most significant byte on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
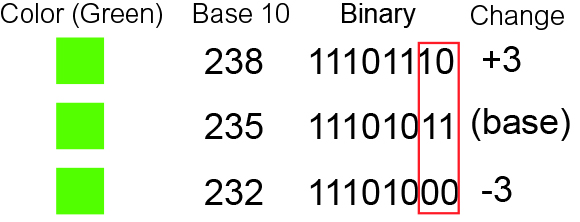 A diagram showing how manipulating the least significant bits of a color can have a very subtle and generally unnoticeable effect on the color. In this diagram, green is represented by its RGB value, both in decimal and in binary. The red box surrounding the last two bits illustrates the least significant bits changed in the binary representation.
A diagram showing how manipulating the least significant bits of a color can have a very subtle and generally unnoticeable effect on the color. In this diagram, green is represented by its RGB value, both in decimal and in binary. The red box surrounding the last two bits illustrates the least significant bits changed in the binary representation.
computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and softw ...
, bit numbering is the convention used to identify the bit positions in a binary number
A binary number is a number expressed in the Radix, base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method for representing numbers that uses only two symbols for the natural numbers: typically "0" (zero) and "1" (one). A ''binary number'' may ...
.
Bit significance and indexing
Incomputing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and softw ...
, the least significant bit (LSb) is the bit position in a binary integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative in ...
representing the lowest-order place of the integer. Similarly, the most significant bit (MSb) represents the highest-order place of the binary integer. The LSb is sometimes referred to as the ''low-order bit''. Due to the convention in positional notation
Positional notation, also known as place-value notation, positional numeral system, or simply place value, usually denotes the extension to any radix, base of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system (or decimal, decimal system). More generally, a posit ...
of writing less significant digits further to the right, the LSb also might be referred to as the ''right-most bit''. The MSb is similarly referred to as the ''high-order bit'' or ''left-most bit''. In both cases, the LSb and MSb correlate directly to the least significant digit and most significant digit of a decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of th ...
integer.
Bit indexing correlates to the positional notation of the value in base 2. For this reason, bit index is not affected by how the value is stored on the device, such as the value's byte order
'' Jonathan_Swift.html" ;"title="Gulliver's Travels'' by Jonathan Swift">Gulliver's Travels'' by Jonathan Swift, the novel from which the term was coined
In computing, endianness is the order in which bytes within a word (data type), word of d ...
. Rather, it is a property of the numeric value in binary itself. This is often utilized in programming via bit shifting: A value of 1 << ''n'' corresponds to the ''n''th bit of a binary integer (with a value of 2n).
Least significant bit in digital steganography
In digitalsteganography
Steganography ( ) is the practice of representing information within another message or physical object, in such a manner that the presence of the concealed information would not be evident to an unsuspecting person's examination. In computing/ ...
, sensitive messages may be concealed by manipulating and storing information in the least significant bits of an image or a sound file. The user may later recover this information by extracting the least significant bits of the manipulated pixels to recover the original message. This allows the storage or transfer of digital information to remain concealed.
 A diagram showing how manipulating the least significant bits of a color can have a very subtle and generally unnoticeable effect on the color. In this diagram, green is represented by its RGB value, both in decimal and in binary. The red box surrounding the last two bits illustrates the least significant bits changed in the binary representation.
A diagram showing how manipulating the least significant bits of a color can have a very subtle and generally unnoticeable effect on the color. In this diagram, green is represented by its RGB value, both in decimal and in binary. The red box surrounding the last two bits illustrates the least significant bits changed in the binary representation.
Unsigned integer example
This table illustrates an example of decimal value of 149 and the location of LSb. In this particular example, the position of unit value (decimal 1 or 0) is located in bit position 0 (n = 0). MSb stands for ''most significant bit'', while LSb stands for ''least significant bit''.Signed integer example
This table illustrates an example of an 8 bit signed decimal value using thetwo's complement
Two's complement is the most common method of representing signed (positive, negative, and zero) integers on computers, and more generally, fixed point binary values. Two's complement uses the binary digit with the ''greatest'' value as the ''s ...
method. The MSb ''most significant bit'' has a negative weight in signed integers, in this case −27 = −128. The other bits have positive weights. The lsb (''least significant bit'') has weight 1. The signed value is in this case −128+2 = −126.
Most- vs least-significant bit first
The expressions ''most significant bit first'' and ''least significant bit at first'' are indications on the ordering of the sequence of the bits in the bytes sent over a wire in a serial transmission protocol or in a stream (e.g. an audio stream). ''Most significant bit first'' means that the most significant bit will arrive first: hence e.g. the hexadecimal number0x12, 00010010 in binary representation, will arrive as the sequence 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 .
''Least significant bit first'' means that the least significant bit will arrive first: hence e.g. the same hexadecimal number 0x12, again 00010010 in binary representation, will arrive as the (reversed) sequence 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0.
LSb 0 bit numbering
When the bit numbering starts at zero for the least significant bit (LSb) the numbering scheme is called ''LSb 0''. This bit numbering method has the advantage that for any unsigned number the value of the number can be calculated by usingexponentiation
In mathematics, exponentiation, denoted , is an operation (mathematics), operation involving two numbers: the ''base'', , and the ''exponent'' or ''power'', . When is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated multiplication ...
with the bit number and a base of 2. The value of an unsigned binary integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative in ...
is therefore
:
where ''bi'' denotes the value of the bit with number ''i'', and ''N'' denotes the number of bits in total.
MSb 0 bit numbering
When the bit numbering starts at zero for the most significant bit (MSb) the numbering scheme is called ''MSb 0''. The value of an unsigned binary integer is therefore :LSb calculation
LSb of a number can be calculated with time complexity of with formulaa & (~ a+1), where & means binary AND and ~ means binary NOT
In computer programming, a bitwise operation operates on a bit string, a bit array or a binary numeral (considered as a bit string) at the level of its individual bits. It is a fast and simple action, basic to the higher-level arithmetic operat ...
.
Other
For MSb 1 numbering, the value of an unsigned binary integer is :PL/I
PL/I (Programming Language One, pronounced and sometimes written PL/1) is a procedural, imperative computer programming language initially developed by IBM. It is designed for scientific, engineering, business and system programming. It has b ...
numbers strings starting with 1 for the leftmost bit.
The Fortran function uses LSb 0 numbering.
See also
*ARINC 429
ARINC 429, the "Mark 33 Digital Information Transfer System (DITS)," is the ARINC technical standard for the predominant avionics data bus used on most higher-end commercial and transport aircraft. It defines the physical and electrical interface ...
*Binary numeral system
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method for representing numbers that uses only two symbols for the natural numbers: typically "0" ( zero) and "1" ( one). A ''binary number'' may als ...
*Signed number representations
In computing, signed number representations are required to encode negative numbers in binary number systems.
In mathematics, negative numbers in any base are represented by prefixing them with a minus sign ("−"). However, in RAM or CPU reg ...
*Two's complement
Two's complement is the most common method of representing signed (positive, negative, and zero) integers on computers, and more generally, fixed point binary values. Two's complement uses the binary digit with the ''greatest'' value as the ''s ...
*Endianness
file:Gullivers_travels.jpg, ''Gulliver's Travels'' by Jonathan Swift, the novel from which the term was coined
In computing, endianness is the order in which bytes within a word (data type), word of digital data are transmitted over a data comm ...
*Binary logarithm
In mathematics, the binary logarithm () is the exponentiation, power to which the number must be exponentiation, raised to obtain the value . That is, for any real number ,
:x=\log_2 n \quad\Longleftrightarrow\quad 2^x=n.
For example, th ...
*Unit in the last place
In computer science and numerical analysis, unit in the last place or unit of least precision (ulp) is the spacing between two consecutive floating-point numbers, i.e., the value the '' least significant digit'' (rightmost digit) represents if it ...
(ULP)
*Find first set
In computer software and hardware, find first set (ffs) or find first one is a bit operation that, given an unsigned Word (computer architecture), machine word, designates the index or position of the least significant bit set to one in the word c ...
* MAC address: Bit-reversed notation
References
{{reflist Binary arithmetic Assembly languages