MyRobotLab on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
InMoov is a humanoid robot, constructed out of 3D printable plastic body components, and controlled by 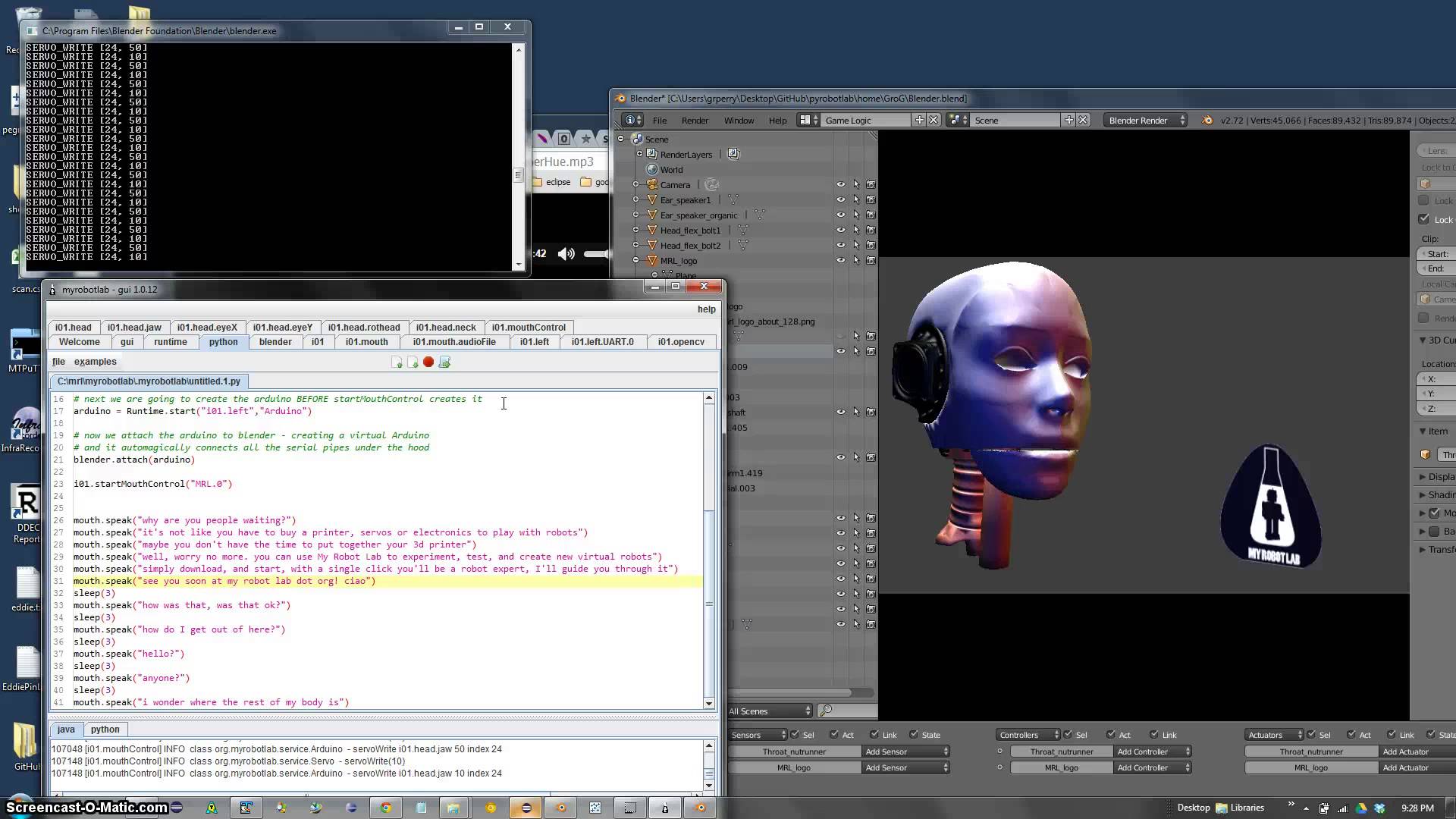 InMoov is able to perceive sound, see, speak and move independently. The robot is able to identify its environment and through micro-cameras in some projects recognize voice commands that are issued by the owner. It features different touch sensors, PIR and 3 dimensional, in addition, the
InMoov is able to perceive sound, see, speak and move independently. The robot is able to identify its environment and through micro-cameras in some projects recognize voice commands that are issued by the owner. It features different touch sensors, PIR and 3 dimensional, in addition, the
Arduino
Arduino () is an Italian open-source hardware and open-source software, software company, project, and user community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for building digital devices. Its hardwar ...
microcontrollers.
InMoov is a robot developed for artistic purposes by French sculptor Gaël Langevin in September 2011. (The first blueprint files were published in January 2012 on Thingiverse.) Its peculiarity is that it is reproducible with a simple 3D printer small format (12cm3) and its files are under Creative Commons
Creative Commons (CC) is an American non-profit organization and international network devoted to educational access and expanding the range of creative works available for others to build upon legally and to share. The organization has release ...
license (CC-BY-NC). The project is a platform for development and robot learning. On this basis and through this concept there were developed different iterations.
InMoov uses MyRobotLab software for control. MyRobotLab is an open source service based robotics framework. Its primarily written in Java, but has bindings for Python. It has a Web UI written in AngularJS which allows remote control. One of the services is a virtual InMoov which can be used to develop or test without the physical robot.
 InMoov is able to perceive sound, see, speak and move independently. The robot is able to identify its environment and through micro-cameras in some projects recognize voice commands that are issued by the owner. It features different touch sensors, PIR and 3 dimensional, in addition, the
InMoov is able to perceive sound, see, speak and move independently. The robot is able to identify its environment and through micro-cameras in some projects recognize voice commands that are issued by the owner. It features different touch sensors, PIR and 3 dimensional, in addition, the Kinect
Kinect is a discontinued line of motion sensing input devices produced by Microsoft and first released in 2010. The devices generally contain RGB color model, RGB cameras, and Thermographic camera, infrared projectors and detectors that map dep ...
allows InMoov to see and analyze the 3-dimensional space of the robot's environment.
Through the use of open technologies and open source components such as printed circuit Arduino, many developers have changed InMoov in order to extend its functions to be used as the basis for many types of development. The most ambitious is the artificial recognition programs because the robot incorporates on its single platform a micro-camera, sensors and operating motion system, and the ability to connect to any computer.
The original prototype participated in the Maker Faire Rome in 2013, where he aroused great interest for its potential as a development model for robotic prostheses. Because its parts can be entirely made with a 3D printer, its potential uses are varied.
References
{{Humanoid robots Open-source hardware Humanoid robots