Monarchy In China on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
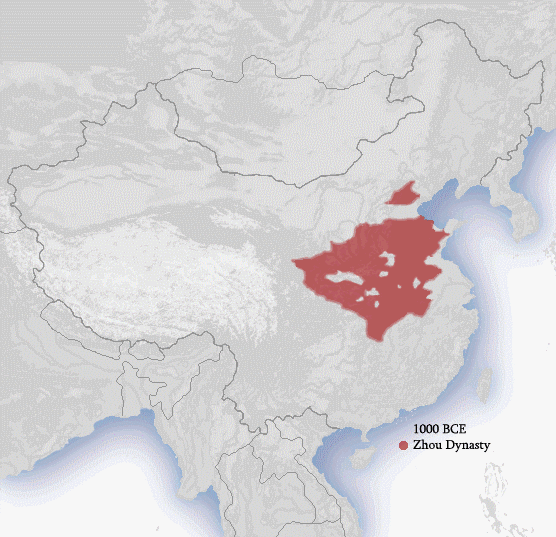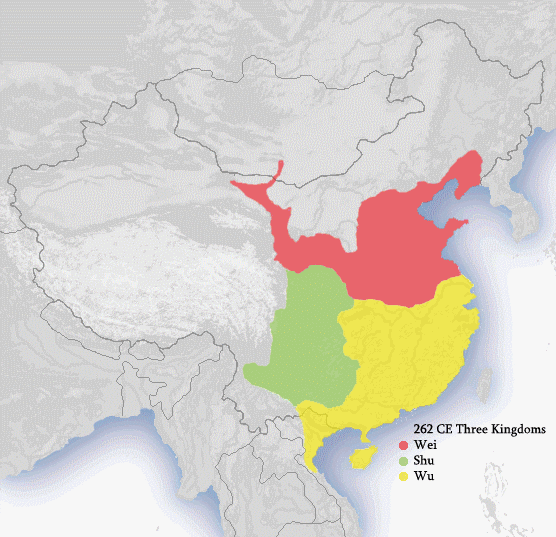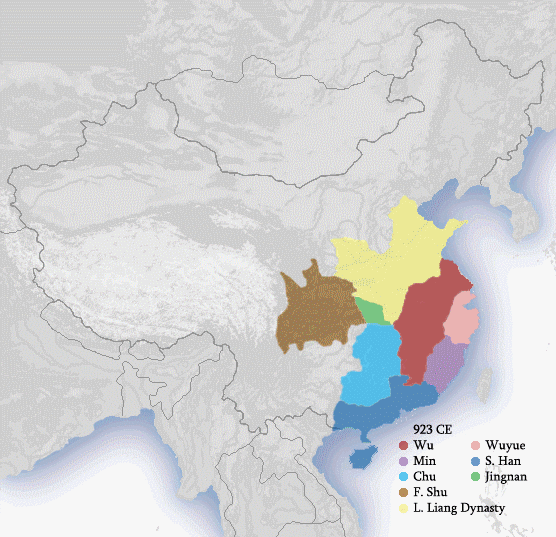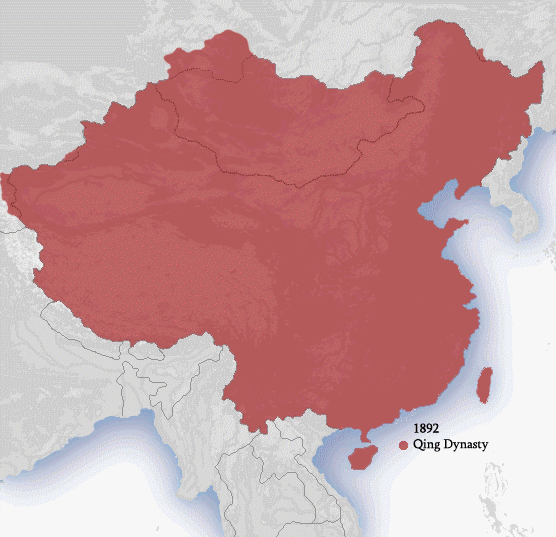 While the Chinese monarchy was originally established along the
While the Chinese monarchy was originally established along the
File:Zhigongtu full.jpg, The ''
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
was a monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for the rest of their life, or until abdication. The extent of the authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutio ...
from prehistoric times up to 1912, when a republic
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
was established. The succession of legendary monarchs
Legendary may refer to:
* Legend, a folklore genre
* Legendary (hagiography)
* J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium
Film and television
* ''Legendary'' (2010 film), a 2010 American sports drama film
* ''Legendary'' (2013 film), a 2013 film feat ...
of China were non-hereditary. Dynastic rule
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family, usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A dynasty may also be referred to as a "house", "family" or "clan", among others.
Historians ...
began when Yu the Great
Yu the Great or Yu the Engineer was a legendary king in ancient China who was credited with "the first successful state efforts at flood control", his establishment of the Xia dynasty, which inaugurated Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic ru ...
established the Xia dynasty
The Xia dynasty (; ) is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, it was established by the legendary figure Yu the Great, after Emperor Shun, Shun, the last of the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors, Fiv ...
, and monarchy lasted until 1912 when dynastic rule collapsed together with the monarchical government. Various attempts at preserving and restoring the Chinese monarchy occurred during and following the Xinhai Revolution, but these regimes were short-lived and lacked widespread recognition.
The monarchy of China took the form of absolute monarchy during most of its existence, even though the actual power of the ruler
A ruler, sometimes called a rule, scale, line gauge, or metre/meter stick, is an instrument used to make length measurements, whereby a length is read from a series of markings called "rules" along an edge of the device. Usually, the instr ...
varied depending on his/her ability to consolidate the rule and various other factors. On 3 November 1911, the Qing dynasty issued the constitutional Nineteen Creeds which limited the power of the emperor, marking the official transition to a constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
. However, after only 3 months, the monarchy was abolished.
During periods of political disunity, China was divided among competing dynasties that often claimed exclusive Chinese politico-cultural orthodoxy; in such cases, more than one Chinese monarchy existed simultaneously. Throughout Chinese history
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
, there were monarchs of both ethnic Han and non-Han origins, including many who were of mixed heritage.
Territorial domains
 While the Chinese monarchy was originally established along the
While the Chinese monarchy was originally established along the Yellow River
The Yellow River, also known as Huanghe, is the second-longest river in China and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system on Earth, with an estimated length of and a Drainage basin, watershed of . Beginning in the Bayan H ...
and Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
in China proper
China proper, also called Inner China, are terms used primarily in the West in reference to the traditional "core" regions of China centered in the southeast. The term was first used by Westerners during the Manchu people, Manchu-led Qing dyn ...
, various Chinese dynasties expanded to incorporate other regions into the Chinese realm.
At various points in time, the Chinese monarchy exercised control over China proper (including Hainan
Hainan is an island provinces of China, province and the southernmost province of China. It consists of the eponymous Hainan Island and various smaller islands in the South China Sea under the province's administration. The name literally mean ...
, Macau
Macau or Macao is a special administrative regions of China, special administrative region of the People's Republic of China (PRC). With a population of about people and a land area of , it is the most List of countries and dependencies by p ...
, and Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
), Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
(both Northeast China
Northeast China () is a geographical region of China, consisting officially of three provinces Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang. The heartland of the region is the Northeast China Plain, the largest plain in China with an area of over . The regi ...
and Outer Manchuria
Outer Manchuria, sometimes called Russian Manchuria, refers to a region in Northeast Asia that is now part of the Russian Far East but historically formed part of Manchuria (until the mid-19th century). While Manchuria now more normatively refer ...
), Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An islan ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
(both Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of China. Its border includes two-thirds of the length of China's China–Mongolia border, border with the country of Mongolia. ...
and Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto'' ...
), Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
,Lockard (2020). p. 262. Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
, Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
, as well as parts of Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, the Korean Peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
, Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
,Hsu (2012). p. 268. and Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
. In particular, certain groups of Western scholars use the term "China proper" to distinguish the "core" region of China populated chiefly by the Han people from the "frontier" regions of the Chinese monarchical realm with significant populations of ethnic minorities.
The Chinese monarchy reached its largest territorial extent under either the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
or the Qing dynasty, depending on the historical source. This discrepancy can be mainly attributed to the ambiguous northern border of the Yuan dynasty: whereas some sources describe the Yuan border as located to the immediate north of the northern shore of Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
, others posit that the Yuan dynasty reached as far north as the Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
coast. Contrastingly, the borders of the Qing dynasty were demarcated and reinforced through a series of international treaties, including the Treaty of Nerchinsk
The Treaty of Nerchinsk of 1689 was the first treaty between the Tsardom of Russia and the Qing dynasty of China after the defeat of Russia by Qing China at the Siege of Albazin in 1686. The Russians gave up the area north of the Amur River as ...
and the Treaty of Kyakhta, and thus were more well-defined. The total area under the control of the Qing dynasty amounted to more than 13 million km at its peak Peak or The Peak may refer to:
Basic meanings Geology
* Mountain peak
** Pyramidal peak, a mountaintop that has been sculpted by erosion to form a point Mathematics
* Peak hour or rush hour, in traffic congestion
* Peak (geometry), an (''n''-3)-d ...
.
Apart from exercising direct control over the Chinese realm, the Chinese monarchy also maintained hegemony over other states through the Chinese tributary system
The tributary system of China (simplified Chinese: 中华朝贡体系, traditional Chinese: 中華朝貢體系, pinyin: Zhōnghuá cháogòng tǐxì), or Cefeng system () at its height was a network of loose international relations centered arou ...
. The Chinese tributary system had its roots during the Western Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring in ...
and lasted until the 19th century AD when the Sinocentric order collapsed.
Dynasties and ethnicities
Since the establishment of the Xia dynasty, China had been ruled by a succession of dynasties. A recurring theme in Chinese history, dynastic transitions occurred typically as a result of military conquest or usurpation. Historians often seek to account for Chinese dynastic transitions using the concept ofdynastic cycle
Dynastic cycle () is an important political theory in Chinese history. According to this theory, each dynasty of China rises to a political, cultural, and economic peak and then, because of moral corruption, declines, loses the Mandate of Heaven, ...
.
In history, China was ruled by dynasties of various ethnic origins. Although it is a common practice in Chinese historiography
Chinese historiography is the study of the techniques and sources used by historians to develop the recorded history of China.
Overview of Chinese history
The recording of events in Chinese history dates back to the Shang dynasty ( 1600–1046 ...
to label a particular dynasty as being ruled by a specific ethnicity, there were Chinese monarchs who had mixed heritage. For instance, the Emperor Xiaoming of the Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were an ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. The Xianbei were likely not of a single ethnicity, but rather a multiling ...
-led Northern Wei dynasty
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei ( zh, c=北魏, p=Běi Wèi), Tuoba Wei ( zh, c=拓跋魏, p=Tuòbá Wèi), Yuan Wei ( zh, c=元魏, p=Yuán Wèi) and Later Wei ( zh, t=後魏, p=Hòu Wèi), was an imperial dynasty of Chi ...
was of mixed Xianbei and Han heritage; he obtained his Han ancestry from his mother, the Empress Ling. Similarly, the Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 165420 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, personal name Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign of 61 ...
of the Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority in China and the people from wh ...
-led Qing dynasty was of mixed Manchu and Han descent; he acquired his Han ancestry from his mother, the Empress Xiaokangzhang
Empress Xiaokangzhang (1638 – 20 March 1663), of the Manchu Bordered Yellow Banner Tunggiya clan, was the concubine of the Shunzhi Emperor and mother of the Kangxi Emperor during the Qing dynasty. She was honoured as Empress Dowager Cihe dur ...
. Therefore, the ethnic identity of the ruling families as assigned by historians should not be regarded as absolute.
Abolition and legacy
On 10 October 1911, theWuchang Uprising
The Wuchang Uprising was an armed rebellion against the ruling Qing dynasty that took place in Wuchang (now Wuchang District of Wuhan) in the Chinese province of Hubei on 10 October 1911, beginning the Xinhai Revolution that successfully overthr ...
broke out in modern-day Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
, marking the start of the Xinhai Revolution. Led by the Tongmenghui
The Tongmenghui of China was a secret society and underground resistance movement founded by Sun Yat-sen, Song Jiaoren, and others in Tokyo, Empire of Japan, on 20 August 1905, with the goal of overthrowing China's Qing dynasty. It was formed ...
, the predecessor of the Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT) is a major political party in the Republic of China (Taiwan). It was the one party state, sole ruling party of the country Republic of China (1912-1949), during its rule from 1927 to 1949 in Mainland China until Retreat ...
, the Xinhai Revolution soon spread to other parts of China. On 1 January 1912, the Republic of China was proclaimed by Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-senUsually known as Sun Zhongshan () in Chinese; also known by Names of Sun Yat-sen, several other names. (; 12 November 186612 March 1925) was a Chinese physician, revolutionary, statesman, and political philosopher who founded the Republ ...
in Nanjing
Nanjing or Nanking is the capital of Jiangsu, a province in East China. The city, which is located in the southwestern corner of the province, has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a population of 9,423,400.
Situated in the Yang ...
. On 12 February 1912, the Xuantong Emperor
Puyi (7 February 190617 October 1967) was the final emperor of China, reigning as the eleventh monarch of the Qing dynasty from 1908 to 1912. When the Guangxu Emperor died without an heir, Empress Dowager Cixi picked his nephew Puyi, aged tw ...
abdicated, marking the end of the Qing dynasty and the Chinese monarchy altogether.
According to the theory of the succession of states
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory (and populace) that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19 ...
and Chinese historiographical tradition, the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
is accepted as the legitimate successor to the Qing dynasty and the Chinese monarchy. In particular, the Imperial Edict of the Abdication of the Qing Emperor issued by the Empress Dowager Longyu
Yehe Nara Jingfen (; 28 January 1868 – 22 February 1913), of the Manchu Bordered Yellow Banner Yehe Nara clan, was the wife and empress consort of Zaitian, the Guangxu Emperor. She was empress consort of Qing from 1889 until her husband's death ...
provided the legal basis for the Republic of China to inherit all territories of the Qing dynasty and to preserve the territorial integrity of the new Chinese state.
The National Day of the Republic of China, celebrated today in the Taiwan Area
The Taiwan Area, also called the Taiwan Area of the Republic of China, the free area of the Republic of China, and the "Tai-Min Area (Taiwan and Fuchien)" , is a term used to refer to the territories under the effective control of the Rep ...
, commemorates the anniversary of the Wuchang Uprising. It was also celebrated officially in mainland China
"Mainland China", also referred to as "the Chinese mainland", is a Geopolitics, geopolitical term defined as the territory under direct administration of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in the aftermath of the Chinese Civil War. In addit ...
between 1912 and 1949 prior to the retreat of the Government of the Republic of China
The Government of the Republic of China is the central government, national authority whose actual-controlled territory consists of Taiwan (island), main island of Taiwan (Formosa), Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu Islands, Matsu, and list of islands of ...
to Taiwan.
Monarchism in post-monarchical China
During and after the Xinhai Revolution, there were various attempts at reviving the Chinese monarchy. All these attempts ultimately ended in failure.Emperorship by Duke of Yansheng or Marquis of Extended Grace
During theXinhai Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China (ROC). The revolution was the culmination of a decade ...
, there were numerous proposals advocating for the replacement of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty by a new dynasty of Han ethnicity. Kong Lingyi (), a 76th-generation descendant of Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the phil ...
and the Duke of Yansheng, was identified as a potential candidate for Chinese emperorship by Liang Qichao
Liang Qichao (Chinese: 梁啓超; Wade–Giles: ''Liang2 Chʻi3-chʻao1''; Yale romanization of Cantonese, Yale: ''Lèuhng Kái-chīu''; ) (February 23, 1873 – January 19, 1929) was a Chinese politician, social and political activist, jour ...
. Meanwhile, gentry in Anhui
Anhui is an inland Provinces of China, province located in East China. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze and Huai rivers, bordering Jiangsu and Zhejiang to the east, Jiang ...
and Hebei
Hebei is a Provinces of China, province in North China. It is China's List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, sixth-most populous province, with a population of over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. It bor ...
supported a restoration of the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
under Zhu Yuxun (), the Marquis of Extended Grace
The Marquis of Extended Grace was a title held by a descendant of the imperial family of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) during the subsequent Qing dynasty (1644–1912). Holders of this title were also called the Marquis of Zhu from the surname ...
. Both suggestions failed to materialize. In the year of 1937, the Japanese during their conquest of China offered the position of "Emperor of China" to the Duke of Yansheng, Kung Te-cheng
Kong Te-cheng () (23 February 1920 – 28 October 2008) was a 77th generation descendant of Confucius in the main line of descent. He was the final person to be appointed Duke Yansheng and the first Sacrificial Official to Confucius. He helped ...
, but he declined the offer.
Empire of China
In 1915,Yuan Shikai
Yuan Shikai (; 16 September 18596 June 1916) was a Chinese general and statesman who served as the second provisional president and the first official president of the Republic of China, head of the Beiyang government from 1912 to 1916 and ...
proclaimed the Empire of China. It soon sparked the National Protection War
The National Protection War ( zh, t=護國戰爭, s=护国战争, p=Hù guó zhànzhēng), also known as the Anti-Monarchy War, was a civil war that took place in China between 1915 and 1916. Following the overthrow of the Qing dynasty three yea ...
and the empire was abolished after 3 months.
Manchu Restoration
In 1917, the Qing loyalistZhang Xun
Zhang Xun (; September 16, 1854 – September 11, 1923), courtesy name Shaoxuan (), art name Songshou Laoren (), nickname Bianshuai (, ), was a Chinese general and Qing loyalist who attempted to restore the abdicated emperor Puyi in the Manch ...
reinstalled Puyi
Puyi (7 February 190617 October 1967) was the final emperor of China, reigning as the eleventh monarch of the Qing dynasty from 1908 to 1912. When the Guangxu Emperor died without an heir, Empress Dowager Cixi picked his nephew Puyi, aged tw ...
to the Chinese throne. This attempt at restoring the Qing dynasty, known as the Manchu Restoration
The Manchu Restoration or Dingsi Restoration (), also known as Zhang Xun Restoration (), or Xuantong Restoration (), was an attempt to restore the Chinese monarchy by General Zhang Xun, whose army seized Beijing and briefly reinstalled the las ...
, lasted only 11 days.
Manchukuo
TheJapanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
puppet state Manchukuo was established in Northeast China
Northeast China () is a geographical region of China, consisting officially of three provinces Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang. The heartland of the region is the Northeast China Plain, the largest plain in China with an area of over . The regi ...
in 1932. This regime subsequently became a monarchy with Puyi as the emperor in 1934. Manchukuo collapsed in 1945 following the Soviet invasion of Manchuria
The Soviet invasion of Manchuria, formally known as the Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation or simply the Manchurian Operation () and sometimes Operation August Storm, began on 9 August 1945 with the Soviet Union, Soviet invasion of the Emp ...
and the unconditional surrender of Japan.
Gallery
Portraits of Periodical Offering of Liang
The ''Portraits of Periodical Offering'' () were tributary documentative paintings (with illustration on each of the portrait) produced by various Chinese dynasties and later as well in other East Asian dynasties, such as Japan and Vietnam. Thes ...
'' illustrates foreign envoys in the imperial court of the Liang dynasty
The Liang dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Liang () or Xiao Liang () in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the third of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It was pre ...
.
File:Reconstructed Danfeng Men.jpg, The reconstructed Danfeng Gate of the Daming Palace, the imperial palace complex of the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
.
File:Liu-Kuan-Tao-Jagd.JPG, A painting by Liu Guandao depicting the Emperor Shizu of Yuan on a hunting expedition.
File:Tribute Giraffe with Attendant.jpg, A Bengali envoy presenting a giraffe as a tributary gift in the name of Sultan Saifuddin Hamza Shah of the Ilyas Shahi dynasty
The Ilyas Shahi dynasty (, ) was the first independent dynasty to set the foundations of the late medieval Sunni Muslim Sultanate of Bengal. Their rule extended from 1342 to 1487, though interrupted with interregna by their slaves as well as th ...
of Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
to the Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzu of Ming, personal name Zhu Di, was the third List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 142 ...
.
File:Inside the Forbidden City.jpg, The Dragon Throne in the Palace of Heavenly Purity within the Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is the Chinese Empire, imperial Chinese palace, palace complex in the center of the Imperial City, Beijing, Imperial City in Beijing, China. It was the residence of 24 Ming dynasty, Ming and Qing dynasty, Qing dynasty L ...
was a symbol of Chinese imperial power. The "Dragon Throne" can also be used metonymically to refer to the monarchy of China.
File:Seal of Qing dynasty.svg, The imperial seal of the Qing dynasty.
See also
*Chinese Empire
Chinese Empire (), or Empire of China, refers to the realm ruled by the Emperor of China during the era of Imperial China. It was coined by western scholars to describe the Ming dynasty, Ming and Qing dynasty, Qing dynasties (or imperial Dyna ...
* Chinese Empire Reform Association
The Chinese Empire Reform Association, abbreviated as C.E.R.A (''Baojiu Da-Qing Huangdi Hui'', ), or, more often, Baohuanghui, ) was a worldwide Chinese political association founded by Kang Youwei (1858–1927) in Victoria, British Columbia on ...
* Chinese expansionism
Territorial expansion took place during multiple periods of Chinese history, especially under the dynasties of Han, Tang, Yuan, and Qing. Chinese expansionism as a motivation or even coherent phenomenon has been contentiously discussed in re ...
* Chinese nobility
The nobility of China represented the upper strata of aristocracy in premodern China, acting as the ruling class until , and remaining a significant feature of the traditional social structure until the end of the imperial period.
The concepts ...
* Chinese sovereign
The Chinese sovereign was the ruler of a particular monarchical regime in the historical periods of ancient China and imperial China. Sovereigns ruling the same regime, and descended from the same paternal line, constituted a dynasty. Several ...
* Conquest dynasty
A conquest dynasty () in the history of China refers to a Chinese dynasty established by non- Han ethnicities which ruled parts or all of China proper, the traditional heartland of the Han people, and whose rulers may or may not have fully assi ...
* Dragon Throne
* Dynasties of China
For most of its history, China was organized into various dynastic states under the rule of hereditary monarchs. Beginning with the establishment of dynastic rule by Yu the Great , and ending with the abdication of the Xuantong Emperor in ...
* Emperor at home, king abroad
Emperor at home, king abroad was a system of conducting relations between states within the Chinese cultural sphere. Rulers of lesser regimes would adopt the title of ''emperor'' (皇帝; or other equivalents) and/or other imperial titles domes ...
* Emperor of China
Throughout Chinese history, "Emperor" () was the superlative title held by the monarchs of imperial China's various dynasties. In traditional Chinese political theory, the emperor was the " Son of Heaven", an autocrat with the divine mandat ...
* Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors
This is a family tree of Chinese monarchs covering the period of the Five Emperors up through the end of the Spring and Autumn period.
Five Emperors
The legendary Five Emperors were traditionally regarded as the founders of the Chinese state. ...
* Family tree of Chinese monarchs (early)
Family (from ) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as m ...
* Family tree of Chinese monarchs (late)
Family (from ) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as ...
* Family tree of Chinese monarchs (middle)
Family (from ) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as ...
* Foreign relations of imperial China
* Golden ages of China
Throughout Chinese history, China had multiple periods of golden age. In Chinese historiography, golden ages on a large scale are known as (, lit. Prosperous Era), while golden ages on a smaller scale are termed as (, lit. Well-Governed Era). L ...
* Historical capitals of China
This is a list of historical capitals of China.
Four Great Ancient Capitals
There are traditionally four major historical capitals of China referred to as the "Four Great Ancient Capitals of China" (). The four are Beijing, Nanjing, Luoyang and X ...
* History of China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the ...
* List of Chinese monarchs
The Chinese sovereign, Chinese monarchs were the rulers of History of China, China during History of China#Ancient China, Ancient and History of China#Imperial China, Imperial periods. The earliest rulers in traditional Chinese historiography a ...
* List of recipients of tribute from China
Central Plain political entities have paid tribute to a number of states and confederations throughout history. China proper also had a strong Confucian tradition, which believed that showing virtue and giving gifts or tribute would civilize " B ...
* List of tributary states of China
This is a list of states that paid tribute to the Imperial dynasties of China under the tributary system. It encompassed states in Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Europe.
List of tributaries
In the 5th centur ...
* Mandate of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven ( zh, t=天命, p=Tiānmìng, w=, l=Heaven's command) is a Chinese ideology#Political ideologies, political ideology that was used in History of China#Ancient China, Ancient China and Chinese Empire, Imperial China to legit ...
* Names of China
The names of China include the many contemporary and historical designations given in various languages for the East Asian country known as in Standard Chinese, a form based on the Beijing dialect of Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin.
The English nam ...
* '' Pax Sinica''
* Political systems of Imperial China
The political systems of Chinese Empire, Imperial China can be divided into a state administrative body, provincial administrations, and a system for official selection. The three notable tendencies in the history of Chinese politics includes, t ...
* Royalist Party
* Sinicization
Sinicization, sinofication, sinification, or sinonization (from the prefix , 'Chinese, relating to China') is the process by which non-Chinese societies or groups are acculturated or assimilated into Chinese culture, particularly the language, ...
* Sinocentrism
Sinocentrism refers to a worldview that China is the cultural, political, or economic center of the world. Sinocentrism was a core concept in various Chinese dynasties. The Chinese considered themselves to be "all-under-Heaven", ruled by the ...
* Sinosphere
The Sinosphere, also known as the Chinese cultural sphere, East Asian cultural sphere, or the Sinic world, encompasses multiple countries in East Asia and Southeast Asia that were historically heavily influenced by Chinese culture. The Sinosph ...
* Succession to the Chinese throne
The Monarchy of China, Chinese monarchy had various methods to determine succession to the Chinese throne before the institution was overthrown in 1911. The Mongols, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty practiced blood tanistry, or competition among brothers, w ...
* Timeline of Chinese history
__NOTOC__
This is a timeline of Chinese history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in China and its dynasties. To read about the background to these events, see History of China. See also the list of Chines ...
* Tongmenghui
The Tongmenghui of China was a secret society and underground resistance movement founded by Sun Yat-sen, Song Jiaoren, and others in Tokyo, Empire of Japan, on 20 August 1905, with the goal of overthrowing China's Qing dynasty. It was formed ...
* Tributary system of China
The tributary system of China (Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: 中华朝贡体系, Traditional Chinese characters, traditional Chinese: 中華朝貢體系, pinyin: Zhōnghuá cháogòng tǐxì), or Cefeng system () at its heig ...
Notes
References
{{Chinese Imperial Government Monarchism in China Monarchies of Asia