electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
is a particular electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field) is a physical field, varying in space and time, that represents the electric and magnetic influences generated by and acting upon electric charges. The field at any point in space and time can be regarde ...
pattern of the radiation in the plane perpendicular (i.e., transverse) to the radiation's propagation
Propagation can refer to:
*Chain propagation in a chemical reaction mechanism
*Crack propagation, the growth of a crack during the fracture of materials
*Propaganda, non-objective information used to further an agenda
*Reproduction, and other forms ...
direction. Transverse modes occur in radio wave
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths g ...
s and microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
s confined to a waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Common types of waveguides include acoustic waveguides which direct sound, optical waveguides which direct light, and radio-frequency w ...
, and also in light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
waves in an optical fiber
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at ...
and in a laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
's optical resonator
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that confines light waves similarly to how a cavity resonator confines microwaves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, ...
.
Transverse modes occur because of boundary condition
In the study of differential equations, a boundary-value problem is a differential equation subjected to constraints called boundary conditions. A solution to a boundary value problem is a solution to the differential equation which also satis ...
s imposed on the wave by the waveguide. For example, a radio wave in a hollow metal waveguide must have zero tangential electric field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) descri ...
amplitude at the walls of the waveguide, so the transverse pattern of the electric field of waves is restricted to those that fit between the walls. For this reason, the modes supported by a waveguide are quantized. The allowed modes can be found by solving Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, Electrical network, electr ...
for the boundary conditions of a given waveguide.
Types of modes
Unguided electromagnetic waves in free space, or in a bulkisotropic
In physics and geometry, isotropy () is uniformity in all orientations. Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence '' anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also ...
dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an Insulator (electricity), electrical insulator that can be Polarisability, polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric ...
, can be described as a superposition of plane wave
In physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of ...
s; these can be described as TEM modes as defined below.
However in any sort of waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Common types of waveguides include acoustic waveguides which direct sound, optical waveguides which direct light, and radio-frequency w ...
where boundary conditions
In the study of differential equations, a boundary-value problem is a differential equation subjected to constraints called boundary conditions. A solution to a boundary value problem is a solution to the differential equation which also satis ...
are imposed by a physical structure, a wave of a particular frequency can be described in terms of a transverse mode
Mode ( meaning "manner, tune, measure, due measure, rhythm, melody") may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* MO''D''E (magazine), a defunct U.S. women's fashion magazine
* ''Mode'' magazine, a fictional fashion magazine which is the setting fo ...
(or superposition of such modes). These modes generally follow different propagation constant
The propagation constant of a sinusoidal electromagnetic wave is a measure of the change undergone by the amplitude and phase of the wave as it propagates in a given direction. The quantity being measured can be the voltage, the current in a ...
s. When two or more modes have an identical propagation constant along the waveguide, then there is more than one modal decomposition possible in order to describe a wave with that propagation constant (for instance, a non-central Gaussian
Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) is the eponym of all of the topics listed below.
There are over 100 topics all named after this German mathematician and scientist, all in the fields of mathematics, physics, and astronomy. The English eponymo ...
laser mode can be equivalently described as a superposition of Hermite-Gaussian modes or Laguerre-Gaussian modes which are described below).
Waveguides
Conductor-based transmission lines
Incoaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ), is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner Electrical conductor, conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting Electromagnetic shielding, shield, with the two separated by a dielectric (Insulat ...
energy is normally transported in the fundamental TEM mode. The TEM mode is also usually assumed for most other electrical conductor line formats as well. This is mostly an accurate assumption, but a major exception is microstrip
Microstrip is a type of electrical transmission line which can be fabricated with any technology where a conductor is separated from a ground plane by a dielectric layer known as ''substrate''. Microstrip lines are used to convey microwave-freq ...
which has a significant longitudinal component to the propagated wave due to the inhomogeneity at the boundary of the dielectric substrate below the conductor and the air above it.
Inhomogeneity also occurs at connectors or bends in a coaxial cable. Non-TEM modes created by connectors are usually negligible unless the signal has a high enough frequency. This is referred to as maximum extraneous-mode-free operation or simply mode-free operation frequency of the connector.
In an optical fiber or other dielectric waveguide, modes are generally of the hybrid type.
Waveguides
Hollow metallic waveguides filled with a homogeneous, isotropic material (usually air) support TE and TM modes but not the TEM mode. In rectangular waveguides, rectangular mode numbers are designated by two suffix numbers attached to the mode type, such as TE''mn'' or TM''mn'', where ''m'' is the number of half-wave patterns across the width of the waveguide and ''n'' is the number of half-wave patterns across the height of the waveguide. In circular waveguides, circular modes exist and here ''m'' is the number of full-wave patterns along the circumference and ''n'' is the number of half-wave patterns along the diameter.Optical fibers
The number of modes in an optical fiber distinguishesmulti-mode optical fiber
Multi-mode optical fiber is a type of optical fiber mostly used for communication over short distances, such as within a building or on a campus. Multi-mode links can be used for data rates up to 800 Gbit/s. Multi-mode fiber has a fairly ...
from single-mode optical fiber
In fiber-optic communication, a single-mode optical fiber, also known as fundamental- or mono-mode, is an optical fiber designed to carry only a single mode (electromagnetism), mode of light - the transverse mode. Modes are the possible solutio ...
. To determine the number of modes in a step-index fiber, the V number needs to be determined: where is the wavenumber
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber (or wave number), also known as repetency, is the spatial frequency of a wave. Ordinary wavenumber is defined as the number of wave cycles divided by length; it is a physical quantity with dimension of ...
, is the fiber's core radius, and and are the refractive indices
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
of the core and cladding, respectively. Fiber with a V-parameter of less than 2.405 only supports the fundamental mode (a hybrid mode), and is therefore a single-mode fiber whereas fiber with a higher V-parameter has multiple modes.
Decomposition of field distributions into modes is useful because a large number of field amplitudes readings can be simplified into a much smaller number of mode amplitudes. Because these modes change over time according to a simple set of rules, it is also possible to anticipate future behavior of the field distribution. These simplifications of complex field distributions ease the signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, Scalar potential, potential fields, Seismic tomograph ...
requirements of fiber-optic communication
Fiber-optic communication is a form of optical communication for transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared or visible light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modul ...
systems.
The modes in typical low refractive index contrast fibers are usually referred to as ''LP'' (linear polarization) modes, which refers to a scalar
Scalar may refer to:
*Scalar (mathematics), an element of a field, which is used to define a vector space, usually the field of real numbers
*Scalar (physics), a physical quantity that can be described by a single element of a number field such a ...
approximation for the field solution, treating it as if it contains only one transverse field component.K. Okamoto, ''Fundamentals of Optical Waveguides'', pp. 71–79, Elsevier Academic Press, 2006, .
Lasers
 In a laser with cylindrical symmetry, the transverse mode patterns are described by a combination of a
In a laser with cylindrical symmetry, the transverse mode patterns are described by a combination of a Gaussian beam
In optics, a Gaussian beam is an idealized beam of electromagnetic radiation whose amplitude envelope in the transverse plane is given by a Gaussian function; this also implies a Gaussian intensity (irradiance) profile. This fundamental (or ...
profile with a Laguerre polynomial
In mathematics, the Laguerre polynomials, named after Edmond Laguerre (1834–1886), are nontrivial solutions of Laguerre's differential equation:
xy'' + (1 - x)y' + ny = 0,\
y = y(x)
which is a second-order linear differential equation. Thi ...
. The modes are denoted where and are integers labeling the radial and angular mode orders, respectively. The intensity at a point (in polar coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system specifies a given point (mathematics), point in a plane (mathematics), plane by using a distance and an angle as its two coordinate system, coordinates. These are
*the point's distance from a reference ...
) from the centre of the mode is given by:
where , is the associated Laguerre polynomial
In mathematics, the Laguerre polynomials, named after Edmond Laguerre (1834–1886), are nontrivial solutions of Laguerre's differential equation:
xy'' + (1 - x)y' + ny = 0,\
y = y(x)
which is a second-order linear differential equation. Thi ...
of order and index , and is the spot size of the mode corresponding to the Gaussian beam radius.
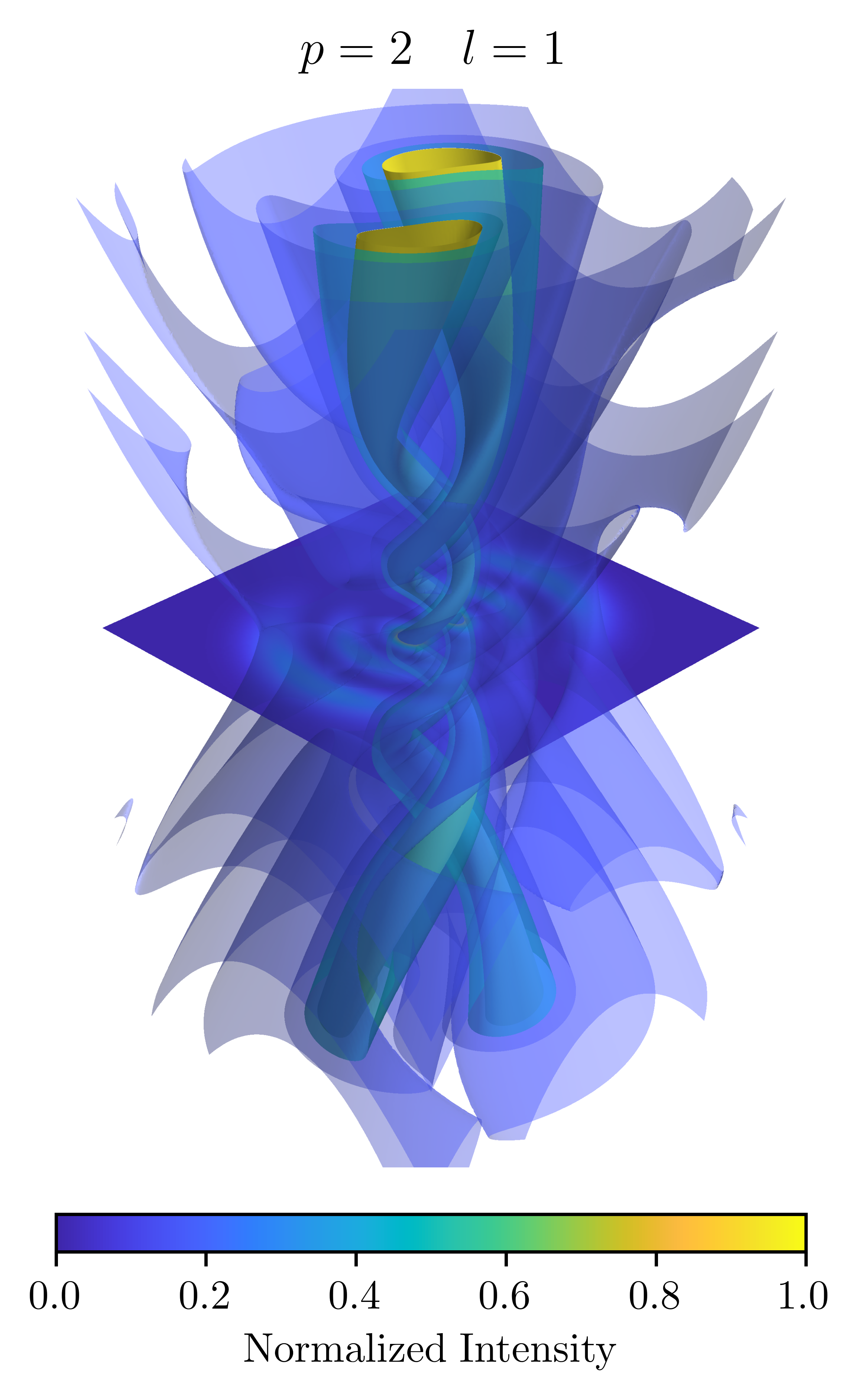 With , the TEM00 mode is the lowest order. It is the fundamental transverse mode of the laser resonator and has the same form as a Gaussian beam. The pattern has a single lobe, and has a constant
With , the TEM00 mode is the lowest order. It is the fundamental transverse mode of the laser resonator and has the same form as a Gaussian beam. The pattern has a single lobe, and has a constant phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
across the mode. Modes with increasing show concentric rings of intensity, and modes with increasing show angularly distributed lobes. In general there are spots in the mode pattern (except for ). The mode, the so-called ''doughnut mode'', is a special case consisting of a superposition of two modes (), rotated with respect to one another.
The overall size of the mode is determined by the Gaussian beam radius , and this may increase or decrease with the propagation of the beam, however the modes preserve their general shape during propagation. Higher order modes are relatively larger compared to the mode, and thus the fundamental Gaussian mode of a laser may be selected by placing an appropriately sized aperture in the laser cavity.
In many lasers, the symmetry of the optical resonator is restricted by polarizing elements such as Brewster's angle windows. In these lasers, transverse modes with rectangular symmetry are formed. These modes are designated with and being the horizontal and vertical orders of the pattern. The electric field pattern at a point for a beam propagating along the z-axis is given by
Gaussian beam
In optics, a Gaussian beam is an idealized beam of electromagnetic radiation whose amplitude envelope in the transverse plane is given by a Gaussian function; this also implies a Gaussian intensity (irradiance) profile. This fundamental (or ...
; Hermite polynomial
In mathematics, the Hermite polynomials are a classical orthogonal polynomial sequence.
The polynomials arise in:
* signal processing as Hermitian wavelets for wavelet transform analysis
* probability, such as the Edgeworth series, as well a ...
. The corresponding intensity pattern is
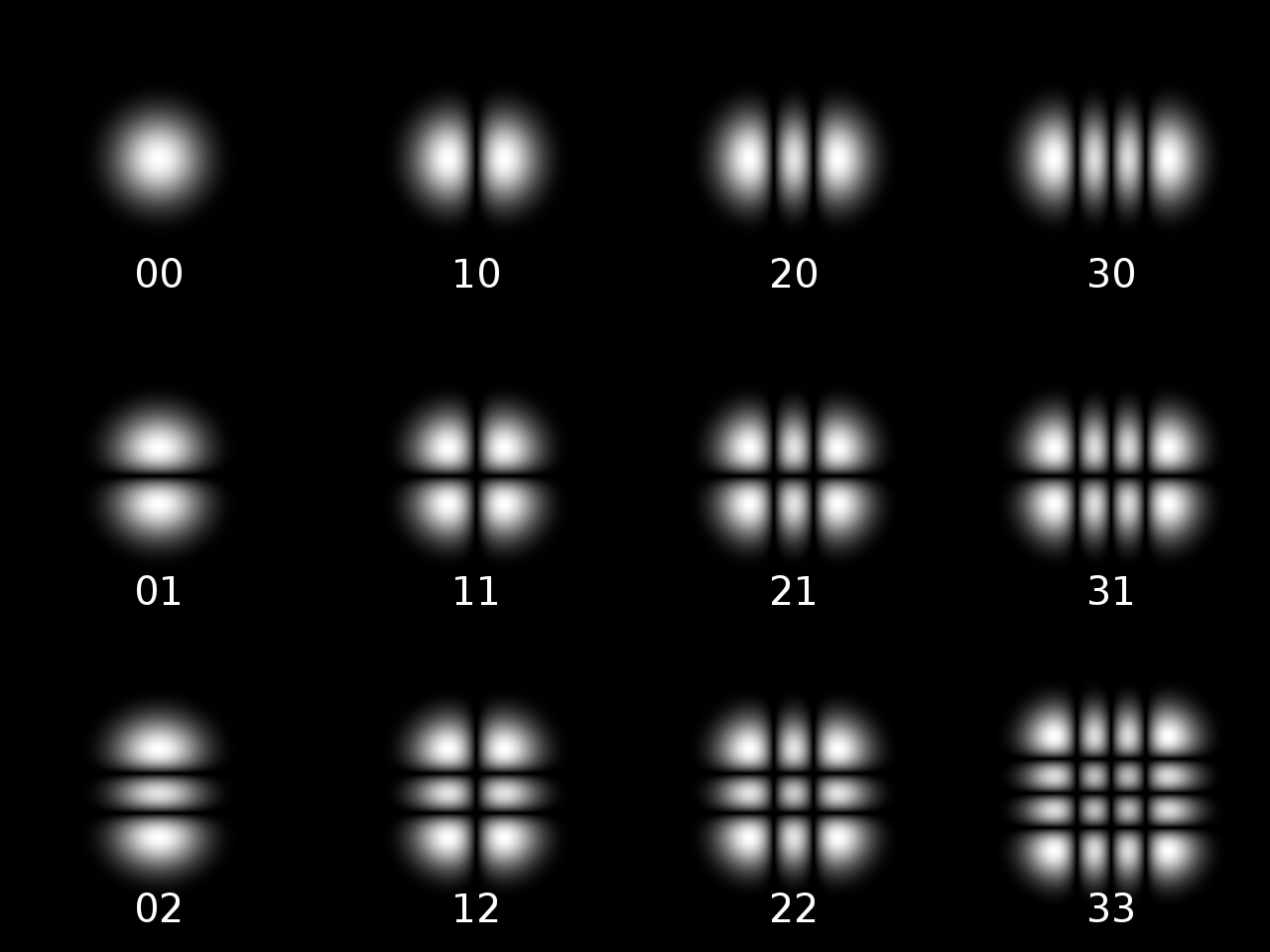 The TEM00 mode corresponds to exactly the same fundamental mode as in the cylindrical geometry. Modes with increasing and show lobes appearing in the horizontal and vertical directions, with in general lobes present in the pattern. As before, higher-order modes have a larger spatial extent than the 00 mode.
The
The TEM00 mode corresponds to exactly the same fundamental mode as in the cylindrical geometry. Modes with increasing and show lobes appearing in the horizontal and vertical directions, with in general lobes present in the pattern. As before, higher-order modes have a larger spatial extent than the 00 mode.
The phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
of each lobe of a is offset by radians with respect to its horizontal or vertical neighbours. This is equivalent to the polarization of each lobe being flipped in direction.
The overall intensity profile of a laser's output may be made up from the superposition of any of the allowed transverse modes of the laser's cavity, though often it is desirable to operate only on the fundamental mode.
See also
*Normal mode
A normal mode of a dynamical system is a pattern of motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. The free motion described by the normal modes takes place at fixed frequencies ...
*Longitudinal mode
A longitudinal mode of a resonant cavity is a particular standing wave pattern formed by waves confined in the cavity. The longitudinal modes correspond to the wavelengths of the wave which are reinforced by constructive interference after man ...
*Laser beam profiler
A laser beam profiler captures, displays, and records the spatial intensity profile of a laser beam at a particular plane transverse to the beam propagation path. Since there are many types of lasers—ultraviolet, visible, infrared, continuo ...
*Spatial filter
A spatial filter is an optical device which uses the principles of Fourier optics to alter the structure of a beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation, typically coherent laser light. Spatial filtering is commonly used to "clean up" the ...
*Transverse wave
In physics, a transverse wave is a wave that oscillates perpendicularly to the direction of the wave's advance. In contrast, a longitudinal wave travels in the direction of its oscillations. All waves move energy from place to place without t ...
References
External links
Detailed descriptions of laser modes
{{DEFAULTSORT:Transverse Mode Wave mechanics Electromagnetic radiation Laser science