000. The stadium is home to the city's football club al-Ittihad (Nablus), al-Ittihad, which is in the main league of the Palestinian Territories. The club participated in the Middle East Mediterranean Scholar Athlete Games in 2000.
After years of contention, Boulder makes Nablus a sister city
23.12 2016; Times of Israel
Welcome To The City of Nablus
Nablus City
Welcome to Palestine
A site explaining the reasons for the devastated Palestinian economy
Nablus the Culture, reviving cultural life in Nablus
Nablus after Five Years of Conflict
December 2005 report by Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, OCHA (PDF).
Archaeological Remains Found in Nablus
Picture showing Nablus from east (Panorama)
Picture showing east region of Nablus (Panorama) – The picture taken from Askar
Bahjat Sabri, "Urban Aspects in the City of Nablus in the First Half of the Nineteenth Century" ''An-Najah University Journal for Research - Humanities'', Volume 6 (1992)
{{Authority control Nablus, Cities in the West Bank History of Palestine (region) Historic Jewish communities Levant Canaanite cities Municipalities of Palestine Palestinian Christian communities
Palestinian
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenous p ...
city in the West Bank
The West Bank is located on the western bank of the Jordan River and is the larger of the two Palestinian territories (the other being the Gaza Strip) that make up the State of Palestine. A landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, located approximately north of Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, with a population of 156,906. Located between Mount Ebal
Mount Ebal (; ) is one of the two mountains near the city of Nablus in the West Bank (Bible, biblical ''Shechem''), and forms the northern side of the valley in which Nablus is situated, the southern side being formed by Mount Gerizim. The mount ...
and Mount Gerizim
Mount Gerizim ( ; ; ; , or ) is one of two mountains in the immediate vicinity of the State of Palestine, Palestinian city of Nablus and the biblical city of Shechem. It forms the southern side of the valley in which Nablus is situated, the nor ...
, it is the capital of the Nablus Governorate
The Nablus Governorate () is an administrative district of Palestine located in the Central Highlands of the West Bank, 53 km north of Jerusalem. It covers the area around the city of Nablus which serves as the ''muhfaza'' (seat) of the go ...
and a commercial and cultural centre of the State of Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
, home to An-Najah National University
An-Najah National University () is a non-governmental public university governed by a board of trustees in Nablus, West Bank, Palestine. The university has 22,000 students and 300 professors in 19 faculties. It is the largest university in the ...
, one of the largest Palestinian institutions of higher learning, and the Palestine Stock Exchange.Amahl Bishara, ‘Weapons, Passports and News: Palestinian Perceptions of U.S. Power as a Mediator of War,’ in John D. Kelly, Beatrice Jauregui, Sean T. Mitchell, Jeremy Walton (eds.''Anthropology and Global Counterinsurgency,''
pp.125-136 p.126. Nablus is under the administration of the
Palestinian National Authority
The Palestinian Authority (PA), officially known as the Palestinian National Authority (PNA), is the Fatah-controlled government body that exercises partial civil control over the Palestinian enclaves in the Israeli-occupied West Bank as a c ...
(PNA).
The modern name of the city can be traced back to the Roman period
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, when it was named by Roman emperor Vespasian
Vespasian (; ; 17 November AD 9 – 23 June 79) was Roman emperor from 69 to 79. The last emperor to reign in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolida ...
in 72 CE. During the Byzantine period
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, conflict between the city's Samaritan
Samaritans (; ; ; ), are an ethnoreligious group originating from the Hebrews and Israelites of the ancient Near East. They are indigenous to Samaria, a historical region of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah that ...
and newer Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
inhabitants peaked in the Samaritan revolts that were eventually suppressed by the Byzantines by 573, which greatly dwindled the Samaritan population of the city. Following the Muslim conquest of the Levant
The Muslim conquest of the Levant (; ), or Arab conquest of Syria, was a 634–638 CE invasion of Byzantine Syria by the Rashidun Caliphate. A part of the wider Arab–Byzantine wars, the Levant was brought under Arab Muslim rule and develope ...
in the 7th century, the city was given its present-day Arabic name of . After the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the Middle Ages. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Muslim conquest ...
, the Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding ...
drafted the laws of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem, also known as the Crusader Kingdom, was one of the Crusader states established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1 ...
in the Council of Nablus
The Council of Nablus was a council of ecclesiastic and secular lords in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem, held on January 16, 1120.
History
The council was convened at Nablus by Warmund, Patriarch of Jerusalem, and King Baldwin II of Jerusalem. ...
, and its Christian, Samaritan, and Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
inhabitants prospered. The city then came under the control of the Ayyubids
The Ayyubid dynasty (), also known as the Ayyubid Sultanate, was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurdish ori ...
and the Mamluk Sultanate
The Mamluk Sultanate (), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz from the mid-13th to early 16th centuries, with Cairo as its capital. It was ruled by a military caste of mamluks ...
. Under the Ottoman Turk
The Ottoman Turks () were a Turkic ethnic group in Anatolia. Originally from Central Asia, they migrated to Anatolia in the 13th century and founded the Ottoman Empire, in which they remained socio-politically dominant for the entirety of the ...
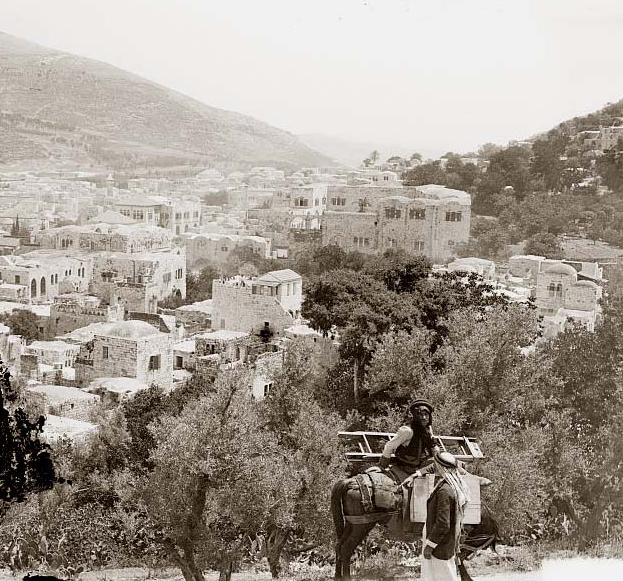
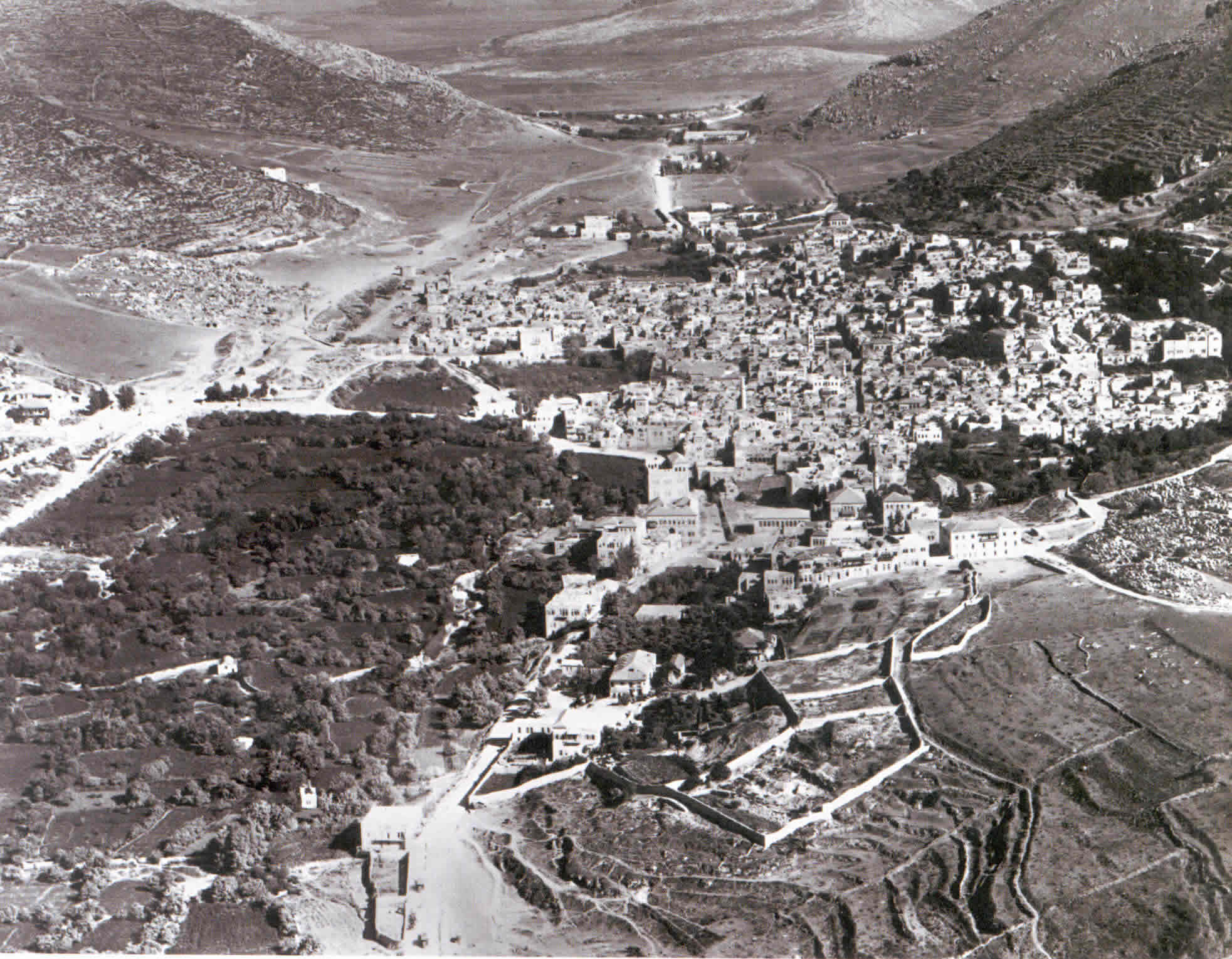
s, who conquered the city in 1517, Nablus served as the administrative and commercial centre for the surrounding area corresponding to the modern-day northern West Bank. Much of Nablus' history is preserved in its Old City, which contains more than 100 monumental buildings.
After the city was captured by British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
forces during World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, Nablus was incorporated into Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine was a British Empire, British geopolitical entity that existed between 1920 and 1948 in the Palestine (region), region of Palestine, and after 1922, under the terms of the League of Nations's Mandate for Palestine.
After ...
in 1922. The 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
saw the entire West Bank, including Nablus, occupied and annexed by Transjordan Transjordan may refer to:
* Transjordan (region), an area to the east of the Jordan River
* Oultrejordain, a Crusader lordship (1118–1187), also called Transjordan
* Emirate of Transjordan, British protectorate (1921–1946)
* Hashemite Kingdom o ...
. Since the 1967 Arab–Israeli War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June ...
, the West Bank has been occupied by Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
; since 1995, it has been governed by the Palestinian Authority
The Palestinian Authority (PA), officially known as the Palestinian National Authority (PNA), is the Fatah-controlled government body that exercises partial civil control over the Palestinian enclaves in the Israeli occupation of the West Bank, ...
as part of Area A of the West Bank. Today, the population is predominantly Muslim, with small Christian and Samaritan minorities.
History
Classical antiquity
 ('new city of the emperor
('new city of the emperor Flavius
The gens Flavia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Its members are first mentioned during the last three centuries of the Republic. The first of the Flavii to achieve prominence was Marcus Flavius, tribune of the plebs in 327 and 323 BC; how ...
') was named in 72 CE by the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
emperor Vespasian
Vespasian (; ; 17 November AD 9 – 23 June 79) was Roman emperor from 69 to 79. The last emperor to reign in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolida ...
and applied to an older Samaritan
Samaritans (; ; ; ), are an ethnoreligious group originating from the Hebrews and Israelites of the ancient Near East. They are indigenous to Samaria, a historical region of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah that ...
village, variously called ('the passage')Negev and Gibson, 2005, p. 175. or . Located between Mount Ebal
Mount Ebal (; ) is one of the two mountains near the city of Nablus in the West Bank (Bible, biblical ''Shechem''), and forms the northern side of the valley in which Nablus is situated, the southern side being formed by Mount Gerizim. The mount ...
and Mount Gerizim
Mount Gerizim ( ; ; ; , or ) is one of two mountains in the immediate vicinity of the State of Palestine, Palestinian city of Nablus and the biblical city of Shechem. It forms the southern side of the valley in which Nablus is situated, the nor ...
, the new city lay west of the Biblical
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) biblical languages ...
city of Shechem
Shechem ( ; , ; ), also spelled Sichem ( ; ) and other variants, was an ancient city in the southern Levant. Mentioned as a Canaanite city in the Amarna Letters, it later appears in the Hebrew Bible as the first capital of the Kingdom of Israe ...
which was destroyed by the Romans that same year during the First Jewish–Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War (66–74 CE), also known as the Great Jewish Revolt, the First Jewish Revolt, the War of Destruction, or the Jewish War, was the first of three major Jewish rebellions against the Roman Empire. Fought in the prov ...
. Holy places at the site of the city's founding include Joseph's Tomb
Joseph's Tomb (, ''Qever Yosef''; , ''Qabr Yūsuf'') is a funerary monument located in Balata village at the eastern entrance to the valley that separates Mounts Gerizim and Ebal, northwest of Jacob's Well, on the outskirts of the West Ban ...
and Jacob's Well
Jacob's Well, also known as Jacob's Fountain or the Well of Shechem, Sychar, is a List of Christian holy sites in the Holy Land, Christian holy site located in Balata village, a suburb of the State of Palestine, Palestinian city of Nablus in t ...
. Because of the city's strategic geographic position and the abundance of water from nearby springs, Neapolis prospered, accumulating extensive territory, including the former Judea
Judea or Judaea (; ; , ; ) is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the pres ...
n toparchy
''Toparchēs'' (, "place-ruler"), anglicized as toparch, is a Greek term for a governor or ruler of a district and was later applied to the territory where the toparch exercised his authority. In Byzantine times, the term came to be applied to inde ...
of Acraba.
Insofar as the hilly topography of the site would allow, the city was built on a Roman grid plan
In urban planning, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogon ...
and settled with veterans who fought in the victorious legions and other foreign colonists. In the 2nd century CE, Emperor Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia '' ...
built a grand theater
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors to present experiences of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The performers may communi ...
in Neapolis that could seat up to 7,000 people. Coins found in Nablus dating to this period depict Roman military emblems and gods and goddesses of the Greek pantheon such as Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
, Artemis
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Artemis (; ) is the goddess of the hunting, hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, transitions, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. In later tim ...
, Serapis
Serapis or Sarapis is a Egyptian Greeks, Graeco-Egyptian god. A Religious syncretism, syncretic deity derived from the worship of the Egyptian Osiris and Apis (deity), Apis, Serapis was extensively popularized in the third century BC on the ord ...
, and Asklepios
Asclepius (; ''Asklēpiós'' ; ) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Greek religion and mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis, or Arsinoe, or of Apollo alone. Asclepius represents the healing aspect of the medical arts; his ...
. Neapolis was entirely pagan
Paganism (, later 'civilian') is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Christianity, Judaism, and Samaritanism. In the time of the ...
at this time. Justin Martyr
Justin, known posthumously as Justin Martyr (; ), also known as Justin the Philosopher, was an early Christian apologist and Philosophy, philosopher.
Most of his works are lost, but two apologies and a dialogue did survive. The ''First Apolog ...
who was born in the city c. 100 CE, came into contact with Platonism
Platonism is the philosophy of Plato and philosophical systems closely derived from it, though contemporary Platonists do not necessarily accept all doctrines of Plato. Platonism has had a profound effect on Western thought. At the most fundam ...
, but not with Christians there. The city flourished until the civil war between Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; ; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through cursus honorum, the ...
and Pescennius Niger
Gaius Pescennius Niger (c. 135 – 194) was a Roman usurper from 193 to 194 during the Year of the Five Emperors. He claimed the imperial throne in response to the murder of Pertinax and the elevation of Didius Julianus, but was defeated by a ...
in 198–9 CE. Having sided with Niger, who was defeated, the city was temporarily stripped of its legal privileges by Severus, who designated these to Sebastia instead.
In 244 CE, Philip the Arab
Philip I (; – September 249), commonly known as Philip the Arab, was Roman emperor from 244 to 249. After the death of Gordian III in February 244, Philip, who had been Praetorian prefect, rose to power. He quickly negotiated peace with the S ...
transformed Flavius Neapolis into a Roman colony named . It retained this status until the rule of Trebonianus Gallus
Gaius Vibius Trebonianus Gallus ( 206 – August 253) was Roman emperor from June 251 to August 253, in a joint rule with his son Volusianus.
Early life
Gallus was born in Italy, in a respected senatorial family with Etruscan ancestry, cer ...
in 251 CE. The speculates that Christianity was dominant in the 2nd or 3rd century, with some sources positing a later date of 480 CE. It is known for certain that a bishop from Nablus participated in the Council of Nicaea in 325 CE.Negev and Gibson, 2005, p. 176. The presence of Samaritans in the city is attested to in literary and epigraphic evidence dating to the 4th century CE. As yet, there is no evidence attesting to a Jewish presence in ancient Neapolis.
Si'on suggested that Neapolis was about 900 acres in size during the Byzantine period, making it three times larger than it was when it was first established as a Roman colony. Magen estimates that around 20,000 people lived there during this period.
Palaestina Prima
Palaestina Prima or Palaestina I was a Byzantine province that existed from the late 4th century until the Muslim conquest of the Levant in the 630s, in the region of Palestine. It was temporarily lost to the Sassanid Empire (Persian Empire) in ...
province under the rule of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
. The tension was a result of Monophysite
Monophysitism ( ) or monophysism ( ; from Greek , "solitary" and , "nature") is a Christological doctrine that states that there was only one nature—the divine—in the person of Jesus Christ, who was the incarnated Word. It is rejected as ...
Christian attempts to prevent the return of the Patriarch of Jerusalem, Juvenal
Decimus Junius Juvenalis (), known in English as Juvenal ( ; 55–128), was a Roman poet. He is the author of the '' Satires'', a collection of satirical poems. The details of Juvenal's life are unclear, but references in his works to people f ...
, to his episcopal see
An episcopal see is the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, making it synonymous with ''diocese'' ...
. However, the conflict did not grow into civil strife.
As tensions among the Christians of Neapolis decreased, tensions between the Christian community and the Samaritans
Samaritans (; ; ; ), are an ethnoreligious group originating from the Hebrews and Israelites of the ancient Near East. They are indigenous to Samaria, a historical region of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah that ...
grew dramatically. In 484, the city became the site of a deadly encounter between the two groups, provoked by rumors that the Christians intended to transfer the remains of Aaron
According to the Old Testament of the Bible, Aaron ( or ) was an Israelite prophet, a high priest, and the elder brother of Moses. Information about Aaron comes exclusively from religious texts, such as the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament ...
's sons and grandsons Eleazar
Eleazar (; ) or Elazar was a priest in the Hebrew Bible, the second High Priest, succeeding his father Aaron after he died. He was a nephew of Moses.
Biblical narrative
Eleazar played a number of roles during the course of the Exodus, from ...
, Ithamar
In the Bible, Ithamar () was the fourth (and the youngest) son of Aaron the High Priest."Ithamar", '' Encyclopaedia Biblica'' Following the construction of the Tabernacle, he was responsible for recording an inventory to ensure that the construc ...
and Phinehas
According to the Hebrew Bible, Phinehas (also spelled Phineas, ; , ''Phinees'', ) was a priest during the Exodus. The grandson of Aaron and son of Eleazar, the High Priests (), he distinguished himself as a youth at Shittim with his zeal again ...
. Samaritans reacted by entering the cathedral of Neapolis, killing the Christians inside and severing the fingers of the bishop Terebinthus. Terebinthus then fled to Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, requesting an army garrison to prevent further attacks. As a result of the revolt, the Byzantine emperor Zeno
Zeno may refer to:
People
* Zeno (name), including a list of people and characters with the given name
* Zeno (surname)
Philosophers
* Zeno of Elea (), philosopher, follower of Parmenides, known for his paradoxes
* Zeno of Citium (333 – 264 B ...
erected a church dedicated to Mary
Mary may refer to:
People
* Mary (name), a female given name (includes a list of people with the name)
Religion
* New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below
* Mary, mother of Jesus, also called the Blesse ...
on Mount Gerizim. He also forbade the Samaritans to travel to the mountain to celebrate their religious ceremonies, and expropriated their synagogue there. These actions by the emperor fueled Samaritan anger towards the Christians further.
Thus, the Samaritans rebelled again under the rule of emperor Anastasius I, reoccupying Mount Gerizim, which was subsequently reconquered by the Byzantine governor of Edessa
Edessa (; ) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, in what is now Urfa or Şanlıurfa, Turkey. It was founded during the Hellenistic period by Macedonian general and self proclaimed king Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Sel ...
, Procopius. A third Samaritan revolt which took place under the leadership of Julianus ben Sabar in 529 was perhaps the most violent. Neapolis' bishop Ammonas was murdered and the city's priests were hacked into pieces and then burned together with the relics of saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the ...
s. The forces of Emperor Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
were sent in to quell the revolt, which ended with the slaughter of the majority of the Samaritan population in the city.
Early Muslim period

Khalid ibn al-Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid ibn al-Mughira al-Makhzumi (; died 642) was a 7th-century Arabs, Arab military commander. He initially led campaigns against Muhammad on behalf of the Quraysh. He later became a Muslim and spent the remainder of his career ...
, a general of the Rashidun army
The Rashidun army () was the core of the Rashidun Caliphate's armed forces during the early Muslim conquests in the 7th century. The army is reported to have maintained a high level of discipline, strategic prowess and organization, grantin ...
of Umar ibn al-Khattab
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muh ...
, in 636 after the Battle of Yarmouk
The Battle of the Yarmuk (also spelled Yarmouk; ) was a major battle between the army of the Byzantine Empire and the Arab Muslim forces of the Rashidun Caliphate. The battle consisted of a series of engagements that lasted for six days in Aug ...
. The city's name was retained in its Arabicized form, . The town prevailed as an important trade center during the centuries of Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
ic Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
rule under the Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a membe ...
, Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 C ...
and Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimid dynasty, Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa ...
dynasties.
Under Muslim rule, Nablus contained a diverse population of Arabs and Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
s, Muslims, Samaritans, Christians and Jew
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly inte ...
s. In the 9th century CE, Al-Yaqubi
ʾAbū al-ʿAbbās ʾAḥmad bin ʾAbī Yaʿqūb bin Ǧaʿfar bin Wahb bin Waḍīḥ al-Yaʿqūbī (died 897/8), commonly referred to simply by his nisba al-Yaʿqūbī, was an Arab Muslim geographer.
Life
Ya'qubi was born in Baghdad to a fam ...
reported that Nablus had a mixed population of Arabs, Ajam
(, ) is an Arabic word for a non-Arab, especially a Persian. It was historically used as a pejorative—figuratively ascribing muteness to those whose native language is not Arabic—during and after the Muslim conquest of Iran. Since the ea ...
(Non-Arabs), and Samaritans. In the 10th century, the Arab geographer al-Muqaddasi
Shams al-Din Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ahmad ibn Abi Bakr, commonly known by the '' nisba'' al-Maqdisi or al-Muqaddasī, was a medieval Arab geographer, author of ''The Best Divisions in the Knowledge of the Regions'' and ''Description of Syri ...
, described it as abundant of olive trees, with a large marketplace, a finely paved Great Mosque, houses built of stone, a stream running through the center of the city, and notable mills.Muqaddasip. 55
He also noted that it was nicknamed "Little
Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
."Semplici, Andrea and Boccia, Mario– Nablus, At the Foot of the Holy Mountain
Med Cooperation, p.6. At the time, the linen produced in Nablus was well known throughout the
Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
.
Crusader period
The city was captured byCrusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding ...
in 1099, under the command of Prince Tancred, and renamed ''Naples''. Though the Crusaders extorted many supplies from the population for their troops who were en route to Jerusalem, they did not sack the city, presumably because of the large Christian population there. Nablus became part of the royal domain
Crown land, also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. Today, in Commonwealth realm ...
of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem, also known as the Crusader Kingdom, was one of the Crusader states established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1 ...
. The Muslim, Eastern Orthodox Christian, and Samaritan populations remained in the city and were joined by some Crusaders who settled therein to take advantage of the city's abundant resources. In 1120, the Crusaders convened the Council of Nablus
The Council of Nablus was a council of ecclesiastic and secular lords in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem, held on January 16, 1120.
History
The council was convened at Nablus by Warmund, Patriarch of Jerusalem, and King Baldwin II of Jerusalem. ...
out of which was issued the first written laws for the kingdom. They converted the Samaritan synagogue in Nablus into a church. The Samaritan community built a new synagogue in the 1130s. In 1137, Arab and Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
* Something related to Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities in the former Ottoman Empire
* The w ...
troops stationed in Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
raided Nablus, killing many Christians and burning down the city's churches. However, they were unsuccessful in retaking the city. Queen Melisende of Jerusalem
Melisende ( 1105 – 11 September 1161) was the queen of Jerusalem from 1131 to 1152. She was the first female ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem and the first woman to hold a public office in the crusader kingdom. She was already legendary in he ...
resided in Nablus from 1150 to 1161, after she was granted control over the city in order to resolve a dispute with her son Baldwin III. Crusaders began building Christian institutions in Nablus, including a church dedicated to the Passion
Passion, the Passion or the Passions may refer to:
Emotion
* Passion (emotion), a very strong feeling about a person or thing
* Passions (philosophy), emotional states as used in philosophical discussions
* Stoic passions, various forms of emotio ...
and Resurrection of Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
, and in 1170 they erected a hospice for pilgrims.
Ayyubid and Mamluk rule
Ayyubid
The Ayyubid dynasty (), also known as the Ayyubid Sultanate, was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egyp ...
s led by Saladin
Salah ad-Din Yusuf ibn Ayyub ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known as Saladin, was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from a Kurdish family, he was the first sultan of both Egypt and Syria. An important figure of the Third Crusade, h ...
captured the city. According to a liturgical manuscript in Syriac, Latin Christians
The Latin Church () is the largest autonomous () particular church within the Catholic Church, whose members constitute the vast majority of the 1.3 billion Catholics. The Latin Church is one of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches in full communion wi ...
fled Nablus, but the original Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
Christian inhabitants remained. Syrian geographer Yaqut al-Hamawi
Yāqūt Shihāb al-Dīn ibn-ʿAbdullāh al-Rūmī al-Ḥamawī (1179–1229) () was a Muslim scholar of Byzantine ancestry active during the late Abbasid period (12th–13th centuries). He is known for his , an influential work on geography con ...
(1179–1229), wrote that Ayyubid Nablus was a "celebrated city in Filastin (Palestine)... having wide lands and a fine district." He also mentions the large Samaritan population in the city.Le Strange, 1890, pp511
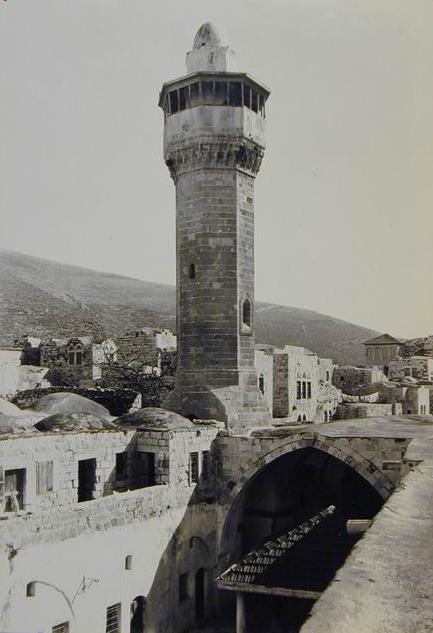
��515 After its recapture by the Muslims, the Great Mosque of Nablus, which had become a church under Crusader rule, was restored as a mosque by the Ayyubids, who also built a
mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be considered a type o ...
in the old city.
In October 1242, Nablus was raided by the Knights Templar
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, mainly known as the Knights Templar, was a Military order (religious society), military order of the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, and one of the most important military ord ...
. This was the conclusion of the 1242 campaign season in which the Templars had joined forces with the Ayyubid emir of Kerak, An-Nasir Dawud
An-Nasir Dawud (1206–1261) was a Kurdish ruler, briefly (1227–1229) Ayyubid sultan of Damascus and later (1229–1248) Emir of Al-Karak.
An-Nasir Dawud was the son of Al-Mu'azzam, the Ayyubid Sultan of Damascus from 1218 to 1227. On his ...
, against the Mamluks. The Templars raided Nablus in revenge for a previous massacre of Christians by their erstwhile ally An-Nasir Dawud. The attack is reported as a particularly bloody affair lasting for three days, during which the Mosque was burned and many residents of the city, Christians alongside Muslims, were killed or sold in the slave markets of Acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), ch ...
.
The successful raid was widely publicized by the Templars in Europe; it is thought to be depicted in a late 13th-century fresco in the Templar church of San Bevignate, Perugia
Perugia ( , ; ; ) is the capital city of Umbria in central Italy, crossed by the River Tiber. The city is located about north of Rome and southeast of Florence. It covers a high hilltop and part of the valleys around the area. It has 162,467 ...
.
In 1244, the Samaritan synagogue, built in 362 by the high priest Akbon and converted into a church by the Crusaders, was converted into al-Khadra Mosque. Two other Crusader churches became the An-Nasr Mosque
An-Nasr Mosque ( ''Masjid an-Nasr'' translated as "Victory Mosque") is a mosque located in Nablus, Palestine. It is situated in the central square of the Old City of Nablus and is donned as the "symbol of Nablus".Semplici, Andrea and Boccia, Ma ...
and al-Masakim Mosque during that century.
The Mamluk dynasty gained control of Nablus in 1260 and during their reign, they built numerous mosques and schools. Under Mamluk rule, Nablus possessed running water, many Turkish bath
A hammam (), also often called a Turkish bath by Westerners, is a type of steam bath or a place of public bathing associated with the Islamic world. It is a prominent feature in the culture of the Muslim world and was inherited from the model ...
s and exported olive oil and soap
Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually u ...
to Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Syria, the Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
, several Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
islands, and the Arabian Desert
The Arabian Desert () is a vast desert wilderness in West Asia that occupies almost the entire Arabian Peninsula with an area of . It stretches from Yemen to the Persian Gulf and Oman to Jordan and Iraq. It is the fourth largest desert in the ...
. The city's olive oil was also used in the Umayyad Mosque
The Umayyad Mosque (; ), also known as the Great Mosque of Damascus, located in the old city of Damascus, the capital of Syria, is one of the largest and oldest mosques in the world. Its religious importance stems from the eschatological reports ...
in Damascus. Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
, the Arab explorer, visited Nablus in 1355, and described it as a city "full of trees and streams and full of olives." He noted that the city grew and exported carob
The carob ( ; ''Ceratonia siliqua'') is a flowering evergreen tree or shrub in the Caesalpinioideae sub-family of the legume family, Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated for its edible fruit, which takes the form of seed pods, and as an ornam ...
jam to Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
and Damascus.
Ottoman era
Nablus came under the rule of theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
in 1517, along with the whole of Palestine. The Ottomans divided Palestine into six ('districts'): Safad
Safed (), also known as Tzfat (), is a city in the Northern District of Israel. Located at an elevation of up to , Safed is the highest city in the Galilee and in Israel.
Safed has been identified with (), a fortified town in the Upper Gal ...
, Jenin
Jenin ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and is the capital of the Jenin Governorate. It is a hub for the surrounding towns. Jenin came under Israeli occupied territories, Israeli occupation in 1967, and was put under the administra ...
, Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, Gaza
Gaza may refer to:
Places Palestine
* Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea
** Gaza City, a city in the Gaza Strip
** Gaza Governorate, a governorate in the Gaza Strip
Mandatory Palestine
* Gaza Sub ...
, Ajlun
Ajloun (, ''‘Ajlūn''), also spelled Ajlun, is the capital town of the Ajloun Governorate, a hilly town in the north of Jordan, located 76 kilometers (around 47 miles) north west of Amman. It is noted for its impressive ruins of the 12th-centur ...
and Nablus
Nablus ( ; , ) is a State of Palestine, Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a population of 156,906. Located between Mount Ebal and Mount Gerizim, it is the capital of the Nablus Governorate and a ...
, all of which were part of Ottoman Syria
Ottoman Syria () is a historiographical term used to describe the group of divisions of the Ottoman Empire within the region of the Levant, usually defined as being east of the Mediterranean Sea, west of the Euphrates River, north of the Ara ...
. These five were subdistricts of the Vilayet of Damascus. Sanjak Nablus was further subdivided into five ('subdistricts'), in addition to the city itself. The Ottomans did not attempt to restructure the political configuration of the region on the local level such that the borders of the were drawn to coincide with the historic strongholds of certain families. Nablus was only one among a number of local centers of power within Jabal Nablus, and its relations with the surrounding villages, such as Beita and Aqraba Akraba (variants: Aqrab, Aqraba, Agrab or Aqrabiyah) may refer to:
Egypt
* Al-Aqrab Prison, a prison in Cairo, Egypt
Iraq
* Tell Agrab, an ancient settlement in Iraq in Diyala Governorate
Palestine
* Aqraba, Nablus, a Palestinian town in the Na ...
, were partially mediated by the rural-based chiefs of the .Doumani, 1995, Chapter: "The 1657 Campaign." During the 16th century, the population was predominantly Muslim, with Jewish, Samaritan and Christian minorities.
After decades of upheavals and rebellions mounted by Arab tribes in the Middle East, the Ottomans attempted to reassert centralized control over the Arab . In 1657, they sent an expeditionary force led mostly by Arab officers from central Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
to reassert Ottoman authority in Nablus and its hinterland, as part of a broader attempt to established centralized rule throughout the empire at that time. In return for their services, the officers were granted agricultural lands around the villages of Jabal Nablus. The Ottomans, fearing that the new Arab land holders would establish independent bases of power, dispersed the land plots to separate and distant locations within Jabal Nablus to avoid creating contiguous territory controlled by individual clans. Contrary to its centralization purpose, the 1657 campaign allowed the Arab officers to establish their own increasingly autonomous foothold in Nablus. The officers raised their families there and intermarried with the local notables of the area, namely the ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' ( ; also spelled ''ulema''; ; singular ; feminine singular , plural ) are scholars of Islamic doctrine and law. They are considered the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam.
"Ulama ...
and merchant families. Without abandoning their nominal military service, they acquired diverse properties to consolidate their presence and income such as soap and pottery factories, bathhouses, agricultural lands, grain mills and, olive and sesame oil presses.
The most influential military family were the Nimrs, who were originally local governors of Homs
Homs ( ; ), known in pre-Islamic times as Emesa ( ; ), is a city in western Syria and the capital of the Homs Governorate. It is Metres above sea level, above sea level and is located north of Damascus. Located on the Orontes River, Homs is ...
and Hama
Hama ( ', ) is a city on the banks of the Orontes River in west-central Syria. It is located north of Damascus and north of Homs. It is the provincial capital of the Hama Governorate. With a population of 996,000 (2023 census), Hama is one o ...
's rural subdistricts. Other officer families included the Akhrami, Asqalan, Bayram, Jawhari, Khammash, Mir'i, Shafi, Sultan and Tamimi families, some of which remained in active service, while some left service for other pursuits. In the years following the 1657 campaign, two other families migrated to Nablus: the Jarrars from Balqa and the Tuqans from northern Syria or Transjordan. The Jarrars came to dominate the hinterland of Nablus, while the Tuqans and Nimrs competed for influence in the town. The former held the post of ('tax collector, strongman') of Nablus longer, though non-consecutively than any other family. The three families maintained their power until the mid-19th century.
 In the mid-18th century,
In the mid-18th century, Zahir al-Umar
Zahir al-Umar al-Zaydani, alternatively spelled Dhaher el-OmarDAAHL Site Rec ...
, the autonomous Arab ruler of the Galilee
Galilee (; ; ; ) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon consisting of two parts: the Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and the Lower Galilee (, ; , ).
''Galilee'' encompasses the area north of the Mount Carmel-Mount Gilboa ridge and ...
became a dominant figure in Palestine. To build up his army, he strove to gain a monopoly over the cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
and olive oil trade of the southern Levant
The Southern Levant is a geographical region that corresponds approximately to present-day Israel, Palestine, and Jordan; some definitions also include southern Lebanon, southern Syria and the Sinai Peninsula. As a strictly geographical descript ...
, including Jabal Nablus, which was a major producer of both crops. In 1771, during the Egyptian Mamluk invasion of Syria, Zahir aligned himself with the Mamluks and besieged Nablus, but did not succeed in taking the city. In 1773, he tried again without success. Nevertheless, from a political perspective, the sieges led to a decline in the importance of the city in favor of Acre. Zahir's successor, Jezzar Pasha
Ahmed Pasha al-Jazzar (, c. 1720–30s7 May 1804) was the Acre-based Bosniak Ottoman governor of Sidon Eyalet from 1776 until his death in 1804 and the simultaneous governor of Damascus Eyalet in 1785–1786, 1790–1795, 1798–1799, and 1803 ...
, maintained Acre's dominance over Nablus. After his reign ended in 1804, Nablus regained its autonomy, and the Tuqans, who represented a principal opposing force, rose to power.
Egyptian rule and Ottoman revival
 In 1831–32 Khedivate Egypt, then led by
In 1831–32 Khedivate Egypt, then led by Muhammad Ali
Muhammad Ali (; born Cassius Marcellus Clay Jr.; January 17, 1942 – June 3, 2016) was an American professional boxer and social activist. A global cultural icon, widely known by the nickname "The Greatest", he is often regarded as the gr ...
, conquered Palestine from the Ottomans. A policy of conscription
Conscription, also known as the draft in the United States and Israel, is the practice in which the compulsory enlistment in a national service, mainly a military service, is enforced by law. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it conti ...
and new taxation
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal person, legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to Pigouvian tax, regulate and reduce nega ...
was instituted which led to a revolt
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a ...
organized by the (notables) of Nablus, Hebron
Hebron (; , or ; , ) is a Palestinian city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Hebron is capital of the Hebron Governorate, the largest Governorates of Palestine, governorate in the West Bank. With a population of 201,063 in ...
and the Jerusalem–Jaffa area. In May 1834, Qasim al-Ahmad
Qasim Pasha al-Ahmad (died 1834) was the chief of the Jamma'in subdistrict of Jabal Nablus during the Ottoman and Egyptian periods in Palestine in the mid-19th century.Doumani, 1995, p.46/ref> He also served as the '' mutassalim'' (tax collect ...
—the chief of the Jamma'in
Jamma'in () is a Palestinian town in the Nablus Governorate of the State of Palestine, in the northern West Bank, located southwest of Nablus, northwest of Salfit and north of Ramallah. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics ...
—rallied the rural sheikhs and (peasants) of Jabal Nablus and launched a revolt against Governor Ibrahim Pasha, in protest at conscription orders, among other new policies. The leaders of Nablus and its hinterland sent thousands of rebels to attack Jerusalem, the center of government authority in Palestine, aided by the Abu Ghosh
Abu Ghosh (; ) is an Arab-Israeli local council in Israel, located west of Jerusalem on the Tel Aviv–Jerusalem highway. It is situated 610–720 meters above sea level. It takes its current name from the dominant clan inhabiting the town, ...
clan, and they conquered the city on 31 May. However, they were later defeated by Ibrahim Pasha's forces the next month. Ibrahim then forced the heads of the Jabal Nablus clans to leave for nearby villages. By the end of August, the countrywide revolt had been suppressed and Qasim was executed.Doumani, 1995, Chapter: "Egyptian rule, 1831–1840."
Egyptian rule in Palestine resulted in the destruction of Acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), ch ...
and thus, the political importance of Nablus was further elevated. The Ottomans wrested back control of Palestine from Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
in 1840–41. However, the Arraba-based Abd al-Hadi clan which rose to prominence under Egyptian rule for supporting Ibrahim Pasha, continued its political dominance in Jabal Nablus.
Throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, Nablus was the principal trade and manufacturing center in Ottoman Syria. Its economic activity and regional leadership position surpassed that of Jerusalem and the coastal cities of Jaffa
Jaffa (, ; , ), also called Japho, Joppa or Joppe in English, is an ancient Levantine Sea, Levantine port city which is part of Tel Aviv, Tel Aviv-Yafo, Israel, located in its southern part. The city sits atop a naturally elevated outcrop on ...
and Acre. Olive oil
Olive oil is a vegetable oil obtained by pressing whole olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea'', a traditional Tree fruit, tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin) and extracting the oil.
It is commonly used in cooking for frying foods, as a cond ...
was the primary product of Nablus and aided other related industries such as soap-making
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually used for washing, b ...
and basket weaving. It was also the largest producer of cotton in the Levant, topping the production of northern cities such as Damascus. Jabal Nablus enjoyed a greater degree of autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be ...
than other under Ottoman control, probably because the city was the capital of a hilly region, in which there were no "foreigners" who held any military or bureaucratic posts. Thus, Nablus remained outside the direct "supervision" of the Ottoman government, according to historian Beshara Doumani
Beshara Doumani () is a Palestinian-American academic who previously served as the president of Birzeit University from 2021 to 2023. Prior to that, he was the Mahmoud Darwish Professor of Palestinian Studies at Brown University. His research focu ...
.Doumani, 1995, Chapter: "Introduction."
World War I and British Mandate
 Between 19 September and 25 September 1918, in the last months of the
Between 19 September and 25 September 1918, in the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign
The Sinai and Palestine campaign was part of the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, taking place between January 1915 and October 1918. The British Empire, the French Third Republic, and the Kingdom of Italy fought alongside the Arab Revol ...
of the First World War the Battle of Nablus took place, together with the Battle of Sharon
The Battle of Sharon fought between 19 and 25 September 1918, began the set piece Battle of Megiddo (1918), Battle of Megiddo half a day before the Battle of Nablus (1918), Battle of Nablus, in which large formations engaged and responded to mov ...
during the set piece Battle of Megiddo. Fighting took place in the Judean Hills
The Judaean Mountains, or Judaean Hills (, or ,) are a mountain range in the West Bank and Israel where Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Hebron and several other biblical sites are located. The mountains reach a height of . The Judean Mountains can be div ...
where the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
's XX Corps and Royal Flying Corps
The Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was the air arm of the British Army before and during the First World War until it merged with the Royal Naval Air Service on 1 April 1918 to form the Royal Air Force. During the early part of the war, the RFC sup ...
attacked the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
's Yildirim Army Group
The Yıldırım Army Group or Thunderbolt Army Group of the Ottoman Empire or Army Group F (German: ''Heeresgruppe F'') was an Army Group of the Ottoman Army during World War I. While being an Ottoman unit, it also contained the German Asia Cor ...
's Seventh Army which held a defensive position in front of Nablus, and which the Eighth Army had attempted to retreat to, in vain.
The 1927 Jericho earthquake
The 1927 Jericho earthquake was a devastating event that shook Mandatory Palestine and Transjordan on July 11 at . The epicenter of the earthquake was in the northern area of the Dead Sea. The cities of Jerusalem, Jericho, Ramla, Tiberias, and N ...
destroyed many of the Nablus' historic buildings, including the An-Nasr Mosque. Though they were subsequently rebuilt by Haj Amin al-Husayni
Mohammed Amin al-Husseini (; 4 July 1974) was a Palestinian Arab nationalist and Muslim leader in Mandatory Palestine. was the scion of the family of Jerusalemite Arab nobles, who trace their origins to the Islamic prophet Muhammad.
Hussein ...
's Supreme Muslim Council
The Supreme Muslim Council (SMC; ) was the highest body in charge of Muslim community affairs in Mandatory Palestine under British control. It was established to create an advisory body composed of Muslims and Christians with whom the High Comm ...
in the mid-1930s, their previous "picturesque" character was lost. During the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
A popular uprising by Palestinian Arabs in Mandatory Palestine against the British administration, later known as the Great Revolt, the Great Palestinian Revolt, or the Palestinian Revolution, lasted from 1936 until 1939. The movement sought i ...
, the British authorities demolished buildings in the Old City quarter of Qaryun suspected of harboring insurgents or hiding weapons.Doumani, 1995, Chapter: Family, Culture, and Trade. Jewish immigration did not significantly impact the demographic composition of Nablus, and it was slated for inclusion in the Arab state envisioned by the United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; , AGNU or AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as its main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ. Currently in its Seventy-ninth session of th ...
's 1947 partition plan for Palestine.
Jordanian period
During the1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
, Nablus came under Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
ian control. Thousands of Palestinian refugees
Palestinian refugees are citizens of Mandatory Palestine, and their descendants, who fled or were expelled from their country, village or house over the course of the 1948 Palestine war and during the 1967 Six-Day War. Most Palestinian refug ...
fleeing from areas captured by Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
i forces arrived in Nablus, settling in refugee camps in and around the city. Its population doubled, and the influx of refugees put a heavy strain on the city's resources. Three such camps still located within the city limits today are Ein Beit al-Ma'
'Ein Beit el Ma (Arabic: ), also known as Camp No. 1 (), is a Palestinian refugee camp established in the northern West Bank in 1950, adjacent to the city of Nablus. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics
The Palestinian Ce ...
, Balata and Askar. During the Jordanian period, the adjacent villages of Rafidia
Rafidiya () is a neighborhood in the western part of the Palestinian city of Nablus. It was a separate village until it was merged into the municipality in 1966. In 1961, Rafidiya had 923 inhabitants, rising to 1,200 in 1983.
History
The remains o ...
, Balata al-Balad, al-Juneid and Askar were annexed to the Nablus municipality. Nablus was annexed by Jordan in 1950.
Israeli period
 The 1967
The 1967 Six-Day War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June ...
ended in the Israeli occupation
Israel has occupied the Golan Heights of Syria and the Palestinian territories since the Six-Day War of 1967. It has previously occupied the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt and southern Lebanon as well. Prior to 1967, control of the Palestinian terr ...
of Nablus. Many Israeli settlement
Israeli settlements, also called Israeli colonies, are the civilian communities built by Israel throughout the Israeli-occupied territories. They are populated by Israeli citizens, almost exclusively of Israeli Jews, Jewish identity or ethni ...
s were built around Nablus during the 1980s and early 1990s. The restrictions placed on Nablus during the First Intifada were met by a back-to-the-land movement to secure self-sufficiency, and had a notable outcome in boosting local agricultural production.
In 1976, Bassam Shakaa
Bassam Shakaa () (1930 – 22 July 2019) was mayor of Nablus from 1976 to 1982.
Biography Early life
Bassam Shakaa was a member of a distinguished family in Nablus.
He became a member of the Jordanian regional branch of the Ba'ath Party ...
was elected mayor. On 2 June 1980, he survived an assassination attempt by the Jewish Underground
The Jewish Underground ( ''HaMakhteret HaYehudit''), or in abbreviated form, simply Makhteret,David S. New''Holy War: The Rise of Militant Christian, Jewish and Islamic Fundamentalism,'' McFarland, 2001, p. 143. was a radical right-wing fundamenta ...
, considered a terrorist group by Israel, which resulted in Shakaa losing both his legs. In the spring of 1982, the Israeli administration removed him from office and installed an army officer who ran the city for the following three and a half years.Middle East International No 270, 7 March 1986, Publishers Lord Mayhew, Dennis Walters
Sir Dennis Murray Walters (28 November 1928 – 1 October 2021) was a British Conservative Party politician who served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Westbury from 1964 to 1992.
Early life
The son of Douglas L. Walters and Clara Walt ...
. Daoud Kuttab
Daoud Kuttab (), (born 1 April 1955) is a Palestinian-American journalist.
Journalism
In 1980, Kuttab began his career at '' Al-Fajr'', an English-language weekly newspaper. Over the next seven years, he was promoted to features editor and th ...
p. 6
On 29 July 1985, the Israeli army imposed a 5-day curfew on the city that was lifted 2 hours a day The curfew was in response to the murder of two Israeli teachers on 21 July near Jenin
Jenin ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and is the capital of the Jenin Governorate. It is a hub for the surrounding towns. Jenin came under Israeli occupied territories, Israeli occupation in 1967, and was put under the administra ...
and the killing of another Israeli on 30 July. Najah University was closed for 2 months for hanging PLO propaganda posters.
In January 1986, the Israeli administration ended with the appointment of Zafer al-Masri as mayor. A popular leader of the Nablus Chamber of Commerce al-Masri began a program of improvements in the town. Despite maintaining that he would have nothing to do with Israeli autonomy plans he was assassinated on 2 March 1986. The assassination was widely believed to be the work of the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine
The Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP; ) is a secular Palestinian Marxist–Leninist organization founded in 1967 by George Habash. It has consistently been the second-largest of the groups forming the Palestine Liberation ...
.
On 18 June 1989 Salah el Bah'sh, aged 17, was shot dead by an Israeli soldier
The Israeli Ground Forces () are the ground forces of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). The commander is the General Officer Commanding with the rank of major general, the ''Mazi'', subordinate to the Chief of General Staff.
An order from Defen ...
whilst walking through the Nablus Casbah
A kasbah (, also ; , , Maghrebi Arabic: ), also spelled qasbah, qasba, qasaba, or casbah, is a fortress, most commonly the citadel or fortified quarter of a city. It is also equivalent to the term in Spanish (), which is derived from the same ...
. Witnesses told B'Tselem, the Israeli Human Rights group, that he was shot in the chest at close range after not responding to a soldier shouting "Ta'amod" (Halt!). The army indicated that an investigation was being carried out. B'Tselem understood that the victim was killed by a rubber bullet
Rubber bullets (also called rubber baton rounds) are a type of baton round. Despite the name, rubber bullets typically have either a metal core with a rubber coating, or are a homogeneous admixture with rubber being a minority component. Altho ...
.
Palestinian control
 Jurisdiction over the city was handed over to the
Jurisdiction over the city was handed over to the Palestinian National Authority
The Palestinian Authority (PA), officially known as the Palestinian National Authority (PNA), is the Fatah-controlled government body that exercises partial civil control over the Palestinian enclaves in the Israeli-occupied West Bank as a c ...
on 12 December 1995, as a result of the Oslo Accords
The Oslo Accords are a pair of interim agreements between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO): the Oslo I Accord, signed in Washington, D.C., in 1993; and the Oslo II Accord, signed in Taba, Egypt, in 1995. They marked the st ...
Interim Agreement on the West Bank. Nablus is surrounded by Israeli settlements
Israeli settlements, also called Israeli colonies, are the civilian communities built by Israel throughout the Israeli-occupied territories. They are populated by Israeli citizens, almost exclusively of Jewish identity or ethnicity, and hav ...
and was site of regular clashes with the Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the State of Israel. It consists of three service branches: the Israeli Ground Forces, the Israeli Air Force, and ...
(IDF) during the First Intifada
The First Intifada (), also known as the First Palestinian Intifada, was a sustained series of Nonviolent resistance, non-violent protests, acts of civil disobedience, Riot, riots, and Terrorism, terrorist attacks carried out by Palestinians ...
when the local prison was known for torture.
In the 1990s, Nablus was a hub of Palestinian nationalist
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenous p ...
activity in the West Bank and when the Second Intifada
The Second Intifada (; ), also known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada, was a major uprising by Palestinians against Israel and its Israeli-occupied territories, occupation from 2000. Starting as a civilian uprising in Jerusalem and October 2000 prot ...
began, arsonists of Jewish shrines in Nablus were applauded. After the controversy over the Jyllands-Posten Muhammad cartoons controversy, Muhammad cartoons in ''Jyllands-Posten'', originally published in Denmark in late September 2006, militias kidnapped two foreigners and threatened to kidnap more as a protest. In 2008, Noa Meir, an Israeli military spokeswoman, said Nablus remains "capital of terror" of the West Bank.
From the start of the Second Intifada
The Second Intifada (; ), also known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada, was a major uprising by Palestinians against Israel and its Israeli-occupied territories, occupation from 2000. Starting as a civilian uprising in Jerusalem and October 2000 prot ...
, which began in September 2000, Nablus became a flash-point of clashes between the IDF and Palestinians. The city has a tradition of political activism, as evinced by its nickname, ''jabal al-nar'' (Fire Mountain)Glenn E. Robinson''Building a Palestinian State: The Incomplete Revolution,''
Indiana University Press, 1997 p.57. and, located between two mountains, was closed off at both ends of the valley by Israeli checkpoints. For several years, movements in and out of the city were highly restricted. Nablus produced more List of Palestinian suicide attacks, suicide bombers than any other city during the Second Intifada. The city and the Palestinian refugee camps, refugee camps of Balata and Askar constituted the center of "knowhow" for the production and operation of the rockets in the West Bank. According to the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, 522 residents of Nablus and surrounding refugee camps, including civilians, were killed and 3,104 injured during IDF military operations from 2000 to 2005. In April 2002, following the Passover massacre—an attack by Palestinian militants that killed 30 Israeli civilians attending a Passover Seder, seder dinner at the Park Hotel in Netanya—Israel launched Operation Defensive Shield, a major Battle of Nablus, military operation targeting in particular Nablus and Jenin. At least 80 Palestinians were killed in Nablus during the operation and several houses were destroyed or severely damaged. The operation also resulted in severe damage to the historic core of the city, with 64 heritage buildings being heavily damaged or destroyed. IDF forces reentered Nablus during Operation Determined Path in June 2002, remaining inside the city until the end of September. Over those three months, there had been more than 70 days of full 24-hour curfews. According to Gush Shalom, IDF bulldozers damaged the al-Khadra Mosque, the Great Mosque, the al-Satoon Mosque and the Greek Orthodox Church in 2002. Some 60 houses were destroyed, and parts of the stone-paving in the old city were damaged. The al-Shifa ''Turkish bath, hammam'' was hit by three rockets from Apache helicopters. The eastern entrance of the Khan al-Wikala (old market) and three soap factories were destroyed in F-16 Fighting Falcon, F-16 bombings. The cost of the damage was estimated at $80 million US. In August 2016, the Old City of Nablus became a site of August 2016 Nablus clashes, fierce clashes between a militant group vs Palestinian police. On 18 August, two Palestinian Civil Police Force, Palestinian Police servicemen were killed in the city. Shortly after the raid of police on the suspected areas in the Old City deteriorated into a gun battle, in which three armed militia men were killed, including one killed by beating following his arrest. The person beaten to death was the suspected “mastermind” behind the August 18 shooting - Ahmed Izz Halaweh, a senior member of the armed wing of the Fatah movement the al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades. His death was branded by the UN and Palestinian factions as a part of “extrajudicial executions.” A widespread manhunt for multiple gunmen was initiated by the police as a result, concluding with the arrest of one suspect Salah al-Kurdi on 25 August.
Geography
 Nablus lies in a strategic position at a junction between two ancient commercial roads; one linking the Sharon plain, Sharon coastal plain to the Jordan Valley (Middle East), Jordan valley, the other linking Nablus to the
Nablus lies in a strategic position at a junction between two ancient commercial roads; one linking the Sharon plain, Sharon coastal plain to the Jordan Valley (Middle East), Jordan valley, the other linking Nablus to the Galilee
Galilee (; ; ; ) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon consisting of two parts: the Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and the Lower Galilee (, ; , ).
''Galilee'' encompasses the area north of the Mount Carmel-Mount Gilboa ridge and ...
in the north, and the biblical Judea
Judea or Judaea (; ; , ; ) is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the pres ...
to the south through the mountains. The city stands at an elevation of around Above mean sea level, above sea level, in a narrow valley running roughly east–west between two mountains: Mount Ebal
Mount Ebal (; ) is one of the two mountains near the city of Nablus in the West Bank (Bible, biblical ''Shechem''), and forms the northern side of the valley in which Nablus is situated, the southern side being formed by Mount Gerizim. The mount ...
, the northern mountain, is the taller peak at , while Mount Gerizim
Mount Gerizim ( ; ; ; , or ) is one of two mountains in the immediate vicinity of the State of Palestine, Palestinian city of Nablus and the biblical city of Shechem. It forms the southern side of the valley in which Nablus is situated, the nor ...
, the southern mountain, is high.
Nablus is located east of Tel Aviv, State of Israel, Israel, west of Amman, Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
and north of Jerusalem. Nearby cities and towns include Huwara and Aqraba Akraba (variants: Aqrab, Aqraba, Agrab or Aqrabiyah) may refer to:
Egypt
* Al-Aqrab Prison, a prison in Cairo, Egypt
Iraq
* Tell Agrab, an ancient settlement in Iraq in Diyala Governorate
Palestine
* Aqraba, Nablus, a Palestinian town in the Na ...
to the south, Beit Furik to the southeast, Tammun to the northeast, Asira ash-Shamaliya to the north and Kafr Qaddum and Tell (town), Tell to the west.
Old City
In the center of Nablus lies the old city, composed of six major quarters: Yasmina, Gharb, Qaryun, Aqaba, Qaysariyya, and Habala. Habala is the largest quarter and its population growth led to the development of two smaller neighborhoods: al-Arda and Tal al-Kreim. The old city is densely populated and prominent families include the Nimrs, Tuqans, and Abd al-Hadis. The large fortress-like compound of the Abd al-Hadi Palace built in the 19th century is located in Qaryun. The Al-Nimr Palace, Nimr Hall and the Tuqan Palace are located in the center of the old city. There are several mosques in the Old City: the Great Mosque of Nablus, An-Nasr Mosque, al-Tina Mosque, al-Khadra Mosque, Hanbali Mosque, al-Anbia Mosque, Ajaj Mosque and others.Semplici, Andrea and Boccia, Mario– Nablus, At the Foot of the Holy Mountain
Med Cooperation, p.17. There are six (
Turkish bath
A hammam (), also often called a Turkish bath by Westerners, is a type of steam bath or a place of public bathing associated with the Islamic world. It is a prominent feature in the culture of the Muslim world and was inherited from the model ...
s) in the Old City, the most prominent of them being al-Shifa and al-Hana. Al-Shifa was built by the Tuqans in 1624. Al-Hana in Yasmina was the last ''hamaam'' built in the city in the 19th century. It was closed in 1928 but restored and reopened in 1994. Several leather tanneries, ''souks'', pottery and textile workshops line the Old City streets. Also located in the Old City is the 15th-century Khan al-Tujjar (Nablus), Khan al-Tujjar caravanserai and the Manara Clock Tower, built in 1906.
Climate
The relatively temperate Mediterranean climate brings hot, dry summers and cool, rainy winters to Nablus. Spring arrives around March–April and the hottest months in Nablus are July and August with the average high being . The coldest month is January with temperatures usually at . Rain generally falls between October and March, with annual precipitation rates being approximately .Demographics
In 1596, the population consisted of 806 Muslim households, 20Samaritan
Samaritans (; ; ; ), are an ethnoreligious group originating from the Hebrews and Israelites of the ancient Near East. They are indigenous to Samaria, a historical region of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah that ...
households, 18 Christian households, and 15 Jewish households. Local Ottoman authorities recorded a population of around 20,000 residents in Nablus in 1849. In 1867 American visitors found the town to have a population of 4,000 'the chief part of whom are Mohammedans', with some Jews and Christians and 'about 150 Samaritans'. In the 1922 census of Palestine, 1922 British census of Palestine, there were a total of 15,947 inhabitants (15,238 Muslims, 544 Christians, 147 Samaritans, 16 Jews, and two Druze). Population continued to grow, rising to 17,189 (16,483 Muslims, 533 Christians, 160 Samaritans, seven Druze, and six Jews) at the 1931 census of Palestine with 309 in nearby suburbs (225 Muslims and 84 Christians).
The 1938 village statistics show a further increase to 19,200. The Village Statistics, 1945, 1945 village statistics list the population as 23,250 (22,360 Muslims, 680 Christians, and 120 "other").
According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS), Nablus had a population of 126,132 in 2007. In the PCBS's 1997 census, the city had a population of 100,034, including 23,397 Palestinian refugees, refugees, accounting for about 24% of the city's residents. Nablus' Old City had a population of 12,000 in 2006. The population of Nablus city comprises 40% of its Nablus Governorate, governorate's inhabitants.
Approximately half of population is under 20 years old. In 1997, the age distribution of the city's inhabitants was 28.4% under the age of 10, 20.8% from 10 to 19, 17.7% from 20 to 29, 18% from 30 to 44, 11.1% from 45 to 64 and 3.7% above the age of 65. The gender distribution was 50,945 males (50.92%) and 49,089 females (49.07%).
Religion
In 891 CE, during the early centuries ofIslam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
ic rule, Nablus had a religiously diverse population of Samaritans, Muslims and Christians. Arab geographer Shams al-Din al-Ansari al-Dimashqi, Al-Dimashqi, recorded that under the rule of the Mamluk Dynasty (Muslim Dynasty based in Egypt), local Muslims, Samaritans, Orthodox Christians, Catholics and Jews populated the city. At the 1931 census of Palestine, 1931 census, the population was counted as 16,483 Muslims, 533 Christians, 6 Jews, 7 Druses and 160 Samaritans. However, this census was taken after the 1929 Palestine riots which drove the Jews out of many majority-Arab cities.
The majority of the inhabitants today are Muslim, but there are small Palestinian Christian, Christian and Samaritan
Samaritans (; ; ; ), are an ethnoreligious group originating from the Hebrews and Israelites of the ancient Near East. They are indigenous to Samaria, a historical region of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah that ...
communities as well. Much of the local Palestinian people, Palestinian Muslim population of Nablus is believed to be descended from Samaritans who converted to Islam. Certain Nabulsi family names are associated with Samaritan ancestry – Muslimani, Yaish, and Shakshir among others. According to the historian Fayyad Altif, large numbers of Samaritans converted because of persecution and because the monotheistic nature of Islam made it easy for them to accept it.
In 1967, there were about 3,500 Christians of various denominations in Nablus, but that figure dwindled to about 650 in 2008. Of the Christian populace, there are seventy Orthodoxy#Christianity, Orthodox Christian families, about thirty Catholic (Roman Catholic and Eastern Melkite Catholic) families and thirty Anglican families. Most Christians used to live in the suburb of Rafidia
Rafidiya () is a neighborhood in the western part of the Palestinian city of Nablus. It was a separate village until it was merged into the municipality in 1966. In 1961, Rafidiya had 923 inhabitants, rising to 1,200 in 1983.
History
The remains o ...
in the western part of the city.
There are seventeen Islamic monuments and eleven mosques in the Old City. Nine of the mosques were established before the 15th century. In addition to Muslim houses of worship, Nablus contains an Orthodox church dedicated to Saint Justin Martyr, built in 1898, and the ancient Samaritan synagogue, which is still in use.Places in NablusNablus Website.
Economy
Beginning in the early 16th century, trade networks connecting Nablus toDamascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
and Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
were supplemented by the establishment of trading posts in the Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
and Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Gulf regions to the south and east, as well as in the Anatolian Peninsula and the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
islands of Crete and Cyprus. Nablus also developed trade relations with Aleppo, Mosul, and Baghdad.Doumani, 1995, Chapter: "The City of Nablus." The Ottoman government oversaw the safety and funding of the annual hajj (''qafilat al-hajj'') from Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
to the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina. Pilgrimage caravans became a key factor in the fiscal and political relationship between Nablus and the central government. For a brief period in the early 17th century, the governor of Nablus, Farrukh Pasha, was appointed leader of
the caravan (''amir al-hajj''), and he constructed a large commercial compound in Nablus for that purpose.
In 1882, there were 32 soap factories and 400 looms exporting their products throughout the Middle East. Nablus exported three-fourths of its soap — the city's most important commodity—to Cairo by caravan through Gaza
Gaza may refer to:
Places Palestine
* Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea
** Gaza City, a city in the Gaza Strip
** Gaza Governorate, a governorate in the Gaza Strip
Mandatory Palestine
* Gaza Sub ...
and the Sinai Peninsula, and by sea through the ports of Jaffa
Jaffa (, ; , ), also called Japho, Joppa or Joppe in English, is an ancient Levantine Sea, Levantine port city which is part of Tel Aviv, Tel Aviv-Yafo, Israel, located in its southern part. The city sits atop a naturally elevated outcrop on ...
and Gaza. From Egypt, and particularly from Cairo and Damietta, Nablus merchants imported mainly rice, sugar, and spices, as well as linen, cotton, and wool textiles. Cotton, soap, olive oil, and textiles were exported to Damascus, whence silks, high-quality textiles, copper, and a number luxury items, such as jewellery were imported. Outside the city limits, extensive fields of olive groves, ficus, fig and pomegranate orchards and grape vineyards covered the slopes. Crops such as tomatoes, cucumbers, melons and ''mulukhiyya'' were grown in the fields and grain mills were scattered across central Samaria. Nablus was also the largest producer of cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
in the Levant, producing over of the product by 1837.Doumani, 1995, Chapter: "Cotton Production in Jabal Nablus."
Today, Nablus has a bustling modern commercial center with restaurants, and shopping malls."Nablus shopping festival brightens up West Bank,"Mohammed Assadi, July 18, 2009, Malaysia Star. Traditional industries such as the production of soap, olive oil, and Palestinian handicrafts continue to operate in Nablus. Other industries include furniture production, tile production, stone quarrying, textile manufacturing and leather tanning. The city is widely known for sweets like kunafah, olive oil, soap and ice-cream. The Vegetable Oil Industry Co. is a Nablus factory that produces olive oil, and vegetable butter which is exported to
Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
. In 2000, the al-Huda Textiles factory in Nablus
produced 500 pieces of clothing daily; however, production dropped to 150–200 pieces in 2002. Al-Huda imports textiles from China and exports finished products to Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
. In 2003, there were eight restaurants and four hotels — the largest being al-Qasr and al-Yasmeen.Kim Lee, 2003, p. 354. The soap industry has suffered from the West Bank closures and IDF incursions. In 2008, only two soap factories were still open.
The Al-Arz ice-cream company is the largest of six ice-cream manufacturers in the Palestinian territories. The Nablus business developed from an ice-factory set up by Mohammad Anabtawi in the town centre in 1950. It produces 50 tons a day, and exports to Jordan and Iraq. Most of the ingredients are imported from Israel.Gideon Levy'Palestinian ice cream's big comeback,'
at Haaretz, 3 August 2012.'They buy the ingredients mainly from Israeli suppliers .' Before 2000, 13.4% of Nablus' residents worked in Israel, with the figure dropping to 4.7% in 2004. The city's manufacturing sector made up 15.7% of the economy in 2004, a drop from 21% in 2000. Since 2000, most of the workforce has been employed in agriculture and local trade. In the wake of the Intifada, unemployment rates rose from 14.2% in 1997 to 60% in 2004. According to an OCHA report in 2008, one of the reasons for the high unemployment was a ring of checkpoints around the city, leading to the relocation of many businesses. Since the removal of the Huwara, Hawara roadblock, the casbah has become a vibrant marketplace. Nablus is home to the Palestine Securities Exchange (PSE) and the al-Quds Financial Index, housed in the al-Qasr building in the Rafidia suburb of the city. The PSE's first trading session took place on 19 February 1997. In 2007, the capitalization of the PSE topped 3.5 million Jordanian dinars.
Education
According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS), in 1997, 44,926 were enrolled in schools (41.2% in primary school, 36.2% in secondary school, and 22.6% in high school). About 19.8% of high school students received bachelor diplomas or higher diplomas. In 2006, there were 234 schools and 93,925 students in theNablus Governorate
The Nablus Governorate () is an administrative district of Palestine located in the Central Highlands of the West Bank, 53 km north of Jerusalem. It covers the area around the city of Nablus which serves as the ''muhfaza'' (seat) of the go ...
; 196 schools are run by the Education Minister of the Palestinian National Authority, Education Ministry of the Palestinian National Authority, 14 by the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East, United Nations Relief and Works Agency (UNRWA) and 24 are private schools.
Nablus is also home to an-Najah National University, the largest List of Palestinian universities, Palestinian university in the West Bank. Founded in 1918 by the an-Najah Nabulsi School, it became a college in 1941 and a university in 1977. An-Najah was closed down by Israeli authorities during the First Intifada
The First Intifada (), also known as the First Palestinian Intifada, was a sustained series of Nonviolent resistance, non-violent protests, acts of civil disobedience, Riot, riots, and Terrorism, terrorist attacks carried out by Palestinians ...
, but reopened in 1991. Today, the university has three campuses in Nablus with over 16,500 students and 300 professors. The university's faculties include seven in the humanities and nine in the sciences.
Nablus has been ranked as one of the best cities in the Middle East to learn Arabic, with achieving 5th rank in the list. For non-Arabic aspirants, An-Najah University has faculties, providing courses related to Arabic language.
Healthcare
There are six hospitals in Nablus, the four major ones being al-Ittihad, St. Lukes, al-Watani (the National) and the Rafidia Surgery Hospital. The latter, located in Rafidia, a suburb in western Nablus, is the largest hospital in the city. Al-Watani Hospital specializes in oncology services. The Anglican St. Lukes hospital was founded in 1900 by the medical missionary Gaskoin Richard Morden WGaskoin Wright; the National Hospital was founded in 1910. In addition to hospitals, Nablus contains the al-Rahma and at-Tadamon clinics, the al-Razi medical center, the Amal Center for Rehabilitation and 68 pharmacies.Pharmaciesan
Hospitals
Nablus Municipality Guides. In addition to that, in 2001, Nablus Speciality Hospital was built, in which it is specialized in open heart surgery, angiograms and angioplasty, angioplasties. Rafidia Surgical Hospital is located in the city.
Culture and arts
Nablus and its culture enjoy a certain renown throughout the Palestinian Territories and the Arab world with significant and unique contributions to Palestinian culture, Palestinian cuisine, cuisine and Palestinian costumes, costume. ''Nabulsi'', meaning "from Nablus", is used to describe items such as Palestinian handicrafts, handicrafts (e.g. Nabulsi soap) and food products (e.g. Nabulsi cheese) that are made in Nablus or in the traditional Nablus style.Traditional costume
Nablus costume was of a distinctive style that employed colorful combinations of various fabrics. Because of its position as important trade center with a flourishing ''souk'' ("market"), in the late 19th century, there was a large choice of fabrics available in the city, fromDamascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
and Aleppo silk to Manchester cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
s and Calico (fabric), calicos. Similar in construction to the garments worn in the Galilee
Galilee (; ; ; ) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon consisting of two parts: the Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and the Lower Galilee (, ; , ).
''Galilee'' encompasses the area north of the Mount Carmel-Mount Gilboa ridge and ...
, both long and short Turkish culture, Turkish style jackets were worn over the ("robe"). For daily wear, were often made of white cotton or linen, with a preference for winged sleeves. In the summer, costumes often incorporated interwoven striped bands of red, green and yellow on the front and back, with appliqué and braidwork popularly decorating the ''qabbeh'' ("square chest piece").
Cuisine
 Nablus is one of the Palestinian cities that sustained elite classes, fostering the development of a culture of "high cuisine", such as that of
Nablus is one of the Palestinian cities that sustained elite classes, fostering the development of a culture of "high cuisine", such as that of Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
or Baghdad. The city is home to a number of food products well known throughout the Levant, the Arab world and the former provinces of the Ottoman Empire.
''Kanafeh'' (or Kunafa) is the best known ''Nabulsi'' sweet. It is made of several fine shreds of pastry noodles with honey-sweetened cheese in the center. The top layer of the pastry is usually dyed orange with food coloring and sprinkled with crushed pistachios. Now made throughout the Middle East, ''kanafeh Nabulsi'' uses a white-brine cheese called ''Nabulsi cheese, jibneh Nabulsi''. Boiled sugar is used as a syrup for ''kanafeh''.
Other sweets made in Nablus include ''baklawa'', "Tamriya", ''mabrumeh'' and ''ghuraybeh'', a plain pastry made of butter, flour and sugar in an "S"-shape, or shaped as fingers or bracelets.
Cultural centers

Soap production
Nabulsi soap or ''sabon nabulsi'' is a type of castile soap produced only in Nablus and made of three primary ingredients: virgin olive oil, water, and a sodium compound. Since the 10th century, Nabulsi soap has enjoyed a reputation for being a fine product, and has been exported across the Arab world and to Europe. Though the number of soap factories decreased from a peak of thirty in the 19th century to only two today, efforts to preserve this important part of Palestinian and Nabulsi cultural heritage continue. Made in a cube-like shape about tall and wide, the color of Nabulsi soap is like that of "the page of an old book." The cubes are stamped on the top with the seal of the factory that produces it. The soap's sodium compound came from the barilla plant. Prior to the 1860s, in the summertime, the barilla would be placed in towering stacks, burned, and then the ashes and coals would be gathered into sacks, and transported to Nablus from the area of modern-dayJordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
in large Camel train, caravans. In the city, the ashes and coals were pounded into a fine natural alkaline soda powder called . Today, is still used in combination with lime.
Local government
The city of Nablus is the ''muhfaza'' (seat) of theNablus Governorate
The Nablus Governorate () is an administrative district of Palestine located in the Central Highlands of the West Bank, 53 km north of Jerusalem. It covers the area around the city of Nablus which serves as the ''muhfaza'' (seat) of the go ...
, and is governed by a municipal council made up of fifteen elected members, including the mayor.
The two primary political parties in the municipal council are Hamas and Fatah. In the 2005 Palestinian municipal elections, the Reform and Change list representing the Hamas faction won 73.4% of the vote, gaining the majority of the municipal seats (13). Palestine Tomorrow, representing Fatah, gained the remaining two seats with 13.0% of the vote. Other political parties, such as the Palestinian People's Party and the Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine failed to gain any seats in the council, though they each received over 1,000 votes.
Yaish's four-year term legally expired in December 2009. While elections in the West Bank were scheduled for 17 July 2010, they were canceled because of Fatah's lack of agreement on list of candidates. Nablus was one of the most important municipalities where Fatah failed to resolve internal conflicts that resulted in two competing Fatah lists: one headed by former mayor Ghassan Shakaa and one headed by Amin Makboul.
In the October 2012 municipal elections, Hamas boycotted the polls, protesting the holding of elections while reconciliation efforts with Fatah were at a standstill. Former mayor Ghassan Shakaa, a former local Fatah leader, won the vote as an independent against Fatah member Amin Makboul and another independent candidate.
Mayors
Modern mayorship in Nablus began in 1869 with the appointment of Sheikh Mohammad Tuffaha by the Ottoman governor of Syria/Palestine. On 2 July 1980,Bassam Shakaa
Bassam Shakaa () (1930 – 22 July 2019) was mayor of Nablus from 1976 to 1982.
Biography Early life
Bassam Shakaa was a member of a distinguished family in Nablus.
He became a member of the Jordanian regional branch of the Ba'ath Party ...
, then mayor of Nablus, lost both of his legs as a result of a car bombing carried out by Israeli militants affiliated with the Gush Emunim Underground movement.
The current mayor, Adly Yaish, a Hamas member, was arrested by the Israel Defense Forces in May 2007, during Operation Summer Rains, launched in retaliation for the kidnapping of Israeli soldier Gilad Shalit by Hamas. Municipal council members Abdel Jabbar Adel Musa "Dweikat", Majida Fadda, Khulood El-Masri, and Mahdi Hanbali were also arrested. He spent 15 months in prison without being charged.
Municipal services
Occupied Housing Units by Locality and Connection to Sewage System in Housing Unit
Occupied Housing Units by Locality and Connection to Water Network in Housing Unit
Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics. Statistic from a 1997 census. The sewage system, established n the early 1950s, also connects the refugee camps of Balata, Askar and Ein Beit al-Ma'. Pipe water is provided for 100% of the city's households, primarily through a public network (99.3%), but some residents receive water through a private system (0.7%). The water network was established in 1932 by the British authorities and is fed by water from four nearby wells: Deir Sharaf, Far'a, al-Badan and Audala.
Fire department
Nablus is one of the few cities in the West Bank to have a fire department, which was founded in 1958. At that time, the "fire brigade" (as it was called) was composed of five members and one extinguishing vehicle. In 2007, the department had seventy members and over twenty vehicles. Until 1986, it was responsible for all of the northern West Bank, but today it only covers the Nablus and Tubas Governorates. From 1997 to 2006, Nablus' fire department extinguished 15,346 fires.Transportation
In the early 20th century, Nablus was the southernmost station of a spur from the Jezreel Valley railway's Afula station, itself a spur from the Hejaz railway. The extension of the railway to Nablus was built in 1911–12. During the beginning of the British Mandate, one weekly train was operated from Haifa to Nablus via Afula andJenin
Jenin ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and is the capital of the Jenin Governorate. It is a hub for the surrounding towns. Jenin came under Israeli occupied territories, Israeli occupation in 1967, and was put under the administra ...
. The railway was destroyed during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
, and the route of the line was bisected by the Green Line (Israel), Green Line.
The main Highway 60 (Israel–Palestine), Beersheba–Nazareth road running through the middle of the West Bank ends in Nablus, although the thoroughfare of local Arabs is severely restricted. The city was connected to Tulkarm, Qalqilya and Jenin
Jenin ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and is the capital of the Jenin Governorate. It is a hub for the surrounding towns. Jenin came under Israeli occupied territories, Israeli occupation in 1967, and was put under the administra ...
by roads which are now blocked by the Israeli West Bank barrier. From 2000 until 2011, Israel maintained Israel Defense Forces checkpoint, checkpoints such as Huwwara checkpoint which effectively cut off the city, severely curtailing social and economic travel. From January 2002, buses, taxis, trucks and private citizens required a permit from the Israeli military authorities to leave and enter Nablus. Since 2011, there has been a relaxation of travel restrictions and the dismantlement of some checkpoints.
The nearest airport is the Ben Gurion International Airport in Lod, Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, but because of restrictions governing the entry of Palestinians to Israel, and their lack of access to foreign Embassies to get travel visas, many residents must travel to Amman, Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
to use the Queen Alia International Airport, which requires passage through a number of checkpoints and the Jordanian border. Taxis are the main form of public transportation within Nablus and the city contains 28 taxi offices and garages.
Sports
International relations
Twin towns and sister cities
Nablus is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned, or has sister city relationships with: * Lille, France * Nazareth, Israel * Dublin, Ireland * Como, Italy * Metropolitan City of Florence, Italy * Naples, Italy * Poznań, Poland * Rabat, Morocco * Stavanger, Norway * Khasavyurt, Russia * Dundee, United Kingdom * Boulder, Colorado, United States23.12 2016; Times of Israel
See also
* List of cities administered by the Palestinian National Authority * List of people from NablusNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*Welcome To The City of Nablus
Nablus City
Welcome to Palestine
A site explaining the reasons for the devastated Palestinian economy
Nablus the Culture, reviving cultural life in Nablus
Nablus after Five Years of Conflict
December 2005 report by Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, OCHA (PDF).
Archaeological Remains Found in Nablus
Picture showing Nablus from east (Panorama)
Picture showing east region of Nablus (Panorama) – The picture taken from Askar
Bahjat Sabri, "Urban Aspects in the City of Nablus in the First Half of the Nineteenth Century" ''An-Najah University Journal for Research - Humanities'', Volume 6 (1992)
{{Authority control Nablus, Cities in the West Bank History of Palestine (region) Historic Jewish communities Levant Canaanite cities Municipalities of Palestine Palestinian Christian communities