Muscle Imbalance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Muscle balance is necessary for muscles to perform their customary roles and move normally; muscle imbalance occurs when there is a lack of parity between corresponding agonist and antagonist muscles. Muscular imbalance can also arise when a muscle performs outside of its normal physiological muscle function.
Muscles are considered balanced when the muscles that surround a joint work together harmoniously, i.e. with appropriate opposing force, to keep the bones aligned where they meet at the joint. This permits normal human movement.
Muscles can be categorized as either functional or pathological. Muscle imbalance can be caused either by adaptation of a functional muscle or by dysfunction in a muscle suffering a pathology.

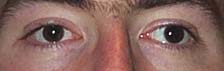 Lazy eye, in particular
Lazy eye, in particular
Symptoms
Classic symptoms of muscle imbalances are usually pain associated with the affected joint. Symptoms can vary depending on what stage their muscular imbalance is, functional or pathological, but commonly exhibit small tissue damage or lesions accompanied by a change in muscle movement patterns. Symptoms may occur after injury or surgery, where the recuperation of the joint affected is left untreated causing either tension or restriction to flexibility and strength of the prime movers.Tennis elbow
Tennis elbow
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis is an enthesopathy (attachment point disease) of the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis on the lateral epicondyle. It causes pain and tenderness over the bony part of the lateral epi ...
is the most common elbow problem among athletes, highly associated with world class tennis players, it is a condition that involves the common wrist extensor origin, in particular the origin of extensor carpi radialis. The causes for tennis elbow includes any activity, not only tennis, where the repetitive use of the extensor muscles of the forearm may cause acute or chronic tendonitis of the tensinous insertion of these muscles at the lateral epicondyle of the elbow. The condition itself is most common with painters, plumbers, and carpenters. Further studied have shown that auto-workers, butchers and cooks also get tennis elbow more often than the rest of the population.
Lazy eye
 Lazy eye, in particular
Lazy eye, in particular strabismus
Strabismus is an eye disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is pointed at an object can alternate. The condition may be present occasionally or constantly. If present during a ...
may be the result of coordination between the extraocular muscles
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in human eye, humans and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior oblique muscle, superior and inferior ...
, which prevents a person on directing both eyes in unison towards the same fixation point. The main cause of strabismus is usually the muscular imbalance of the six surrounding muscles that allow both eyes to focus on the same object. As each eye does not have the same focus, different images are sent to the brain, confusing it, resulting in the brain ignoring the image from the weaker eye and if left untreated will cause a loss of vision in the ignored eye called amblyopia
Amblyopia, also called lazy eye, is a disorder of sight in which the brain fails to fully process input from one eye and over time favors the other eye. It results in decreased vision in an eye that typically appears normal in other aspects. Amb ...
. Further symptoms of strabismus include decreased vision, double vision
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occ ...
, headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
s, asthenopia
Eye strain, also medically termed as asthenopia (), is a common eye condition characterized by non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, pain in or around the eyes, blurred vision, headache, and occasional double vision.
These symptoms tend to ...
and eye fatigue.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's Vertebral column, spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others ...
, is a medical condition where a person's spine has several irregular curves that are located between the neck and the pelvis. Symptoms of scoliosis in mild cases usually exhibit abnormal posture, back pain, tingling or numbness in the legs and in worse cases can exhibit breathing problems, fatigue, permanent deformities and in rare cases heart problems.
Functional and pathological muscle imbalance
Functional imbalance
Functional Imbalances are when the muscles adapt in response for detailed muscle movement patterns, including unequal values in strength or flexibility of antagonistic muscle groups, usually apparent in athletes of different sports ranging from soccer to baseball. This type of imbalance is the first stage, it is painless, atraumatic (causes minimal tissue injury), adaptive to change and activity specific. Studies confirm this as they find the link between muscle imbalance and athletes who perform at elite levels, this also relates to injury occurrence is not treated to muscle specific rehabilitation.Pathological imbalance
Pathological muscle imbalance occurs when the imbalance of the muscles begin to inhibit function. This pathological muscle imbalance may or may not result from a traumatic event, it is usually associated with pain and dysfunction, although there are cases where pain is not apparent, however pathological muscle imbalances ultimately lead to joint dysfunction and changes in normative muscle movement patterns. It would be good to note that this imbalance can progress to either tissue damage and pain or altered movement pattern, with the constant being tightness or weakness. A study has shown that athletes that exhibit shoulder pain have been linked to have decreasedrotator cuff
The rotator cuff (SITS muscles) is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles a ...
muscle strength and have concluded that they are more susceptible to rotator cuff tear
Rotator cuff tendinopathy is a process of senescence. The pathophysiology is mucoid degeneration. Most people develop rotator cuff tendinopathy within their lifetime.
As part of rotator cuff tendinopathy, the tendon can thin and develop a defec ...
s and type II superior labrum anterior and posterior lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
s.
Diagnosis
Muscle imbalance can be characterized by different factors, namely where the muscle imbalance is on the body, diagnosis varies for these specific areas as each area needs to be handled differently. Other signs include joint pain or muscular pain, abnormal joint movement patterns or in some cases, muscle tears and lesions. It can be diagnosed by demonstrating any one of the following: * Joint inflammation and pain caused by musclelesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
.
* Abnormal muscle movement pattern resulting from the compensation of the joint inflammation.
* Patient history of previous injury can predict an onset of muscular imbalance
Treatment
Although treatment for tennis elbow prior 2010 was unknown because the etiology remained unclear, tests confirmed that the cause was an imbalance with the agonist-antagonist functional relationship. Treatment now includes anti-inflammatory medicines, rest, equipment check, physical therapy, braces, steroid injections, shock wave therapy and if symptoms persist after 6 to 12 months, doctors may recommend surgery. Although treatment varies depending on how bad eye alignment is and also the underlying causes of strabismus. Treatment for strabismus may includeorthoptics
Orthoptics is a profession allied to the eye care profession. Orthoptists are the experts in diagnosing and treating defects in eye movements and problems with how the eyes work together, called binocular vision. These can be caused by issues with ...
a term used for eye muscle training, this treatment can be provided by orthoptists
Vision therapy (VT), or behavioral optometry, is an umbrella term for alternative medicine treatments using eye exercises, based around the pseudoscientific claim that vision problems are the true underlying cause of learning difficulties, partic ...
and also optometrists
Optometry is the healthcare practice concerned with examining the eyes for visual defects, prescribing corrective lenses, and detecting eye abnormalities.
In the United States and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a post-baccalaureate f ...
. Other treatment may include wearing eye patches aimed at strengthening the weaker eye while inhibiting the stronger eye, an alternative to eye patches is the use of an opaque lens, other treatments may include eye drops to temporarily inhibit the stronger eye and at any age eye muscle surgery can be done to correct the muscular balance of the ocular muscles.
Although the cause of scoliosis can sometimes remain unknown (idiopathic scoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others, it increases ove ...
) there is treatment available that targets at strengthening the back muscles, for milder cases usually do not require medical attention, more severe cases require either muscle strengthening exercises aimed at the back muscles and even special back braces or surgery can be recommended if the case is extreme. Studies have shown that treatment with a special back brace among children ranging from 10–16 years can be successful and using this method of muscle training scoliosis can be cured with non-surgical treatment.
Prognosis
In terms of selective muscle weakness or poor flexibility muscular imbalance is frequently regarded as anetiological
Etiology (; alternatively spelled aetiology or ætiology) is the study of causation or origination. The word is derived from the Greek word ''()'', meaning "giving a reason for" (). More completely, etiology is the study of the causes, origin ...
factor in the onset of musculoskeletal disorder
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are injuries or pain in the human musculoskeletal system, including the joints, ligaments, muscles, nerves, tendons, and structures that support limbs, neck and back. MSDs can arise from a sudden exertion (e.g. ...
s. There are a variety of areas that can be affected, each causing different symptoms hence there are also different treatments available, but in general cases muscle strengthening techniques were developed for the use on the weak or tight muscles.
History
For a long time muscular imbalance had many different theories that revolved around it. It wasn't until 1949 when there was a first manual on muscle testing appeared, written by therapists Henry and Florence Kendall,http://www.polioplace.org/people/florence-peterson-kendall which discusses muscle weakness in polio patients and treatments approaching tight and weak muscles. In the 1960s Dr. George Goodheart and Dr. Vladimir Janda each took their own paths in treating patients with muscular imbalance, Goodheart focusing on muscle weakness being the primary cause of muscle imbalance, whilst Janda took on the muscle tightness approach, both developed a large following that continues on today.Controversies
There is evidence to support two different approaches to muscular imbalance, the first is a biomechanical approach that believed the cause was due from repeated movements in one direction or sustained postures, this was widespread by Kendall. The second is a neuromuscular imbalance due to certain muscle groups being tight or weak, popularized by Janda this approach is based on movement patterns that evolve from birth. Today there are many different types of therapists who treat muscle imbalance, these include chiropractors, osteopaths, physical therapists, medical doctors and massage therapists each assessing tightness or weakness as the primary cause of muscular imbalance.References
{{reflist Muscular disorders