Moskovskaya Oblast on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Moscow Oblast (, , informally known as , ) is a

 There are more than three hundred rivers with the length above in Moscow Oblast. All rivers are calm and have well-developed valleys and
There are more than three hundred rivers with the length above in Moscow Oblast. All rivers are calm and have well-developed valleys and
Rivers of Moscow region
Moscow, MGPU, 2003. Most rivers belong to the basin of the
 Moscow Oblast lies within the zone of forests and steppes with forests covering over 40% of the region.
Moscow Oblast lies within the zone of forests and steppes with forests covering over 40% of the region.
 The mammals of Moscow Oblast include
The mammals of Moscow Oblast include
File:Mustela Erminea head.jpg, Stoat
File:Gartenspitzmaus.jpg, Lesser white-toothed shrew
File:Kid-jbk.jpg, Roe deer fawn
File:Micromysminutus1.jpg,
 The territory of what is now Moscow Oblast had been inhabited for more than twenty thousand years. Numerous mounds and settlements from Iron Age were discovered there. Up to the 9–10th centuries, the Moskva River basin and adjacent lands were inhabited by Finnic peoples. Slavs populated the area only in the 10th century. In mid-12th century, the lands became part of Vladimir-Suzdal, Vladimir-Suzdal Principality. Several important cities were founded around that time, including Volokolamsk (1135), Moscow (1147), Zvenigorod (1152), and
The territory of what is now Moscow Oblast had been inhabited for more than twenty thousand years. Numerous mounds and settlements from Iron Age were discovered there. Up to the 9–10th centuries, the Moskva River basin and adjacent lands were inhabited by Finnic peoples. Slavs populated the area only in the 10th century. In mid-12th century, the lands became part of Vladimir-Suzdal, Vladimir-Suzdal Principality. Several important cities were founded around that time, including Volokolamsk (1135), Moscow (1147), Zvenigorod (1152), and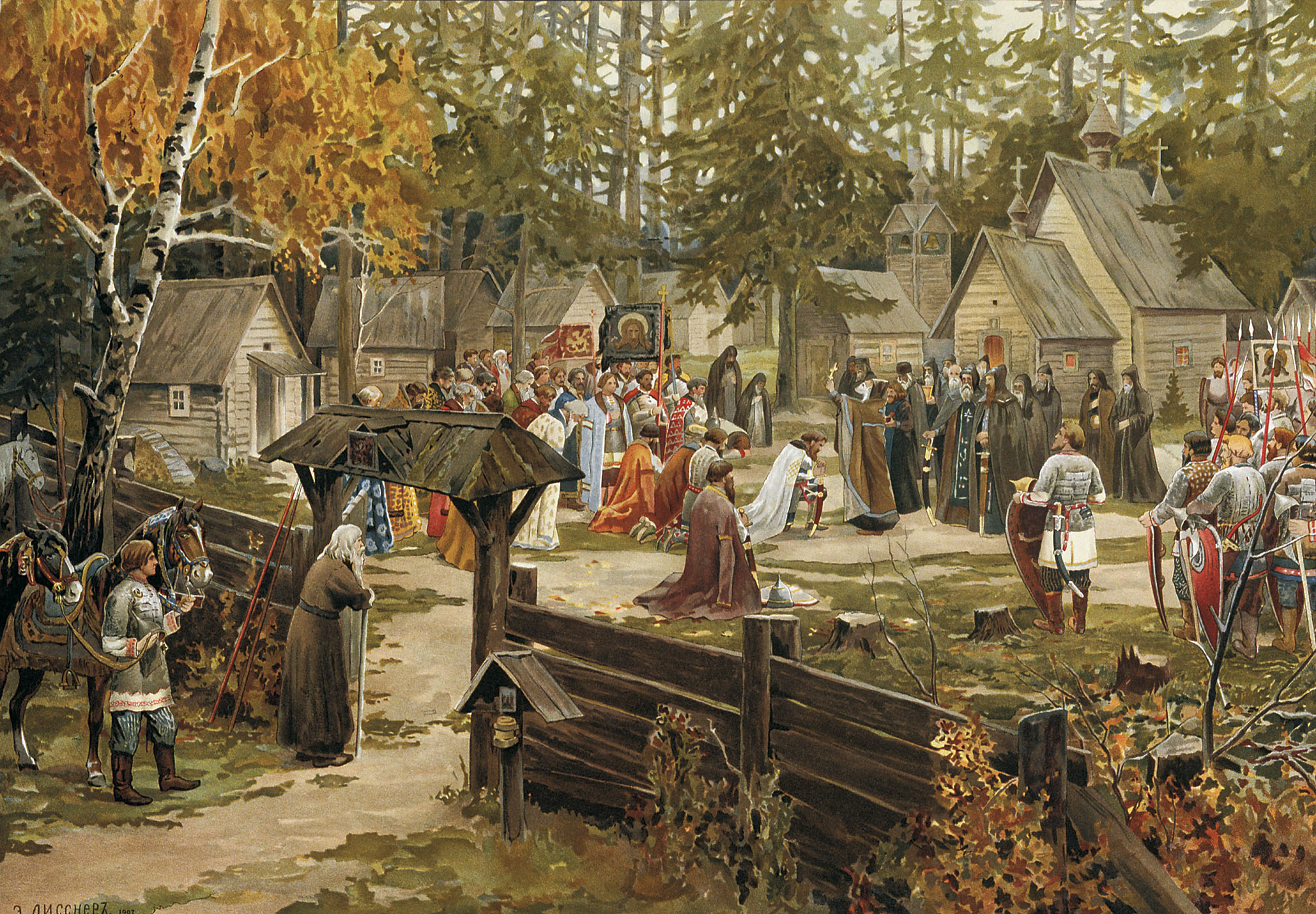  In the 13th century, the land around Moscow was part of Grand Duchy of Moscow, which subsequently was the center of the unification of Russian lands, in particular the Mongol raids. In 1380, from Kolomna the prince Dmitry Donskoy led his troops to defeat the Mongols at the Battle of Kulikovo. The southern part of Moscow Oblast was then part of the Principality of Ryazan; it was attached to Moscow only in the 1520.
In 1708, Moscow Governorate was established by the decree of Peter the Great; the area included most of the present Moscow Oblast. The Battle of Borodino, which decided the outcome of the French invasion of Russia was fought in 1812 near Mozhaysk.
Industries developed in Moscow Oblast in the 17–19th centuries. They were centered in Noginsk, Bogorodsk, Pavlovsky Posad, and
In the 13th century, the land around Moscow was part of Grand Duchy of Moscow, which subsequently was the center of the unification of Russian lands, in particular the Mongol raids. In 1380, from Kolomna the prince Dmitry Donskoy led his troops to defeat the Mongols at the Battle of Kulikovo. The southern part of Moscow Oblast was then part of the Principality of Ryazan; it was attached to Moscow only in the 1520.
In 1708, Moscow Governorate was established by the decree of Peter the Great; the area included most of the present Moscow Oblast. The Battle of Borodino, which decided the outcome of the French invasion of Russia was fought in 1812 near Mozhaysk.
Industries developed in Moscow Oblast in the 17–19th centuries. They were centered in Noginsk, Bogorodsk, Pavlovsky Posad, and
Moscow Oblast (in Russian)
Official site of Moscow Oblast (in Russian) In 1941 and 1942, one of the most significant military operations of World War II—the Battle of Moscow—was fought in the Moscow Oblast. Germany reached Solnechnogorsky, Klinsky, Istrinsky, Lobninsky, Khimkinsky, Naro-Fominsky, Volokolamsky, Kolomensky, Kashirsky, Serybryano-Prudsky Districts and others. According to the Constitution of Russia, adopted in December 1993, Moscow Oblast is one of the 83 federal subjects of Russia.
 In terms of industrial production, Moscow Oblast is second in Russia, after the city of Moscow. The industry of the Oblast relies on imported raw materials, strong scientific and technological base and highly skilled workforce; it is closely linked with the industry of Moscow.
Well developed are machinery and metalworking. There are plants for the thermal and nuclear power engineering (ZiO-Podolsk in Podolsk), nuclear fuel (TVEL in Elektrostal), space and missile (S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia, Energia in Korolyov (city), Korolyov, Lavochkin in Khimki, NGO engineering in Reutov, FTSDT "Union" in Dzerzhinsky, Moscow Oblast, Dzerzhinsky – development of solid rocket fuel, etc., IBC "Horizon" in Dzerzhinsky (town), Dzerzhinsky – power plants for aircraft, etc.); locomotives (Kolomna Locomotive Works, Kolomna factory), metro cars (Metrowagonmash in Mytischi), electric trains (Demikhovsky Engineering Works), cars (SeAZ), buses (Likinsky bus plant in Likino-Dulyovo); agricultural machines, excavators and cranes (
In terms of industrial production, Moscow Oblast is second in Russia, after the city of Moscow. The industry of the Oblast relies on imported raw materials, strong scientific and technological base and highly skilled workforce; it is closely linked with the industry of Moscow.
Well developed are machinery and metalworking. There are plants for the thermal and nuclear power engineering (ZiO-Podolsk in Podolsk), nuclear fuel (TVEL in Elektrostal), space and missile (S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia, Energia in Korolyov (city), Korolyov, Lavochkin in Khimki, NGO engineering in Reutov, FTSDT "Union" in Dzerzhinsky, Moscow Oblast, Dzerzhinsky – development of solid rocket fuel, etc., IBC "Horizon" in Dzerzhinsky (town), Dzerzhinsky – power plants for aircraft, etc.); locomotives (Kolomna Locomotive Works, Kolomna factory), metro cars (Metrowagonmash in Mytischi), electric trains (Demikhovsky Engineering Works), cars (SeAZ), buses (Likinsky bus plant in Likino-Dulyovo); agricultural machines, excavators and cranes (
File:Bus LiAZ-5292.20.jpeg, LiAZ (Russia), LiAZ-5292
File:Ka-52 061.jpg, Kamov Ka-50, Ka-52 "Alligator" by Kamov
File:ТЭП70БС-035 2009-03.jpg, Diesel TEP70BS (Kolomna plant)
File:Ra2m.jpg, Railcar Rail bus (Metrovagonmash)
File:ED4MKM-AERO.jpg, Electric train ED4MKM-AERO (Demikhovsky Engineering Works)
Light industry is the oldest in the region; it was started in the 17th century and with 35% contribution was leading the gross industrial production. There is still production of cotton (in Yegoryevsk,
File:Частная коллекция гжель.JPG, Examples of the Gzhel style
File:Жостовский поднос.jpg, Example of Zhostovo painting
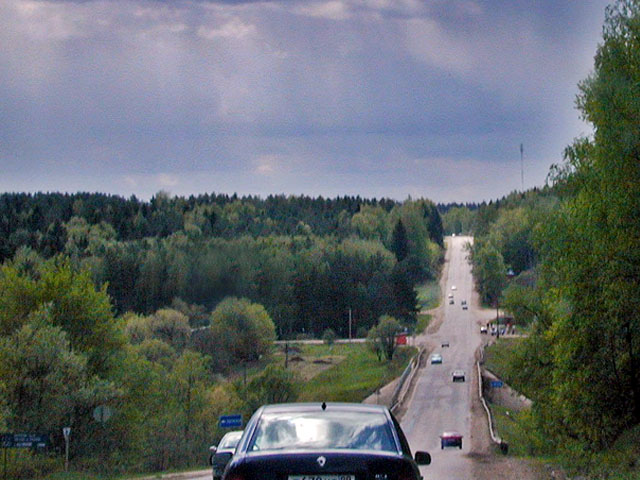
 Moscow Oblast has a dense transport network, including roads, railways and waterways along the largest rivers, lakes and reservoirs. Land routes are radially diverging from Moscow and crossed by one railway and MKAD, two highway rings. Neither railways nor roads, built for the most part many years ago, can cope with the steadily mounting traffic flows. About half of the roads are overloaded and three quarters do not meet modern requirements. Insufficient width of the roads and frequent repairs cause traffic jams.
Moscow Oblast has the highest density of railways in Russia. Eleven major radial lines originate in Moscow and run through the Oblast; the total length of the railways reaches 2,700 km. Almost all railroads are electrified. The largest rail hubs are
Moscow Oblast has a dense transport network, including roads, railways and waterways along the largest rivers, lakes and reservoirs. Land routes are radially diverging from Moscow and crossed by one railway and MKAD, two highway rings. Neither railways nor roads, built for the most part many years ago, can cope with the steadily mounting traffic flows. About half of the roads are overloaded and three quarters do not meet modern requirements. Insufficient width of the roads and frequent repairs cause traffic jams.
Moscow Oblast has the highest density of railways in Russia. Eleven major radial lines originate in Moscow and run through the Oblast; the total length of the railways reaches 2,700 km. Almost all railroads are electrified. The largest rail hubs are
 Moscow Oblast was awarded three Order of Lenin, Orders of Lenin, on 3 January 1934, 17 December 1956 and 5 December 1966.
The highest executive organ is the Government of Moscow Oblast. Eighteen ministries act as the executive bodies of state authority. The powers, tasks, functions and competence of the Government are defined by the Charter of the Moscow Region. The Governor of the Moscow Oblast will be elected with the term of 5 years.Charter of Moscow Oblast
Moscow Oblast was awarded three Order of Lenin, Orders of Lenin, on 3 January 1934, 17 December 1956 and 5 December 1966.
The highest executive organ is the Government of Moscow Oblast. Eighteen ministries act as the executive bodies of state authority. The powers, tasks, functions and competence of the Government are defined by the Charter of the Moscow Region. The Governor of the Moscow Oblast will be elected with the term of 5 years.Charter of Moscow Oblast
(in Russian) The Regional Duma of Moscow Oblast was formed on 12 December 1993. It consists of 50 deputies also serving a 5-year term. Sergey Shoygu was elected as Governor of Moscow Oblast in April 2012 by the Moscow Oblast Duma. Shoygu left office after only six months with his appointment when he was appointed as Ministry of Defence (Russia), Minister of Defence by Vladimir Putin. Andrey Yuryevich Vorobyov, Andrei Vorobyov was appointed as acting governor and won a full term to the office in the Moscow Oblast gubernatorial election, 2013, 2013 elections.
 Zorky Krasnogorsk, Zorky from Krasnogorsk has become List of Russian bandy champions, national bandy champions three times. In the 2017–18 season, Zorky is back in Russian Bandy Super League, Super League, after one season in the second-tier league. Obukhovo, Noginsky District, Moscow Oblast, Obukhovo is the only location in Russia without a Super League team which has a bandy venue with artificial ice. A plan for artificial ice also existed in Korolyov, Moscow Oblast, Korolyov. However, the project was abandoned. Although an indoor ice hockey-sized arena entered the plans instead, the official reason given was financial problems.
The Russian rink bandy, Rink Bandy Cup 2017 was played in Balashikha.
Zorky Krasnogorsk, Zorky from Krasnogorsk has become List of Russian bandy champions, national bandy champions three times. In the 2017–18 season, Zorky is back in Russian Bandy Super League, Super League, after one season in the second-tier league. Obukhovo, Noginsky District, Moscow Oblast, Obukhovo is the only location in Russia without a Super League team which has a bandy venue with artificial ice. A plan for artificial ice also existed in Korolyov, Moscow Oblast, Korolyov. However, the project was abandoned. Although an indoor ice hockey-sized arena entered the plans instead, the official reason given was financial problems.
The Russian rink bandy, Rink Bandy Cup 2017 was played in Balashikha.
 The 2008 European Speed Skating Championships and the 2016 World Single Distance Speed Skating Championships were held in
The 2008 European Speed Skating Championships and the 2016 World Single Distance Speed Skating Championships were held in
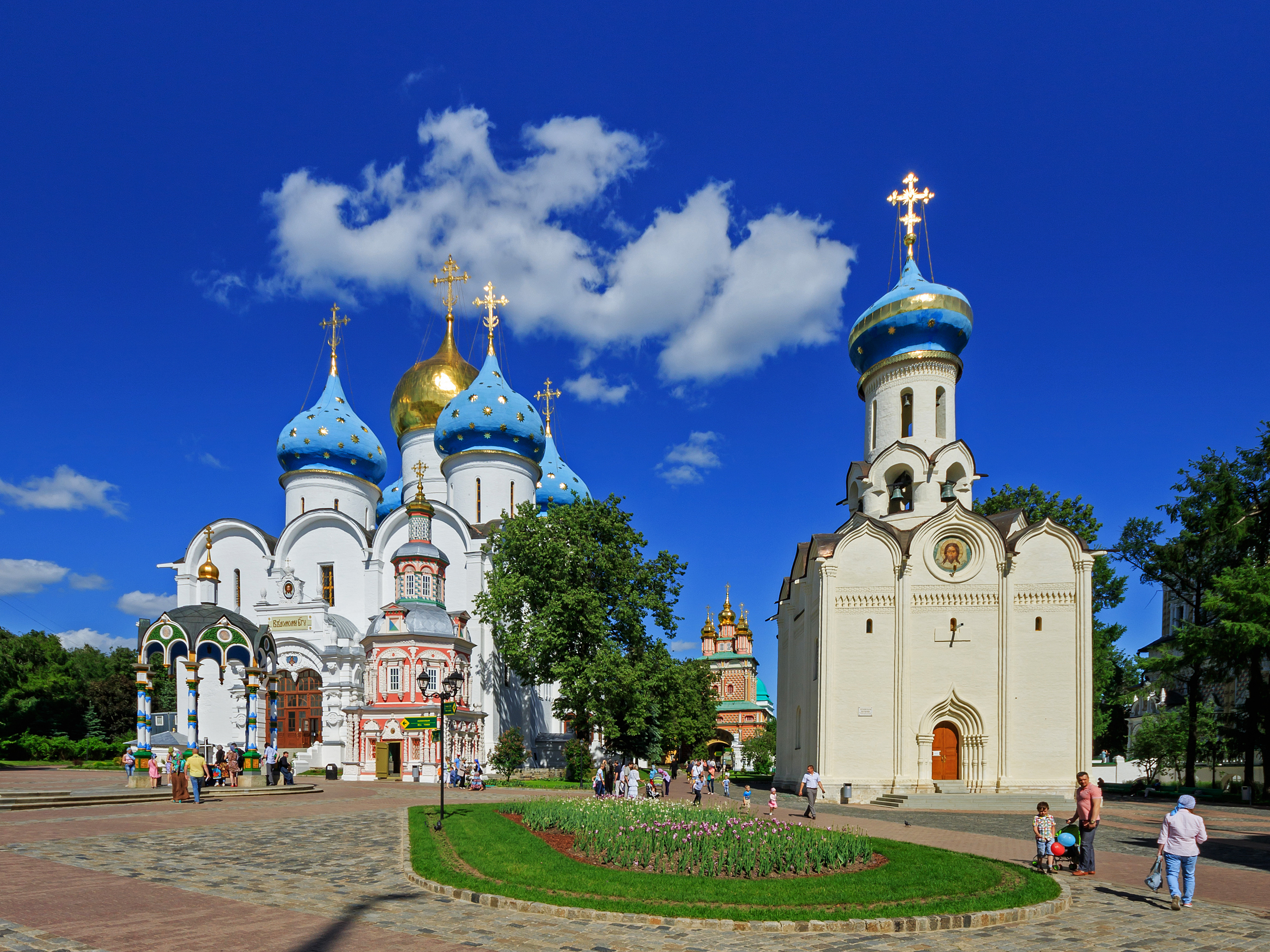
 Moscow Oblast has numerous therapeutic and recreational facilities located mainly in western, northwestern and northern parts, and also near Moscow. Of great importance for recreation are forests, which occupy over 40% of the region, as well as horticultural activities. The region has the highest number (over 1 million) of dachas with associated individual gardens. Also numerous are manor complexes, such as those in Abramtsevo, Sergiyevo-Posadsky District, Moscow Oblast, Abramtsevo, Muranovo, Ostafievo, historical towns (Vereya, Naro-Fominsky District, Moscow Oblast, Vereya, Volokolamsk,
Moscow Oblast has numerous therapeutic and recreational facilities located mainly in western, northwestern and northern parts, and also near Moscow. Of great importance for recreation are forests, which occupy over 40% of the region, as well as horticultural activities. The region has the highest number (over 1 million) of dachas with associated individual gardens. Also numerous are manor complexes, such as those in Abramtsevo, Sergiyevo-Posadsky District, Moscow Oblast, Abramtsevo, Muranovo, Ostafievo, historical towns (Vereya, Naro-Fominsky District, Moscow Oblast, Vereya, Volokolamsk,
 After the population decline from 6,693,623 as of the Soviet Census (1989), 1989 Census to 6,618,538 in the Russian Census (2002), 2002 Census the population of the oblast grew to 7,095,120 (Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census). It increased further to 8,524,665 according to the 2021 Census despite the fact that some parts of its territory were ceded to Moscow. The average population density, at 190 inhabitants/km2 (2021), is the largest in Russia, due to a high proportion of urban population (78.5% in 2021). The highest density occurs in and around Moscow (Lyuberetsky District, Lyubertsy, Balashikha, Khimki, Krasnogorsk, etc.) and the lowest – about 20 people/km2 – is in the outlying areas of Lotoshinsky, Shakhovskoy, Mozhaysk and Meshchersk lowlands.
After the population decline from 6,693,623 as of the Soviet Census (1989), 1989 Census to 6,618,538 in the Russian Census (2002), 2002 Census the population of the oblast grew to 7,095,120 (Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census). It increased further to 8,524,665 according to the 2021 Census despite the fact that some parts of its territory were ceded to Moscow. The average population density, at 190 inhabitants/km2 (2021), is the largest in Russia, due to a high proportion of urban population (78.5% in 2021). The highest density occurs in and around Moscow (Lyuberetsky District, Lyubertsy, Balashikha, Khimki, Krasnogorsk, etc.) and the lowest – about 20 people/km2 – is in the outlying areas of Lotoshinsky, Shakhovskoy, Mozhaysk and Meshchersk lowlands.
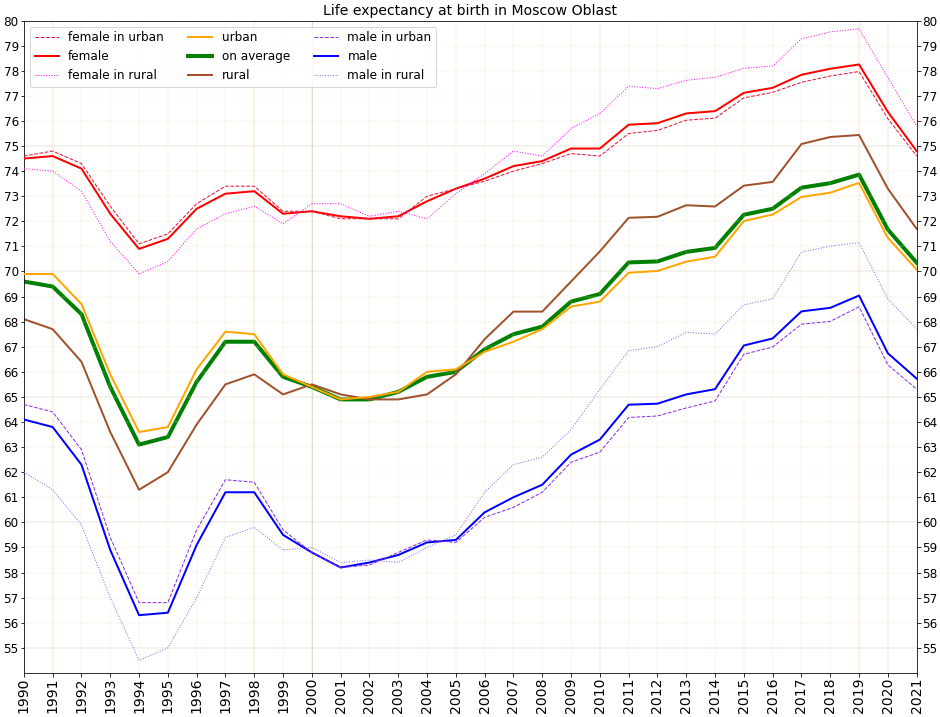
1.34 children per woman Life expectancy (2021):
Total — 70.35 years (male — 65.73, female — 74.80)
 The three largest cities of the oblast are Balashikha (215,494), Khimki (207,425), and Podolsk (186,961). Most other towns have ten to fifty thousand people. The smallest town is Vereya, Naro-Fominsky District, Moscow Oblast, Vereya in Naro-Fominsky District with a population of . Among the urban-type settlements, the largest is Nakhabino (36,546) followed by Tomilino (30,605). The oldest populated place in the oblast is Volokolamsk, first mentioned in 1135; slightly younger towns are Zvenigorod (1152), Dmitrov (1154), and Kolomna (1177).
The city of Baikonur in Kazakhstan also belongs administratively to the oblast, as part of Odintsovsky District.
The most intensive formation of towns occurred in 1938–1940. The youngest towns are Golitsyno, Moscow Oblast, Golitsyno and Kubinka. They existed for quite some time, but were granted town status only in 2004. Some recent towns separated from the other towns, such as Yubileyny, Moscow Oblast, Yubileyny and Peresvet.
New projects have been announced at the beginning of the 21st century. One of them is Rublyovo-Arkhangelsk, which is designed for 30,000 inhabitants with high income and is called by the media the "city for millionaires". Another is "Great Domodedovo, south of the Moscow Ring Road, which is designed for 450,000 residents. The new city A101 was designed for 300,000 residents in 2009 and the sale of its land in Leninsky District, Moscow Oblast, Leninsky District has already begun; the city's construction is planned to take thirty-five years.
A part of Moscow Oblast's former territory, mainly to the southwest of the city of Moscow, was merged with the federal cities of Russia, federal city of
The three largest cities of the oblast are Balashikha (215,494), Khimki (207,425), and Podolsk (186,961). Most other towns have ten to fifty thousand people. The smallest town is Vereya, Naro-Fominsky District, Moscow Oblast, Vereya in Naro-Fominsky District with a population of . Among the urban-type settlements, the largest is Nakhabino (36,546) followed by Tomilino (30,605). The oldest populated place in the oblast is Volokolamsk, first mentioned in 1135; slightly younger towns are Zvenigorod (1152), Dmitrov (1154), and Kolomna (1177).
The city of Baikonur in Kazakhstan also belongs administratively to the oblast, as part of Odintsovsky District.
The most intensive formation of towns occurred in 1938–1940. The youngest towns are Golitsyno, Moscow Oblast, Golitsyno and Kubinka. They existed for quite some time, but were granted town status only in 2004. Some recent towns separated from the other towns, such as Yubileyny, Moscow Oblast, Yubileyny and Peresvet.
New projects have been announced at the beginning of the 21st century. One of them is Rublyovo-Arkhangelsk, which is designed for 30,000 inhabitants with high income and is called by the media the "city for millionaires". Another is "Great Domodedovo, south of the Moscow Ring Road, which is designed for 450,000 residents. The new city A101 was designed for 300,000 residents in 2009 and the sale of its land in Leninsky District, Moscow Oblast, Leninsky District has already begun; the city's construction is planned to take thirty-five years.
A part of Moscow Oblast's former territory, mainly to the southwest of the city of Moscow, was merged with the federal cities of Russia, federal city of
Draft of adopted measures of the capital and oblast governments with regards to the expansion of the borders of Moscow
The housing stock of the oblast is approximately 125 million square meters. Almost all the houses are equipped with water supply, sewerage, gas, central heating and hot water. However, the telephone network is underdeveloped in rural areas. In the competition for the most comfortable city of 2006 in the Moscow Oblast the winner was
Геология, рельеф и полезные ископаемые Московского региона
. Moscow, MGPU, 2003.
federal subject
The federal subjects of Russia, also referred to as the subjects of the Russian Federation () or simply as the subjects of the federation (), are the administrative division, constituent entities of Russia, its top-level political division ...
of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
(an oblast
An oblast ( or ) is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term ''oblast'' is often translated i ...
). With a population of 8,524,665 ( 2021 Census) living in an area of , it is one of the most densely populated regions in the country and is the second most populous federal subject. The oblast has no official administrative center
An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune, is located.
In countries with French as the administrative language, such as Belgiu ...
; its public authorities are located in Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
and Krasnogorsk (the Moscow Oblast Duma
The Moscow Oblast Duma () is the regional parliament of Moscow Oblast, a federal subject of Russia.
It consists of 50 deputies that, since 2011, are elected under a mixed-member proportional system, with 25 members elected in party lists and ...
and the local government), and also across other locations in the oblast.According to Article 24 of the Charter of Moscow Oblast, the government bodies of the oblast are located in the city of Moscow and throughout the territory of Moscow Oblast. However, Moscow is not named the official administrative center of the oblast.
Located in European Russia
European Russia is the western and most populated part of the Russia, Russian Federation. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the country's sparsely populated and vastly larger eastern part, Siberia, which is situated in Asia ...
between latitudes 54° and 57° N and longitudes 35° and 41° E, Moscow Oblast borders Tver Oblast
Tver Oblast (, ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Tver. From 1935 to 1990, it was known as Kalinin Oblast (). Population:
Tver Oblast is a region of lakes, such as Seliger and Brosno. Much o ...
in the northwest, Yaroslavl Oblast
Yaroslavl Oblast is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast), which is located in the Central Federal District, surrounded by the Tver Oblast, Tver, Moscow Oblast, Moscow, Ivanovo Oblast, Ivanovo, Vladimir Oblast, Vlad ...
in the north, Vladimir Oblast
Vladimir Oblast () is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Vladimir, which is located east of Moscow. As of the 2010 Census, the oblast's population was 1,443,693.
The UNESCO World Heritage L ...
in the northeast and east, Ryazan Oblast
Ryazan Oblast (, ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Ryazan, which is also the oblast's largest city.
Geography
Ryazan Oblast ...
in the southeast, Tula Oblast
Tula Oblast () is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (an Oblasts of Russia, oblast) of Russia. It is geographically located in European Russia and is administratively part of the Central Federal District, covering an area of . It has a ...
in the south, Kaluga Oblast
Kaluga Oblast () is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Kaluga. The Russian Census (2021), 2021 Russian Census found a population o ...
in the southwest, and Smolensk Oblast
Smolensk Oblast (), informally also called Smolenshchina (), is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative centre is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Smolensk. As of the 2021 Russ ...
in the west. The oblast mostly surrounds the federal city
The term federal city is a title for certain cities in Germany, Switzerland, Russia, and several national capitals.
Germany
In Germany, the former West German capital Bonn has been designated with the title of federal city (''Bundesstadt''), ma ...
of Moscow, which is not part of the oblast, but rather a separate federal subject in its own right. The oblast is highly industrialized
Industrialisation ( UK) or industrialization ( US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive reorganisation of an economy for the ...
, with the major industries being metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
, oil refining
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial processes, industrial process Factory, plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refining, refined into products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, Bitumen, asphalt base, ...
, and mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines and mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and engineering mathematics, mathematics principl ...
, along with the food, energy, and chemical industries.
Geography

Relief
The oblast is mostly flat, with some hills with a height of about in the western and extensive lowlands in the eastern part. From the southwest to northeast, the oblast is crossed by the border of the Moscow glacier to the north of the common ice-erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
form with moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and Rock (geology), rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a gla ...
ridges, and to the south are only erosional landforms. The western and northern parts of the oblast contain the Moscow Uplands. Their average height peaks at about near Dmitrov
Dmitrov () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center of Dmitrovsky District, Moscow Oblast, Dmitrovsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located to the north of Moscow on the Yakhroma River and the Mosc ...
and the upper point of lies near the village of Shapkino in Mozhaysky District
Mozhaysky District is the name of several administrative and municipal districts in Russia:
* Mozhaysky District, Moscow, a district in Western Administrative Okrug of the federal city of Moscow
*Mozhaysky District, Moscow Oblast, an administrati ...
. The northern part of the Moscow Uplands is steeper than the southern part. The uplands contain lakes of glacial origin, such as Lakes Nerskoye and Krugloye. To the north of the Moscow Uplands lies the alluvial Verhnevolzhsk Depression; It is marshy and flat with the height varying between about and .
To the south stretches a hilly area of the Moskvoretsko-Oksk plain. Its greatest height of lies in the area of Tyoply Stan, within the Moscow city limits. The plain has clearly defined river valleys, especially in the south parts, and occasional karst
Karst () is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble carbonate rocks such as limestone and Dolomite (rock), dolomite. It is characterized by features like poljes above and drainage systems with sinkholes and caves underground. Ther ...
relief, mostly in Serpukhovsky District
Serpukhovsky District () is an administrativeLaw #11/2013-OZ and municipalLaw #78/2005-OZ district (raion), one of the thirty-six in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It is located in the south of the oblast. The area of the district is . Its administrative ...
. In the extreme south, after the Oka River, lies the Central Russian Upland
The Central Russian Upland (also: Middle Russian Upland () and East European Upland) is an upland area of the East European Plain and is an undulating plateau with an average elevation of . Its highest peak is measured at . The southeastern porti ...
. It contains numerous gullies and ravines and has average height above 200 m with the maximum of 236 m near Pushchino
Pushchino ( rus, Пущино, p=ˈpuɕːɪnə) is a town in Moscow Oblast, Russia, an important scientific center of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Situated south of Moscow, and 13 km south-east of Serpukhov, on the right side of the Ok ...
.
Most of the eastern part of Moscow Oblast is taken by the vast Meshchera Lowlands
Meshchera Lowlands (Meshchyora Lowlands) (), also referred to as simply Meshchera/Meshchyora, is a spacious lowland in the middle of the European Russia. It is named after the Finnic Meshchera people, which used to live there (later mixing ...
with much wetland in their eastern part. Their highest hill peaks at but the average heights are . Most lakes of the lowlands, such as Lakes Chyornoye and Svyatoye, are of glacial origin. Here lies the lowest natural elevation of the region, the water level of Oka River at .
Geology and minerals
Geology
Moscow Oblast is located in the central part of the East European craton. Like all cratons, the latter is composed of the crystalline basement and sedimentary cover. The basement consists of Archaean andProterozoic
The Proterozoic ( ) is the third of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8 Mya, and is the longest eon of Earth's geologic time scale. It is preceded by the Archean and followed by the Phanerozo ...
rocks and the cover is deposited in the Palaeozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of ...
, Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
and Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three g ...
eras. The lowest depth of the basement () is to the south of Serebryanye Prudy
Serebryanye Prudy (, lit. ''Silver Ponds'') is an types of inhabited localities in Russia, urban locality (a urban-type settlement, work settlement) and the administrative center of Serebryano-Prudsky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on ...
, in the very south area of the oblast, and the largest () is to the east of Sergiyev Posad
Sergiyev Posad ( rus, Сергиев Посад, p=ˈsʲɛrgʲɪ(j)ɪf pɐˈsat) is a city that is the administrative center of Sergiyevo-Posadsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia. Population:
The city contains the Trinity Lavra of St. Sergi ...
, in the northeast region.
Tertiary
Tertiary (from Latin, meaning 'third' or 'of the third degree/order..') may refer to:
* Tertiary period, an obsolete geologic period spanning from 66 to 2.6 million years ago
* Tertiary (chemistry), a term describing bonding patterns in organic ch ...
deposits are almost absent within the oblast. Significantly more abundant are deposits of the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
and Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
periods. In the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
period, a sea was covering Moscow Oblast, as evidenced by phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
deposits and a variety of sands. Cretaceous sediments are most common in the north of the oblast. The sea was wider in Jurassic than in Cretaceous period. Typical Jurassic deposits, in the form of black clay, are found within and around the city of Moscow and in the valley of the Moscow River
The Moskva (, ''Moskva-reka'') is a river that flows through European Russia, western Russia. It River source, rises about west of Moscow and flows roughly east through the Smolensk Oblast, Smolensk and Moscow Oblasts, passing through central M ...
. Carboniferous deposits in Moscow Oblast are represented by dolomite, limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
, and marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, Clay minerals, clays, and silt. When Lithification, hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
M ...
. Coal deposits rich in organic remains occur in the south, especially in Serpukhovsky District, and in the western regions. Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
deposits were also found within the region.
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
deposits are widely distributed in Moscow Oblast; their thickness decreases from the northwest to southeast. It is believed that there were four glaciations in the area. The first occurred in the Lower Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
and spread to the east–west part of the Oka River valley, it left almost no trace in the region. In the Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, more widely known as the Middle Pleistocene (its previous informal name), is an Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale or a Stage (stratigraphy), stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocen ...
, there were two powerful glaciations. The Dnieper glacier covered a large part of the Russian Plain, whereas the Moscow glaciation stopped just south of the present city of Moscow. The last glaciation, the Valdai glaciation, occurred in the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
; it did not directly affect the territory of Moscow Oblast, but left traces in the form of fluvioglacial deposits
Fluvioglacial landforms or glaciofluvial landforms are those that result from the associated erosion and deposition of sediments caused by glacial meltwater. Glaciers contain suspended sediment loads, much of which is initially picked up from the ...
, mainly in the north area. The glaciers left behind a moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and Rock (geology), rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a gla ...
loam
Loam (in geology and soil science) is soil composed mostly of sand (particle size > ), silt (particle size > ), and a smaller amount of clay (particle size < ). By weight, its mineral composition is about 40–40–20% concentration of sand–si ...
with pebbles and boulders of various rocks, such as granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
, gneiss
Gneiss (pronounced ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. This rock is formed under p ...
, quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock that was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tecton ...
, dolomite, limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
and sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
. Its thickness varies between a few meters at watersheds and 100 m at moraine ridges.
Minerals
Moscow Oblast is rich in minerals. Sands from the sediments of different periods (mainly Quaternary and Cretaceous) are of high quality and are widely used in construction. Quartz sand (milledquartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
) is used in the glass industry, their production is conducted from the end of 17th century near Lyubertsy
Lyubertsy (, ) is a city and the administrative center of Lyuberetsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia.
Demographics
Population:
History
It was first mentioned in 1621 and was granted town status in 1925. It is sometimes described as a wo ...
. Much of the production is currently halted due to environmental concerns, and only the Yeganovskoye field is being exploited; its silica sand reserves are 33 million tonnes and annual production reaches 675,000 tonnes. Sand and gravel deposits are abundant within the Smolensk-Moscow Upland. Sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
deposits are developed in Klinsky and Dmitrovsky Districts.
There are numerous clay deposits within the oblast; fusible clay is excavated in Sergiyev Posad
Sergiyev Posad ( rus, Сергиев Посад, p=ˈsʲɛrgʲɪ(j)ɪf pɐˈsat) is a city that is the administrative center of Sergiyevo-Posadsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia. Population:
The city contains the Trinity Lavra of St. Sergi ...
. The Yeldiginskoye field near the village of Sofrino
Sofrino () is an urban locality (an urban-type settlement) in Pushkinsky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencie ...
has reserves estimated at 30 million cubic meters; its annual production reaches . Refractory white clay occurs in the eastern region, in the Carboniferous and Jurassic sediments, and is extracted from the 14th century near Gzhel
Gzhel (Russian: Гжель, IPA: �ʐelʲ is a Russian style of blue and white pottery, blue and white ceramics which takes its name from the Gzhel (selo), Moscow Oblast, village of Gzhel and surrounding area, where it has been produced sinc ...
. The largest (Kudinovskoye) deposit is near the town of Elektrougli
Elektrougli () is a town in Noginsky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Moscow–Nizhny Novgorod railway, east of Moscow and southeast of Noginsk, the administrative center of the district. Population:
Name
In 1899 was establ ...
with the reserves of 3 billion tonnes. Also widespread are loams which are used in brick manufacture and limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
s ("white stone"). The famous Myachkovo deposit of carboniferous limestone provided material that went for cladding of such buildings in Moscow as the Bolshoi Theater
The Bolshoi Theatre ( rus, Большо́й теа́тр, r=Bol'shoy teatr, p=bɐlʲˈʂoj tʲɪˈat(ə)r, t=Grand Theater) is a historic opera house in Moscow, Russia, originally designed by architect Joseph Bové. Before the October Revoluti ...
. The mining in Myachkovo had been stopped and currently, limestone is provided by the quarries of Podolsky, Voskresensky, and Kolomensky District
Kolomensky District () is an administrativeLaw #11/2013-OZ and municipalLaw #43/2005-OZ district (raion), one of the thirty-six in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It is located in the southeast of the oblast and borders with Lukhovitsky, Ozyorsky, Stupi ...
s. The latter district also provides marble-like limestone.
Other industrial minerals of Moscow Oblast are dolomite, limestone tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock co ...
, and marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, Clay minerals, clays, and silt. When Lithification, hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
M ...
; mostly in the southern and eastern parts. Dolomite is used in the cement industry. Its mining is concentrated mainly near Shchyolkovo
Shchyolkovo ( rus, Щёлково, p=ˈɕːɵlkəvə) is a city and the administrative center of Shchyolkovsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River ( Oka's tributary), northeast of Moscow. Population: 112,865 ( 20 ...
, the reserves exceed 20 million tonnes and the annual production is about 650 tonnes.
Phosphates are produced in the Yegorevskoye and Severskoye fields. Meshchera and Verkhnevolzhsk Lowlands are rich in peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of the most ...
. The largest mines are "Ryazanovskoe" (840,000 tonnes per year) and "Radovitsky moss" (760,000 tonnes per year), both around Yegoryevsk
Yegoryevsk () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center of Yegoryevsky District, Moscow Oblast, Yegoryevsk Urban Settlement in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the bank of the Guslitsa River southeast of ...
. There are deposits of brown coal
Lignite (derived from Latin ''lignum'' meaning 'wood'), often referred to as brown coal, is a soft, brown, Combustion, combustible sedimentary rock formed from naturally compressed peat. It has a carbon content around 25–35% and is considered ...
beyond the Oka River, but they have no commercial value. There are also minor deposits of titanium and iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the f ...
in Serpukhovsky and Serebryano-Prudsky Districts.
Salts of potassium salt are being developed around Serpukhov and Yegoryevsk. There are also numerous mineral springs near Zvenigorod, Klin, and Serpukhov. They include surface springs and reservoirs at the depth of . Deeper, at there is a large sea of salt extending beyond Moscow Oblast. Waters with the salt concentration up to 300 g/L are used in the local food industry and spas.
Climate
The climate of Moscow Oblast ishumid continental
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depe ...
, with clearly expressed seasonality – short but warm summers and long, cold winters; the continentality increases from northwest to southeast. The period of the average temperature below lasts 130–150 days, beginning in early or mid-November and ending in late March (or very early April). The average annual temperature varies from to . The coldest months are January and February with the average temperature of in the west and in the east. With the arrival of arctic air, the temperature drops to below that may last up to twenty days during the winter, with the temperatures reaching . The minimum temperature of was observed in Naro-Fominsk
Naro-Fominsk () is a town and the administrative center of Naro-Fominsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Nara River, southwest from Moscow.
History
The Fominskoye village was first mentioned in Russian chronicles under the ...
. Thaws often occur in December and February due to the Atlantic, and rarely the Mediterranean cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an ant ...
s. The thaws usually last several days, and their total number from November to March can reach fifty. Snow starts accumulating in November, though sometimes in late October or early December, and disappears in mid-April (sometimes in late March). The snow depth is and the soil freezes to . The warmest month is July with the average temperature of in the northwest and in the southeast. The maximum temperature of was recorded in Kolomna
Kolomna (, ) is a historic types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, situated at the confluence of the Moskva River, Moskva and Oka Rivers, (by rail) southeast of Moscow. Population:
History
Mentioned for the fir ...
during 2010 Northern Hemisphere summer heat waves. The average annual rainfall is , the precipitation is maximal in the northwestern and minimal in the southeastern regions. The summer precipitation is usually , but severe droughts occur once in 25–30 years, with less than of rain over June–August.
Rivers and lakes
 There are more than three hundred rivers with the length above in Moscow Oblast. All rivers are calm and have well-developed valleys and
There are more than three hundred rivers with the length above in Moscow Oblast. All rivers are calm and have well-developed valleys and floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high Discharge (hydrolog ...
s. They are mostly fed by melting snow and the flood falls on April–May. The water level is low in summer and increases only with heavy rain. The rivers freeze over from late November until mid-April. The only navigable rivers are the Volga
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
, the Oka, and the Moskva River
The Moskva (, ''Moskva-reka'') is a river that flows through western Russia. It rises about west of Moscow and flows roughly east through the Smolensk and Moscow Oblasts, passing through central Moscow. About southeast of Moscow, at the cit ...
.Wagner BB, Klevkova IRivers of Moscow region
Moscow, MGPU, 2003. Most rivers belong to the basin of the
Volga
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
, which itself only crosses a small part in the north of Moscow Oblast, near the border with Tver Oblast
Tver Oblast (, ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Tver. From 1935 to 1990, it was known as Kalinin Oblast (). Population:
Tver Oblast is a region of lakes, such as Seliger and Brosno. Much o ...
. The second largest river of the region is the Oka. The northern part of Moscow Oblast includes such Volga tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
as the Shosha, the Lama
Lama () is a title bestowed to a realized practitioner of the Dharma in Tibetan Buddhism. Not all monks are lamas, while nuns and female practitioners can be recognized and entitled as lamas. The Tibetan word ''la-ma'' means "high mother", ...
, the Dubna
Dubna ( rus, Дубна́, p=dʊbˈna) is a town in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It has a status of '' naukograd'' (i.e. town of science), being home to the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, an international nuclear physics research center and o ...
, the Sestra, and the Yakhroma. On the south flow the tributaries of the Oka, including the Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an independent agency of the United States government within the executive branch, charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It is also task ...
, the Protva
The Protva () is a river in the Moscow and Kaluga oblasts in Russia. It is a left tributary of the Oka. It is long, and has a drainage basin of .Lopasnya River
The Lopasnya () is a river in Moscow Oblast in Russia. It is a left tributary of the Oka. It is 108 km in length, with a drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, ...
s. The Moskva River, which almost entirely flows within the oblast, also belongs to the Oka basin. The eastern and northeastern regions, including much of Meschersk Depression, are irrigated by the tributaries of the Klyazma River
The Klyazma (, ''Klyaz'ma'' or ''Kliazma''), a river in the Moscow, Nizhny Novgorod, Ivanovo and Vladimir Oblasts in Russia, forms a left tributary of the Oka.
, which itself is a main tributary of the Oka.
The Moscow Canal
The Moscow Canal (), named the Moskva–Volga Canal until 1947, is a canal in Russia that connects the Moskva (river) with the Volga. It is located in Moscow itself and in the Moscow Oblast. The canal connects to the Moskva River in Tushino (an ...
crosses the northern part of Moscow Oblast through the Ikshinskyoe, Klyazminskoye, Pyalovskoye, and Pestovskoye Reservoirs. In the basin of the Moskva River, there are also Ozerninskoye, Mozhayskoye, Istrinskoye, and Ruza Reservoirs, providing Moscow with drinking water.
There are about 350 lakes in the oblast, almost all are shallow (5–10 m) and many are of glacial origin. The largest are () and Svyatoye () whereas the deepest () is Lake Glubokoye in Ruzsky District
Ruzsky District () is an administrativeLaw #11/2013-OZ and municipalLaw #76/2005-OZ district (raion), one of the thirty-six in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It is located in the west of the oblast. The area of the district is . Its administrative center ...
. There are also many marshes, especially within the Meshchersk and Verkhnevolzhsk lowlands.
Soils
The oblast is dominated by relatively infertilepodsol
Podzols, also known as podosols, spodosols, or espodossolos, are the typical soils of coniferous or Taiga, boreal forests and also the typical soils of eucalypt forests and heathlands in southern Australia. In Western Europe, podzols develop on he ...
soils which require fertilizers for commercial agriculture. On the hills there is more loam
Loam (in geology and soil science) is soil composed mostly of sand (particle size > ), silt (particle size > ), and a smaller amount of clay (particle size < ). By weight, its mineral composition is about 40–40–20% concentration of sand–si ...
and the low-lying areas have more of bog, sandy loam and sand. Chernozem
Chernozem ( ),; also called black soil, regur soil or black cotton soil, is a black-colored soil containing a high percentage of humus (4% to 16%) and high percentages of phosphorus and ammonia compounds. Chernozem is very fertile soil and can ...
is scarce and occurs only south of the Oka River. Gray forest soils are spread between the Oka, Moskva, and Klyazma Rivers, mostly in Ramensky and Voskresensky Districts. Marshy soils are common in Meshchersk and Verkhnevolzhsk lowlands. Valleys of large rivers are rich in alluvial soils. In general, soils are heavily polluted with chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and household and industrial waste, especially around Moscow, Orekhovo-Zuyevo
Orekhovo-Zuyevo (, ) is an industrial city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located east of Moscow in a forested area on the Klyazma River (a tributary of the Oka). Orekhovo (), often pronounced only as ''Orekh'', is a Russian word which means "nut ...
, Noginsk
Noginsk (), known as Bogorodsk () until 1930, is a Classification of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Noginsky District, Bogorodsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located east of the Moscow Ring Road on ...
, and Voskresensk.
Flora
Coniferous
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
(mainly fir) trees dominate the northern (Verkhnevolzhsk lowlands) and western parts (Mozhaysky, Lotoshinsky, and Shakhovsky Districts). Forests of Meshchora consist primarily of pine; in waterlogged lowlands, there are individual alder
Alders are trees of the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus includes about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species ex ...
forests. Central and eastern regions have coniferous-deciduous forests with the main tree species of spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' ( ), a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal (taiga) regions of the Northern hemisphere. ''Picea'' ...
, pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
, birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 3 ...
, and aspen
Aspen is a common name for certain tree species in the Populus sect. Populus, of the ''Populus'' (poplar) genus.
Species
These species are called aspens:
* ''Populus adenopoda'' – Chinese aspen (China, south of ''P. tremula'')
* ''Populus da ...
often mixed with bushes of hazel
Hazels are plants of the genus ''Corylus'' of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family, Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K ...
. To the south lies the subzone of broad-leaved forests of oak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
, lime
Lime most commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a color between yellow and green
Lime may also refer to:
Bo ...
, maple
''Acer'' is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the soapberry family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated si ...
and elm
Elms are deciduous and semi-deciduous trees comprising the genus ''Ulmus'' in the family Ulmaceae. They are distributed over most of the Northern Hemisphere, inhabiting the temperate and tropical- montane regions of North America and Eurasia, ...
. Moscow-Oka Upland is the transition zone which is dominated by spruce, for example, in the upper reaches of the Lopasnya River
The Lopasnya () is a river in Moscow Oblast in Russia. It is a left tributary of the Oka. It is 108 km in length, with a drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, ...
. Valleys of the Oka are covered in pine forests of the steppe type and the far south regions (Serebryano-Prudsky and partially Serpukhovsky Districts) are cultivated steppes with occasional lime and oak groves.
The intensive cutting of Moscow region forests in the 18–19th centuries reduced them and changed their species: conifers were replaced by birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 3 ...
and aspen
Aspen is a common name for certain tree species in the Populus sect. Populus, of the ''Populus'' (poplar) genus.
Species
These species are called aspens:
* ''Populus adenopoda'' – Chinese aspen (China, south of ''P. tremula'')
* ''Populus da ...
. There is almost no logging nowadays and the forests are being restored, especially around Moscow.
Swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
s are prevalent in the eastern areas, such as Shatursky and Lukhovitsky Districts. The natural floodplain meadows are almost gone. The number of native plant species is reduced, but some foreign species flourish, such as Canadian maple. Endemic species include water caltrop
The water caltrop is any of three extant species of the genus ''Trapa'': ''Trapa natans'', ''Trapa bicornis'' and the endangered ''Trapa rossica''. It is also known as buffalo nut, bat nut, devil pod, ling nut, mustache nut, singhara nut or wate ...
and lady's slipper.
Fauna
 The mammals of Moscow Oblast include
The mammals of Moscow Oblast include badger
Badgers are medium-sized short-legged omnivores in the superfamily Musteloidea. Badgers are a polyphyletic rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united by their squat bodies and adaptions for fossorial activity rather than by the ...
, squirrel, beaver
Beavers (genus ''Castor'') are large, semiaquatic rodents of the Northern Hemisphere. There are two existing species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers are the second-large ...
, otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among ...
, muskrat
The muskrat or common muskrat (''Ondatra zibethicus'') is a medium-sized semiaquatic rodent native to North America and an introduced species in parts of Europe, Asia, and South America.
The muskrat is found in wetlands over various climates ...
, stoat
The stoat (''Mustela erminea''), also known as the Eurasian ermine or ermine, is a species of mustelid native to Eurasia and the northern regions of North America. Because of its wide circumpolar distribution, it is listed as Least Concern on th ...
, Russian desman
The Russian desman (''Desmana moschata''; ''vykhukhol'') is a small semiaquatic mammal that inhabits the Volga river, Volga, Don River, Russia, Don and Ural River basins in Russia. Some authorities, citing old Soviet sources, claim the animal ca ...
, raccoon dog
''Nyctereutes'' (Greek: ''nyx, nykt-'' "night" + ''ereutēs'' "wanderer") is a genus of canid which includes only two extant species, both known as raccoon dogs: the common raccoon dog (''Nyctereutes procyonoides'') and the Japanese raccoon do ...
, hedgehog, hare (mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
and European
European, or Europeans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe and other West ...
), shrew
Shrews ( family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to dif ...
s ( common shrew, Eurasian pygmy shrew, lesser white-toothed shrew, Eurasian water shrew, etc.), weasel
Weasels are mammals of the genus ''Mustela'' of the family Mustelidae. The genus ''Mustela'' includes the least weasels, polecats, stoats, ferrets, and European mink. Members of this genus are small, active predators, with long and slend ...
, fox, moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tal ...
, wild boar, European mole
The European mole (''Talpa europaea'') is a mammal of the order Eulipotyphla. It is also known as the common mole and the northern mole.
This mole lives in a tunnel system, which it constantly extends. It uses these tunnels to hunt its prey. ...
, brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing and painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors Orange (colour), orange and black.
In the ...
and black rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is n ...
s, marten
A marten is a weasel-like mammal in the genus ''Martes'' within the subfamily Guloninae, in the family Mustelidae. They have bushy tails and large paws with partially retractile claws. The fur varies from yellowish to dark brown, depending on ...
, mice and voles
Voles are small rodents that are relatives of lemmings and hamsters, but with a stouter body; a longer, hairy tail; a slightly rounder head; smaller eyes and ears; and differently formed molar (tooth), molars (high-crowned with angular cusps i ...
(wood mouse
The wood mouse (''Apodemus sylvaticus'') is a Muridae, murid rodent native to Europe and northwestern Africa. It is closely related to the yellow-necked mouse (''Apodemus flavicollis'') but differs in that it has no band of yellow fur around the ...
, yellow-necked mouse
The yellow-necked mouse (''Apodemus flavicollis''), also called yellow-necked field mouse or yellow-necked wood mouse, is closely related to the wood mouse, with which it was long confused. It was only recognised as a separate species in 1894. I ...
, house mouse
The house mouse (''Mus musculus'') is a small mammal of the rodent family Muridae, characteristically having a pointed snout, large rounded ears, and a long and almost hairless tail. It is one of the most abundant species of the genus '' Mus''. A ...
, Eurasian harvest mouse
The harvest mouse (''Micromys minutus'') is a small rodent native to Europe and Asia. It is typically found in fields of cereal crops, such as wheat and oats, in reed beds and in other tall ground vegetation, such as long grass and hedgerows. I ...
, northern birch mouse
The northern birch mouse (''Sicista betulina'') is a small rodent about long (without the tail), weighing . It lives in northern Europe and Asia in forest and marsh zones.
It hibernates in burrows. It eats shoots, grains, berries, and sometime ...
, bank vole
The bank vole (''Clethrionomys glareolus'') is a small vole with red-brown fur and some grey patches, with a tail about half as long as its body. A rodent, it lives in woodland areas and is around in length. The bank vole is found in much of Eu ...
, field vole
The short-tailed field vole, short-tailed vole, or simply field vole (''Microtus agrestis'') is a grey-brown vole, around 10 cm in length, with a short tail. It is one of the most common mammals in Europe, with a range extending from the Atl ...
, tundra vole
The tundra vole (''Alexandromys oeconomus'') or root vole is a medium-sized vole found in Northern and Central Europe, Asia, and northwestern North America, including Alaska and northwestern Canada. In the western part of the Netherlands, the tu ...
, European water vole
The European water vole (''Arvicola amphibius'') or northern water vole is a semi-aquatic rodent. It is often informally called the water rat, though it only superficially resembles a true rat. Water voles have rounder noses than rats, deep bro ...
), European mink
The European mink (''Mustela lutreola''), also known as the Russian mink and Eurasian mink, is a semiaquatic species of mustelid native to Europe.
It is similar in colour to the American mink, but is slightly smaller and has a less specialize ...
, deer (roe
Roe, ( ) or hard roe, is the fully ripe internal egg masses in the ovaries, or the released external egg masses, of fish and certain marine animals such as shrimp, scallop, sea urchins and squid. As a seafood, roe is used both as a cooking, c ...
, red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–750 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a seconda ...
, spotted), hazel
Hazels are plants of the genus ''Corylus'' of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family, Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K ...
and fat dormouse, and European polecat
The European polecat (''Mustela putorius''), also known as the common polecat, black polecat and forest polecat, is a mustelid species native to Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. It is of a generally dark brown colour, with a pale underbel ...
. At the borders there are occasional bears, lynxes and wolves. In the southern areas there are also speckled ground squirrel
The speckled ground squirrel or spotted souslik (''Spermophilus suslicus'') is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae from Eastern Europe. ''Spermophilus suslicus'' consists of three subspecies: ''S. s. boristhenicus'', ''S. s. guttatus'', ...
, dwarf hamster, great jerboa and beech marten
The beech marten (''Martes foina''), also known as the stone marten, house marten or white breasted marten, is a species of marten native to much of Europe and Central Asia, though it has established a feral population in North America. It is li ...
. Some areas contain stable populations of imported animals, such as flying squirrel
Flying squirrels (scientifically known as Pteromyini or Petauristini) are a tribe (biology), tribe of 50 species of squirrels in the family (biology), family Squirrel, Sciuridae. Despite their name, they are not in fact capable of full flight i ...
, American mink
The American mink (''Neogale vison'') is a semiaquatic species of Mustelidae, mustelid native to North America, though human introduction has expanded its range to many parts of Europe, Asia, and South America. Because of range expansion, the Am ...
and Siberian roe deer
The Siberian roe deer, eastern roe deer, or Asian roe deer (''Capreolus pygargus''), is a species of roe deer found in northeastern Asia. In addition to Siberia and Mongolia, it is found in Kazakhstan, the Tian Shan Mountains of Kyrgyzstan, east ...
. In the oblast, there are more than a dozen kinds of bat and moth.Tourov SS, Wildlife of Podmoskovie, Moscow, 1961
There are more than 170 species of birds in the area with large numbers of crows, sparrows, ducks, magpies, woodpeckers, thrushes
The thrushes are a passerine bird family, Turdidae, with a worldwide distribution. The family was once much larger before biologists reclassified the former subfamily Saxicolinae, which includes the chats and European robins, as Old World flycat ...
, grouses, bullfinch
Bullfinch is a name given to two groups of passerine birds.
True bullfinches
The true bullfinches are thick-billed finches in the passerine family Fringillidae. They comprise the genus '' Pyrrhula''. These birds are distributed across Asia and Eu ...
es, nightingale
The common nightingale, rufous nightingale or simply nightingale (''Luscinia megarhynchos''), is a small passerine bird which is best known for its powerful and beautiful song. It was formerly classed as a member of the thrush family Turdidae, ...
s, corncrakes, northern lapwings, white storks, grey herons, seagulls and grebes. Over forty species are being hunted.
Rivers and lakes of Moscow Oblast are rich in fish, such as ruffe, carp, bream, bass (fish), bass, Rutilus, roaches, Chinese sleeper, perch and pike (fish), pike. There are six species of reptiles: three lizards (Anguis fragilis, slowworm, viviparous lizard and sand lizard) and three snakes (Vipera berus, European adder, grass snake and Coronella, smooth snake). There is evidence for bog turtles in some areas. Amphibians are represented by 11 species including smooth newt, great crested newt, common toad, European green toad, common frog, moor frog, marsh frog, Pelobates fuscus, common spadefoot and European fire-bellied toad. Insects are numerous, with bees alone accounting for more than 300 species.
In Serpukhovsky District, there is the Prioksko-Terrasny Nature Reserve which contains protected wisents. Near Moscow lies Losiny Ostrov National Park of federal significance.
Eurasian harvest mouse
The harvest mouse (''Micromys minutus'') is a small rodent native to Europe and Asia. It is typically found in fields of cereal crops, such as wheat and oats, in reed beds and in other tall ground vegetation, such as long grass and hedgerows. I ...
File:Podiceps cristatus 5 (Marek Szczepanek).jpg, Great crested grebe
Environment
The ecological situation in the Moscow Oblast is serious. The areas adjacent to Moscow, and industrial zones in the east and south-east regions are heavily polluted. Most contamination originates from emissions from Kashira Power Plant, Kashira and Shatura Power Stations and disposal of household and industrial waste. For example, the Timohovskaya dump is one of the largest in Europe; other objects of concern are aging oil storage tanks, and nuclear waste in the Sergiyevo-Posadsky District. Contamination level is highest in Moscow, Voskresensk and Klin, high in Dzerzhinsky, Moscow Oblast, Dzerzhinsky,Kolomna
Kolomna (, ) is a historic types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, situated at the confluence of the Moskva River, Moskva and Oka Rivers, (by rail) southeast of Moscow. Population:
History
Mentioned for the fir ...
, Mytishchi, Podolsk, Serpukhov, Shchyolkovo
Shchyolkovo ( rus, Щёлково, p=ˈɕːɵlkəvə) is a city and the administrative center of Shchyolkovsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River ( Oka's tributary), northeast of Moscow. Population: 112,865 ( 20 ...
, and Elektrostal, and low in Prioksko-Terrasny Biosphere Reserve. The major contaminants are formaldehyde and phenol in Moscow; ammonia and hydrogen fluoride
in Voskresensk; formaldehyde in Klin, Kolomna, Mytishchi and Podolsk, phenol in Serpukhov. The most polluted rivers are Moscow, Oka and Klyazma. In the Moscow area and in major cities (in particular, in Podolsk, Orekhovo-Zuyevo, Serpukhov, Lukhovitsy and Stupino) also heavily polluted are groundwaters.
History
 The territory of what is now Moscow Oblast had been inhabited for more than twenty thousand years. Numerous mounds and settlements from Iron Age were discovered there. Up to the 9–10th centuries, the Moskva River basin and adjacent lands were inhabited by Finnic peoples. Slavs populated the area only in the 10th century. In mid-12th century, the lands became part of Vladimir-Suzdal, Vladimir-Suzdal Principality. Several important cities were founded around that time, including Volokolamsk (1135), Moscow (1147), Zvenigorod (1152), and
The territory of what is now Moscow Oblast had been inhabited for more than twenty thousand years. Numerous mounds and settlements from Iron Age were discovered there. Up to the 9–10th centuries, the Moskva River basin and adjacent lands were inhabited by Finnic peoples. Slavs populated the area only in the 10th century. In mid-12th century, the lands became part of Vladimir-Suzdal, Vladimir-Suzdal Principality. Several important cities were founded around that time, including Volokolamsk (1135), Moscow (1147), Zvenigorod (1152), and Dmitrov
Dmitrov () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center of Dmitrovsky District, Moscow Oblast, Dmitrovsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located to the north of Moscow on the Yakhroma River and the Mosc ...
(1154). In the first half of the 13th century, the entire Vladimir-Suzdal Principality, including the Moscow area, was Mongol invasion of Rus', conquered by the Mongols.
 In the 13th century, the land around Moscow was part of Grand Duchy of Moscow, which subsequently was the center of the unification of Russian lands, in particular the Mongol raids. In 1380, from Kolomna the prince Dmitry Donskoy led his troops to defeat the Mongols at the Battle of Kulikovo. The southern part of Moscow Oblast was then part of the Principality of Ryazan; it was attached to Moscow only in the 1520.
In 1708, Moscow Governorate was established by the decree of Peter the Great; the area included most of the present Moscow Oblast. The Battle of Borodino, which decided the outcome of the French invasion of Russia was fought in 1812 near Mozhaysk.
Industries developed in Moscow Oblast in the 17–19th centuries. They were centered in Noginsk, Bogorodsk, Pavlovsky Posad, and
In the 13th century, the land around Moscow was part of Grand Duchy of Moscow, which subsequently was the center of the unification of Russian lands, in particular the Mongol raids. In 1380, from Kolomna the prince Dmitry Donskoy led his troops to defeat the Mongols at the Battle of Kulikovo. The southern part of Moscow Oblast was then part of the Principality of Ryazan; it was attached to Moscow only in the 1520.
In 1708, Moscow Governorate was established by the decree of Peter the Great; the area included most of the present Moscow Oblast. The Battle of Borodino, which decided the outcome of the French invasion of Russia was fought in 1812 near Mozhaysk.
Industries developed in Moscow Oblast in the 17–19th centuries. They were centered in Noginsk, Bogorodsk, Pavlovsky Posad, and Orekhovo-Zuyevo
Orekhovo-Zuyevo (, ) is an industrial city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located east of Moscow in a forested area on the Klyazma River (a tributary of the Oka). Orekhovo (), often pronounced only as ''Orekh'', is a Russian word which means "nut ...
and were dominated by textile production. The first railway in Russia was constructed in the Moscow Oblast in 1851, connecting Moscow and Saint Petersburg, and in 1862 the line to Nizhny Novgorod was opened.
In the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR, ''Central Industrial Oblast'' was established on January 14, 1929.''Administrative-Territorial Structure of the Union Republics. 1987.'', p. 179 It included the abolished Moscow Governorate, Moscow, Ryazan Governorate, Ryazan, Tver Governorate, Tver, Tula Governorate, Tula, Vladimir Governorate, Vladimir, and Kaluga Governorates. The oblast was divided into ten okrugs and had the administrative center in Moscow. On June 3, 1929, the area was renamed ''Moscow Oblast'' and on July 30, 1930, the division into ten okrugs was abolished.
Parts of the then bulky ''Moscow Oblast'' were gradually transferred to other divisions. In particular, twenty-six districts became part of Kalinin Oblast in January 1935, and another seventy-seven districts were separated in September 1937 as Tula Oblast, Tula and Ryazan Oblast
Ryazan Oblast (, ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Ryazan, which is also the oblast's largest city.
Geography
Ryazan Oblast ...
s. Borovsky District, Borovsky, , Maloyaroslavetsky District, Maloyaroslavetsky, Ugodsko-Zavodsky District, Ugodsko-Zavodsky, and Petushinsky Districts were transferred in 1944 to Kaluga and Vladimir Oblasts.Pages of HistoryMoscow Oblast (in Russian)
Official site of Moscow Oblast (in Russian) In 1941 and 1942, one of the most significant military operations of World War II—the Battle of Moscow—was fought in the Moscow Oblast. Germany reached Solnechnogorsky, Klinsky, Istrinsky, Lobninsky, Khimkinsky, Naro-Fominsky, Volokolamsky, Kolomensky, Kashirsky, Serybryano-Prudsky Districts and others. According to the Constitution of Russia, adopted in December 1993, Moscow Oblast is one of the 83 federal subjects of Russia.
Economy
Industry
 In terms of industrial production, Moscow Oblast is second in Russia, after the city of Moscow. The industry of the Oblast relies on imported raw materials, strong scientific and technological base and highly skilled workforce; it is closely linked with the industry of Moscow.
Well developed are machinery and metalworking. There are plants for the thermal and nuclear power engineering (ZiO-Podolsk in Podolsk), nuclear fuel (TVEL in Elektrostal), space and missile (S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia, Energia in Korolyov (city), Korolyov, Lavochkin in Khimki, NGO engineering in Reutov, FTSDT "Union" in Dzerzhinsky, Moscow Oblast, Dzerzhinsky – development of solid rocket fuel, etc., IBC "Horizon" in Dzerzhinsky (town), Dzerzhinsky – power plants for aircraft, etc.); locomotives (Kolomna Locomotive Works, Kolomna factory), metro cars (Metrowagonmash in Mytischi), electric trains (Demikhovsky Engineering Works), cars (SeAZ), buses (Likinsky bus plant in Likino-Dulyovo); agricultural machines, excavators and cranes (
In terms of industrial production, Moscow Oblast is second in Russia, after the city of Moscow. The industry of the Oblast relies on imported raw materials, strong scientific and technological base and highly skilled workforce; it is closely linked with the industry of Moscow.
Well developed are machinery and metalworking. There are plants for the thermal and nuclear power engineering (ZiO-Podolsk in Podolsk), nuclear fuel (TVEL in Elektrostal), space and missile (S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia, Energia in Korolyov (city), Korolyov, Lavochkin in Khimki, NGO engineering in Reutov, FTSDT "Union" in Dzerzhinsky, Moscow Oblast, Dzerzhinsky – development of solid rocket fuel, etc., IBC "Horizon" in Dzerzhinsky (town), Dzerzhinsky – power plants for aircraft, etc.); locomotives (Kolomna Locomotive Works, Kolomna factory), metro cars (Metrowagonmash in Mytischi), electric trains (Demikhovsky Engineering Works), cars (SeAZ), buses (Likinsky bus plant in Likino-Dulyovo); agricultural machines, excavators and cranes (Lyubertsy
Lyubertsy (, ) is a city and the administrative center of Lyuberetsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia.
Demographics
Population:
History
It was first mentioned in 1621 and was granted town status in 1925. It is sometimes described as a wo ...
, Dmitrov
Dmitrov () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center of Dmitrovsky District, Moscow Oblast, Dmitrovsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located to the north of Moscow on the Yakhroma River and the Mosc ...
, Balashikha); stainless steel (Elektrostal), cables (Podolsk), optical devices (Krasnogorsky plant, Lytkarino Optical Glass Factory).
There are many defense enterprises, such as Russian Center for demonstrations of weapons, military equipment and technology in Krasnoarmeysk, Moscow Oblast, Krasnoarmeysk; Kamov, Phazotron, Bazalt, NPP Zvezda, MKB Fakel, MKB Raduga, National Research Institute of Aviation Systems, Krasnozavodsk Chemical Plant, Tikhomirov Scientific Research Institute of Instrument Design, Moscow Research Institute "Agat", Dolgoprudnenskoe Scientific Production Plant, and many others.
Chemical industry of the Oblast produces acids (Shchyolkovo
Shchyolkovo ( rus, Щёлково, p=ˈɕːɵlkəvə) is a city and the administrative center of Shchyolkovsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River ( Oka's tributary), northeast of Moscow. Population: 112,865 ( 20 ...
), mineral fertilizers (plants named "Phosphates" and "Mineral fertilizers" in Voskresensk, Moscow Oblast, Voskresensk), synthetic fibers (Serpukhov and Klin, Klinsky District, Moscow Oblast, Klin), plastics (Orekhovo-Zuyevo
Orekhovo-Zuyevo (, ) is an industrial city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located east of Moscow in a forested area on the Klyazma River (a tributary of the Oka). Orekhovo (), often pronounced only as ''Orekh'', is a Russian word which means "nut ...
), varnishes and paints (Sergiyev Posad, Odintsovsky paint factories), pharmaceuticals (Staraya Kupavna). There is a well-developed industry of construction materials with production of cement in Voskresensk and Kolomna (Shchurovsky cement factory), earthenware, porcelain in the Likino-Dulyovo (Dulevo Porcelain Factory) and Verbilki and dry mortar plant in Krasnogorsk.
Noginsk
Noginsk (), known as Bogorodsk () until 1930, is a Classification of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Noginsky District, Bogorodsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located east of the Moscow Ring Road on ...
, Orekhovo-Zuyevo
Orekhovo-Zuyevo (, ) is an industrial city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located east of Moscow in a forested area on the Klyazma River (a tributary of the Oka). Orekhovo (), often pronounced only as ''Orekh'', is a Russian word which means "nut ...
), wool (in Pavlovsky Posad and Pushkino, Pushkinsky District, Moscow Oblast, Pushkino) and jerseys (in Ivanteyevka, Moscow Oblast, Ivanteyevka and Dmitrov
Dmitrov () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center of Dmitrovsky District, Moscow Oblast, Dmitrovsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located to the north of Moscow on the Yakhroma River and the Mosc ...
). The silk production in Naro-Fominsk
Naro-Fominsk () is a town and the administrative center of Naro-Fominsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Nara River, southwest from Moscow.
History
The Fominskoye village was first mentioned in Russian chronicles under the ...
had been stopped. Traditional and renowned crafts include Gzhel
Gzhel (Russian: Гжель, IPA: �ʐelʲ is a Russian style of blue and white pottery, blue and white ceramics which takes its name from the Gzhel (selo), Moscow Oblast, village of Gzhel and surrounding area, where it has been produced sinc ...
, Zhostovo painting and Fedoskino miniature. Large foreign investment projects include the plant for manufacturing household appliances (TV sets, washing machines, refrigerators, etc.) by the South Korean company LG Corp., LG built near the village of Dorokhovo.
Energy
In 1999, Moscow Oblast consumed 15.4 billion m3 of natural gas, 3.32 million tonnes of oil, 2.13 million tonnes of coal and 8.5 billion kWh of electricity. Electricity for the Oblast is provided by the Kashirskaya thermal power plant (TPP, 1910 MW), Dzerzhynskaya TPP No 22 (1300 MW), Thermal Power Plant 27 (1100 MW), Shatura Power Station (1100 MW), Zagorskaya Pumped-storage hydroelectricity, hydroelectric power plant (1200 MW), Elektrogorsk TPP (623 MW) and several smaller plants. Major new energy project in the region is the construction of Zagorsk hydroelectric plant with the capacity of 840 MW. The deficit of energy is provided by powerlines connecting the region with Saint Petersburg, Volga Hydroelectric Station and other energy suppliers.Agriculture
Agriculture has a relatively minor role in the economy of the Oblast. Only 25% of land is cultivated and another 15% are used for other activities such as livestock farming. Agriculture is the least developed in the northern, eastern and western border regions. In the southern region, especially south of the Oka River, more than 50% of land is used in agriculture. Horticulture is typical for the southern region with most of the sown area (more than 3/5) occupied by forage crops. Large areas are reserved for grains, especially wheat, barley, oats and rye, and significant role plays potato. Greenhouses are very common and Moskovsky, Moscow Oblast, Moskovsky city hosts the largest greenhouse complex in Europe. Also grown are flowers and mushrooms. Livestock farming predominates over the crop, and is primarily aimed at the production of milk and meat. In addition to cattle, commonly bred are pigs and chickens. The economic crisis of the 1990s in Russia had severely affected the agriculture of Moscow Oblast. In particular, in the 2000s, as compared with 1970–80s, the grain production has fallen by more than 3 times; potatoes by 2.5 times; vegetables, livestock and poultry by 30%; milk by 2 times and eggs by 4 times.Transport
 Moscow Oblast has a dense transport network, including roads, railways and waterways along the largest rivers, lakes and reservoirs. Land routes are radially diverging from Moscow and crossed by one railway and MKAD, two highway rings. Neither railways nor roads, built for the most part many years ago, can cope with the steadily mounting traffic flows. About half of the roads are overloaded and three quarters do not meet modern requirements. Insufficient width of the roads and frequent repairs cause traffic jams.
Moscow Oblast has the highest density of railways in Russia. Eleven major radial lines originate in Moscow and run through the Oblast; the total length of the railways reaches 2,700 km. Almost all railroads are electrified. The largest rail hubs are
Moscow Oblast has a dense transport network, including roads, railways and waterways along the largest rivers, lakes and reservoirs. Land routes are radially diverging from Moscow and crossed by one railway and MKAD, two highway rings. Neither railways nor roads, built for the most part many years ago, can cope with the steadily mounting traffic flows. About half of the roads are overloaded and three quarters do not meet modern requirements. Insufficient width of the roads and frequent repairs cause traffic jams.
Moscow Oblast has the highest density of railways in Russia. Eleven major radial lines originate in Moscow and run through the Oblast; the total length of the railways reaches 2,700 km. Almost all railroads are electrified. The largest rail hubs are Orekhovo-Zuyevo
Orekhovo-Zuyevo (, ) is an industrial city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located east of Moscow in a forested area on the Klyazma River (a tributary of the Oka). Orekhovo (), often pronounced only as ''Orekh'', is a Russian word which means "nut ...
and Bekasovo, Moscow Oblast, Bekasovo. Regular navigation is carried on the rivers Volga, Oka and Moscow, as well as on the Moscow Canal
The Moscow Canal (), named the Moskva–Volga Canal until 1947, is a canal in Russia that connects the Moskva (river) with the Volga. It is located in Moscow itself and in the Moscow Oblast. The canal connects to the Moskva River in Tushino (an ...
. Major river ports are in Serpukhov and Kolomna. Also well-developed is pipeline transport. There are two major oil lines, two natural gas rings and numerous radial lines connecting Moscow with the largest gas producing regions of the country.
Moscow and Moscow Oblast have several international passenger airports, namely Sheremetyevo International Airport, Sheremetyevo (with two terminals), Vnukovo International Airport, Vnukovo, Domodedovo International Airport, Domodedovo and Ostafyevo International Airport, Ostafyevo. There is also Bykovo Airport, Bykovo Airport, which is used for freight. The largest military airport is Chkalovsky Airport, Chkalovsky (near Shchyolkovo
Shchyolkovo ( rus, Щёлково, p=ˈɕːɵlkəvə) is a city and the administrative center of Shchyolkovsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River ( Oka's tributary), northeast of Moscow. Population: 112,865 ( 20 ...
) which also processes some civilian passenger and cargo flights.
Major highways of Moscow Oblast are as follows:
*M1 highway (Russia), Minsk highway (M1 "Belarus" Moscow – Belarus) (E101)
*M2 highway (Russia), Simferopol highway (M2 "Crimea") Moscow – Belgorod (E105)
*M3 highway (Russia), Kiev highway (M3 "Ukraine" Moscow – Kaluga – Bryansk – Kyiv)
*M4 highway (Russia) (M4 "Don" Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
– Voronezh - Rostov-on-Don - Krasnodar) (E115)
*M5 highway (Russia), Ryazan highway (M5 "Ural" Moscow – Chelyabinsk) (E30)
*M7 highway (Russia), Nizhny Novgorod highway (M7 "Volga" Moscow – Ufa) (E22)
*M8 highway (Russia), Kholmogory – Yaroslavl highway (M8 "Kholmogory" Moscow – Arkhangelsk) (E115)
*M9 highway (Russia), Novorizhskoe highway (M9 "Baltic" Moscow – Riga) (E22)
*M10 highway (Russia), Leningrad highway (M10 "Russia" Moscow – Tver – Novgorod – Saint Petersburg) (E105)
*Mozhaysk highway (A100 Moscow – Borodino (village), Mozhaysky District, Moscow Oblast, Borodino)
*М11 Neva Moscow–Saint Petersburg motorway
*Russian route A101, Kaluga highway (A101, Moscow – Troitsk, Moscow Oblast, Troitsk – Obninsk – Kaluga)
*Schelkovskoe highway (A103 Moscow – Shchyolkovo
Shchyolkovo ( rus, Щёлково, p=ˈɕːɵlkəvə) is a city and the administrative center of Shchyolkovsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River ( Oka's tributary), northeast of Moscow. Population: 112,865 ( 20 ...
– Chernogolovka)
*Dmitrovskoe (A104 Moscow – Dubna)
*Small Concrete Ring (A107)
*Large Concrete Ring (А108)
* Central Ring Road (А113)
*Yegoryevsk highway (R105 Moscow – Kasimov)
*Pyatnitskoe highway (R111 Moscow – Solnechnogorsk)
*Rogachev highway (P113 Lobnya – Rogachevo, Dmitrovsky District, Moscow Oblast, Rogachevo)
*Nosovihinskoe highway (Moscow – Likino-Dulyovo)
*Warsaw highway (Moscow – Podolsk – Obninsk – Roslavl)
*Borovskoye highway (Moscow – Vnukovo District, Vnukovo)
*Rublyovo-Uspenskoe highway
*Dzerzhynsk highway (Dzerzhinsky, Moscow Oblast, Dzerzhinsky – Kotelniki – Novoryazanskoye highway)
*Ostashkovskoye highway (Moscow – Mytischi)
Government and awards
 Moscow Oblast was awarded three Order of Lenin, Orders of Lenin, on 3 January 1934, 17 December 1956 and 5 December 1966.
The highest executive organ is the Government of Moscow Oblast. Eighteen ministries act as the executive bodies of state authority. The powers, tasks, functions and competence of the Government are defined by the Charter of the Moscow Region. The Governor of the Moscow Oblast will be elected with the term of 5 years.Charter of Moscow Oblast
Moscow Oblast was awarded three Order of Lenin, Orders of Lenin, on 3 January 1934, 17 December 1956 and 5 December 1966.
The highest executive organ is the Government of Moscow Oblast. Eighteen ministries act as the executive bodies of state authority. The powers, tasks, functions and competence of the Government are defined by the Charter of the Moscow Region. The Governor of the Moscow Oblast will be elected with the term of 5 years.Charter of Moscow Oblast(in Russian) The Regional Duma of Moscow Oblast was formed on 12 December 1993. It consists of 50 deputies also serving a 5-year term. Sergey Shoygu was elected as Governor of Moscow Oblast in April 2012 by the Moscow Oblast Duma. Shoygu left office after only six months with his appointment when he was appointed as Ministry of Defence (Russia), Minister of Defence by Vladimir Putin. Andrey Yuryevich Vorobyov, Andrei Vorobyov was appointed as acting governor and won a full term to the office in the Moscow Oblast gubernatorial election, 2013, 2013 elections.
Science
Moscow Oblast has a high density of scientific research institutions, especially related to engineering and military technologies. The latter started developing in the region in 1930–1940s in Zhukovsky (city), Zhukovsky (aeronautical engineering), Klimovsk (development of small arms), Reutov (Missile Engineering), Fryazino (microwave electronics) and Korolyov (city), Korolyov (space technology). They were later joined by famous centers for basic sciences in Troitsk, Moscow Oblast, Troitsk, Chernogolovka (physics and chemistry), Dubna and Protvino (nuclear physics) andPushchino
Pushchino ( rus, Пущино, p=ˈpuɕːɪnə) is a town in Moscow Oblast, Russia, an important scientific center of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Situated south of Moscow, and 13 km south-east of Serpukhov, on the right side of the Ok ...
(biology). Moscow Oblast hosts Mission Control Centers for spacecraft (in Korolyov) and military satellites (Krasnoznamensk, Moscow Oblast, Krasnoznamensk), as well as a number of test sites.
Sport
Bandy
 Zorky Krasnogorsk, Zorky from Krasnogorsk has become List of Russian bandy champions, national bandy champions three times. In the 2017–18 season, Zorky is back in Russian Bandy Super League, Super League, after one season in the second-tier league. Obukhovo, Noginsky District, Moscow Oblast, Obukhovo is the only location in Russia without a Super League team which has a bandy venue with artificial ice. A plan for artificial ice also existed in Korolyov, Moscow Oblast, Korolyov. However, the project was abandoned. Although an indoor ice hockey-sized arena entered the plans instead, the official reason given was financial problems.
The Russian rink bandy, Rink Bandy Cup 2017 was played in Balashikha.
Zorky Krasnogorsk, Zorky from Krasnogorsk has become List of Russian bandy champions, national bandy champions three times. In the 2017–18 season, Zorky is back in Russian Bandy Super League, Super League, after one season in the second-tier league. Obukhovo, Noginsky District, Moscow Oblast, Obukhovo is the only location in Russia without a Super League team which has a bandy venue with artificial ice. A plan for artificial ice also existed in Korolyov, Moscow Oblast, Korolyov. However, the project was abandoned. Although an indoor ice hockey-sized arena entered the plans instead, the official reason given was financial problems.
The Russian rink bandy, Rink Bandy Cup 2017 was played in Balashikha.
Speed skating
 The 2008 European Speed Skating Championships and the 2016 World Single Distance Speed Skating Championships were held in
The 2008 European Speed Skating Championships and the 2016 World Single Distance Speed Skating Championships were held in Kolomna
Kolomna (, ) is a historic types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, situated at the confluence of the Moskva River, Moskva and Oka Rivers, (by rail) southeast of Moscow. Population:
History
Mentioned for the fir ...
.
Association football
FK Khimki and Saturn Ramenskoye are the most supported clubs that represent the region. The third professional club Znamya Truda is the oldest existing football club in the country founded in 1909.Culture and recreation

 Moscow Oblast has numerous therapeutic and recreational facilities located mainly in western, northwestern and northern parts, and also near Moscow. Of great importance for recreation are forests, which occupy over 40% of the region, as well as horticultural activities. The region has the highest number (over 1 million) of dachas with associated individual gardens. Also numerous are manor complexes, such as those in Abramtsevo, Sergiyevo-Posadsky District, Moscow Oblast, Abramtsevo, Muranovo, Ostafievo, historical towns (Vereya, Naro-Fominsky District, Moscow Oblast, Vereya, Volokolamsk,
Moscow Oblast has numerous therapeutic and recreational facilities located mainly in western, northwestern and northern parts, and also near Moscow. Of great importance for recreation are forests, which occupy over 40% of the region, as well as horticultural activities. The region has the highest number (over 1 million) of dachas with associated individual gardens. Also numerous are manor complexes, such as those in Abramtsevo, Sergiyevo-Posadsky District, Moscow Oblast, Abramtsevo, Muranovo, Ostafievo, historical towns (Vereya, Naro-Fominsky District, Moscow Oblast, Vereya, Volokolamsk, Dmitrov
Dmitrov () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center of Dmitrovsky District, Moscow Oblast, Dmitrovsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located to the north of Moscow on the Yakhroma River and the Mosc ...
, Zaraysk, Zvenigorod, Istra, Istrinsky District, Moscow Oblast, Istra, Kolomna
Kolomna (, ) is a historic types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, situated at the confluence of the Moskva River, Moskva and Oka Rivers, (by rail) southeast of Moscow. Population:
History
Mentioned for the fir ...
, Sergiyev Posad
Sergiyev Posad ( rus, Сергиев Посад, p=ˈsʲɛrgʲɪ(j)ɪf pɐˈsat) is a city that is the administrative center of Sergiyevo-Posadsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia. Population:
The city contains the Trinity Lavra of St. Sergi ...
, Serpukhov, etc.), monasteries (Trinity Lavra of St. Sergius, Joseph-Volokolamsk Monastery, Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, Nikolo-Ugresh monastery, etc.), and museums (Anton Chekhov, Chekhov museum in Melikhovo, Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky, Tchaikovsky museum in Klin, Serpukhov Historical and Art Museum, etc.). The oldest surviving building is the Kamenskoye Church.
Demographics
 After the population decline from 6,693,623 as of the Soviet Census (1989), 1989 Census to 6,618,538 in the Russian Census (2002), 2002 Census the population of the oblast grew to 7,095,120 (Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census). It increased further to 8,524,665 according to the 2021 Census despite the fact that some parts of its territory were ceded to Moscow. The average population density, at 190 inhabitants/km2 (2021), is the largest in Russia, due to a high proportion of urban population (78.5% in 2021). The highest density occurs in and around Moscow (Lyuberetsky District, Lyubertsy, Balashikha, Khimki, Krasnogorsk, etc.) and the lowest – about 20 people/km2 – is in the outlying areas of Lotoshinsky, Shakhovskoy, Mozhaysk and Meshchersk lowlands.
After the population decline from 6,693,623 as of the Soviet Census (1989), 1989 Census to 6,618,538 in the Russian Census (2002), 2002 Census the population of the oblast grew to 7,095,120 (Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census). It increased further to 8,524,665 according to the 2021 Census despite the fact that some parts of its territory were ceded to Moscow. The average population density, at 190 inhabitants/km2 (2021), is the largest in Russia, due to a high proportion of urban population (78.5% in 2021). The highest density occurs in and around Moscow (Lyuberetsky District, Lyubertsy, Balashikha, Khimki, Krasnogorsk, etc.) and the lowest – about 20 people/km2 – is in the outlying areas of Lotoshinsky, Shakhovskoy, Mozhaysk and Meshchersk lowlands.
Ethnic groups in Moscow Oblast (2021 Census)
Vital statistics
Vital statistics for 2024: *Births: 71,434 (8.3 per 1,000) *Deaths: 96,608 (11.2 per 1,000) Total fertility rate (2024):1.34 children per woman Life expectancy (2021):
Total — 70.35 years (male — 65.73, female — 74.80)
Religion
According to a 2012 survey 45.5% of the population of Moscow Oblast adheres to the Russian Orthodox Church, 3% are nondenominational Christianity, unaffiliated generic Christians, 2% are Orthodox Christian believers who do not belong to church or belong to non-Russian Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox churches, 1% are adherents of Rodnovery (the Slavic folk religious movement) and 1% to Islam. In addition, 29% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious", 9% is Irreligion, Non-Religious, and 9.5% follows other religions or did not give an answer to the question.Administrative and municipal divisions
Administratively, the oblast is divided into 38 city of federal subject significance, cities/towns under oblast jurisdiction and 36 raion, administrative districts, consisting of 46 town of district significance, towns of district significance, 72 urban-type settlements, and 6,119 rural localities. As of 2011, Moscow Oblast is Municipal divisions of Russia, municipally subdivided into 38 urban okrugs and 36 raion, municipal districts, which consist of 114 urban settlements and 193 rural settlements. The three largest cities of the oblast are Balashikha (215,494), Khimki (207,425), and Podolsk (186,961). Most other towns have ten to fifty thousand people. The smallest town is Vereya, Naro-Fominsky District, Moscow Oblast, Vereya in Naro-Fominsky District with a population of . Among the urban-type settlements, the largest is Nakhabino (36,546) followed by Tomilino (30,605). The oldest populated place in the oblast is Volokolamsk, first mentioned in 1135; slightly younger towns are Zvenigorod (1152), Dmitrov (1154), and Kolomna (1177).
The city of Baikonur in Kazakhstan also belongs administratively to the oblast, as part of Odintsovsky District.
The most intensive formation of towns occurred in 1938–1940. The youngest towns are Golitsyno, Moscow Oblast, Golitsyno and Kubinka. They existed for quite some time, but were granted town status only in 2004. Some recent towns separated from the other towns, such as Yubileyny, Moscow Oblast, Yubileyny and Peresvet.
New projects have been announced at the beginning of the 21st century. One of them is Rublyovo-Arkhangelsk, which is designed for 30,000 inhabitants with high income and is called by the media the "city for millionaires". Another is "Great Domodedovo, south of the Moscow Ring Road, which is designed for 450,000 residents. The new city A101 was designed for 300,000 residents in 2009 and the sale of its land in Leninsky District, Moscow Oblast, Leninsky District has already begun; the city's construction is planned to take thirty-five years.
A part of Moscow Oblast's former territory, mainly to the southwest of the city of Moscow, was merged with the federal cities of Russia, federal city of
The three largest cities of the oblast are Balashikha (215,494), Khimki (207,425), and Podolsk (186,961). Most other towns have ten to fifty thousand people. The smallest town is Vereya, Naro-Fominsky District, Moscow Oblast, Vereya in Naro-Fominsky District with a population of . Among the urban-type settlements, the largest is Nakhabino (36,546) followed by Tomilino (30,605). The oldest populated place in the oblast is Volokolamsk, first mentioned in 1135; slightly younger towns are Zvenigorod (1152), Dmitrov (1154), and Kolomna (1177).
The city of Baikonur in Kazakhstan also belongs administratively to the oblast, as part of Odintsovsky District.
The most intensive formation of towns occurred in 1938–1940. The youngest towns are Golitsyno, Moscow Oblast, Golitsyno and Kubinka. They existed for quite some time, but were granted town status only in 2004. Some recent towns separated from the other towns, such as Yubileyny, Moscow Oblast, Yubileyny and Peresvet.
New projects have been announced at the beginning of the 21st century. One of them is Rublyovo-Arkhangelsk, which is designed for 30,000 inhabitants with high income and is called by the media the "city for millionaires". Another is "Great Domodedovo, south of the Moscow Ring Road, which is designed for 450,000 residents. The new city A101 was designed for 300,000 residents in 2009 and the sale of its land in Leninsky District, Moscow Oblast, Leninsky District has already begun; the city's construction is planned to take thirty-five years.
A part of Moscow Oblast's former territory, mainly to the southwest of the city of Moscow, was merged with the federal cities of Russia, federal city of Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
on July 1, 2012.Official website of the Government of MoscowDraft of adopted measures of the capital and oblast governments with regards to the expansion of the borders of Moscow
The housing stock of the oblast is approximately 125 million square meters. Almost all the houses are equipped with water supply, sewerage, gas, central heating and hot water. However, the telephone network is underdeveloped in rural areas. In the competition for the most comfortable city of 2006 in the Moscow Oblast the winner was
Kolomna
Kolomna (, ) is a historic types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, situated at the confluence of the Moskva River, Moskva and Oka Rivers, (by rail) southeast of Moscow. Population:
History
Mentioned for the fir ...
followed by Balashikha (for cities with population over 100,000) and Vidnoye, Moscow Oblast, Vidnoye (<100,000) and then by Mytishchi and Noginsk
Noginsk (), known as Bogorodsk () until 1930, is a Classification of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Noginsky District, Bogorodsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located east of the Moscow Ring Road on ...
.
Sister regions
* Bratislava Region, Bratislava, Slovakia * Chüy Region, Kyrgyzstan * Île-de-France (region), Île-de-France, France * Jiangsu, China * City Municipality of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia * Palembang, Indonesia * Buenos Aires Province, ArgentinaPartner regions
Moscow Oblast cooperates with: * Ahal Region, Turkmenistan (1995)See also
*List of rural localities in Moscow OblastReferences
Notes
Sources
* *"СССР. Административно-территориальное деление союзных республик. 1987." (''USSR. Administrative-Territorial Structure of the Union Republics. 1987'') / Составители В. А. Дударев, Н. А. Евсеева. — М.: Изд-во «Известия Советов народных депутатов СССР», 1987. — 673 с. *B.B. Wagner, B.O. Manucharyants.Геология, рельеф и полезные ископаемые Московского региона
. Moscow, MGPU, 2003.
External links
* * – Moscow Oblast {{Use mdy dates, date=January 2016 Moscow Oblast, States and territories established in 1929 1929 establishments in Russia