Mutilated victory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mutilated victory () is a term coined by Gabriele D'Annunzio at the end of
 Italy joined
Italy joined 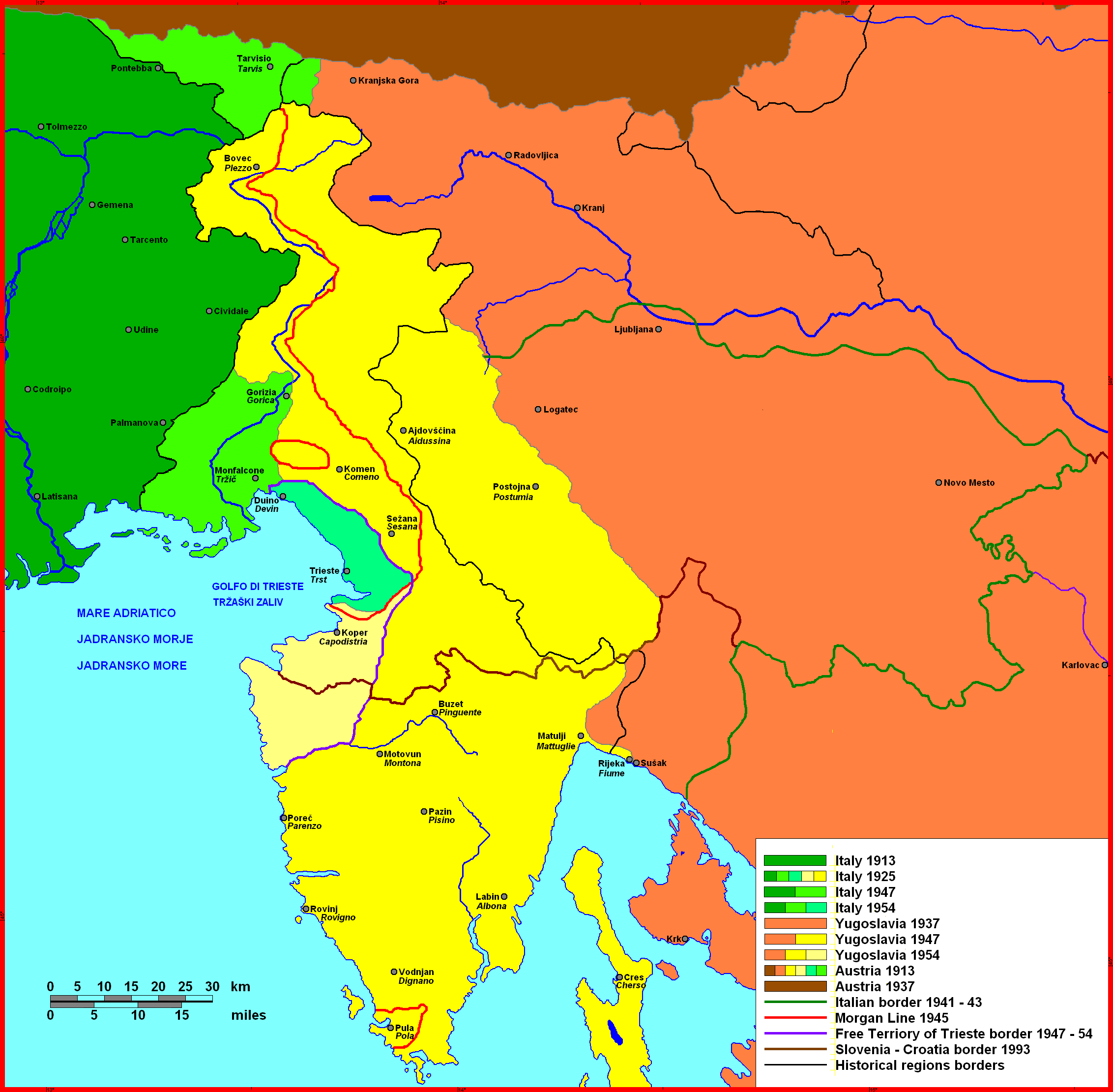 Therefore, most of the criticism directed against the Allies and the government focused on
Therefore, most of the criticism directed against the Allies and the government focused on
 These demands were outlined by the Italian Foreign Minister Sidney Sonnino to secure a strong Italian presence in the Mediterranean. The acquisition of the area surrounding the Adriatic, especially the port city of Trieste, would strengthen Italian naval presence and keep pace with possible postwar territorial gains in the area by the other members of the Entente. The demands for lands carved from the Ottoman Empire and the African colonies were motivated by national ambition.
Sonnino however delayed a declaration of war against Germany although Italy had declared war on Austria-Hungary. By May 1915, the Italian push towards Ljubljana reached a stalemate with Austrian forces in the Alps while Britain, France and Germany were embroiled in a stalemate of their own on the Western Front. The outcome of the war was not yet clear, and Sonnino stood by a position of neutrality with Germany. That would soften as Sonnino realized Italy’s army was in no position to carry out a protracted war, and pressure from within Italy demanded solidarity with the Entente. The Italian government declared war on Germany on 28 August 1916.
These demands were outlined by the Italian Foreign Minister Sidney Sonnino to secure a strong Italian presence in the Mediterranean. The acquisition of the area surrounding the Adriatic, especially the port city of Trieste, would strengthen Italian naval presence and keep pace with possible postwar territorial gains in the area by the other members of the Entente. The demands for lands carved from the Ottoman Empire and the African colonies were motivated by national ambition.
Sonnino however delayed a declaration of war against Germany although Italy had declared war on Austria-Hungary. By May 1915, the Italian push towards Ljubljana reached a stalemate with Austrian forces in the Alps while Britain, France and Germany were embroiled in a stalemate of their own on the Western Front. The outcome of the war was not yet clear, and Sonnino stood by a position of neutrality with Germany. That would soften as Sonnino realized Italy’s army was in no position to carry out a protracted war, and pressure from within Italy demanded solidarity with the Entente. The Italian government declared war on Germany on 28 August 1916.
Vittoria mutilata
on Fondazione Feltrinelli, Erica Grossi. {{Authority control 1919 in Italy Modern history of Italy Italian nationalism Italian irredentism Gabriele D'Annunzio
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, used by a part of Italian nationalists to denounce the partial infringement (and request the full application) of the 1915 pact of London concerning territorial rewards in favour of the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
.
As a condition for entering the war against Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Italy was promised, in the treaty of London signed in 1915 with the powers of the Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It was built upon th ...
, recognition of control over Southern Tyrol, the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (, , , , ) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. It consisted of three regions: the Margraviate of Istria in the south, Gorizia and Gradisca in the north, and the Imperial Free City ...
and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
. These lands were inhabited by Italians
Italians (, ) are a European peoples, European ethnic group native to the Italian geographical region. Italians share a common Italian culture, culture, History of Italy, history, Cultural heritage, ancestry and Italian language, language. ...
which had not become part of the Kingdom upon Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
in the late 19th century, Austrian German
Austrian German (), Austrian Standard German (ASG), Standard Austrian German (), Austrian High German (), or simply just Austrian (), is the variety of Standard German written and spoken in Austria and South Tyrol. It has the highest prestige ( ...
s (Tyrol
Tyrol ( ; historically the Tyrole; ; ) is a historical region in the Alps of Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary, f ...
eans) and Slavs (Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( ), are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, Slovenian culture, culture, and History of Slove ...
and Croats
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
). Additionally, Italy was assured ownership of the Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; , ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger and 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. This island group generally define ...
, possessions in Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
, and a sphere of influence around the Turkish city of Antalya
Antalya is the fifth-most populous city in Turkey and the capital of Antalya Province. Recognized as the "capital of tourism" in Turkey and a pivotal part of the Turkish Riviera, Antalya sits on Anatolia's southwest coast, flanked by the Tau ...
, alongside a possible enlargement of her colonial presence in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
.
At the end of the war, despite the initial intention of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
to remain faithful to the pact, objections by the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, eventually supported by the British and the French, and in particular conflict over the concept of self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
spelled out by President Wilson in his Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms to the United States Congress ...
, led to the partial disapplication of the agreement and to the retraction of some promises recognized at the onset of the conflict. Italy completed the national unification of the country by annexing the provinces of Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin language, Ladin and ; ; ; ; ; ), also known in English as Trent, is a city on the Adige, Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the Trentino, autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th ...
and Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
, and also gained South Tyrol
South Tyrol ( , ; ; ), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano – South Tyrol, is an autonomous administrative division, autonomous provinces of Italy, province in northern Italy. Together with Trentino, South Tyrol forms the autonomo ...
, Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
and some colonial compensations, but was not awarded Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, with the exception of the city of Zara. Fiume
Rijeka (;
Fiume ( �fjuːme in Italian and in Fiuman Venetian) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and in 2021 had a po ...
, a city with a sizeable Italian population, although not included in the Pact of London, was occupied for a year by volunteers led by D'Annunzio, leading to an international crisis.
Together with the economical cost of mobilization and the social turmoil ensuing from the end of the war, the partial infringement of the treaty is generally believed to have fuelled the consolidation of Italian irredentism
Italian irredentism ( ) was a political movement during the late 19th and early 20th centuries in Kingdom of Italy, Italy with irredentism, irredentist goals which promoted the Unification of Italy, unification of geographic areas in which indig ...
and Italian nationalism, and became a focal point in the propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded l ...
, among others, of the National Fascist Party
The National Fascist Party (, PNF) was a political party in Italy, created by Benito Mussolini as the political expression of Italian fascism and as a reorganisation of the previous Italian Fasces of Combat. The party ruled the Kingdom of It ...
, which sought to expand the borders of the Italian state.
Description
 Italy joined
Italy joined World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
in 1915 on the side of the Allies, after negotiating the secret Treaty of London with the Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It was built upon th ...
(Britain, France, and Russia). According to the secret pacts of London, the following territories were promised to Italy in case of victory: Trentino
Trentino (), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento (; ; ), is an Autonomous province#Italy, autonomous province of Italy in the Northern Italy, country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the Regions of Italy, region of Tren ...
and South Tyrol
South Tyrol ( , ; ; ), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano – South Tyrol, is an autonomous administrative division, autonomous provinces of Italy, province in northern Italy. Together with Trentino, South Tyrol forms the autonomo ...
, the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (, , , , ) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. It consisted of three regions: the Margraviate of Istria in the south, Gorizia and Gradisca in the north, and the Imperial Free City ...
(Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
, Gorizia and Gradisca, and Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
), territories in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, possessions in Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
( Vlora and Saseno), and compensations in case of a colonial partition of the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
' empires. The content of the pact of London was made public in 1917 by the Russians, following their withdrawal from the War after the communist revolution, in order to criticize the "old diplomacy" of the capitalist European powers. While France and Britain remained bound by the treaty of London, the US president Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
(who joined the Allies in 1917) opposed it and presented on January 8, 1918 Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms to the United States Congress ...
to redraw the map of Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
on the basis of nationality
Nationality is the legal status of belonging to a particular nation, defined as a group of people organized in one country, under one legal jurisdiction, or as a group of people who are united on the basis of culture.
In international law, n ...
and ethnicity
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they Collective consciousness, collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, ...
. During the decisive Italian offensive, the nationalist poet Gabriele D'Annunzio coined the term ''mutilated victory'' by publishing an article in the Corriere della Sera dated October 24, 1918 and titled "Our victory will not be mutilated".
Italy's prime minister Vittorio Orlando, one of the Big Four of World War I, and his foreign minister Sidney Sonnino, an Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
of British origins, arrived at the Paris Peace Conference, 1919 in order to secure most of the London pacts. Considerable results were achieved with the treaties and agreements signed in 1919 and 1920. Most importantly, Trent-South Tyrol
South Tyrol ( , ; ; ), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano – South Tyrol, is an autonomous administrative division, autonomous provinces of Italy, province in northern Italy. Together with Trentino, South Tyrol forms the autonomo ...
and the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (, , , , ) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. It consisted of three regions: the Margraviate of Istria in the south, Gorizia and Gradisca in the north, and the Imperial Free City ...
(Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
, Gorizia and Gradisca, and Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
) became part of the Italian regions of Trentino-Alto Adige and Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
- Venezia Giulia. The colonial compensations obtained by Italy were: the recognition and enlargement of the Italian Islands of the Aegean; the enlargement of the Italian possessions in Libya and in the Horn of Africa; and the establishment of an Italian sphere of influence over the Ottoman area of Antalya
Antalya is the fifth-most populous city in Turkey and the capital of Antalya Province. Recognized as the "capital of tourism" in Turkey and a pivotal part of the Turkish Riviera, Antalya sits on Anatolia's southwest coast, flanked by the Tau ...
, later abandoned with the independence of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
. Italy also received the province of Zadar
Zadar ( , ), historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian, ; see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited city in Croatia. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar ...
with some islands in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
and set up an Italian protectorate over Albania with the occupation of Vlora, which lasted until 1920 when domestic opposition within the Italian Armed Forces and the Vlora war led Italy to voluntarily abandon Albania; with the treaty of Tirana, Italy retained the island of Saseno and recognition of Albania as being within its sphere of influence (which was confirmed by the League of Nations in 1921). Finally, the disintegration of its two main rival powers (Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
in Europe and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
in the Mediterranean) and the entrance in the League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
' security council as a permanent member, cemented Italy's status as a great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
.
 Therefore, most of the criticism directed against the Allies and the government focused on
Therefore, most of the criticism directed against the Allies and the government focused on Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
and the city of Fiume
Rijeka (;
Fiume ( �fjuːme in Italian and in Fiuman Venetian) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and in 2021 had a po ...
(which was later occupied by a contingent led by Gabriele D'Annunzio). A more substantial transfer of Dalmatian territories to Italy (favoured by Sonnino) was complicated to achieve because of its Slavic population, whereas Fiume was ethnically an Italian city (and as such proposed by Orlando as an alternative), but not included in the Pact of London. Wilson vetoed these proposals on the ground that already many Germanophones and Slavs were to be placed under Italian administration. This led Orlando and Sonnino to temporarily abandon the conference in protest. Orlando had refused to see the outcome of the war as a mutilated victory and once replied to calls for greater expansion that "Italy today is a great state... on par with the great historic and contemporary states. This is, for me, our main and principal expansion." But the disgruntled climate ultimately forced Orlando to resign, and the treaties he had negotiated were signed by his successors Francesco Saverio Nitti and Giovanni Giolitti
Giovanni Giolitti (; 27 October 1842 – 17 July 1928) was an Italian statesman. He was the prime minister of Italy five times between 1892 and 1921. He is the longest-serving democratically elected prime minister in Italian history, and the sec ...
.
From a contemporary historical point of view, it has sometimes been observed how much of Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who, upon assuming office as Prime Minister of Italy, Prime Minister, became the dictator of Fascist Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 un ...
's foreign policy was presented as an attempt to amend the injustices lamented as stemming from the mutilated victory: Fiume was taken in 1924, Albania was turned into a client state under Zog I and merged into the Kingdom in 1939, and Dalmatia was annexed during the occupation of Yugoslavia—events that have been sporadically accused of prolonging Italy's participation in World War II. Some historians have at times seen the actions carried by the Fascist government on the subject as part of a larger imperialist project that brought Italy to descend into foreign affairs, by intervening in Spain, conquering Ethiopia, and occupying southern France
Southern France, also known as the south of France or colloquially in French as , is a geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi atlantique'', Atlas e ...
and Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
. For historian Gaetano Salvemini "Fascism originated, grew, triumphed, and ultimately died, on the myth of mutilated victory". Conversely, attempts to include in the Italian nation state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the State (polity), state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly ...
the detached lands populated by Italophones have also been lauded and supported, with subjects failing to recognize said urgency being decried by poet Gabriele D’Annunzio as "insane and vile".
Notwithstanding the political characterisations of the Interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
, the final settlement of peace after the end of World War II, which had deprived Italy of all of the lands to the east of the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
(except for the city of Trieste), proved to be unpopular among the Italian opinion and object of harsh criticism, being described by President Luigi Einaudi
Luigi Numa Lorenzo Einaudi (; 24 March 1874 – 30 October 1961) was an Italian politician, economist and banker who served as President of Italy from 1948 to 1955 and is considered one of the founding fathers of the 1946 Italian institutional ...
as leading to a condition of "painfully mutilated" national unity.
Italy and the Triple Alliance
Angered by the French seizure ofTunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
, in which Italy had extensive economic interests and had viewed as a possible area for colonial annexation, in 1882, Italy joined the Triple Alliance with Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
as a means of defending against further French aggression and gaining diplomatic backing for coming disputes. The alliance, however, proved troublesome. Italy and Austria-Hungary had been rivals for many years; the latter had, for years, held northeastern Italy, opposed Italian unification, and it still held Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
and Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
, Zara and the coast of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, the primary targets of the Italian irredentist movement.
As such, in the years before 1914, Italy engaged in diplomatic maneuvers to ally itself with the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. In 1902, Italy concluded a secret treaty with Britain in which Italy abandoned the Triple Alliance, with the stipulation that it be given the territories currently controlled by Austria.
Treaty of London (1915)
AfterWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
erupted, the pressure by both sides for Italy to enter the war increased. On April 26, 1915, the Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It was built upon th ...
and Italy signed a secret agreement, called the Treaty of London, that stipulated the terms of Italy’s participation in World War I against the Germany-Austrian Alliance. If Italy declared war on Germany and the Entente emerged victorious, Italy would be awarded territories of the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful Dynasty, dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout ...
in the Southern Alps and in the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, specifically the regions of Trentino
Trentino (), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento (; ; ), is an Autonomous province#Italy, autonomous province of Italy in the Northern Italy, country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the Regions of Italy, region of Tren ...
and the South Tyrol
South Tyrol ( , ; ; ), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano – South Tyrol, is an autonomous administrative division, autonomous provinces of Italy, province in northern Italy. Together with Trentino, South Tyrol forms the autonomo ...
(up to the northern limit of the Brenner Pass
The Brenner Pass ( , shortly ; ) is a mountain pass over the Alps which forms the Austria-Italy border, border between Italy and Austria. It is one of the principal passes of the Alps, major passes of the Eastern Alpine range and has the lowes ...
), the Friuli-Julian area, Trieste and the surrounding area, Istria, and the North of the Dalmatian Cost including the city of Šibenik
Šibenik (), historically known as Sebenico (), is a historic town in Croatia, located in central Dalmatia, where the river Krka (Croatia), Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea. Šibenik is one of the oldest Croatia, Croatian self-governing cities ...
. Other possible territories included in the treaty were the city of Vlorë
Vlorë ( ; ; sq-definite, Vlora) is the List of cities and towns in Albania, third most populous city of Albania and seat of Vlorë County and Vlorë Municipality. Located in southwestern Albania, Vlorë sprawls on the Bay of Vlorë and is surr ...
in Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
, some part on the south Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
n coast, as well as a share of the German colonial empire
The German colonial empire () constituted the overseas colonies, dependencies, and territories of the German Empire. Unified in 1871, the chancellor of this time period was Otto von Bismarck. Short-lived attempts at colonization by Kleinstaat ...
.
 These demands were outlined by the Italian Foreign Minister Sidney Sonnino to secure a strong Italian presence in the Mediterranean. The acquisition of the area surrounding the Adriatic, especially the port city of Trieste, would strengthen Italian naval presence and keep pace with possible postwar territorial gains in the area by the other members of the Entente. The demands for lands carved from the Ottoman Empire and the African colonies were motivated by national ambition.
Sonnino however delayed a declaration of war against Germany although Italy had declared war on Austria-Hungary. By May 1915, the Italian push towards Ljubljana reached a stalemate with Austrian forces in the Alps while Britain, France and Germany were embroiled in a stalemate of their own on the Western Front. The outcome of the war was not yet clear, and Sonnino stood by a position of neutrality with Germany. That would soften as Sonnino realized Italy’s army was in no position to carry out a protracted war, and pressure from within Italy demanded solidarity with the Entente. The Italian government declared war on Germany on 28 August 1916.
These demands were outlined by the Italian Foreign Minister Sidney Sonnino to secure a strong Italian presence in the Mediterranean. The acquisition of the area surrounding the Adriatic, especially the port city of Trieste, would strengthen Italian naval presence and keep pace with possible postwar territorial gains in the area by the other members of the Entente. The demands for lands carved from the Ottoman Empire and the African colonies were motivated by national ambition.
Sonnino however delayed a declaration of war against Germany although Italy had declared war on Austria-Hungary. By May 1915, the Italian push towards Ljubljana reached a stalemate with Austrian forces in the Alps while Britain, France and Germany were embroiled in a stalemate of their own on the Western Front. The outcome of the war was not yet clear, and Sonnino stood by a position of neutrality with Germany. That would soften as Sonnino realized Italy’s army was in no position to carry out a protracted war, and pressure from within Italy demanded solidarity with the Entente. The Italian government declared war on Germany on 28 August 1916.
Wilson's opposition
In January 1917, British Foreign SecretaryArthur Balfour
Arthur James Balfour, 1st Earl of Balfour (; 25 July 184819 March 1930) was a British statesman and Conservative Party (UK), Conservative politician who served as the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1902 to 1905. As Foreign Secretary ...
wrote a letter to American President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
expressing his disapproval of the promise to give Italy the Adriatic territories. In a later trip to the United States in May to speak with American diplomat Edward M. House about the pact, Balfour made it clear that Britain had no particular ill will against Austria-Hungary and that the planned transfer of the Slavic lands to Italy would only create more problems. While American-Italian diplomatic dialogue regarding the claims did not take place prior to the Peace Conference, Wilson’s own stance on the matter was clear in his Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms to the United States Congress ...
, which urged for the Italian border with Austria to be redrawn along "clearly recognizable lines of nationality". His first point urged for no international agreements to be negotiated in secret so he refused to recognise the arrangements made under the pact. Sonnino's plans for securing the Adriatic were ignored, as were the imperial aims of Italy, and concessions were made in the form of postwar American economic aid.
Aftermath
The cause of mutilated victory was embraced by many Italians, particularly in the irredentist, monarchical, militaristic factions. The poet Gabriele D'Annunzio criticized in print and in speeches the failures of Prime Minister Vittorio Emanuele Orlando at the proceedings in Versailles, particularly in his attempts to acquire the city ofFiume
Rijeka (;
Fiume ( �fjuːme in Italian and in Fiuman Venetian) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and in 2021 had a po ...
( Croatian: ''Rijeka''), which, notwithstanding the fact that its inhabitants were more than 90% ethnic Italians, was supposed to be ceded by Austria to the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. On September 12, 1919, D’Annunzio took matters into his own hands and led a militia of 2,600 men against a mixed force of Allied soldiers to occupy the city. In Fiume, the victors established the Italian Regency of Carnaro, an unrecognized state based on the Charter of Carnaro.
While the regime would be short-lived, its effect on the people and politics of the Kingdom of Italy would leave their mark on the following decades of Italian history. Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who, upon assuming office as Prime Minister of Italy, Prime Minister, became the dictator of Fascist Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 un ...
was resolute to endorse the safeguard of national unity during the period of the creation of the '' Fasci Italiani di Combattimento'', the precursor of the National Fascist Party. Mussolini, an interventionist in World War I, attributed Italy’s great price of over 1.2 million casualties and 148 billion lire of expenditure to the weakness of the national government and to the disloyal attitude of the country’s former allies.Mack Smith, Denis (1997). Modern Italy. The University of Michigan Press.
See also
* Italian entry into World War I * Italian front (World War I) *Military history of Italy during World War I
Although a member of the Triple Alliance, Italy did not join the Central Powers – Germany and Austria-Hungary – when the war started with Austria-Hungary's declaration of war on Serbia on 28 July 1914. In fact, the two Central Powers had tak ...
* Stab in the back myth
* Pyrrhic victory
A Pyrrhic victory ( ) is a victory that inflicts such a devastating toll on the victor that it is tantamount to defeat. Such a victory negates any true sense of achievement or damages long-term progress.
The phrase originates from a quote from ...
References
Bibliography
* Burgwyn, H. James. ''The Legend of the Mutilated Victory'' (Greenwood Press, 1993). * Lowe, C.J. ''Italian Foreign Policy 1870-1940'' (2002). * Mack Smith, Denis. ''Modern Italy'' (University of Michigan Press, 1997). * Wilcox, Vanda. "From heroic defeat to mutilated victory: The myth of Caporetto in Fascist Italy". in Jenny Macleod, ed. ''Defeat and Memory'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2008) pp. 46–61.External links
Vittoria mutilata
on Fondazione Feltrinelli, Erica Grossi. {{Authority control 1919 in Italy Modern history of Italy Italian nationalism Italian irredentism Gabriele D'Annunzio