Multicast Lightpaths on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A
A
 Several protection schemes have been proposed in the literature to protect the
Several protection schemes have been proposed in the literature to protect the

 Shared backup path protection (SBPP) for multicast connections:
The SBPP technique can be used for multicast connections at the optical layer because of its resource efficiency, due to the fact that the backup paths can share wavelength channels on links while their corresponding primary paths are link disjoint. Paths can share links with working paths and protection paths of other leaves.
In a shared backup path protection before failure FE and FA are primary paths. The optical line is reserved for shared protection of both FE and FA.
Path protection technique for multicast connections (multiple unicast connections):
Shared backup path protection (SBPP) for multicast connections:
The SBPP technique can be used for multicast connections at the optical layer because of its resource efficiency, due to the fact that the backup paths can share wavelength channels on links while their corresponding primary paths are link disjoint. Paths can share links with working paths and protection paths of other leaves.
In a shared backup path protection before failure FE and FA are primary paths. The optical line is reserved for shared protection of both FE and FA.
Path protection technique for multicast connections (multiple unicast connections):
multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
session requires a "point-to-multipoint" connection from a source node to multiple destination nodes. The source node is known as the ''root''. The destination nodes are known as ''leaves''. In the modern era, it is important to protect multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
connections in an optical mesh network
An optical mesh network is a type of Optical networking, optical telecommunications network employing wired fiber-optic communication or wireless free-space optical communication in a Mesh networking, mesh network architecture.
Most optical mesh ...
. Recently, multicast applications have gained popularity as they are important to protecting critical sessions against failures such as fiber cuts, hardware faults, and natural disasters.
Multicast applications
Multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
applications may include multimedia
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms, such as Text (literary theory), writing, Sound, audio, images, animations, or video, into a single presentation. T ...
, medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
, digital audio
Digital audio is a representation of sound recorded in, or converted into, digital signal (signal processing), digital form. In digital audio, the sound wave of the audio signal is typically encoded as numerical sampling (signal processing), ...
, HDTV
High-definition television (HDTV) describes a television or video system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since at least 1933; in more recent times, it ref ...
, video conferencing
Videotelephony (also known as videoconferencing or video calling) is the use of audio signal, audio and video for simultaneous two-way communication. Today, videotelephony is widespread. There are many terms to refer to videotelephony. ''Vide ...
, interactive distance learning, and distributed games.
Multi-casting switch architecture
In order to support multi-casting, the WDM network requiresmulticast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
-capable wavelength-routing switches at the network node. These switches are capable of replicating data streams from one input port to multiple output ports. There are two types of switch architectures that are usually used:N. Singhal and B. Mukherjee, "Protecting multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
sessions in WDM optical mesh networks," J. Lightwave Technol., vol. 21, Apr. 2003
* The first type of switch architecture is an opaque switch architecture which utilizes electronic cross-connects with optical-electrical-optical (OEO) conversion.
* The other is transparent switch architecture which utilizes all optical cross-connect
An optical cross-connect (OXC) is a device used by telecommunications carriers to switch high-speed optical signals in a fiber optic network, such as an optical mesh network.
In the 1980s, when transmission speeds supported by optical fibers in ...
s (OXCs).
Multicast lightpaths protection
Multicast lightpaths protection refers to the network's prompt response to reroute traffic onto an alternative path in the event of a failure. In a dedicated backup path, resources are exclusively allocated to a single connection and not shared with other connections along the backup path. In a shared backup path, resources may be shared between multiple backup paths for different connections.Protecting multicast sessions
 Several protection schemes have been proposed in the literature to protect the
Several protection schemes have been proposed in the literature to protect the multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
connections. The simplest idea to protect the multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
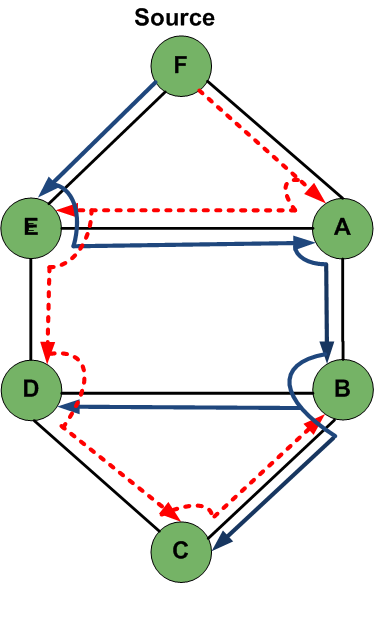
tree from single fiber failure is to compute a link disjoint backup tree. In a link disjoint backup tree, a multicast session from source node F to destination nodes A, B, C, D and E forms a light tree. F is the root and the remaining nodes are the leaves. The primary light tree is shown in solid lines and (directed-link-disjoint) the back up light tree is shown in dotted lines carrying traffic from source node to destinations.
The ring based approach is also proposed to protect multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
session.
The segment protection scheme is another way to protect multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
connections. A segment in a multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
tree is defined as the sequence of edges from the source or any splitting node (on a tree) to a leaf node or to a downstream splitting node. A destination node is always considered as a segment end node because it is either a leaf node in a tree or a splitting node.
A multicast protection scheme through spanning paths is also one of the key approaches to protecting multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
sessions.H. Luo, L. Li, and H. Yu, "Algorithm for Protecting Light-trees in Survivable Mesh Wavelength-division-multiplexing Networks", Journal of Optical Networking, vol. 5, no. 12, pp. 1071–1083, 2006. A spanning path in a multicast tree is defined as a path from a leaf node to any other leaf node in the light tree. The scheme derives backup paths for every spanning path in the multicast tree.
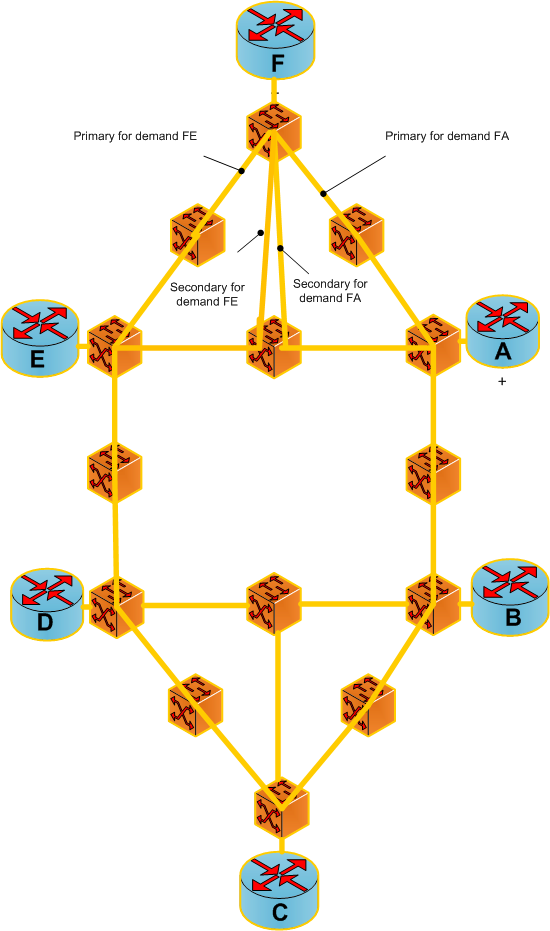
Concept of DBPP and SBPP on multicast connections
Dedicated backup path protection (DBPP) for multicast connections: Depending on the network topology, a dedicated backup path concept can be applied for multicast traffic. A dedicated backup path protection is a multicast session from source node F to destination nodes A, B, C, D, and E which form the light tree. A dedicated backup path protection scheme can be applied to protect multicast traffic from link failure. This is easy to achieve with one-to-one protection where the dedicated backup path is already provisioned and traffic is simply switched to it on failure.

 Shared backup path protection (SBPP) for multicast connections:
The SBPP technique can be used for multicast connections at the optical layer because of its resource efficiency, due to the fact that the backup paths can share wavelength channels on links while their corresponding primary paths are link disjoint. Paths can share links with working paths and protection paths of other leaves.
In a shared backup path protection before failure FE and FA are primary paths. The optical line is reserved for shared protection of both FE and FA.
Path protection technique for multicast connections (multiple unicast connections):
Shared backup path protection (SBPP) for multicast connections:
The SBPP technique can be used for multicast connections at the optical layer because of its resource efficiency, due to the fact that the backup paths can share wavelength channels on links while their corresponding primary paths are link disjoint. Paths can share links with working paths and protection paths of other leaves.
In a shared backup path protection before failure FE and FA are primary paths. The optical line is reserved for shared protection of both FE and FA.
Path protection technique for multicast connections (multiple unicast connections):
Importance
Protection schemes for multicast connections are important for the following reasons: # Loss of connectivity: network failures such as fiber cuts in a communication network occur often enough to cause service disruption, and lead to significant information loss in the absence of adequate backup mechanisms. # SLA: it is important for providers to follow SLAs and guaranteed service. It is important to protectmulticast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
connections to maintain the SLA.
# Business reputation: network availability is one of the key aspects of multicasting connections. A company loses money and reputation when its network fails.
See also
*Availability
In reliability engineering, the term availability has the following meanings:
* The degree to which a system, subsystem or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at ...
* IP multicast
IP multicast is a method of sending Internet Protocol (IP) datagrams to a group of interested receivers in a single transmission. It is the IP-specific form of multicast and is used for streaming media and other network applications. It uses speci ...
* Optical add-drop multiplexer
An optical add-drop multiplexer (OADM) is a device used in wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) systems for multiplexing and routing different channels of light into or out of a single-mode fiber (SMF). This is a type of optical node, which ...
* Optical mesh network
An optical mesh network is a type of Optical networking, optical telecommunications network employing wired fiber-optic communication or wireless free-space optical communication in a Mesh networking, mesh network architecture.
Most optical mesh ...
* Optical transport network
* Unicast
Unicast is data transmission from a single sender (red) to a single receiver (green). Other devices on the network (yellow) do not participate in the communication.
In computer networking, unicast is a one-to-one transmission from one point in ...
Notes
{{Reflist Fiber-optic communications