Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
is a
risk factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often use ...
for many chronic physical and mental illnesses.
The health effects of being overweight but not obese are controversial, with some studies showing that the mortality rate for individuals who are classified as overweight (
BMI 25.0 to 29.9) may actually be lower than for those with an ideal weight (BMI 18.5 to 24.9). Health risks for those who are overweight may be decreasing because of improvements in medical care.
Some obesity-associated medical conditions may be the result of stress caused by medical discrimination against people who are obese, rather than the direct effects of obesity, and some may be exacerbated by the relatively poor healthcare received by people who are obese.
Medical discrimination
Because of the social stigma of obesity, people who are obese may receive poorer healthcare than people within the normal
BMI weight range, potentially contributing to the relationship between obesity and poor health outcomes.
People who experience weight-related discrimination, irrespective of their actual weight status, similarly have poorer health outcomes than those who do not experience weight-related discrimination.
People who are obese are also less likely to seek medical care than people who are not obese, even if the weight gain is caused by medical problems. Peter Muennig, a professor in the
Department of Health Policy and Management at Columbia University,
has proposed that obesity-associated medical conditions may be caused "not from adiposity alone, but also from the psychological stress induced by the social stigma associated with being obese".
Cardiological risks

Body weight is not considered to be an independently predictive risk factor for
cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
by current (as of 2014) risk assessment tools. Mortality from cardiovascular disease has decreased despite increases in obesity, and at least one clinical trial was stopped early because the weight loss intervention being tested did not reduce cardiovascular disease.
Ischemic heart disease
Abdominal obesity is associated with
cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheuma ...
including
angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of parti ...
and
myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
.
However, overall obesity (as measured by BMI) may lead to false diagnoses of myocardial infarction and may decrease mortality after acute myocardial infarction.
In 2008, European guidelines concluded that 35% of ischemic heart disease among adults in Europe is due to obesity.
Congestive heart failure
Having obesity is associated to about 11% of
heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF ...
cases in males and 14% in females.
High blood pressure
More than 85% of those with
hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
have a BMI greater than 25, although diet is probably a more important factor than body weight.
[ Risk estimates indicate that at least two-thirds of people with hypertension can be directly attributed to obesity. The association between obesity and hypertension has been found in animal and clinical studies, which have suggested that there are multiple potential mechanisms for obesity-induced hypertension. These mechanisms include the activation of the ]sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
as well as the activation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. As of 2007, it was unclear whether there is an association between hypertension and obesity in children, but there is little direct evidence that blood pressure has increased despite increases in pediatric overweight.
Abnormal cholesterol levels
Obesity is associated with increased levels of LDL cholesterol
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall dens ...
and lower levels of HDL cholesterol in the blood.
Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
Obesity increases one's risk of venous thromboembolism
Venous thrombosis is the blockage of a vein caused by a thrombus (blood clot). A common form of venous thrombosis is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when a blood clot forms in the deep veins. If a thrombus breaks off ( embolizes) and flows to the lun ...
by approximately 2.3 fold.
Dermatological risks
Obesity is associated with the incidence of stretch marks, acanthosis nigricans, lymphedema
Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized edema, swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system. The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns inters ...
, cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of ...
, hirsutism
Hirsutism is excessive body hair on parts of the body where hair is normally absent or minimal. The word is from early 17th century: from Latin ''hirsutus'' meaning "hairy". It usually refers to a male pattern of hair growth in a female that ma ...
, and intertrigo
Intertrigo, commonly called “skin fold dermatitis”, refers to a type of inflammatory rash (dermatitis) of the superficial skin that occurs within a person's body folds. These areas are more susceptible to irritation and subsequent infection d ...
.
Endocrine risks

Diabetes mellitus
The link between obesity and type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
is so strong that researchers in the 1970s started calling it " diabesity".[ Excess weight is behind 64% of cases of diabetes in males and 77% of cases in females.]
Gynecomastia
In some individuals, obesity can be associated with elevated peripheral conversion of androgens into estrogens.
Gastrointestinal risks
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Several studies have shown that the frequency and severity of GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or ...
symptoms increase with BMI, such that people who are underweight have the fewest GERD symptoms,[
]
Cholelithiasis (gallstones)
Obesity causes the amount of cholesterol in bile to rise, in turn the formation of stone can occur [
]
Reproductive system (or genital system)
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
Due to its association with insulin resistance, the risk of obesity increases with polycystic ovarian syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or polycystic ovarian syndrome, (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The name is a misnomer, as not all women with this condition develop cysts on their ovaries. The name origi ...
(PCOS). In the US approximately 60% of patients with PCOS have a BMI greater than 30. It remains uncertain whether PCOS contributes to obesity, or the reverse.
Infertility
Obesity can lead to infertility in both males and females. This is primarily due to excess estrogen interfering with normal ovulation
Ovulation is an important part of the menstrual cycle in female vertebrates where the egg cells are released from the ovaries as part of the ovarian cycle. In female humans ovulation typically occurs near the midpoint in the menstrual cycle and ...
in females[ and altering ]spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle. This process starts with the Mitosis, mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of ...
in males. It is believed to cause 6% of primary infertility.odds ratio
An odds ratio (OR) is a statistic that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and B. The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of event A taking place in the presence of B, and the odds of A in the absence of B ...
1.3.[
]
Complications of pregnancy
Obesity is related to many complications in pregnancy including: haemorrhage, infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
, increased hospital stays for the mother, and increased NICU requirements for the infant. Obese females also have increased risk of preterm birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the Childbirth, birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 ...
s and low birth weight infants.
Obese females have more than twice the rate of C-sections compared to females of "normal" weight. Some have suggested that this may be due in part to the social stigma of obesity.
Birth defects
Those who are obese during pregnancy have a greater risk of having a child with a number of congenital malformation
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
s including: neural tube defects
Neural tube defects (NTDs) are a group of birth defects in which an opening in the spine or cranium remains from early in human development. In the third week of pregnancy called gastrulation, specialized cells on the dorsal side of the embry ...
such as anencephaly and spina bifida
Spina bifida (SB; ; Latin for 'split spine') is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the vertebral column, spine and the meninges, membranes around the spinal cord during embryonic development, early development in pregnancy. T ...
, cardiovascular anomalies, including septal anomalies, cleft lip and palate, anorectal malformation, limb reduction anomalies, and hydrocephaly.
Intrauterine fetal death
Maternal obesity is associated with an increased risk of intrauterine fetal death.[
]
Buried penis
Excess body fat in morbid obesity can, in some cases, completely obscure or "bury" the penis.
Neurological risks

Stroke
Ischemic stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop ...
is increased in both men and women who are obese.[
]
Meralgia paresthetica
Meralgia paresthetica is a neuropathic pain or numbness of the thighs, sometimes associated with obesity.
Migraines
Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
(and headaches in general) is comorbid with obesity.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
The risk of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a nerve compression syndrome associated with the collected signs and symptoms of Pathophysiology of nerve entrapment#Compression, compression of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Carpal tunn ...
is estimated to rise 7.4% for each 1 kg/m2 increase of body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is ...
.
Dementia
One review found that those who are obese do not have a significantly higher rate of dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
than those with "normal" weight.
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, or unexplained high pressure in the cranium, is a rare condition that can cause visual impairment, frequent severe headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
, and tinnitus
Tinnitus is a condition when a person hears a ringing sound or a different variety of sound when no corresponding external sound is present and other people cannot hear it. Nearly everyone experiences faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely ...
. It is most commonly seen in obese women, and the incidence of idiopathic intracranial hypertension is increasing along with increases in the number of people who are obese.
Multiple sclerosis
Obese female individuals at 18 years of age have a greater than twofold increased risk of multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
compared to females with a BMI between 18.5 and 20.9.
Cancer
 Many cancers occur at increased frequency in those who are overweight or obese. A study from the United Kingdom found that approximately 5% of cancer is due to excess weight. These
Many cancers occur at increased frequency in those who are overweight or obese. A study from the United Kingdom found that approximately 5% of cancer is due to excess weight. These cancers
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
include:
* breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
* ovarian cancer
* esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer (American English) or oesophageal cancer (British English) is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include dysphagia, difficulty in swallowing and weigh ...
* colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the Colon (anatomy), colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include Lower gastrointestinal ...
* hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
HCC most common ...
* pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of ...
* gallbladder cancer
* stomach cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a malignant tumor of the stomach. It is a cancer that develops in the Gastric mucosa, lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a numb ...
* endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer is a cancer that arises from the endometrium (the epithelium, lining of the uterus or womb). It is the result of the abnormal growth of cells (biology), cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. The first s ...
* cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix or in any layer of the wall of the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later sympt ...
* prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, ...
* renal cell carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the Proximal tubule, proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cance ...
* non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tire ...
* multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibody, antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone ...
A high body mass index ( BMI) is associated with a higher risk of developing ten common cancers including 41% of uterine cancers and at least 10% of gallbladder, kidney, liver and colon cancers in the UK. For those undergoing surgery for cancer, obesity is also associated with an increased risk of major postoperative complications compared with those of "normal" weight.
Psychiatric risks

Depression
Obesity has been associated with depression, likely due to social factors rather than physical effects of obesity.[ However, it is possible that obesity is caused by depression (due to reduced physical activity or, in some people, increases in appetite).]
Social stigmatization
Obese people draw negative reactions from others, and people are less willing to help obese individuals in any situation due to social stigmatization. People who are obese also experience fewer educational and career opportunities, on average earn a lesser income,
Respiratory system
Obstructive sleep apnea
Obesity is a risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway lea ...
.
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome

Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS) is a condition in which severely overweight people fail to breathe rapidly or deeply enough, resulting in low oxygen levels and high blood carbon dioxide (CO2) levels. The syndrome is often associated with ...
is defined as the combination of obesity, hypoxia during sleep, and hypercapnia
Hypercapnia (from the Greek ''hyper'', "above" or "too much" and ''kapnos'', "smoke"), also known as hypercarbia and CO2 retention, is a condition of abnormally elevated carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood. Carbon dioxide is a gaseous pro ...
during the day, resulting from hypoventilation
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide ( hypercap ...
.
Chronic lung disease
Obesity is associated with a number of chronic lung diseases, including asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
and COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
.[ It is believed that a systemic pro-inflammatory state induced by some causes of obesity may contribute to airway inflammation, leading to asthma.
]
Complications during general anaesthesia
Obesity significantly reduces and stiffens the functional lung volume, requiring specific strategies for respiratory management under general anesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is medically induced loss of consciousness that renders a patient unarousable even by painful stimuli. It is achieved through medications, which can be injected or inhaled, often with an analgesi ...
.
Obesity and asthma
The low grade systemic inflammation of obesity has been shown to worsen lung function in asthma and increase the risk of developing an asthma exacerbation.
COVID-19
A study in England found a linear increase in severe COVID-19 resulting in hospitalisation and death for those whose BMI is above 23, and a linear increase in admission to an intensive care unit across the whole BMI spectrum. The difference in COVID-19 risk from having a high BMI was most pronounced in people aged under 40, or who were black. A study from Mexico found that obesity alone was responsible for a 2.7 times increased risk of death from COVID-19, while comorbidities with diabetes, immunosuppression or high blood pressure increased the risk further. A study from the United States found that there was an inverse correlation between age and BMI of COVID patients; the younger the age group, the higher its BMI.
Rheumatological and orthopedic risks
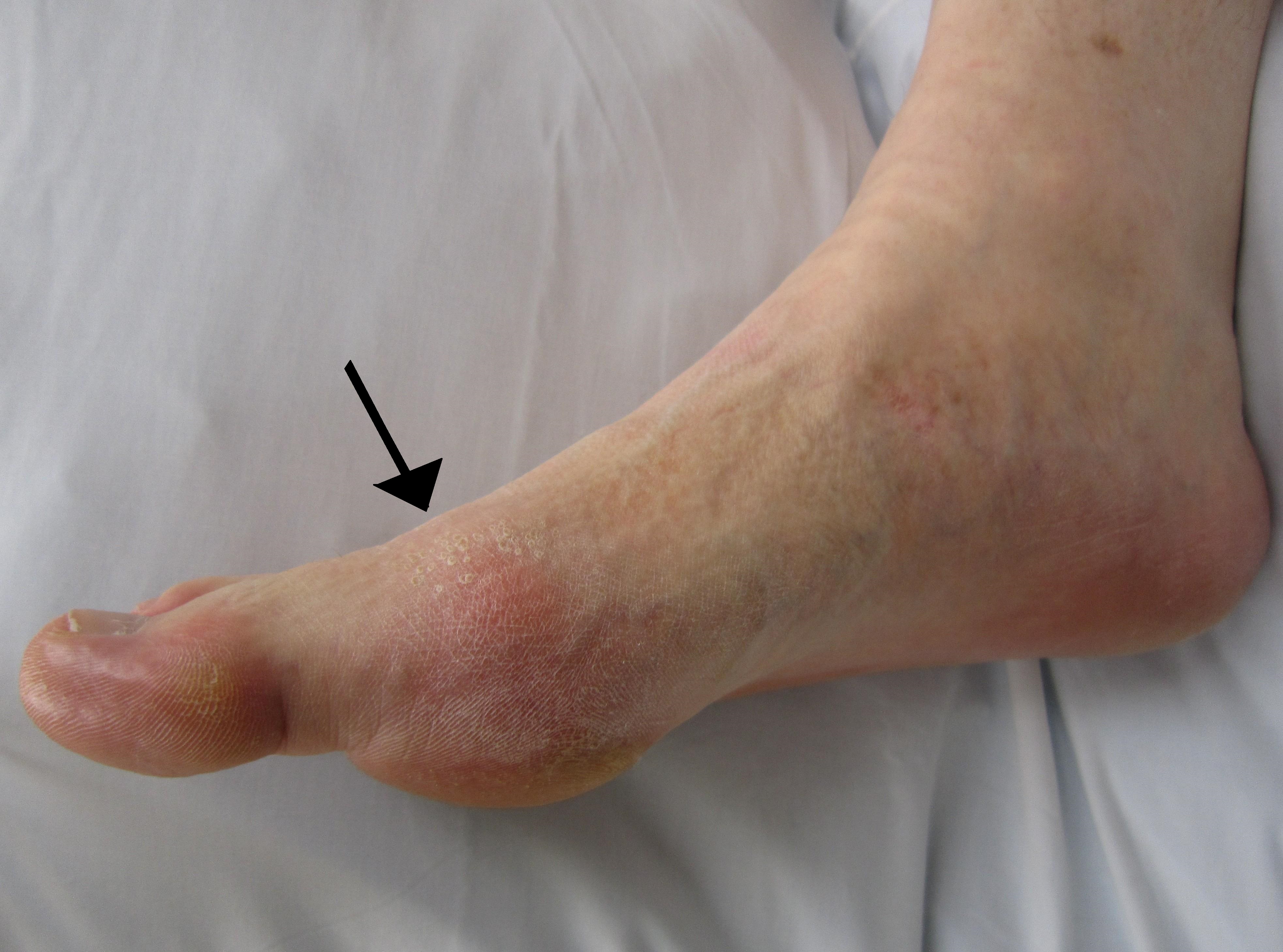
Gout
Compared to men with a BMI of 21–22.9, men with a BMI of 30–34.9 have 2.33 times more gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of pain in a red, tender, hot, and Joint effusion, swollen joint, caused by the deposition of needle-like crystals of uric acid known as monosodium urate crysta ...
, and men with a BMI ≥ 35 have 2.97 times more gout. Weight loss decreases these risks.
Poor mobility
There is a strong association between obesity and musculoskeletal pain and disability.
Osteoarthritis
Increased rates of arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
are seen in both weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing joints.[ Weight loss and exercise act to reduce the risk of osteoarthritis.
]
Low back pain
Obese individuals are twice to four times more likely to have lower back pain than their "normal" weight peers.
Traumatic injury
In females, low BMI is a risk factor for osteoporotic fractures in general.
Urological and nephrological risks
Urinary incontinence
Urge, stress, and mixed incontinence all occur at higher rates in obese people. The rates of urinary incontinence are about double that found in the "normal" weight population. Urinary incontinence improves with weight loss.
Chronic kidney disease
Obesity increases one's risk of chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of long-term kidney disease, defined by the sustained presence of abnormal kidney function and/or abnormal kidney structure. To meet criteria for CKD, the abnormalities must be present for at least three mo ...
by three to four times.
Hypogonadism
In males, obesity and metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndro ...
both increase estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
and adipokine production. This reduces gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and rele ...
, in turn reducing both luteinizing hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH, also known as luteinising hormone, lutropin and sometimes lutrophin) is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of LH is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (G ...
and follicle stimulating hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, ...
. The result is reduction of the testis
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
' production of testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
and a further increase in adipokine levels. This then feeds back to cause further weight gain.
Erectile dysfunction
Obese male individuals can experience erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and durat ...
, and weight loss can improve their sexual functioning.
See also
* Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS) is a condition in which severely overweight people fail to breathe rapidly or deeply enough, resulting in low oxygen levels and high blood carbon dioxide (CO2) levels. The syndrome is often associated with ...
* Obesity paradox
References
Further reading
* Review
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Obesity Associated Morbidity
Medical conditions related to obesity
 Body weight is not considered to be an independently predictive risk factor for
Body weight is not considered to be an independently predictive risk factor for 
 Many cancers occur at increased frequency in those who are overweight or obese. A study from the United Kingdom found that approximately 5% of cancer is due to excess weight. These
Many cancers occur at increased frequency in those who are overweight or obese. A study from the United Kingdom found that approximately 5% of cancer is due to excess weight. These